Abstract
Shewanella putrefaciens is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause seafood spoilage under low-temperature conditions. The bacterium easily forms biofilms to enhance its survival in challenging environments. Our previous research revealed that the biofilm formed by S. putrefaciens WS13 under the low temperature (4 °C) has larger biomass and tighter structure than at an optimum growth temperature (30 °C). In this study, comparative transcriptome analysis was further performed to get insights into the global-level of gene expression in the biofilm formed by S. putrefaciens WS13 under the refrigerating and optimal temperatures using Illumina RNA-Sequencing technique. The results revealed that a total of 761 genes were differentially expressed, of which 497 were significantly up-regulated and 264 were significantly down-regulated (p<0.05). The qRT-PCR results of randomly selected differentially expressed genes (DEGs) confirmed the RNA sequencing results. Comparison of transcriptome data revealed 28 significantly changed metabolic pathways under the cold stress, including the down-regulated chemotaxis, and motility, and up-regulated tryptophan metabolism, histidine biosynthesis, and quorum sensing, which benefited the biofilm formation of S. putrefaciens WS13 under the adverse circumstance. This study provided useful data for better understanding of the biofilm formation of S. putrefaciens, and also laid a theoretical foundation for novel vaccine and drug targets against the severe spoilage bacterium under the cold stress.
Introduction
Shewanella putrefaciens is a severe spoilage bacterium in seafood, particularly under low temperature conditions. The bacterium inhabits ubiquitously in the environment because of its excellent environmental adaptability (Xie et al., 2018; Zhen-Quan et al., 2018). The amount of S. putrefaciens cells has often been used as an index to evaluate the quality of seafood (Gram et al., 2002). S. putrefaciens can reduce trimethylamine oxide, the umami taste substance in seafood, to trimethylamine, and generate histamine and other harmful volatile substances (Vogel et al., 2005), which poses a serious threat to the seafood processing industry (Xie et al., 2011; Hou et al., 2013).
S. putrefaciens is easy to adhere to the surface of food processing equipment such as stainless steel to form a biofilm that is composed of polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids (Bagge et al., 2001; Flemming and Wingender, 2010). Biofilm can enhance the stress tolerance of bacterial cells (Bagge et al., 2001; Flemming et al., 2016; Yan and Xie, 2021). Recently, our prior study revealed that the biofilm formed by S. putrefaciens under 4 °C had 1.61-fold larger biomass and tighter structure than that at 30°C (Yan and Xie, 2020). Therefore, it was speculated that the formation of biofilm could enhance the survival ability of S. putrefaciens under the cold stress. However, few information on transcriptome profiles and regulatory factors of S. putrefaciens biofilm cells under the cold stress is available so far.
With increased breakthrough of sequeneing technology, RNA-Sequencing (RNA-Seq) technique has been use to study bacterial differential express genes (DEGs), transcript structures, new transcripts and isomers, and alternative splicing and allele-specific expression under adverse circumstances, such as Clostridium acetobutylicum in a high-salt environment (Ao et al., 2020), and Escherichia coli under different heating methods. In recent years, gene expression between biofilm cells and planktonic cells under stress conditions (Charlebois et al., 2016; Ao et al., 2020), has been investigated at the transcriptomic level in Clostridium acetobutylicum (Dong et al., 2015), Porphyromonas gingivalis (Lo et al., 2009), and Gardnerella vaginalis (Castro et al., 2017). However, current literature on the molecular mechanism of biofilm formation of spoilage bacteria under the cold stress is still rare. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to determine DEGs during the formation of S. putrefaciens WS13 biofilm under the cold stress by transcriptomics analysis. The results in this study will provide crucial clues for the targeted inhibition of the biofilm of S. putrefaciens under the low temperature.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
S. putrefaciens WS13 strain was isolated from spoilage shrimp Litopenaeus vanname in refrigerator (Chen et al., 2019). The isolate was maintained in Luria Broth (LB, Land Bridge Technology, Beijing, China) with 50% (v/v) glycerol at -80 °C freezer in our laboratory at Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China. S. putrefaciens WS 13 was inoculated in 9 mL LB medium (pH 7.4) and incubated at 30°C with shaking at 200 rpm for 12 h, and repeated twice for further analysis.
Biofilm Assay
Biofilm assay was performed according to the method described by Yan and Xie (2020). S. putrefaciens WS13 were incubated overnight to approximately 8 log colony forming units (CFU) mL-1 (OD600nm≈0.8), and diluted with fresh LB medium (1:100, v/v). A 1 mL of diluted culture was added to each well of sterile 24-well polystyrene microtiter plates. Each sample was tested in six replicates. The samples were incubated at 4°C, and 30°C statically to form biofilms for 24h, and 84 h, respectively. Plastic wraps were used to minimize evaporative loss (Yan and Xie, 2020).
RNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and RNA Sequencing
Mature biofilm cells of S. putrefaciens WS13 at 4°C and 30°C were harvested at 24h, and 84h, respectively. RNA extraction, cDNA library preparation, and RNA sequencing were carried out as described previously (Ao et al., 2020).
Quality Control and Mapping
Raw paired end reads were trimmed using Fastp v 0.20.0 software (https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp), and low-quality reads and removing reads with size inferior to 50 bp. The clean reads were separately aligned to the reference genome of S. putrefaciens WS 13 (GenBank: CP028435.1) with orientation mode using HISAT2 v 2.1.0 software (http://daehwankimlab.github.io/hisat2/). Next, the mapped reads of each sample were assembled using StringTie v 1.3.6 software in a reference-based approach. All sequences were quantified as Fragments Per Kilobase Million Mapped Reads (FPKM) by StringTie. The formula was defined as FPKM = 106×F/(NL×10-3), where F is the number of fragments assigned to a certain gene in a certain sample, N is the total number of mapped reads in the certain sample, and L is the length of the certain gene.
Differential Expression Gene Analysis
DEGs were determined by DEseq2, and genes with FDR <0.05 and |log2 fold change| >1 were identified as DEGs. DEGs were aligned against Gene Ontology (GO, http://geneontology.org/) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) (https://www.genome.jp/kegg/) databases. The R package cluster Profiler (http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/clusterProfiler.html) was used to identify enriched GO terms and KEGG pathways with a cut-off of P-value < 0.05. DGEs in biofilm formation of S. putrefaciens WS 13 were further analyzed using hierarchical clustering. FDR<0.05 is the standard for screening genes with significant differential expression. The gene expression level of S. putrefaciens mature biofilm cells at 4°C was used as a reference, whether a gene was up-regulated or down-regulated was determined by comparing its expression level with that at 4°C.
Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay
To validate the transcriptome data, ten DEGs were selected randomly for qRT-PCR assay, and 16S rRNA gene was used as the internal reference (Table 1). qRT-PCR was using an ABI Stepone Plus Platform (Thermo, USA). Each gene was analyzed in three biological samples, and three reaction repeats were performed for each biological sample as described previously.
Table 1
| Gene ID | Gene name | Forward | Reverse | Fragment size (bp) | TM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVV84311.1 | rpsD | CTAACACACCGTAAATACGACGAA | TAAACTGGAAACTGCACCTGGA | 110 | 60 |
| AVV84994.1 | GAGTGGTAATAAGGTTGGCGTC | GGTGTATCTGGGCAAGTAGGGT | 250 | 60 | |
| AVV84995.1 | GTAACTCACCCATACCGGAAATAA | CCCAAGTCTAAAGCAGACCAAG | 130 | 60 | |
| AVV82000.1 | sucA | TGAAGCGGTTGCTTTTGTGT | ATAGATCTTACGTGGTGTAGGGTGT | 181 | 60 |
| AVV84336.1 | fusA | GGAAAAACGCCGTAAAGAAAA | GTTGAAAATCAGCCAAAGCAA | 107 | 60 |
| AVV85624.1 | gabD | TAGATGATGTACAGACCTGTCCCG | ACTTTCCCTACTACCAAATTGCG | 405 | 60 |
| AVV86072.1 | TTCTGTTATACCCGCTTTGCTTT | CTGTTTAGTCTGTCACGGTTCTGT | 298 | 60 | |
| AVV84898.1 | speC | AGAAGCCTGCTTGTTGTTTGTGT | GGTTGATCGTATTGGTCATCTATGT | 173 | 60 |
| AVV82314.1 | uspE | AGCATTATTAACCACGCCATC | AATTCAGCATCTAACTGAGCAGC | 497 | 60 |
| AVV84205.1 | katG | TCGAGCGTTTTAAATGCTTCG | CATGGTGGTAATACCTCCGTCAC | 143 | 60 |
| 16S | CGGTGAATACGTTCYCGG | GGWTACCTTGTTACGACTT | 128 | 60 |
Genes and primers used in the qRT-PCR assay.
Statistical Analyses
All the experiments were conducted in six independent biological replicates. Related data to biofilm formation were tested using Duncan’s multiple range test in SPSS 22.0 software (IBM, New York, USA). All data were reported as mean ± standard deviation. Differences with a p value < 0.05 were regarded as statistically significant.
Results and Discussion
Determination of Transcriptomes of Biofilm Cells Formed by S. putrefaciens WS13
Based on our prior research (Yan and Xie, 2020), the biofilm of S. putrefaciens WS13 grown in LB medium (pH=7.2) reached maturity at 24 h and 84 h at 4°C and 30°C, respectively (Figures not shown). The cells of mature biofilm at both temperatures were collected, and transcriptomes at a global gene expression level were obtained using Illumina RNA sequencing technique for the further analysis.
Identification of DEGs in S. putrefaciens WS13 Induced by the Cold Stress
DEGs of the biofilm cells formed by S. putrefaciens WS13 at 4°C and 30°C were identified, and the results are shown in Figure 1. A total of 761 DEGs were discovered, among which the expression of 497 DEGs was significantly up-regulated, and 264 DEGs were significantly down-regulated (p <0.05).
Figure 1
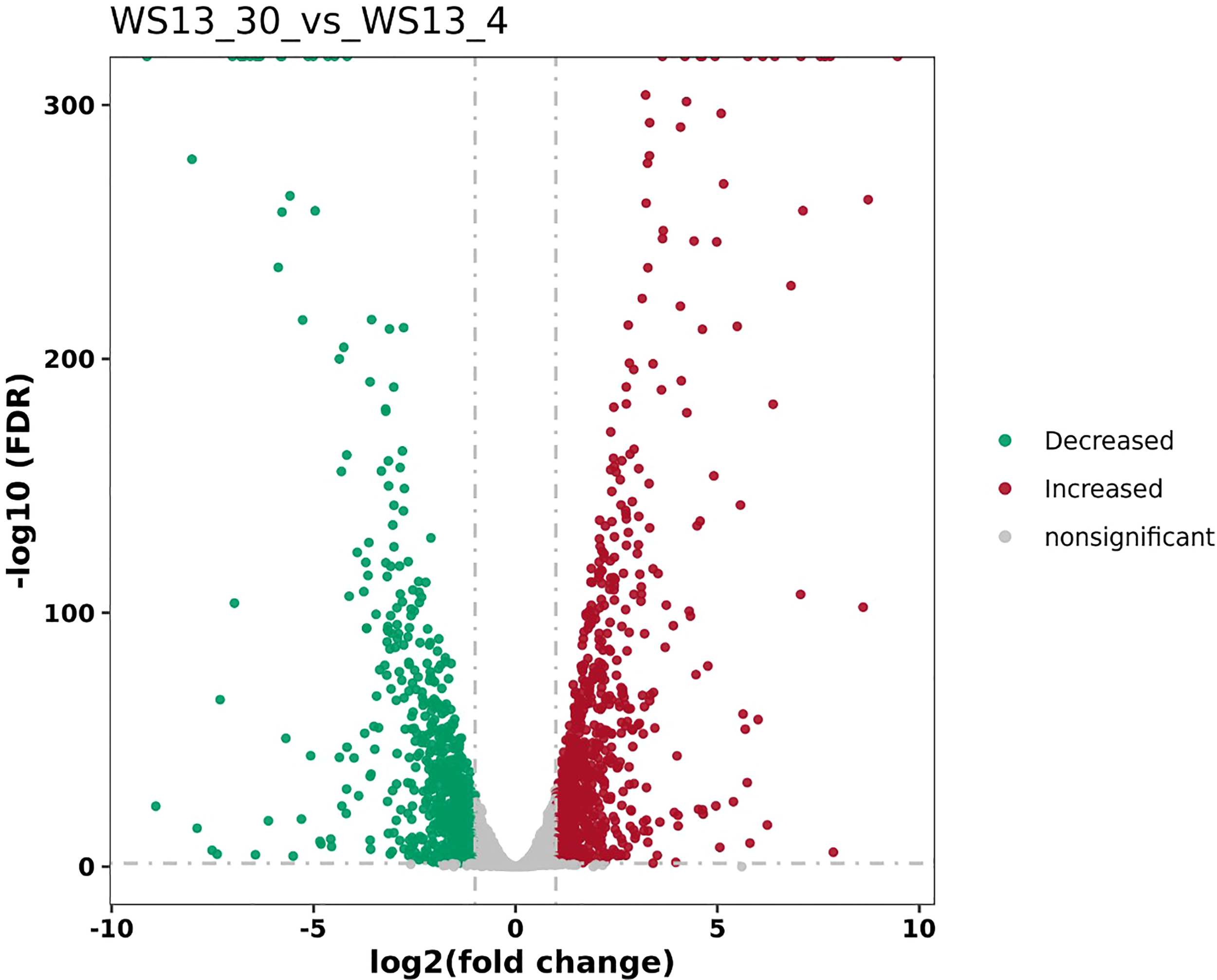
The volcano plots of DEGs between biofilms formed by S. putrefaciens WS13 under 4°C and 30°C.
All DEGs were classified into three major functional categories in the Gene Ontology (GO) database, including biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF). The GO enrichment analysis of the DEGs revealed that the most abundant GO function was the peptide metabolic process (11.51%, 64/556), followed by protein-containing complex subunit organization (10.61%, 59/556), translation (10.25%, 57/556), peptide biosynthetic process (10.25%, 57/556), and ion transport (9.89%, 55/556) in BP, whereas cellular respiration (5.04%, 28/556), ATP hydrolysis coupled transmembrane transport (2.52%, 14/556), and ATP hydrolysis coupled ion transmembrane transport (2.52%, 14/556) showed an opposite pattern (Figure 2). The protein-containing complex (23.20%, 129/556) was the most enriched DEGs in CC, while the percentages of the DEGs in the structural constituent of ribosome (6.83%, 38/556), and structural molecule activity (6.83%, 38/556) was the highest, followed by the rRNA binding (3.60%, 20/556) in MF (Figure 2).
Figure 2
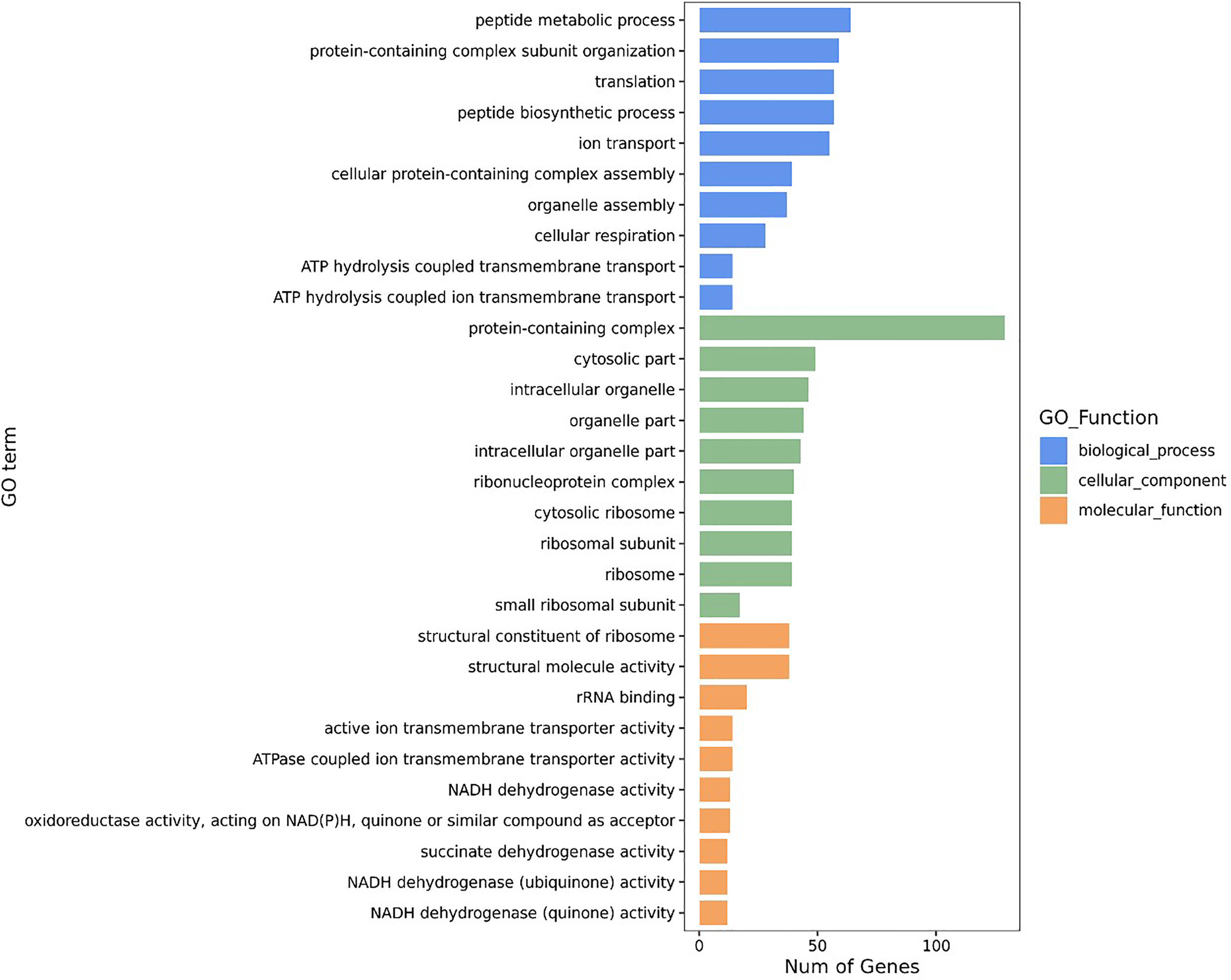
GO enrichment analyses of DEGs.
The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was further performed on the identified DEGs in the obtained transcriptomes of S. putrefaciens biofilm cells, and the results revealed 28 significantly changed metabolic pathways, including ribosome, oxidative phosphorylation, citrate cycle, transporters, photosynthesis proteins, histidine metabolism, photosynthesis, tryptophan metabolism, pyruvate metabolism, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, carbon fixation pathways in prokaryotes, lysine degradation, MAPK signaling pathway-plants, propanoate metabolism, butanoate metabolism, mitochondrial biogenesis, inositol phosphate metabolism, β-alanine metabolism, longevity regulating pathway-worm, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, pathways of neurodegeneration-multiple diseases, translation factor, and others, antimicrobial resistance genes, membrane trafficking, phenylalanine metabolism, and longevity regulating pathway-multiple species (Figure 3).
Figure 3
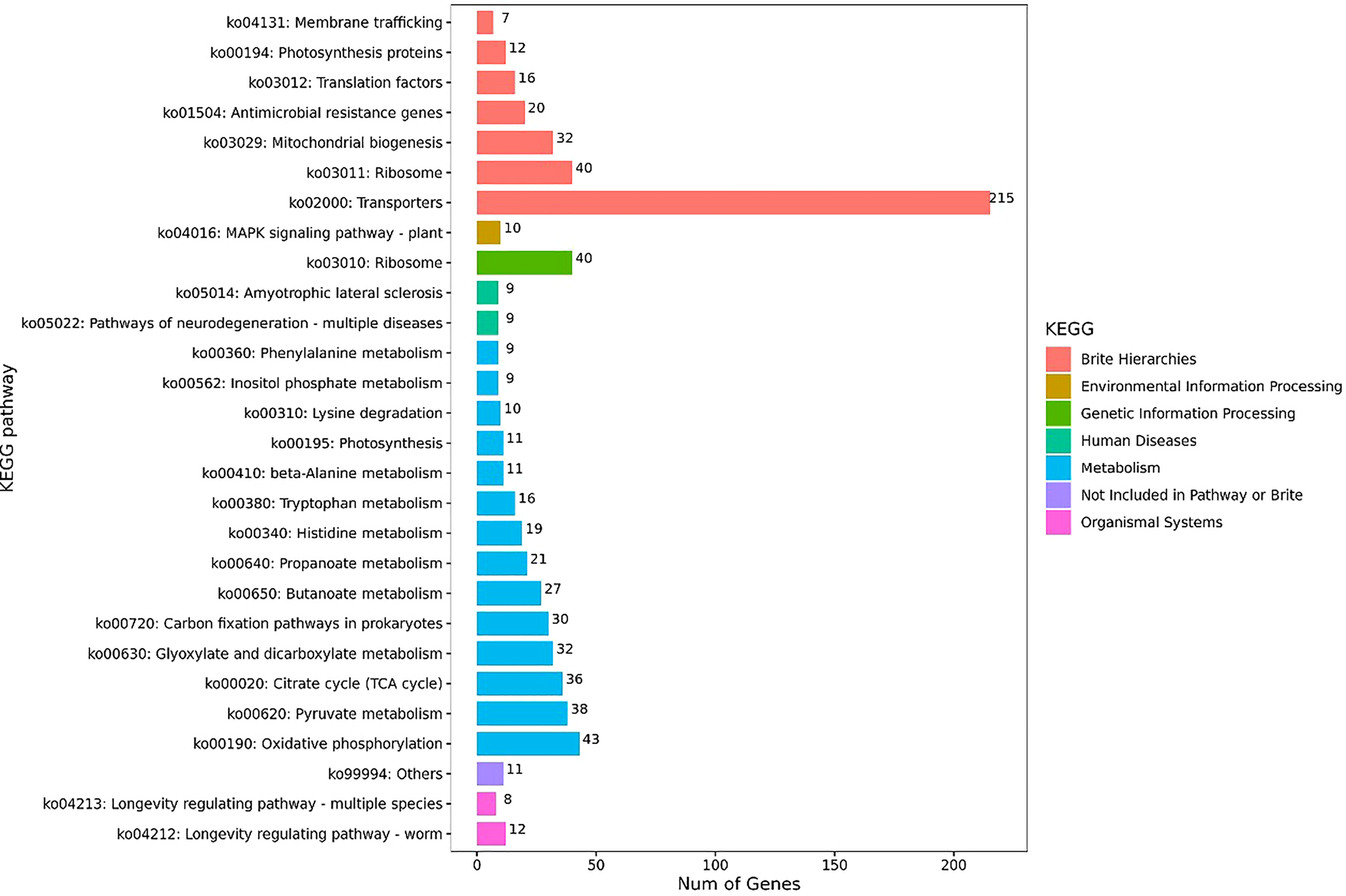
KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs.
Identified DEGs Involved in Biofilm Formation of S. putrefaciens WS13 at the Cold Stress
Four significantly altered metabolic pathways associated with biofilm formation were found in S. putrefaciens WS13 at 4°C, including the biofilm formation, amino acid metabolism, two-component system (TCS), and quorum sensing (QS Table 2).
Table 2
| Matabolic pathway | Gene ID | Name | Log2FC | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biofilm formation - Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ||||
| AVV85673.1 | -2.77 | Hypothetical protein SPWS13_3995 | ||
| AVV82533.1 | -3.75 | Crp/Fnr family transcriptional regulator | ||
| AVV82532.1 | -5.68 | Crp/Fnr family transcriptional regulator | ||
| AVV85155.1 | nrfG | -2.66 | Nitrite reductase | |
| AVV83548.1 | -1.96 | GntR family transcriptional regulator | ||
| AVV85962.1 | flgM | -1.01 | Anti-sigma-28 factor FlgM | |
| AVV85989.1 | flrA | -1.01 | Fis family transcriptional regulator | |
| AVV85720.1 | -1.10 | Membrane protein | ||
| AVV85731.1 | -1.87 | Serine/threonine protein phosphatase | ||
| Tryptophan metabolism | ||||
| AVV82001.1 | sucB | 2.79 | Dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase | |
| AVV85789.1 | amiE | 1.60 | Amidase | |
| AVV82915.1 | katE | 2.84 | Catalase | |
| AVV84271.1 | 5.68 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | ||
| AVV82993.1 | 1.69 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase | ||
| AVV85788.1 | amiE | 2.36 | Amidase | |
| AVV85097.1 | pdhD | 1.53 | Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase | |
| AVV86128.1 | fadJ | 2.12 | Multifunctional fatty acid oxidation complex subunit alpha | |
| AVV82394.1 | bkdB | 1.15 | Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase | |
| AVV82994.1 | 1.17 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase | ||
| Histidine metabolism | ||||
| AVV82365.1 | -3.60 | TonB-dependent receptor | ||
| AVV82366.1 | -2.85 | TonB-dependent receptor | ||
| AVV82367.1 | -1.83 | TonB-dependent receptor | ||
| AVV84622.1 | hutI | -2.21 | Imidazolonepropionase | |
| AVV84105.1 | -1.24 | Arginase | ||
| AVV84398.1 | urdA | -1.38 | Cytochrome C | |
| AVV82368.1 | -1.34 | TonB-dependent receptor | ||
| AVV84082.1 | -1.21 | Hypothetical protein SPWS13_2316 | ||
| AVV86163.1 | hutH | -1.08 | Histidine ammonia-lyase | |
| AVV82091.1 | hisC | 2.88 | Histidinol-phosphate aminotransferase | |
| AVV84271.1 | 5.68 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | ||
| AVV82088.1 | 2.89 | Hypothetical protein SPWS13_0228 | ||
| AVV82089.1 | hisH | 2.58 | Imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase | |
| AVV82090.1 | hisB | 2.52 | Imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase | |
| AVV82092.1 | hisD | 1.84 | Histidinol dehydrogenase | |
| AVV82087.1 | hisF | 2.35 | Imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase | |
| AVV82086.1 | hisI | 1.94 | Phosphoribosyl-AMP cyclohydrolase | |
| AVV84178.1 | hutH | 1.00 | Histidine ammonia-lyase | |
| AVV82085.1 | hisI | 1.83 | Phosphoribosyl-ATP pyrophosphatase | |
| Lysine degradation | ||||
| AVV82001.1 | sucB | 2.79 | Dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase | |
| AVV84271.1 | 5.68 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | ||
| AVV82993.1 | 1.69 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase | ||
| AVV85097.1 | pdhD | 1.53 | Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase | |
| AVV86128.1 | fadJ | 2.12 | Multifunctional fatty acid oxidation complex subunit alpha | |
| AVV82394.1 | bkdB | 1.15 | Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase | |
| AVV82994.1 | 1.17 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase | ||
| Two-component system | ||||
| AVV84741.1 | nrfC | -6.34 | 4Fe-4S ferredoxin 4Fe-4S ferredoxin | |
| AVV85250.1 | petA | -9.12 | Ubiquinol-cytochrome C reductase | |
| AVV83964.1 | -3.21 | Chemotaxis protein | ||
| AVV82196.1 | hydA | -3.63 | Quinone-reactive Ni/Fe-hydrogenase small chain | |
| AVV82533.1 | -3.75 | Crp/Fnr family transcriptional regulator | ||
| AVV84073.1 | -2.62 | Histidine kinase | ||
| AVV83344.1 | glnA | -2.11 | Glutamine synthetase | |
| AVV82195.1 | hydB | -3.36 | Hydrogenase 2 large subunit | |
| AVV85596.1 | -2.04 | Chemotaxis protein | ||
| AVV83291.1 | -1.60 | Sensor histidine kinase | ||
| AVV83573.1 | frdA | -1.82 | Fumarate reductase | |
| AVV86289.1 | cheV | -1.50 | Chemotaxis protein CheW | |
| AVV85217.1 | CheC | -1.57 | Chemotaxis protein CheC | |
| AVV83574.1 | frdA | -1.66 | Fumarate reductase | |
| AVV82532.1 | -5.68 | Crp/Fnr family transcriptional regulator | ||
| AVV85476.1 | norR | -1.52 | Transcriptional regulator | |
| AVV84252.1 | glnL | -1.94 | Nitrogen regulation protein NR(II) | |
| AVV85586.1 | -1.79 | Amino acid ABC transporter substrate-binding protein | ||
| AVV82193.1 | hyaC | -2.37 | Hydrogenase Ni/Fe-hydrogenase, b-type cytochrome subunit | |
| AVV82194.1 | hydB | -2.43 | Hydrogenase 2 large subunit | |
| AVV84209.1 | glnA | -1.56 | Glutamine synthetase | |
| AVV83483.1 | -1.28 | Chemotaxis protein | ||
| AVV84098.1 | -1.32 | Chemotaxis protein | ||
| AVV83827.1 | -1.14 | Peptidase | ||
| AVV84924.1 | -1.35 | Cell division protein ZapB | ||
| AVV83129.1 | motA | -1.45 | Flagellar motor protein PomA | |
| AVV85069.1 | frdC | -1.56 | Fumarate reductase | |
| AVV82265.1 | ampC | -1.20 | Beta-lactamase | |
| AVV85068.1 | frdC | -1.15 | Fumarate reductase | |
| AVV82166.1 | -1.00 | Chemotaxis protein | ||
| AVV84289.1 | -1.85 | Histidine kinase | ||
| AVV84253.1 | glnL | -1.47 | Nitrogen regulation protein NR(II) | |
| AVV84398.1 | urdA | -1.38 | Cytochrome C | |
| AVV83971.1 | psrB | -1.96 | Polysulfide reductase subunit B | |
| AVV85962.1 | flgM | -1.01 | Anti-sigma-28 factor FlgM | |
| AVV84053.1 | maeB | -1.05 | Malate dehydrogenase | |
| AVV84712.1 | cusB | -2.01 | RND transporter MFP subunit | |
| AVV84254.1 | glnL | -1.32 | Nitrogen regulation protein NR(II) | |
| AVV84075.1 | -1.54 | Response regulator receiver protein | ||
| AVV83905.1 | -1.15 | Chemotaxis protein | ||
| AVV85989.1 | flrA | -1.01 | Fis family transcriptional regulator | |
| AVV85931.1 | -1.09 | Membrane protein cyd operon protein YbgT | ||
| AVV83697.1 | glnK | -1.66 | Nitrogen regulatory protein P-II 1 | |
| AVV85720.1 | -1.10 | Membrane protein | ||
| AVV85990.1 | flrB | -1.38 | Sensor histidine kinase | |
| AVV83549.1 | cydA | -2.29 | Cytochrome D ubiquinol oxidase subunit I | |
| AVV85070.1 | frdA | -1.23 | Fumarate reductase | |
| AVV84287.1 | frdC | -4.57 | Fumarate reductase | |
| AVV83377.1 | glnB | -1.11 | Nitrogen regulatory protein P-II | |
| AVV84286.1 | frdB | -4.81 | Fumarate reductase iron-sulfur subunit | |
| AVV83550.1 | cydB | -1.80 | Ubiquinol oxidase subunit II, cyanide insensitive | |
| AVV83918.1 | ttrB | -1.97 | Tetrathionate reductase subunit B | |
| AVV84284.1 | frdA | -4.55 | Fumarate reductase flavoprotein subunit | |
| AVV86161.1 | -2.76 | Cytochrome C flavocytochrome c | ||
| AVV85991.1 | flrC | -1.11 | Fis family transcriptional regulator | |
| AVV84288.1 | frdD | -3.58 | Fumarate reductase | |
| AVV84265.1 | cpxA | -1.06 | Sensor histidine kinase | |
| AVV83919.1 | ttrC | -1.95 | Polysulfide reductase | |
| AVV84285.1 | frdA | -1.65 | Fumarate reductase flavoprotein subunit | |
| Quorum sensing | ||||
| AVV84313.1 | secY | 2.27 | Preprotein translocase subunit SecY | |
| AVV86104.1 | secF | 2.06 | Preprotein translocase subunit SecF | |
| AVV84314.1 | secY | 2.13 | Preprotein translocase, SecY subunit | |
| AVV84540.1 | yidC | 1.61 | Membrane protein insertase | |
| AVV85368.1 | 2.07 | RND transporter | ||
| AVV84996.1 | 1.41 | Outer membrane adhesin-like protein | ||
| AVV83999.1 | 1.41 | Hypothetical protein SPWS13_2218 | ||
| AVV86108.1 | 4.64 | Peptidase S8 | ||
| AVV82086.1 | hisI | 1.94 | Phosphoribosyl-AMP cyclohydrolase | |
| AVV82884.1 | dppB | 1.22 | Peptide ABC transporter permease | |
| AVV82009.1 | 1.72 | Hypothetical protein SPWS13_0149 | ||
| AVV86102.1 | yajC | 1.14 | Preprotein translocase subunit YajC | |
| AVV86191.1 | trpG | 1.13 | Anthranilate synthase subunit II | |
| AVV82085.1 | hisI | 1.83 | Phosphoribosyl-ATP pyrophosphatase | |
| AVV84384.1 | 1.11 | Cytochrome B561 | ||
| AVV82919.1 | gadB | 1.76 | Glutamate decarboxylase | |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | ||||
| AVV83139.1 | ykgG | -3.15 | L-lactate dehydrogenase complex protein LldG | |
| AVV83137.1 | Nan | -3.32 | L-lactate dehydrogenase complex protein LldE | |
| AVV83138.1 | Nan | -3.01 | L-lactate dehydrogenase complex protein LldF | |
| AVV85349.1 | Nan | -1.53 | Acetoin utilization protein AcuB | |
| AVV85417.1 | sfsA | -1.26 | Sugar fermentation stimulation protein A | |
| Energy metabolism | ||||
| AVV84740.1 | nrfB | -6.79 | Cytochrome c nitrite reductase small subunit | |
| AVV84741.1 | nrfC | -6.35 | Polysulfide reductase chain B | |
| AVV84742.1 | nrfD | -5.78 | Protein NrfD | |
| AVV85151.1 | ccmF | -3.50 | Cytochrome c-type biogenesis protein NrfE | |
| AVV85149.1 | ccmH | -3.58 | Formate-dependent nitrite reductase complex subunit NrfG | |
| AVV85155.1 | nrfG | -2.67 | Formate-dependent nitrite reductase complex subunit NrfG | |
| AVV83971.1 | psrB | -1.96 | Polysulfide reductase chain B | |
| AVV82007.1 | Nan | -1.06 | Ferredoxin/flavodoxin—NADP+ reductase | |
| AVV83970.1 | psrC | -1.72 | Polysulfide reductase chain C | |
| AVV85150.1 | ccmF | -3.15 | Cytochrome c-type biogenesis protein NrfE | |
The major DEGs in biofilm cells of S. putrefaciens WS13 induced by the cold stress.
Some genes encoding transcripitional regulators were slightly down-regulated (p<0.05), such as flgM, and flrA genes. The former that encodes an anti-sigma-28 factor FlgM can regulate the expression of flagellar genes in a complex regulatory network controlling chemotaxis, swimming and biofilm formation in Rhodobacter sphaeroides (Wilkinson et al., 2011). It has been reported that the flrA gene that encodes Fis family transcriptional regulator was strongly sensitive to environmental stress (Gang et al., 2016). The silencing of the flrA gene led to deficiencies in adhesion, motility, flagellar assembly, biofilm formation and exopolysaccharide (EPS) production in Vibrio alginolyticus (Gang et al., 2016). These results suggested that the reduction of flagellar synthesis and motility may have enhanced the biofilm formation of S. putrefaciens WS13 at 4°C.
Identified DEGs Involved in Amino Acid Metabolism in S. putrefaciens Biofilm at the Cold Stress
The biofilm is composed of extracellular substances secreted by S. putrefaciens WS13, such as polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and other substances. Proteins play a crucial role in maintaining the structural stability of biofilms (Yan and Xie, 2020). Amino acids are key intermediates in both carbon and nitrogen metabolisms in microorganisms. Bacterial amino acid metabolism is usually sensitive to environmental stress. In this study, comparative transtriptomics analyses revealed remarkedly changed DEGs in the amino acid metabolism in biofilm cells of S. putrefaciens WS13 under the cold stress. These DEGs were significantly enriched in the amide biosynthetic process, peptide metabolic process, translation, peptide biosynthetic process, and other protein-related GO functions. For example, interestingly, all the DEGs involved in the tryptophan metabolism were significantly up-regulated in the S. putrefaciens WS13 biofilm at 30°C, including the sucB, amiE, katE, pdhD, fadJ, and bkdB genes (2.23 fold to 7.15 fold) (p<0.05). It has been reported that the tryptophan biosynthesis genes were up-regulated in the biofilms of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica (Domka et al., 2007; Hamilton et al., 2009). It was shown that exogenous tryptophan significantly accelerated the biofilm formation of S. enterica and Fusobacterium nucleatum and completely restored the deleted mutant of S. enterica in biofilm formation (Hamilton et al., 2009; Sasaki-Imamura et al., 2010). In the amino acid metabolism, some DEGs involved in histidine metabolism were significantly up-regulated in S. putrefaciens WS13 at 4°C (2.23 fold to 61.60 fold) (p<0.05). It has been reported that under the acetate, butyrate, or butanol stress, the genes involved in histidine biosynthesis were up-regulated in C. acetobutylicum (Alsaker et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2013). The induction of histidine biosynthesis genes was also observed under the acid tolerance in Lactobacillus casei (Broadbent et al., 2010). Amino acid metabolism played a vital role in bacterial adaptation to certain circumstances including metabolite stress (Alsaker et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2013), oxygen tolerance (Hillmann et al., 2009), and sporulation (Jones et al., 2008). The highly increased amino acid metabolism may enable bacterial cells to adjust the structure and function of biofilm in response to the cold stress.
Identified DEGs Involved in TCSs in S. putrefaciens Biofilm at the Cold Stress
Bacteria have a variety of signal transduction systems, which can sense external signal stimuli and respond adaptively to changes (e.g., osmolarity, light, temperature, and oxygen) in the surrounding environment (Liu et al., 2013). TCS that compose of histidine protein kinases (HKs) and response regulators (RRs) are widely present in gram-negative bacteria. TCSs are very important signaling pathways that coordinate responses to environmental stimulus, and regulates bacterial sporulation, biofilm formation, competence, and chemotaxis (Sieuwerts et al., 2010). In this study, comparative transcriptomic analyses revealed 59 DEGs involved in the TCSs, which were all significantly up-regulated in S. putrefaciens WS13 at 4°C, e.g., cheV (2.84 fold), motA (2.75 fold). For example, bacterial chemotaxis system is a typical coupling protein-dependent signal transduction system and play a crucial role in bacterial colonigetion and adhesion. It has been reported that the up-regulated genes involved in chemotaxis significantly reduced the ability of adhesion of the organism, motility, chemotaxis, and biofilm formation in Vibrio harveyi. Environmenal factors such as temperatures, salinities, and pH values affected the chemotactic gene expression involved in the regulation of adhesion ability (Xu et al., 2021). In this study, the cheW and cheC genes were significantly down-regulated in the biofilm formation by S. putrefaciens at the cold stress. The cheV gene encodes a linker protein, while the cheC encoding protein has phosphatase activity (Moon et al., 2016). Moreover, expression of six additional genes coding for chemotaxis proteins were all reduced at the transcriptional level in S. putrefaciens at 4°C, including the AVV85596.1 (0.24 fold), AVV83483.1 (0.41 fold), AVV84098.1 (0.40 fold), and AVV83905.1 (0.45 fold). These results suggested inhibital chemotaxis and/or motility of the bacterium. The movement of flagella via the flagellar motor complex affected mature biofilm architecture (Wood et al., 2006). In this study, the motA gene that encodes a key component of the motor compelx was significantly down-regulated (-1.45 fold) (p<0.05) suggesting poor motility forming flatter microcolony structures of S. putrefaciens biofilm at 4°C. Additionally, the DEGs enriched in TCSs may sense external signal stimulation and regulate the movement ability of microbial cells, thereby affecting the biofilm formation.
Identified DEGs Involved in QS in S. putrefaciens Biofilm at the Cold Stress
Biofilm formation is essentially coordinated through a cell density-dependent gene regulation system known as QS (Fuqua et al., 1994; Kjelleberg and Molin, 2002; Parsek and Greenberg, 2005). In this study, remarkly, the DEGs involved in the QS were significantly down-regulated in S. putrefaciens at 4°C, including secY (4.83 fold), secF (4.20 fold), hisI (3.83 fold), gadB (3.38 fold), yidC (3.06 fold), dppB (2.34 fold), yajC (2.21 fold), trpG (2.19 fold). For example, YidC has been recognized as a drug to inhibit biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus (Hofbauer et al., 2018). Expression of the yidC gene was significantly influenced bu pH and starvation stress in Vibrio alginolyticus, and the bacterial adhesion was significantly decreased after silencing of the yidC gene (Lemos et al., 2004). YidC function as integral membrane chaperone/insertase associated with the classical SecYEG translocon, which could contribute to inhibit biofilm formation (Hofbauer et al., 2018). The upregulated expression of the secY and yidC genes involved in extracellular polymeric substances was also observed in the stage of biofilm maturation of Bifidobacterium Longun FGSZY16M3 (Liu et al., 2021). In this study, the secF gene expression was also highly increased by 2.06 fold, which encodes a component of the Sec translocon. Additionally, expression of the yajC (1.14 fold), dppB (1.22fold), and AVV84996.1 (1.41 fold) were significantly increased in S. putrefaciens WS13 biofilm at the cold stress, which encode a potein translocase subunit YajC, a peptide ABC transporter permease, and an outer membrane adhesin-like protein, respectively. These results suggested QS plays an important role in the biofilm formation of S. putrefaciens at the cold stress.
Identified DEGs Involved in the Other Key Metabolic Pathways in S. putrefaciens Biofilm at the Cold Stress
Energy metabolism such as carbohydrate metabolism, pyruvate metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation, and citrate cycle helps bacteria adapt to the changing environment. In this study, approximately 5 DEGs involved in the carbohydrate metabolism were significantly down-regulated (0.10 fold to 0.41 fold) in S. putrefaciens WS13 biofilm formed at 30°C (p<0.05). For energy metabolism, approximately 10 DEGs were significantly down-regulated (0.01 fold to 0.48 fold) at 30°C. For example, expression of the ppsA gene was increased by 2.62 fold in S. putrefaciens at 4°C which can promote biofilm formation by enhancing bacterial adhesion (Ao et al., 2020). Moreover, approximately 11 DEGs involved in aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis were highly down-regulated (2.02 fold to 5.15 fold) in S. putrefaciens WS13 biofilm at 4°C, which may have released amino acids to feed the energy-providing pathways (Bénédicte et al., 2009), and benefited the survival of S. putrefaciens WS13 under the cold stress.
Confirmation of the DEGs by the qRT-PCR Assay
The relative expression levels of randomly selected DEGs were determined and calculated using 16S rRNA as the internal reference gene, including: AVV84311.1, AVV84994.1, AVV84995.1, AVV82000.1, AVV84336.1, AVV85624.1, AVV86072.1, AVV84898.1, AVV82314.1, and AVV84205.1. The obtained qRT-PCR results (Table 3) confirmed the transcription changes of these DEGs in the comparative transcriptome analyses.
Table 3
| Index | Sample Name | Assay Name | mean ΔCT | ΔΔCT | Fold Change | Up/Down | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S30 | AVV84311.1 | -11.36 | -2.87 | 7.29 | Up | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV84311.1 | -8.49 | |||||
| 2 | S30 | AVV84994.1 | -8.63 | -5.23 | 37.46 | Up | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV84994.1 | -3.40 | |||||
| 3 | S30 | AVV84995.1 | -10.56 | -3.96 | 15.52 | Up | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV84995.1 | -6.60 | |||||
| 4 | S30 | AVV82000.1 | -8.12 | -4.33 | 20.06 | Up | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV82000.1 | -3.79 | |||||
| 5 | S30 | AVV84336.1 | -8.30 | -3.54 | 11.67 | Up | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV84336.1 | -4.75 | |||||
| 6 | S30 | AVV85624.1 | -4.72 | 2.30 | 0.20 | Down | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV85624.1 | -7.02 | |||||
| 7 | S30 | AVV86072.1 | -5.59 | 2.57 | 0.17 | Down | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV86072.1 | -8.16 | |||||
| 8 | S30 | AVV84898.1 | -5.43 | 5.29 | 0.03 | Down | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV84898.1 | -10.72 | |||||
| 9 | S30 | AVV82314.1 | -3.06 | 2.26 | 0.21 | Down | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV82314.1 | -5.32 | |||||
| 10 | S30 | AVV84205.1 | -5.54 | 1.85 | 0.28 | Down | 16S |
| WS4 | AVV84205.1 | -7.39 |
The results of the qRT-PCR assay.
Conclusions
This study was the first to characterize the global-level gene expression of biofilm cells of S. putrefaciens WS13 under the cold stress. Distinct transcriptomic profiles were obtained using Illumina RNA sequencing technique. Comparative transcriptomic analyses revealed a total of 761 DEGs in the biofilm formed at 4°C, among which the expression of 497 DEGs was significantly up-regulated, and 264 DEGs were significantly inhibited (p<0.05). Although carbohydrate and energy metabolisms were repressed in the biofilm cells at the harsh condition, S. putrefaciens WS13 reduced chemotaxis, and mobility, but enhanced histidine biosynthesis, tryptophan metabolism, and QS to construct the biofilm and survive at the cold stress. This work provides valuable insights into the transcriptiomic regulation in biofilm cells under cold stress and laid a theoretical foundation for the targeted inhibition of the biofilm formation of the severe spoilage S. putrefaciens WS13.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972142), Shanghai Engineering Research Center Construction Special Fund from Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (19DZ2284000), the Startup Foundation for Young Teachers of Shanghai Ocean University.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Statements
Data availability statement
Raw data of the transcriptomes was deposited in NCBI database under the accession number PRJNA759975 (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/759975).
Author contributions
JX, JY conceived the idea. JY carried out the laboratory work and wrote the paper. ZY assisted in the data analysis. JX revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1
Alsaker K. V. Paredes C. Papoutsakis E. T. (2010). Metabolite Stress and Tolerance in the Production of Biofuels and Chemicals: Gene-Expression-Based Systems Analysis of Butanol, Butyrate, and Acetate Stresses in the Anaerobe Clostridium Acetobutylicum. Biotechnol. Bioengineering.105 (6), 1131–1147. doi: 10.1002/bit.22628
2
Ao X. Zhao J. Yan J. Liu S. Zhao K. J. P. (2020). Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum RS66CD Biofilm in High-Salt Conditions and Planktonic Cells. Peer J.8 (13), e9639. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9639
3
Bagge D. Hjelm M. Johansen C. Huber I. Gram L. J. A. Microbiology E. (2001). Shewanella Putrefaciens Adhesion and Biofilm Formation on Food Processing Surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.67 (5), 2319–2325. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.5.2319-2325.2001
4
Bénédicte F. Kelley W. L. Lew D. Götz F. Proctor R. A. Vaudaux P. (2009). Transcriptomic and Metabolic Responses of Staphylococcus Aureus Exposed to Supra-Physiological Temperatures. BMC Microbiol.9 (1), 76–76. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-76
5
Broadbent J. R. Larsen R. L. Deibel V. Steele J. L. (2010). Physiological and Transcriptional Response of Lactobacillus Casei ATCC 334 to Acid Stress. J. Bacteriol.192 (9), 2445–2458. doi: 10.1128/JB.01618-09
6
Castro J. França A. Bradwell K. R. Serrano M. G. Jefferson K. K. Cerca N. (2017). Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Gardnerella Vaginalis Biofilms vs. Planktonic Cultures Using RNA-Seq. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes3 (1), 3.
7
Charlebois A. Jacques M. Archambault M. (2016). Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Clostridium Perfringens Biofilms and Planktonic Cells. Avian Pathol.45 (5), 593–601. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2016.1189512
8
Chen L. Yang S. Qian Y. Xie J. (2019). Sequencing and Analysis of the Shewanella Putrefaciens WS13 Genome. J. Biobased Materials Bioenergy13 (2), 182–187. doi: 10.1166/jbmb.2019.1850
9
Domka J. Lee J. Bansal T. Wood T. K. (2007). Temporal Gene-Expression in Escherichia Coli K-12 Biofilms. Environ. Microbiol.9 (2), 332–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01143.x
10
Dong L. Xu J. Wang Y. Yong C. Ying H. (2015). Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Clostridium Acetobutylicum Biofilm and Planktonic Cells. J. Biotechnol.218, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.11.017
11
Flemming H. C. Wingender J. J. N. R. M. (2010). The Biofilm Matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.8 (9), 623–633. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2415
12
Flemming H. C. Wingender J. Szewzyk U. Steinberg P. Rice S. A. Kjelleberg S. J. N. R. M. (2016). Biofilms: An Emergent Form of Bacterial Life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.14 (9), 563–575. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.94
13
Fuqua W. C. Winans S. C. Greenberg E. P. (1994). Quorum Sensing in Bacteria: The LuxR-LuxI Family of Cell Density-Responsive Transcriptional Regulators. J. Bacteriol.176 (2), 269–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.2.269-275.1994
14
Gang L. Huang L. Su Y. Qin Y. Yan Q. J. E. M. (2016). Flra, flrB and flrC Regulate Adhesion by Controlling the Expression of Critical Virulence Genes in Vibrio Alginolyticus. Emerging Microbes infections5 (8), e85. doi: 10.1038/emi.2016.82
15
Gram L. Ravn L. Rasch M. Bruhn J. B. Christensen A. B. Givskov M. (2002). Food Spoilage–Interactions Between Food Spoilage Bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol.78 (1-2), 79–97. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(02)00233-7
16
Hamilton S. Bongaerts R. J. Mulholland F. Cochrane B. Porter J. Lucchini S. et al . (2009). The Transcriptional Programme of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium Reveals a Key Role for Tryptophan Metabolism in Biofilms. BMC Genomics10 (1), 599. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-599
17
Hillmann F. Doring C. Riebe O. Ehrenreich A. Fischer R. J. Bahl H. J. (2009). The Role of PerR in O2-Affected Gene Expression of Clostridium Acetobutylicum. J. Bacteriol.191 (19), 6082–6093. doi: 10.1128/JB.00351-09
18
Hofbauer B. Vomacka J. Stahl M. Korotkov V. S. Jennings M. C. Wuest W. et al . (2018). Dual Inhibitor of Staphylococcus Aureus Virulence and Biofilm Attenuates Expression of Major Toxins and Adhesins. Biochemistry57 (11), 1814–1820. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01271
19
Hou H. M. Zhang G. L. Sun L. M. (2013). Preliminary Analysis of Bacterial Flora in Turbot Scophthalmus Maximus Cultured in Deep Well Seawater. Advanced Materials Res.781-784, 1677–1680. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.781-784.1677
20
Jones S. W. Paredes C. J. Tracy B. Cheng N. Biology R. S. J. G. (2008). The Transcriptional Program Underlying the Physiology of Clostridial Sporulation. Genome Biol.9 (7), R114. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-7-r114
21
Kjelleberg S. Molin S. (2002). Is There a Role for Quorum Sensing Signals in Bacterial Biofilms? Microbiology5 (3), 0–258. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(02)00325-9
22
Lemos J. A. C. Brown T. A. Burne R. A. (2004). Effects of RelA on Key Virulence Properties of Planktonic and Biofilm Populations of Streptococcus Mutans. Infection Immun.72 (3), 1431–1440. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.3.1431-1440.2004
23
Liu Z. Li L. Fang Z. Lee Y. Zhao J. Zhang H. et al . (2021). Integration of Transcriptome and Metabolome Reveals the Genes and Metabolites Involved in Bifidobacterium Bifidum Biofilm Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22 (14), 7596. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147596
24
Liu Z. X. Li H. C. Wei Y. P. Chu W. Y. Chong Y. L. Long X. H. et al . (2013). Signal Transduction Pathways in Synechocysti Ssp. PCC 6803 and Biotechnological Implications Under Abiotic Stress. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol.35 (2), 269–280. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2013.838662
25
Lo A. W. Seers C. A. Boyce J. D. Dashper S. G. Slakeski N. Lissel J. P. et al . (2009). Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Porphyromonas Gingivalis Biofilm and Planktonic Cells. BMC Microbiol.9 (1), 18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-18
26
Moon K. H. Hobbs G. Motaleb M. A. (2016). Borrelia Burgdorferi CheD Promotes Various Functions in Chemotaxis and the Pathogenic Life Cycle of the Spirochete. Infection Immun.84 (6), IAI.01347–15. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01347-15
27
Parsek M. R. Greenberg E. P. (2005). Sociomicrobiology: The Connections Between Quorum Sensing and Biofilms. Trends Microbiol.13 (1), 27–33. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.007
28
Sasaki-Imamura T. Yano A. Yoshida Y. (2010). Production of Indole From L-Tryptophan and Effects of These Compounds on Biofilm Formation by Fusobacterium Nucleatum ATCC 25586. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.76 (13), 4260–4268. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00166-10
29
Sieuwerts S. Molenaar D. van Hijum S. A. F. T. Beerthuyzen M. Stevens M. J. A. Janssen P. W. M. et al . (2010). Mixed-Culture Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Molecular Basis of Mixed-Culture Growth in Streptococcus Thermophilus and Lactobacillus Bulgaricus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.76 (23), 7775–7784. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01122-10
30
Vogel B. F. Venkateswaran K. Satomi M. Gram L. (2005). Identification of Shewanella Baltica as the Most Important H2S-Producing Species During Iced Storage of Danish Marine Fish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.71 (11), 6689–6697. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.11.6689-6697.2005
31
Wang Q. Venkataramanan K. Huang H. Papoutsakis E. T. Wu C. H. (2013). Transcription Factors and Genetic Circuits Orchestrating the Complex, Multilayered Response of Clostridium Acetobutylicum to Butanol and Butyrate Stress. BMC Syst. Biol.7 (1), 120. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-7-120
32
Wilkinson D. A. Chacko S. J. Venien-Bryan C. Wadhams G. H. Armitage J. P. (2011). Regulation of Flagellum Number by FliA and FlgM and Role in Biofilm Formation by Rhodobacter Sphaeroides. J. Bacteriol.193 (15), 4010–4014. doi: 10.1128/JB.00349-11
33
Wood T. K. Barrios A. Herzberg M. Lee J. (2006). Motility Influences Biofilm Architecture in Escherichia Coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.72(2), 361–367. doi: 10.1007/s00253-005-0263-8
34
Xie J. Hou W. F. Tang Y. Lan W. Q. J. S. T. o F. (2011). Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Phytic Acid Against Shewanella Putrefacens. Sci. Technol. Food Industry32 (10), 85–88. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2011.10.051
35
Xie J. Cheng Y. Yang S. Zhang Z. Qian Y. (2018). Effect of Shewanella Putrefaciens on the Amino Acids Metabolism and Biogenic Amines Production in Litopenaeus Vannamei. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci.18 (1), 169—175. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.01.022
36
Xu X. Li H. Qi X. Chen Y. Jiang X. Qin Y. et al . (2021). Chea, Cheb, Cher, Chev, and cheY Are Involved in Regulating the Adhesion of Vibrio Harveyi. Front. Cell. Infection Microbiol.10, 591751. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.591751
37
Yan J. Xie J. (2020). Comparative Proteome Analysis of Shewanella Putrefaciens WS13 Mature Biofilm Under Cold Stress. Front. Microbiol.11, 1225. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01225
38
Yan J. Xie J. (2021). Removal of Shewanella Putrefaciens Biofilm by Acidic Electrolyzed Water on Food Contact Surfaces. LWT- Food Sci. Technol.151 (2), 112044. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112044
39
Zhen-Quan Y. Xiao-Ya ,.T. Hui Z. Sheng-Qi R. Lu G. Zhi-Ming P. et al . (2018). Isolation and Characterization of Virulent Phages Infecting Shewanella Baltica and Shewanella Putrefaciens, and Their Application for Biopreservation of Chilled Channel Catfish (Ictalurus Punctatus). Int. J. Food Microbiol.292, 107–117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.12.020
Summary
Keywords
Shewanella putrefaciens WS 13, biofilm, cold stress, transcriptome, specific spoilage organism
Citation
Yan J, Yang Z and Xie J (2022) Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Shewanella putrefaciens WS13 Biofilms Under Cold Stress. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12:851521. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.851521
Received
10 January 2022
Accepted
18 May 2022
Published
22 June 2022
Volume
12 - 2022
Edited by
Qingli Dong, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Reviewed by
Justin Kaspar, The Ohio State University, United States; Cui Xiaowen, Kyushu University, Japan; Cong Liu, Jiangsu Normal University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2022 Yan, Yang and Xie.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Xie, jxie@shou.edu.cn
This article was submitted to Molecular Bacterial Pathogenesis, a section of the journal Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.