- 1Hammad Department of Medicine, Liaquat National Hospital and Medical College, Karachi, Pakistan
- 2Department of Medicine, Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Pakistan
- 3Department of Medicine, Saidu Medical College, Swat, Pakistan
- 4Department of Medicine, Dow Medical College, Karachi, Pakistan
- 5Department of Medicine, Karachi Medical and Dental College, Karachi, Pakistan
- 6Department of Medicine, Dow International Medical College, Karachi, Pakistan
- 7Department of Medicine, Niazi Medical and Dental College, Sargodha, Pakistan
- 8Department of Medicine, Rashid Latif Medical College, Lahore, Pakistan
- 9Department of Medicine, Women Medical and Dental College, Abbottabad, Pakistan
- 10Community Department, University of Bakht Alruda, Ad Duwaym, Sudan
Traditionally, Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), a pivotal class of drug, mimics the actions of endogenous Glucagon-like peptide-1, which have been found to be remarkable in the treatment of type 2 diabetes alongside other comorbidities. GLP-1 receptors being widely available in the different organs and tissues such as the brain, lung, pancreas, stomach, heart, and endometrium has explained the broader therapeutic application of GLP-1RA. The recent studies have explored the physiological effects of GLP-1RA on body organs, establishing them as a potential therapeutic option for a wide range of diseases. Activation of GLP-1 receptors contribute to regulation of blood glucose levels, weight management, cardiovascular health, and potential neuroprotection, while also having a positive influence on musculoskeletal health. This review has emphasized the expanded role of GLP-1RA by highlighting the most significant and notable studies. While GLP-1RA has proven clinical efficacy, the need for more comprehensive studies, to ensure their long-term safety, is essential to optimize their therapeutic role and improve patient outcomes on a global scale. Addressing the significant gap for research on cost effectiveness of these drugs is also crucial for their accessibility in comparison to other drugs. Nevertheless, the limited data available calls for a platform for future research to carry out the expanded therapeutic effects of GLP-1RA.
1 Introduction
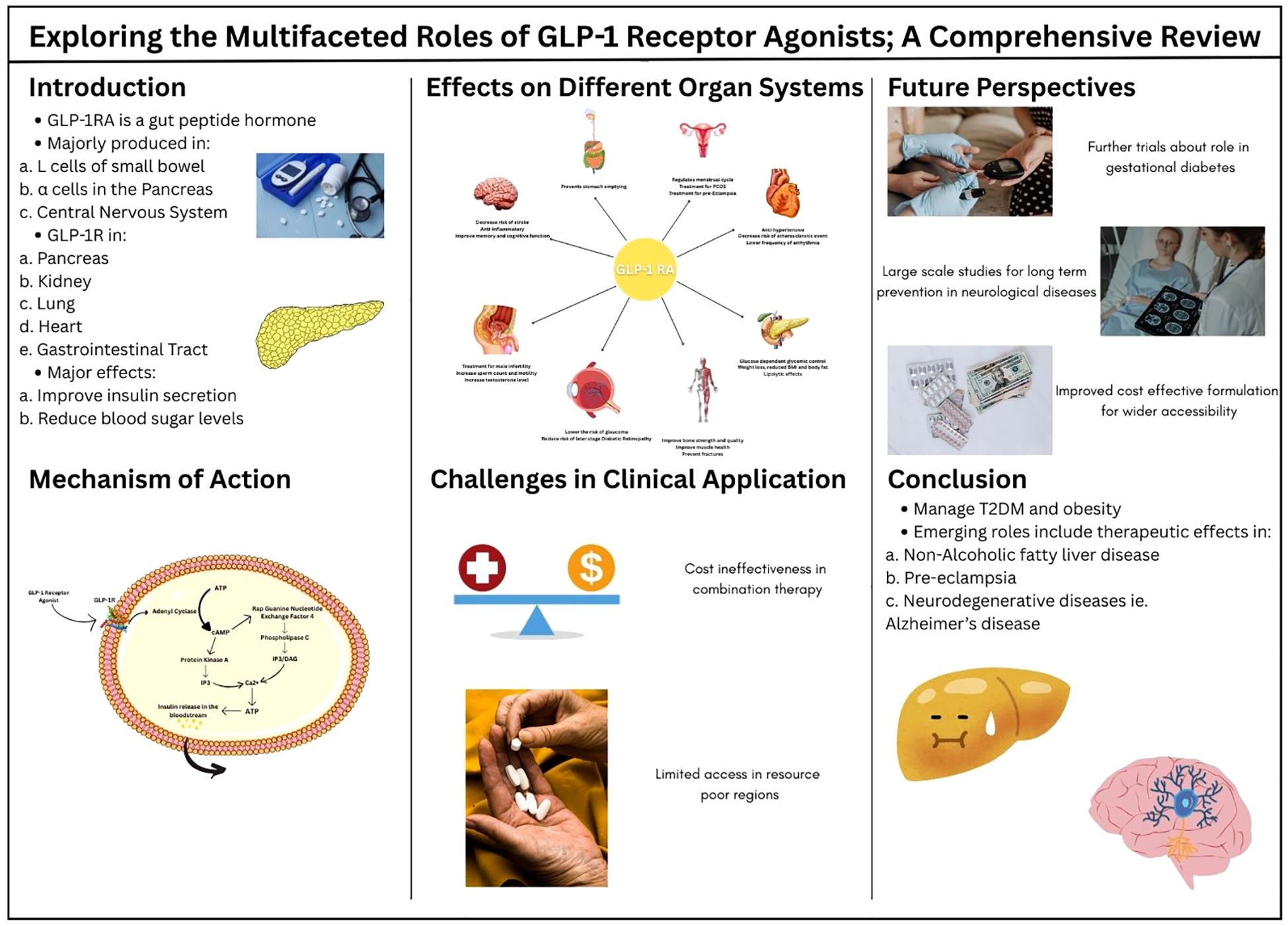
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a gut peptide hormone that functions as an incretin that plays a key role in controlling satiety and various other physiological functions. It is majorly found circulating in the blood as GLP-1(7-36) amide that is produced primarily from three tissues of the human body: enteroendocrine L cells in the distal small bowel, α cells in the pancreas, and the central nervous system (1, 2). GLP-1 acts by coupling with the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R), which is a 463 amino acid hepta helical G- protein coupled receptor. This receptor is found on pancreatic α and β cells has many effects, a few detailing, regulating glucose levels in the body, improving myocardial function and cardiac output, and delaying gastric emptying.GLP-1 interacts with GLP-1R resulting in the glucose-dependent release of insulin, lowering the plasma glucose levels in the body. In addition, GLP-1 indirectly inhibits glucagon secretion by stimulating release of insulin and somatostatin or by directly engaging with GLP-1R found on α cells of the pancreas (2). GLP-1R are also found in smooth muscle cells in the walls of arteries in kidneys and lungs, myocytes of the sinoatrial node of the heart, and Brunner’s glands of gastrointestinal tract (3). The wide distribution of GLP-1R underscores the variety and significance of its biological functions. Moreover GLP-1R agonists (GLP-1RAs) interact with GLP-1R inducing similar effects as that of GLP-1.
Surprisingly, it took approximately 20 years from the discovery of GLP-1 to the authorized approval of worldwide utilized GLP-1 RAs. Due to the rapid renal clearance of small peptides like GLP-1, along with its deactivation by dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4), development of stable peptides, with an increased resistance to DPP4 was required (4). In addition, the side effects recorded in clinical trials of GLP-1RAs development programs, nausea and vomiting, prolonged the launch of the drugs (3, 4) Liraglutide and semaglutide are two of the most potent GLP-RAs. Liraglutide was selected as the foremost GLP-1 RA drug to be used for once daily dosing due to its high receptor potency and pharmacokinetics (5). GLP-1 and GLP-1RAs can induce many other effects according to the regions where GLP-1 receptors are found. GLP-1RAs are currently used in treatment of cardiovascular diseases, neurological diseases, metabolic dysfunctions, obesity, peri operative procedures, infertility and many more (6).
The origin of GLP-1 and its physiological pathway was discovered in the 1980s by the decoding of nucleotide sequences of mammalian preproglucagons, the precursors of proglucagon (4). The post translational processing of proglucagon resulted in the formation of glucagon and Glicentin-related pancreatic polypeptide (GRPP) (7). Furthermore, when processed in the intestine, proglucagon yields glicentin, which may be catalyzed further to oxyntomodulin (7). Within minutes of food ingestion, more prominently in carbohydrates and fats, L cells found in the small bowel and colon release GLP-1 into the bloodstream. The exact mechanism with which this occurs is unclear, but it is suspected that neural factors play a key role in this mechanism.
When GLP-1 interacts with GLP-1R, this triggers cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) formation and initiates subsequent pathways (2). A comprehensive understanding of the systemic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists is crucial because these medications impact multiple organ systems beyond their primary role in glucose regulation. GLP-1 RAs not only improve insulin secretion and reduce blood sugar levels, but they also affect appetite control, weight management, and cardiovascular health. A deeper knowledge of their broad effects can optimize their therapeutic use in treating conditions like type 2 diabetes, obesity, and heart disease, while minimizing side effects and improving patient care. This narrative review aims to explore the effects of GLP-1RAs on the multiple systems of the body.
2 Methodology
A structured literature search was conducted using PubMed/MEDLINE and Google Scholar, with the Boolean search string: (“GLP-1 receptor agonist” OR “GLP-1RA”) AND (“multifaceted roles” OR “pleiotropic effects”). The initial search yielded 1,929 records (PubMed: 29; Google Scholar: 1,900). After removing 420 duplicates and excluding 23 articles prior to screening, 1,509 records remained for title and abstract review. Of these, 1,200 studies were excluded due to lack of relevance or unsuitable study design. The remaining 309 articles underwent full-text assessment. An additional 202 articles were excluded for the following reasons: irrelevant study population (n=60), unrelated interventions (n=90), insufficient or incomplete data (n=52), and language limitations (non-English). Ultimately, 107 studies were included in this narrative review.
The selection process is illustrated in the flow diagram (Figure 1).
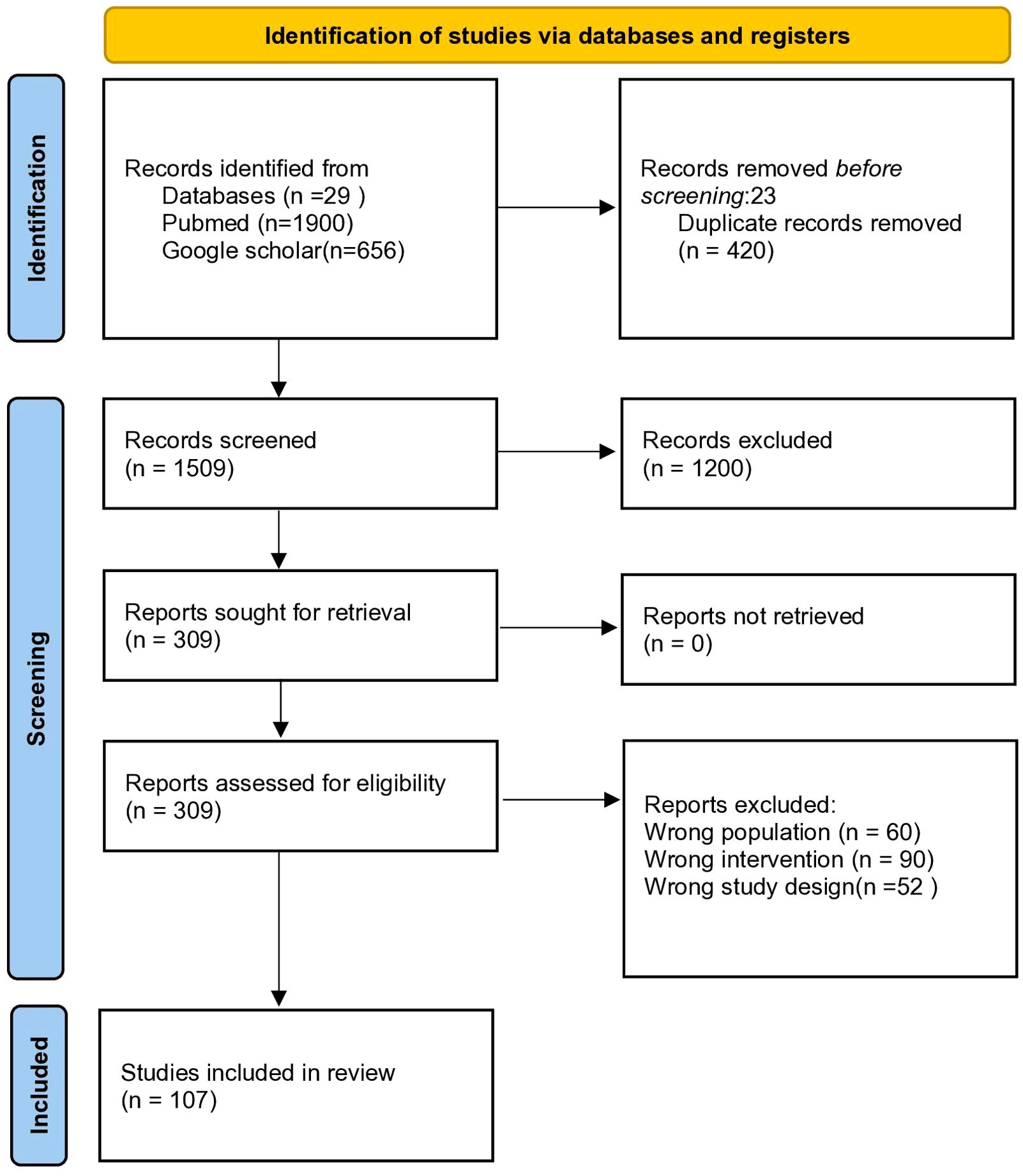
Figure 1. PRISMA-style flow diagram illustrating the literature selection process for this narrative review on the multifaceted roles of GLP-1 receptor agonists.
3 Mechanism of action
GLP-1RA mimics the role of GLP-1, a hormone released by the intestines after consumption of glucose-rich foods (8). GLP-1RA is administered subcutaneously to bypass the digestive system, except for semaglutide which is given orally (9). It binds to the GLP-1 receptor in various metabolic sites, mainly the pancreas where it stimulates them for the release of insulin by the β cells. As a result, glucose uptake by the intestine and the muscles increases (10). It also plays a role in inhibiting β cell apoptosis, which is common in conditions like Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and enhancing their growth (11). Moreover, it inhibits glucagon release from the α cells of the pancreas and promotes slow stomach emptying, hence giving the feeling of fullness and reduces body weight (12).
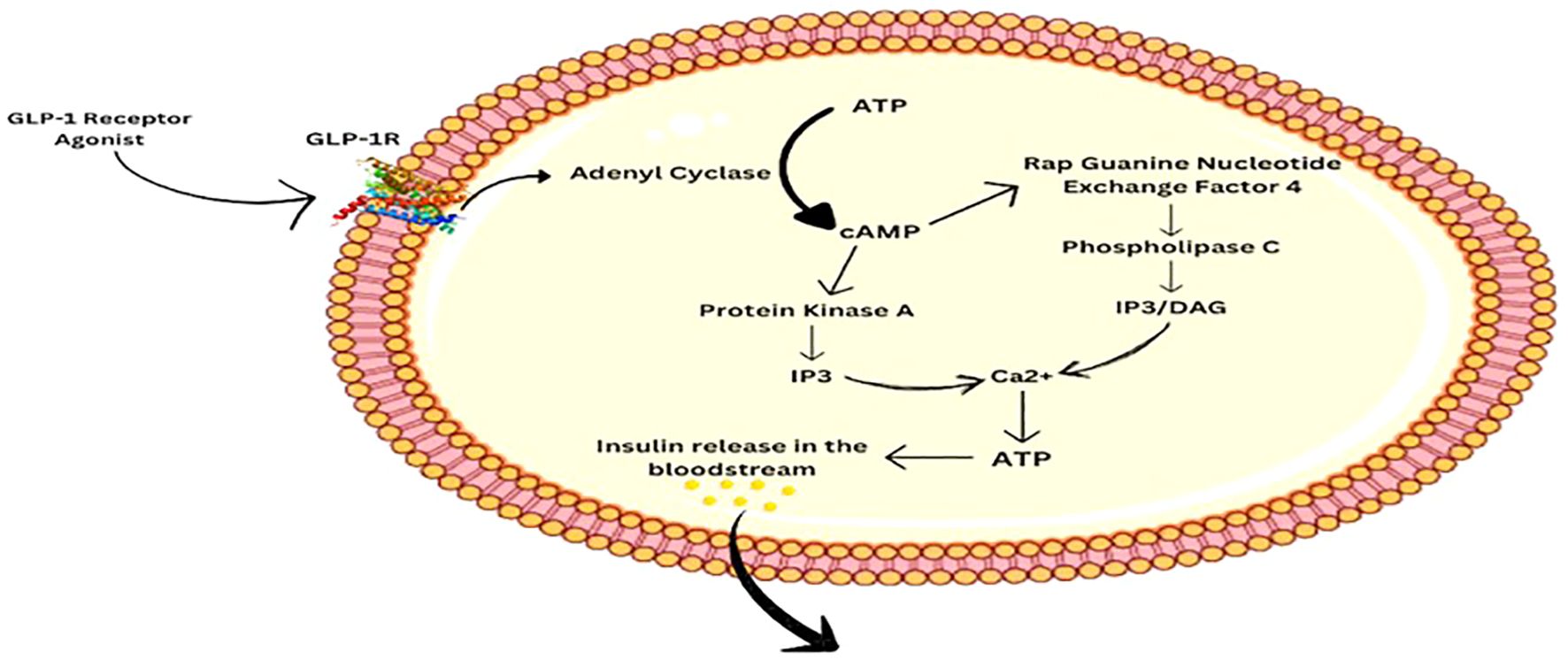
GLP-1R is a G protein-coupled receptor. When the hormone or the receptor agonist binds to it, a series of cascade effects occur, eventually leading to the release of Ca2+. The binding of GLP-1RA to GLP-1R activates adenyl cyclase, which facilitates the conversion of ATP to cAMP. cAMP then activates Protein Kinase A (PKA) and Rap Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor 4 (RGNEF4), both of which function for rising intercellular Ca2+ levels. PKA causes membrane depolarization and eventually Ca2+ release via the Inositol Triphosphate pathway (IP3). RGNEF4 aids in Ca2+ release via IP3 as well as the Diacylglycerol (DAG) pathway by activating Phospholipase C. Elevated levels of calcium in the intracellular space promote ATP production, which then facilitates the release of Insulin into the bloodstream (6, 10) as shown in Figure 2. Eventually, it leads to uptake of glucose by the body cells and decreasing the level in the blood.
4 Efficacy of GLP1 RA
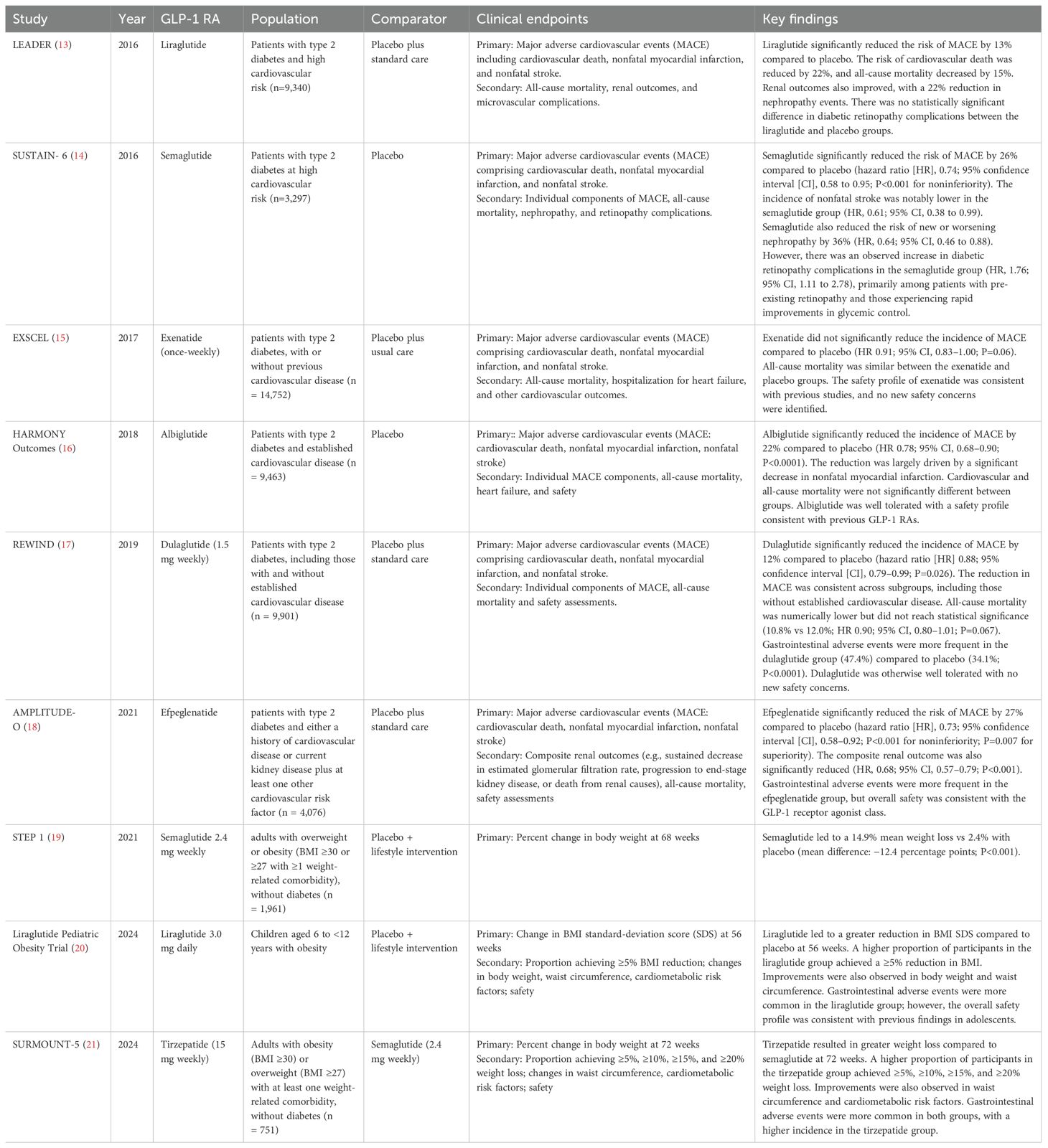
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have demonstrated significant clinical benefits that extend well beyond glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Emerging evidence from key clinical trials highlights their multifaceted roles across various physiological systems, including cardiovascular, renal, hepatic, and neurological domains, as shown in Figure 3. These agents exhibit anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective effects, suggesting a broader therapeutic potential.
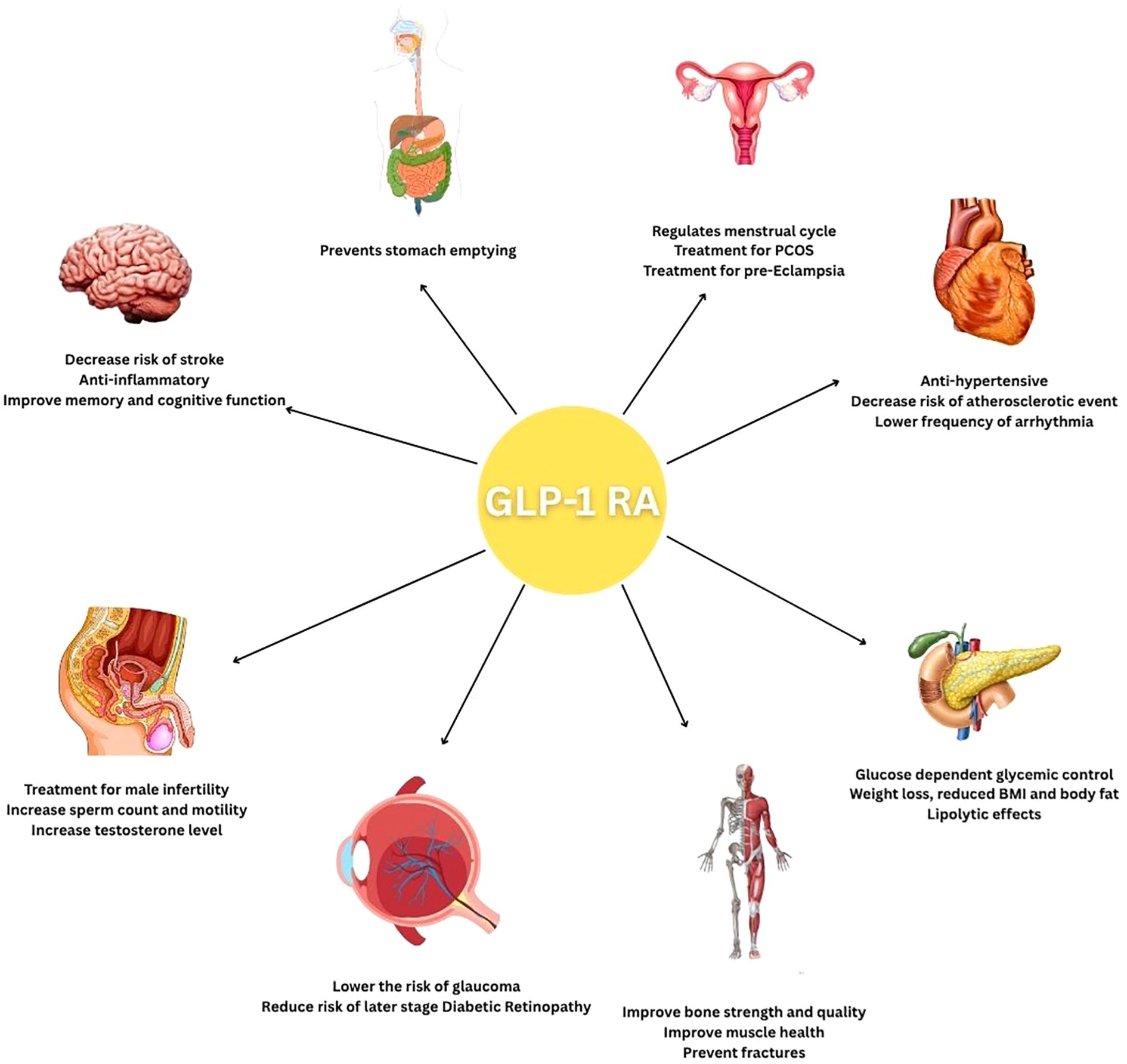
Figure 3. A cartoon summarizing the disease groups and organs in which GLP-1 receptor agonists are expected to be effective.
Table 1 summarizes major clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of GLP-1RAs across different organ systems, illustrating the expanding scope of their clinical utility.
4.1 Central nervous system effects
GLP-1R is distributed throughout various regions in the brain, with the highest concentrations being found in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex, areas mainly responsible for cognitive function, memory improvement, and learning (10). The receptors are also predominantly found in the brainstem, hypothalamus, cerebellum, and limbic system (22), as well as in microglia and astrocytes (23). The GLP-1RA needs to cross the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) to act on the brain and exert neuroprotective effects (12, 22). Drugs like exenatide and lixisenatide have a greater penetration ability as compared to liraglutide (10).
GLP-1RA plays a key role in promoting CNS health in conditions like T2DM and lowering the risk of stroke (23). After crossing the BBB, the GLP-1RA binds to the GLP-1R and mimics the action of the GLP-1 hormone, stimulating the intracellular accumulation of cAMP, which via the action of PKA/RGNEF4 results in neuroprotective effects (10). However, the exact pathway is still unknown.
In the brain, GLP-1RAs perform anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic functions (12). By reducing inflammation, Liraglutide protects the neuron from inflammatory damage and stimulates neural cell and stem cell proliferation (22), as well as neurite outgrowth, which is important for synaptic functions that play a key role in improving memory in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Parkinson’s Disease (PD). GLP-1RA also minimizes oxidative stress, which is a significant factor in the progression of neurodegenerative diseases (24). They attain this by inhibiting the intracellular accumulation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and increasing the expression of glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase, thus improving the adverse cellular changes induced by ROS. Furthermore, the expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is enhanced, which is essential for the proper functioning of brain neurons (22). It inhibits neural apoptosis and increases survival and regeneration, thus forming new connections, ultimately contributing to improved cognitive function (12, 25)
Appetite regulation is a common function of many GLP-1RAs, which act on the hypothalamus- the center of hunger and energy balance- and promote feelings of fullness, eventually leading to weight loss (26). Toxic accumulation of Amyloid β protein, commonly associated with Parkinson’s Disease (27), disrupts Long Term Potentiation (LTP) (24); however, it can be reversed by GLP-1RA like Exendin-4 (Ex-4), leading to improvement in cognitive functions and memory (22). Additionally, Ex-4 also inhibits MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) toxin, mainly responsible for the destruction of dopaminergic neurons in Substantia Nigra in the brain, which is the main cause of Parkinson’s Disease (24). By improving insulin signaling, GLP-1RAs reduce insulin resistance, leading to improvements in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease (6). They are not only protective in the early stages of Alzheimer’s Disease but can also reverse key pathophysiological features like amyloid β protein and tau hyperphosphorylation, thereby protecting the neurons from further damage (10). Liraglutide also has antidepressant effects, as seen in many patients with neurodegenerative diseases, by preventing the loss of insulin receptors (28). Exenatide has shown effectiveness in reducing motor defects in Parkinson’s Disease by preserving dopaminergic neurons and enhancing neurotransmitter function, thus improving the overall outcome (29).
4.2 Cardiovascular system effects
GLP-1 receptor agonists have a very close connection with cardiovascular outcomes and prevention of many diseases. It has been proven that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists control blood glucose concentrations through a multitude of mechanisms, such as increased satiety, slow stomach emptying, decreased glucagon secretion, and increased insulin synthesis/secretion. Patients with T2DM and a high cardiovascular risk might reduce their risk of atherosclerotic events via the use of GLP-1RA (30). GLP-1RAs lower plasma lipid levels and lower blood pressure, both of which contribute to a reduction of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (31). The main causes of coronary heart disease, end-stage renal failure, acquired blindness from central retinal artery occlusion (32). and various neuropathies are accelerated atherosclerosis and microvascular problems. These elements could be contributing to the high mortality rates and disabilities seen in those with diabetes (33).
Many physicians and researchers have become interested in the potential cardiovascular advantages of GLP-1 and GLP-1-based medication since the discovery of GLP-1Rs on cardiomyocytes. Small-scale clinical trials revealed that GLP-1 and GLP-1-based medicines may have positive effects on low-grade inflammation, blood pressure, cholesterol, and microcirculation (34). More significantly, GLP-1RAs have been shown in large, randomized CV outcome trials (CVOTs) to lower CVD in patients with type 2 diabetes (34). Liraglutide and Semaglutide most effectively lower Hb1Ac and regulate glucose thereby reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes which is a main cause of cardiovascular problems. Liraglutide has a half-life of 13 hours in humans and semaglutide has a half-life of 160 hours (35). Recent cardiovascular outcome trials involving GLP-1 receptor agonists, especially liraglutide and semaglutide, have shown a significant reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) among patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk for cardiovascular disease (14, 36). These effects are thought to result from anti-atherosclerotic actions, possibly mediated by anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Humans treated with liraglutide have been shown to have reduced inflammation, which is linked to decreased levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and CD163, a cluster of differentiation (37). Atherosclerosis is a consequence that diabetic people may experience as a result of injury to their vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) (38). GLP-1RAs help improve endothelial damage and slow the advancement of cardiovascular disorders. They exert direct positive impacts on the coronary vascular endothelium, such as oxidative stress reduction and increase in nitric oxide, which at least partially account for their antihypertensive and antiatherosclerotic properties (39). LDL and C-reactive protein (CRP) lipid distribution in atherosclerosis were improved by liraglutide with metformin in newly diagnosed diabetic patients following standard statin therapy (40).
Due to their various modes of action, which include vasodilation, natriuresis, glucose and weight control, and direct cardioprotective effects, GLP-1 receptor agonists have therapeutic potential for treatment of heart failure (41). Ischemic heart disease, dilated cardiomyopathy, valvular heart disease, and hypertensive heart disease are among the main causes of heart failure (42).
Obesity is a major cause of cardiovascular diseases. It is linked to elevated levels of fibrinogen and C-reactive protein, diabetes, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, all of which raise the risk of CVD events (43). Obesity has been demonstrated to raise the risk of high blood pressure in addition to CVD (43). Treating obesity can be greatly beneficial for the prevention of CVD. Agents that have been shown to be remarkably effective in promoting weight loss and improving metabolic outcomes include liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide. These agents have been supported by important clinical trials, including Satiety and Clinical Adipose Liraglutide Evidence (SCALE), Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) program trials, and Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity (SURMOUNT-1) (44). Hence, these agents can prevent obesity, thereby reduce CVD.
It is less evident how GLP-1 agonists directly affect arrhythmias, some studies suggest they may reduce frequency of arrythmias because their favorable effects on metabolism and over all cardiovascular health. Arrhythmia risk may be lowered, by better glycemic control and a decrease in obesity-related cardiovascular risk factors. It is less clear how GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) directly influence arrhythmia risk; however, emerging evidence suggests a potential protective effect. Some studies indicate that GLP-1 RAs may help reduce the frequency of arrhythmias due to their beneficial impact on metabolic parameters and overall cardiovascular health (45) A recent systematic review and meta-regression analysis found that semaglutide significantly reduced the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes (46). These findings highlight the need for further investigation into the antiarrhythmic potential of GLP-1 RAs.
One of the main causes of the excess cardiovascular risk in diabetics is the coexistence of hypertension. Through a diuretic mechanism and other effects on the kidneys, GLP-1 can lower blood pressure. On a different level, GLP-1RAs reduce the concentration of angiotensin II (Ang II), which lowers arterial hypertension in T2DM and improves systemic insulin sensitivity (31). Regarding the enhancement of hard cardiovascular outcomes while preserving cardiovascular safety, GLP-1RAs have proved encouraging efficacy.
4.3 Gastrointestinal effects
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is greatly impacted by GLP-1RAs. They prevent the stomach from emptying, and this helps in regulating postprandial glucose levels. Higher doses cause more inhibition in this dose-dependent effect. Tachyphylaxis, which reduces gastrointestinal side symptoms such nausea and vomiting, might result with prolonged use. GLP-1RAs work by way of neural pathways, specifically the vagus nerve. On the other hand, gastric emptying is not considerably impacted by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), emphasizing the distinct functions of these incretins in GI function (47).
A study examined the potential advantages and disadvantages of using GLP-1RAs to help obese but non-diabetic patients lose weight. With 8,847 participants over eight randomized controlled trials (RCTs), it was shown that 375 out of 1,000 people lost 10% of their body weight over the course of two years, with a net benefit probability of 0.91 in the second year and 0.97 in the first. The study did, however, also highlighted several negative side effects, including constipation (118 occurrences), diarrhea (100 events), and abdominal pain (41 events per 1,000) (48).
Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are among the gastrointestinal adverse effects linked to GLP-1 RAs. These effects are influenced by factors such as dosage and background medications. A systematic analysis reported that using metformin alongside GLP-1RAs in type 2 diabetes management increases the risk of nausea and vomiting. Additionally, lixisenatide was associated with fewer gastrointestinal symptoms compared to exenatide, while long-acting GLP-1RAs generally caused less nausea and vomiting but more diarrhea than short-acting agents (49). Among individual drugs, liraglutide has been noted to carry a relatively higher risk of nausea and vomiting. Nevertheless, compared to placebo, none of the GLP-1RAs significantly increased the risk of serious gastrointestinal complications (50).
4.4 Metabolic effects
GLP-1RA are emerging as highly versatile drugs, as their unraveling features now adds to a broader potential in future. GLP-1RA has shown explicit effects in controlling blood glucose levels. Unlike sulfonylureas, which stimulate insulin secretion independently of blood glucose and can lead to hypoglycemia, GLP-1RAs improve glycemic control in a glucose-dependent manner, thereby minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia. They achieve this by signaling a cascade consisting of cAMP and protein kinase A and the closure of K ATP gates, induced by PKA cycle, marks the initiation of glucose dependent insulin secretion into the bloodstream (51).
Also, GLP-1 RA seems to regulate glucose homeostasis by exhibiting glucagonostatic effects meaning suppression of glucagon by acting on pancreatic α cells, which in turn reduce hepatic production of glucose (52). Interestingly, GLP-1 receptors are also found on pancreatic delta cells, producing somatostatin, an inhibitory hormone, further dampening glucagon secretion (53). A study conducted on rodents has also revealed that GLP-1RAs can exert glucagonotropic effects depending on glucose levels, adding complexity to their role in glucagon regulation (52). Moreover, these drugs promote the neogenesis of pancreatic β cells by enhancing B cell proliferation and reducing apoptosis, contributing to the preservation and expansion of insulin-secreting cells (54).
Liraglutide has been reported to lower the BMI by approximately 5% (55) and semaglutide with an average of 15% compared to a placebo (56). A recent comparison of GLP-1RAs versus placebo in both pediatric and adult populations demonstrated the significant efficacy of GLP-1RAs in promoting weight loss, highlighting their potential across diverse age groups (57).
Furthermore, a statistical analysis was executed to unearth the potential of lixisenatide, both alone and in combination with insulin, on gastric emptying. The study confirmed that lixisenatide exerts a more pronounced effect on postprandial glycemic variations with a modest effect on fasting glucose levels. This is largely attributed to glucagon suppression and slow gastric emptying. In contrast, insulin primarily affects fasting glucose levels with minimal influence on post meal glucose levels and no relation to gastric emptying (58).
The improved regulation of glycemia by GLP-1RA, along with their ability to reduce lipid synthesis, enhanced beta oxidation of free fatty acids and autophagy of fat cells contributes to their lipid modulation properties (59). It has been proposed that GLP 1 exerts a lipolytic effect by breaking down triglycerides into free fatty acids in pancreatic β cells. This process aids in ATP production, which subsequently stimulates insulin secretion (60).
Oral semaglutide has been found to improve fasting blood glucose levels in a trial conducted over a 12 week period with improved levels of triglycerides, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), low- density lipoprotein (LDL) and apolipoprotein B48 (ApoB48) and no change in high density lipoprotein (HDL) (61). Furthermore, type 2 diabetes has been linked to an increased risk of visceral fat, including epicardial adipose tissue (EAT), which expresses GLP-1 and GLP-2 receptors. In a study of 80 obese people with type 2 diabetes receiving semaglutide and dulaglutide, a 20% reduction in the thickness of EAT was observed (62) One meta-analysis demonstrated the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs, showing reductions in blood pressure and lipid profile, with a significant increase in HDL levels (63).
4.5 Musculoskeletal effects
T2DM raises the risk of fractures, poor bone repair, and other factors that lead to brittle bones (64). GLP-1RAs have demonstrated encouraging positive benefits on bone strength and quality. The blood flow to bones is vital for skeletal health, and GLP-1RAs may improve it, while the precise processes are not entirely known. This is especially important for older people with type 2 diabetes, as they have an increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures (65). GLP-1 receptor analogs, such as exenatide, have a beneficial effect on bone health in women with type 2 diabetes who have gone through menopause (66). The anti-resorptive effects of the therapy were demonstrated by lower RANK and RANKL levels and increased osteoprotegerin (OPG) levels. Significant weight reduction was seen, but bone mineral density (BMD) did not change. This implies that GLP-1RAs may support BMD maintenance during weight loss, providing a dual advantage in the management of diabetes (67). GLP-1R agonists have shown potential benefits in muscle health by decreasing muscle atrophy and inflammation, as well as improving muscle microvasculature and endurance (68). They suppress muscle atrophic factors like myostatin and promote myogenic factors, which can enhance muscle protein synthesis and mitochondrial function. These effects suggest that GLP-1R agonists may mitigate the muscular deleterious effects associated with conditions like idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (68). GLP-1RAs are essential for preventing fractures in people with T2DM because they greatly increase bone mass, trabecular and cortical architecture, and total bone strength. They counteract the imbalance between bone production and resorption that is typical in type 2 diabetes by promoting bone formation and enhancing blood supply to bones. Although skeletal effects are beneficial in preclinical investigations, clinical evidence on fracture risk is still uncertain. To better understand these connections and evaluate GLP-1RAs’ potential as a therapeutic approach for treating skeletal frailty in diabetes patients, especially the elderly more extensive long-term research is required (65). GLP-1RAs stimulate the production of new bone while blocking its resorption, increasing BMD and improving bone quality. Nutrient absorption may be hampered by gastrointestinal side effects, which would exacerbate their impact on musculoskeletal health. To fully understand GLP-1RAs’ effects on bone metabolism in a range of patient groups, particularly regarding osteoporosis and fracture risk management, more randomized controlled studies are necessary (69).
A study that investigated the effects of insulin and GLP-1RAs (exenatide and dulaglutide) on BMD over a 52-week duration gathered 70 individuals with type 2 diabetes. When compared to a placebo, exenatide dramatically raised BMD at the femoral neck and whole hip. Femoral neck BMD decreased after using dulaglutide, although not as much as when using a placebo. Moreover, insulin glargine increased BMD. The study emphasizes the necessity of more investigation to comprehend the processes behind these impacts on fracture risk and bone metabolism (70).
It has been demonstrated that GLP-1 agonists significantly increase the mass of the femur and vertebrae (71). Most of the clinical evidence points to GLP-1RAs as having no discernible effect on BMD or fracture rates, indicating that they have a neutral effect on bone health. For people with diabetes who are more likely to have a bone fracture, this neutrality is essential. Sclerostin (SOST) mRNA levels have been discovered to be lowered by GLP-1, which is known to inhibit the formation of new bone. This decrease could encourage osteoblast development and differentiation, which would benefit the skeleton (69).
In individuals with T2DM, the risk of fractures was assessed using a network meta-analysis and systematic review to determine the relationship between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i), GLP-1 RAs, and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i). With a median follow-up duration of 26 weeks, a total of 177 randomized controlled trials involving 165,081 participants were included. Comparison with other antidiabetic medicines like insulin, metformin, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, α -glucosidase inhibitors placebo showed no statistically significant increase in fracture risk for DPP-4i, GLP-1 RAs, or SGLT-2i. The investigation specifically showed that these drugs did not increase the risk of any fractures, confirming their safety profile in clinical practice (72).
4.6 Ophthalmological effects
4.6.1 Glaucoma
GLP-1R agonists exhibit anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, suggesting they could also be beneficial in neurodegenerative diseases (73). Glaucoma is one such disease, characterized by the degeneration of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and optic nerve atrophy, leading to progressive and permanent vision loss. It is the leading cause of irreversible blindness globally, with projections indicating it could affect over 100 million individuals by 2040 (74). Regardless of the glaucoma type, all current treatments focus on lowering intraocular pressure (IOP) by either reducing aqueous humor production or enhancing its outflow (75).
A recent registry-based case-control study, summarized in Table 2, involving 1,961 patients found that the use of GLP-1R agonists is linked to a lower risk of glaucoma (Sterling et al., 2021 (76). This finding strongly encourages further investigation into the potential of agents that enhance GLP-1R signaling as treatments for glaucoma (79).
The use of GLP-1 agonists has been associated with a reduced incidence of glaucoma in diabetic patients (80). A study utilizing a national database found that individuals treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists had a significantly lower risk of developing glaucoma compared to those who were not on these medications. This study, which included around 6,400 patients, employed Cox regression analysis and confirmed that diabetic patients using GLP-1R agonists—such as exenatide, liraglutide, dulaglutide, and semaglutide were less likely to receive a new glaucoma diagnosis (76). A study shows that GLP-1 receptor agonists show a notably reduced incidence of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), ocular hypertension, and the requirement for first-line glaucoma treatments compared to metformin in individuals with type 2 diabetes (80). A summary of clinical studies elucidating the use of antidiabetics against glaucoma is given in Table 2.
4.6.2 Retinal disease
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the most prevalent microvascular complication of diabetes and the leading cause of preventable blindness among working-age individuals (81). Currently, nearly 100 million people globally are affected by DR, and as the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, this number is expected to grow, posing a significant burden on public health (82).
The secretion of VEGF and IL-6 is crucial in diabetic eye diseases (83). In a study, cells were treated with 30 mM glucose with or without liraglutide (50, 100 nM) for 24 hours, after which VEGF-A and IL-6 levels were measured using ELISA. The level of VEGF-A significantly increased from 75.6 to 138.6 pg/mL in high glucose (HG)-stimulated human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs) but decreased to 102.1 pg/mL and 92.5 pg/mL with 50 nM and 100 nM liraglutide, respectively. Similarly, IL-6 levels in the control, HG, 50 nM liraglutide, and 100 nM Liraglutide groups were 135.2, 256.8, 191.6, and 172.9 pg/mL, respectively. These findings indicate that Liraglutide suppresses the release of VEGF-A and IL-6 in HG-stimulated HRECs (84). Liraglutide. Research indicates that VEGF levels in the serum of patients with DR progressively rise as the disease worsens, highlighting its critical role in the development of DR and its correlation with disease severity. Additionally, factors secreted by retinal cells, like IL-6, promote the proliferation of different retinal cell types, contributing to the formation of new blood vessels and the progression of diabetic retinopathy (84).
A meta-analysis was done which indicates that albiglutide is linked to a higher risk of early-stage DR compared to placebo, while showing a reduced risk of late-stage DR compared to insulin (85) Furthermore, the other six FDA-approved GLP-1RAs do not demonstrate a statistically significant association with DR. To fully understand the differences in the mechanisms and long-term effects of GLP-1RAs on the retina, a combination of clinical trials and mechanism studies is necessary (85). The results from the SUSTAIN 6 trial indicated that patients treated with semaglutide experienced a significantly higher incidence of DR compared to those receiving placebo (86).
4.7 Pregnancy-related effects
Although type 2 diabetes and obesity have been effectively treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, their role in pregnancy and breastfeeding has been a controversial debate due to potential risks to the mother’s health and fetal outcomes (87). Decisions about therapy during nursing should be carefully weighed (88) since each medication taken by a woman in this period has potential adverse effects that are obvious to the fetus. Certain detrimental effects on a child’s health are strongly correlated with maternal obesity and gestational diabetes underscoring the need for a safer and more efficient drug (89).
Since none of the GLP-1RA are approved in pregnancy, a cohort study approved the potency of liraglutide, in early pregnancy, despite its adverse outcomes such as preterm birth, preeclampsia and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) (90). These adverse effects were likely to be due to pre-existing factors i.e. obesity and diabetes. An identical study undertaken across 6 countries evaluated the tolerability of GLP-1 agonists in pregnant women and their effects on fetal outcomes (91). Study reported women with pregestational diabetes unveiled higher risks of cardiac malformations in the fetus, due to diabetes rather than the drug itself. Additionally, the prevalent use of GLP-1 agonists was highlighted emphasizing the need for more research in future (91).
An observational cohort study involving 168 pregnant women exposed to GLP-1 receptor agonists during the first trimester found a 2.6% prevalence of major birth defects, comparable to 2.3% in the diabetic reference group. While prior literature cites a 5–10% defect rate among women with pregestational diabetes, this study did not report any significant pregnancy losses following the use of GLP-1RA (92).
A systematic review executed on animal and human studies alongside case studies (93) demonstrated a dearth of human evidence on the excretion of GLP-1 agonists in breast milk, even though GLP-1 agonists, being large peptides, could be precisely present in human milk, although the exact amount is unclear (89). However, skeletal deformities and growth defects were prominently seen in rat models with no conspicuous findings in humans (93).
In addition to aforementioned properties of GLP-1 agonists, it can also reduce hypertension by activating and phosphorylating endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathways, thus increasing the bioavailability of nitric oxide which promotes vasodilation. Owing to these effects, liraglutide, a GLP-1 analog, has been studied as a potential drug for the treatment of pre-eclampsia, a pregnancy specific disorder, defined as new-onset hypertension after 20th week of gestation accompanied by proteinuria, as it is found to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects (89). Pre-eclampsia has emerged as a notifiable cause of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality (94).
Placental ischemia, as the causative factor for preeclampsia, leads to dysfunction of maternal vascular endothelium causing reduced synthesis of vasodilators and increased synthesis of endothelin, a potent vasoconstrictor. Production of pro angiogenic factors such as PIGF and VEGFZ and reactive oxidative species also plays a role in endothelial disruption (95). All these effects accentuate total peripheral resistance and impaired renal function raising blood pressure (95).
A study conducted on rat model demonstrated that liraglutide effectively reduced the mean arterial pressure, a cardinal feature for preeclampsia, leading to decreased blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine via renal vasodilation; however, it negatively affected the fetal weight, yet it was considered negligible due to liraglutide’s known effect of suppressing appetite (94). Moreover, liraglutide also displayed a boosted effect on levels of nitric oxide in mesenteric vessels and protection against endothelial dysfunction by increased production of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1(PAI-1) and vascular adhesion molecule (VAM) (96).
As GLP-1 agonists have garnered attention for management of obesity due to their effect on reducing insulin sensitivity, they are now being considered a therapeutic option for the treatment of PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome), one of the most common causes of subfertility, diagnosed via Rotterdam’s criteria: oligomenorrhea, hyperandrogenism and polycystic ovaries (97). A statistical analysis assimilated various studies which insisted that GLP-1 agonists play a pivotal role in regulating menstrual cycle, ameliorating pregnancy rates and addressing infertility, a key concern in PCOS, though these benefits appeared to be temporary as drugs were only prescribed for 12 weeks and IVF pregnancies were unaffected. Thus, creating a void to conduct future studies to examine longer duration treatment to check their prolonged effects (98).
A comparative study conducted between GLP-1RA + Metformin in contrast to cyproterone acetate/ethinylestradiol + Metformin in overweight PCOS women, conducted over a period of 12 weeks, implied that GLP-1 RA+Metformin was superior in reducing the waist circumferences as well as preserving blood sugar levels by improved HbA1c levels and regulating menstrual cycle. Conversely, CPA/EE showed a stronger effect to reduce androgens levels (99). Similarly, a homogenous trial compared GLP-1RA against a placebo in PCOS women, demonstrating the significance of GLP-1RA analogs liraglutide and semaglutide, specifically. The results proved their efficacy by diminishing total testosterone and serum triglycerides, directly impacting the waist circumference and BMI (100), hence proving to be reliable therapy for PCOS.
There is a significant gap in research concerning the use of GLP-1 agonists during pregnancy, due to of lack of human studies as well as lack of data on their effects on lactation and fetal outcomes. More studies conducted with female rodent models and human subjects are needed to address these issues to ensure better maternal and fetal outcomes.
4.8 Effects on male reproductive system
GLP-1RAs may be very helpful in treating male infertility, especially in individuals who are obese and diabetic. Due to the expression of GLP-1 receptors in testicular cells, they can raise testosterone levels and increase sperm motility and metabolism (101). Also, they have a favorable impact on Sertoli cell metabolism, which is important in the production of sperm (102).
The effects of liraglutide on male obesity-associated functional hypogonadism (FH) are examined in this study. They designed a 16-week prospective randomized open-label study with 30 men, with BMI 41.2 ± 8.4 kg/m2 and aged 46.5 ± 10.9 years. An average of 7.9 ± 3.8 kg of weight was lost as a result of liraglutide medication, which also markedly improved general health and sexual performance. While luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) increased significantly (P < 0.001), total testosterone levels increased by+2.6 ± 3.5 nmol/L. On the other hand,0.9 ± 4.5 kg less weight was lost with testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) and +5.9 ± 7.2 nmol/L more advantageous for males with FH associated with obesity if lifestyle changes are unsuccessful (103). GLP-1 receptors are present in Sertoli and Leydig cells, which means that these drugs have the potential to directly affect testicular function in addition to improving hormonal balance. Studies show that GLP-1RAs enhance insulin production, motility, and sperm metabolism, all of which can result in improved sperm parameters. Furthermore, there is a correlation between improvements in sperm count and concentration and weight loss linked to GLP-1RA usage. However, more clinical research is required to validate these findings and investigate the long-term implications of using GLP-1RAs to treat male infertility because the precise pathways by which they affect male reproductive health are not entirely understood (101). Through a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial, the effects of the GLP-1RA dulaglutide on sexual desire in healthy men were evaluated in a study. The study used the Massachusetts General Hospital-Sexual Functioning Questionnaire (MGH-SFQ) to assess sexual desire in 24 volunteers, ages 18 to 50. The results showed no discernible differences in hormone levels or sexual desire between dulaglutide and placebo, suggesting that dulaglutide had no negative effects on a healthy man’s ability to have sex. This gives certainty regarding its clinical application (104).
In order to close a knowledge gap regarding the relationship between metabolism and reproduction, the study investigates the effects of GLP-1 on the reproductive axis in healthy men (105) Enrolling eighteen fit male subjects ensured they were free of mental or physical illnesses and did not use prohibited substances. A single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled crossover design was used in the study, which improves the validity of the results. The findings imply that GLP-1 may have an impact on reproductive hormones, pointing to possible treatment approaches for type 2 diabetes and obesity-related hypogonadism in males (105).
4.9 Effects on general anaesthesia
One of the major concerning side effects of GLP-1RA use in anesthesia are the complications of the GI tract presenting as delayed gastric emptying and elevated gastric residual content along with other symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension and dyspepsia) (106). This leads to increase in gastric volumes and putting the patients at increased risk of aspiration during sedation (107).
The use of short acting GLP-1RA drugs has shown to improve glycemic control and promote insulin sectretion (53). However, these agents increase risk of intra-operative pulmonary aspiration according to a case report secondary to delayed emptying and presence of gastric residues despite fasting (108, 108)
To prevent these events, the recent recommendations from the American Society of Anesthesiology guidelines suggest discontinuing GLP-1 receptor agonists 1 day prior in patients on daily dosing and 1 week prior in patients on weekly injection dosing (108). Additionally, a precautionary step is to carry out an inexpensive and quick procedure like gastric ultrasound to look for any residues within the stomach prior to giving general anesthesia (109).
6 Adverse effects of GLP1-RA
In contrast to the advantages of GLP-1RA the analogues have gastrointestinal side effects distinctly nausea, emesis and reduced appetite with lower risk of hypoglycemia compared to other glucose lowering drugs (110). According to FDA, GLP-1RA had not shown evident risk of pancreatitis and pancreatic tumor (111). However, GLP-1RA are contraindicated for use in individuals with predisposition to MEN2 and medullary thyroid carcinoma (112). Additionally a meta-analysis found use of GLP-1RA was associated with higher risk of gallbladder and biliary disease with high doses for longer duration (113). These notable side effects can deter people from conforming to treatment plans.
7 Discussion
GLP-1 RAs have shown effects beyond their initial application in managing T2DM. GLP-1RA secondary to direct and mechanistic indirect effects on physiological systems have raised a need to further understand their potential in clinical practice. GLP-1RA, liraglutide and semaglutide are widely known for the therapeutic effects in management of T2DM for glycaemic control, Obesity for Weight Management along with Cardioprotective outcomes with influence on blood pressure, lipids and β -cell function (5). GLP-1RA have also shown neuroprotective effects with decreasing progression of neurodegenerative diseases and regulating neuronal activity (114). The newly discovered conjunctive use of GLP-1RA can improve clinical outcomes in patients with multiple chronic illnesses that have overlapping pathophysiology and help improve quality of life with early introduction.
Considering the expansive spread of GLP 1R throughout the systems in body and identifying the potential to modulate its effects with GLP-1RA is a paradigm shift in early intervention. GLP-1RA have shown to control HbA1C levels in patients with T2DM alongside alleviating the frequently existing comorbids, HTN and dyslipidaemia in combination with SGLT2 inhibitors (115). GLP-1RA as an independent class of drug is also noteworthy in reduction of weight in patients with and without poor glycaemic control with multiple trials backing the efficacy of agents including semaglutide and liraglutide (116). Cardiovascular outcomes have been investigated in clinical trials which suggested a reduction in cardiovascular events and mortality without risk of notable adverse effects. Meanwhile these agents have the potential to reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patient with T2DM as a drug class, individual drugs have different potency and effects they need tailored approach to align with patient treatment goals rather than generalized use (117). The GLP-1RA are limited to use in individuals without established cardiovascular disease which limits the use widely but provides its benefit for at risk population. Similarly, GLP-1RA have shown to have a neuroprotective effect including delay in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease onset as well progressions (118). Phase I and II clinical trials conducted have shown improved cognitive and motor function with different drugs from GLP-1RA group although the small sized and limited duration of trials have not provided a conclusive result to influence the practice, although with further advancement in ongoing trials effects observed may be noteworthy for intervention in future practice (119).
GLP-1RA have an amalgam of therapeutic effects assisting in providing combined intervention for diseases which are also complication of treatment of diabetes and anti-diabetic drugs. Use of GLP-1RA is protective and prevents bone fractures over a longer period of use in T2DM patients in a recent trial in 2020 liraglutide showed to have decreased bone resorption compared to placebo (120). Another use of GLP-1RA is also under study in ELAD (121), a phase II b clinical trial to provide strong evidence in using GLP-1RA as neuroprotective agents against Alzheimer’s Disease. These uses of GLP-1RA beyond the proven use in treatment and prevention of cardiovascular risk with obesity (110) as well as in diabetics add a new dimension to use them in early. The possibility of providing preventive regimen in multi system pathologies is a significant use of the GLP-1RA in improving disease outcomes and preventing morbidity.
8 Challenges in clinical application
Considering the enumerated benefits of GLP-1RA compared to other glucose-lowering drugs including the reduction in HbA1c and weight reduction benefits alongside decreased risk for hypoglycaemia (122) it is not cost effective if used in combination with another incretin (107). However, studies support GLP-1RA to be cost effective in comparison to insulin therapy as per the healthcare models in high income countries while the parameter for comparison between the two include the increased risk of hypoglycaemia and all-cause mortality alongside emergency room visits and hospitalization. This counteracts the high GLP-1RA purchasing, pharmacy and administration cost (123). The overall inflated cost adds to limitation of access to these drugs in resource poor nations (124).
9 Limitations of this review
This review does not cover the more expanded literature about the individual GLP-1RA drug administration, efficacy and side effects. A generalized GLP-1RA use has been explored across different clinical pathologies, although most of the literature narrated does not explore effects of GLP-1RA on diabetics and non-diabetics with concomitant renal and liver dysfunctions.
10 Future perspectives
In the recent era advancements seen in application of GLP-1RA is extensively appreciated to battle obesity and metabolic syndrome along with associated cardiovascular risks. However, a chasm is present for large scale studies to see the role GLP-1RA in neurological diseases including ocular pathologies, present studies are inconclusive about the implications in long term preventions in different populations. Alongside further clinical trials would benefit in learning about the role of GLP-1RA in gestational diabetes and implications on fetal and placental diseases. Responses to the less chartered topics will provide an insight into better and safer clinical practices.
In addition to finding the effects on multiple populations and pathophysiological impact of drug mechanisms, the future needs improved cost effective formulation and preparation to make GLP-1RA widely accessible. The potential to decrease burden of morbidity and mortality secondary to obesity, DM and cardiovascular diseases is a power GLP-1 RA can help harness to safe resources and improve quality of life as well as life span of populations at risk.
10.1 Future therapeutic effects
As advancements continue and overcome current gaps, GLP1-RAs are expected to become a drug of choice as a monotherapy or as combination therapy for a wide range of diseases. These include Alzheimer’s Disease where neuroprotective effects are under investigation followed by stroke under similar notion (125) Futhermore, in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) they show evidence of improved liver histology and hepatic steatosis (126) in PCOS they may help in regulation of weight, reproductive and metabolic parameters simultaneously (127) GLP1-Ras are also under study with their ability to modulate the hemodynamic and inflammatory pathways to treat CKD (128) and Heart failure (129). Additionally the immunomodulatory and anti inflammatory potential might be prove useful in treating sepsis (130).
11 Conclusion
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists are pivotal in managing T2DM and obesity, enhancing glycaemic control by boosting insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, delaying gastric emptying, and promoting satiety. They also reduce cardiovascular disease risk, as seen with semaglutide and liraglutide. Emerging roles include treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, preeclampsia, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, due to anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. GLP-1RAs may benefit glaucoma by reducing aqueous humour production. Despite their potential side effects like delayed gastric emptying, pancreatitis, and GI symptoms warrant tailored regimens. Future research will explore novel pathways and expand therapeutic applications.
Author contributions
BH: Writing – original draft. NZ: Writing – original draft. MU: Writing – original draft. SF: Writing – original draft. FI: Writing – original draft. HW: Writing – original draft. MM: Writing – original draft. KA: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. FA: Writing – original draft. KZ: Writing – review & editing. MA: Writing – review & editing. ME: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1
GLP-1R: GLP-1 receptor
GLP-1Ras: GLP-1R agonists
DPP4: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4
GRPP: Glicentin-related pancreatic polypeptide
cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
T2DM: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
PKA: Protein Kinase A
RGNEF4: Rap Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor 4
IP3: Inositol triphosphate pathway
DAG: Diacylglycerol
CNS: Central Nervous System
BBB: Blood Brain Barrier
AD: Alzheimer’s Disease
PD: Parkinson’s Disease
ROS: Reactive Oxygen Species
BDNF: Brain-Derived Neurotrophic factor
LTP: Long Term Potentiation
Ex-4: Exendin-4
MPTP: 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
CVOTs: CV outcome trials
CRP: C-reactive protein
SCALE: Satiety and Clinical Adipose Liraglutide Evidence
STEP: Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity
BMI: Body Mass Index
VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein
LDL: Low-density lipoprotein
ApoB48: Apolipoprotein B48
EAT: Epicardial adipose tissue
DPP-4i: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors
SGLT-2i: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor
RGCs: Retinal Ganglion Cells
IOP: Intraocular pressure
DR: Diabetic Retinopathy
GDM: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1
VAM: Vascular adhesion molecule
PCOS: Polycystic ovarian syndrome
FH: Functional hypogonadism
References
1. Graaf Cd, Donnelly D, Wootten D, Lau J, Sexton P, Miller M, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 and its class B G protein-coupled receptors: A long march to therapeutic successes. Pharmacol. Rev. (2016) 68:954–1013. doi: 10.1124/PR.115.011395
2. Drucker DJ. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab. (2006) 3:153–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.004
3. Pyke C, Heller RS, Kirk RK, Ørskov C, Reedtz-Runge S, and Kaastrup P. GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: Novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology. (2014) 155:1280–90. doi: 10.1210/EN.2013-1934
4. Drucker DJ, Habener JF, and Holst JJ. Discovery, characterization, and clinical development of the glucagon-like peptides. J. Clin. Invest. (2017) 127:4217–27. doi: 10.1172/JCI97233
5. Knudsen LB and Lau J. The discovery and development of liraglutide and semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). (2019) 10:155/XML/NLM. doi: 10.3389/FENDO.2019.00155/XML/NLM
6. Zhao X, Wang M, Wen Z, Lu Z, Cui L, Fu C, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists: beyond their pancreatic effects. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). (2021) 12:721135/XML/NLM. doi: 10.3389/FENDO.2021.721135/XML/NLM
7. Holst JJ. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. (2007) 87:1409–39. doi: 10.1152/PHYSREV.00034.2006
8. Rajagopal D, Al Rashid S, Prasad M, and Fareed M. Unveiling the potential role of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists in offering protection of the cardiovascular, renal, and neural systems: an updated narrative review. Cureus. (2024) 16. doi: 10.7759/CUREUS.65910
9. Muzurović EM, Volčanšek Š, Tomšić KZ, Janež A, Mikhailidis DP, Rizzo M, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of obesity/metabolic syndrome, prediabetes/diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—Current evidence. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. (2022) 27. doi: 10.1177/10742484221146371
10. Nowell J, Blunt E, Gupta D, and Edison P. Antidiabetic agents as a novel treatment for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. (2023) 89. doi: 10.1016/J.ARR.2023.101979
11. Collins L and Costello RA. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists. Jonesboro, Arkansas, United States: StatPearls (2024). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551568/.
12. García-Casares N, González-González G, de la Cruz-Cosme C, Garzón-Maldonado FJ, de Rojas-Leal C, Ariza MJ, et al. Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on neurological complications of diabetes. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. (2023) 24:655–72. doi: 10.1007/S11154-023-09807-3
13. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JFE, Nauck MA, et al. LEADER Steering Committee on behalf of the LEADER Trial Investigators. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl. J. Med. (2016) 375:311–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603827
14. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jódar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. New Engl. J. Med. (2016) 375:1834–44. doi: 10.1056/NEJMOA1607141/SUPPL_FILE/NEJMOA1607141_DISCLOSURES.PDF
15. Holman RR, Bethel MA, Mentz RJ, Thompson VP, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, et al. EXSCEL Study Group. Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl. J. Med. (2017) 377:1228–39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1612917
16. Green JB, Hernandez AF, D’Agostino RB, Granger CB, Janmohamed S, Jones NP, et al. Harmony Outcomes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the effect of albiglutide on major cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus—Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics. Am. Heart J. (2018) 203:30–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2018.03.030
17. Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. REWIND Investigators. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. (2019) 394:121–30. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31149-3
18. Gerstein HC, Sattar N, Rosenstock J, Ramasundarahettige C, Pratley RE, Lopes RD, et al. Efpeglenatide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl. J. Med. (2021) 385:2097–107. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2108269
19. Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, Davies M, van Gaal LF, Lingvay I, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl. J. Med. (2021) 384:989–1002. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
20. Fox CK, Auerbach P, Barrientos-Pérez M, Gies I, Hale PM, Marcus C, et al. SCALE Kids Trial Group. Liraglutide for children 6 to <12 years of age with obesity. N Engl. J. Med. (2024) 391:1123–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2407379
21. Aronne LJ, Horn DB, le Roux CW, Ho W, Falcon BL, Valderas EG, et al. SURMOUNT-5 Trial Investigators. Tirzepatide as compared with semaglutide for the treatment of obesity in adults without diabetes. N Engl. J. Med. (2025). doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2416394
22. Du H, Meng X, Yao Y, and Xu J. The mechanism and efficacy of GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1033479. doi: 10.3389/FENDO.2022.1033479
23. Kopp KO, Glotfelty EJ, Li Y, and Greig NH. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and neuroinflammation: Implications for neurodegenerative disease treatment. Pharmacol. Res. (2022) 186. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106550
24. Salcedo I, Tweedie D, Li Y, and Greig NH. Neuroprotective and neurotrophic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1: An emerging opportunity to treat neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular disorders. Br. J. Pharmacol. (2012) 166:1586–99. doi: 10.1111/J.1476-5381.2012.01971.X
25. Ji C, Xue GF, Lijun C, Feng P, Li D, Li L, et al. A novel dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist is neuroprotective in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson′s disease by increasing expression of BNDF. Brain Res. (2016) 1634:1–11. doi: 10.1016/J.BRAINRES.2015.09.035
26. Shah M and Vella A. Effects of GLP-1 on appetite and weight. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. (2014) 15:181–7. doi: 10.1007/S11154-014-9289-5
27. Kalinderi K, Papaliagkas V, and Fidani L. GLP-1 receptor agonists: A new treatment in parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2024) 25:3812. doi: 10.3390/IJMS25073812
28. Chen X, Zhao P, Wang W, Guo L, and Pan Q. The antidepressant effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Geriatric Psychiatry. (2024) 32:117–27. doi: 10.1016/J.JAGP.2023.08.010
29. Li Y, Perry T, Kindy MS, Harvey BK, Tweedie D, Holloway HW, et al. GLP-1 receptor stimulation preserves primary cortical and dopaminergic neurons in cellular and rodent models of stroke and Parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. (2009) 106:1285–90. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.0806720106
30. Ferreira JP, Saraiva F, Sharma A, Vasques-Nóvoa F, Angélico-Gonçalves A, Leite AR, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes with and without chronic heart failure: A meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled outcome trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. (2023) 25:1495–502. doi: 10.1111/DOM.14997
31. Ma X, Liu Z, Ilyas I, Little PJ, Kamato D, Sahebka A, et al. Glp-1 receptor agonists (Glp-1ras): Cardiovascular actions and therapeutic potential. Int. J. Biol. Sci. (2021) 17:2050–68. doi: 10.7150/IJBS.59965
32. Hayreh SS. Retinal and optic nerve head ischemic disorders and atherosclerosis: Role of serotonin. Prog. Retin Eye Res. (1999) 18:191–221. doi: 10.1016/S1350-9462(98)00016-0
33. Yamagishi SI and Matsui T. Pleiotropic effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)-based therapies on vascular complications in diabetes. Curr. Pharm. Des. (2012) 17:4379–85. doi: 10.2174/138161211798999456
34. Heuvelman VD, Van Raalte DH, and Smits MM. Cardiovascular effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: From mechanistic studies in humans to clinical outcomes. Cardiovasc. Res. (2020) 116:916–30. doi: 10.1093/CVR/CVZ323
35. Pearson S, Kietsiriroje N, and Ajjan RA. Oral semaglutide in the management of type 2 diabetes: A report on the evidence to date. Diabetes Metab. Syndrome Obes. (2019) 12:2515–29. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S229802
36. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. From Univ. Texas Southwest-ern Med. Center. (2016) 375:311–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJMOA1603827
37. Le R, Nguyen MT, Allahwala MA, Psaltis JP, Marathe CS, Marathe JA, et al. Cardiovascular protective properties of GLP-1 receptor agonists: more than just diabetic and weight loss drugs. J. Clin. Med. (2024) 13:4674. doi: 10.3390/JCM13164674
38. Doran AC, Meller N, and McNamara CA. Role of smooth muscle cells in the initiation and early progression of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. (2008) 28:812–9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.159327
39. Menghini R, Casagrande V, Rizza S, and Federici M. GLP-1RAs and cardiovascular disease: is the endothelium a relevant platform? Acta Diabetol. (2023) 60:1441–8. doi: 10.1007/S00592-023-02124-W
40. Anholm C, Kumarathurai P, Pedersen LR, Samkani A, Walzem RL, Nielsen OW, et al. Liraglutide in combination with metformin may improve the atherogenic lipid profile and decrease C-reactive protein level in statin treated obese patients with coronary artery disease and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Atherosclerosis. (2019) 288:60–6. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.07.007
41. Ferhatbegović L and Mršić D. Macić-Džanković A. The benefits of GLP1 receptors in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthcare. (2023) 4:1293926. doi: 10.3389/FCDHC.2023.1293926
42. Barbagelata L, Masson W, Lobo M, and Bluro I. Semaglutide and heart failure: Updated meta-analysis. Curr. Probl Cardiol. (2024) 49. doi: 10.1016/J.CPCARDIOL.2024.102721
43. Akil L and Anwar Ahmad H. Relationships between obesity and cardiovascular diseases in four southern states and colorado. J. Health Care Poor Underserved. (2011) 22:61. doi: 10.1353/HPU.2011.0166
44. Alhomoud IS, Talasaz AH, Chandrasekaran P, Brown R, Mehta A, and Dixon DL. Incretin hormone agonists: Current and emerging pharmacotherapy for obesity management. Pharmacotherapy. (2024) 44. doi: 10.1002/PHAR.4607
45. Liu Z, Bian N, Wu S, Fan Y, Li H, Yu J, et al. A meta-analysis evaluating indirectly GLP-1 receptor agonists and arrhythmias in patients with type 2 diabetes and myocardial infarction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. (2022) 9:1019120/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FCVM.2022.1019120/BIBTEX
46. Zhang HD, Ding L, Liu K, Mi LJ, Zhang AK, Yu FY, et al. Semaglutide for the prevention of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndrome. (2024) 18. doi: 10.1016/J.DSX.2024.103067
47. Liu QK. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications of GLP-1 and dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonists. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1431292. doi: 10.3389/FENDO.2024.1431292
48. Moll H, Frey E, Gerber P, Geidl B, Kaufmann M, Braun J, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists for weight reduction in people living with obesity but without diabetes: a living benefit–harm modelling study. EClinicalMedicine. (2024) 73. doi: 10.1016/J.ECLINM.2024.102661
49. Bettge K, Kahle M, Abd El Aziz MS, Meier JJ, and Nauck MA. Occurrence of nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea reported as adverse events in clinical trials studying glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A systematic analysis of published clinical trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. (2017) 19:336–47. doi: 10.1111/DOM.12824
50. Liu L, Shi H, Shi Y, Wang A, Guo N, Tao H, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in children and adolescents with obesity or overweight: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pharmaceuticals. (2024) 17. doi: 10.3390/PH17070828
51. Light PE, Manning Fox JE, Riedel MJ, and Wheeler MB. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium channels via a protein kinase A- and ADP-dependent mechanism. Mol. Endocrinology. (2002) 16:2135–44. doi: 10.1210/ME.2002-0084
52. Zhang Y, Parajuli KR, Fava GE, Gupta R, Xu W, Nguyen LU, et al. GLP-1 receptor in pancreatic A-cells regulates glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent bidirectional manner. Diabetes. (2019) 68:34–44. doi: 10.2337/DB18-0317
53. Zheng Z, Zong Y, Ma Y, Tian Y, Pang Y, Zhang C, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2024) 9:1. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01931-z
54. Doyle ME and Egan JM. Mechanisms of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pancreas. Pharmacol. Ther. (2007) 113:546–93. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.11.007
55. Maljaei MB and Bahreini A. Liraglutide for adolescents with obesity. N Engl. J. Med. (2020) 383:1193. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2023284
56. Zhong P, Zeng H, Huang M, Fu W, and Chen Z. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: a meta-analysis. Endocrine. (2022) 75:718–24. doi: 10.1007/S12020-021-02945-1
57. Katole NT, Salankar HV, Khade AM, Kale JS, Bankar NJ, Gosavi P, et al. The antiobesity effect and safety of GLP-1 receptor agonist in overweight/obese adolescents without diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus. (2024) 16. doi: 10.7759/CUREUS.66280
58. Meier JJ, Menge BA, Schenker N, Erdmann S, Kahle-Stephan M, Schliess F, et al. Effects of sequential treatment with lixisenatide, insulin glargine, or their combination on meal-related glycaemic excursions, insulin and glucagon secretion, and gastric emptying in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. (2020) 22:599–611. doi: 10.1111/DOM.13935
59. Rochoń J, Kalinowski P, Grąt M, and Szymanek-Majchrzak K. Role of gut-liver axis and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. (2024) 30:2964–80. doi: 10.3748/WJG.V30.I23.2964
60. MacDonald PE, El-kholy W, Riedel MJ, Salapatek AMF, Light PE, and Wheeler MB. The multiple actions of GLP-1 on the process of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes. (2002) 51. doi: 10.2337/DIABETES.51.2007.S434
61. Dahl K, Brooks A, Almazedi F, Hoff ST, Boschini C, and Bækdal TA. Oral semaglutide improves postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism, and delays gastric emptying, in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. (2021) 23:1594–603. doi: 10.1111/DOM.14373
62. Iacobellis G and Villasante Fricke AC. Effects of semaglutide versus dulaglutide on epicardial fat thickness in subjects with Type 2 diabetes and obesity. J. Endocr. Soc. (2020) 4:1–9. doi: 10.1210/JENDSO/BVZ042
63. Ansari HUH, Qazi SU, Sajid F, Altaf Z, Ghazanfar S, Naveed N, et al. Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight and cardiometabolic parameters in individuals with obesity and without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine Practice. (2024) 30:160–71. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2023.11.007
64. Moseley KF. Type 2 diabetes and bone fractures. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. (2012) 19:128. doi: 10.1097/MED.0B013E328350A6E1
65. Mabilleau G, Pereira M, and Chenu C. Novel skeletal effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. J. Endocrinology. (2018) 236:R29–42. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0278
66. Tufail E, Sanyal S, Mithal A, Sanyal S, and Chattopadhyay N. The role of glucagon-like peptides in osteosarcopenia. J. Endocrinology. (2025) 264. doi: 10.1530/JOE-24-0210
67. Akyay OZ, Canturk Z, Selek A, Cetinarslan B, Tarkun İ, Cakmak Y, et al. The effects of exenatide and insulin glargine treatments on bone turnover markers and bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med. (United States). (2023) 102:E35394. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035394
68. Rajagopal S, Alruwaili F, Mavratsas V, Serna MK, Murthy VL, and Raji M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy: from mechanisms of action to clinical applications. Cureus. (2023) 15:e51352. doi: 10.7759/CUREUS.51352
69. Zhao C, Liang J, Yang Y, Yu M, and Qu X. The impact of glucagon-like peptide-1 on bone metabolism and its possible mechanisms. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). (2017) 8:98. doi: 10.3389/FENDO.2017.00098
70. Cai TT, Li HQ, Jiang LL, Wang HY, Luo MH, Su XF, et al. Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on bone mineral density in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 52-week clinical study. BioMed. Res. Int. (2021) 2021. doi: 10.1155/2021/3361309
71. Daniilopoulou I, Vlachou E, Lambrou GI, Ntikoudi A, Dokoutsidou E, Fasoi G, et al. The impact of GLP1 agonists on bone metabolism: A systematic review. Medicina. (2022) 58:224. doi: 10.3390/MEDICINA58020224
72. Chai S, Liu F, Yang Z, Yu S, Liu Z, Yang Q, et al. Risk of fracture with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis combining 177 randomized controlled trials with a median follow-up of 26 weeks. Front. Pharmacol. (2022) 13:825417. doi: 10.3389/FPHAR.2022.825417
73. Hölscher C. Central effects of GLP-1: new opportunities for treatments of neurodegenerative diseases. J. Endocrinology. (2014) 221:T31–41. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0221
74. Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T, and Cheng CY. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. (2014) 121:2081–90. doi: 10.1016/J.OPHTHA.2014.05.013/ATTACHMENT/4DFFCC6A-BE96-4720-96C7-1DA6395D6ECE/MMC5.PDF
75. Cui QN, Stein LM, Fortin SM, and Hayes MR. The role of glia in the physiology and pharmacology of glucagon-like peptide-1: implications for obesity, diabetes, neurodegeneration and glaucoma. Br. J. Pharmacol. (2022) 179:715–26. doi: 10.1111/BPH.15683
76. Sterling J, Hua P, Dunaief JL, Cui QN, and VanderBeek BL. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist use is associated with reduced risk for glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmology. (2023) 107:215–20. doi: 10.1136/BJOPHTHALMOL-2021-319232
77. Sharma A, Mariam A, Zacherle E, Milinovich A, Bauman J, Sugano DS, et al. Elucidating the role of weight loss and glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2024) 26(11):5347–57. doi: 10.1111/dom.15896
78. Huang YN, Liao WL, Huang JY, Lin YJ, Yang SF, Huang CC, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in individuals with obesity and without type 2 diabetes: A global retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2024) 26(11):5222–32. doi: 10.1111/dom.15869
79. Mouhammad ZA, Vohra R, Horwitz A, Thein A, Rovelt J, Cvenkel B, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists – potential game changers in the treatment of glaucoma? Front. Neurosci. (2022) 16:824054/XML/NLM. doi: 10.3389/FNINS.2022.824054/XML/NLM
80. Muayad J, Loya A, Hussain ZS, Chauhan MZ, Alsoudi AF, De Francesco T, et al. Comparative effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and metformin on glaucoma risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ophthalmology. (2025) 132:271–9. doi: 10.1016/J.OPHTHA.2024.08.023
81. Cheung N, Mitchell P, and Wong TY. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet. (2010) 376:124–36. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)62124-3
82. Curran K, Peto T, Jonas JB, friedman D, Kim JE, Leasher J, et al. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by diabetic retinopathy: a meta-analysis from 2000 to 2020. Eye (Basingstoke). (2024) 38:2047–57. doi: 10.1038/S41433-024-03101-5
83. Jung BJ, Lee MY, and Jeon S. Systemic factors related to intraocular levels of interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor in diabetic retinopathy. J. Ophthalmol. (2019) 2019:4831967. doi: 10.1155/2019/4831967
84. Hou L, Du J, Dong Y, Wang M, Wang L, and Zhao J. Liraglutide prevents cellular senescence in human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs) mediated by SIRT1: an implication in diabetes retinopathy. Hum. Cell. (2024) 37:666–74. doi: 10.1007/S13577-024-01038-1/FIGURES/8
85. Kapoor I, Sarvepalli SM, D’Alessio D, Grewal DS, and Hadziahmetovic M. GLP-1 receptor agonists and diabetic retinopathy: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Surv Ophthalmol. (2023) 68:1071–83. doi: 10.1016/J.SURVOPHTHAL.2023.07.002
86. Sharma A, Parachuri N, Kumar N, Saboo B, Tripathi HN, Kuppermann BD, et al. Semaglutide and the risk of diabetic retinopathy—current perspective. Eye (Basingstoke). (2022) 36:10–1. doi: 10.1038/S41433-021-01741-5
87. Drummond RF, Seif KE, and Reece EA. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use in pregnancy: A review. Am. J. Obstet Gynecol. (2024) 232. doi: 10.1016/J.AJOG.2024.08.024
88. Graham DL, Madkour HS, Noble BL, Schatschneider C, and Stanwood GD. Long-term functional alterations following prenatal GLP-1R activation. Neurotoxicol Teratol. (2021) 87. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2021.106984
89. Wang J, Johnson T, Sahin L, Tassinari MS, Anderson PO, Baker TE, et al. Evaluation of the safety of drugs and biological products used during lactation: workshop summary. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. (2017) 101:736–44. doi: 10.1002/CPT.676
90. Hviid K, Banasik K, Mortensen LH, Madsbad S, Geiker NR, and Westergaard D. P-779 GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment in early pregnancy and risk of pregnancy complications - A nationwide cohort study. Hum. Reproduction. (2024) 39. doi: 10.1093/HUMREP/DEAE108.041
91. Cesta CE, Rotem R, Bateman BT, Chodick G, Cohen JM, Furu K, et al. Safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists and other second-line antidiabetics in early pregnancy. JAMA Intern. Med. (2024) 184:144–52. doi: 10.1001/JAMAINTERNMED.2023.6663
92. Dao K, Shechtman S, Weber-Schoendorfer C, Diav-Citrin O, Murad RH, Berlin M, et al. Use of GLP1 receptor agonists in early pregnancy and reproductive safety: a multicentre, observational, prospective cohort study based on the databases of six Teratology Information Services. BMJ Open. (2024) 14. doi: 10.1136/BMJOPEN-2023-083550
93. Muller DRP, Stenvers DJ, Malekzadeh A, Holleman F, Painter RC, and Siegelaar SE. Effects of GLP-1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors during pregnancy and lactation on offspring outcomes: a systematic review of the evidence. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1215356. doi: 10.3389/FENDO.2023.1215356
94. Younes ST, Maeda KJ, Sasser J, and Ryan MJ. The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist liraglutide attenuates placental ischemia-induced hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. (2020) 318:H72–7. doi: 10.1152/AJPHEART.00486.2019
95. Warrington JP, George EM, Palei AC, Spradley FT, and Granger JP. Recent advances in the understanding of the pathophysiology of preeclampsia. Hypertension. (2013) 62:666–73. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.00588
96. Gaspari T, Liu H, Welungoda I, Hu Y, Widdop RE, Knudsen LB, et al. A GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide inhibits endothelial cell dysfunction and vascular adhesion molecule expression in an ApoE-/- mouse model. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. (2011) 8:117–24. doi: 10.1177/1479164111404257
97. Ben-Shlomo I and Younis JS. Basic research in PCOS: Are we reaching new frontiers? Reprod. BioMed. Online. (2014) 28:669–83. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.02.011
98. Zhou L, Qu H, Yang L, and Shou L. Effects of GLP1RAs on pregnancy rate and menstrual cyclicity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Endocr. Disord. (2023) 23. doi: 10.1186/S12902-023-01500-5
99. Liao M, Li X, Zhang H, Zhou L, Shi L, Li W, et al. Effects and plasma proteomic analysis of GLP-1RA versus CPA/EE, in combination with metformin, on overweight PCOS women: a randomized controlled trial. Endocrine. (2024) 83:227–41. doi: 10.1007/S12020-023-03487-4
100. Austregésilo de Athayde De Hollanda Morais B, Martins Prizão V, de Moura de Souza M, Ximenes Mendes B, Rodrigues Defante ML, Cosendey Martins O, et al. The efficacy and safety of GLP-1 agonists in PCOS women living with obesity in promoting weight loss and hormonal regulation: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Diabetes Complications. (2024) 38. doi: 10.1016/J.JDIACOMP.2024.108834
101. Varnum AA, Pozzi E, Deebel NA, Evans A, Eid N, Sadeghi-Nejad H, et al. Impact of GLP-1 agonists on male reproductive health—A narrative review. Medicina (B Aires). (2023) 60:50. doi: 10.3390/MEDICINA60010050
102. Cannarella R, Calogero AE, Condorelli RA, Greco EA, Aversa A, and La Vignera S. Is there a role for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of male infertility? Andrology. (2021) 9:1499–503. doi: 10.1111/ANDR.13015
103. Jensterle M, Podbregar A, Goricar K, Gregoric N, and Janez A. Effects of liraglutide on obesity-associated functional hypogonadism in men. Endocr. Connect. (2019) 8:195–202. doi: 10.1530/EC-18-0514
104. Lengsfeld S, Probst L, Emara Y, Werlen L, Vogt DR, Bathelt C, et al. Effects of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist dulaglutide on sexuality in healthy men: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. EBioMedicine. (2024) 107. doi: 10.1016/J.EBIOM.2024.105284
105. Izzi-Engbeaya C, Jones S, Crustna Y, Machenahalli PC, Papadopoulou D, Modi M, et al. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on the reproductive axis in healthy men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. (2020) 105:1119–25. doi: 10.1210/CLINEM/DGAA072
106. Vetrugno L, Deana C, Da Porto A, Boero E, Bellini V, Biasucci DG, et al. A narrative review of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists prior to deep sedation or general anesthesia. J. Anesthesia Analgesia Crit. Care. (2025) 5:16. doi: 10.1186/S44158-025-00237-Y
107. Sherwin M, Hamburger J, Katz D, and DeMaria S. Influence of semaglutide use on the presence of residual gastric solids on gastric ultrasound: a prospective observational study in volunteers without obesity recently started on semaglutide. Can. J. Anesthesia. (2023) 70:1300–6. doi: 10.1007/S12630-023-02549-5
108. Klein SR and Hobai IA. Semaglutide, delayed gastric emptying, and intraoperative pulmonary aspiration: a case report. Can. J. Anesthesia. (2023) 70:1394–6. doi: 10.1007/S12630-023-02440-3
109. Fezza R, Rains B, Fezza T, and Fezza JP. Emerging anesthesia risks with semaglutide. Plast. Reconstr Surg. Glob Open. (2023) 11:e5427. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005427
110. DeFronzo RA, Okerson T, Viswanathan P, Guan X, Holcombe JH, and MacConell L. Effects of exenatide versus sitagliptin on postprandial glucose, insulin and glucagon secretion, gastric emptying, and caloric intake: A randomized, cross-over study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. (2008) 24:2943–52. doi: 10.1185/03007990802418851
111. Egan AG, Blind E, Dunder K, de Graeff PA, Hummer BT, Bourcier T, et al. Pancreatic safety of incretin-based drugs — FDA and EMA assessment. New Engl. J. Med. (2014) 370:794–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMP1314078
112. Brunton S. GLP-1 receptor agonists vs. DPP-4 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes: Is one approach more successful or preferable than the other? Int. J. Clin. Pract. (2014) 68:557–67. doi: 10.1111/IJCP.12361
113. He L, Wang J, Ping F, Yang N, Huang J, Li Y, et al. Association of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use with risk of gallbladder and biliary diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Intern. Med. (2022) 182:513. doi: 10.1001/JAMAINTERNMED.2022.0338
114. McClean PL, Gault VA, Harriott P, and Hölscher C. Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues enhance synaptic plasticity in the brain: A link between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. (2010) 630:158–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.12.023
115. Castellana M, Cignarelli A, Brescia F, Perrini S, Natalicchio A, Laviola L, et al. Efficacy and safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists as add-on to SGLT2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. (2019) 9. doi: 10.1038/S41598-019-55524-W
116. O'Neil PM, Birkenfeld AL, McGowan B, Mosenzon O, Pedersen SD, Wharton S, et al. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo and active controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. Lancet. (2018) 392:637–49. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31773-2
117. Bethel MA, Patel RA, Merrill P, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, Mentz RJ, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2018) 6:105–13. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30412-6
118. Marsico F, Paolillo S, Gargiulo P, Bruzzese D, Dell'Aversana S, Esposito I, et al. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on major cardiovascular events in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus with or without established cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. Heart J. (2020) 41:3346–58. doi: 10.1093/EURHEARTJ/EHAA082
119. Batista AF, Bodart-Santos V, De Felice FG, and Ferreira ST. Neuroprotective actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues in alzheimer’s and parkinson’s diseases. CNS Drugs. (2019) 33:209–23. doi: 10.1007/S40263-018-0593-6
120. Hygum K, Harsløf T, Jørgensen NR, Rungby J, Pedersen SB, and Langdahl BL. Bone resorption is unchanged by liraglutide in type 2 diabetes patients: A randomised controlled trial. Bone. (2020) 132. doi: 10.1016/J.BONE.2019.115197
121. Femminella GD, Frangou E, Love SB, Busza G, Holmes C, Ritchie C, et al. Evaluating the effects of the novel GLP-1 analogue liraglutide in Alzheimer’s disease: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (ELAD study). Trials. (2019) 20:1–10. doi: 10.1186/S13063-019-3259-X/FIGURES/2
122. Bennett WL, Bass EB, and Bolen S. Correction: Comparative effectiveness and safety of medications for type 2 diabetes. Ann. Intern. Med. (2011) 155:67–8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-1-201107050-00016/ASSET/IMAGES/16FF1.JPG
123. Yang CY, Chen YR, Ou HT, and Kuo S. Cost-effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists versus insulin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a real-world study and systematic review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. (2021) 20:1–10. doi: 10.1186/S12933-020-01211-4/FIGURES/1
124. Karagiannis T, Bekiari E, and Tsapas A. Socioeconomic aspects of incretin-based therapy. Diabetologia. (2023) 66:1859–68. doi: 10.1007/S00125-023-05962-Z/TABLES/1
125. Bak AM, Egefjord L, Gejl M, Steffensen C, Stecher CW, Smidt K, et al. Targeting amyloid-beta by glucagon-like peptide -1 (GLP-1) in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. (2011) 15:1153–62. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.600691
126. Dougherty JA, Guirguis E, and Thornby KA. A systematic review of newer antidiabetic agents in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Pharmacotherapy. (2021) 55:65–79. doi: 10.1177/1060028020935105
127. Lin S, Deng Y, Huang J, Li M, Sooranna SR, Qin M, et al. Efficacy and safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists on weight management and metabolic parameters in PCOS women: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. (2025) 15. doi: 10.1038/S41598-025-99622-4
128. Guo J, Wei M, Zhang W, Jiang Y, Li A, Wang C, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, and Finerenone in type 2 diabetes mellitus with non-dialysis chronic kidney disease: a network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Front. Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1517272/FULL. doi: 10.3389/FPHAR.2025.1517272/FULL
129. Bonfioli GB, Rodella L, Metra M, and Vizzardi E. GLP-1 receptor agonists as promising anti-inflammatory agents in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Heart Fail Rev. (2024) 30:131. doi: 10.1007/S10741-024-10450-6
Keywords: glucagon-like peptide-1, type 2 diabetes, endothelial function, obesity, metabolic syndrome
Citation: Hammad BF, Zafar N, Ullah M, Faisal SJ, Iftikhar F, Waheed H, Muzaffar MW, Ahmed K, Ashraf F, Zahid K, Akhtar M and Mahmmoud Fadelallah Eljack M (2025) Exploring the multifaceted roles of GLP-1 receptor agonists; a comprehensive review. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 6:1590530. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2025.1590530
Received: 09 March 2025; Accepted: 18 June 2025;
Published: 10 July 2025.
Edited by:
Angelo Maria Patti, University of Palermo, ItalyReviewed by:
Anapaula Sommer Vinagre, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, BrazilJun Eguchi, Okayama University, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Hammad, Zafar, Ullah, Faisal, Iftikhar, Waheed, Muzaffar, Ahmed, Ashraf, Zahid, Akhtar and Mahmmoud Fadelallah Eljack. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohammed Mahmmoud Fadelallah Eljack, bS5tYWhtbW91ZDk2QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Bisma Fatima Hammad, orcid.org/0000-0001-5558-3889
Nimrah Zafar, orcid.org/0009-0005-0960-5270
Muneeb Ullah, orcid.org/0009-0007-9150-7796
Syeda Jazilah Faisal, orcid.org/0009-0006-7517-7670
Fizzah Iftikhar, orcid.org/0009-0006-9380-632X
Haadia Waheed, orcid.org/0009-0005-4387-1580
Muhammad Waleed Muzaffar, orcid.org/0009-0002-2320-1385
Khadija Ahmed, orcid.org/0000-0002-9310-062X
Faz Ashraf, orcid.org/0009-0006-3908-3597
Komal Zahid, orcid.org/0009-0003-3616-3653
Maimoona Akhtar, orcid.org/0009-0002-1595-2023
Mohammed Mahmmoud Fadelallah Eljack, orcid.org/0000-0002-2370-9368
 Bisma Fatima Hammad
Bisma Fatima Hammad Nimrah Zafar2†
Nimrah Zafar2† Syeda Jazilah Faisal
Syeda Jazilah Faisal Fizzah Iftikhar
Fizzah Iftikhar Khadija Ahmed
Khadija Ahmed Komal Zahid
Komal Zahid Mohammed Mahmmoud Fadelallah Eljack
Mohammed Mahmmoud Fadelallah Eljack