- 1Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
- 2Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China
- 3Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Nanjing Jinling Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
- 4Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Nanjing Jinling Hospital, Medical School, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
Purpose: This study aimed to assess a novel lateral flow assay (LFA) for Aspergillus IgG detection in patients with non-neutropenic invasive aspergillosis (IA).
Methods: Aspergillus IgG LFA and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were performed in non-neutropenic IA patients and control group (proven community acquired pneumonia and healthy persons), respectively. The diagnostic performance of Aspergillus IgG LFA for IA was evaluated and compared with ELISA method.
Results: 33 cases of acute IA, 30 cases of subacute IA and 80 controls were enrolled in this study. The level of plasma Aspergillus IgG LFA in the IA group was significantly higher than that in the control group (190.5 AU/mL vs 50.3 AU/mL, P < 0.001). In total, the sensitivity/specificity/PPV/NPV of Aspergillus IgG LFA was 65.1%/97.5%/95.4%/78.0%. The sensitivity and specificity of Aspergillus IgG LFA were equivalent to those of Aspergillus IgG ELISA with a 120 AU/mL cut-off, but exhibited significantly higher specificity (97.5% vs 87.5%, P = 0.021) compared to the ELISA with an 80 AU/mL cut-off. The consistency was strong among the two methods (P < 0.001, Kappa = 0.67/0.68). The sensitivities/specificities/PPVs/NPVs of Aspergillus IgG LFA were 57.6%/97.5%/90.5%/84.8% for patients with acute IA, and 73.3%/97.5%/91.7%/90.7% for patients with subacute IA, respectively. The “any-positive” strategy, which combined Aspergillus IgG LFA with sputum culture and serum galactomannan (GM), had a sensitivity/specificity/PPV/NPV of 81.1%/94.7%/95.6%/78.3%. The sensitivity/specificity/PPV/NPV of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) GM was 65.0%/90.0%/92.9%/56.3%. When combined Aspergillus IgG LFA with BALF GM, the figures were 87.5%/85.0%/92.1%/77.3%.
Conclusions: Compared to the Aspergillus IgG ELISA, the Aspergillus IgG LFA exhibits comparable or superior diagnostic efficiency in IA patients, while offering a faster and more convenient option for clinical diagnosis. The “any-positive” strategy of combined diagnosis with Aspergillus IgG LFA serves as a valuable supplement to current diagnostic approaches, particularly benefiting patients who cannot tolerate invasive bronchoscopic procedures.
1 Background
The latest epidemiological survey indicated that over 2.1 million people developed invasive aspergillosis (IA) annually, resulting in over 1.8 million of deaths each year (Denning, 2024). The diagnosis of IA primarily relies on host factor, clinical manifestation and mycological evidence (Ullmann et al., 2018; Donnelly et al., 2020; Bassetti et al., 2024). However, non-neutropenic patients with IA lack specificity in clinical symptoms and radiological manifestations, leaving challenges and rendering difficult diagnosis in clinical practice (Liu et al., 2021).
Non-neutropenic IA patients exhibit limited Aspergillus vascular invasion, yielding low serum galactomannan (GM) antigen detection rates (Dagenais and Keller, 2009; Zhou et al., 2017). Conventional airway culture suffers from low sensitivity, prolonged processing (> 72 hours), and inability to discriminate infection from colonization (Baker and Denning, 2023). Although bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF)-based diagnostics (GM, polymerase chain reaction [PCR]/next generation sequencing [NGS]) exhibit superior sensitivity, their invasiveness prevents their use in cardiopulmonary-compromised patients (Zhou et al., 2017; Baker and Denning, 2023; Zhu et al., 2023a). Therefore, it highlights the clinical need for non-invasive yet sensitive detection methods.
Aspergillus IgG antibody (Aspergillus IgG) is produced in response to Aspergillus infection (Delliere and Aimanianda, 2023). The detection of Aspergillus IgG in serum or plasma aids in diagnosing acute and subacute IA, but definitive diagnosis requires integration with clinical presentation and other corroborating evidence (Yu et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2023; Sheng et al., 2024). The available Aspergillus IgG assays include precipitin detection, counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CIE), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immune chromatography technology (ICT), etc (Page et al., 2015; Baker and Denning, 2023). The Aspergillus IgG ELISA method has demonstrated its superiority in accuracy, stability and turn-around time (TAT) over the precipitin detection and CIE (Baxter et al., 2013; Page et al., 2015). Commercial Aspergillus IgG ELISA kits typically require a processing time of 2 to 4 hours (Page et al., 2015). Meanwhile, it is cost-effective to perform this test when an adequate number of samples are collected, which ultimately leads to a longer TAT. The detection of Aspergillus IgG using the ICT method has outstanding advantages, including the ability to detect a single sample, simple operation and a short TAT (less than 30 minutes) (Baker and Denning, 2023).
Timely identification and intervention of IA are vital for improving patient outcomes and reducing mortality (Page et al., 2015). However, current studies of Aspergillus IgG ICT primarily focus on patients with chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA) (Piarroux et al., 2019; Stucky Hunter et al., 2019; Rozaliyani et al., 2020; Ray et al., 2022; Singh et al., 2022; Zhu, 2023b). In this study, we evaluated the performance of a novel Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay (LFA) based on fluorescence ICT for the diagnosis of acute and subacute IA in non-neutropenic patients.
2 Methods
2.1 Patients and samples
This retrospective, controlled study included a total of 143 non-neutropenic patients (consisting of 63 cases with IA and 80 controls), identified at Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital and Nanjing Jinling Hospital from June 2018 to September 2023. Out of the 63 patients with IA, 33 (52.4%) had acute IA and 30 (47.6%) had subacute IA. There were 3 (9.1%) patients with proven diagnosis and 30 (90.9%) patients with probable diagnosis in the acute IA group. There were 1 (3.3%) patient with proven diagnosis and 29 (96.7%) patients with probable diagnosis in the subacute IA group. The control group consisted of 50 patients with proved community acquired pneumonia (CAP) and 30 healthy volunteers without any evidence of Aspergillus infection or colonization. All diagnoses were based on clinical evidence and verified by experienced specialists. Blood samples used in this study were obtained prior to the initiation of antifungal therapy. These samples were the surplus plasma from previous clinical studies and clinical routine tests, which were stored in a −80°C refrigerator.
2.2 The diagnostic criteria of IA
The diagnosis of IA was established according to the 2020 guideline from EORTC/MSG (Donnelly et al., 2020), with minor modifications. Proven IA required histopathologic evidence for Aspergillus hyphae in sterile lung specimens. Probable IA needed evidence of at least one host factor, clinical manifestation and mycological evidence. Host factors included but were not limited to solid organ transplant, prolonged use of corticosteroids or immunosuppressive agents, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), severe influenza, diabetes and/or malnutrition (Ullmann et al., 2018). The radiological features consisted of dense, well-circumscribed lesions with or without a halo sign, an air crescent sign, cavity and/or consolidation. Mycological evidence included positive results of GM test, PCR test and/or sputum/BALF/bronchial brush/aspirate culture (Donnelly et al., 2020). The diagnosis of non-neutropenic IA for intensive care unit (ICU) patients relied on the 2024 consensus definitions from the study group of the ESGCIP, EFISG, ESICM, ECMM, MSGERC, ISAC and ISHAM (Bassetti et al., 2024). Host factors included COVID-19, solid tumors, moderate/severe COPD, influenza, decompensated liver cirrhosis and/or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The radiologic findings included pulmonary infiltrate and/or cavity. Mycological evidence included positive results of GM test and/or BALF culture. The detection of Aspergillus nucleic acid in this study was conducted using NGS (Zhu et al., 2023a). Aspergillus IgG was not included as one of the diagnostic criteria for IA.
2.3 Aspergillus IgG antibody assay
The Aspergillus fluorescence IgG LFA (Dynamiker, Tianjin, China) was utilized for the semi-quantitative detection of Aspergillus galactomannan IgG antibody in human plasma samples. The test kit was stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. Prior to use, the required number of test cards, reagents and plasma samples were brought to room temperature. Plasma samples were diluted to 1:200 using phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing protein. Subsequently, 90–100 μL of the diluted sample were added to the sample well of each test card. Within 15 to 20 minutes, fluorescence signal was obtained by scanning the detection area with specialized fluorescence immunoanalyzer (Dynamiker, Tianjin, China). Then, the result could be read in digital form (Figure 1). According to the manufacturer’s instructions, results greater than 135 AU/mL were considered positive, results less than 135 AU/mL were considered negative. The minimum detection limit of this reagent was 10 AU/mL.
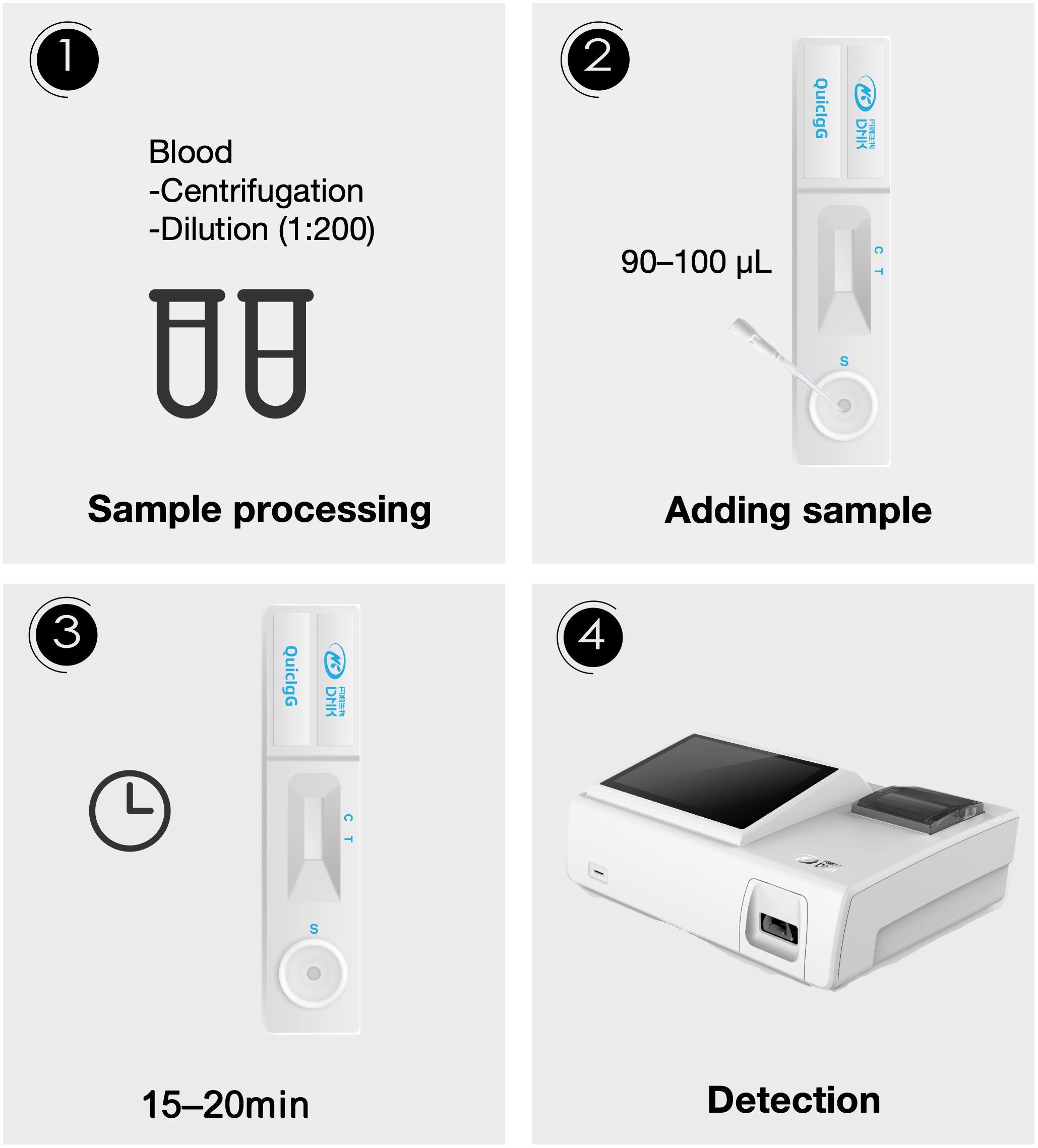
Figure 1. The flow chart of the Aspergillus IgG assay via fluorescence lateral flow technique. Step 1: Blood samples were centrifuged, then the plasma was diluted 1:200. Step 2: 90–100 μL of the diluted sample was added to the sample well of the test card. Step 3: A 15–20 minute incubation period was allowed. Step 4: Detection was performed using an optical device.
The Aspergillus fumigatus IgG ELISA test kit from Dynamiker (Tianjin, China) was utilized for the quantitative detection of Aspergillus IgG in plasma samples. Plasma samples were diluted to 1:1000 and tested following the manufacturer’s instructions. Results greater than 120 AU/mL were considered positive, results less than 80 AU/mL were considered negative, and results between 80 and 120 AU/mL were deemed borderline. The minimum detection limit of this reagent was 31.3 AU/mL.
2.4 GM test and culture
Detection of GM in BALF and serum was conducted using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent double antibody sandwich assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, CA, USA) by the clinical central laboratories. Qualified expectorated sputum and BALF samples were cultured on Sabouraud dextrose agar by the clinical microbiology laboratories.
2.5 Statistical analysis
SPSS 27.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and R statistical software 4.2.3 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) were used for data analysis. GraphPad Prism 10 (GraphPad Software, CA, USA) was used to draw graphs. Categorical variables were analyzed using Pearson’s chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test, with results presented as frequency counts (percentages). McNemar’s test was used for paired categorical variables. Continuous data were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test for comparisons between two groups, and the Kruskal-Walis test for comparisons involving more than two groups. Results were presented as the median with the interquartile range (IQR). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to obtain sensitivity, specificity, Youden index (sensitivity+specificity-1) and optimal threshold. The association between Aspergillus IgG ELISA and Aspergillus IgG LFA was assessed by Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient and Kappa consistency test (0–0.2, very weak; 0.21–0.4, weak; 0.41–0.6, moderate; 0.61–0.8, strong; and 0.81–1, almost perfect). P value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 The characteristics of patients with IA
The characteristics of the study population are shown in Table 1. Patients with IA had a median age of 64 (IQR 56-72) years, and 76.2% of them were male. The positive rate of Aspergillus IgG LFA (65.1%) was significantly higher than that of serum GM (27.1%, P < 0.001) and sputum culture (30.4%, P = 0.001), comparable to BALF GM (65.0%, P = 0.824) and Aspergillus IgG ELISA (69.8%, P = 0.549), and significantly lower than that of BALF NGS (88.9%, P = 0.035). The positive rates of only A. fumigatus infection and other Aspergillus infection except A. fumigatus were 67.9% and 60.0%, respectively (P = 0.709)(Table 2).
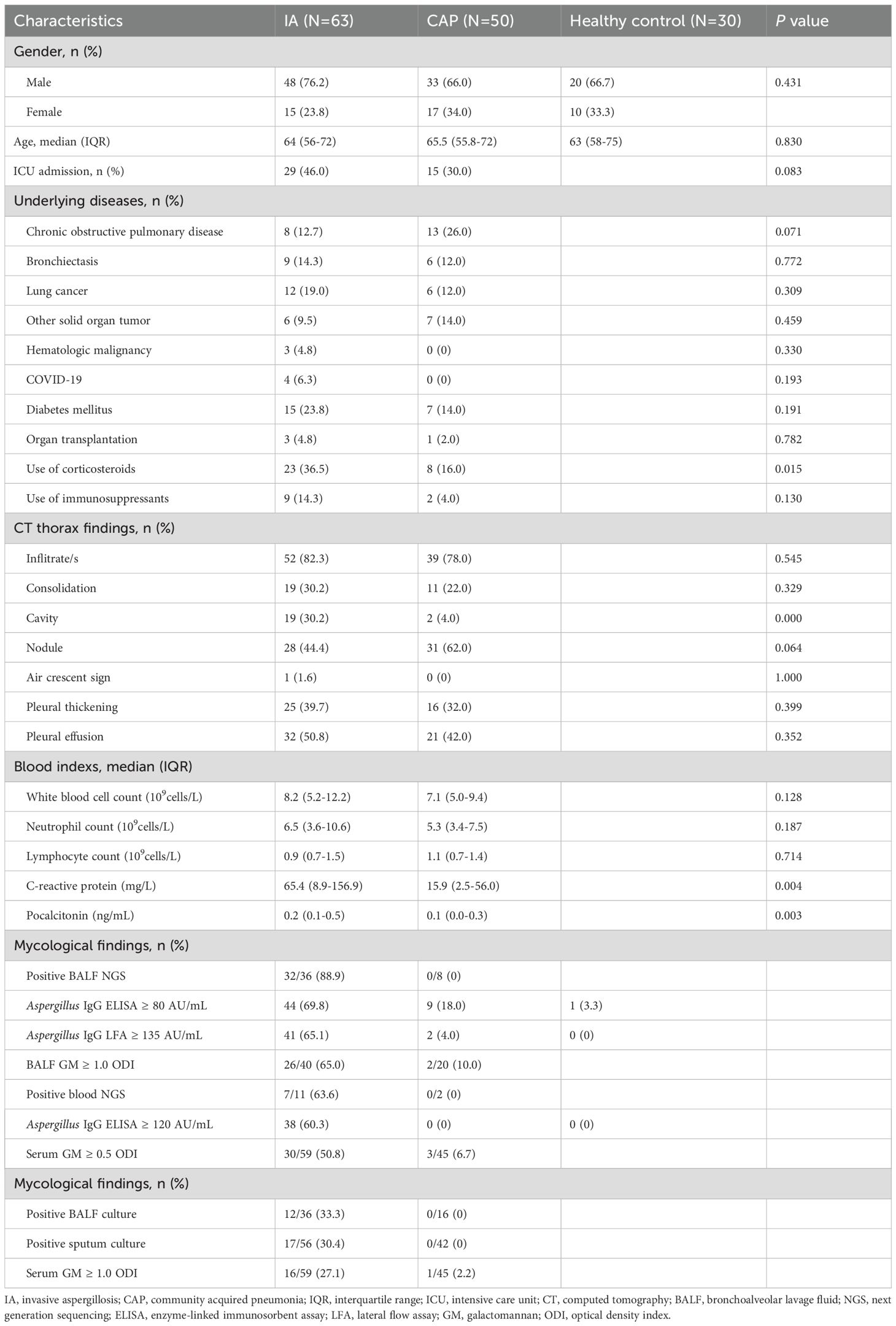
Table 1. The characteristics of invasive aspergillosis group, community acquired pneumonia group and healthy control.
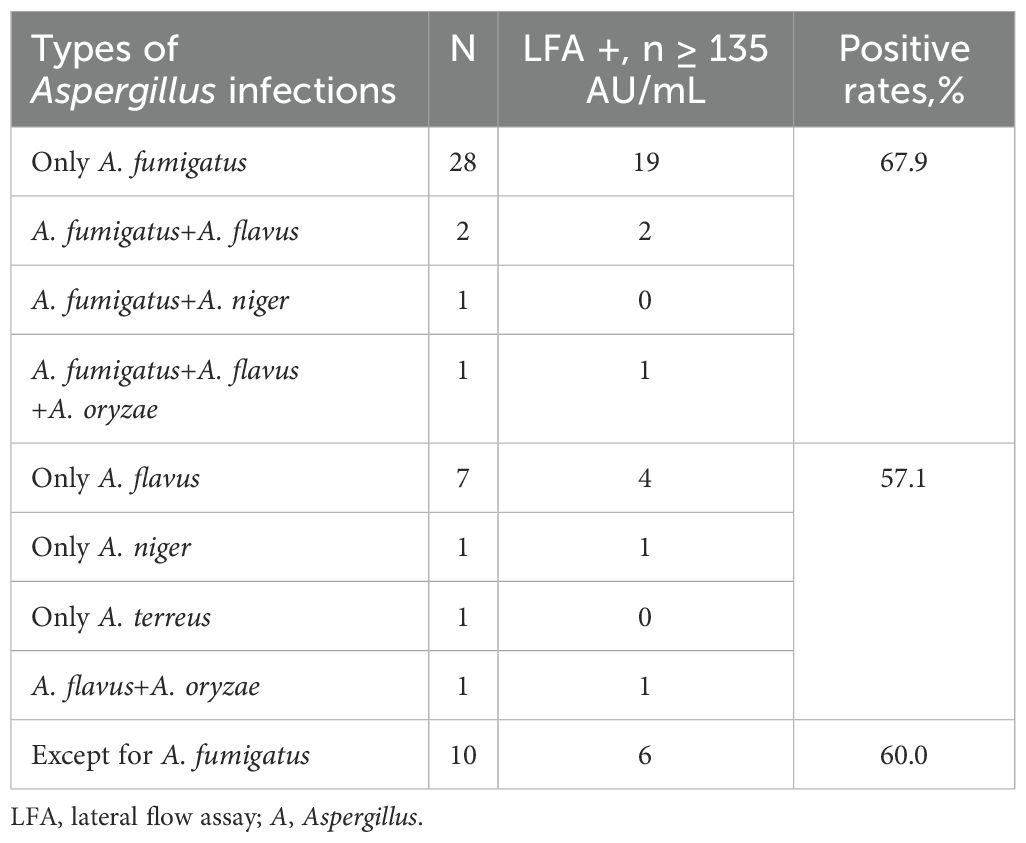
Table 2. The positive rates of Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay in invasive aspergillosis patients with different types of Aspergillus infections.
3.2 The correlation between Aspergillus IgG LFA and Aspergillus IgG ELISA
The levels of Aspergillus IgG LFA and Aspergillus IgG ELISA in patients with IA were significantly higher than those in control groups, respectively (Median[IQR]: 190.5 [94.5-481.4] vs 50.3 [31.4-75.2] AU/mL for LFA, P <0.001; 143.0 [67.3-215.7] vs 36.8 [31.3-60.8] AU/mL for ELISA, P< 0.001) (Figures 2A, B). There were no significant differences in the levels of Aspergillus IgG LFA (160.5[72.5-469.2] vs 251.7[100.0-488.4] AU/mL, P = 0.466) and Aspergillus IgG ELISA (143.0[61.7-204.1] vs 144.1[69.8-237.4] AU/mL, P = 0.527) between the acute IA group and the subacute IA group (Figures 2C, D).
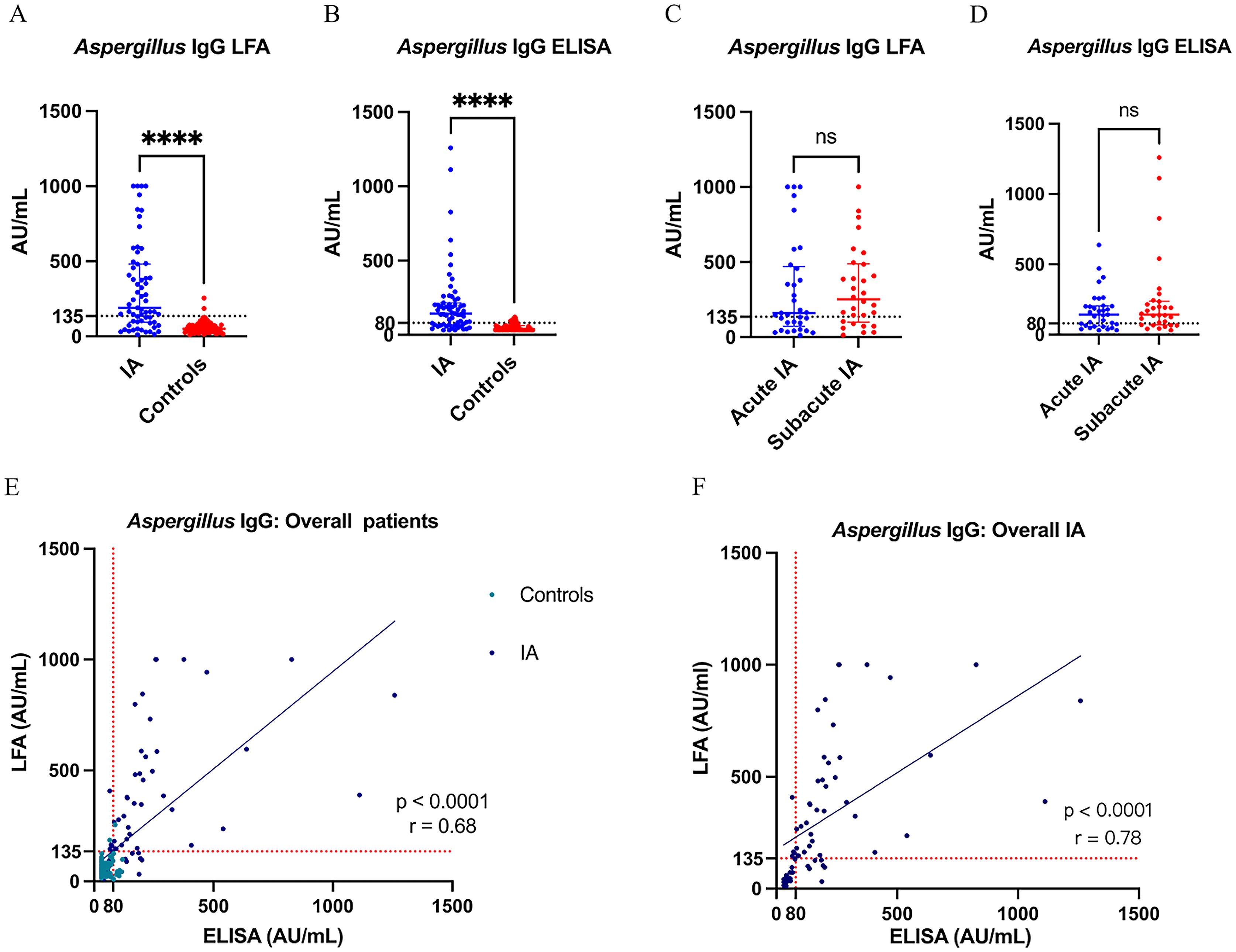
Figure 2. (A, B) The levels of Aspergillus IgG LFA and Aspergillus IgG ELISA in overall IA and control groups; (C, D) The levels of Aspergillus IgG LFA and Aspergillus IgG ELISA in acute IA and subacute IA groups; (E, F) Scatter diagram of Aspergillus IgG LFA vs Aspergillus IgG ELISA in overall and IA patients. **** P < 0.001; ns, not significant (P > 0.05); the value of r represented correlation coefficient. LFA, lateral flow assay; IA, invasive aspergillosis; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
For all 143 patients of this study, the Aspergillus IgG LFA showed a strong correlation with the Aspergillus IgG ELISA (P < 0.0001, r = 0.68) (Figure 2E). The consistency was strong among the two methods (P < 0.001, overall agreement = 85.3%, Kappa = 0.68, cut-off value of Aspergillus IgG = 80AU/mL; P < 0.001, overall agreement = 86.7%, Kappa = 0.67, cut-off value of Aspergillus IgG = 120AU/mL) (Table 3).
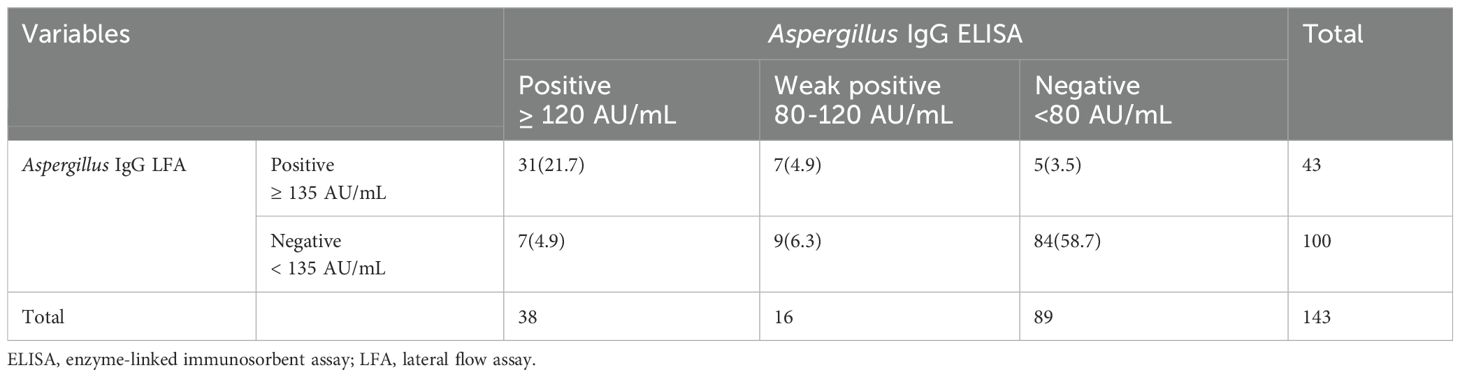
Table 3. Consistency analysis of Aspergillus IgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay in all patients..
For the IA group, the Aspergillus IgG LFA showed a strong correlation with the Aspergillus IgG ELISA (P < 0.0001, r = 0.78) (Figure 2F). The consistency was moderate among the two methods (P < 0.001, overall agreement = 82.5%, Kappa = 0.60, cut-off value of Aspergillus IgG = 80AU/mL; P = 0.001, overall agreement = 73.0%, Kappa = 0.43, cut-off value of Aspergillus IgG = 120AU/mL) (Table 4).
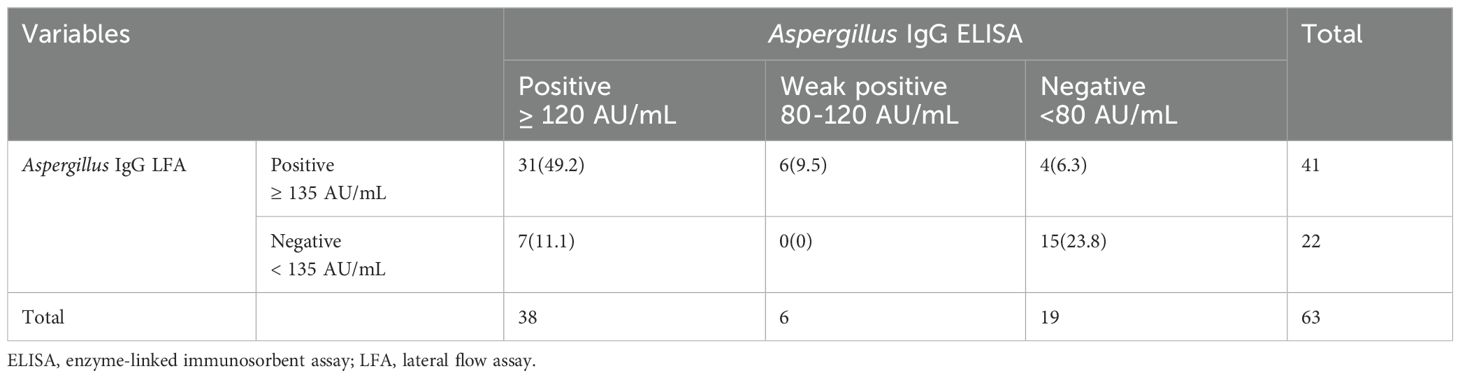
Table 4. Consistency analysis of Aspergillus IgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay in invasive aspergillosis patients.
3.3 Comparing the diagnostic performance of Aspergillus IgG LFA with Aspergillus IgG ELISA
The area under ROC curves of Aspergillus IgG LFA vs ELISA were 0.842 (95% CI: 0.768, 0.915) vs 0.882 (95% CI: 0.825, 0.938) for overall IA patients (Figure 3A), 0.812 (95% CI: 0.705, 0.919) vs 0.863 (95% CI: 0.783, 0.944) for patients with acute IA (Figure 3B), and 0.874 (95% CI: 0.780, 0.967) vs 0.903 (95% CI: 0.834, 0.971) for patients with subacute IA (Figure 3C), respectively. There were no significant differences between the two methods across the three groups (P were 0.126, 0.123 and 0.406, respectively).
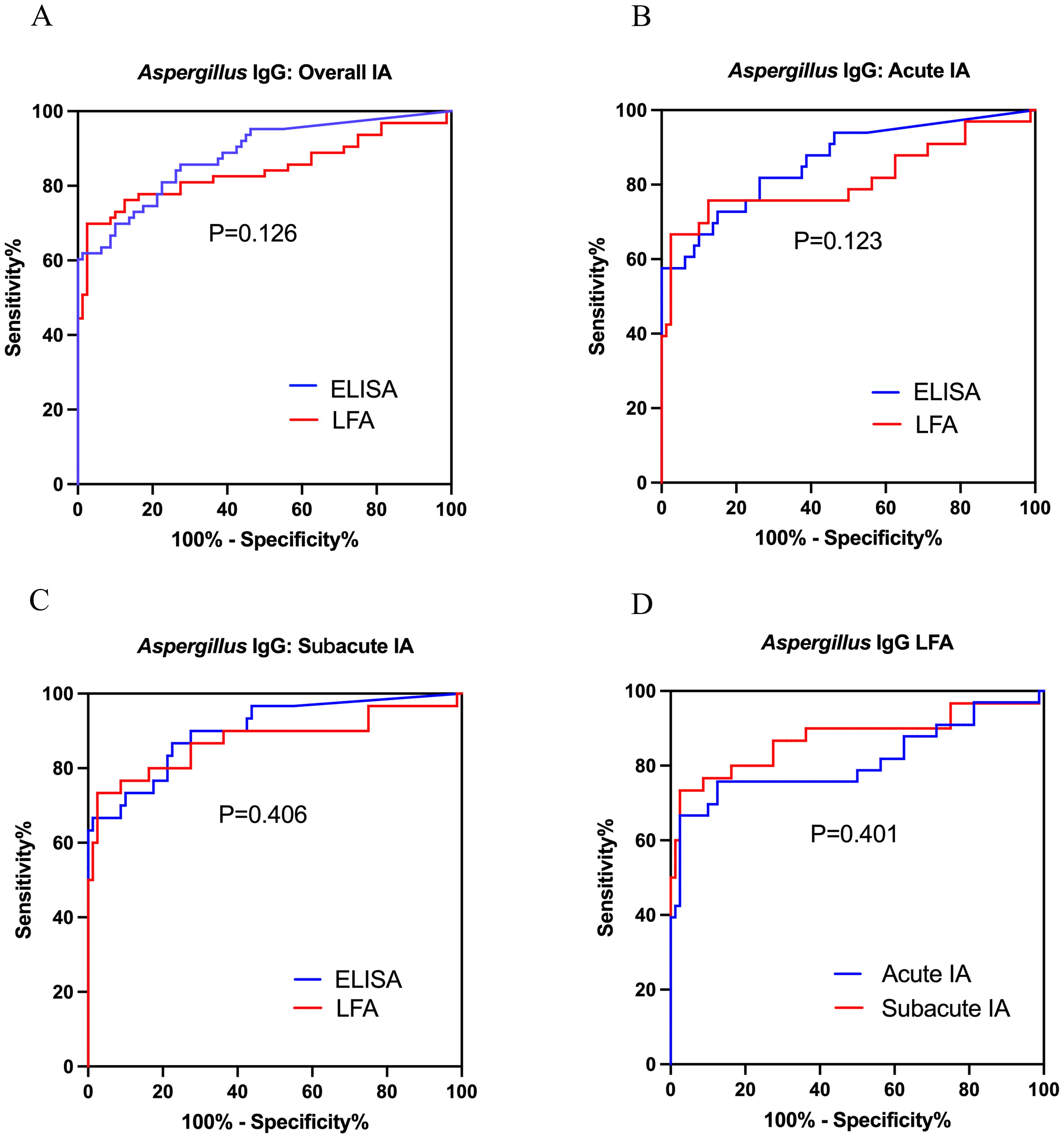
Figure 3. Receiver operating characteristic curves were used to evaluate the performance of Aspergillus IgG LFA and ELISA in diagnosing acute IA, subacute IA or overall IA group, compared to CAP group and healthy control. (A) LFA vs ELISA in overall IA; (B) LFA vs ELISA in acute IA; (C) LFA vs ELISA in subacute IA; (D) LFA in acute IA and subacute IA. IA, invasive aspergillosis; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; LFA, lateral flow assay.
In total, the sensitivity and specificity of Aspergillus IgG LFA were equivalent to these of the Aspergillus IgG ELISA with a cut-off value of 120 AU/mL (65.1% vs 60.3% for sensitivity, P = 0.629; 97.5% vs 100% for specificity, P = 0.497). Compared to the Aspergillus IgG ELISA with a cut-off value of 80 AU/mL, the Aspergillus IgG LFA had equivalent sensitivity (65.1% vs 69.8% for sensitivity, P = 0.549), but significantly higher specificity (97.5% vs 87.5% for specificity, P = 0.021)(Table 5).
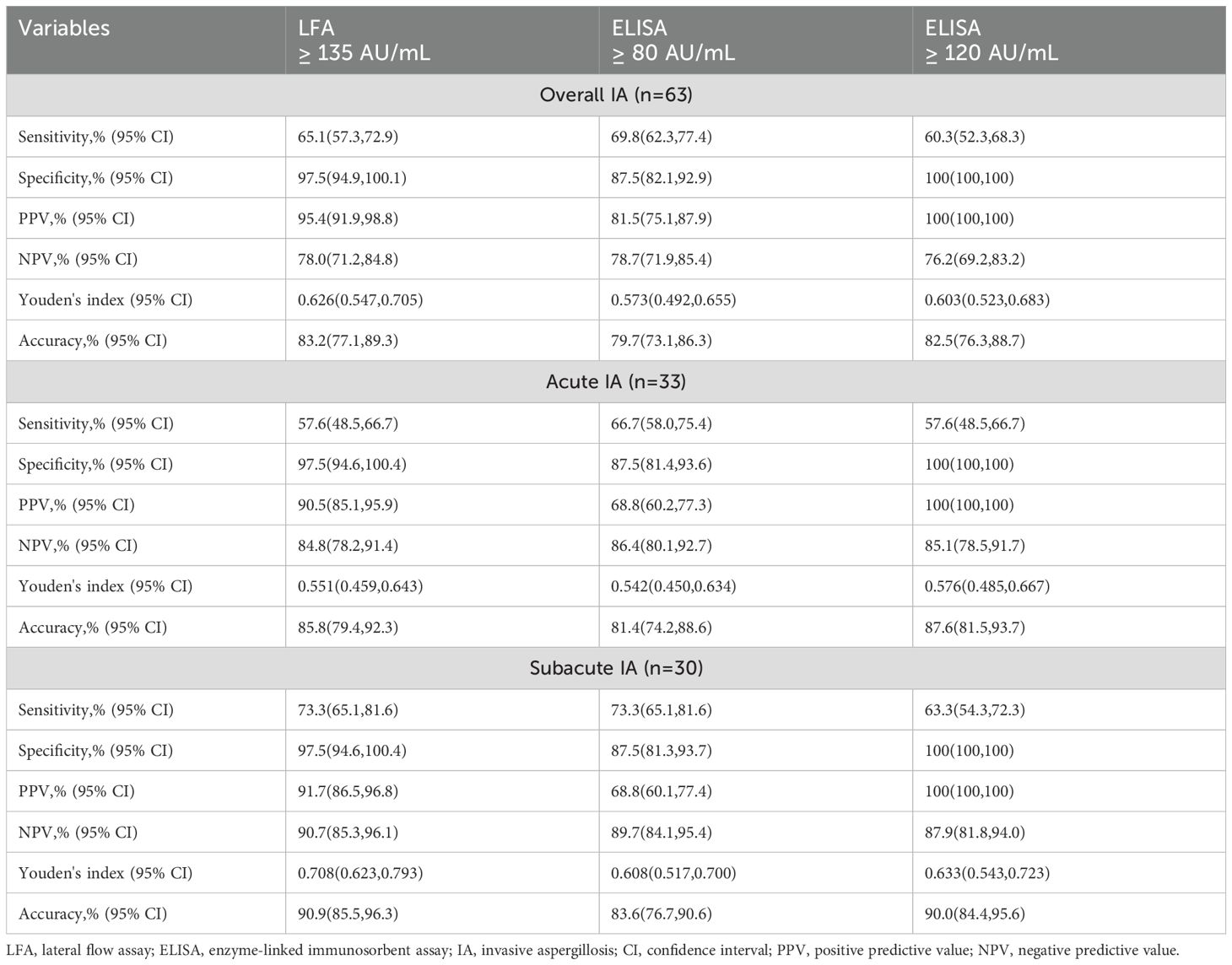
Table 5. The diagnostic performances of Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay and Aspergillus IgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
3.4 Comparing the diagnostic performance of Aspergillus IgG LFA between patients with acute IA and subacute IA
The ROC curves of Aspergillus IgG LFA had no significant differences between patients with acute and subacute IA (AUC0.812 [95% CI: 0.705, 0.919] vs 0.874 [95% CI: 0.780, 0.967], P =0.401) (Figure 3D). The sensitivities, PPVs and NPVs of the Aspergillus IgG LFA were equivalent between patients with acute and subacute IA (57.6% vs 73.3% for sensitivity, P = 0.190; 90.5% vs 91.7% for PPV, P = 1.000; 84.8% vs 90.7% for NPV, P =0.231) (Table 5).
3.5 The optimal cut-off values of Aspergillus IgG LFA for patients with acute IA, subacute IA and overall IA
According to the ROC curves, the optimal cut-off values were determined to be 126, 136 and 126 AU/mL for patients with acute IA, subacute IA and overall IA, respectively (Figure 3). The corresponding sensitivities/specificities/PPVs/NPVs were as follows: 66.7%/97.5%/91.7%/87.6% for patients with acute IA, 73.3%/97.5%/91.7%/90.7% for patients with subacute IA, and 69.8%/97.5%/95.7%/80.4% for overall IA patients, respectively.
3.6 The evaluation of the combined diagnostic performance of Aspergillus IgG LFA in patients with IA
A total of 53 IA patients and 38 CAP patients had Aspergillus IgG LFA, sputum culture, and serum GM results. For these patients, the use of an “any-positive” strategy, which combined sputum culture with serum GM, had a sensitivity of 43.4% (23/53) and a specificity of 97.4% (37/38). When combined with Aspergillus IgG LFA, the sensitivity significantly improved to 81.1% (43/53, P < 0.001), while maintaining a comparable specificity of 94.7% (36/38, P = 1.000).
A total of 40 IA patients and 20 CAP patients had Aspergillus IgG LFA and BALF GM results. For these patients, the sensitivity and specificity of BALF GM were 65.0% (26/40) and 90.0% (18/20), respectively. The use of an “any-positive” strategy, which combined Aspergillus IgG LFA with BALF GM, significantly improved sensitivity to 87.5% (35/40, P = 0.004), while maintaining comparable specificity to that of BALF GM alone at 85.0% (17/20, P = 1.000).
4 Discussion
This study demonstrated that Dynamiker Aspergillus IgG LFA had good diagnostic performance in non-neutropenic patients with acute and subacute IA (Figure 3), showing equivalent sensitivity and specificity to the Aspergillus IgG ELISA with a 120 AU/mL cut-off, but exhibiting significantly higher specificity compared to the ELISA with an 80 AU/mL cut-off (Table 5). This method demonstrated comparable or superior efficiency to the Aspergillus IgG ELISA, offering a novel and effective tool for the detection of Aspergillus IgG. The combined diagnosis with Aspergillus IgG LFA serves as a valuable supplement to current diagnostic approaches (Table 6).
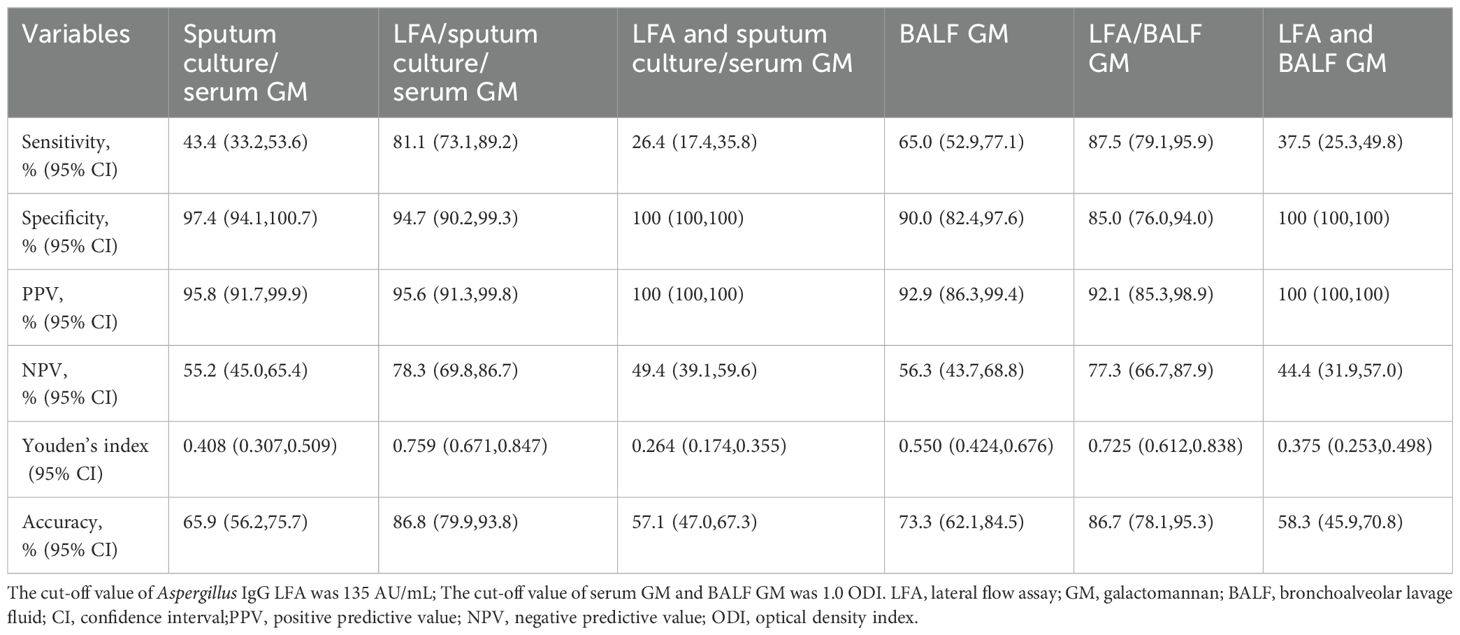
Table 6. Combined diagnostic performances of Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay with other non-invasive tests (sputum culture, serum galactomannan) or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan in invasive aspergillosis patients.
The diagnosis of IA in non-neutropenic patients typically depends heavily on positive results of BALF GM, in which sensitivity and specificity were 55%-74% and 90%-99%, respectively (Zhou et al., 2017; Dai et al., 2021; Lu et al., 2023). In this study, the sensitivity and specificity of the BALF GM were 65.0% and 90.0%, respectively (Table 6). Additionally, the efficacy of BALF PCR in diagnosing IA is supported by sufficient evidence, but its main focus is on the population of hematological malignancies (HM) and/or hematopoietic stem cell/solid organ transplantation (HSCT/SOT). A meta-analysis showed that PCR had higher sensitivity for the diagnosis of IA in non-neutropenic patients such as COPD, solid tumors and autoimmune diseases with prolonged corticosteroid therapy, compared to those with HM and/or HSCT/SOT (88% vs 68%, P < 0.001) (Han et al., 2023). In this study, the sensitivity of BALF NGS in non-neutropenic IA patients was 88.9% (Table 1). The Aspergillus IgG LFA exhibited a sensitivity of 65.1%, which, although lower than that of BALF NGS, was comparable to BALF GM testing. As a non-invasive method, it offers advantages in procedural safety, patient tolerance, and clinical workflow simplification.
Among noninvasive tests, plasma Aspergillus IgG ELISA (Lu et al., 2023) and LFA (Table 1) had higher sensitivities than serum GM and sputum culture in non-neutropenic patients with IA, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of Aspergillus IgG ELISA were 50%-69% and 77%-89% in non-neutropenic patients with IA, respectively (Yu et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2023; Sheng et al., 2024). In this study, the sensitivity and specificity of Aspergillus IgG ELISA for non-neutropenic patients with acute and subacute IA were 60%-69% and 87%-100%, respectively (Table 3). Previous studies included patients with suspected IA, rather than randomly selected patients with CAP, so the specificity was lower than in this study. Piarroux et al. found that the sensitivity and specificity of the LDBio Aspergillus ICT (Lyons, France) in patients with acute and subacute IA were 67% (14/21) and 96%, respectively (Piarroux et al., 2019). In our study, we observed the sensitivity and specificity of the Dynamiker Aspergillus IgG LFA in non-neutropenic patients with acute and subacute IA were 65.1% (41/63) and 97%, respectively (Table 5).
The diagnostic role of Aspergillus IgG LFA in non-neutropenic patients with IA is rarely reported. In this study, we demonstrated that Aspergillus IgG LFA had reliable diagnostic value for non-neutropenic patients with acute and subacute IA (Figure 3). According to the manufacturer’s instructions, 135 AU/mL was determined as the cut-off value. In non-neutropenic patients with IA, it was in better agreement with the ELISA threshold of 80 AU/mL (Table 4). In this study, the optimal cut-off values for non-neutropenic patients with IA were determined to be 126 AU/mL (Figure 3).
The LDBio Aspergillus IgG ICT and Era Biology Aspergillus IgG LFA (Tianjin, China) serve as tools for the qualitative detection of Aspergillus IgG, and the results are determined visually (Piarroux et al., 2019; Stucky Hunter et al., 2019; Rozaliyani et al., 2020; Ray et al., 2022; Singh et al., 2022; Zhu, 2023b). Stucky et al. reported that the sensitivities of the LDBio Aspergillus IgG ICT and ELISA method were 91.6% and 80.5%, respectively; however, the accuracy of quantifying Aspergillus IgG based on the test line strength of ICT was unreliable (Stucky Hunter et al., 2019). Ray et al. determined that the sensitivities of the Aspergillus IgG ELISA and LDBio Aspergillus IgG ICT were 82.4% and 67.6%, respectively, with specificities of 82% and 81% (Ray et al., 2022). Zhu et al. reported that the Aspergillus IgG ELISA and Era Biology Aspergillus IgG LFA had sensitivities of 55.2% and 54.3%, and specificities of 89.1% and 92.7%, respectively (Zhu, 2023b). Therefore, the diagnostic performance of Aspergillus IgG ELISA and LFA is still controversial. At present, relevant studies have taken CPA patients as research objects. There are no studies comparing the diagnostic effectiveness of the two methods in non-neutropenic patients with IA.
Alternatively, the Dynamiker Aspergillus IgG LFA provides a feasible option for the semi-quantitative detection of Aspergillus IgG, and the results can be read in digital form. The Aspergillus IgG LFA had a strong correlation with the Aspergillus IgG ELISA (Figures 2E, F). The sensitivity and specificity of the Dynamiker Aspergillus IgG LFA were comparable to those of the Aspergillus IgG ELISA when using a cut-off value of 120 AU/mL. However, the Dynamiker Aspergillus IgG LFA exhibited significantly higher specificity when the cut-off value of Aspergillus IgG ELISA was set at 80 AU/mL (Table 5).
While the detection of Aspergillus IgG can be a valuable component in diagnosing IA, due to issues such as specificity problems and insufficient sensitivity in acute infections (Table 5), it is generally not sufficient as a standalone test for a definitive diagnosis, particularly in non-neutropenic patients. Clinical interpretation requires the integration of various diagnostic modalities, including radiographic findings, other microbiological evidence, and host risk factor assessment. Therefore, we evaluated the diagnostic value of combining Aspergillus IgG LFA with non-invasive examinations and BALF GM testing (Table 6). Employing the “any-positive” strategy demonstrated that this approach significantly improved the sensitivity of existing diagnostic methods while maintaining comparable specificity. This combined strategy serves as a valuable supplement to current diagnostic approaches, particularly benefiting cardiopulmonary-compromised patients who cannot tolerate invasive bronchoscopic procedures.
Currently, Aspergillus GM LFA is the most frequently reported LFA reagent for the detection of IA. Numerous studies (Mercier et al., 2020; Jani et al., 2021; Mercier et al., 2021) have demonstrated its superior performance in detecting BALF specimens from patients with HM and/or allogeneic stem cell transplantation. In IA patients without HM, the sensitivity and specificity of serum Aspergillus GM LFA were reported to be 50% and 93%, respectively (Alhan et al., 2023); the sensitivity and specificity of BALF Aspergillus GM LFA were 58%-69% and 68%-75%, respectively (Jenks et al., 2019). Consequently, the diagnostic performance of plasma Aspergillus IgG LFA in non-neutropenic IA seems comparable to that of BALF Aspergillus GM LFA. However, further research is required for a comprehensive comparison.
The limitations of this study are attributed to the retrospective study design, samll sample size, and the limited availability of clinical data. A larger prospective multicenter study is necessary to further validate the performance of Aspergillus IgG LFA in broader populations. This study defines diagnostic cut-off values of Aspergillus IgG LFA for patients with IA that need to be further validated in a new IA cohort. Of course, Aspergillus IgG LFA also has potential limitations, such as cross-reactivity with other fungal infections, inability to detect low concentrations of IgG antibodies, and differences among different manufacturers, etc. In addition, there are few studies comparing the diagnostic efficiency of various Aspergillus IgG ICT/LFA detection kits, so comparison of the diagnostic performance of existing kits is a necessary aspect for future work.
5 Conclusion
In summary, the Dynamiker Aspergillus IgG LFA represents a rapid, user-friendly, and highly effective auxiliary tool for the clinical diagnosis of non-neutropenic patients with IA.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Ethics Committees of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because this research was a retrospective, non-interventional study. The specimens used in this study were the surplus plasma from previous clinical studies and clinical routine tests, so the Ethics Committee approved the waiver of informed consent for all participants in this study. All data used in the current study were anonymous.
Author contributions
YaL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. HZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. YW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. CS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YuL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YC: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XC: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YuL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Project of National Science and Technology Major Project (2024ZD0522500), the Project of Natural Science Foundation of China (82270019), and General Program of Clinical Research, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital (2023-LCYJ-MS-18).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1659574.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
EORTC/MSG, The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Mycoses Study Group; ESGCIP, The Study Group for Infections in Critically Ill Patients of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; EFISG, The Fungal Infection Study Group of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; ESICM, The European Society of Intensive Care Medicine; ECMM, The European Confederation of Medical Mycology; MSGERC, The Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium; ISAC, The International Society of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy; ISHAM, The International Society for Human and Animal Mycology.
References
Alhan, O., Saba, R., Akalin, E. H., Ener, B., Ture Yuce, Z., Deveci, B., et al. (2023). Diagnostic efficacy of Aspergillus galactomannan lateral flow assay in patients with hematological Malignancies: A prospective multicenter study. Mycopathologia 188, 643–653. doi: 10.1007/s11046-023-00749-7
Baker, J. and Denning, D. W. (2023). The SSS revolution in fungal diagnostics: speed, simplicity and sensitivity. Br. Med. Bull. 147, 62–78. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldad011
Bassetti, M., Giacobbe, D. R., Agvald-Ohman, C., Akova, M., Alastruey-Izquierdo, A., Arikan-Akdagli, S., et al. (2024). Invasive Fungal Diseases in Adult Patients in Intensive Care Unit (FUNDICU): 2024 consensus definitions from ESGCIP, EFISG, ESICM, ECMM, MSGERC, ISAC, and ISHAM. Intensive Care Med. 50, 502–515. doi: 10.1007/s00134-024-07341-7
Baxter, C. G., Denning, D. W., Jones, A. M., Todd, A., Moore, C. B., and Richardson, M. D. (2013). Performance of two Aspergillus IgG EIA assays compared with the precipitin test in chronic and allergic aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 19, E197–E204. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12133
Dagenais, T. R. and Keller, N. P. (2009). Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 22, 447–465. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00055-08
Dai, Z., Cai, M., Yao, Y., Zhu, J., Lin, L., Fang, L., et al. (2021). Comparing the diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan, serum galactomannanan, and serum 1,3-beta-d-glucan in non-neutropenic respiratory disease patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Med. (Baltimore) 100, e25233. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025233
Delliere, S. and Aimanianda, V. (2023). Humoral immunity against Aspergillus fumigatus. Mycopathologia 188, 603–621. doi: 10.1007/s11046-023-00742-0
Denning, D. W. (2024). Global incidence and mortality of severe fungal disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 24, e428–e438. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00692-8
Donnelly, J. P., Chen, S. C., Kauffman, C. A., Steinbach, W. J., Baddley, J. W., Verweij, P. E., et al. (2020). Revision and update of the consensus definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European organization for research and treatment of cancer and the mycoses study group education and research consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 71, 1367–1376. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz1008
Han, Y., Wu, X., Jiang, G., Guo, A., Jin, Z., Ying, Y., et al. (2023). Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid polymerase chain reaction for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis among high-risk patients: a diagnostic meta-analysis. BMC Pulm Med. 23, 58. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02343-5
Jani, K., Mcmillen, T., Morjaria, S., and Babady, N. E. (2021). Performance of the sona aspergillus galactomannan lateral flow assay in a cancer patient population. J. Clin. Microbiol. 59, e0059821. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00598-21
Jenks, J. D., Mehta, S. R., Taplitz, R., Aslam, S., Reed, S. L., and Hoenigl, M. (2019). Point-of-care diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in non-neutropenic patients: Aspergillus Galactomannan Lateral Flow Assay versus Aspergillus-specific Lateral Flow Device test in bronchoalveolar lavage. Mycoses 62, 230–236. doi: 10.1111/myc.2019.62.issue-3
Liu, L., Gu, Y., Wang, Y., Shen, K., and Su, X. (2021). The clinical characteristics of patients with nonneutropenic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 8, 631461. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.631461
Lu, Y., Liu, L., Li, H., Chen, B., Gu, Y., Wang, L., et al. (2023). The clinical value of Aspergillus-specific IgG antibody test in the diagnosis of nonneutropenic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 29, 797.e791–797.e797. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2023.02.002
Mercier, T., Dunbar, A., Veldhuizen, V., Holtappels, M., Schauwvlieghe, A., Maertens, J., et al. (2020). Point of care aspergillus testing in intensive care patients. Crit. Care 24, 642. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03367-7
Mercier, T., Guldentops, E., Lagrou, K., and Maertens, J. (2021). Prospective evaluation of the turbidimetric beta-D-glucan assay and 2 lateral flow assays on serum in invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 72, 1577–1584. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa295
Page, I. D., Richardson, M., and Denning, D. W. (2015). Antibody testing in aspergillosis–quo vadis? Med. Mycol 53, 417–439. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myv020
Piarroux, R. P., Romain, T., Martin, A., Vainqueur, D., Vitte, J., Lachaud, L., et al. (2019). Multicenter evaluation of a novel immunochromatographic test for anti-aspergillus IgG detection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 9, 12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00012
Ray, A., Chowdhury, M., Sachdev, J., Sethi, P., Meena, V. P., Singh, G., et al. (2022). Efficacy of LD bio aspergillus ICT lateral flow assay for serodiagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Fungi (Basel) 8, 400. doi: 10.1183/13993003.congress-2022.2719
Rozaliyani, A., Rosianawati, H., Handayani, D., Agustin, H., Zaini, J., Syam, R., et al. (2020). Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in post tuberculosis patients in Indonesia and the role of LDBio aspergillus ICT as part of the diagnosis scheme. J. Fungi (Basel) 6, 318. doi: 10.3390/jof6040318
Sheng, L., J., W., Yao, Y., Zhou, J., and Zhou, H. (2024). Value evaluation of quantitative aspergillus fumigatus-specific IgG antibody test in the diagnosis of non-neutropenic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Infect. Drug Resist. 17, 2043–2052. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S460513
Singh, S., Choudhary, H., Agnihotri, S., Sehgal, I. S., Agarwal, R., Kaur, H., et al. (2022). LDBio Aspergillus immunochromatographic test lateral flow assay for IgG/IgM antibody detection in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: Single-centre evaluation and meta-analysis. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 40, 204–210. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmmb.2022.03.002
Stucky Hunter, E., Richardson, M. D., and Denning, D. W. (2019). Evaluation of LDBio aspergillus ICT lateral flow assay for IgG and IgM antibody detection in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 57, e00538–19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00538-19
Ullmann, A. J., Aguado, J. M., Arikan-Akdagli, S., Denning, D. W., Groll, A. H., Lagrou, K., et al. (2018). Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 24 Suppl 1, e1–e38. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.01.002
Yu, Q., He, J., Xing, B., Li, X., Qian, H., Zhang, H., et al. (2020). Potential value of serum Aspergillus IgG antibody detection in the diagnosis of invasive and chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in non-agranulocytic patients. BMC Pulm Med. 20, 89. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-1125-y
Zhou, W., Li, H., Zhang, Y., Huang, M., He, Q., Li, P., et al. (2017). Diagnostic value of galactomannan antigen test in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from patients with nonneutropenic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 55, 2153–2161. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00345-17
Zhu, R. Z., Cheng, J., Luo, Y., Qiu, W., Huang, J., Jiang, Y., et al. (2023b). Diagnostic laboratory features and performance of an aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay in a chronic pulmonary aspergillosis cohort. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, e0026423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00264-23
Keywords: acute invasive aspergillosis, subacute invasive aspergillosis, non-neutropenic patients, Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay, diagnosis
Citation: Lu Y, Zhong H, Wang Y, Sun C, Li Y, Cai Y, Cai X, Wang J, Zhong J and Su X (2025) Evaluation of a novel Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay for the diagnosis of non-neutropenic patients with acute and subacute invasive aspergillosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1599425. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1599425
Received: 25 March 2025; Accepted: 04 June 2025;
Published: 20 June 2025; Corrected: 25 July 2025.
Edited by:
Gloria M. González-González, Autonomous University of Nuevo León, MexicoReviewed by:
Marina Bubonja-Sonje, University of Rijeka, CroatiaMaría Guadalupe Frías De León, Hospital Regional de Alta Especialidad de Ixtapaluca, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Lu, Zhong, Wang, Sun, Li, Cai, Cai, Wang, Zhong and Su. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Su, c3V4aW5qc0AxNjMuY29t
 Yajie Lu
Yajie Lu Huanhuan Zhong2,3
Huanhuan Zhong2,3 Chao Sun
Chao Sun Xiaomin Cai
Xiaomin Cai Xin Su
Xin Su