- 1Sharett Institute of Oncology, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
- 2Faculty of Medicine, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel
- 3Radiology Department, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
- 4Pathology Department, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
- 5Surgery Department, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
- 6Department of Genetic and Metabolic Diseases, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
Background: Germline BRCA1/2 pathogenic variant (PV) carriers have high lifetime risk of developing breast cancer and therefore subjected to intense lifetime screening. However, solid data on the effectiveness of high-risk screening of the BRCA1/2 carrier population is limited.
Patients and Methods: Retrospectively, we analyzed 346 women diagnosed with breast tumors. Patients were divided according to the timing of BRCA1/2 PVrecognition, before (BRCA-preDx awareness, N = 62) or after (BRCA-postDx awareness group, N = 284) cancer diagnosis.
Results: Median follow-up times were 131.42 and 93.77 months in the BRCA-preDx awareness and BRCA-postDx awareness groups, respectively. In the BRCA-preDx awareness group, 78.7% of the patients had invasive tumors and 21.3% were diagnosed with pure ductal carcinoma in situ. In contrast, in the BRCA-postDx awareness group over 93% of women were diagnosed with invasive cancer and only 6.4% had in situ disease. The mode of tumor detection differed significantly between the groups: 71.9% in the BRCA-postDx awareness group and 26.2% in the BRCA-preDx awareness group were diagnosed after personally palpating a lump. Tumor size and nodal involvement were significantly more favorable in the BRCA-preDx awareness group. T stage was significantly lower in the BRCA-preDx awareness group: 54.84% at T1 and 20.96% at Tis. In the BRCA-postDx awareness group, only 37.54% were at T1 and 6.49% at Tis. The N stage was also significantly lower in the BRCA-preDx awareness group: 71% had no lymph node metastases, compared with 56.1% in the BRCA-postDx awareness group. Additionally, therapeutic procedures varied between the groups: BRCA-preDx awareness group patients underwent more breast conserving surgeries. Axillary lymph node dissection was done in 38% of women in the BRCA-postDx awareness group and in only 8.7% of the BRCA-preDx awareness group patients. Interestingly, improved survival was found among patients who underwent high-risk screening (hazard ratio=0.34).
Conclusions: High-risk screening might facilitate downstaging of detected breast tumor among BRCA1/2 carrier population.
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most prevalent non-cutaneous cancer among women (1). In general, once diagnosed, early and accurate detection of the tumor size and degree of spreading is very important, since treatment in the early stages of the disease can improve the prognosis and save lives (2).
Women who carry a BRCA1 or BRCA2 pathogenic variant (PV) are at an increased risk of developing breast cancer. These women hold a lifetime risk as high as 60% to 90% (3), and also a risk of developing it at younger age than women in the general population (4). Finding BRCA1/2 PV significantly alters medical management (5) and prompts earlier and more frequent screening and risk-reduction surgeries (6).
As part of the high-risk screening, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network’s (NCCN) Guidelines state that for BRCA1/2 carriers, annual magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and clinical breast exams should start at age 25, and mammograms should start at the age of 30 (7).
There is evidence that for carriers of BRCA2 PV, a combination of MRI screening and annual mammography can have a survival benefit (8, 9). On the other hand, for BRCA1 PV carriers the high-risk screening appears to be less effective. This might be because of the high prevalence of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) in BRCA1 carriers, an aggressive subtype with a poor prognosis (10).
Mammography can detect lesions at a minimal size of 1 mm and reveal breast cancer several years before it can be detected in a physical examination (11). MRI is even more sensitive screening modality than mammography alone (11), and the combination of the two is the most sensitive method for detecting breast cancer (12). However, information on the effectiveness of high-risk screening for the BRCA carrier population is limited. Frequent physical examination, mammography, and MRI, starting as early as possible in the high-risk population of BRCA carriers, are commonly used.
Here we aimed to determine whether high-risk screening has the potential to benefit BRCA1/2 PV carrier population.
Methods
Study Design & Patients
This retrospective study included 346 high-risk women who were diagnosed with breast cancer in 1996–2020 at the Oncology Department of the Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center in Jerusalem. The study focused on patients diagnosed during 1996-2020 due to the data accessibility.
The high-risk women are BRCA1/2 PV carriers. The 346 patients were divided into two groups in order to determine the impact of high-risk screening. The BRCA-preDx awareness group comprised 62 women who knew that they were carriers of BRCA PVs. Therefore, they were offered intensified screening prior to breast cancer diagnosis. The BRCA-postDx awareness group consisted of 284 patients who first were diagnosed with breast cancer and only then they were found to carry BRCA PV. Therefore, the BRCA-postDx awareness group was not under high-risk screening. In 2009, the Israeli Ministry of Health added the reimbursement of annual MRI as a standard screening modality for BRCA1/2 carriers. Therefore, we re-analyzed the data based on a cutoff at 2009 and separated the patients diagnosed before and after 2009 in each group.
Before 2009, the recommended screening included biannual clinical evaluation, breast ultrasound from the age of 25 years or 10 years prior to the age of diagnosis of family member, whatever comes first, and annual mammography from the age of 35 years. After 2009, annual MRI as a standard screening modality for BRCA1/2 carriers.
The Hadassah Institutional Review Board approved the study and all patients gave written informed consent.
Clinical data were obtained from electronic medical records of Hadassah Medical Center. The data included demographics and information regarding the breast cancer: tumor size, lymph node status and distant metastasis (TNM), date of first diagnosis, pathology, receptor status, type of surgery, BRCA PV type, how the first diagnosis was made, family history, and follow-up.
Exclusion criteria were prior diagnosis of cancer and high-risk mutation other than BRCA PV.
Statistical Analysis
Association between two categorical variables was tested using the χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test. Continuous variables were compared between two independent groups by use of the two-sample t-test or the non-parametric Mann-Whitney test. The non-parametric test was used for variables that were not normally distributed. The Kaplan-Meier survival model was used for assessing survival, with the log-rank test for the comparison of survival curves. The Cox regression model was applied as the multivariable model for survival. Lead time bias correction was done as described previously (13), it assumes an exponential distribution of the sojourn time, the period during which the tumor is asymptomatic but screen-detectable, with a rate of transition to symptomatic disease λ. Thus, 1/λ is the mean sojourn time and is typically around 4. Duffy calculates an expected additional follow-up time to be subtracted from the calculated time-to-event of the study group. Where T is the last know follow-up time: follow-up correction time = (1-e^(-λT))/λ.
All statistical tests used were two-tailed, and a P-value of 0.05 or less was considered statistically significant. We used SSPS software for the statistical analysis.
Results
Study Population
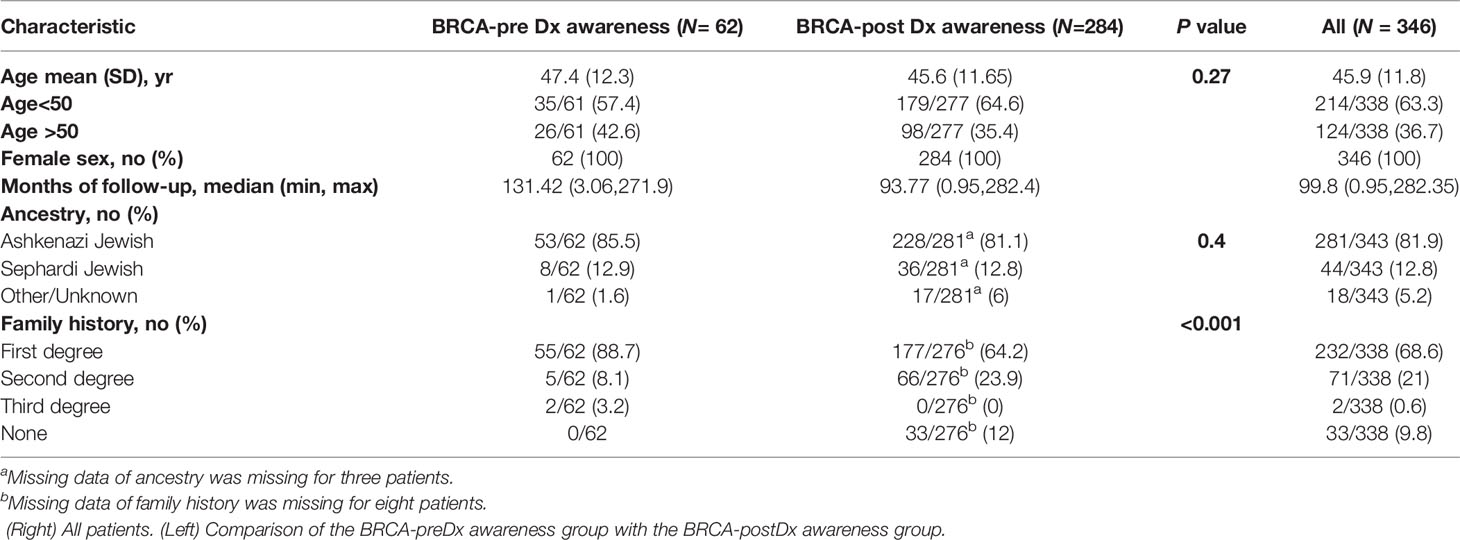
The total study population included 346 female patients (Table 1). The median age at diagnosis was 45.9 years (range 25–81). The BRCA-preDx awareness group included 62 patients and the BRCA-postDx awareness group 284 with similar mean age at diagnosis. In the BRCA-preDx awareness group, the majority of the patients (55/62, 88.7%) had at least one immediate family member who had a history of cancer, and all had a family history of cancer. In the BRCA-postDx awareness group, only 64.2% (177/276) of the patients had at least one immediate family member who had history of cancer, and 12% (33/276) had no family history of cancer (P < 0.001).
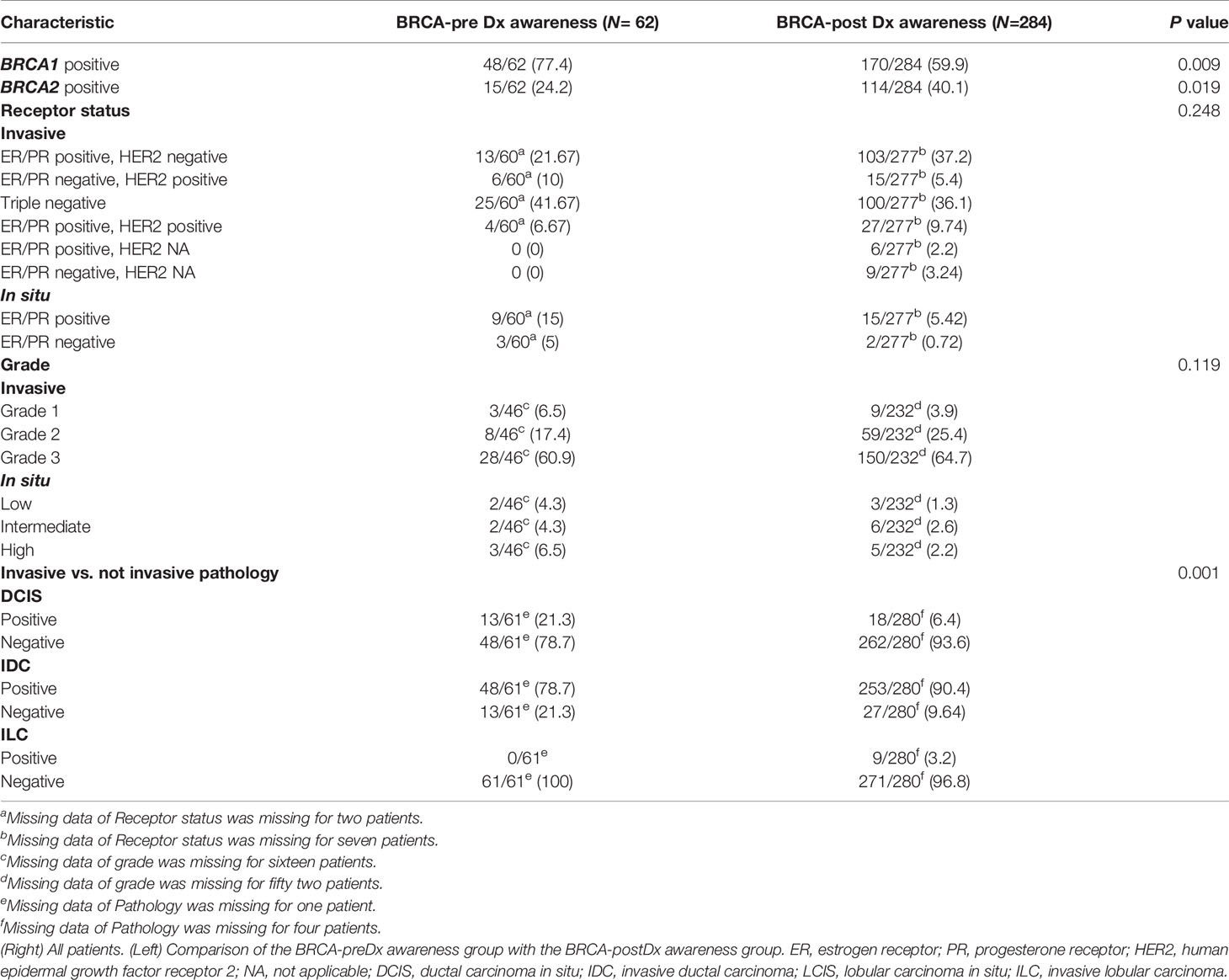
The patients’ breast tumors characteristics are described in detail in Table 2. Interestingly, BRCA1 PV was more frequent in the BRCA-preDx awareness group (48/62, 77.4%) compared with the BRCA-postDx awareness group (170/284, 59.9%; P = 0.009). One patient was positive for both BRCA1/2 PVs. DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) was a more common pathology result in the BRCA-preDx awareness group, with 21.3% (13/61) of the patients having a pure DCIS at the time of diagnosis, compared with the BRCA-postDx awareness group’s 6.4% (18/280; P = 0.001). IDC (invasive ductal carcinoma) was the pathologic diagnosis in 78.7% (48/61) of the patients in the BRCA-preDx awareness group, and in 90.4% (253/280) of the patients in the BRCA-postDx awareness group (P = 0.001). There were no statistically significant differences in receptor status or tumor grade between the groups.
Mode of Tumor Detection
The mode of detection differed significantly between the groups; 71.9% of the patients in the BRCA-postDx awareness group were diagnosed with breast cancer after they personally palpated a lump in their breast (Figure 1). That appears in contrast to the BRCA-preDx awareness group, where 26.2% of the patients personally palpated a lump (P < 0.001). In the BRCA-preDx awareness group, MRI was the diagnostic tool in 37.7% (23/61) of the cases, versus the BRCA-postDx awareness group where it accounted for only one case (0.4%, 1/267). In patients of younger ages, tumors were detected by self-palpation more frequently than by mammography in both study groups (Supplementary Figure 1).
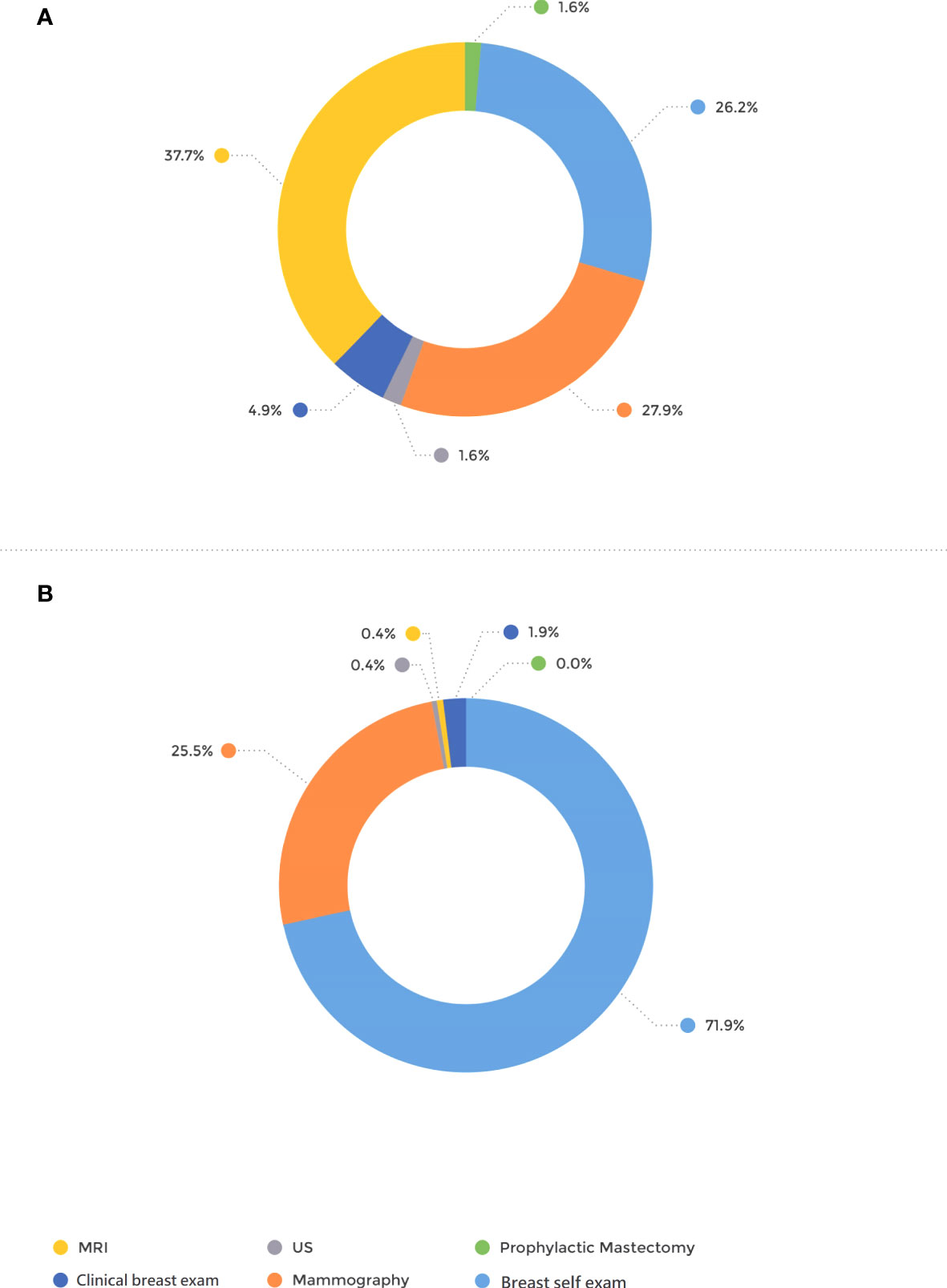
Figure 1 Mode of tumor detection. (A) BRCA-preDx awareness group. (B) BRCA-postDx awareness group. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; US, ultrasound.
Tumor Stage at Diagnosis
Furthermore, TNM staging was significantly more favorable in the BRCA-preDx awareness group. T stage was significantly lower in the BRCA-preDx awareness group (Figure 2): the majority of the patients were diagnosed at T1 (34/62, 54.8%), and 21% (13/62) of the patients were diagnosed at Tis. In the BRCA-postDx awareness group, only 37.5% (104/277) of the patients were diagnosed at T1 and 6.9% (19/277) of patients at Tis (P < 0.001). The N stage was also significantly lower in the BRCA-preDx awareness group. Within the BRCA-preDx awareness group, 71% of the patients were diagnosed with no lymph nodal metastases (44/62), while in the BRCA-postDx awareness group only somewhat more than half of the patients were diagnosed with no lymph node metastases (157/280, 56.1%; P = 0.007). Distant metastases were found in 3.4% of the patients in the BRCA-preDx awareness group and in 7.1% of the patients in the BRCA-postDx awareness group (non-significant trend).
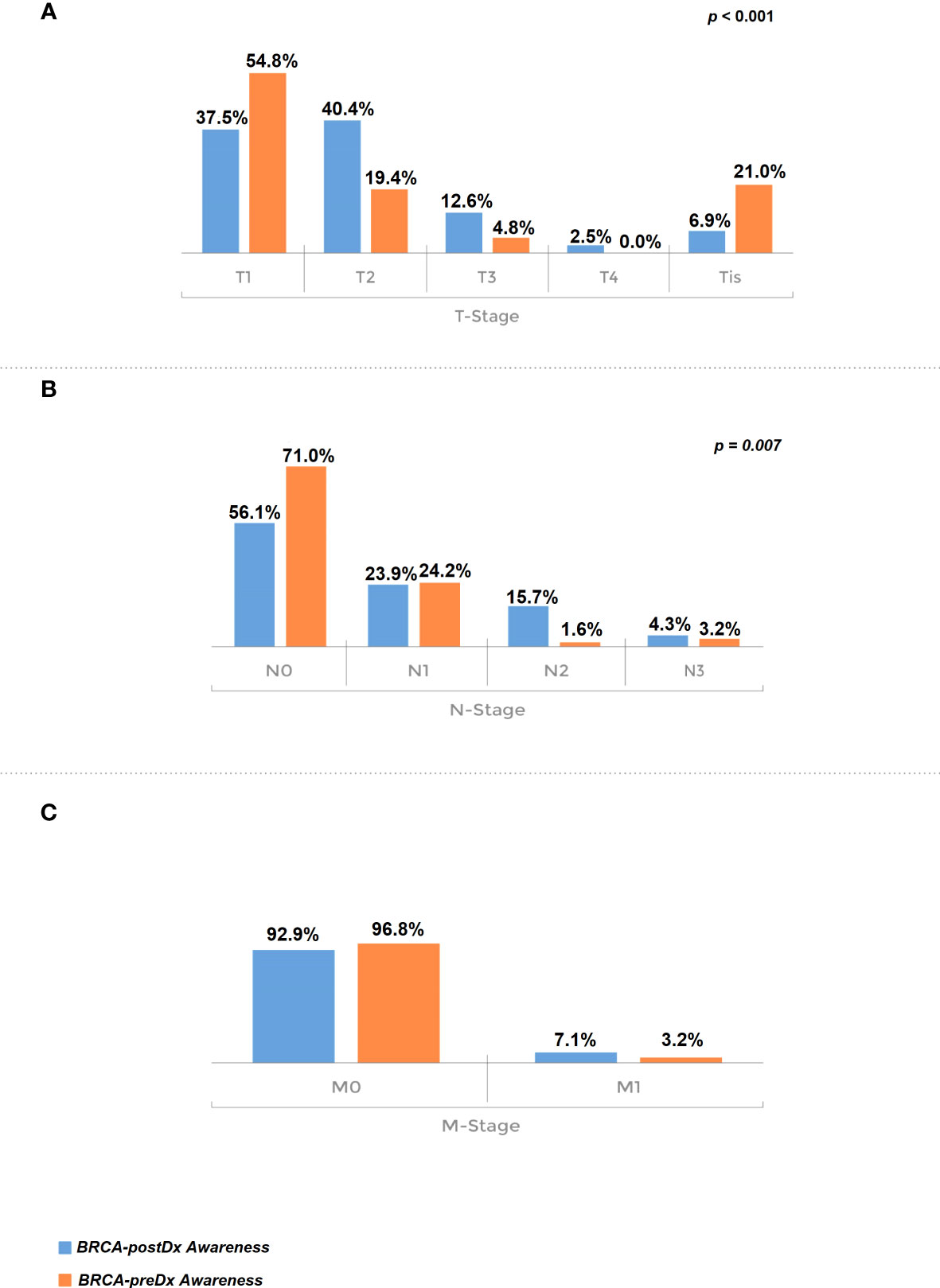
Figure 2 Tumor stage at diagnosis. (A) T stage, comparison of the BRCA-preDx awareness group with the BRCA-postDx awareness group. (B) N stage: comparison of the BRCA-preDx awareness group with the BRCA-postDx awareness group. (C) M stage: comparison of the BRCA-preDx awareness group with the BRCA-postDx awareness group.
Therapeutic Procedures Among the Study Population
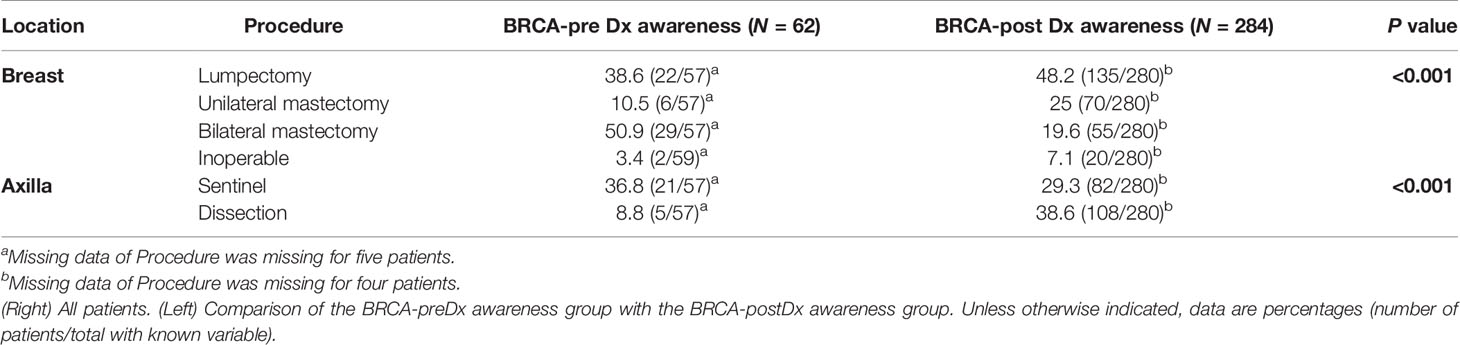
Significantly, less patients in the BRCA-postDx awareness group underwent breast conserving surgeries compared with the BRCA-preDx awareness group (Table 3). Thirty-eight percent of patients from the BRCA-postDx awareness group had axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) compared with only 8.8% (5/57, P < 0.001) in the BRCA-preDx awareness group. In addition, mastectomy was more frequently performed within the BRCA-postDx awareness group compared with the BRCA-preDx awareness group. Prophylactic bilateral mastectomy after diagnosis was less common in the BRCA-postDx awareness group (55/280, 19.6%) than in the BRCA-preDx awareness group (29/57, 50.9%; P < 0.001).
Outcomes Following Inclusion of MRI in the National Health Services
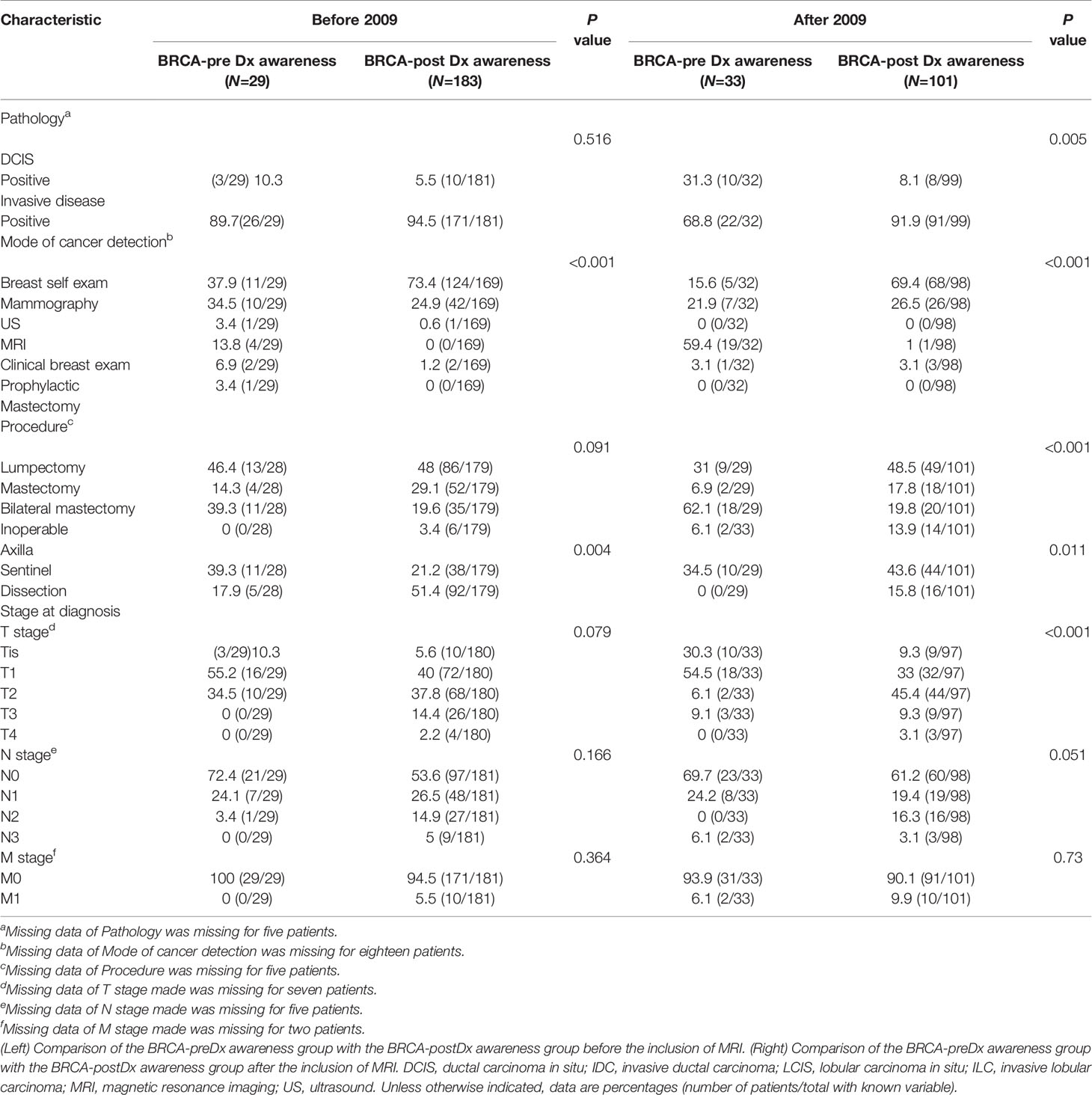
The BRCA-preDx awareness group included 29 patients diagnosed before and 33 patients after 2009, and the BRCA-postDx awareness group included 183 patients diagnosed before 2009 and 101 after 2009 (Table 4). Not surprisingly, the wider use of MRI had a clear effect. Until 2009, pathology results were similar between the groups, however, after 2009 the differences became significant: 31.3% (10/32) of patients had pure DCIS in the BRCA-preDx awareness group, while only 8.1% (8/99) did within the BRCA-postDx awareness group(P = 0.005). Additionally, before 2009, the tumor was diagnosed through MRI in 13.8% (4/29) of the patients in the BRCA-preDx awareness group (P < 0.001), and this rose to 59.4% after 2009 (P < 0.001). Furthermore, the staging of invasive tumors at diagnosis was also affected, and a major downstaging in the BRCA-preDx awareness group was noted (T2–T4: 34.5% before 2009, 15.2% after 2009; P = 0.012). The difference in N stage between BRCA-preDx awareness and BRCA-postDx awareness is apparent only after 2009.
Overall Survival
During our study period (1996–2020), 72 patients died. Sixty-six (23.2%) women died in the 238 BRCA-postDx awareness group, compared with six patients (9.7%) from the BRCA-preDx awareness group. In the overall study period analysis, we have found significantly improved survival in the BRCA-preDx awareness group (P = 0.008, Figure 3A). Correction for lead time bias was done and the results remained statistically significant (Supplementary Figure 2, p=0.0135). Further univariate analysis of our data found that there is no statistical difference in survival when patients are divided according to BRCA status (Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Figure 3). Additional factors which are also significantly associated with improved survival are PR status and TNM staging. In a multivariate analysis, only PR status and M stage were significant (Supplementary Table 1).
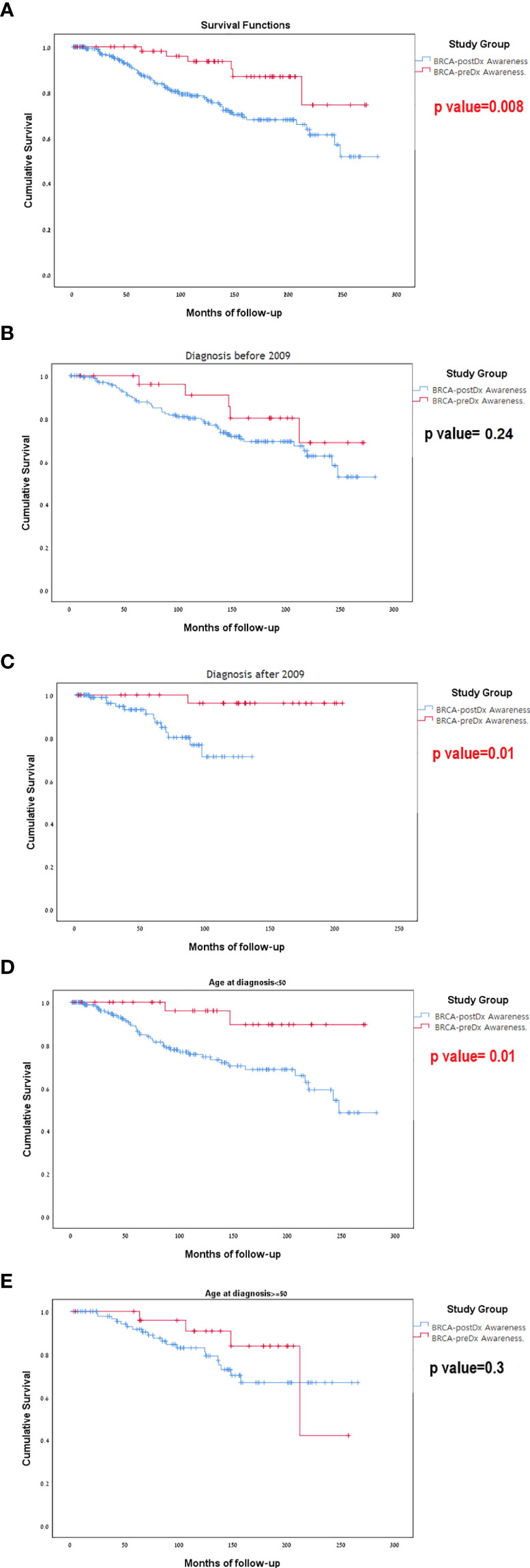
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival. (A) BRCA-preDx awareness cohort and BRCA-postDx awareness cohort. (B) BRCA-preDx awareness cohort and BRCA-postDx awareness cohort before 2009. (C) BRCA-preDx awareness cohort and BRCA-postDx awareness cohort after 2009. (D) BRCA-preDx awareness cohort and BRCA-postDx awareness cohort before the age of 50 years. (E) BRCA-preDx awareness cohort and BRCA-postDx awareness cohort after the age of 50 years.
In the sub-group analysis, there was no significant different in survival for between the BRCA-preDX group and the BRCA-postDx group prior to 2009 when MRI was not covered (p=0.237, Figure 3B): but there was statistically significant difference in survival after 2009 when MRI introduced (p=0.011, Figure 3C). Young women (age<50) with a diagnosis of breast cancer and BRCA-preDx awareness had improved survival (p=0.01) compared to women who were identified to harbor a BRCA PV after their breast cancer diagnosis (Figure 3D). Among older women (age>50), awareness of their BRCA status before their diagnosis of breast cancer did not improve their survival compared to women identified to have BRCA after their initial diagnosis (p=0.305, Figure 3E).
Discussion
In this retrospective study, we found a potential downstaging effect of high-risk screening with several key differences between patients who were offered high-risk screening and those who were not.
First, breast cancer in the BRCA-preDx awareness group was more often detected by imaging, mostly MRI, while in the BRCA-postDx awareness group self-palpation was most prevalent. We attribute this difference to the use of MRI in the BRCA-preDx awareness group, as suggested by international guidelines (7, 14) and previous studies that have shown that MRI has superior sensitivity in the BRCA1/2 carrier population (15, 16). Second, we show that more in situ pathology was found in the BRCA-preDx awareness group. Moreover, invasive tumors’ TNM staging was significantly more favorable in the BRCA-preDx awareness group: the tumors were smaller, less axillary involvement and importantly, axillary surgeries were more conservative. These findings are in line with the scientific background on which the current guidelines were established (7): MRI is more sensitive than mammography for women at high risk of developing breast cancer (17–19). The use of combined screening modalities elevates the sensitivity of the examination (15, 19) and can lead to detection at favorable stages compared with mammography alone (20). Additionally, mammography alone has a higher false-negative rate in BRCA PVcarriers (21), in high-density breast tissue (21–23) and in rapidly growing aggressive tumors (24, 25). All of these are more frequent characteristics among high-risk young women (7). To strengthen our findings, sub-analysis using the year of the beginning of widespread use of MRI made the above-mentioned differences even more apparent (e.g., improved staging and more in situ tumors after 2009).
Even though studies show that the addition of MRI is superior to mammography alone in BRCA1/2 carriers in detecting breast cancer, the currently available data has not shown a clear survival benefit from many of the above screening recommendations (16, 26–28). For example, the starting age and the age limit for high-risk screening are not well-known and based on limited observational data (26, 28). The interval time between each screening is also not well established, and there is only partial comparative information regarding different interval durations based on age (15).
A small hint of improved efficacy of high-risk screening was shown in a recent paper by Hadar et al. (29) The authors described a limited population (42 out of 105 BRCA1/2 carriers) who knew that they were BRCA carriers prior to cancer diagnosis, were under high-risk screening, and had better outcomes with a possible survival advantage. Our work shows an interesting improvement in survival in young women who underwent high-risk screening. Taken together, our data imply that the introduction of MRI-based screening was the probable driver behind this survival gain due to its ability to detect smaller tumors.
Our study has several limitations. The compliance with high-risk screening in the BRCA-preDx awareness group patients is largely unknown. We do not have additional information on subsequent procedures (e.g. salpingo-oophorectomy) or therapies such as chemotherapy and hormonal therapies. Additionally, we lack data about cancer recurrence rates in both groups. However, we believe that the long follow-up period compensates for the above-mentioned drawbacks and adds important insights to those from published cohorts (16).
In summary, our data emphasize the importance of high-risk MRI-based screening among BRCA1/2 PV carriers. This study shows a favorable effect on staging for women who have had awareness of their BRCA status before cancer diagnosis and had participated in intensified screening. Further studies are needed to refine the optimal screening protocols to maximize the survival benefit from high-risk screening programs.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Hadassah Medical Center IRB. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
Conception and design: SS, ALG, TS, and TP. Collection and assembly data: SS, ALG, TH, YC, LK, OM,YA-L, GZ, AG, BM, EC, VM, TS, and TP. Data analysis and interpretation: SS, ALG, TH, YC, and TP. Manuscript writing: SS, ALG, AZ, and TP. SS and ALG had equally contributed to this manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
ALG was supported by the 2020 Conquer Cancer-ICRF Career Development Award.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank T. Bdolah-Abram from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem for her help with the statistical analysis. The study was conducted as part of the requirements for SS’s M.D. certificate in the Faculty of Medicine, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.683656/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | How the first diagnosis was made with regard to age. BRCA-preDx awareness group (right) and BRCA-postDx awareness group (left). MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; US, ultrasound.
Supplementary Figure 2 | Survival analysis following lead-time bias correction. BRCA-preDx awareness cohort and BRCA-postDx awareness cohort.
Supplementary Figure 3 | Survival analysis according to BRCA1 and BRCA2 status. BRCA-preDx and BRCA-postDx awareness cohort separated according to BRCA1/2.
Supplementary Table 1 | Univariate and multivariate analyses of overall survival.
References
1. Henry DA, Lee MC, Almanza D, Ahmed KM, Sun W, Boulware DC, et al. Trends in Use of Bilateral Prophylactic Mastectomy vs High-Risk Surveillance in Unaffected Carriers of Inherited Breast Cancer Syndromes in the Inherited Cancer Registry (ICARE). Breast Cancer Res Treat (2019) 174(1):39–45. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-5057-7
2. Shamsi M, Islamian JP. Breast Cancer: Early Diagnosis and Effective Treatment by Drug Delivery Tracing. Nucl Med Rev (2017) 20(1):45–8. doi: 10.5603/NMR.2017.0002
3. Le-Petross HT, Whitman GJ, Atchley DP, Yuan Y, Gutierrez-Barrera A, Hortobagyi GN, et al. Effectiveness of Alternating Mammography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Screening Women With Deleterious BRCA Mutations at High Risk of Breast Cancer. Cancer (2011) 117(17):3900–7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25971
4. Bick U, Engel C, Krug B, Heindel W, Fallenberg EM, Rhiem K, et al. High-Risk Breast Cancer Surveillance With MRI: 10-Year Experience From the German Consortium for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat (2019) 175(1):217–28. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05152-9
5. Domchek S. Broadening Criteria for BRCA1/2 Evaluation. Endocr Rev (2010) 31(5):702–55. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0041
6. Nelson HD, Pappas M, Cantor A, Haney E, Holmes R. Risk Assessment, Genetic Counseling, and Genetic Testing for BRCA- Related Cancer in Women: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA - J Am Med Assoc (2019) 322(7):666–85. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.8430
7. Daly MB, Pal T, Berry MP, Buys SS, Dickson P, Domchek SM, et al. Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, and Pancreatic. JNCCN (2021) 19(1):77–102. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.0001
8. Evans DG, Harkness EF, Howell A, Wilson M, Hurley E, Holmen MM, et al. Intensive Breast Screening in BRCA2 Mutation Carriers Is Associated With Reduced Breast Cancer Specific and All Cause Mortality. Hered Cancer Clin Pract (2016) 14:8. doi: 10.1186/s13053-016-0048-3
9. Saadatmand S, Obdeijn IM, Rutgers EJ, Oosterwijk JC, Tollenaar RA, Woldringh GH, et al. Survival Benefit in Women With BRCA1 Mutation or Familial Risk in the MRI Screening Study (MRISC). Int J Cancer (2015) 137(7):1729–38. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29534
10. Bick U. Intensified Surveillance for Early Detection of Breast Cancer in High-Risk Patients. Breast Care (2015) 10(1):13–20. doi: 10.1159/000375390
11. Griffin JL, Pearlman MD. Breast Cancer Screening in Women at Average Risk and High Risk. Obstet Gynecol (2010) 116(6):1410–21. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181fe714e
12. Healy NA, O’Keeffe SA. Determination of Recall Rates for Assessment in High-Risk Women Undergoing Annual Surveillance Breast MRI. Clin Radiol (2016) 71(11):1143–7. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2016.07.011
13. Duffy SW, Nagtegaal ID, Wallis M, Cafferty FH, Houssami N, Warwick J, et al. Correcting for Lead Time and Length Bias in Estimating the Effect of Screen Detection on Cancer Survival. Am J Epidemiol (2008) 168(1):98–104. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwn120
14. Clinical N, Guidelines P, Guidelines N. Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis The University of Texas. (2020).
15. Lee CH. Annual Screening Strategies in BRCA1 and BRCA2 Gene Mutation Carriers: A Comparative Effectiveness Analysis. Breast Dis (2013) 24(1):41–2. doi: 10.1016/j.breastdis.2013.01.034
16. Warner E, Hill K, Causer P, Plewes D, Jong R, Yaffe M, et al. Prospective Study of Breast Cancer Incidence in Women With a BRCA1 or BRCA2 Mutation Under Surveillance With and Without Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J Clin Oncol (2011) 29(13):1664–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.0835
17. Leach MO. Screening With Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Mammography of a UK Population at High Familial Risk of Breast Cancer: A Prospective Multicentre Cohort Study (MARIBS). Lancet (2005) 365(9473):1769–78. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66481-1
18. Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, Tutt A, Wu P, Mergui-Roelvink M, et al. New England Journal Medicine. N Engl J Med (2009) 361(2):123–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0900212
19. Helvie M. Surveillance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Carriers. JAMA (2005) 293(8):1317–25. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.8.931-a
20. Cardoso F, Kyriakides S, Ohno S, Penault-Llorca F, Poortmans P, Rubio IT, et al. Early Breast Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann Oncol (2019) 30(8):1194–220. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz173
21. Tilanus-Linthorst M, Verhoog L, Obdeijn IM, Bartels K, Menke-Pluymers M, Eggermont A, et al. A BRCA1/2 Mutation, High Breast Density and Prominent Pushing Margins of a Tumor Independently Contribute to a Frequent False-Negative Mammography. Int J Cancer (2002) 102(1):91–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10666
22. Van Gils CH, Otten JDM, Verbeek ALM, Hendriks JHCL, Holland R. Effect of Mammographic Breast Density on Breast Cancer Screening Performance: A Study in Nijmegen, the Netherlands. J Epidemiol Community Health (1998) 52(4):267–71. doi: 10.1136/jech.52.4.267
23. Stoutjesdijk MJ, Boetes C, Jager GJ, Beex L, Bult P, Hendriks JHC, et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Mammography in Women With a Hereditary Risk of Breast Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst (2001) 93(14):1095–102. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.14.1095
24. Buist DSM, Porter PL, Lehman C, Taplin SH, White E. Factors Contributing to Mammography Failure in Women Aged 40 – 49 Years. JNCI: J Nat Cancer Institute (2004) 96:(19). doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh269
25. Eisinger F, Juliain-Reynier C, Sobol H. Re: Biologic Characteristics of Interval and Screen-Detected Breast Cancers [2]. J Natl Cancer Inst (2000) 92(18):1533–4. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.18.1533
26. Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, Harms S, Leach MO, Lehman CD, et al. American Cancer Society Guidelines for Breast Screening With MRI as an Adjunct to Mammography. ACS J (2007) 57(2):75–89. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.57.2.75
27. Chubiz JEC, Lee JM, Gilmore ME, Chung Y, Ryan PD, Gazelle GS. Cost-Effectiveness of Alternating MRI and Digital Mammography Screening in BRCA1 and BRCA2 Gene Mutation Carriers. Cancer (2014) 119(6):1266–76. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27864.Cost-Effectiveness
28. Chiarelli AM, Prummel MV, Muradali D, Majpruz V, Horgan M, Carroll JC, et al. Effectiveness of Screening With Annual Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Mammography: Results of the Initial Screen From the Ontario High Risk Breast Screening Program. J Clin Oncol (2014) 32(21):2224–30. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.52.8331
Keywords: breast cancer, BRCA1/2, high-risk, survival, screening, downstaging
Citation: Shraga S, Grinshpun A, Zick A, Kadouri L, Cohen Y, Maimon O, Adler-Levy Y, Zeltzer G, Granit A, Maly B, Carmon E, Meiner V, Sella T, Hamburger T and Peretz T (2021) “High-Risk Breast Cancer Screening in BRCA1/2 Carriers Leads to Early Detection and Improved Survival After a Breast Cancer Diagnosis”. Front. Oncol. 11:683656. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.683656
Received: 21 March 2021; Accepted: 03 August 2021;
Published: 02 September 2021.
Edited by:
Philip Poorvu, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, United StatesReviewed by:
Brittany Bychkovsky, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, United StatesFrancesca Poggio, San Martino Hospital (IRCCS), Italy
Copyright © 2021 Shraga, Grinshpun, Zick, Kadouri, Cohen, Maimon, Adler-Levy, Zeltzer, Granit, Maly, Carmon, Meiner, Sella, Hamburger and Peretz. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Albert Grinshpun, QWxiZXJ0Z0BoYWRhc3NhaC5vcmcuaWw=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Shay Shraga
Shay Shraga Albert Grinshpun1,2*†
Albert Grinshpun1,2*† Luna Kadouri
Luna Kadouri Avital Granit
Avital Granit Vardiella Meiner
Vardiella Meiner Tamar Sella
Tamar Sella Tamar Peretz
Tamar Peretz