- 1Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, King Faisal University, Al-Ahsa, Saudi Arabia
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Kafrelsheikh University, Kafrelsheikh, Egypt
- 3Research Center for Asian Infectious Diseases, Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
- 4Division of Cellular and Molecular Biology, Department of Cancer Biology, Institute of Medical Science, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
- 5Department of Microbiology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, South Korea
- 6Division of Molecular Virology, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
- 7Department of Chemistry and Biomolecular Science, Faculty of Engineering, Gifu University, Gifu, Japan
- 8Senior Professor Office, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), capable of zoonotic transmission, has been associated with emerging viral pneumonia in humans. In this study, a set of highly potent peptides were designed to prevent MERS-CoV fusion through competition with heptad repeat domain 2 (HR2) at its HR1 binding site. We designed eleven peptides with stronger estimated HR1 binding affinities than the wild-type peptide to prevent viral fusion with the cell membrane. Eight peptides showed strong inhibition of spike-mediated MERS-CoV cell-cell fusion with IC50 values in the nanomolar range (0.25–2.3 µM). Peptides #4–6 inhibited 95–98.3% of MERS-CoV plaque formation. Notably, peptide four showed strong inhibition of MERS-CoV plaques formation with EC50 = 0.302 µM. All peptides demonstrated safe profiles without cytotoxicity up to a concentration of 10 μM, and this cellular safety, combined with their anti-MERS-CoV antiviral activity, indicate all peptides can be regarded as potential promising antiviral agents.
Introduction
The Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causes severe respiratory manifestations, including fever, persistent cough, and pneumonia, with occasional gastrointestinal symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and death from renal failure (Assiri et al., 2013; Nassar et al., 2018). MERS-CoV is fatal for approximately one-third of people infected (Ahmadzadeh et al., 2020), which is regarded as a high fatality rate.
There is no vaccine or drug currently approved to prevent or treat MERS-CoV. The current preventative measures comprise avoidance of behaviors that lead to transmission and general health practices of handwashing, avoiding contact between the hands and the eyes and nose, and covering the nose and mouth when sneezing. Medical care comprises general supportive treatment of body organs and the use of previously known antivirals in combination with interferon (Sheahan et al., 2020). However, there is still no specific treatment produced specifically for MERS-CoV control.
The MERS-CoV genome produces four structural proteins: spike (S), membrane (M), envelope (E), and nucleocapsid (N). Fusion between the viral and cell membrane is accomplished by the two subunits of viral S protein (S1 and S2), important for completing the virus replication cycle (Bosch et al., 2003). The S1 subunit recognizes the host cell receptor, while S2 mediates the fusion process (Song et al., 2018; Hoffmann et al., 2020). Membrane fusion starts with the interaction of the HR1 and HR2 domains of S2, bringing the viral and cell membranes in proximity. Virus entry inhibitors, including attachment and fusion inhibitors, comprise an important class of antiviral drugs. Attachment inhibitors usually interfere with S binding to its receptors, which is more frequently affected by the high mutation rate (Xia et al., 2019). Fusion inhibitors interfere with the replication cycle following the attachment step and interfere with the consecutive steps of viral and cell membrane fusion. Therefore, fusion inhibitors remain an attractive strategy for discovering new antiviral drugs, especially as they affect conserved viral sequences.
Drug discovery trials against MERS-CoV comprised the production of monoclonal antibodies (Widjaja et al., 2019; Hussen et al., 2020) or repurposing previously utilized antiviral agents (Falzarano et al., 2013). In addition, a peptide sequence found in the HR2 region of wild-type MERS-CoV has been shown to have some inhibitory effect on MERS-CoV membrane fusion (Lu et al., 2014). However, this previous work has not resulted in new MERS-CoV inhibitors.
Our research group recently revealed the structure of new potential small inhibitors of the MERS-CoV fusion process by targeting cavities on the surface of HR1 (Kandeel et al., 2020). In this study, stronger fusion inhibitor peptides were designed by modification or mutation of the wild-type MERS-CoV HR2 domain, a portion of the fusion protein. The designed peptides inhibited spike protein-mediated MERS-CoV cell-cell fusion and MERS-CoV infection of cells. Thus, these peptides may be useful in preventing or treat MERS-CoV infection.
Material and Methods
Peptide Design
S2 HR2 was selected as the targeted peptide design site based on the findings of several studies targeting SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and HIV. These studies demonstrated that HR2-derived peptides were more potent than HR1 analogs (Liu et al., 2004; Lu et al., 2014; Shabane et al., 2019). In this study, the 36-amino acids wild-type HR2 peptide (Table 1, peptide 1 or SEQ ID NO: 1) was modified to obtain analogs demonstrating stronger inhibition of MERS-CoV replication (Accepted Patent, USPTO application no. 16/857136). This parent peptide was synthesized and used as a reference for comparison with the other eleven mutant peptides.
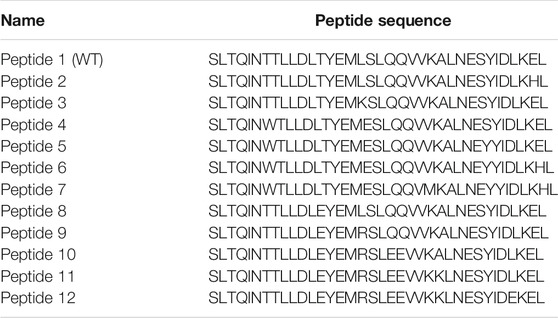
TABLE 1. The sequence of peptides used in this study. The sites of WT peptide mutations are underlined.
Several computational trials were performed to optimize a new sequence related to peptide 1. Several systematic point mutations were initially generated for each amino acid in the peptide 1 sequence, providing 684 candidates with potentially improved binding energies between HR1 and HR2 (Dehouck et al., 2013). Several point mutations were then combined to yield peptides with a lower free energy of binding with HR1. Finally, eleven peptides were synthesized (Cambridge, ON, Canada, Table 1, Peptides 2-12 or SEQ ID NOs: 2-12). The peptides were purified by HPLC, and the exact mass was determined by mass spectrometry to ensure maximal purity.
Cell Lines and Virus
Two 293FT-based reporter cell lines that constitutively express individual split proteins (DSP1-7 and DSP8-11 proteins) were used for cell-cell fusion assays (Wang et al., 2014). The cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1 g/ml puromycin.
Vero cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, United States) for the plaque assay. The cells were maintained in DMEM containing 10% FBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States), 25 mm HEPES, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin.
MERS-CoV was obtained with permission from the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CoV/KOR/KNIH/002_05_2015, Permission No. 1-001-MER-IS-2015001). MERS-CoV amplification and quantification were performed as described previously (Kandeel et al., 2020).
Dual Split Protein Assay to Monitor Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Membrane Fusion
MERS-CoV-S-mediated membrane fusion was quantitatively evaluated via DSP assay using 293FT cells as previously described (Yamamoto et al., 2016). The dimerization of DSP1-7 and DSP8-11 after cell-cell fusion can be quantified based on the values of fluorescence/luminescence upon formation of tight DSP complexes. The effector cells express MERS-CoV-S protein with DSP8-11, while the target cells express the MERS-CoV receptor and transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) with DSP1-7. The cells were grown in 10 cm culture dishes (4 × 106 cells/10 ml) 24 h before the assays. Cells were treated with 6 µM EnduRen (Promega, Madison, WI, United States), a substrate for Renilla luciferase, for 2 h to activate EnduRen. Each peptide was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and added to 384-well plates (Greiner Bioscience, Frickenhausen, Germany), then 50 µl of each single-cell suspension (effector and target cells) was added to the wells using a Multidrop dispenser (Thermo Fisher Scientific). After incubation at 37°C for 4 h, luciferase activity was measured using a Centro xS960 luminometer (Berthold, Germany).
Plaque Assay After Treatment With Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Inhibitor Peptides and Cytotoxicity Studies
The plaque reduction assay was performed as reported previously (Kandeel et al., 2020). Briefly, Vero cells were cultivated on six-well plates for 12 h at 6 × 105 cells/well. In an initial study, MERS-CoV was mixed with each peptide at a final concentration of 10 µM for 30 min at 37 °C. The mixtures of MERS-CoV and each peptide were added to Vero cells in each well and then incubated for 1 h. The supernatants were subsequently removed, and DMEM/F12 medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 0.6% oxoid agar was transferred to each well. Four days after infection, plaque formation was observed by staining with crystal violet, and plaque numbers were counted. The plaque reduction assay was repeated in a dose-dependent manner using 2-fold serially diluted samples of Peptides 4, 5, or 6 to investigate the inhibitory properties of candidate peptides.
For the cytotoxicity assay, Vero cells (1 × 103 cells/well) were incubated in 96-well plates for 12 h. The peptides were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and cells were treated with the peptides or DMSO only for three days. The proliferation of Vero cells was analyzed using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) (Dojindo, Rockville, MD, United States). CCK-8 solution was added to each well and incubated for 4 h at 37 °C. CCK-8 absorbance was read at 450 nm using a microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Peptide Properties
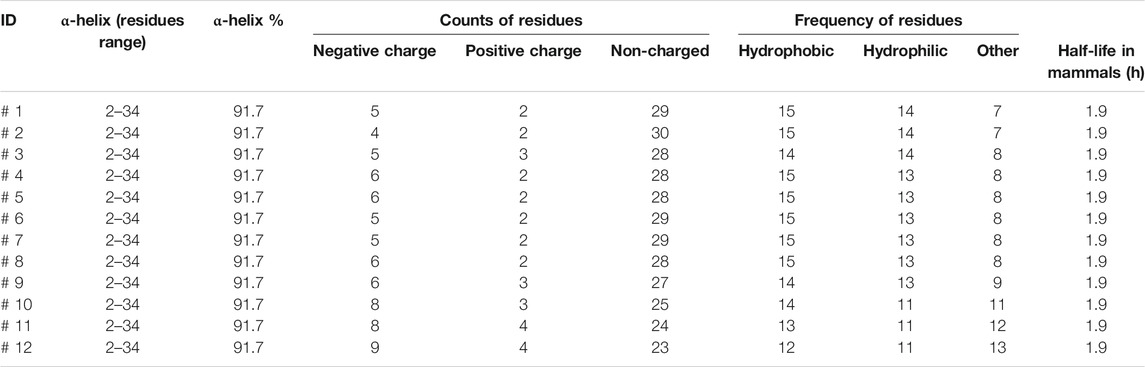
Markers of peptide properties were computationally analyzed by CLC genomics software. The parameters included α-helix (residues range), α-helix%, counts of the negative charge, positive charge and non-charged residues, counts of hydrophobic, hydrophilic, other residues, and half-life in mammals.
Results
The Peptide Sequences
The site of peptide design is shown in Figure 1. The MERS-CoV S protein is composed of two subunits S1 and S2 (Figure 1A). The S2 subunits share in the membrane fusion process, and in the full fusion state, trimers of HR1 and HR2 form the fusion core (Figure 1B). The peptides were designed to target the HR1 cavity that binds HR2 during the fusion core formation. The designed peptides were 36 amino acids long, similar to the wild type HR2 or mutated with an estimated stronger binding with HR1. The site and alignment of peptides are provided in Figures 1C,D. The peptides contained from 1 to 10 amino acid mutations, with predicted improved binding with MERS CoV HR1. The upper diagonal panel in Figure 2 shows the number of amino acid differences between each peptide. The lower diagonal panel provides the % identity, between 72.22 and 97.22%. Peptides 9, 11, and 12 showed the largest differences in amino acid composition from the wild type.
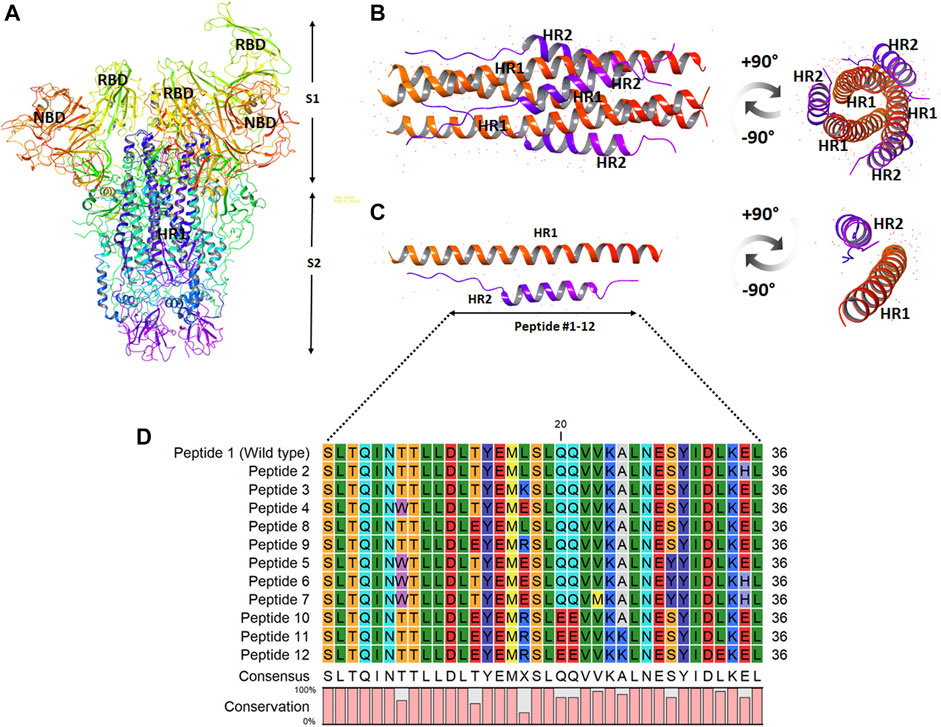
FIGURE 1. The design and sequence of peptides 1–12. (A) The structure of MERS-CoV spike ectodomain showing the spike S1 and S2 subunits. (B) The fusion core showing trimers of HR1 and HR2 in a full fusion state. (C) Monomers of the fusion core showing HR1-HR2 binding. The site of fusion peptide design is represented by the bidirectional arrow. (D) The sequence of the synthesized peptides 1–12. The color scale indicates the degree of residue conservation.
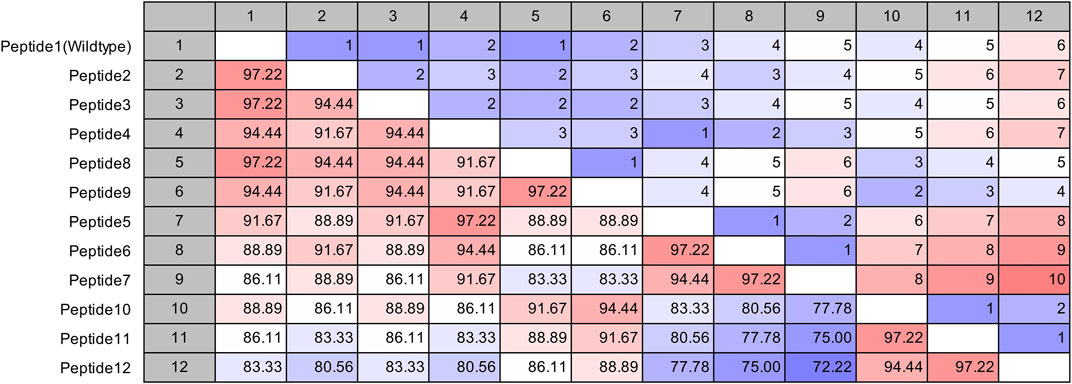
FIGURE 2. Pairwise comparison of the synthesized MERS-CoV inhibitor peptides. The upper diagonal panel shows the number of amino acid differences. The lower diagonal panel shows the identity. The color scale indicates extreme values.
DSP Assay for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus S-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion
The strength of the 12 synthesized peptides on S protein-mediated MERS-CoV fusion was evaluated as previously established (Yamamoto et al., 2016). All peptides showed significant inhibition at 10 µM (Figure 3A), yet no peptide demonstrated direct inhibition of DSP reporter activity at 10 µM (Figure 3B). The peptides inhibited MERS-CoV fusion in a dose-dependent manner. The IC50 values were from the low nanomolar to the low micromolar range (Table 2). The most effective peptides were 11 and 12 (IC50 = 0.25 µM), followed by three peptides (#5, 8, and 10) with IC50 = 0.3–0.6 µM.
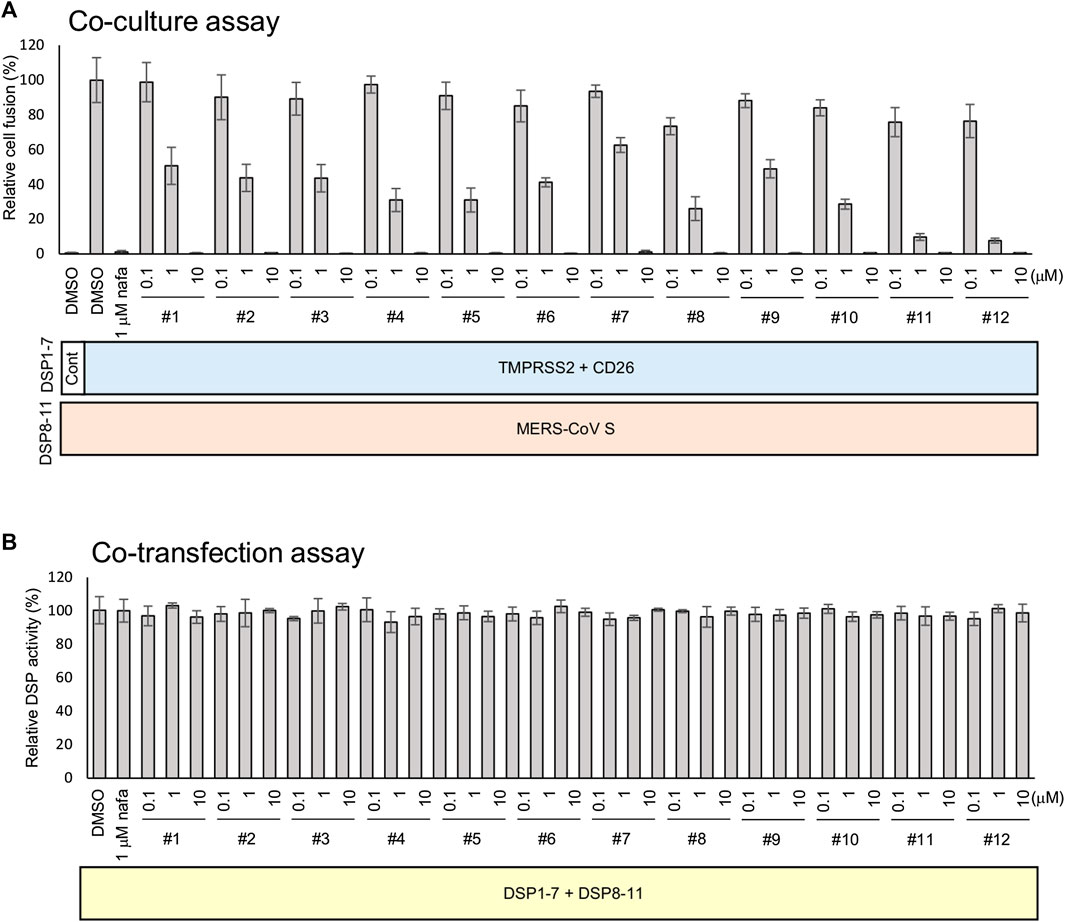
FIGURE 3. The effect of peptides on the TMPRSS2-dependent cell-cell fusion assay of MERS-CoV. (A) The effect of each peptide on coculture fusion using DSP as a reporter. Peptides were tested at different concentrations, and the proteins in addition to the reporters (DSPs) transduced into the effector and target cells are indicated below the graph. Nafamostat was used as an inhibitor of the TMPRSS2 pathway. The relative cell fusion was represented as the DSP value (RL activity measured in RLU) normalized to that of the control assay with DMSO alone. (B) The effect of each peptide on RL measurement. Each peptide was added to cells co-expressing DSP1-7 and DSP8-11 to evaluate its direct inhibitory effects on RL. The relative DSP signal is indicated on the vertical axis by representing the control value with DMSO alone to 100%.
Plaque Inhibition Assay
The peptides were initially screened at 10 µM concentration in MERS-CoV plaque assay (Figure 4). All peptides inhibited MERS-CoV plaque formation. Based on the degree of plaque inhibition, three peptide classes were identified: strong, moderate, and weak inhibitors. Three peptides (Bosch et al., 2003; Bosch et al., 2003; Song et al., 2018; Sheahan et al., 2020) strongly reduced MERS-CoV plaque formation by more than 95%. Five other peptides, 2, 7, 10, 11, and 12, showed 69–74% inhibition of plaque formation. Peptides 1 and 3 showed a 64% decrease in MERS CoV replication. To quantitatively evaluate the effect of peptides on viral replication, the plaque assay was repeated at different concentrations of peptides 4, 5, and 6 using two-fold serially diluted concentration from 50 µM. As shown in Figure 5, MERS-CoV plaque formation decreased in a concentration-dependent manner.
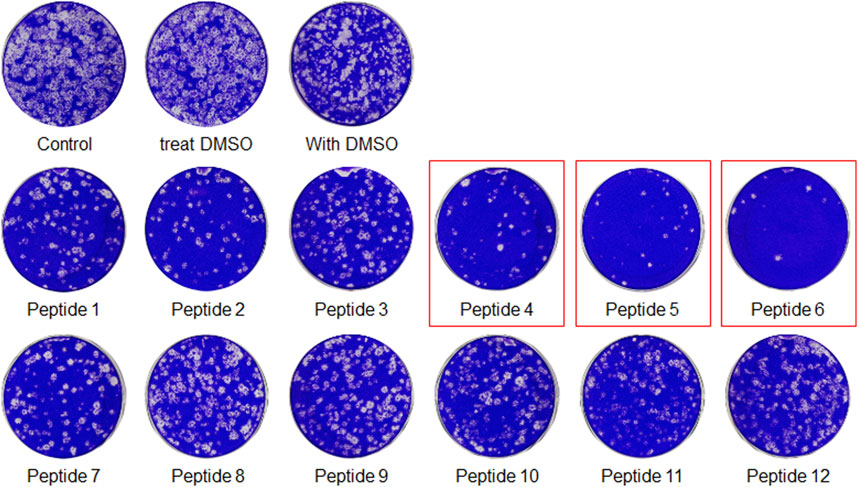
FIGURE 4. The plaque formation assay for MERS-CoV inhibitor peptides. MERS-CoV was pre-incubated with 10 µM of each peptide for 30 min at 37°C. The mixture of the virus and each peptide was added to the Vero cells and incubated for 1 h. After the incubation, the medium was replaced with DMEM/F12 containing 0.6% oxoid agar. The plaques were stained with crystal violet 4 days after infection. Plaque number was quantified and relative production of viral particles is shown, with virus production of a DMSO-treated control representing 100%.
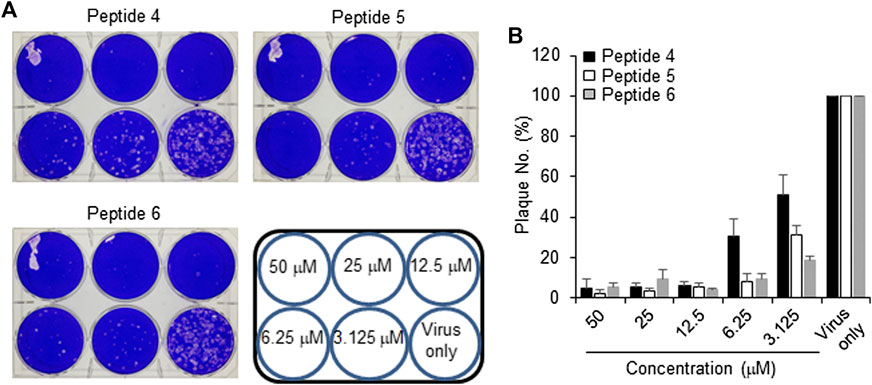
FIGURE 5. Effect of inhibitor peptides on MERS-CoV infection. MERS-CoV was pre-incubated with two-fold serially diluted peptide 4, 5 or 6 (n = 3) for 30 min at 37°C. Vero cells were treated with the mixture of the virus and each peptide and then incubated for 4 days in DMEM/F12 containing 0.6% oxoid agar. The plaques were observed by staining with crystal violet and counted (A) A representative picture showing the plaque reduction assay (B) Quantification of the plaque reduction assay against MERS-CoV after treatment with each peptide.
Cytotoxicity and Viability
The cytotoxicity of peptides 4, 5 or 6, or DMSO (control) was examined in Vero cells for 3 days using concentrations up to 50 µM. No cytotoxicity was observed at or below 10 µM for any tested peptide (Figure 6). Thus, peptides 4, 5, and 6 have a safe cellular profile without cytotoxicity.
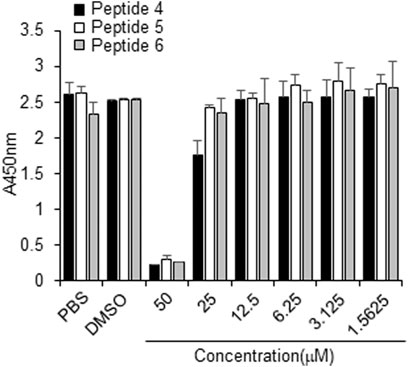
FIGURE 6. Effect of peptides 4, 5, and 6 on the proliferation of Vero cells. Peptides (100 µM) were dissolved in 10% DMSO, and then the peptides were two-fold serially diluted in PBS. Vero cells were treated with PBS, 1% DMSO, or indicated peptide concentrations for 3 days, followed by the CCK-8 assay.
Molecular Properties of Peptides
The designed peptides computationally demonstrated stronger binding with MERS-CoV HR1. The peptides showed 1–6 mutations relative to the wild type. Despite the mutations, all peptides maintained high α-helix content with a constant residues range of 2–34 and a high helix content rate of 91.7% (Table 3). The negative and positive charged residues were in the ranges 4–9 and 2–4, respectively. Most of the peptide compositions were from the non-charged regions (23–30 residues).
Discussion
Despite the emerging and fatal nature of MERS-CoV, structure-based drug discovery studies to combat this virus are very limited. Computational studies have substantially contributed to the drug discovery process, especially through lead identification and optimization (Koutsoukas et al., 2011). Small molecule inhibitors against several MERS-CoV targets were provided to the research community (Xia et al., 2014; Kumar et al., 2016; Galasiti Kankanamalage et al., 2018). Recently, we designed the first generation of small chemical MERS-CoV fusion inhibitor molecules (Kandeel et al., 2020). In addition, several designed peptides were proven efficient in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 replication (Kandeel et al., 2021). Complementing these efforts were short peptides demonstrating stronger inhibition in the nanomolar range than the previously provided small molecules, which showed inhibition of MERS-CoV fusion in the low micromolar range. The discovery of new drugs and the design of novel vaccines are the two most powerful tools for controlling viral diseases. In this context, fusion inhibitors were a promising class of antiviral drugs extensively studied in treating influenza virus (Kadam et al., 2017), dengue virus (De La Guardia & Lleonart, 2014), respiratory syncytial virus (Feng et al., 2015), African swine fever virus (Hakobyan et al., 2018), measles virus (Welsch et al., 2013), HIV (Jing et al., 2002), SARS-CoV (Liu et al., 2004; Sainz et al., 2006; Chu et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2009), and MERS-CoV (Lu et al., 2014).
Recently, peptide-based therapeutics have contributed enormously in terms of improved stability and systemic bioavailability. The advantages of developing peptide drugs are their predictable and optimizable absorption distribution, metabolism, and excretion properties (Fosgerau & Hoffmann, 2015). The premise of using peptide drugs as fusion inhibitors has successfully delivered a clinical drug for treating HIV (Ding et al., 2017). Cell membranes and body barrier penetration have been improved using optimized amphipathic and α-helical peptides (Stalmans et al., 2015). More robust tools have been used to improve the oral bioavailability of therapeutic peptides, e.g., oral application of insulin-polyarginine conjugates (Morishita et al., 2007). Inhalable peptides were also used with promising results in treating pulmonary and systemic diseases (Greene et al., 2020; Waxman et al., 2021). These technologies offer a promising future for peptide drug development.
The spike-activated CoV entry into cells was proven to be by either direct membrane fusion or endocytosis (Seyedpour et al., 2020). In these entry paths, the viral spike must be activated by cellular proteases such as TMPRSS2 and cathepsin L for membrane fusion and endocytosis, respectively. The expression of TMPRSS2 in human tissues was found to be specific for each cell type (Sungnak et al., 2020; Ziegler et al., 2020). In mouse models, the spread of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV was limited by a TMPRSS2-knockout (Iwata-Yoshikawa et al., 2019). In this study, the S-mediated dual split cell-cell fusion in 293FT cells was dependent on TMPRSS2 expression. Thus, these findings suggest that the peptides may inhibit the TMPRSS2-dependent plasma membrane fusion of MERS-CoV. The 293FT cell lines utilized were overexpressing TMPRSS2. As Vero cells lack expression of TMPRSS2, viruses enter by the endocytic pathway (Hoffmann et al., 2020). Therefore, the observed effect of peptides suggests the potential dual action of the peptides on both membrane fusion and endocytosis paths.
The selection of a peptide 36 amino acids in length was based on previous cell-cell fusion assays (Lu et al., 2014). In this study, the 36-mer peptide inhibited MERS-CoV S-mediated cell-cell fusion in the low nanomolar to the low micromolar range. In the drug discovery process, the binding of the fragment to its target is usually in the millimolar to micromolar range (Li, 2020). Current clinically used drugs operate within the micromolar range (Lomenick et al., 2009). Weak binding affinity has been defined as within the millimolar or high micromolar range (Li, 2020). Novel antiviral compounds with IC50 values in the low micromolar range are expected to be promising lead structures (Liu et al., 2004). One example is enfuvirtide, an FDA-approved fusion inhibitor of HIV-1 that showed extended IC50 values from 10 ng/ml to 7 μg/ml (2 nm–7 µM concentrations) (Greenberg, 2007). Based on these data, the reported peptides in our work could have clinical implications in controlling MERS-CoV infection.
The mechanism of action of fusion inhibitors is provided in Figure 7. The MERS-CoV S protein is composed of the S1 and S2 subunits (Figure 7A). The S1 subunit recognizes the host cell membrane through the receptor binding domain (RBD). After cleavage by host proteases, the fusion protein (FP) of S2 binds the host cell membrane in the presence of viral proteins across the host membrane (TM) and an intracellular portion called the cytoplasmic domain (CP). For fusion to occur, the host and viral membranes come in close apposition via the interaction of HR1 and HR2 (Figure 7C). The peptides developed in this study were designed to target a surface cavity on HR1, thus competing with HR2 for their binding sites on HR1 and preventing the viral fusion process.
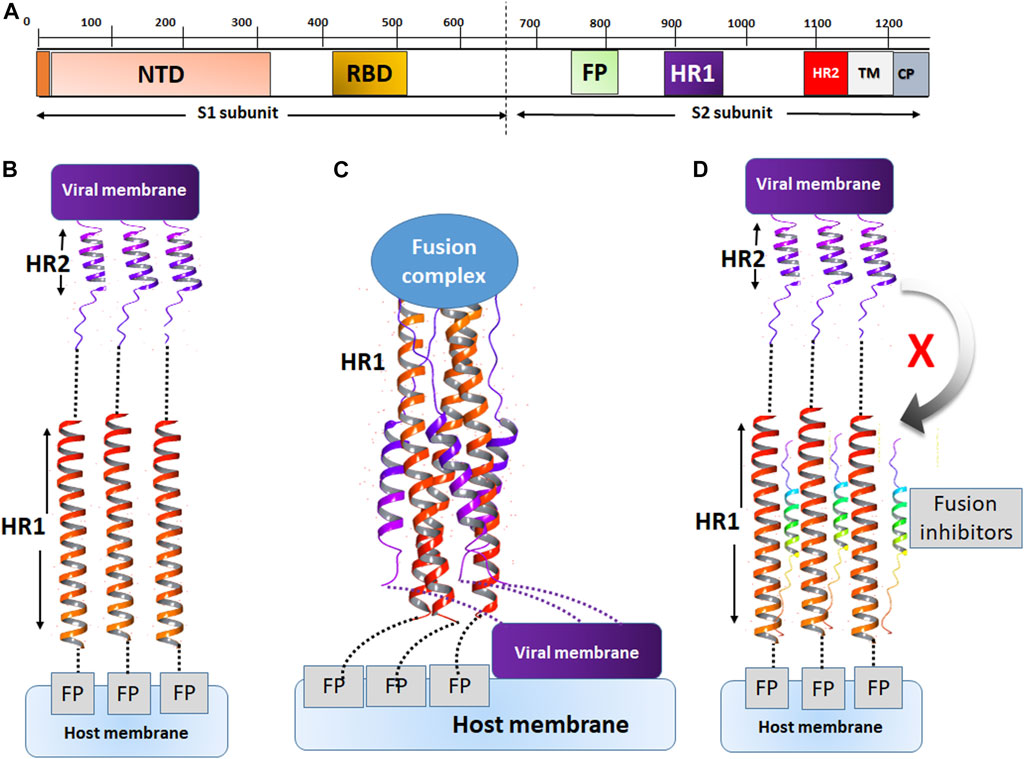
FIGURE 7. The mechanism of action of fusion inhibitors. (A) The composition of MERS-CoV S protein. The S1 subunit contains the nucleotide binding domain (NBD) and the receptor binding domain (RBD). The S2 subunit contains the fusion protein (FP), HR1, HR2, the transmembrane domain (TM) and the cytoplasmic domain (CP). (B) The prefusion conformation. HR2 assists in the fusion between the viral and host cell membranes. (C) The conformation of fusion state. The viral and cell membranes move in close position and membrane fusion occurs. (D) The fusion inhibitor peptides bind to HR2 and prevent the recognition of HR2 onto its binding sites on HR1.
Recent reports indicate that the improved α–helicity of HR2 in SARS-CoV-2 produced stronger fusion complexes with HR1, compared with SARS-CoV (Zhu et al., 2020). In addition, fusion peptides with enhanced α-helical content have been associated with higher antiviral efficacy (Sainz et al., 2006). In this study, all peptides showed similar α-helical content of 91.7% (Table 3). The strong MERS-CoV S-mediated inhibition we observed in the cell-cell fusion assays might be attributed to the combination of the improved energy of binding as well as the improved peptide α–helicity. Interestingly, a CoV HR2 derived peptide (HKU4-HR2P2) from a bat was able to inhibit MERS-CoV-mediated cell-cell fusion at a concentration of 380 nm (Xia et al., 2019). In another study, the EC50 of strong peptide P1 against MERS-CoV infection was 3.013 µM (Gao et al., 2013). Multiple systematic mutations with charged residues in MERS-CoV HR2 lead to the discovery of potent peptides that inhibited cell-cell fusion with IC50 values of 550–930 nm. Based on these data, the present peptides demonstrated notable potency by inhibiting cell-cell fusion at 250 nm concentration.
In conclusion, in the search for new anti-MERS-CoV agents, a structure-based approach was used to develop a MERS-CoV fusion protein inhibitor. A set of peptides were provided with potent inhibition of cell-cell fusion and MERS CoV replication. These peptides may be effective in optimizing specific anti-MERS CoV agents.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author Contributions
MK designed research, performed research, collected data, analyzed data, wrote the paper. MY performed research, collected data, analyzed data. AA-T Analyzed the data. BKP performed research, analyzed data. AW performed research, analyzed data. JG analyzed data. YK analyzed data. H-JK designed research, performed research, collected data, analyzed data, revised the paper. KO-h analyzed data. J-iI designed research, performed research, collected data, analyzed data, revised the paper.
Funding
This project is funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Faisal University under Strategic projects track (Grant No. 171001). H-JK was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation (2016M3A9B6916708) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT in the Republic of Korea. This work was supported in part by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan (16H06575 to JI), from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (18K15235 and 20K07610 to MY), and by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) (Program of Japan Initiative for Global Research Network on Infectious Diseases (JGRID) JP20wm0125002 to MY, JG, and YK).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Faisal University for the financial support under Strategic projects track (Grant No. 171001).
References
Ahmadzadeh, J., Mobaraki, K., Mousavi, S. J., Aghazadeh-Attari, J., Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M., and Mohebbi, I. (2020). The Risk Factors Associated with MERS-CoV Patient Fatality: A Global Survey. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 96 (3), 114876. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.114876
Assiri, A., Al-Tawfiq, J. A., Al-Rabeeah, A. A., Al-Rabiah, F. A., Al-Hajjar, S., Al-Barrak, A., et al. (2013). Epidemiological, Demographic, and Clinical Characteristics of 47 Cases of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Disease from Saudi Arabia: a Descriptive Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 13 (9), 752–761. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(13)70204-4
Bosch, B. J., Van der Zee, R., De Haan, C. A. M., and Rottier, P. J. M. (2003). The Coronavirus Spike Protein Is a Class I Virus Fusion Protein: Structural and Functional Characterization of the Fusion Core Complex. J. Virol. 77 (16), 8801–8811. doi:10.1128/jvi.77.16.8801-8811.2003
Chu, L.-H. M., Chan, S.-H., Tsai, S.-N., Wang, Y., Cheng, C. H.-K., Wong, K.-B., et al. (2008). Fusion Core Structure of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV): In Search of Potent SARS-CoV Entry Inhibitors. J. Cel. Biochem. 104 (6), 2335–2347. doi:10.1002/jcb.21790
De La Guardia, C., and Lleonart, R. (2014). Progress in the Identification of Dengue Virus Entry/fusion Inhibitors. Biomed. Research International 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/825039
Dehouck, Y., Kwasigroch, J. M., Rooman, M., and Gilis, D. (2013). BeAtMuSiC: Prediction of Changes in Protein-Protein Binding Affinity on Mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 41 (Web Server issue), W333–W339. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt450
Ding, X., Zhang, X., Chong, H., Zhu, Y., Wei, H., Wu, X., et al. (2017). Enfuvirtide (T20)-Based Lipopeptide Is a Potent HIV-1 Cell Fusion Inhibitor: Implications for Viral Entry and Inhibition. J. Virol. 91 (18), e00831. doi:10.1128/jvi.00831-17
Falzarano, D., De Wit, E., Rasmussen, A. L., Feldmann, F., Okumura, A., Scott, D. P., et al. (2013). Treatment with Interferon-Α2b and Ribavirin Improves Outcome in MERS-CoV-Infected Rhesus Macaques. Nat. Med. 19 (10), 1313–1317. doi:10.1038/nm.3362
Feng, S., Hong, D., Wang, B., Zheng, X., Miao, K., Wang, L., et al. (2015). Discovery of Imidazopyridine Derivatives as Highly Potent Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 6 (3), 359–362. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00008
Fosgerau, K., and Hoffmann, T. (2015). Peptide Therapeutics: Current Status and Future Directions. Drug Discov. Today 20 (1), 122–128. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2014.10.003
Galasiti Kankanamalage, A. C., Kim, Y., Damalanka, V. C., Rathnayake, A. D., Fehr, A. R., Mehzabeen, N., et al. (2018). Structure-guided Design of Potent and Permeable Inhibitors of MERS Coronavirus 3CL Protease that Utilize a Piperidine Moiety as a Novel Design Element. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 150, 334–346. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.004
Gao, J., Lu, G., Qi, J., Li, Y., Wu, Y., Deng, Y., et al. (2013). Structure of the Fusion Core and Inhibition of Fusion by a Heptad Repeat Peptide Derived from the S Protein of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. J. Virol. 87 (24), 13134–13140. doi:10.1128/jvi.02433-13
Greenberg, M. L. (2007). Enfuvirtide: from Basic Science to FDA Approval. Entry Inhibitors HIV Ther. 1, 161–177. doi:10.1007/978-3-7643-7783-0_11
Greene, S. F., Nikula, K. J., Poulin, D., McInally, K., and Reynolds, J. A. (2020). Long-Term Nonclinical Pulmonary Safety Assessment of Afrezza, a Novel Insulin Inhalation Powder. Toxicol. Pathol. 42, 334. doi:10.1177/0192623320960420
Hakobyan, A., Galindo, I., Nañez, A., Arabyan, E., Karalyan, Z., Chistov, A. A., et al. (2018). Rigid Amphipathic Fusion Inhibitors Demonstrate Antiviral Activity against African Swine Fever Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 99 (1), 148–156. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.000991
Hoffmann, M., Kleine-Weber, H., Schroeder, S., Krüger, N., Herrler, T., Erichsen, S., et al. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 181 (2), 271–280.e8. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hussen, J., Kandeel, M., Hemida, M. G., and Al-Mubarak, A. I. A. (2020). Antibody-Based Immunotherapeutic Strategies for COVID-19. Pathogens 9 (11), 917. doi:10.3390/pathogens9110917
Iwata-Yoshikawa, N., Okamura, T., Shimizu, Y., Hasegawa, H., Takeda, M., and Nagata, N. (2019). TMPRSS2 Contributes to Virus Spread and Immunopathology in the Airways of Murine Models after Coronavirus Infection. J. Virol. 93 (6). doi:10.1128/jvi.01815-18
Jing, S., Zhao, Q., and Debnath, A. (2002). Peptide and Non-peptide HIV Fusion Inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 8 (8), 563–580. doi:10.2174/1381612024607180
Kadam, R. U., Juraszek, J., Brandenburg, B., Buyck, C., Schepens, W. B. G., Kesteleyn, B., et al. (2017). Potent Peptidic Fusion Inhibitors of Influenza Virus. Science 358 (6362), 496–502. doi:10.1126/science.aan0516
Kandeel, M., Yamamoto, M., Tani, H., Kobayashi, A., Gohda, J., Kawaguchi, Y., et al. (2021). Discovery of New Fusion Inhibitor Peptides against SARS-CoV-2 by Targeting the Spike S2 Subunit. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 29, 282. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2020.201
Kandeel, M., Yamamoto, M., Al-Taher, A., Watanabe, A., Oh-Hashi, K., Park, B. K., et al. (2020). Small Molecule Inhibitors of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Fusion by Targeting Cavities on Heptad Repeat Trimers. Biomolecules Ther. 28 (4), 311–319. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2019.202
Koutsoukas, A., Simms, B., Kirchmair, J., Bond, P. J., Whitmore, A. V., Zimmer, S., et al. (2011). From In Silico Target Prediction to Multi-Target Drug Design: Current Databases, Methods and Applications. J. Proteomics 74 (12), 2554–2574. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2011.05.011
Kumar, V., Tan, K.-P., Wang, Y.-M., Lin, S.-W., and Liang, P.-H. (2016). Identification, Synthesis and Evaluation of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV 3C-like Protease Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 24 (13), 3035–3042. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2016.05.013
Li, Q. (2020). Application of Fragment-Based Drug Discovery to Versatile Targets. Front. Mol. Biosciences 7, 180. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2020.00180
Liu, I.-J., Kao, C.-L., Hsieh, S.-C., Wey, M.-T., Kan, L.-S., and Wang, W.-K. (2009). Identification of a Minimal Peptide Derived from Heptad Repeat (HR) 2 of Spike Protein of SARS-CoV and Combination of HR1-Derived Peptides as Fusion Inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 81 (1), 82–87. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.10.001
Liu, S., Xiao, G., Chen, Y., He, Y., Niu, J., Escalante, C. R., et al. (2004). Interaction between Heptad Repeat 1 and 2 Regions in Spike Protein of SARS-Associated Coronavirus: Implications for Virus Fusogenic Mechanism and Identification of Fusion Inhibitors. The Lancet 363 (9413), 938–947. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(04)15788-7
Lomenick, B., Hao, R., Jonai, N., Chin, R. M., Aghajan, M., Warburton, S., et al. (2009). Target Identification Using Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106 (51), 21984–21989. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910040106
Lu, L., Liu, Q., Zhu, Y., Chan, K. H., Qin, L., Li, Y., et al. (2014). Structure-based Discovery of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Fusion Inhibitor. Nat. Commun. 5, 3067. doi:10.1038/ncomms4067
Morishita, M., Kamei, N., Ehara, J., Isowa, K., and Takayama, K. (2007). A Novel Approach Using Functional Peptides for Efficient Intestinal Absorption of Insulin. J. Controlled Release 118 (2), 177–184. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.12.022
Nassar, M. S., Bakhrebah, M. A., Meo, S. A., Alsuabeyl, M. S., and Zaher, W. A. (2018). Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Infection: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and Clinical Characteristics. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 22 (15), 4956–4961. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201808_15635
Sainz, B., Mossel, E. C., Gallaher, W. R., Wimley, W. C., Peters, C. J., Wilson, R. B., et al. (2006). Inhibition of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Associated Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Infectivity by Peptides Analogous to the Viral Spike Protein. Virus. Res. 120 (1-2), 146–155. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2006.03.001
Seyedpour, S., Khodaei, B., Loghman, A. H., Seyedpour, N., Kisomi, M. F., Balibegloo, M., et al. (2020). Targeted Therapy Strategies against SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Mechanisms: A Systematic Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. J. Cel Physiol 236, 2364. doi:10.1002/jcp.30032
Shabane, P. S., Izadi, S., and Onufriev, A. V. (2019). General Purpose Water Model Can Improve Atomistic Simulations of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Theor. Comput. 15 (4), 2620–2634. doi:10.1021/acs.jctc.8b01123
Sheahan, T. P., Sims, A. C., Leist, S. R., Schäfer, A., Won, J., Brown, A. J., et al. (2020). Comparative Therapeutic Efficacy of Remdesivir and Combination Lopinavir, Ritonavir, and Interferon Beta against MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 1–14. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-13940-6
Song, W., Gui, M., Wang, X., and Xiang, Y. (2018). Cryo-EM Structure of the SARS Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein in Complex with its Host Cell Receptor ACE2. PLoS Pathog. 14 (8), e1007236. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1007236
Stalmans, S., Bracke, N., Wynendaele, E., Gevaert, B., Peremans, K., Burvenich, C., et al. (2015). Cell-Penetrating Peptides Selectively Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier In Vivo. PloS one 10 (10), e0139652. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0139652
Sungnak, W., Huang, N., Huang, N., Bécavin, C., Berg, M., Queen, R., et al. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 Entry Factors Are Highly Expressed in Nasal Epithelial Cells Together with Innate Immune Genes. Nat. Med. 26 (5), 681–687. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6
Wang, H., Li, X., Nakane, S., Liu, S., Ishikawa, H., Iwamoto, A., et al. (2014). Co-expression of Foreign Proteins Tethered to HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein on the Cell Surface by Introducing an Intervening Second Membrane-Spanning Domain. PloS one 9 (5), e96790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096790
Waxman, A., Restrepo-Jaramillo, R., Thenappan, T., Ravichandran, A., Engel, P., Bajwa, A., et al. (2021). Inhaled Treprostinil in Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 325. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2008470
Welsch, J. C., Talekar, A., Mathieu, C., Pessi, A., Moscona, A., Horvat, B., et al. (2013). Fatal Measles Virus Infection Prevented by Brain-Penetrant Fusion Inhibitors. J. Virol. 87 (24), 13785–13794. doi:10.1128/jvi.02436-13
Widjaja, I., Wang, C., van Haperen, R., Gutiérrez-Álvarez, J., van Dieren, B., Okba, N. M. A., et al. (2019). Towards a Solution to MERS: Protective Human Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Different Domains and Functions of the MERS-Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein. Emerging Microbes & Infections 8 (1), 516–530. doi:10.1080/22221751.2019.1597644
Xia, S., Yan, L., Xu, W., Agrawal, A. S., Algaissi, A., Tseng, C. K., et al. (2019). A Pan-Coronavirus Fusion Inhibitor Targeting the HR1 Domain of Human Coronavirus Spike. Sci. Adv. 5 (4), eaav4580. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aav4580
Xia, S., Lan, Q., Pu, J., Wang, C., Liu, Z., Xu, W., et al. (2019). Potent MERS-CoV Fusion Inhibitory Peptides Identified from HR2 Domain in Spike Protein of Bat Coronavirus HKU4. Viruses 11 (1), 56. doi:10.3390/v11010056
Xia, S., Liu, Q., Wang, Q., Sun, Z., Su, S., Du, L., et al. (2014). Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Entry Inhibitors Targeting Spike Protein. Virus. Res. 194, 200–210. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2014.10.007
Yamamoto, M., Matsuyama, S., Li, X., Takeda, M., Kawaguchi, Y., Inoue, J.-i., et al. (2016). Identification of Nafamostat as a Potent Inhibitor of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus S Protein-Mediated Membrane Fusion Using the Split-Protein-Based Cell-Cell Fusion Assay. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60 (11), 6532–6539. doi:10.1128/aac.01043-16
Zhu, Y., Yu, D., Yan, H., Chong, H., and He, Y. (2020). Design of Potent Membrane Fusion Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2, an Emerging Coronavirus with High Fusogenic Activity. J. Virol. 94 (14). doi:10.1128/jvi.00635-20
Ziegler, C. G. K., Allon, S. J., Nyquist, S. K., Mbano, I. M., Miao, V. N., Tzouanas, C. N., et al. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues. Cell 181 (5), 1016–1035.e19. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.035
Keywords: coronavirus, MERS-CoV, fusion inhibitors, antivirals, drug discovery
Citation: Kandeel M, Yamamoto M, Park BK, Al-Taher A, Watanabe A, Gohda J, Kawaguchi Y, Oh-hashi K, Kwon H-J and Inoue J-i (2021) Discovery of New Potent anti-MERS CoV Fusion Inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 12:685161. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.685161
Received: 24 March 2021; Accepted: 06 May 2021;
Published: 02 June 2021.
Edited by:
Abdur Rauf, University of Swabi, PakistanReviewed by:
Oscar Herrera-Calderon, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, PeruNaveed Muhammad, Abdul Wali Khan University Mardan, Pakistan
Copyright © 2021 Kandeel, Yamamoto, Park, Al-Taher, Watanabe, Gohda, Kawaguchi, Oh-hashi, Kwon and Inoue. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mahmoud Kandeel, bWthbmRlZWxAa2Z1LmVkdS5zYQ==; Hyung-Joo Kwon, aGpvb2t3b25AaGFsbHltLmFjLmty; Jun-ichiro Inoue, anVuLWlAaW1zLnUtdG9reW8uYWMuanA=
 Mahmoud Kandeel
Mahmoud Kandeel Mizuki Yamamoto3,4
Mizuki Yamamoto3,4 Byoung Kwon Park
Byoung Kwon Park Jin Gohda
Jin Gohda Hyung-Joo Kwon
Hyung-Joo Kwon