- School of Biological Sciences, University of Nebraska-Lincoln (UNL), Lincoln, NE, United States
The neural basis and genetic mechanisms for sensory evolution are increasingly being explored in depth across many closely related members of the Drosophila genus. This has, in part, been achieved due to the immense efforts toward adapting gene-editing technologies for additional, non-model species. Studies targeting both peripheral sensory variations, as well as interspecies divergence in coding or neural connectivity, have generated numerous, tangible examples of how and where the evolution of sensory-driven animal behavior has occurred. Here, we review and discuss studies that each aim to identify the neurobiological and genetic components of sensory system evolution to provide a comparative overview of the types of functional variations observed across both perceptual input and behavioral output. In addition, we examined the roles neuroecology and neuroevolution play in speciation events, such as courtship and intraspecies communication, as well as those aspects related to behavioral divergence in host navigation or egg-laying preferences. Through the investigation of comparative, large-scale trends and correlations across diverse, yet closely related species within this highly ecologically variable genus of flies, we can begin to describe the underlying pressures, mechanisms, and constraints that have guided sensory and nervous system evolution within the natural environments of these organisms.
Introduction
This is an exciting time to be an evolutionary neuroethologist, a behavioral ecologist, and a sensory physiologist, as a foundation of tools and technologies is, for the first time, largely in place to study neural variation across a broad range of organisms as well as their corresponding behavioral innovations. Neurogenetic research examines the role of genetics in the development and function of the nervous system. This field of study considers neural characteristics, such as phenotypes, and is mainly based on the observation that the nervous systems of individuals, even of those belonging to the same species, may not be completely identical. Most of the research pertaining to neurogenetics has revolved around Drosophila melanogaster, where decades of experiments have outlined the major operations of the central brain, from genome to connectome. Moreover, many relatives of D. melanogaster, which, again, has been one of the foundational workhorses for modern genetics, are starting to become laboratory models in their own right (Goldman-Huertas et al., 2015; O'Grady and DeSalle, 2018; Gloss et al., 2019; Auer et al., 2020). This family of invertebrates (Insecta: Diptera: Drosophilidae) has continued to provide a successful avenue for innovative research partly because of the strong base of knowledge afforded by a single model species (i.e., Drosophila melanogaster), as well as because of the relatively simple brain (e.g., ~100,000 neurons) (Scheffer, 2020). Here, CRISPR-Cas9 and other transgenic tools have already begun to be established for many closely related Drosophila species (Bono et al., 2015), including D. melanogaster (Port et al., 2020), D. simulans (Seeholzer et al., 2018) , D. yakuba and D. santomea (Ding et al., 2019) , D. pseudoobscura (Ramaekers et al., 2019) , D. subobscura (Tanaka et al., 2017) , D. sechellia (Auer et al., 2020) , D. suzukii (Karageorgi et al., 2017), as well as D. mojavensis (Khallaf et al., 2020). In addition, several other members of this fly genus are still in ongoing transgenic production in laboratories around the world.
Another central advantage of working with this genus is that species within Drosophila are well-known to be quite a variable in their host material and microbial associations (Becher et al., 2012; Markow, 2015; Jezovit et al., 2017). Thus, this group of flies, in addition to a multitude of genomic datasets and emerging molecular tools, also provides drastic evolutionary divergence in host utilization and behavioral innovation, for example, from host material preferences toward differing stages of fruit decay, true herbivory, mycophagy, and even including florivory species (Figure 1A). Therefore, this genus represents ecologies across a rather complete spectrum of plant and microbial host phenology, not to mention several more unique ecological adaptations such as egg-laying in the gills of land crabs and their fermenting urine repositories (Carson, 1974; Stensmyr et al., 2008), as well as within protein-rich resources such as bat guano at the base of underground caves (Tosi et al., 1990). Beyond the variable host material utilization, members of this genus are also found across rather diverse habitats, such as islands, temperate and tropical rainforests, high-elevation mountains, as well as deserts (Figure 1B). Habitats can include large ambient variations in temperature, humidity, light-level, and three-dimensional spatial variance, such as from ground to tree tops or across altitudinal gradients (e.g., from the sea level to mountains). Each new environment (or microhabitat within a single ecological type) can provide variations in plant host availability, fruit type, and microbial availability. Thus, the relatively rapid and immense radiation of host diversity within this insect genus provides a plethora of opportunities to uncover ecological and evolutionary mechanisms for any associated chemosensory or multimodal sensory divergence that accompanies unique host adaptation or shifts in habitat preference, as well as interspecific behavioral deviations in courtship or reproductive barriers.
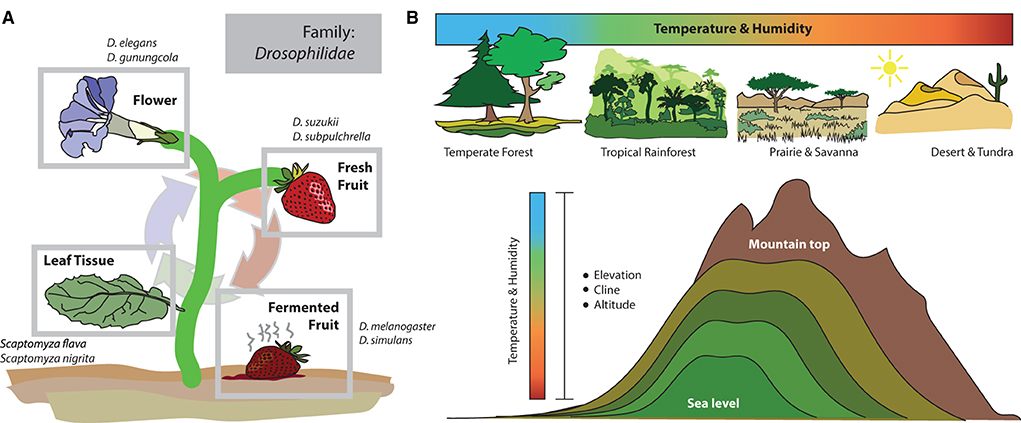
Figure 1. Ecology and habitat use within the Drosophila genus. (A) The most well-studied species, Drosophila melanogaster, and its closest relatives, primarily utilize fermenting fruit and sites of heavy bacteria and yeast growth. Therefore, this genus is often known as fruit flies (or vinegar flies). However, within this family and genus (Drosophilidae: Drosophila), there are species that target more diverse host resources, including flowers, fresh/ripening fruits, and even leaf tissues. But how the sensory systems of each new species evolve, and the mechanisms for that adaptation are less well-known. (B) Members of the Drosophila genus are found across a multitude of ecological zones and habitats, including very different environments regarding temperature and humidity, as well as altitude and light availability. This makes the genus an ideal model for studying adaptation to new habitats (and microhabitats), including how sensory systems and the brain change in order to maximize evolutionary success in each new ecological niche.
Over the past decade, while several reviews have emerged to keep up with cutting-edge research within the singular species, D. melanogaster, fewer reviews exist that examine the wider scope of neurobiology, behavior and sensory ecology research that is being conducted across the breadth of the entire Drosophila genus. Here, we hope to step back and examine an overview of this rapidly expanding, broad area of research in order to discuss various examples of sensory adaptations at the periphery as well as within numerous components of the primary and secondary processing centers within the brain. In general, this review focuses on how inter- and intraspecies variations in olfactory and other sensory input arise, as well as how their associated neural substrates can provide rationales for ongoing speciation mechanisms and adaptations toward novel environments. This can have direct connections to studies of climate change in an increasingly unstable world, as well as connections to agricultural advancement in the form of understanding host plant adaptations and the plasticity provided by genetic variation across populations of introduced insect pest species (Olazcuaga et al., 2021). While the majority of neural and behavioral frontiers are outlined using the laboratory strains of D. melanogaster (e.g., Oregon R and Canton S), an increasing body of literature is revisiting theories and hypotheses using non-melanogaster species to confirm these previous results and test long-held beliefs in ecology, evolution, and developmental biology. As a summary, this review also formulates potential avenues for examining the burgeoning field of multimodal neural integration and proposes studies or objectives for the future of behavioral neurobiology to maximize the potential use of this incredibly diverse genus of flies, from the laboratory into the field, and vice versa.
Chemosensory evolution
Serving as the anchor species for our understanding of peripheral detection and primary processing of chemical information, D. melanogaster research has provided an in-depth model of how the brain receives and perceives olfactory information within its environment (Figure 2). This animal uses both its antennae as well as its maxillary palps (as the predominant chemosensory organs on the head of the fly) to detect its chemical environment. Covering these structures (i.e., antenna and palp) are a series of single hairs, or sensillum, that come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Categorically, these sensilla include basiconic (large and small), coeloconic, trichoid, and intermediate types, which are all distinct in their morphology (Shanbhag et al., 2001; Lin and Potter, 2015; Keesey et al., 2019b). Each sensillum, in turn, possesses a specific set of olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs), which themselves contain and express single or combinations of co-expressed olfactory receptors (ORs). It is important to note that sensilla can also express other types of chemosensory receptors, such as ionotropic receptors (IRs), as well as gustatory receptors (GRs), which are better reviewed in other literature (Rytz et al., 2013; Scott, 2018; Dweck and Carlson, 2020). For olfaction in D. melanogaster, each OSN within a sensillum contains between 1 and 4 ORs. In total, this species has roughly ~1,200 OSNs, which are distributed across ~400 sensilla on each antenna, and ~60 sensilla on each palp (Stocker, 2001; Grabe et al., 2016). Researchers can record from the whole antennal or entire palp, using electroantennograms (EAG) and electropalpograms (EPG), or from each neuron within one of the sensory hairs, utilizing single sensillum recording (SSR) (Figure 3). Other body sections in D. melanogaster also contain chemosensory sensillum types, including areas such as the wings, legs, and ovipositor; however, these body regions have been studied more recently, and will continue to be the next frontier in our understanding of Drosophila chemosensation, neurobiology, and connectomics.
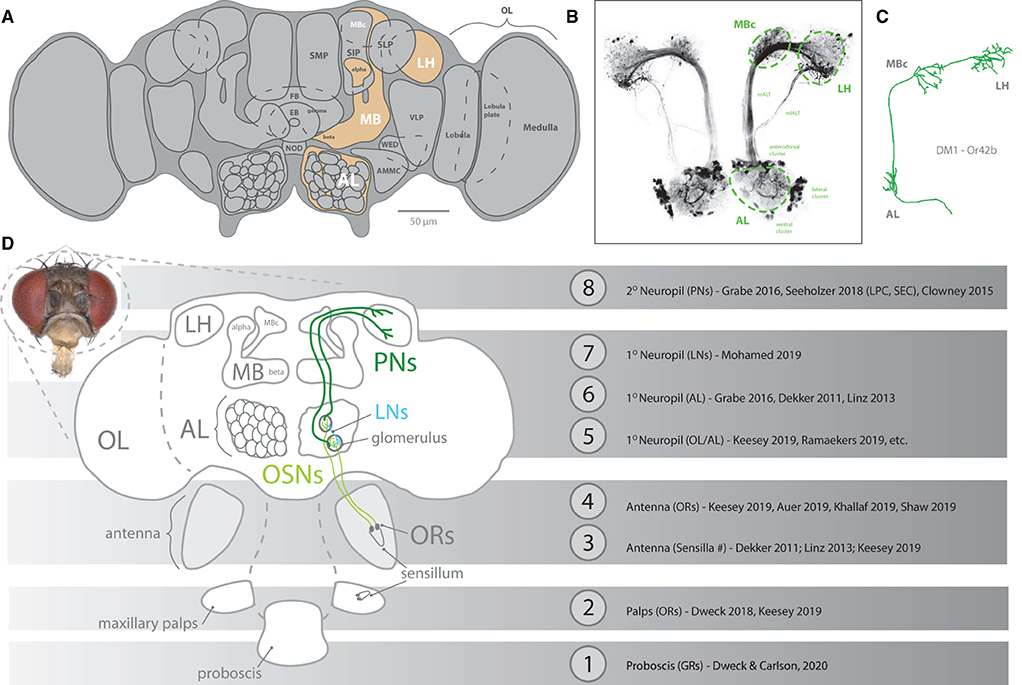
Figure 2. An overview diagram of chemosensation. (A) The brain of Drosophila melanogaster, identifying neuropils related to olfaction (orange). Primary processing occurs in the AL (using glomeruli), with subsequent secondary processing in high brain regions, such as MB and LH. (B) Neural staining of AL and tracts toward both MB and LH, including clusters of cell bodies for projection neurons. (C) Reconstruction of a single projection neuron pathway from AL to high brain centers. (D) Schematic of pathways from peripheral olfactory organs, such as antenna and maxillary palps, where sensillum expresses olfactory receptors (ORs) within olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs). These peripheral OSNs first connect to a glomerulus within the AL before projection neurons (PNs) carry this signal onto the MB and LH. A multitude of papers have provided robust description and assessment of each stage (#1-8) of olfaction and gustation. AL, antennal lobe; OL, optic lobe; MB, mushroom body; LH, lateral horn; LN, lateral interneurons; PN, projection neurons; OR, olfactory receptor; OSN, olfactory sensory neuron.
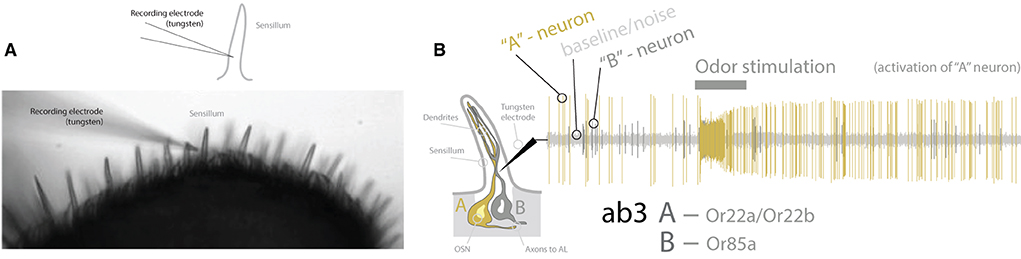
Figure 3. Methodology for recording from OSNs. (A) Drawn schematic and microscope image of recording electrode puncturing inside the shaft of the sensillum. This is the primary method, single sensillum recording (SSR), for Drosophila chemosensory deorphanization, which identifies which odors best activate each OSN and OR expressed at the periphery of the fly. (B) A diagram of the interior of a sensillum [e.g., antennal basiconic three (ab3)], showing two OSNs (“A” and “B”). Recordings provide baseline/noise, as well as large “A” neuron spikes and small “B” neuron spikes. Two amplitudes (e.g., large and small spikes) are indicative of two OSNs. Spikes occur spontaneously pre-stimulation but increase following stimulation with odor/ligand. In this example, only the “A” neuron increases firing; thus, this odor stimulation (e.g., odor/ligand) is activating only this neuron and odorant receptor (OR) type. OR, olfactory receptor; OSN, olfactory sensory neuron; ab3, antennal basiconic three; Or22a, olfactory receptor type 22a; AL, antennal lobe.
Neurobiology of chemosensation
Chemical signals detected by each sensillum on the antenna are transported into the primary olfactory processing center of the Drosophila brain (Figure 2), which is called the antennal lobe (AL). Within the AL, glomeruli are also interconnected to a few (e.g., sparse connections), or many partners (e.g., global connections), and these interconnected glomeruli often participate in modulation of the signal strength in each other. These connections are via lateral interneurons (LNs), and can provide increases or decreases in responses across the AL based on chemical detection of odor combinations coming from the antenna and/or palp (Das et al., 2017; Mohamed et al., 2019). Some stimuli, especially aversive, negative or dangerous chemical cues, often appear to have reduced LN connectivity within the AL, with the argument being that these so-called labeled lines are processed faster or with less relative modulation (Stensmyr et al., 2012; Ebrahim et al., 2015; Keesey and Hansson, 2021). Other stimuli, usually those odorants linked to mating or courtship behaviors, also appear to be less interconnected within the AL. However, in general, the Drosophila olfactory LNs are both highly diverse and highly variable in their connections within the antennal lobe, which is thought to contribute to the combinatorial and concentration or ratio-dependent nature of olfactory preference behavior.
After neural signals from the antenna or palp reach and are processed within the AL, projection neurons (PNs) transfer this information to the secondary processing centers (Figures 4, 5), also called the higher brain centers, which include both the mushroom body (MB) as well as the lateral horn (LH) (Grabe et al., 2016; Huoviala et al., 2018; Keesey and Hansson, 2021). The MB serves as a center for learning and memory, where PNs with larger arborization or branching have been suggested as indicative of the higher degree of modulation and plasticity in that behavior (Grabe et al., 2016; Keesey et al., 2020a). Here again, labeled-line circuits, frequently indicative of negative or sex-related odorants, usually have fewer connections and synaptic partners within the MB, and may, in turn, be less malleable (Stensmyr et al., 2012; Ebrahim et al., 2015; Keesey et al., 2020a). The LH, on the other hand, serves as the center for innate behavior, and can be subdivided into 3 main regions, including attractive, aversive, and pheromone/courtship stimulation (Figure 4). These higher brain centers (e.g., MB and LH) have been less explored outside of D. melanogaster when compared to the periphery and AL; however, with increasing molecular tools being developed across this genus, there will continue to be an acceleration of research in the coming years into novel species for comparison of these higher brain processing centers.
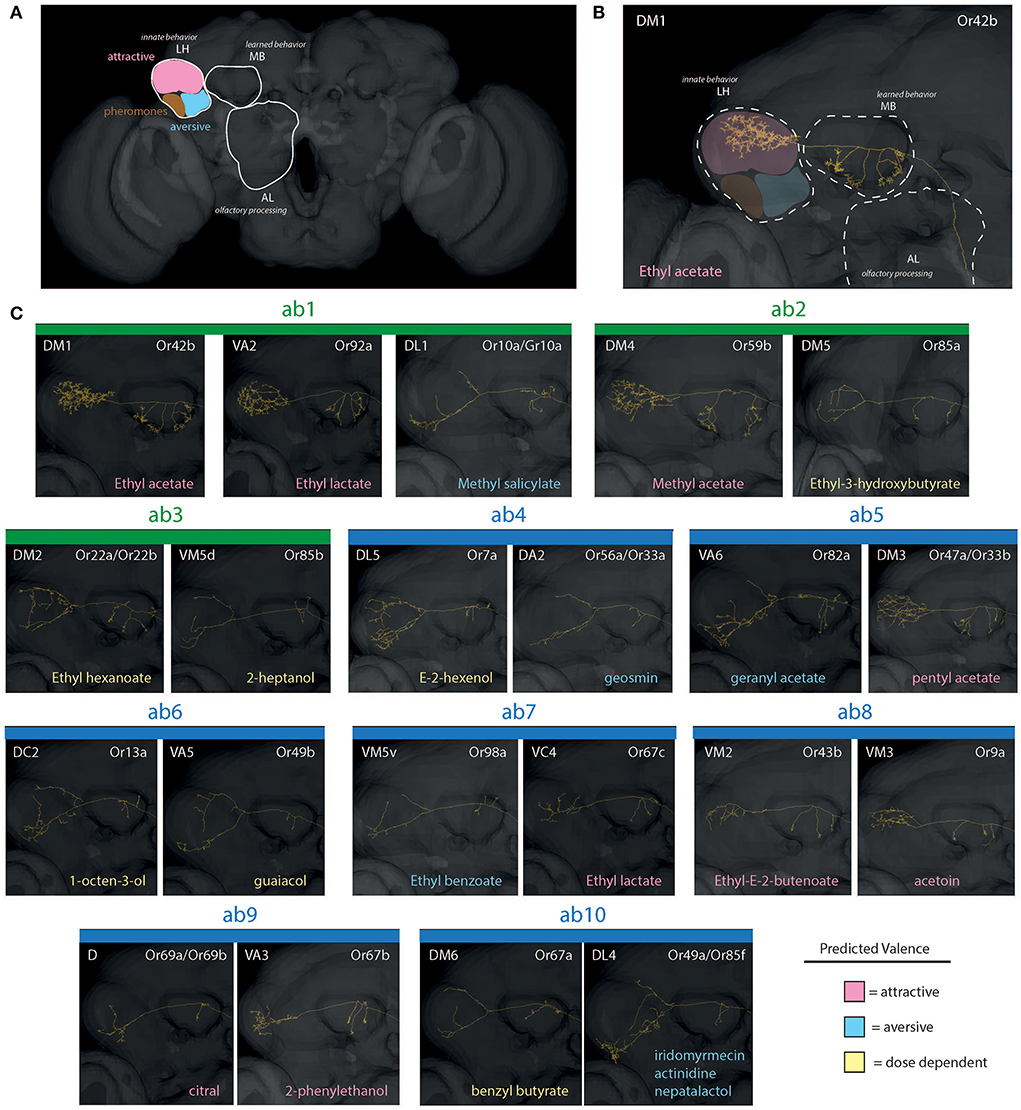
Figure 4. Reconstructions of PNs for olfaction (basiconic sensilla). (A) An overview of neuropils, including AL, MB, and LH. Here, the LH is further subdivided into distinct innate behavioral zones related to chemosensory stimuli. (B) A close up example of the single neuron pathway through AL, MB, and into LH (in this case, within an attractive zone of innate behavior). (C) Projection neurons (PNs) from antennal basiconics (ab1-ab10; green = large basiconic; blue = small basiconic). The ab1, for example, depicting 2 predicted attractive regions of LH (pink), and 1 predicted aversive arborization (blue). Most aversive odorants possess projection neurons that map toward the lower portion of the LH, thus appear as “Y” shaped. Also, note differences in arborizations within MB between attractive and aversive neuron subtypes, with attractive neurons have many arborizations and aversive having only a few (e.g., DA2 in ab4 vs. DM1 in ab1 sensillum). AL, antennal lobe; OL, optic lobe; MB, mushroom body; LH, lateral horn; PN, projection neurons.
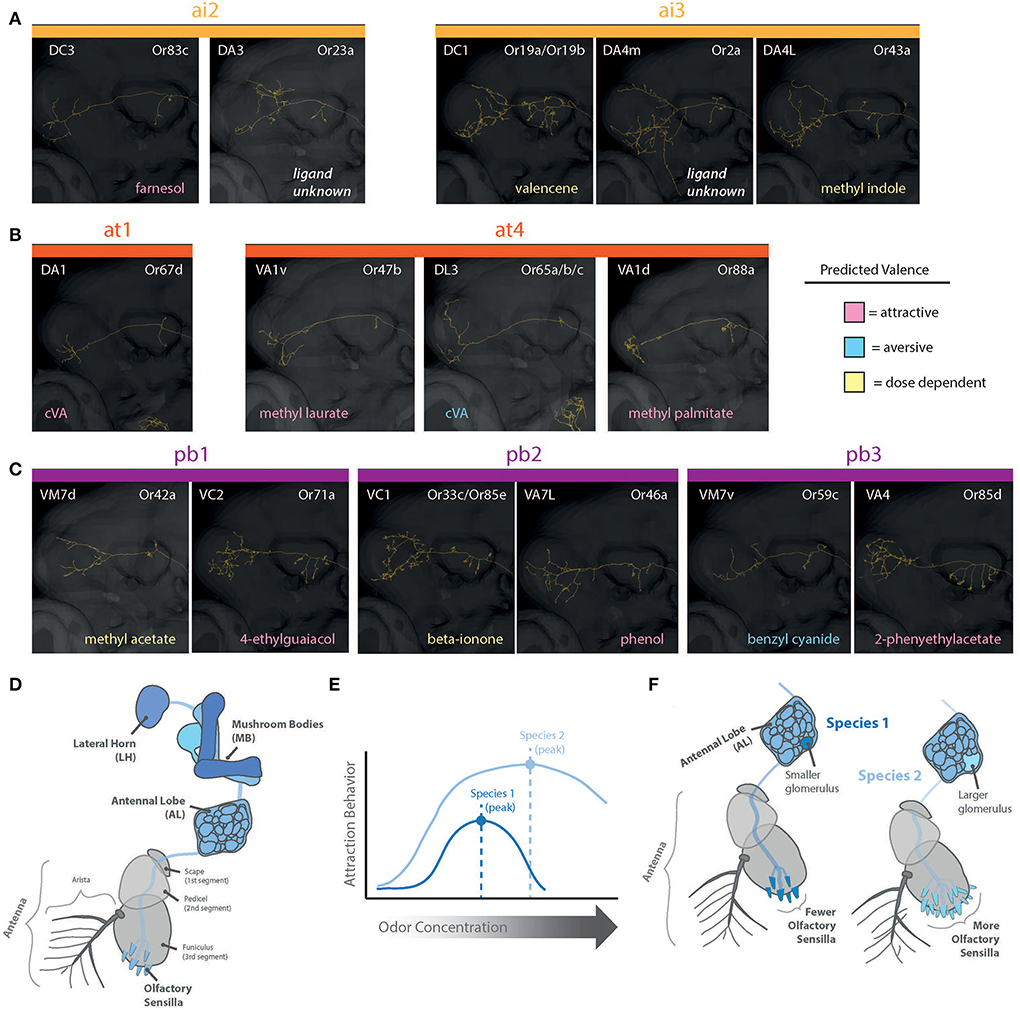
Figure 5. Reconstructions of PNs for olfaction (intermediate, trichoid, and palp sensilla). Shown are pathways through MB and into LH. (A) Projection neurons (PNs) from antennal intermediate sensilla (ai1 and ai3) and predicted behavioral valence as well as strongest excitatory odorant/ligand. (B) Projection neurons (PNs) from antennal trichoid sensilla (at1 and at4) and predicted behavioral valence as well as strongest excitatory odorant/ligand. (C) Projection neurons (PNs) from palp basiconic sensilla (pb1-pb3) and predicted behavioral valence as well as strongest excitatory odorant/ligand. (D) Olfaction (blue) is primarily from antenna and maxillary palps (shown are antennal pathways), where chemicals are detected within sensillum types, and these neurons then map into the brain of the fly. Primary olfactory processing is within the AL, and then subsequently within the MB and LH (i.e., the higher brain centers). (E) Species can differ in sensitivity and behaviors toward concentrations of the same detected odorant. (F) Species vary in the abundance of each sensillum type. Larger numbers of a sensillum type correlate with a larger corresponding glomerulus volume for those odorants within the AL. AL, antennal lobe; OL, optic lobe; MB, mushroom body; LH, lateral horn; PN, projection neurons.
For D. melanogaster, the AL features over 60 glomeruli (plural), which resemble a cluster of grapes, where each glomerulus (singular) receives all input from a specific OSN type at the periphery (i.e., all sensilla containing one subset of OSNs). For example, the DM2 glomerulus receives input from every copy of the ab3A OSN (ab3; antennal basiconic number 3), which contains and expresses the Or22a olfactory receptor. Thus, in each Drosophila species, the size of a single glomerulus in the AL relates to the total abundance of a sensillum and OSN type across the antenna or palp (Linz et al., 2013; Dekker et al., 2015; Grabe et al., 2016). Put another way, the size of a glomerulus in a species is directly proportional to the number of detection inputs coming from the sensory periphery (Figures 5D,F). For some species that have more ab3 sensilla than D. melanogaster, such as D. sechellia, the relative size of their corresponding DM2 glomerulus is greatly enlarged (Dekker et al., 2006; Linz et al., 2013). These relative increases in abundance do appear to come at a cost, where D. sechellia also has an extremely reduced set of the ab2 sensillum (Linz et al., 2013; Keesey et al., 2019b). Most examined species within the genus have around 60–70 total glomeruli, although there are large phylogenetic changes across the genus, and more research is needed to compare whole AL changes as opposed to studies of single glomerulus gains and losses.
Pheromones circuits changes between species
Olfaction represents one of the most well-studied sensory systems across the Drosophila genus. Beyond the underlying neurobiology, this includes chemical ecology research pertaining to both host navigation as well as courtship and mate acceptance from a wide variety of species. Here, pheromones, or volatile organic molecules that elicit a behavioral response from individuals of the same or related species, and other chemicals produced by the fly body, can be used to communicate between members of the same or opposite sex, are a classic study system to examine speciation, adaptation, and chemical divergence (Thistle et al., 2012; Fan et al., 2013; Seeholzer et al., 2018; Khallaf et al., 2021). Within the genus Drosophila, there are two main categories of volatile pheromones, including sexually dimorphic odorants, such as cis-vaccenyl acetate (cVA), which is produced only by the male accessory glands (Benton et al., 2007), as well as sexually monomorphic odorants, here including aggregation and courtship pheromones, such as methyl laurate (ML), that are produced by both sexes, presumably through the fat body and via regulated metabolic processes (Dweck et al., 2015; Lin et al., 2016). Lastly, there are also cuticular hydrocarbons (CHCs), which, in addition to their functional role in desiccation resistance [e.g., where short-chain hydrocarbons are associated with tropical habitats and longer-chain hydrocarbons are associated with arid environments (Jezovit et al., 2017)], are also detected on the surface of the flies and function as mostly non-volatile, gustatory, or contact-mediated pheromone cues (Fan et al., 2013; Depetris-Chauvin et al., 2015; Lebreton et al., 2017). It is also important to mention that, while most insect-borne odorants (pheromones) are identified via body washes or whole insect extraction protocols, that these compounds are also sometimes deposited directly onto host substrates, and that frass, feces, anal droplets, and other insect waste products can also directly contribute to the chemical detection of an insect species, its sex, or its mating status (Wada-Katsumata et al., 2015; Keesey et al., 2016; Khallaf et al., 2020; Revadi et al., 2021), as well as contribute toward novel pheromone discovery (Tumlinson et al., 1969).
While many insects, including Drosophila species, can detect pheromones from both sexes, it remains unclear whether insects detect and/or respond to odorants produced by their own body. However, studies of aggression and competitive courtship suggest that detection of self-produced pheromones can elicit an escalation in intraspecific behaviors. Here, it has often been observed that multiple males competing for a single female increase the fervor of courtship dynamics, as well as reduce the latency of female acceptance (Dweck et al., 2015; Keesey et al., 2020a). Despite this, it has been shown that keeping males in large groups (as opposed to isolated or in small groups prior to testing) can reduce courtship fervor in subsequent behavioral trials due to constant, habituation-like peripheral detection of cVA (Benton et al., 2007), where cVA can reduce male courtship and increase male-male aggression (Wang and Anderson, 2010). Opposingly, it has been shown that group housing can affect male behavioral response via Or47b, a different pheromone-detecting receptor, and provide a significant advantage to males in higher-density rearing conditions when compared to isolated males, here via detection of palmitoleic acid and other fatty acid-activating ligands (Lin et al., 2016; Sethi et al., 2019). Thus, some pheromone detection pathways appear to afford behavioral advantages, depending on social density or context. Similar to this last example, it is clear that some volatiles from host materials can also increase courtship behaviors of males in the presence of females (Lebreton et al., 2015; Das et al., 2017), as most Drosophila species for which natural history is known exhibit heightened courtship dynamics, increased copulation success, and reduced latency when courtship occurs actively on the preferred host substrates (e.g., fermenting fruit for most of the melanogaster species clade). This relationship between food and sex odors is an increasingly important topic of neural research across different Drosophila species (Lebreton et al., 2015; Das et al., 2017), and flies reared on natural fermentation or host substrates appear to be at an advantage when compared to flies from laboratory diet only (Keesey et al., 2020a). Other ambient conditions like temperature, humidity, and the light level also contribute to courtship dynamics across each species and are discussed in more detail later in this review.
Several sex-specific pheromones, such as cVA, can also be transmitted from male to female during copulation events, and variations in the utilization of this odorant exist across the Drosophila genus in a phylogenetic manner (Khallaf et al., 2021). For example, the presence of cVA can inhibit the courtship behavior of other males toward a recently mated female (Ziegler et al., 2013; Lebreton et al., 2014). While most members of the melanogaster clade produce and behaviorally respond similarly toward cVA, other close relatives within the genus appear to have reduced or lost the production and detection of this pheromone, such as in the case of the agricultural pest, D. suzukii (Dekker et al., 2015; Keesey et al., 2016; Khallaf et al., 2021). The variation in behavioral response toward male-produced cVA also appears to be related to an evolutionary rebalancing of the neural circuits that control the innate valence associated with this odor, as two separate neural pathways determine behavioral attraction or aversion toward cVA (e.g., DA1:Or67a, and DL3: Or65a). Here, D. suzukii is repelled by this male-produced pheromone, mostly due to a volumetric reduction in the attractive glomerulus (DA1: Or67a), as well as a relative increase in the correspondingly aversive glomerulus (DL3: Or65a) (Dekker et al., 2015; Keesey and Hansson, 2021). Thus, the function of odorant detection can alter, or even reverse its meaning or valence between different Drosophila species and provide variation in behavioral roles for a specific pheromone in nature, even in cases where both species produce and detect that same odorant compound. This is often the result of paired neural circuits or coding strategies in the brain that simultaneously detect the same chemical cue at the periphery, but where one detection pathway regulates positive or attractive behaviors, while a second pathway regulates and balances negative or aversive responses. Moreover, this is often regulated by differences in sensitivity of the two receptors. This balancing act in the brain serves to modulate relative strength of response across Drosophila species toward the same peripheral detection of a chemical compound. Thus, concentration of odors becomes hugely important in the differences in behaviors observed across even close species, as the relative balance of attractive and/or repellent effects of an odorant can shift through gains and losses in a type of olfactory and gustatory neurons, changes in sensitivity of receptors toward that odorant, or via changes in the relative representation (e.g., amount or signal strength) of an odorant that is conveyed into the higher brain centers for behavioral decision-making.
A complete reversal in behavioral valence was also shown for another chemosensory pheromone, 7,11-heptacosadiene, a CHC which promotes courtship behaviors in D. melanogaster, but suppresses courtship in a close, sister species, D. simulans (Seeholzer et al., 2018). Here, researchers show that males of both species detect 7,11-heptacosadiene using homologous peripheral sensory neurons, but that, subsequently, this signal is differentially propagated within higher brain centers. Therefore, again, a change in the balance of excitation vs. inhibition onto courtship-promoting neurons in the central brain transforms a normally positive pheromonal cue in D. melanogaster into a negative stimulus for D. simulans (Seeholzer et al., 2018). Similarly, vinegar flies and mosquitoes appear to both detect geosmin, an earthy mold odorant, but these Dipterans show opposite behavioral responses, with vinegar flies being repelled and mosquitoes being attracted, at least in regard to oviposition (Stensmyr et al., 2012; Melo et al., 2020). This further reveals how species-specific chemosensory responses can emerge from evolutionary conservation of peripheral detection mechanisms, but subsequent deviation of central brain circuitry, and demonstrates how flexibility in neural circuits can contribute to behavioral evolution toward the same odorant across species. Here, it is less clear why some odorants are detected by so many orders of insects, such as geosmin, 2-heptanol, and Z-3-hexenol. While the fundamental mechanisms for a valence shift and neural rewiring remain to be fully elucidated, the most likely source, whether directed or random, appears to be a potential developmental process (Prieto-Godino et al., 2017, 2020; Seeholzer et al., 2018; Auer et al., 2021). Here, the birth and death process of chemosensory receptors offers unique opportunities for evolutionary processes to add, eliminate or potentially replace proteins that function in detection of olfactory and gustatory cues.
The chemosensation of host preference
Beyond pheromone detection, a plethora of odorant receptors (ORs) have also been shown to be highly variable across the Drosophila genus. Here, individual species are shown to vary in either the presence or absence (i.e., gains and losses) of specific Ors (Ometto et al., 2013; Goldman-Huertas et al., 2015; Ramasamy et al., 2016), or that different species of Drosophila vary widely in the relative abundance and expression of those same odorant-detecting genes and receptor types (Dekker et al., 2006; Linz et al., 2013; Keesey et al., 2015, 2019b; Auer et al., 2021). In this case, as more species within Drosophila are examined, there appears to be a trend in either the relative increase or decrease in the number of specific odorant or gustatory receptors (i.e., the abundance or expression level) within and across sensory sensillum types (Figures 5D,F), especially following ecological or host preference specialization, such as in D. sechellia or D. erecta (Dekker et al., 2006; Linz et al., 2013; Keesey et al., 2015, 2019b). For these two species, the ab3-like sensillum and Or22a homologs vary greatly between close relatives in both function and abundance; in this case, there is a substantial increase in ab3 sensillum abundance compared to other melanogaster relatives (Figures 5D,F). Importantly, often, only a few receptors appear to repeatedly change between species, with most chemosensory proteins being conserved in their function as well as relative expression or abundance (Keesey et al., 2022).
For most of the examined Drosophila species, at least within the Sophophora subgenus, OR and OSN pairings within a sensillum are also usually quite well-conserved in relation to the model species, D. melanogaster (i.e., the Ab4 sensillum generally contains both Or7a and Or56a in each examined Drosophila species), and current theories convey that this conserved pairing at the periphery serves a specific mission in regulating species-specific behavioral valence (Stensmyr et al., 2012; Keesey et al., 2019b; Wu et al., 2022). Here, again, this conserved pairing motif is likely due to developmental programming within the eye-antennal imaginal disc (Prieto-Godino et al., 2020; Yan et al., 2020). However, in the evolutionary cases of gains and losses of receptors, this common receptor pairing can sometimes be disrupted, with one or both receptor proteins lost in the genome and subsequently lost in functional expression at the periphery, for example, becoming a pseudogene. In these cases, via either novel OR replacements, or a reorganization of expression patterns, new combinations or pairings can potentially occur (Prieto-Godino et al., 2016, 2020; Keesey et al., 2019b; Auer et al., 2021). Here, chemosensory receptors, such as ORs and IRs that are co-expressed (i.e., functionally overlaid with another receptor within a single sensory neuron, such as Or33a and Or56a, together in ab4B), show a potential higher likelihood of being reorganized or transferred toward another sensillum or to be found with a new pairing partner across examined species (Prieto-Godino et al., 2017, 2020; Keesey et al., 2019b). In these cases, it is hypothesized that co-expression events, where an OSN/GRN contains two or more functional receptors (e.g., co-expression), are potential snap shots of evolutionary selection processes in action, and provide a framework for behavioral and chemosensory preference changes to occur within populations and between diverging species (Shaw et al., 2019; Khallaf et al., 2020; Auer et al., 2021; Dweck et al., 2021). This occurs for example, in the melanogaster clade of species, between Or22a and Or22b expression patterns (Aguadé, 2009; Shaw et al., 2019), or among Or67a duplicates and paralogues in D. melanogaster, D. mauritiana, D. simulans, and D. sechellia strains (Auer et al., 2021). Moreover, the co-expressed ORs, IRs, and GRs in the peripheral chemosensory system create dynamic differences in OSN/GRN function in terms of odorant sensitivity and the apparent best ligands for binding and activation of that neural circuit (Dweck et al., 2021; Task et al., 2022). These co-expressed proteins most likely provide enough variation in olfactory/gustatory function that ecological and evolutionary forces can create selection for specific receptors (or co-expressed combinations) to be kept or lost across evolutionary time and habitat adaptations.
Future research in chemosensation
Despite decades of work focused on the complete deorphanization of odorant receptors in D. melanogaster, several chemosensory receptors remain without a best excitatory ligand or known ecological and behaviorally relevant function. This includes, for example, Or2a and Or23a, both of which are expressed in the reclassified antennal intermediate sensillum types (Lin and Potter, 2015). However, artificial activation of these circuits has shown that they project into the primary olfactory neuropils and are completely functional as well as behaviorally active (Chin et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2022). While it is likely that these receptors and their as-of-yet-unknown ligands play a role in social dynamics or courtship, similar to the other identified members of trichoid and intermediate sensillum types, more work is still needed in the future to confirm these predictions. Therefore, even in the most studied species, D. melanogaster, there is still room for identification of novel odorants from natural substrates, such as host materials, the insect body or insect waste products. As research expands into non-model species from the Drosophila genus, an increasing dearth of functional olfactory and gustatory information arises, where, for most species, more is known about their genome than their ecology, behavior, or natural history. However, genomic studies include expansive datasets about chemosensory receptor gene expression, as well as gains and losses of receptors across OR, GR, and IR lineages (Crava et al., 2016; Hickner et al., 2016; Ramasamy et al., 2016; Khallaf et al., 2021). Thus, much of the groundwork is already laid for functional testing and chemosensory examination of diverse Drosophila species, especially given the immense genomic databases for comparison toward olfactory and gustatory homologs in these non-melanogaster species. This leaves open considerable avenues for future research to identify and compare chemosensory, behavioral, and neurobiological or circuitry variations across species (Seeholzer et al., 2018), as well as questions about how these closely related insects navigate their unique natural habitats, chemical environments, and search for mates. Here, it is likely in the near future that additional studies will continue to emerge that compare functional dynamics of protein structure with genomic variation in receptor function (e.g., changes in binding affinity for olfactory and gustatory cues) (Auer et al., 2020).
Evolution of the visual sensory system
Most of our understanding of visual processing of the compound eye within this genus comes again from studies of the type species, D. melanogaster. Here, this species has been examined for many key elements of the visual system functionality, from light and wavelength perception by photoreceptors to the primary neural processing centers of visual stimuli via sections of the optic lobe (Larderet et al., 2017; Perry et al., 2017; Sharkey et al., 2020; Kind et al., 2021). Much of what is understood about animal color vision is derived from studies of vertebrates, and only more recently have studies begun to reveal the neural basis of wavelength information processing by insects. Color, or wavelength information processing, has been investigated in D. melanogaster using behavioral experiments, as well as by visualizing neural responses directly inside the fly brain, for example, in response to light stimulation using genetic or molecular tools that aid fluorescence (Schnaitmann et al., 2013, 2018, 2020; Heath et al., 2020). These and other studies of this singular species make it clear that vinegar flies utilize visual information to navigate their environment (Fisher et al., 2019) as well as identify object movement, light intensity, contrast, and color.
The D. melanogaster visual sensory system is made up of around 800 ommatidia or single facets of the compound eye (Posnien et al., 2012; Gaspar et al., 2020; Sharkey et al., 2020). The many hexagonal-shaped ommatidia include at the surface a convex cone (cornea), as well as photoreceptor cells that surround the rhabdomere that runs nearly the full length of singular ommatidium (Figure 6). Each individual ommatidium, which is composed of almost 20 cell types, includes eight total photoreceptor cells. The sections of the ommatidia containing the photoreceptor cells and rhabdomere are called the retina. The eight photoreceptors, which span most of the length of the retinal cell, can be divided into two main categories, depending on their spectral sensitivity: the six outer photoreceptors (R1, R2…R6) and the two inner photoreceptors (R7 and R8). The outer R1–R6 cells represent the major class of photoreceptors in the retina and are involved primarily in image formation and, also, the detection of movement. These cells have peripherally located rhabdomeres, extending the full length of the retina, and they express a single opsin type, called Rh1. Moreover, the outer photoreceptor cells project their neural axons to the most distal portion of the optic lobe, the lamina. The second group, the two inner photoreceptors, consists of two cells in the center of each rhabdomere termed R7 and R8. These two cells are stacked, with each spanning only about half of the total retina in length. The central cells R7 and R8 are involved in color vision and detection of polarized light. These cells, in turn, project their axons through the lamina and into the second most distal layer of the optic lobe, the medulla. Sensitivity of the inner photoreceptors is largely determined by the underlying visual pigment, and ommatidia from D. melanogaster can be further subdivided into two major classes, “pale” (p) or “yellow” (y), depending on the arrangement of opsins within the inner rhabdomere. The “pale” ommatidia subtype expresses the opsins Rh3 (in R7 cells) and Rh5 (in R8 cells) and represents ~30% of the total ommatidia, while the “yellow” ommatidia subtype expresses the opsins Rh4 (in R7 cells) and Rh6 (in R8 cells) and makes up ~70% of the total ommatidia. Together, these ommatidia subtypes (pale and yellow) provide an interlaced mosaic across the compound eye that detects wavelengths of light or provides color vision in D. melanogaster adults (Posnien et al., 2012; Hilbrant et al., 2014; Schnaitmann et al., 2020).
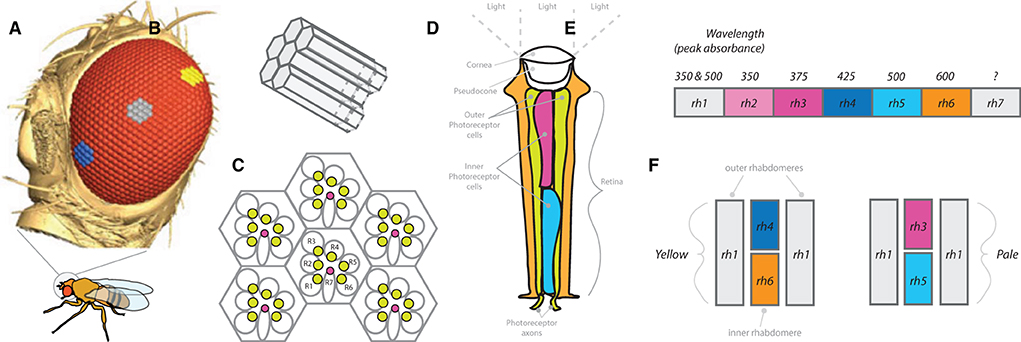
Figure 6. Compound eye and peripheral visual sensory system. (A) Side view of Drosophila head, showing compound eye (red) and hexagonal ommatidium (blue, grey and yellow cluster examples). Size, distribution, and number of ommatidia can vary widely across Drosophila species (as well as across populations or strains). (B) Single cluster of ommatidia that receives light stimulation within the rhabdomere to activate photoreceptor neurons. (C) Example arrangement of clusters of ommatidia with rhabdomeres (R1-R7), where R1-R6 relate to outer photoreceptor neurons, while R7 represents the inner photoreceptor neuron. (D) Diagram of a single ommatidium. (E) Each ommatidium contains combinations of rhodopsins (rh1-rh7), where these combinations determine wavelength of light absorbance spectrums for that particular photoreceptor. (F) Examples of pale and yellow ommatidium subtypes.
In addition to D. melanogaster, more recent research has ventured to identify and describe many visual sensory elements of other species or strains within this genus of flies (Figure 7). This includes studies that identify differences in total number of ommatidia across differing populations of D. melanogaster. Thus, this new frontier that examines ecological and evolutionary variation in the periphery visual system is also beginning to build a foundation of knowledge (Posnien et al., 2012; Keesey et al., 2019a; Gaspar et al., 2020), including several cases of genetic investment and molecular tool development across diverse species, such as differences observed through larval development or within the optic lobe (Tanaka et al., 2017; Ramaekers et al., 2019). Species that have a long history of visual behavioral comparisons include the obscura clade, especially D. persimilis, D. pseudoobscura, and D. subobscura. These species have strikingly divergent vision, including at the neural level as well as during behavioral trials, with D. pseudoobscura having less-positive phototaxis than D. subobscura (Kekić and Marinković, 1974; Keesey et al., 2020b), and D. pseudoobscura also being less phototactic than D. persimilis (Spassky and Dobzhansky, 1967). Thus, even close relatives within the Drosophila genus can have strong variation in visual priority or sensitivity to light, which is reflected in their behavior, genetic architecture, development, as well as neuroanatomy. It has been proposed that these obscura species, where at least two of which are sympatric, differ in niche space utilization through variation in phototaxis as well as light-related courtship dynamics (Keesey et al., 2020b). However, few species have had individual visual circuits analyzed or traced, and few species (i.e., other than D. melanogaster) have been addressed in regard to reconstructions of sections of the OL, or how ommatidia type variation in the compound eye across species transfers into observable changes (if any) in the associated neurobiology of vision and visual behavior.
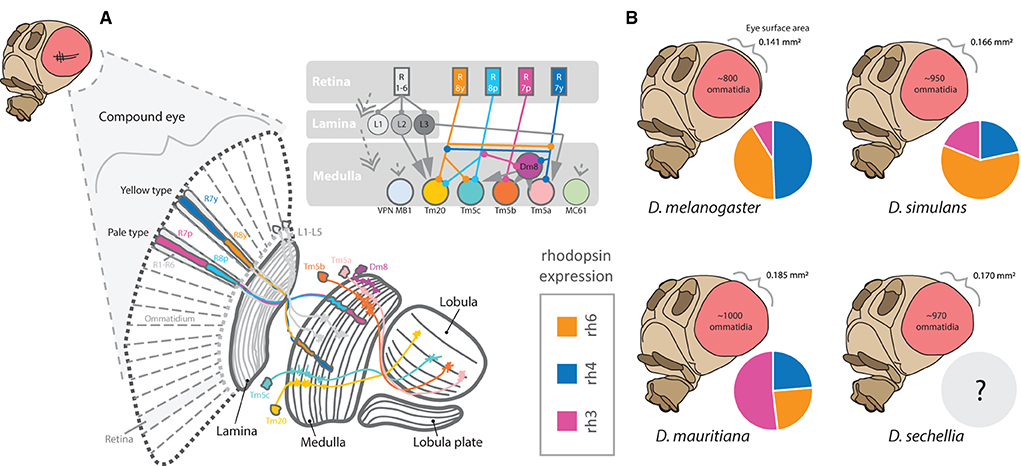
Figure 7. An overview of visual processing in the fly brain. (A) The compound eye contains hundreds of ommatidia, including two primary types, yellow and pale. Each ommatidium projects into the retina of the compound eye. These ommatidia contain distinct rhabdomeres expressing combinations of rhodopsins (rh1-rh7). Photoreceptors associated with rhabdomere/rhodopsin combinations detect light, wavelength, color, and visual movement, where these stimulation and information from the compound eye are then passed into the optic lobe. The optic lobe contains 4 major components, including the lamina, medulla, lobula, and lobula plates. (B) The number of ommatidia varies significantly between even close relatives. In addition, the ratio or allocation of ommatidia containing different rhodopsins (e.g., rh3) for color vision is also quite variable. Thus, while overall eye size differs between the species, the increase in visual sensory inputs does not appear to be uniform.
Several studies have documented shifts between species in the proportions of photoreceptor types that compose the retinal mosaic within the compound eye (Posnien et al., 2012; Hilbrant et al., 2014; Gaspar et al., 2020). Here, it has been shown that species such as D. mauritiana can have substantially more Rh3-containing ommatidia when compared to D. melanogaster or D. simulans, whereas D. melanogaster has more Rh4, and D. simulans has more Rh6, when compared to the other two species (Posnien et al., 2012). Thus, rhodopsin expression appears rather variable between those species that have been examined, and likely contributes to differences in both color perception, contrast preferences, and visually linked search behaviors (Figure 7). In general, species and strains of Drosophila vary markedly in the total number of ommatidia that compose the compound eye, as well as vary in the facet size or diameter of each ommatidium (Posnien et al., 2012; Hilbrant et al., 2014; Keesey et al., 2019a; Gaspar et al., 2020). What is less clear is whether species with relatively larger eyes have evolved specific changes in rhodopsin type and abundances, and if phylogenetic proximity is predictive of priority and functional preference in color, contrast, and motion vision across visually mediated behaviors. For example, Drosophila species may differ in their preference for colors, types of visual contrast, or the priority of visual stimuli vs. those that are olfactory (Keesey et al., 2019a). Moreover, rearing density in laboratory vials appears to modify adult body size, although it is still unclear if different sized adults within a species or population create variation in sensory structures or sensory allocation of neural resources (Keesey et al., 2019a). Interestingly, new studies suggest that D. melanogaster is able to detect wavelengths of red light (Sharkey et al., 2020), a portion of the visible spectrum that has been previously thought to be invisible to flies and to most insects in general. This may cause some adjustment in how future behavioral trials are run in the dark, where red light was often used to allow researchers (or cameras) to operate in the dark but was thought to be invisible to the flies.
While chemosensation is hugely important for mediating courtship behaviors, once outside of the melanogaster clade of species, vision appears to become increasingly important as well. Studies have often shown that D. melanogaster, for example, performs equally well regarding courtship latency and courtship success when in complete darkness as compared to trials in a well-illuminated arena. On the other hand, many other species perform far better across courtship metrics when in light (as opposed to dark) courtship trials, something that has been attributed to the necessity of visual stimulation for some species of flies to mate successfully or more quickly (Sakai et al., 2002; Keesey et al., 2019a, 2020b). However, it does appear that populations or strains within each species, even D. melanogaster and D. simulans, can have quite variable responses to light vs. dark courtship trials (Shahandeh et al., 2020); thus, additional research is still needed to identify the roles of genetics and neurocircuits (as well as relative eye size) in mediating this behavioral variation (Posnien et al., 2012; Hilbrant et al., 2014; Keesey et al., 2019a; Shahandeh et al., 2020). This disparity within and across species may be directly related to a natural developmental variation in eye size and the potential tradeoff between investment invision and olfaction, for example, due to the sharing of a singular developmental structure (i.e., the eye-antenna imaginal disc from the larva) that gives rise to both sensory structures and neuropils in the adults (Keesey et al., 2019a; Ramaekers et al., 2019; Gaspar et al., 2020). Interestingly, research pertaining to fruitless genes, which are linked to a cluster of ~2,000 neurons that completely control all courtship preferences and behaviors in the Drosophila genus (Kimura et al., 2008; Yu et al., 2010; Seeholzer et al., 2018; Hindmarsh Sten et al., 2021), has been shown to map extensively into the optic lobes of some species, such as D. subobscura (Tanaka et al., 2017). This may prove to be a vital aspect of explaining relative variance in visual courtship reliance or the necessity of light during courtship within certain populations and across particular species. This difference in fruitless labeling of the optic lobe may also explain phototaxis differences between members of the obscura clade, such as for D. pseudoobscura that generally prefers darker environments, compared to D. persimilis and D. subobscura, that each prefers brighter light levels (Brown, 1964; Spassky and Dobzhansky, 1967; Kekić and Marinković, 1974; Keesey et al., 2020b). However, more work is required to test fruitless labeling of visual neurons and their role in explaining ecological and evolutionary variation in light-dependent courtship behaviors. It is also unclear what role the ocelli play in visually mediated behaviors, such as phototaxis, general light preference or courtship, and additional work will be required to begin to compare neurons related to these photoreceptor types found on the crown of the head.
Beyond the total amount of light, color or even visual contrast, sight-mediated behaviors also include sensitivity to object motion. Recent studies have highlighted the vital role movement plays in D. melanogaster courtship (Hindmarsh Sten et al., 2021), especially in relation to identification, orientation, and tracking of a potential female mate by males that have been sexually aroused via chemosensation. In this case, activation of P1 neurons and LC10a visual projection neurons results in faithful following and courtship ethology by males toward a variety of moving targets (Hindmarsh Sten et al., 2021). These neural circuits, in turn, may be important for other species that appear to utilize wing pigmentation as part of their courtship dance, such as D. suzukii and other spotted wing species, where wing pigmentation may stimulate motion detection circuits in the female (as in this species only males possess a wing pigment). It was shown that a close relative of D. suzukii loses courtship effectiveness when male wing pigmentation is removed, further suggesting the role these spots play in female acceptance for this species group (Hegde et al., 2005). Why some species are sexually dimorphic in regard to wing pigmentation is less clear, but could also be related to motion vision differences in neurobiology between males and females of these species. Sexual dimorphisms in phenotypes and genotypes are common in many Drosophila species, and, while the underlying neural correlates and behaviors are less well-explored, it is clear that males and females do differ in their neurobiology (Kimura et al., 2008; Nojima et al., 2021). It has been proposed that wing pigmentation across the Drosophila phylogeny is correlated with visually mediated courtship behaviors (Keesey et al., 2019a, 2020b), although more data are needed to test hypotheses related to evolutionary mechanisms. It will be important in the future to compare eye size variability across species (or within populations) in regard to visually mediated courtship behaviors, and contrast these differences to the relative use of wing signaling during courtship, male position in front or behind the female, as well as other visually dependent courtship metrics (e.g., across trials using different wavelengths or intensities of light) (Grossfield, 1971; Kekić and Marinković, 1974; Ripfel and Becker, 1982; Sakai et al., 2002). In the future, behavioral studies comparing the visual preferences of many species within the Drosophila genus could provide novel insights into how the eye prioritizes different types of visual input, including color, motion, and contrast detection. Again, the modern genomic resources afforded by many species across the genus Drosophila create an open atmosphere for testing various hypotheses about visually mediated behavior differences, especially as related to the neurobiology of these flies.
Evolution of the auditory sensory system
Wings are used for more than potential visual signaling, and a wide variety of species within the Drosophila genus performs complex auditory routines during courtship using primarily different types of wing vibration (Murthy, 2010; Riabinina et al., 2011; Coen et al., 2016), in addition to leg and abdominal tapping on host substrates (Mazzoni et al., 2013; Hernández et al., 2016; Keesey et al., 2020b). Sound is primarily detected by the antenna of these flies, more specifically via the Johnston's organ (JO), found between the second and third antennal segments (Figure 8). The JO, which acts as a sensitive push-pull and stretch system for specific types and frequencies of auditory information, is composed of around 500 mechanosensory receptor neurons, which, after activation, send their electrical information toward the antennal mechanosensory and motor center (AMMC) in the adult brain (Tootoonian et al., 2012; Pézier et al., 2014). This neuropil receives mechanosensory input not only from the JO but also from other mechanosensory cells across the head, and the AMMC can be functionally broken down into five subgroups (A-E). Here, Subgroups A and B of the AMMC specifically detect sound vibrations, while Subgroups C and E detect gravity and wind deflections (e.g., associated with movement of the arista). The more centrally located Subgroup D appears to detect a combination of all of these auditory cues, including vibration sounds, gravity as well as wind deflections (Kamikouchi et al., 2009; Tootoonian et al., 2012; Matsuo et al., 2014; Hulse et al., 2021).
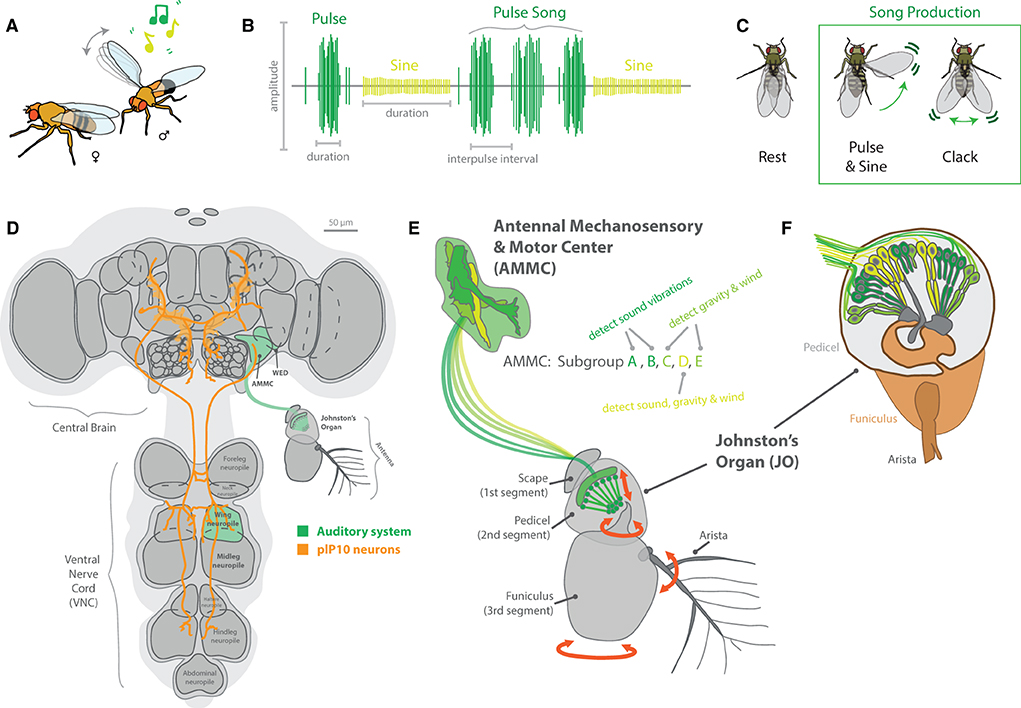
Figure 8. Auditory signaling and neurobiology in the melanogaster clade of species. (A) For most members of the Drosophila genus, males perform elaborate dances when a female is present. This often includes an auditory component, usually generated by the vibration of one or both wings. (B) Each species in the melanogaster clade creates a unique song, generally composed of distinct auditory frequencies. The songs of these species possess two main components, a pulse and sine, which are separated based on amplitude, duration, and interpulse intervals. (C) Some members have been shown to also produce other song elements, called clacks, which are generated by bursts of activity in both wings without full extension. (D) The neurobiology of song relates to two main brain regions, the central brain and the ventral nerve cord (VNC). To connect these regions, plP10 neurons extend the full length of these brain regions, and encode auditory information reception as well as production by the muscle movements from the thorax (e.g., wings and legs). (E) Auditory (green) sensory stimuli are detected by mechanosensory motions of the antenna. This is primarily related to the Johnston's Organ (JO), which detects torsion and movement of the antenna as well as the arista. Vibration and movement neurons pass that sensory information into the primary processing center in the brain, the antennal mechanosensory and motor center (AMMC). This region of the brain has 5 subgroups, each responding to sound, vibration, gravity, and/or wind stimulation. (F) A detailed view of the JO, highlighting the push-pull and stretch system for specific types and frequencies of auditory and vibration stimulation. Around 500 mechanosensory receptor neurons send their electrical information toward the AMMC in the adult brain after activation in the antenna.
Genetic advancements in a variety of Drosophila species have led to discoveries of variation in the neurobiology of these auditory circuits, from antennal perception to appendage production of sound (Ding et al., 2019). Here, descending neurons from the central brain (in the head of the fly) toward the ventral nerve cord (VNC; in the thorax) control various aspects of wing vibration signals (Figure 8). The VNC contains several ganglia that pertain to each of the six legs, as well as toward each of the two wings. These differences in neuroanatomy are reflected in behavioral changes between males and females, as well as among closely related species (Coen and Murthy, 2016). Variations in song production include changes in auditory frequency as well as song element types. For example, D. melanogaster generates primarily two song elements, pulse and sine, using one fully extended wing (Shirangi et al., 2013; Ding et al., 2019). In this case, wing pulses represent waveforms with a typically short duration in the order of milliseconds, which are usually repeated to form sets or sequenced events, called “pulse songs.” Sine songs represent more continuous, pure-tone-like waveforms with a longer typical duration, usually lasting over several seconds (Riabinina et al., 2011). The short auditory bursts of wing pulses often have larger amplitudes as well when compared to sine waveforms (Figure 8B). In addition, pulse songs can be characterized by two major descriptors: the principal frequency component of the individual pulse (intrapulse frequency, or IPF) and the time interval between pulses within a set or sequence (interpulse interval, or IPI). In turn, each species of Drosophila interweaves these two primary sound elements (pulse and sine) to form their own, typical courtship song, which can utilize one or both wings in sound production. In the case of D. yakuba and D. santomea, these melanogaster relatives also produce a third type of song element, called clacks, which is higher frequency, and is generated by vibrating both wings simultaneously but without full wing extension (Ding et al., 2019). Thus, wing vibration, as well as variation across neuronal and muscle control of wing movement in the VNC, all contributes to differences in the auditory repertoire of each individual species.
As more species are studied in greater depth for auditory communication, additional sound elements have been reported, such as leg and abdominal tapping (Mazzoni et al., 2013; Hernández et al., 2016; Keesey et al., 2020b). These lower tone or frequency sound-producing behaviors sometimes coincide with wing-related vibratory cues, or can represent drastic changes in sound preference, such as the complete loss of wing vibration in non-singing species, such as D. subobscura (Ripfel and Becker, 1982; Tanaka et al., 2017; Keesey et al., 2020b). It is also noted that some species have wing vibration or singing by both male and female, although the genetics and neurobiology behind this sexual dimorphic behavior have yet to be elucidated. However, it is clear that, even within D. melanogaster, there are strongly sexually dimorphic neural innervation patterns related to both sound production as well as sound reception (Coen and Murthy, 2016). It is possible that wing shape or size plays a role in sound generation, although these elements as well as potential visual cues (e.g., wing spots) have not been investigated together in relation to courtship preferences, especially as related to sexually dimorphic species. For species where the male spends considerable time in front of the female, this sometimes coincides with proboscis extension by the male (Tanaka et al., 2017; Keesey et al., 2020b), which is generally considered to be a nuptial or nutrition gift (and may also represent an olfactory or gustatory signal). Interestingly, legs and wings share close neuropil proximity in the VNC, and future work could address differences in neural innervation within and across these areas of the thorax; for example, in species such as D. subobscura that do not sing with their wings but, rather, where males tap their middle pair of legs during similar timepoints of the courtship ethology of song production in other species (Brown, 1965; Keesey et al., 2020b).
Research has already narrowed the search for key circuits related to song production in D. melanogaster (von Philipsborn et al., 2011; Coen et al., 2014, 2016; Clemens et al., 2018; Ding et al., 2019). Here, the P1 is a cluster of about 20 central brain neurons per hemisphere of the central brain (also related to pheromone detection and motion vision, see above sections); the plP10 is a pair of neurons that descend from the central brain down to the VNC in the thorax (Figure 8D). Lastly, the vPR6 is a set of around 5 thoracic interneurons per side that connect to the motor neurons (e.g., ps1) of each wing's musculature. Optogenetic activation of these neurons (P1, plP10, vPR6) results in male D. melanogaster song production, even in the absence of a female (Clemens et al., 2018). In observations of mating, especially those aided by video and computer annotation or animal pose estimation, the distance the male is from the female appears to play a vital role in the type, amplitude, and frequency of songs produced, and further separates species-specific behavioral differences across the melanogaster clade. Thus, the interface between visual and auditory cues will need to continue to be described and disentangled during studies of courtship ethology. Many historic papers from the last century have observed and described courtship, especially wing movement, song production, and potential auditory information exchange between male and female flies (Spieth, 1952; Brown, 1965; Ewing and Bennet-Clark, 1967; Noor and Aquadro, 1998). However, current methods that employ animal pose estimation and more discrete video measurements of courtship ethology are now in place to overlay with modern neurogenetics to untangle the nervous system variability related to sound production as well as detection (Clemens et al., 2018; Deutsch et al., 2019; Pereira et al., 2019). For example, it has recently been noted that male song production can change based on the distance to the female, including both amplitude and frequency variations (Clemens et al., 2018). This study showed that visual feedback (e.g., perceived distance from males to females) influences the probability of a male producing each song element. Moreover, that a male's song choice, in turn, affects female response, where female behavioral feedback then contributes to modulation of male song amplitude, again in accordance with the distance of the male's approach during courtship. Although these details might seem small, they are proving increasingly important to dissect mechanistically how multimodal stimulation contributes to species-specific ethologies such as courtship dances. While D. melanogaster remains the best studied model species (although individuality and population variance still need to be addressed), the tools are already in place to expand these research directions into additional species across this ecologically broad family and genus of flies.
Evolution of the hygro- and thermosensory systems
In addition to smell, sight, and sound, the temperature and the humidity of the environment also have a strong effect on the speed and efficiency of male and female courtship within the Drosophila genus, as well as a strong effect on general navigational preference behaviors (Hamada et al., 2008; Rosenzweig et al., 2008; Umezaki et al., 2018; Simões et al., 2021). Here, some flies have broad or narrow ranges of acceptable thermal gradients for successful copulation or host preference (Figure 9), and it is often difficult to unravel the behavioral connection between temperature and the humidity level. Relatively, recent studies have highlighted the detection of humidity via IRs within the sacculus of the antenna (Enjin et al., 2016). Moreover, this research has begun to outline differences in preference, especially between flies originating from desert (dry) or rainforest (wet) environments. Again, these same proteins (e.g., Ir25a, Ir40a, Ir93a) are also responsible for behavioral preference in warm vs. cold temperature trials (Knecht et al., 2016; Budelli et al., 2019). Thus, it will be important in the future to attempt to disentangle temperature from humidity in the brain of the fly, although these ambient conditions may simply infer similar environment stimuli and thus be, in some cases, redundant sensory systems to assess their preferred natural microhabitat. Alternatively, optimal temperature and humidity for each fly species may also represent ideal growth conditions for its preferred yeast and bacterial gardens, as related to the most efficient microbial toolkit to breakdown its preferred host material (e.g., cactus vs. fruit), where these species-specific gut microbes are transmitted to new substrates via the oral-fecal route (Becher et al., 2012; Keesey et al., 2016, 2017; Koerte et al., 2020). In the future, experiments should be conducted to examine the optimal growth curves for species-specific yeast as correlated with insect behavioral preferences for both environmental temperature and humidity, as this may lend further support for the hypothesis that insect hosts maximize ideal conditions for their own microorganism production (such as that observed in bark and pine beetles, as well as fungal-farming ants) (Mueller et al., 2011; Ranger et al., 2018). The fly hygro- and thermal preferences may, therefore, be linked to their digestive microbiome, as it is already well-supported that Drosophila flies maximize courtship speed and efficiency between males and females that are active on preferred host material in regard to the site of feeding and oviposition (Ziegler et al., 2013; Lebreton et al., 2015; Das et al., 2017; Koerte et al., 2020). Moreover, as mentioned in the previous sections of this review on olfactory behavior, food and sex are intimately entangled in the neurobiology of each Drosophila species, where males and females first meet on their preferred natural host substrates, such as fallen fruits, before any courtship ethology naturally begins in the wild (as opposed to Lepidopterans that can call a mate from long distances, but not necessarily copulating on the host plant).
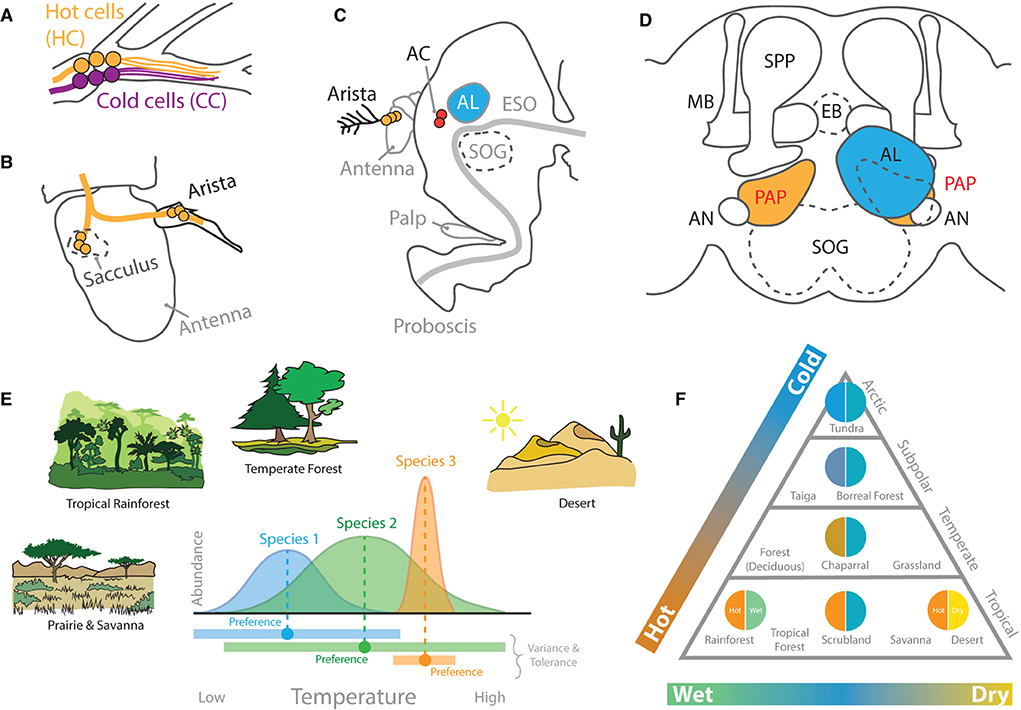
Figure 9. Thermosensation and hygrosensation in D. melanogaster. (A) Six neurons at the base of the arista on the fly antenna detect hot and cold stimulations. (B) Neurons within the sacculus inside the third antennal segment also contribute to both temperature and humidity detection. These merge with innervation from the arista before heading into the central brain. (C) A side view of the D. melanogaster head. Neurons from the arista related to heat detection transmit their information to AC neurons in close proximity to the AL and SOG. (D) A frontal view of the central brain structures related to thermal sensory systems, which include primarily the proximal antennal protocerebrum (PAP), named for its proximity to the AL and antennal nerve (AN). The PAP subsequently innervates with the AL, MB, as well as LH in D. melanogaster adults. (E) Hypothetical examples of how fly species can vary in habitat and ecological preferences. Some species may have wider (or more narrow) ranges of acceptable temperatures. These differences may relate to individual or species-level variation in their neurobiology and genomes. (F) A biome triangle of ecological or habitat classifications based on average temperature and humidity levels. Drosophila species are found across huge variations in both thermal and hygrosensation niches in the wild. However, most of what we know comes from only a few species, such as D. melanogaster, which originates from sub-Saharan tropical rainforests, a habitat that is both hot and wet. HC, hot cells; CC, cold cells; AC, anterior cell neurons; ESO, esophagus; SOG, suboesophageal ganglion; MB, mushroom body; SPP, super peduncular protocerebrum; EB, ellipsoid body neurons.
The thermal sensory system within D. melanogaster is primarily expressed in the antennae (Figure 9). Within the brain, neuropils in close proximity to the AL (i.e., the posterior antennal lobe, PAL; also called the proximal antennal protocerebrum, PAP) detect hot and cold (Gallio et al., 2011; Frank et al., 2015). In turn, temperature preference appears to be controlled by these neuropils, which respond to warmer and hot temperatures via transient receptor potential A1 (TrpA1) at the periphery. Moreover, dTrpA1 expression was identified within three distinct cell types in the central brain, including lateral cell (LC), ventral cell (VC), and anterior cell (AC) neurons. However, behavioral trials have narrowed temperature preference down to just one of these three, namely, the anterior cells (ACs) (Hamada et al., 2008; Umezaki et al., 2018; Simões et al., 2021). These AC neurons, in turn, connect via arborizations to AL glomeruli, namely, VL2a and VL2p, as well as toward both the MB and LH of the fly, thus connecting thermal sensation with chemosensory circuits (Hamada et al., 2008; Tang et al., 2013; Frank et al., 2015). Here, AC neurons via dTrpA1 expression inside the arista play a strong role in heat avoidance, or the fly's ability to detect dangerously high temperatures. Interestingly, transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), which represent 13 groups of proteins, are expressed across several of the sensory systems of the fly, including visual, mechanosensory, auditory, and thermal (Montell, 2005). However, only the members of the TRP-A group of proteins appear to confer thermal detection in flies (e.g., dTRPA1, dTRPA2, dTRPA3, and painless) (Montell, 2005; Sokabe et al., 2008; Neely et al., 2011). A larger body of research has examined the functional roles of TRPs in mammalian models, such as the house mouse (Gallio et al., 2011). Here, the range of functions ascribed to mammalian and invertebrate TRP channels appears to be remarkably similar. This is especially apparent in comparisons between the mammalian and fly TRPs. Due to functional similarities and the range of genetic tools available, the fruitfly represents a very appealing model organism for continuing to dissect the functions of TRPs as well as the molecular pathways that lead to their activation from the periphery into the brain (Montell, 2005; Gallio et al., 2011; Neely et al., 2011). In addition to TRP channels, some evidence also highlights the role of gustatory receptors (GRs) in detection of thermal cues. Moreover, while GRs differ widely from TRPs in their primary protein structure and predicted molecular architecture across the cellular membrane, recent studies have supported that both protein types (e.g., TRP and GR) can contribute to temperature detection in flies, which, in turn, promotes the discovery of new molecular mechanisms of temperature responsiveness and opportunities to engineer new tools for extrinsic control of behavior via thermal stimuli. For example, the Gr28b(D) gene product has a neurophysiological response threshold similar to TRPA1 when tested in adult D. melanogaster neurons (Ni et al., 2013). At the periphery, the antenna contains these GR-expressing neurons that detect heat; more specifically, the Gr28b.d protein confers D. melanogaster with the ability to behaviorally avoid high temperature extremes (Ni et al., 2013; Simões et al., 2021). This GR appears to only be expressed in a few neurons near the base of each arista on the fly antenna. Therefore, the peripheral sensory system for noxious temperature detection (including both TRP and GR sensors) is relatively small (in regard to the number of sensory neurons), although the behaviors associated with both thermo- and hygrosensation appear to be strong and often species-specific (Enjin et al., 2016). In addition to the arista, hot and cold temperature detection at the periphery of the fly also appears to map to the sacculus within the adult antenna (Gallio et al., 2011; Budelli et al., 2019). This overlaps with the areas previously described above as playing a strong role in hygrosensation (Enjin et al., 2016). Thus, there continues to be correlational evidence to support the neural entanglements of temperature and humidity sensation as well as species behavioral preferences for these entwined signals of environmental microhabitats.
How thermo- or hygrosensation behaviors differ across diverse species has not always been addressed using standardized, modern methods, and large-scale behavioral trials would lend support toward disentangling temperature from water sensation in the future, especially in comparison to the previous research (Brown, 1965; Markow, 1979). Moreover, studies on D. melanogaster have shown that there is, again, strong individuality in preference for these ambient conditions (Kain et al., 2015), and that this behavioral variance may correlate with metabolic conditions or other physiological states (Umezaki et al., 2018). Again, it is likely that multimodal cues play an important role in modulating fly responses to both temperature and humidity (Figures 9E,F), especially across more natural environments (as opposed to those maintained in the laboratory), such as daily or seasonal fluctuations in light, altitudinal gradients, as well as temperature and water availability (Markow, 1979, 2015; Markow and O'Grady, 2007). While considerable progress is continuing to be made in dissecting the neural mechanisms of hygro- and thermosensation in D. melanogaster, additional research is required in the future to compare these two behaviors and sensory signals as well as the underlying neurobiology in additional non-melanogaster species (Enjin et al., 2016). Moreover, experiments into additional species could help explain ecological and evolutionary preferences in thermal behavior via the examination of morphological, circuitry or abundance changes in sensory receptors as well as their corresponding neuropils in the central brain of each new species. For example, via studies across species that each prefers the warmest temperatures but differs widely in humidity preference (e.g., tropical rainforest vs. desert species) (Figure 9F). Here, while studies of D. melanogaster support the redundant importance of high temperature and high humidity, this may be a result of the sub-Saharan and tropical rainforest origins of this model species. Furthermore, the examination of species from other ecological zones (e.g., temperate or alpine forests) may identify stronger behavioral differences between temperature and humidity preferences, as well as corresponding shifts in circuitry, preference, and valence within the brain.
Discussion
Multimodal integration: The future of understanding behavior more completely?
Previous research has often fragmented the brain into discrete studies of singular sensory systems, such as olfactory, visual or auditory neural structures. This specialization in research has provided hugely successful efforts toward unraveling specific sensory circuits, from the periphery into the brain, as well as toward motor output or behavioral decision-making in various flies. This divide-and-conquer approach has led to many advances in the understanding of the Drosophilid nervous system. However, as each sensory system individually nears completion via the connectome (Scheffer, 2020; Hulse et al., 2021) as well as complete identification of necessary and sufficient neural circuits responsible for the many behavioral repertoires observed for D. melanogaster, more recent studies have utilized similar methodology and adapted them for an increasingly array of novel species for comparison within this genus. For example, a huge amount of resources has gone into creating genomic and molecular tools across many model species within Drosophila, such as D. simulans (Seeholzer et al., 2018) , D. yakuba and D. santomea (Ding et al., 2019) , D. pseudoobscura (Ramaekers et al., 2019) , D. subobscura (Tanaka et al., 2017) , D. sechellia (Auer et al., 2020) , D. suzukii (Karageorgi et al., 2017) as well as D. mojavensis (Khallaf et al., 2020). This continued push into comparative sensory and neurobiology across the Drosophila genus is allowing for the testing of hypotheses related to big picture questions, such as ecological, evolutionary, and developmental mechanisms for changes observed in the brain. Worth mentioning is that, often, natural behaviors are the last to be examined in modern research, where, again, more is usually known about a Drosophilid species' genome as compared to its ecology or natural history. However, it is increasingly apparent that, to fully understand behavior (and ecological as well as evolutionary variation), researchers will need to combine forces and start to map the interfaces between each individual sensory system. This is creating a need for either team formation of specialists across the many sensory modalities, or the need to train new scientists to more broadly consider all aspects of the neurobiology and behaviors of these species. As a chemical ecologist, I know I have been trained to see the world of the fly through chemosensory lenses, but, in order to better think like the whole organism we study, future objectives will need to consider more than just the olfactory and gustatory systems. One of the goals of this review is, therefore, to provide a general overview of the research across several senses within the fly, and to encourage more scientific awareness, connections, and potential discussions between the nervous system specialties of researchers around the world.
While many previous studies have existed, which examine sensory-linked behaviors in a multitude of Drosophila species, these data are often before modern techniques, and methods were available. There is also the importance of consistent behavioral methods for trials across species for comparison; however, few studies have tested many species simultaneously, resulting in ambiguity in whether variances between species are the result of differences in methodology or underlying neural circuitry. Ambient conditions in the laboratory have increasingly been shown to have large ramifications in behavioral trials, even within populations of the same species. This will require an increase in the understanding of physiological states as well as individuality, and their respective roles in modulating behavioral responses to the same sensory cues (Crava et al., 2019; Honegger et al., 2019; Linneweber et al., 2020; Vogt et al., 2021). With all this in mind, the general need exists for a more extensive behavioral Olympics across the Drosophila genus that will control for environmental gradients, such as the light level, temperature, relative humidity, barometric pressure, and time of day (Figure 10). Again, with more knowledge about genomes than the ecology of most species, there is also a large knowledge gap between genotypes and phenotypes, as well as between laboratory and field experiments. Several prominent model organisms, such as the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus), are seeing a recent revolution in lab to field studies (and vice versa), as well as attempts to examine more natural populations in comparison to pure lab strains (Barrett et al., 2019). This avenue for future research may continue to be an important step in testing hypotheses derived from Drosophilids, many of which have been maintained for thousands of generations on standard diets and within laboratory-controlled conditions. A central advantage to many Drosophila species is that they have been collected from geographically variable conditions and populations, thus, again, providing a potential foundation of genotypes to compare in relation to behavioral phenotypes (Sprengelmeyer et al., 2020; Olazcuaga et al., 2021). These often commercially available population resources will continue to provide important assets for sensory comparisons within and between each species. As mentioned before, even D. melanogaster, the most extensively studied model organism within this genus, still shows behavioral variance at the individual and population level. Thus, in the future, it will be important to confirm what stocks or strains of each new species represents the average or median behavioral sensory output, perhaps including some general agreement on what a normal response looks like for each fly species across various behaviors.
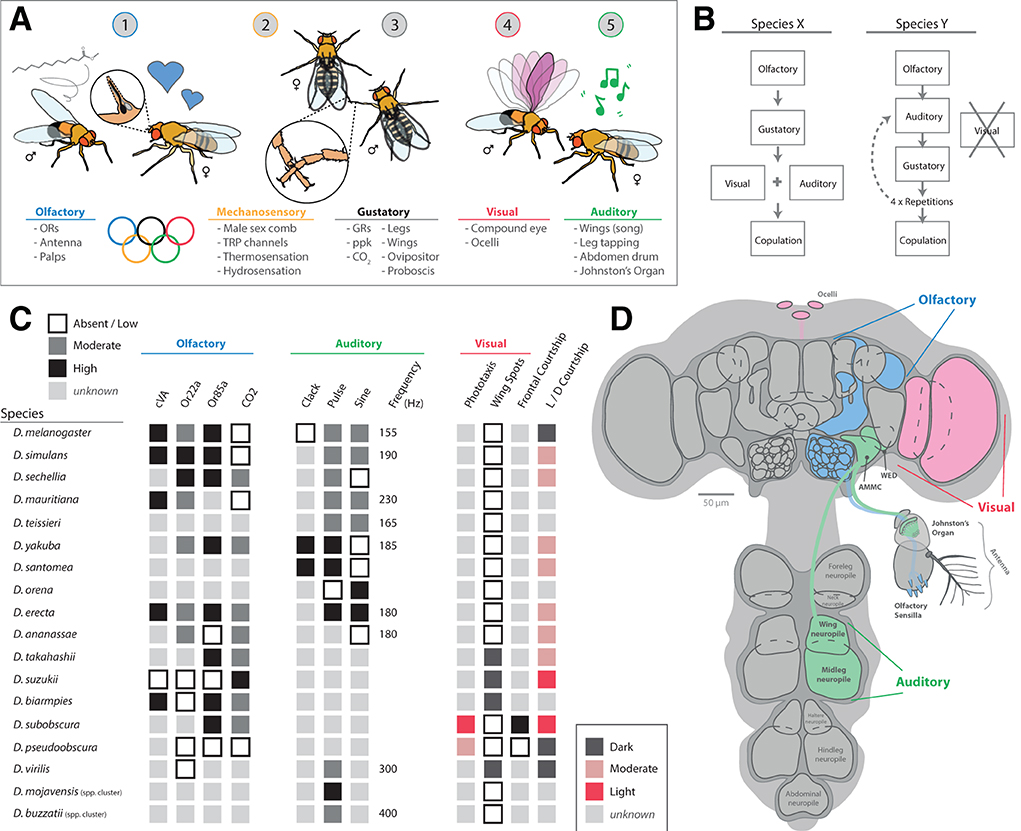
Figure 10. Multimodal sensory integration. (A) Courtship is a great behavior to address multimodal activation, as many sensory systems are active in different stages across male and female dances as well as mate selection. (B) Each species uses five primary senses (smell, taste, sight, sound, and touch) in different temporal and spatial patterns, as well as species-specific differences in a dominant mode (e.g., visual vs. olfactory courtship priorities). (C) An example table of species examinations across sensory cues during courtship dances. (D) An overview diagram of sensory integration and neural pathway overlay for sight, sound, and smell.
Researchers at the forefront of the field of behavioral neurobiology are increasingly considering the neural circuitry of multimodal behaviors, such as courtship (Pavlou and Goodwin, 2013; Clowney et al., 2015; Seeholzer et al., 2018; Anholt et al., 2020). Here, courtship is a great scheme to attempt to unravel, as it involves taste, smell, sight, sound, as well as more ambient conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and host substrate (i.e., the combination of food and sex odors). These mating rituals observed between a male and a female of each species also offer innately fixed behavioral syndromes, where performances can be rather robotic and represent common routines, which makes them ideal for teasing apart sensory-driven cues that transition between each feature of a rather complex courtship dance. In the case of D. melanogaster, although many of the individual neurons involved in courtship have been identified, additional elements that mediate or modulate these sensory signals, and the neural circuits that interpret this information in the higher brain centers, still need to be fully described (Pavlou and Goodwin, 2013; Seeholzer et al., 2018; Galili and Jefferis, 2019). Thus, even in an extremely well-studied model such as D. melanogaster, the circuit connections and neural dynamics between two or more sensory systems have yet to be illuminated. Therefore, there is ample room in the future to examine the roles of several sensory systems simultaneously. Moreover, each new species within the genus Drosophila also offers a new round of complexity to unravel, as most species have specific courtship routines that allow males and females to identify proper mating partners accurately and succinctly, even in cases of spatial or temporal overlap on the same host substrates as other similar species. While almost all species in this genus use each sensory modality for courtship, the types, timing, syntax, and relative preference appear to be quite variable (although, again, quite consistent within a given species across each individual). Multimodal behaviors also occur in relation to the selection of oviposition and feeding sites. In this case, species within the Drosophila genus are generally assumed to optimize their sensory systems to both find food for themselves, and, also, especially in the case of the female, to optimize finding sites of nutrition for future generations. As noted previously, sex differences are apparent in neurobiology (Kimura et al., 2008; Nojima et al., 2021), and males and females detect and perceive slightly different sensory worlds. In addition, species-specific differences also occur, for example, in olfactory preferences across different stages of fruit fermentation (as is the case between D. melanogaster and D. suzukii). Crucially, the chemosensory system of each species can vary in IR, OR, and GR expression, both in regard to functional dynamics (e.g., tuning differences toward a particular chemical compound), as well as abundance or relative strength of stimulus detection (e.g., number of sensilla or receptors for a given chemical cue) (Dekker et al., 2006; Linz et al., 2013; Keesey et al., 2015; Grabe et al., 2016). This same principle most likely applies to all the other senses, such as vision, where each species devotes differing numbers of ommatidia toward the detection of color, motion, and light intensity (Posnien et al., 2012; Hilbrant et al., 2014). It has been proposed that neural raw materials for the senses are a finite resource during development; thus, Drosophila species might experience a tradeoff between linked sensory systems, such as the inverse correlation observed for sizes of visual and olfactory peripheral structures and their underlying primary neuropils (Keesey et al., 2019a, 2020b). More research is needed to identify any additional tradeoffs or correlations between other sensory systems, as well as other potential evolutionary mechanisms. In the future, another important avenue to explore will be the primacy of sensory preference. Or put another way, how does each species prioritize the importance of a given sensory behavior (e.g., vision vs. olfaction)? Here, it may be useful to conduct behavioral studies that put sensory stimuli in congruence or conflict; for example, by testing flies in behavioral assays that combine visual and olfactory cues, or in trials that separate these stimuli in space and time. These types of behavioral tests will provide important measures of neural priority or order of operation regarding decision-making by each species, where, in this example, some may be more visually guided as opposed to olfactory. This same prioritization of sensory systems most likely already occurs during courtship, where, again, most species have the same categories of sensory stimulation, although the order of operation differs (as well as the necessity, such as in light-dependent courtship) (Brown, 1964; Grossfield, 1971; Keesey et al., 2020b; Shahandeh et al., 2020).
The concurrence of several sensory modalities has been shown in other Dipterans, such as the mosquito, where the necessity of CO2, body heat, and visual objects needs to align to maximize host navigation and, ultimately, feeding acceptance of a host (Mcmeniman et al., 2014). A similar combination of heat and smell was also required to enhance the capture of blowflies (Diptera: Calliphoridae), including natural deception by a flower mimicking decaying animal matter in order to attract unwitting pollinators (Angioy et al., 2004). Although this specific sensory combination (heat and smell) has not been as intimately explored across the Drosophila genus, as mentioned previously, temperature preferences may be related to microbial needs, such as the yeast and bacteria that are necessary to break down preferred plant host substrates (Becher et al., 2012). It is also likely that desiccation-related compounds, such as CHCs, which also act as pheromones for most examined species, are linked to evolutionary optimization across relatively wet and dry, or hot and cold environments. Consequently, it could be hypothesized that overlap of thermal and chemosensory systems in the nervous system may be common, although, again, more research is needed to identify senses that are positively or negatively correlated across this genus.
With all this in mind, one of the largest gaps in current research involves large-scale behavioral testing of many species across high-throughput regimes for addressing the function of each sensory system. Despite robust publication records in cellular, molecular, and genetic components of the senses of many species (sometimes including wonderfully detailed neural maps), there still exists a paucity of functional data for ecological and evolutionary comparison. For example, while, for many members of the Drosophila genus, there are large genetic screens of olfactory receptors based on presence and absence of expressed gene orthologs (at least for adult flies), there are far fewer studies of receptor sensitivity, relative abundance and expression patterns, or behavioral valence toward any correspondingly active odorants. Here, using methodology adapted from successful studies of D. melanogaster, functional and behavioral screens could be conducted to examine each new species for several sensory modalities, such as wavelength/color vision trials, as well as olfactory, thermal, hygro, and gustatory preferences. In a perfect world, this might include neural tracing or maps and scaled metrics of each sensory system in several species beyond the melanogaster clade. Again, with gene-editing and transgenic tools increasingly being adapted for new species within this genus, it is likely in the near future to see opportunities for using GCaMP to aid neural fluorescence of sensory circuit activation, as well as the development of receptor-specific knockouts or mutant lines to combine questions of necessary and sufficient neural and behavioral function for similar processing pathways within non-melanogaster species. Moreover, publicly shared videos of behavior (a resurgent trend in many modern Drosophila publications) may allow diverse researchers to compare different behavioral interests using the same images (e.g., courtship analyses).
In general, the low hanging fruit related to broad sensory behavioral screening may relate to ambient ecological conditions, such as temperature and humidity preferences, as well as phototaxis. These three cues (e.g., light, temperature, and water availability) provide a wide ecological and evolutionary view of habitat and microhabitat preferences between species, including potential deviations that create spatial (or temporal) niche spaces and geographic separations between otherwise concurrent or sympatric insect species. Temperature, humidity, and the light level also directly contribute to the types of plant species found within a microhabitat, as well as the available microbial communities, where plant and microbe hosts are essential to the life cycle and reproductive success of all known Drosophila species. Here, if we assume the sensory systems of each fly species are optimized to find their preferred host materials, then identifying ecological zones of highest likelihood for plants and microbial associations may yield substantial understanding of current habitats as well as those in the future world created during the Anthropocene, or the age during which human activity has been the dominant influence on climate and the environment.
It is fortunate that resurgence in video analysis is, again, resurfacing in animal behavioral and neurobiology. Here, the roles of video analyses in addressing multimodal behavior and the underlying neurobiological differences between species cannot be overstated. A frame-by-frame detail, when combined with computer algorithms (e.g., deep learning) for automatic tracking of individuals and limb movements, provides an unprecedented detail and efficiency for behavioral analysis in the form of discretely measurable variables that can, in turn, be examined across individuals as well as between similar species. The burgeoning fields of animal pose estimation, including programs like SLEAP and DeepLabCut (Mathis et al., 2018; Pereira et al., 2019), and use video tools and computer-assisted data logging to unravel complexity in multimodal communication during courtship that is otherwise not feasible (i.e., extremely time-consuming) through tradition methods such as human observation of these behaviors. This new age of behavioral quantification, aided by big datasets and the reduced cost of hardware and software resources, provides, perhaps, the best opportunity to tackle the nuances of multimodal ethology, where individuals, populations, species, and their genetic underpinnings are also widely available as tools for most research labs to adjust and then document behavior shifts. Although video analysis methods continue to rise in importance once again across research in neurobiology, they are still reliant on the importance of high-throughput and standardized behavioral trials. Moreover, keen observation of natural behaviors and a novel, ecologically relevant hypothesis generation are still required to maximize the use of animal pose estimation. Therefore, while the modern materials and molecular tools are largely in place to begin to disentangle multimodal sensory decision-making across the Drosophila genus like never before, substantial hard work still awaits, as inducing consistent behavior is still often the crux of most research efforts seeking to fully understand courtship, host navigation, as well as animal perception of their natural environments.
Author contributions
The author confirms being the sole contributor of this work and has approved it for publication.
Funding
IK was funded through the University of Nebraska—Lincoln (UNL) and the School of Biological Sciences (SBS).
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to all the colleagues who have conducted this research on Drosophila sensory neuroecology as well as animal behavior, and we apologize to anyone whose work we could not presently include or discuss based on length restrictions. Access to the literature was graciously provided by this institution. We thank members of the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology (MPICE) for their comments on this review.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aguadé, M. (2009). Nucleotide and copy-number polymorphism at the odorant receptor genes Or22a and Or22b in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Biol. Evol. 26, 61–70. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn227
Angioy, A., Stensmyr, M. C., Urru, I., Puliafito, M., Collu, I., and Hansson, B. S. (2004). Function of the heater: the dead horse arum revisited. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 271, 13–15. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2003.0111
Anholt, R. R. H., O'Grady, P., Wolfner, M. F., and Harbison, S. T. (2020). Evolution of reproductive behavior. Genetics 214, 49–73. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302263
Auer, T. O., Álvarez-ocaña, R., Cruchet, S., Benton, R., and Arguello, R. (2021). Odorant receptor copy number change, co-expression, and positive selection establish peripheral coding differences between fly species. bioRxiv. 1–25. doi: 10.1101/2021.09.19.460991
Auer, T. O., Khallaf, M. A., Silbering, A. F., Zappia, G., Ellis, K., Álvarez-Ocaña, R., et al. (2020). Olfactory receptor and circuit evolution promote host specialization. Nature 579, 402–408. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2073-7
Barrett, R. D. H., Laurent, S., Mallarino, R., Pfeifer, S. P., Xu, C. C. Y., Foll, M., et al. (2019). Linking a mutation to survival in wild mice. Science 363, 499–504. doi: 10.1126/science.aav3824
Becher, P. G., Flick, G., Rozpedowska, E., Schmidt, A., Hagman, A., Lebreton, S., et al. (2012). Yeast, not fruit volatiles mediate Drosophila melanogaster attraction, oviposition and development. Funct. Ecol. 26, 822–828. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2012.02006.x
Benton, R., Vannice, K. S., and Vosshall, L. B. (2007). An essential role for a CD36-related receptor in pheromone detection in Drosophila. Nature 450, 289–293. doi: 10.1038/nature06328
Bono, J. M., Olesnicky, E. C., and Matzkin, L. M. (2015). Connecting genotypes, phenotypes and fitness: Harnessing the power of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. Mol. Ecol. 24, 3810–3822. doi: 10.1111/mec.13252
Brown, R. G. B. (1964). Courtship behaviour in the Drosophila obscura group. I: D. pseudoobscura. Behaviour 23, 61–106. doi: 10.1163/156853964X00094
Brown, R. G. B. (1965). Courtship behaviour in the Drosophila Obscura group. Part II. Comparative studies. Behaviour 25, 281–322. doi: 10.1163/156853965X00174
Budelli, G., Ni, L., Berciu, C., van Giesen, L., Knecht, Z. A., Chang, E. C., et al. (2019). Ionotropic receptors specify the morphogenesis of phasic sensors controlling rapid thermal preference in drosophila. Neuron 101, 738–747.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.12.022
Carson, H. L. (1974). Three flies and three islands: parallel evolution in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 3517–3521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3517
Chin, S. G., Maguire, S. E., Huoviala, P., Jefferis, G. S. X. E., and Potter, C. J. (2018). Olfactory neurons and brain centers directing oviposition decisions in drosophila. Cell Rep. 24, 1667–1678. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.018
Clemens, J., Coen, P., Roemschied, F. A., Pereira, T. D., Mazumder, D., Aldarondo, D. E., et al. (2018). Discovery of a new song mode in drosophila reveals hidden structure in the sensory and neural drivers of behavior. Curr. Biol. 28, 2400–2412.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.06.011
Clowney, E. J., Iguchi, S., Bussell, J. J., Scheer, E., and Ruta, V. (2015). Multimodal chemosensory circuits controlling male courtship in drosophila. Neuron 87, 1036–1049. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.07.025
Coen, P., Clemens, J., Weinstein, A. J., Pacheco, D. A., Deng, Y., and Murthy, M. (2014). Dynamic sensory cues shape song structure in Drosophila. Nature 507, 233–237. doi: 10.1038/nature13131
Coen, P., and Murthy, M. (2016). Singing on the fly: Sensorimotor integration and acoustic communication in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 38, 38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2016.01.013
Coen, P., Xie, M., Clemens, J., and Murthy, M. (2016). Sensorimotor transformations underlying variability in song intensity during drosophila courtship. Neuron 89, 629–644. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.12.035
Crava, C. M., Ramasamy, S., Ometto, L., Anfora, G., and Rota-Stabelli, O. (2016). Evolutionary insights into taste perception of the invasive pest Drosophila suzukii. G3 6, 4185–4196. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.036467
Crava, C. M., Sassù, F., Tait, G., Becher, P. G., and Anfora, G. (2019). Functional transcriptome analyses of Drosophila suzukii antennae reveal mating-dependent olfaction plasticity in females. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 105, 51–59. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2018.12.012
Das, S., Trona, F., Khallaf, M. A., Schuh, E., Knaden, M., and Hansson, B. S. (2017). Electrical synapses mediate synergism between pheromone and food odors in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, E9962–E9971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1712706114
Dekker, T., Ibba, I., Siju, K. P., Stensmyr, M. C., and Hansson, B. S. (2006). Olfactory shifts parallel superspecialism for toxic fruit in Drosophila melanogaster sibling, D. sechellia. Curr. Biol. 16, 101–109. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.11.075
Dekker, T., Revadi, S., Mansourian, S., Ramasamy, S., Lebreton, S., Becher, P. G., et al. (2015). Loss of Drosophila pheromone reverses its role in sexual communication in Drosophila suzukii. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 282:3018. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.3018
Depetris-Chauvin, A., Galagovsky, D., and Grosjean, Y. (2015). Chemicals and chemoreceptors: ecologically relevant signals driving behavior in Drosophila. Front. Ecol. Evol. 3, e041. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2015.00041
Deutsch, D., Clemens, J., Thiberge, S. Y., Guan, G., and Murthy, M. (2019). Shared song detector neurons in drosophila male and female brains drive sex-specific behaviors. Curr. Biol. 29, 3200–3215.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.008
Ding, Y., Lillvis, J. L., Cande, J., Berman, G. J., Arthur, B. J., Long, X., et al. (2019). Neural evolution of context-dependent fly song. Curr. Biol. 29, 1089–1099.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.02.019
Dweck, H. K. M., and Carlson, J. R. (2020). Molecular logic and evolution of bitter taste in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2020, 1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.11.005
Dweck, H. K. M., Ebrahim, S. A. M., Thoma, M., Mohamed, A. A. M., Keesey, I. W., Trona, F., et al. (2015). Pheromones mediating copulation and attraction in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, E2829–E2835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504527112
Dweck, H. K. M., Talross, G. J. S., Wang, W., and Carlson, J. R. (2021). Evolutionary shifts in taste coding in the fruit pest Drosophila suzukii. Elife 2021, 1–29. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64317.sa2
Ebrahim, S. A. M., Dweck, H. K. M., Stökl, J., Hofferberth, J. E., Trona, F., Weniger, K., et al. (2015). Drosophila avoids parasitoids by sensing their semiochemicals via a dedicated olfactory circuit. PLoS Biol. 13, 1–18. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002318
Enjin, A., Zaharieva, E. E., Frank, D. D., Mansourian, S., Suh, G. S. B., Gallio, M., et al. (2016). Humidity sensing in drosophila. Curr. Biol. 26, 1352–1358. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.03.049
Ewing, A. W., and Bennet-Clark, H. C. (1967). The courtship songs of Drosophila. Behaviour 31, 288–301. doi: 10.1163/156853968X00298
Fan, P., Manoli, D. S., Ahmed, O. M., Chen, Y., Agarwal, N., Kwong, S., et al. (2013). Genetic and neural mechanisms that inhibit drosophila from mating with other species. Cell 154, 89–102. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.008
Fisher, Y. E., Lu, J., D'Alessandro, I., and Wilson, R. I. (2019). Sensorimotor experience remaps visual input to a heading-direction network. Nature 576, 121–125. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1772-4
Frank, D. D., Jouandet, G. C., Kearney, P. J., MacPherson, L. J., and Gallio, M. (2015). Temperature representation in the Drosophila brain. Nature 519, 358–361. doi: 10.1038/nature14284
Galili, D. S., and Jefferis, G. S. X. E. (2019). Behavior: why male flies sing different songs. Curr. Biol. 29, R243–R245. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.02.054
Gallio, M., Ofstad, T. A., Macpherson, L. J., Wang, J. W., and Zuker, C. S. (2011). The coding of temperature in the Drosophila brain. Cell 144, 614–624. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.028
Gaspar, P., Arif, S., Sumner-Rooney, L., Kittelmann, M., Bodey, A. J., Stern, D. L., et al. (2020). Characterization of the genetic architecture underlying eye size variation within drosophila melanogaster and drosophila simulans. G3 Genes, Genomes, Genet. 10, 1005–1018. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400877
Gloss, A. D., Dittrich, A. C. N., Lapoint, R. T., Huertas, B. G., Verster, K. I., Pelaez, J. L., et al. (2019). Evolution of herbivory remodels a Drosophila genome. bioRxiv 2019:767160. doi: 10.1101/767160
Goldman-Huertas, B., Mitchell, R. F., Lapoint, R. T., Faucher, C. P., Hildebrand, J. G., and Whiteman, N. K. (2015). Evolution of herbivory in Drosophilidae linked to loss of behaviors, antennal responses, odorant receptors, and ancestral diet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 3026–3031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424656112
Grabe, V., Baschwitz, A., Dweck, H. K. M., Lavista-Llanos, S., Hansson, B. S., and Sachse, S. (2016). Elucidating the neuronal architecture of olfactory glomeruli in the Drosophila antennal lobe. Cell Rep. 16, 3401–3413. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.063
Grossfield, J. (1971). Geographic distribution and light-dependent behavior in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 68, 2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2669
Hamada, F. N., Rosenzweig, M., Kang, K., Pulver, S. R., Ghezzi, A., Jegla, T. J., et al. (2008). An internal thermal sensor controlling temperature preference in Drosophila. Nature 454, 217–220. doi: 10.1038/nature07001
Heath, S. L., Christenson, M. P., Oriol, E., Saavedra-Weisenhaus, M., Kohn, J. R., and Behnia, R. (2020). Circuit Mechanisms Underlying Chromatic Encoding in Drosophila Photoreceptors. Curr. Biol. 30, 264–275.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.11.075
Hegde, S. N., Chethan, B. K., and Krishna, M. S. (2005). Mating success of males with and without wing patch in Drosophila biarmipes. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 43, 902–909.
Hernández, M. V., Cecile, C., and Fabre, G. (2016). The elaborate postural display of courting Drosophila persimilis flies produces substrate-borne vibratory signals. J. Insect Behav. 2016, 578–590. doi: 10.1007/s10905-016-9579-8
Hickner, P. V., Rivaldi, C. L., Johnson, C. M., Siddappaji, M., Raster, G. J., and Syed, Z. (2016). The making of a pest: Insights from the evolution of chemosensory receptor families in a pestiferous and invasive fly, Drosophila suzukii. BMC Genomics 17, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2983-9
Hilbrant, M., Almudi, I., Leite, D. J., Kuncheria, L., Posnien, N., Nunes, M. D. S., et al. (2014). Sexual dimorphism and natural variation within and among species in the Drosophila retinal mosaic. BMC Evol. Biol. 14, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12862-014-0240-x
Hindmarsh Sten, T., Li, R., Otopalik, A., and Ruta, V. (2021). Sexual arousal gates visual processing during Drosophila courtship. Nature 595, 549–553. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03714-w
Honegger, K. S., Smith, M. A.-Y., Churgin, M. A., Turner, G. C., and de Bivort, B. L. (2019). Idiosyncratic neural coding and neuromodulation of olfactory individuality in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 23292–23297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1901623116
Hulse, B., Haberkern, H., Franconville, R., Turner-Evans, D. B., Takemura, S., Wolff, T., et al. (2021). A connectome of the Drosophila central complex reveals network motifs suitable for flexible navigation and context-dependent action selection. Elife 9:e57443. doi: 10.7554/eLife.66039
Huoviala, P., Dolan, M. J., Love, F. M., Frechter, S., Roberts, R. J. V., Mitrevica, Z., et al. (2018). Neural circuit basis of aversive odour processing in Drosophila from sensory input to descending output. bioRxiv. 1–24. doi: 10.1101/394403
Jezovit, J. A., Levine, J. D., and Schneider, J. (2017). Phylogeny, environment and sexual communication across the Drosophila genus. J. Exp. Biol. 220, 42–52. doi: 10.1242/jeb.143008
Kain, J. S., Zhang, S., Akhund-Zade, J., Samuel, A. D. T., Klein, M., and de Bivort, B. L. (2015). Variability in thermal and phototactic preferences in Drosophila may reflect an adaptive bet-hedging strategy. Evolution (N. Y). 69, 3171–3185. doi: 10.1111/evo.12813
Kamikouchi, A., Inagaki, H. K., Effertz, T., Hendrich, O., Fiala, A., Göpfert, M. C., et al. (2009). The neural basis of Drosophila gravity-sensing and hearing. Nature 458, 165–171. doi: 10.1038/nature07810
Karageorgi, M., Bräcker, L. B., Lebreton, S., Minervino, C., Cavey, M., Siju, K. P., et al. (2017). Evolution of multiple sensory systems drives novel egg-laying behavior in the fruit pest Drosophila suzukii. Curr. Biol. 27, 847–853. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.055
Keesey, I. W., Doll, G., Das Chakraborty, S., Baschwitz, A., Lemoine, M., Kaltenpoth, M., et al. (2020a). Alcohol boosts pheromone production in male flies and makes them sexier. bioRxiv Neurosci. Available online at: http://biorxiv.org/cgi/content/short/2020.08.09.242784v1?rss=1&utm_source=researcher_app&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=RESR_MRKT_Researcher_inbound.
Keesey, I. W., Grabe, V., Gruber, L., Koerte, S., Obiero, G. F., Bolton, G., et al. (2019a). Inverse resource allocation between vision and olfaction across the genus Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 10:1162. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09087-z
Keesey, I. W., Grabe, V., Knaden, M., and Hansson, B. S. (2020b). Divergent sensory investment mirrors potential speciation via niche partitioning across Drosophila. Elife 9, 1–24. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57008
Keesey, I. W., and Hansson, B. S. (2021). “The neuroethology of labeled lines in insect olfactory systems,” in Insect Pheromone Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2nd Edn, eds G. J. Blomquist and R, G, Vogt (Academic Press), 285–327. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-819628-1.00010-9
Keesey, I. W., Knaden, M., and Hansson, B. S. (2015). Olfactory specialization in Drosophila suzukii supports an ecological shift in host preference from rotten to fresh fruit. J. Chem. Ecol. 41, 121–128. doi: 10.1007/s10886-015-0544-3
Keesey, I. W., Koerte, S., Khallaf, M. A., Retzke, T., Guillou, A., Grosse-Wilde, E., et al. (2017). Pathogenic bacteria enhance dispersal through alteration of Drosophila social communication. Nat. Commun. 8:265. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00334-9
Keesey, I. W., Koerte, S., Retzke, T., Haverkamp, A., Hansson, B. S., and Knaden, M. (2016). Adult frass provides a pheromone signature for Drosophila feeding and aggregation. J. Chem. Ecol. 42, 739–747. doi: 10.1007/s10886-016-0737-4
Keesey, I. W., Zhang, J., Depetris-Chauvin, A., Obiero, G. F., Gupta, A., Gupta, N., et al. (2022). Functional olfactory evolution in Drosophila suzukii and the subgenus Sophophora. iScience 25:104212. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104212
Keesey, I. W., Zhang, J., Depetris-chauvin, A., Obiero, G. F., Knaden, M., and Hansson, B. S. (2019b). Evolution of a pest: towards the complete neuroethology of Drosophila suzukii and the subgenus Sophophora. bioRxiv. 1–16. doi: 10.1101/717322
Kekić, V., and Marinković, D. (1974). Multiple-choice selection for light preference in Drosophila subobscura. Behav. Genet. 4, 285–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01074161
Khallaf, M. A., Auer, T. O., Grabe, V., Depetris-Chauvin, A., Ammagarahalli, B., Zhang, D. D., et al. (2020). Mate discrimination among subspecies through a conserved olfactory pathway. Sci. Adv. 6:aba5279. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba5279
Khallaf, M. A., Cui, R., Weißflog, J., Erdogmus, M., Svato,š, A., Dweck, H. K. M., et al. (2021). Large-scale characterization of sex pheromone communication systems in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 12, 1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24395-z
Kimura, K., ichi Hachiya, T., Koganezawa, M., Tazawa, T., and Yamamoto, D. (2008). Fruitless and doublesex coordinate to generate male-specific neurons that can initiate courtship. Neuron 59, 759–769. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.06.007
Kind, E., Longden, K. D., Nern, A., Zhao, A., Sancer, G., Flynn, M. A., et al. (2021). Synaptic targets of photoreceptors specialized to detect color and skylight polarization in Drosophila. Elife 10, 1–48. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71858
Knecht, Z. A., Silbering, A. F., Ni, L., Klein, M., Budelli, G., Bell, R., et al. (2016). Distinct combinations of variant ionotropic glutamate receptors mediate thermosensation and hygrosensation in Drosophila. Elife 5, 1–15. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17879
Koerte, S., Keesey, I. W., Easson, M. L. A. E., Gershenzon, J., Hansson, B. S., and Knaden, M. (2020). Variable dependency on associated yeast communities influences host range in Drosophila species. Oikos 129, 964–982. doi: 10.1111/oik.07180
Larderet, I., Fritsch, P. M. J., Gendre, N., Larisa Neagu-Maier, G., Fetter, R. D., Schneider-Mizell, C. M., et al. (2017). Organization of the drosophila larval visual circuit. Elife 6, 1–23. doi: 10.7554/eLife.28387
Lebreton, S., Borrero-Echeverry, F., Gonzalez, F., Solum, M., Wallin, E. A., Hedenström, E., et al. (2017). A Drosophila female pheromone elicits species-specific long-range attraction via an olfactory channel with dual specificity for sex and food. BMC Biol. 15, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0427-x
Lebreton, S., Grabe, V., Omondi, A. B., Ignell, R., Becher, P. G., Hansson, B. S., et al. (2014). Love makes smell blind: Mating suppresses pheromone attraction in Drosophila females via Or65a olfactory neurons. Sci. Rep. 4, 1–6. doi: 10.1038/srep07119
Lebreton, S., Trona, F., Borrero-Echeverry, F., Bilz, F., Grabe, V., Becher, P. G., et al. (2015). Feeding regulates sex pheromone attraction and courtship in Drosophila females. Sci. Rep. 5, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/srep13132
Lin, C. C., and Potter, C. J. (2015). Re-classification of Drosophila melanogaster trichoid and intermediate sensilla using fluorescence-guided single sensillum recording. PLoS ONE 10, 1–14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139675
Lin, H. H., Cao, D. S., Sethi, S., Zeng, Z., Chin, J. S. R., Chakraborty, T. S., et al. (2016). Hormonal modulation of pheromone detection enhances male courtship success. Neuron 90, 1272–1285. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.05.004
Linneweber, G. A., Andriatsilavo, M., Dutta, S., Hellbruegge, L., Liu, G., Ejsmont, R. K., et al. (2020). A neurodevelopmental origin of behavioral individuality. Science 367, 1112–1119. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw7182
Linz, J., Baschwitz, A., Strutz, A., Dweck, H. K. M., Sachse, S., Hansson, B. S., et al. (2013). Host plant-driven sensory specialization in Drosophila erecta. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 280:20130626. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.0626
Markow, T. A. (1979). Phototactic behavior of Drosophila species at different temperatures. Am. Nat. 114, 884–892. doi: 10.1086/283535
Markow, T. A., and O'Grady, P. M. (2007). Drosophila biology in the genomic age. Genetics 177, 1269–1276. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.074112
Mathis, A., Mamidanna, P., Cury, K. M., Abe, T., Murthy, V. N., Mathis, M. W., et al. (2018). DeepLabCut: markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 1281–1289. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0209-y
Matsuo, E., Yamada, D., Ishikawa, Y., Asai, T., Ishimoto, H., and Kamikouchi, A. (2014). Identification of novel vibration- and deflection-sensitive neuronal subgroups in Johnston's organ of the fruit fly. Front. Physiol. 5, 179. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00179
Mazzoni, V., Anfora, G., and Virant-Doberlet, M. (2013). Substrate vibrations during courtship in three Drosophila species. PLoS ONE 8, 708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080708
Mcmeniman, C. J., Corfas, A., Matthews, B. J., Ritchie, S. A., and Vosshall, L. B. (2014). Multimodal integration of carbon dioxide and other sensory cues drives mosquito attraction to humans. Cell 156, 1060–1071. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.044
Melo, N., Wolff, G. H., Costa-da-Silva, A. L., Arribas, R., Triana, M. F., Gugger, M., et al. (2020). Geosmin attracts aedes aegypti mosquitoes to oviposition sites. Curr. Biol. 30, 127–134.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.11.002
Mohamed, A. A. M., Retzke, T., Das Chakraborty, S., Fabian, B., Hansson, B. S., Knaden, M., et al. (2019). Odor mixtures of opposing valence unveil inter-glomerular crosstalk in the Drosophila antennal lobe. Nat. Commun. 10:9069. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09069-1
Montell, C. (2005). Drosophila TRP channels. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 451, 19–28. doi: 10.1007/s00424-005-1426-2
Mueller, U. G., Mikheyev, A. S., Hong, E., Sen, R., Warren, D. L., Solomon, S. E., et al. (2011). Evolution of cold-tolerant fungal symbionts permits winter fungiculture by leafcutter ants at the northern frontier of a tropical ant-fungus symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 4053–4056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015806108
Murthy, M. (2010). Unraveling the auditory system of Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 20, 281–287. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2010.02.016
Neely, G. G., Keene, A. C., Duchek, P., Chang, E. C., Wang, Q. P., Aksoy, Y. A., et al. (2011). TrpA1 regulates thermal nociception in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 6:e024343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024343
Ni, L., Bronk, P., Chang, E. C., Lowell, A. M., Flam, J. O., Panzano, V. C., et al. (2013). A gustatory receptor paralogue controls rapid warmth avoidance in Drosophila. Nature 500, 580–584. doi: 10.1038/nature12390
Nojima, T., Rings, A., Allen, A. M., Billeter, J., Neville, M. C., Goodwin, S. F., et al. (2021). A sex-specific switch between visual and olfactory inputs underlies adaptive sex differences in behavior A sex-specific switch between visual and olfactory inputs underlies adaptive sex differences in behavior. Curr. Biol. 2021, 1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.12.047
Noor, M. A. F., and Aquadro, C. F. (1998). Courtship songs of Drosophila pseudoobscura and D. persimilis: Analysis of variation. Anim. Behav. 56, 115–125. doi: 10.1006/anbe.1998.0779
O'Grady, P. M., and DeSalle, R. (2018). Phylogeny of the genus Drosophila. Genetics 209, 1–25. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300583
Olazcuaga, L., Loiseau, A., Parrinello, H., Paris, M., Fraimout, A., Guedot, C., et al. (2021). A whole-genome scan for association with invasion success in the fruit fly drosophila suzukii using contrasts of allele frequencies corrected for population structure. Mol. Biol. Evol. 37, 2369–2385. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa098
Ometto, L., Cestaro, A., Ramasamy, S., Grassi, A., Revadi, S., Siozios, S., et al. (2013). Linking genomics and ecology to investigate the complex evolution of an invasive Drosophila pest. Genome Biol. Evol. 5, 745–757. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evt034
Pavlou, H. J., and Goodwin, S. F. (2013). Courtship behavior in Drosophila melanogaster: Towards a “courtship connectome.” Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 23, 76–83. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2012.09.002
Pereira, T. D., Aldarondo, D. E., Willmore, L., Kislin, M., Wang, S. S. H., Murthy, M., et al. (2019). Fast animal pose estimation using deep neural networks. Nat. Methods 16, 117–125. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0234-5
Perry, M., Konstantinides, N., Pinto-Teixeira, F., and Desplan, C. (2017). Generation and evolution of neural cell types and circuits: insights from the drosophila visual system. Annu. Rev. Genet. 51, 501–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120215-035312
Pézier, A., Jezzini, S. H., Marie, B., and Blagburn, J. M. (2014). Engrailed alters the specificity of synaptic connections of Drosophila auditory neurons with the giant fiber. J. Neurosci. 34, 11691–11704. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1939-14.2014
Port, F., Strein, C., Stricker, M., Rauscher, B., Heigwer, F., Zhou, J., et al. (2020). A large-scale resource for tissue-specific CRISPR mutagenesis in Drosophila. Elife 9, 1–20. doi: 10.7554/eLife.53865
Posnien, N., Hopfen, C., Hilbrant, M., Ramos-Womack, M., Murat, S., Schönauer, A., et al. (2012). Evolution of eye morphology and Rhodopsin expression in the Drosophila melanogaster species subgroup. PLoS ONE 7, 1–11. doi: 10.1371/annotation/a72ae6bf-afe8-4244-b175-e303f02686f8
Prieto-Godino, L. L., Rytz, R., Bargeton, B., Abuin, L., Arguello, J. R., Peraro, M. D., et al. (2016). Olfactory receptor pseudo-pseudogenes. Nature 539, 93–97. doi: 10.1038/nature19824
Prieto-Godino, L. L., Rytz, R., Cruchet, S., Bargeton, B., Abuin, L., Silbering, A. F., et al. (2017). Evolution of acid-sensing olfactory circuits in Drosophilids. Neuron 93, 661–676.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.024
Prieto-Godino, L. L., Silbering, A. F., Khallaf, M. A., Cruchet, S., Bojkowska, K., Pradervand, S., et al. (2020). Functional integration of “undead” neurons in the olfactory system. Sci. Adv. 6:aaz7238. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz7238
Ramaekers, A., Claeys, A., Kapun, M., Mouchel-Vielh, E., Potier, D., Weinberger, S., et al. (2019). Altering the temporal regulation of one transcription factor drives evolutionary trade-offs between head sensory organs. Dev. Cell 50, 780–792.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.07.027
Ramasamy, S., Ometto, L., Crava, C. M., Revadi, S., Kaur, R., Horner, D. S., et al. (2016). The evolution of olfactory gene families in Drosophila and the genomic basis of chemical-ecological adaptation in Drosophila suzukii. Genome Biol. Evol. 8, 2297–2311. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw160
Ranger, C. M., Biedermann, P. H. W., Phuntumart, V., Beligala, G. U., Ghosh, S., Palmquist, D. E., et al. (2018). Symbiont selection via alcohol benefits fungus farming by ambrosia beetles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115, 4447–4452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716852115
Revadi, S. V., Giannuzzi, V. A., Vetukuri, R. R., Walker, W. B., and Becher, P. G. (2021). Larval response to frass and guaiacol: detection of an attractant produced by bacteria from Spodoptera littoralis frass. J. Pest Sci. 94, 1105–1118. doi: 10.1007/s10340-021-01352-9
Riabinina, O., Dai, M., Duke, T., and Albert, J. T. (2011). Active process mediates species-specific tuning of Drosophila ears. Curr. Biol. 21, 658–664. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.03.001
Ripfel, J., and Becker, J. (1982). Light-dependent mating of Drosophila subobscura and species discrimination. Behav. Genet. 12, 241–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01067846
Rosenzweig, M., Kang, K. J., and Garrity, P. A. (2008). Distinct TRP channels are required for warm and cool avoidance in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 14668–14673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805041105
Rytz, R., Croset, V., and Benton, R. (2013). Ionotropic Receptors (IRs): Chemosensory ionotropic glutamate receptors in Drosophila and beyond. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 43, 888–897. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.02.007
Sakai, T., Isono, K., Tomaru, M., Fukatami, A., and Oguma, Y. (2002). Light wavelength dependency of mating activity in the Drosophila melanogaster species subgroup. Genes Genet. Syst. 77, 187–195. doi: 10.1266/ggs.77.187
Scheffer, L. K. (2020). A connectome and analysis of the adult Drosophila central brain. Elife 57443, 1–83. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57443
Schnaitmann, C., Garbers, C., Wachtler, T., and Tanimoto, H. (2013). Color discrimination with broadband photoreceptors. Curr. Biol. 23, 2375–2382. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.10.037
Schnaitmann, C., Haikala, V., Abraham, E., Oberhauser, V., Thestrup, T., Griesbeck, O., et al. (2018). Color processing in the early visual system of drosophila. Cell 172, 318–330.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.018
Schnaitmann, C., Pagni, M., and Reiff, D. F. (2020). Color vision in insects: insights from Drosophila. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sensory, Neural, Behav. Physiol. 206, 183–198. doi: 10.1007/s00359-019-01397-3
Scott, K. (2018). Gustatory Processing in Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 63, 15–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-020117-043331
Seeholzer, L. F., Seppo, M., Stern, D. L., and Ruta, V. (2018). Evolution of a central neural circuit underlies Drosophila mate preferences. Nature 559, 564–569. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0322-9
Sethi, S., Lin, H. H., Shepherd, A. K., Volkan, P. C., Su, C. Y., and Wang, J. W. (2019). Social Context Enhances Hormonal Modulation of Pheromone Detection in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 29, 3887–3898.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.09.045
Shahandeh, M. P., Brock, C., and Turner, T. L. (2020). Light dependent courtship behavior in Drosophila simulans and D. melanogaster. PeerJ 2020:9499. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9499
Shanbhag, S. R., Hekmat-Scafe, D., Kim, M. S., Park, S. K., Carlson, J. R., Pikielny, C., et al. (2001). Expression mosaic of odorant-binding proteins in Drosophila olfactory organs. Microsc. Res. Tech. 55, 297–306. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1179
Sharkey, C. R., Blanco, J., Leibowitz, M. M., Pinto-Benito, D., and Wardill, T. J. (2020). The spectral sensitivity of Drosophila photoreceptors. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74742-1
Shaw, K. H., Johnson, T. K., Anderson, A., De Bruyne, M., and Warr, C. G. (2019). Molecular and Functional Evolution at the Odorant Receptor Or22 Locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Biol. Evol. 36, 919–929. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msz018
Shirangi, T. R., Stern, D. L., and Truman, J. W. (2013). Motor control of drosophila courtship song. Cell Rep. 5, 678–686. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.09.039
Simões, J. M., Levy, J. I., Zaharieva, E. E., Vinson, L. T., Zhao, P., Alpert, M. H., et al. (2021). Robustness and plasticity in Drosophila heat avoidance. Nat. Commun. 12, 1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22322-w
Sokabe, T., Tsujiuchi, S., Kadowaki, T., and Tominaga, M. (2008). Drosophila painless is a Ca2+-requiring channel activated by noxious heat. J. Neurosci. 28, 9929–9938. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2757-08.2008
Spassky, B., and Dobzhansky, T. (1967). Responses of various strains of Drosophila pseudoobscuraand Drosophila persimilis to light and to gravity. Am. Nat. 101, 59–63. doi: 10.1086/282469
Spieth, H. T. (1952). Mating Behavior Within the Genus Drosophila (Diptera). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. Available online at: https://digitallibrary.amnh.org/handle/2246/934
Sprengelmeyer, Q. D., Mansourian, S., Lange, J. D., Matute, D. R., Cooper, B. S., Jirle, E. V., et al. (2020). Recurrent Collection of Drosophila melanogaster from Wild African Environments and Genomic Insights into Species History. Mol. Biol. Evol. 37, 627–638. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msz271
Stensmyr, M. C., Dweck, H. K. M., Farhan, A., Ibba, I., Strutz, A., Mukunda, L., et al. (2012). A conserved dedicated olfactory circuit for detecting harmful microbes in Drosophila. Cell 151, 1345–1357. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.09.046
Stensmyr, M. C., Stieber, R., and Hansson, B. S. (2008). The Cayman crab fly revisited - Phylogeny and biology of Drosophila endobranchia. PLoS ONE 3, e01942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001942
Stocker, R. F. (2001). Drosophila as a focus in olfactory research: Mapping of olfactory sensilla by fine structure, odor specificity, odorant receptor expression, and central connectivity. Microsc. Res. Tech. 55, 284–296. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1178
Tanaka, R., Higuchi, T., Kohatsu, S., Sato, K., and Yamamoto, D. (2017). Optogenetic activation of the fruitless -labeled circuitry in Drosophila subobscura males induces mating motor acts. J. Neurosci. 37, 11662–11674. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1943-17.2017
Tang, X., Platt, M. D., Lagnese, C. M., Leslie, J. R., and Hamada, F. N. (2013). Temperature integration at the AC thermosensory neurons in drosophila. J. Neurosci. 33, 894–901. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1894-12.2013
Task, D., Lin, C., Vulpe, A., Afify, A., Ballou, S., Jefferis, G. S. X. E., et al. (2022). Chemoreceptor co-expression in drosophila olfactory neurons. eLIFE. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72599
Thistle, R., Cameron, P., Ghorayshi, A., Dennison, L., and Scott, K. (2012). Contact chemoreceptors mediate male-male repulsion and male-female attraction during drosophila courtship. Cell 149, 1140–1151. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.045
Tootoonian, S., Coen, P., Kawai, R., and Murthy, M. (2012). Neural representations of courtship song in the Drosophila brain. J. Neurosci. 32, 787–798. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5104-11.2012
Tosi, D., Martins, M., Vilela, C. R., and Pereira, M. A. Q. R. (1990). On a new cave-dwelling species of bat-guano-breeding Drosophilia closely related to D.repleta wollaston (Diptera, drosophilidae). Rev. Bras. Genet. 13, 19–31.
Tumlinson, J. H., Hardee, D. D., Gueldner, R. C., Thompson, A. C., Hedin, P. A., and Minyard, J. P. (1969). Sex pheromones produced by male boll weevil: Isolation, identification, and synthesis. Science 166, 1010–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3908.1010
Umezaki, Y., Hayley, S. E., Chu, M. L., Seo, H. W., Shah, P., and Hamada, F. N. (2018). Feeding-state-dependent modulation of temperature preference requires insulin signaling in drosophila warm-sensing neurons. Curr. Biol. 28, 779–787.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.060
Vogt, K., Zimmerman, D., Schlichting, M., Hernandez-Nunez, L., Qin, S., Malacon, K., et al. (2021). Internal state configures olfactory behavior and early sensory processing in Drosophila larvae. Sci. Adv. 7:eabd6900. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd6900
von Philipsborn, A. C., Liu, T., Yu, J. Y., Masser, C., Bidaye, S. S., and Dickson, B. J. (2011). Neuronal control of drosophila courtship song. Neuron 69, 509–522. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.011
Wada-Katsumata, A., Zurek, L., Nalyanya, G., Roelofs, W. L., Zhang, A., and Schal, C. (2015). Gut bacteria mediate aggregation in the German cockroach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 15678–15683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504031112
Wang, L., and Anderson, D. J. (2010). Identification of an aggression-promoting pheromone and its receptor neurons in Drosophila. Nature 463, 227–231. doi: 10.1038/nature08678
Wu, S.-T., Chen, J.-Y., Martin, V., Ng, R., Zhang, Y., Grover, D., et al. (2022). Valence opponency in peripheral olfactory processing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119:34119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2120134119
Yan, H., Jafari, S., Pask, G., Zhou, X., Reinberg, D., and Desplan, C. (2020). Evolution, developmental expression and function of odorant receptors in insects. J. Exp. Biol. 223:e208215. doi: 10.1242/jeb.208215
Yu, J. Y., Kanai, M. I., Demir, E., Jefferis, G. S. X. E., and Dickson, B. J. (2010). Cellular organization of the neural circuit that drives Drosophila courtship behavior. Curr. Biol. 20, 1602–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.08.025
Keywords: olfaction, neurobiology, vision, courtship, ecology, brain, animal behavior, speciation
Citation: Keesey IW (2022) Sensory neuroecology and multimodal evolution across the genus Drosophila. Front. Ecol. Evol. 10:932344. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.932344
Received: 29 April 2022; Accepted: 30 June 2022;
Published: 29 July 2022.
Edited by:
Sharon Rose Hill, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, SwedenReviewed by:
Jeffrey A. Riffell, University of Washington, United StatesXin-Cheng Zhao, Henan Agricultural University, China
Yuki Ishikawa, Nagoya University, Japan
Copyright © 2022 Keesey. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ian W. Keesey, aWtlZXNleTJAdW5sLmVkdQ==
 Ian W. Keesey
Ian W. Keesey