- 1College of Science and Health Professions, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences (KSAU-HS), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 2King Abdullah International Medical Research Center (KAIMRC), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 3College of Medicine, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences (KSAU-HS), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 4College of Public Health and Health Informatics, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Introduction: Increasing evidence shows that hyperglycemia-induced glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity that usually accompany diabetes development damage the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of the hepatocytes in diabetic patients. Clinical studies highlighted the association between type 2 diabetes mellitus, comorbidities, and medications with liver function. The objective of this study is to explore the association between liver function tests’ abnormalities and comorbidities, medications, and other risk factors in type 2 diabetes patients registered in the Best-Care system of the Saudi Ministry of National Guard-Health Affairs.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study employing a chart of patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. We drew a simple random sample of 523 T2DM patients who had a liver function test from the Best-Care database of the Ministry. We applied various statistical analyses, including Student’s independent t-test, Pearson’s chi-squared test, Fisher’s exact test, and odd ratios, to measure associations between different variables and liver function tests’ abnormalities.
Results: About 35% of patients included in this study showed an abnormal level of gamma-glutamyl transferase and prothrombin time. Abnormalities of serum albumin, prothrombin time, and total serum protein tests were significantly associated with age (P < 0.05). Gamma-glutamyl transferase test abnormalities were significantly associated with gender (P < 0.05). The study found associations between several comorbidities and the abnormalities of liver function tests. These tests include the total bilirubin, albumin, total serum protein, gamma-glutamyl trans, international normalized ratio, and alanine aminotransferase. The associations were at significant levels (P < 0.05). Liraglutide was significantly associated with aspartate aminotransferase (OR = 14.40, 95% CI = 2.8, 73.2), while allopurinol was significantly associated with international normalized ratios (OR = 24.67, 95% CI = 2.95, 206.58) and total serum protein (OR = 5.44, 95% CI = 1.43, 20.83).
Discussion: This study is the first to examine the association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and liver function tests’ abnormalities in Saudi Arabia. Although the results have a limited generalizability due to inherent biases, the findings align with similar studies in other populations. The study stresses the need to monitor liver functions, especially of T2DM patients who suffer from other conditions.
1 Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic condition characterized by an abnormal elevation of glucose levels in the blood, i.e., hyperglycemia (1). According to a recent International Diabetes Federation report, approximately 17.7% of the adult population in Saudi Arabia has DM (2). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported a comparable prevalence in the U.S. population close to 14.7% (3). Several resources rank Saudi Arabia as having one of the highest prevalences of DM in North Africa and the Middle East (4–6). Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is often accompanied by comorbidities such as overweight or obesity, hyperlipidemia, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and cardiovascular disease (7, 8). Growing evidence indicates that patients with DM are at higher risk of several chronic liver diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, alcoholic cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis C, and hemochromatosis (9–14). The liver plays an essential role in glucose homeostasis by coordinating several glucose formation and utilization pathways at normal physiological levels. These pathways include glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, glycolysis, and gluconeogenesis at normal physiological levels (15). Hyperglycemia occurs when the rates of glucose formation persist to exceed the rates of glucose utilization (16). Investigators proposed that hyperglycemia-induced glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity have deleterious effects on the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of the hepatocytes (17–20). They predicted that these damages could potentially trigger a series of events that lead to the death of the hepatocytes and thus elevate liver function tests (LFTs) values (10).
LFTs are typically categorized into three groups: first, liver function indicators, including prothrombin time (PT), international normalized ratio (INR), albumin (ALB), and total serum protein (TP). Second, liver injury indicators include gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), lactate dehydrogenase, and glutamate dehydrogenase. Third, viral hepatitis serological tests (21). Several clinical studies underlined the association of T2DM with elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and GGT, particularly in older individuals (22–26). Beyond the physiological effects of T2DM, pharmacological interventions further influence LFT outcomes (27). Other studies showed that insulin-sensitizing agents like metformin and pioglitazone decrease aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and ALT (28). Insulin stimulators like sulfonylureas, on the other hand, have been associated with elevated levels of ALT and GGT (22). One study showed that alpha-glucosidase inhibitors such as acarbose cause a significant rise in ALT, AST, and total bilirubin (TBIL). In some cases, this drug increased the risk of hepatotoxicity (29). Moreover, many diabetic patients take protective therapy against diabetic complications, and this can contribute to elevated LFTs. For example, statins, widely used medications by diabetics, have been associated with 5% of cases of clinical liver injury (30).
One study estimated that diabetic patients and DM-related expenditures cost Saudi Arabia about 17 billion SAR in 2013, which represented approximately 0.61% of the country’s GDP that year, estimated at 2.8 trillion SAR (31). The study projected that this cost could rise up to 27 billion SAR in the following years (32). In most cases, DM is associated with one or more risk factors and comorbidities (33). These comorbidities significantly impact the type and volume of medical health care utilization, ultimately increasing T2DM health costs (34). Additionally, several studies showed that many of these comorbidities, including cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular events, and CKD, contribute to liver damage (35–37). Identifying these comorbidities could enhance the development of better and less costly DM management programs that fit the different health care needs of different comorbidities’ profiles (34, 38).
The aim of this study is to examine the association between LFTs abnormalities and DM, considering risk factors, comorbidities, and medications. We used the reference values of LFTs adopted by the Best-Care system of the Saudi Ministry of National Guard-Health Affairs (MNGHA) to indicate abnormalities.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design and subjects
We conducted a cross-sectional study using chart reviews, targeting MNGHA T2DM patients who tested liver function in the hospital. We calculated the sample size using the Cochrane formula n=p(1-p) (z/m)^2, where p is the estimated proportion of abnormality, z is the critical value corresponding to the confidence level, and m is the margin of error. For p=0.5, a confidence level of 95% (z=1.96), and a margin of error of 5%, the desired sample size is 385 participants (39). It is important to notice that some records were missing information like BMI and medication. To compensate for this missing information, we collected the records of a total of 523 T2DM patients who matched our inclusion and exclusion criteria dated from April 2015 to December 2022. Our inclusion criteria included all T2DM patients with previous LFTs. The study included male and female patients with T2DM who had done an LFT in the hospital. The study excluded T2DM patients who hadn’t done an LFT before and non-diabetics with existing LFTs.
2.2 Data collection
We extracted a simple random sample of 523 T2DM patients from the MNGHA Best-Care database. All patients were T2DM patients and had done an LFT. We collected the last measured LFT of every sample and used it for analysis. To decide whether an LFT is normal or not, we used the reference values of the Best-Care system.
2.3 Statistical analysis
We used the Social Sciences Statistical Package (SPSS) version 20 to perform descriptive and inferential statistical analyses. We measured and reported the descriptive statistics parameters including the means, standard deviations, counts, value ranges, and percentages for sample characteristics, comorbidities, clinical characteristics, LFTs estimates, and medications. For the inferential statistics, we used confidence intervals to estimate the prevalence of each LFT. Then we applied independent t-test, the Pearson’s t-test, Fisher’s exact test, or odds ratios (OR) to examine the association between the sample characteristics, comorbidities, and medications with LFTs after checking the corresponding assumptions.
3 Results
3.1 Sample characteristics
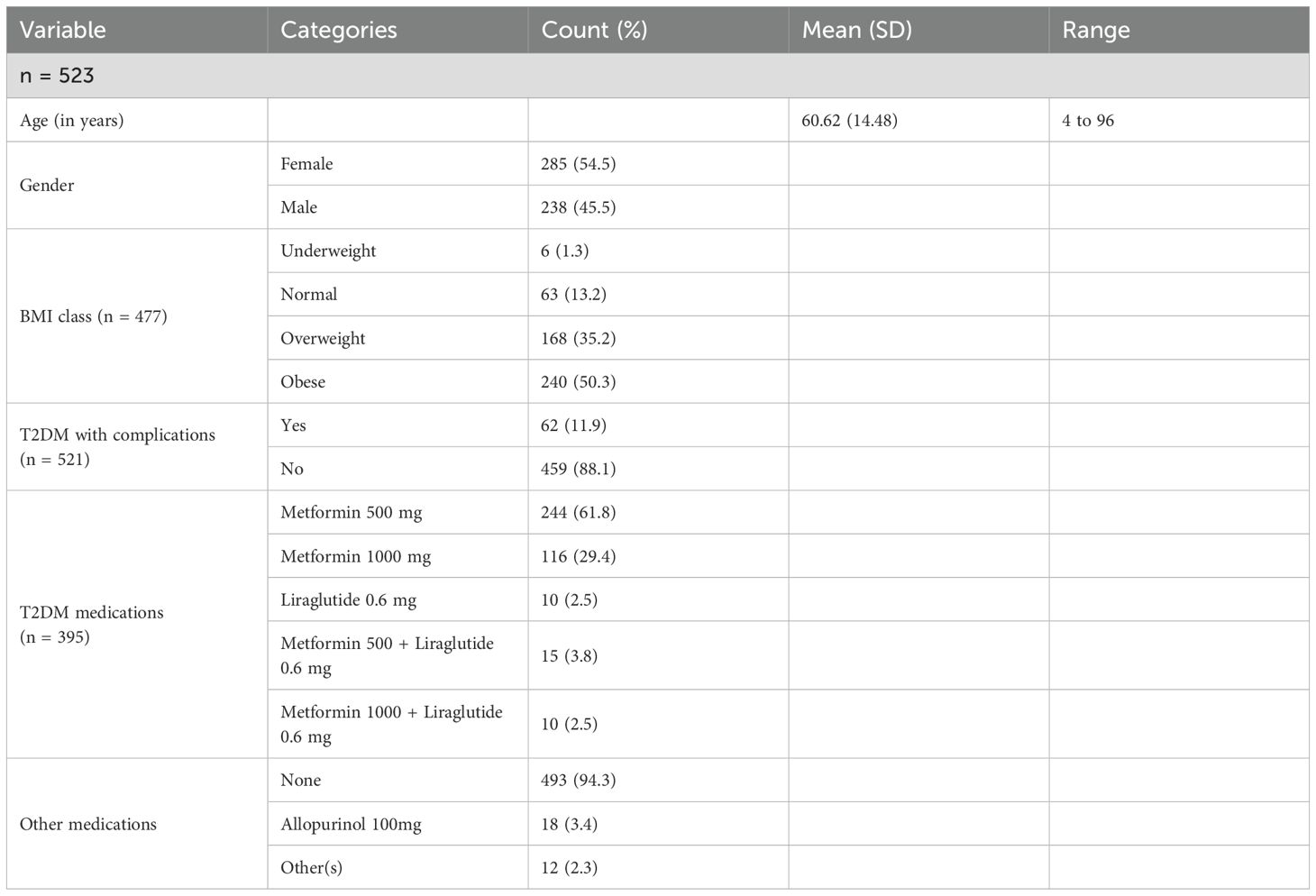
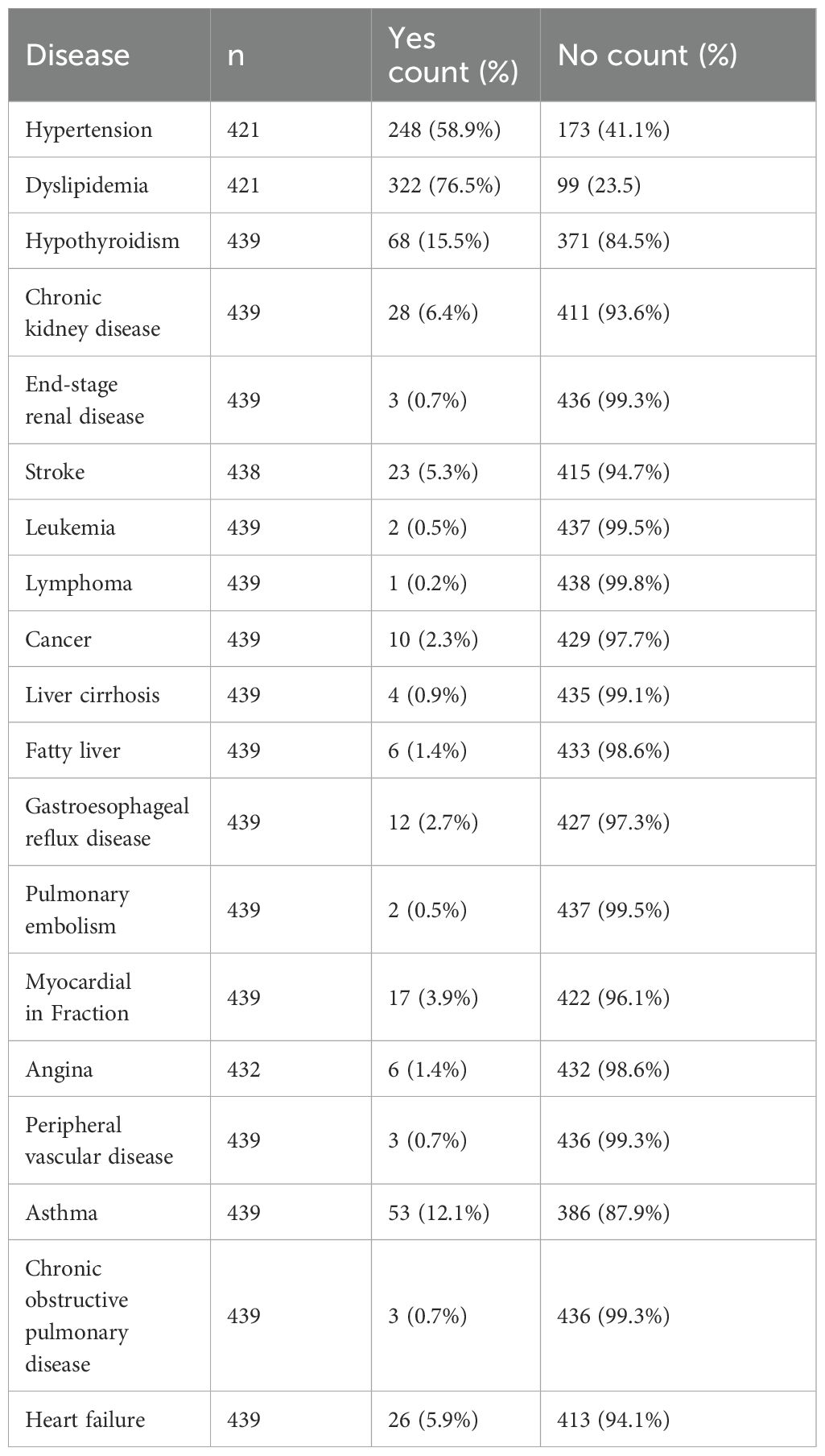
To estimate the proportions of abnormal LFTs among T2DM patients with a 95% confidence interval and a 5% margin of error, the minimal sample size needed was 385 patients. However, due to the possibility of incomplete data records, we collected a simple random sample of size 531 patients from the MNGHA Best-Care database. After removing incomplete data records, we used a net of 523 patient records for analysis. The mean age of our patients is 60.62 ± 14.52 years with a range from 4 to 96 years old. Most of the patients are females (54.5%), obese (50.3%), and have no complications (88.1%). In addition, the majority use metformin 500 mg medication (59.7%), followed by metformin 1000 mg medication (29.9%). Furthermore, the vast majority (94.3%) do not use other medication; see Table 1 below. Many T2DM patients suffered from other conditions, mainly hypertension (58.9%) and dyslipidemia (76.5%); see Table 2 below.
3.2 Liver function tests
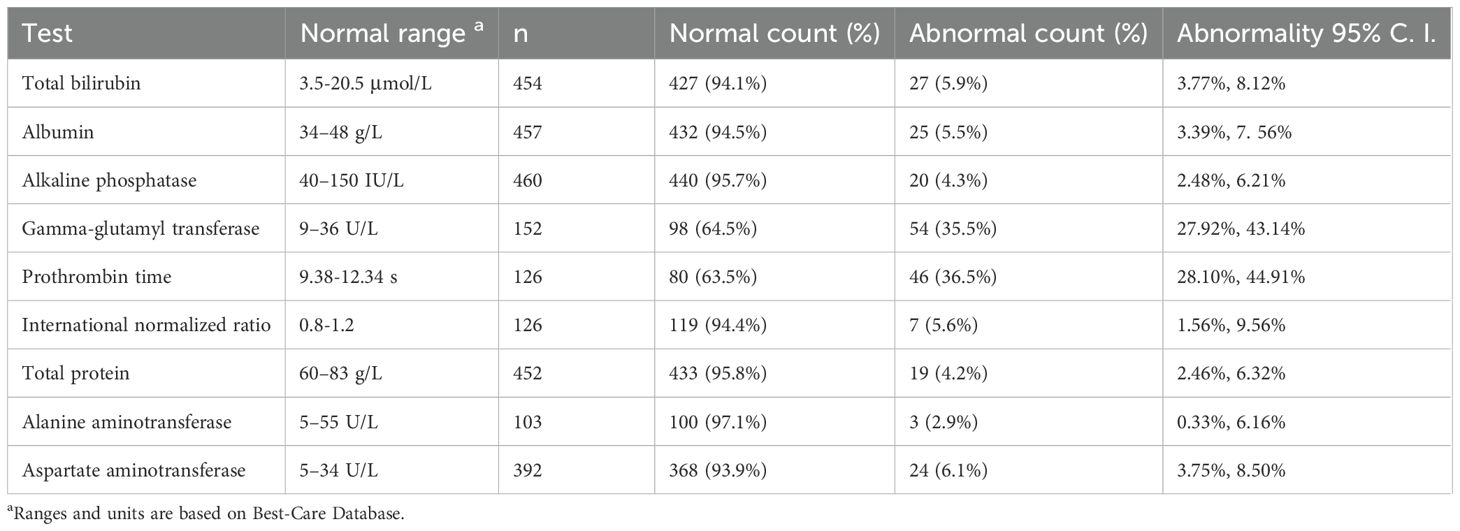
The point and interval estimate of the abnormality detected by the nine LFTs are listed below (Table 3). We noticed that aside from the GGT and PT tests, the abnormalities of other LFTs were small (≤ 6.1%).
3.3 General characteristics association with liver function tests
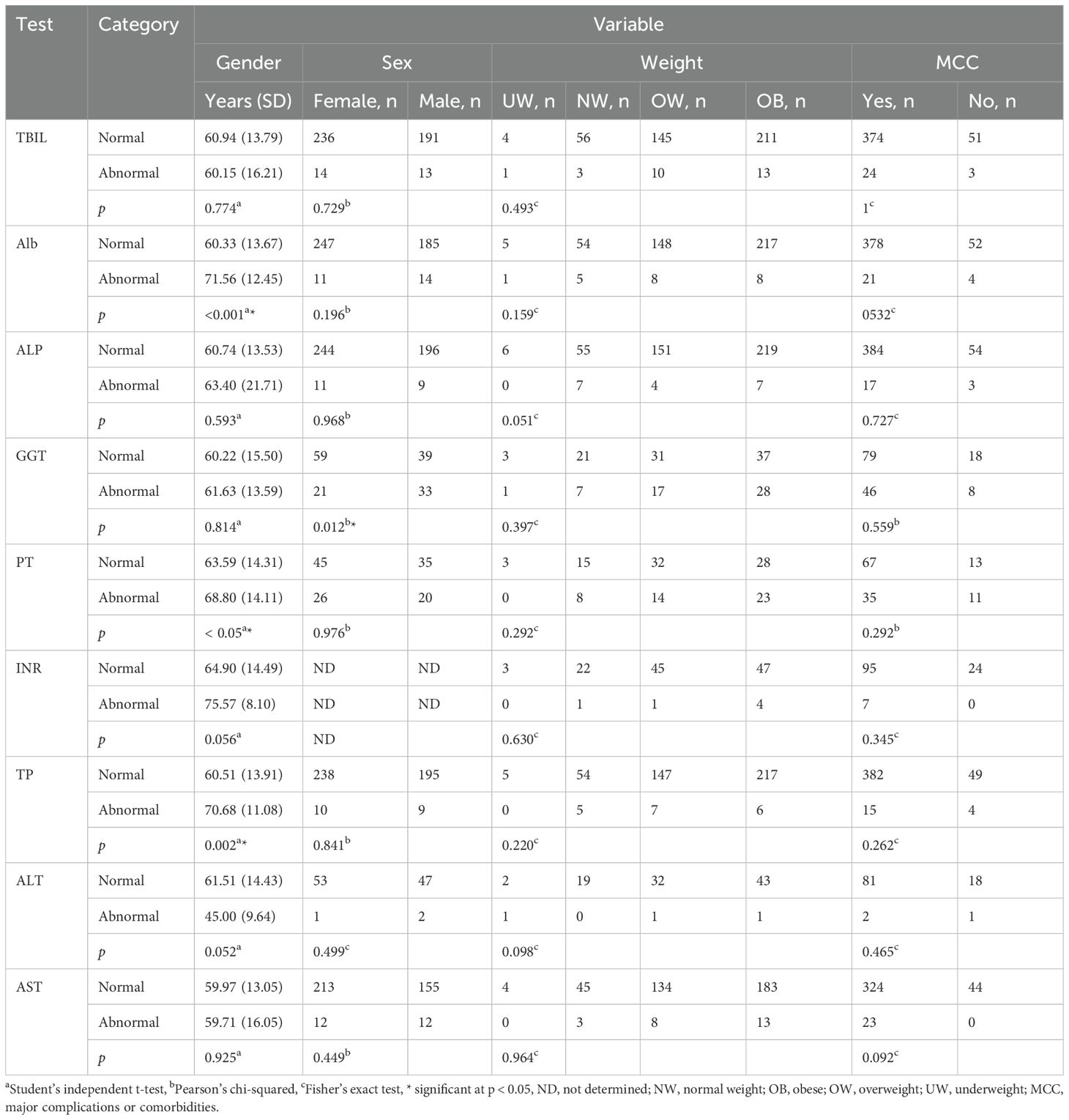
Student’s independent t-test revealed a significant difference in average age between the normal and abnormal groups of ALB, PT, and TP tests (p < 0.05) (Table 4). It is important to note that we did not calculate the OR values for age since we did not categorize the age into groups (Supplementary Table S1). OR values and Pearson’s chi-squared test showed a strong association between gender (female as reference) and the GGT test (p < 0.05, OR = 2.38, 95% CI = 1.21, 4.7). OR values and Fisher’s exact test showed no association between LTFs and body weight (normal weight as a reference). Similarly, OR values and Fisher’s exact test showed no association between LTFs and major complications (no complications as a reference) (Supplementary Table S1, Table 4).
3.4 Comorbidities association with liver function tests
In order to enhance the clarity of the presented results and avoid confusion, we categorized the observed associations between comorbidities and LFT’s into four groups based on their statistical significance. These categories are: associations supported by both OR and hypothesis tests like t-test, Pearson’s chi-squared test, or Fisher’s exact test; associations suggested by hypothesis tests but not quantified by odds ratios due to indeterminate values; associations suggested by odds ratios but not statistically significant when examined by hypothesis tests; and cases where no statistically significant associations were detected.
3.4.1 Associations supported by odds ratios and hypothesis tests
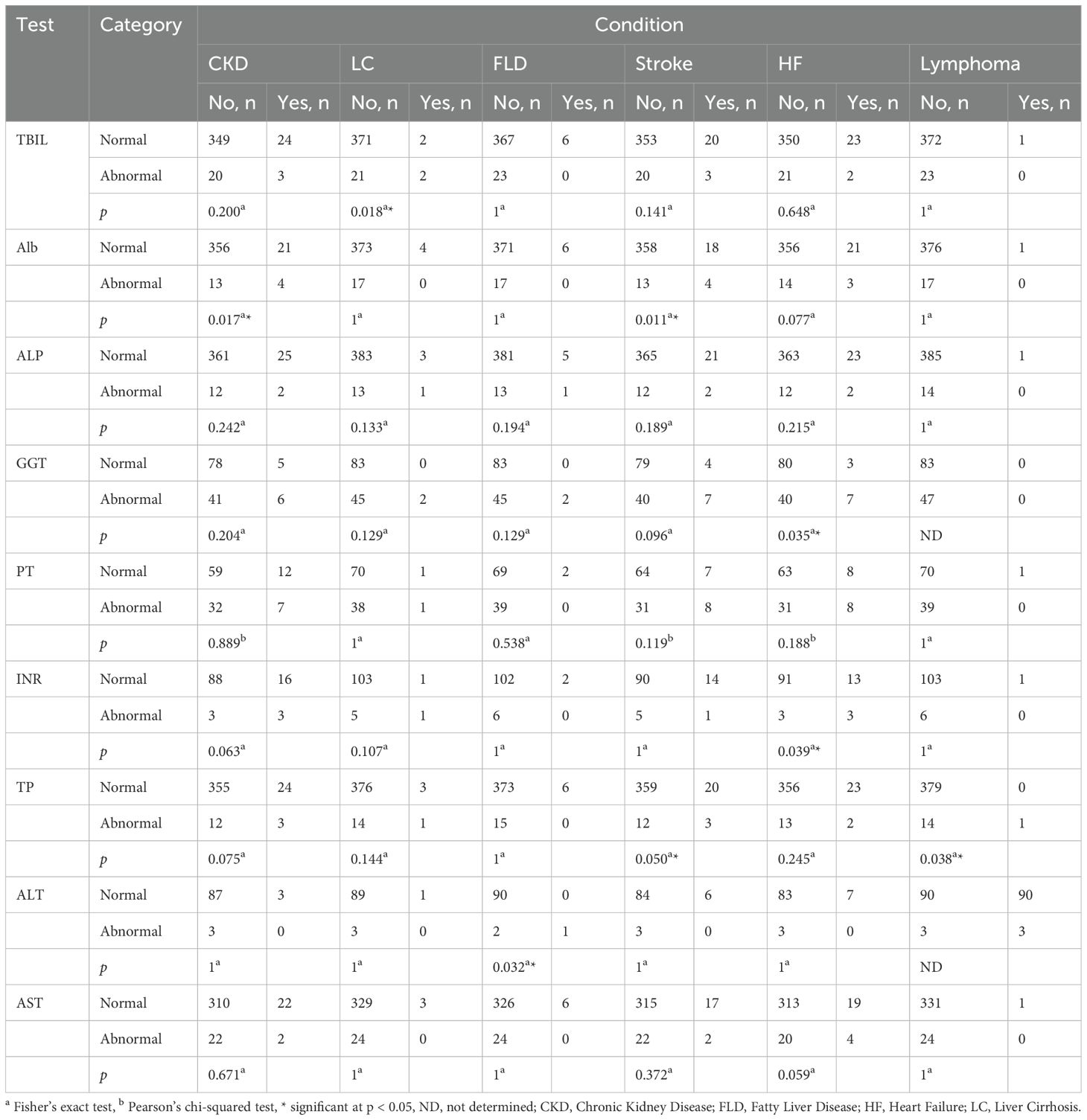
We observed a significant association between liver cirrhosis (LC) and the TBIL test (p < 0.05, OR = 17.67, 95% CI = 2.38, 131.69). We also found that stroke and CKD were significantly associated with the ALB test (p < 0.05, OR = 5.22, 95% CI = 1.57, 17.39; p < 0.05, OR = 6.12, 95% CI = 1.82, 20.66). In addition, heart failure (HF) is significantly associated with both the GGT and INR tests (p < 0.05, OR = 4.67, 95% CI = 1.15, 19.02; p < 0.05, OR = 7.00, 95% CI = 1.28, 38.42). Stroke was significantly associated with the TP test (p < 0.05, OR = 4.49, 95% CI = 1.18, 17.19) (Table 5; Supplementary Table S2).
3.4.2 Associations indicated by hypothesis tests but not quantified by odds ratios
In some cases, Fisher’s exact test revealed significant associations between certain comorbidities and LFTs (p < 0.05). Due to the small number of cases, ORs could not be reliably calculated, and associations could not be statistically confirmed. We observed this outcome in the case of lymphoma association with TP and the association of fatty liver disease (FLD) with the ALT test (Table 5; Supplementary Table S2).
3.4.3 Associations indicated by odds ratios but not statistically significant by hypothesis tests
In other cases, the OR values indicated associations between comorbidities and LFTs. However, Fisher’s exact and Pearson’s chi-squared tests did not confirm these associations (p > 0.05). We observed this outcome in the associations of CKD with INR (p = 0.063, OR = 5.50, 95% CI = 1.02, 29.71), LC with INR (p = 0.107, OR = 20.60, 95% CI = 1.12, 379.5), heart failure (HF) with AST (p = 0.059, OR = 3.30, 95% CI = 1.03, 10.61), end-stage renal disease (ESRD) with ALB (p = 0.124, OR = 11.72, 95% CI = 91.01, 136.090), ESRD with alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (p = 0.102, OR = 14.77, 95% CI = 91.26, 173.450), ESRD with TP (p = 0.110, OR = 13.46, 95% CI = 91.16, 157.450), pulmonary embolism (PE) with TBIL (p = 0.113, OR = 16.91, 95% CI = 1.03, 279.47), PE with TP (p = 0.075, OR = 27.00, 95% CI = 1.61, 454.21), leukemia with TP (p = 0.075, OR = 27.00, 95% CI = 1.61, 454.21), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) with INR (p = 0.107, OR = 20.60, 95% CI = 1.12, 379.5), myocardial infarction (MI) with TBIL (p = 0.058, OR = 4.15, 95% CI = 1.1, 15.77), and MI with AST (p = 0.060, OR = 4.17, 95% CI = 1.08, 16.1) (Supplementary Tables S2, S3). It is important to note that some of the previously presented CIs are implausibly wide, likely due to small sample sizes. This limits the interpretability of these associations and increases their uncertainty. For that reason, we did not consider these associations significant.
3.4.4 No statistically significant associations detected
Finally, we did not observe any association between LFT abnormalities and hypertension, dyslipidemia, hypothyroidism, gastroesophageal reflux, peripheral vascular disease, cancer, and angina (Supplementary Table S3).
3.5 Medication association with liver function tests
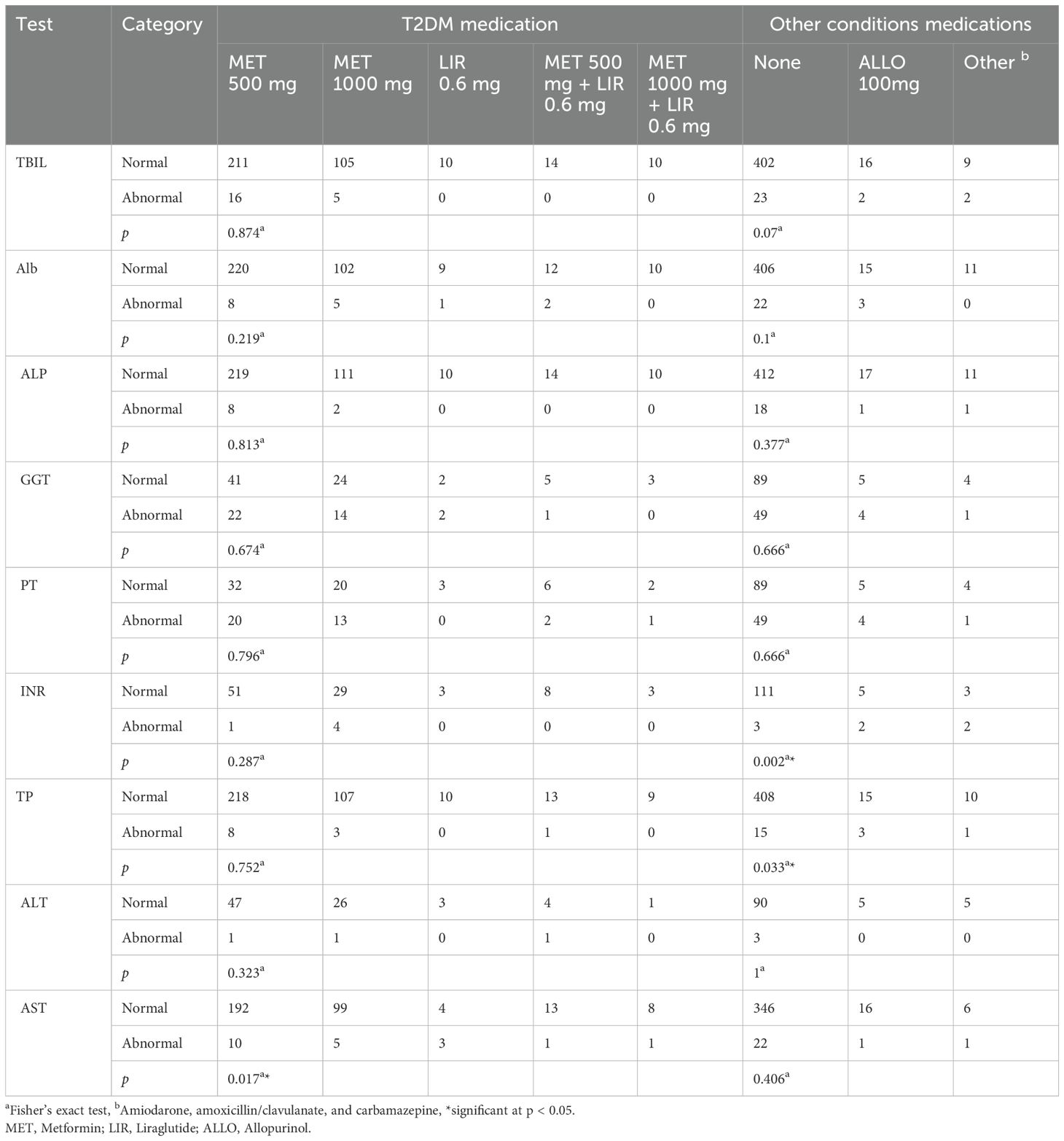
Patients received one of five types of treatments for T2DM: 500 mg metformin per day, 1000 mg of metformin daily, 0.6 mg of liraglutide daily, 500 mg of metformin plus 0.6 mg of liraglutide daily, or 1000 mg of metformin plus 0.6 mg of liraglutide daily. Fisher’s exact test revealed that T2DM medications were significantly associated with the AST test. Calculated OR values of each treatment using the 500 mg metformin as a reference revealed that the 0.6 mg liraglutide per day treatment is significantly associated with AST (OR = 14.40, 95% CI = 2.84, 73.23). We also used Fisher’s exact test to measure the association between LFT and non-diabetes treatments. These treatments include allopurinol, amiodarone, amoxicillin/clavulanate, and carbamazepine. Fisher’s exact test revealed that non-diabetes medications were significantly associated with the INR and TP tests. Calculated OR values of these treatments using “no treatment” as reference revealed that 100 mg of allopurinol per day treatment has a significant association with INR (OR = 14.80, 95% CI = 2.01, 109.48) and TP (OR = 5.44, 95% CI = 1.43, 20.83). In addition, the OR value of the group of patients who received non-diabetes treatments other than allopurinol revealed an association with INR (OR = 24.67, 95% CI = 2.95, 206.58) (Table 6, Supplementary Table S4).
4 Discussion
4.1 Principal findings
This study investigated the relationship between LFTs and DM and their association with various risk factors, including age, sex, obesity, comorbidities, and medications in patients diagnosed with T2DM who had done LFT in the MNGHA hospitals. T2DM patients who suffer from CKD, FLD, stroke, HF, LC, or lymphoma have at least one abnormal liver test. Metformin treatment of T2DM is significantly associated with abnormal AST levels.
Almost 35.5% of T2DM patients in this study showed an abnormal GGT test. This finding is consistent with multiple previous studies that emphasized the association between hyperglycemia and T2DM and high GGT levels (13, 22–26). Multiple studies confirmed GGT association with T2DM in different ethnic populations (40–47). Despite this pronounced association, there is no clear biological mechanism that explains the involvement of GGT in DM development (48–50). Some researchers speculated that GGT, a marker for hepatic steatosis, is also an indicator of insulin resistance during DM development. The inverse relationship between GGT and insulin sensitivity supports this speculation (51–53). Other researchers stressed the association between GGT and fat accumulation in the liver. Liver fat accumulation is associated with insulin resistance and T2DM development. The increased GGT levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients support this prediction (51, 54, 55). The relationship between GGT and oxidative stress can also explain the association between increased GGT levels and T2DM development (49, 56). The increased levels of GGT usually indicate an increase in cellular oxidative stress (57, 58). The pancreatic insulin-producing cells, beta cells, have less efficient antioxidant enzymes (59, 60). For that reason, they are more vulnerable to oxidative stress damages, which could ultimately compromise their ability to secrete insulin (61, 62). On the other hand, researchers noticed that T2DM male patients have significantly more GGT abnormalities compared to female patients. A previous study found that normal levels of GGT of males between the ages of 50 and 70 years old are usually higher than the normal levels of GGT in females of the same age group (63). In relation to the findings of the previous study, the normal GGT range in MNGHA Best Care is 9–36 U/L. Taking these sex-related differences into account, we can reasonably predict that more males have GGT levels closer to the upper limit. Those males are more likely to fill in the abnormal level category.
Approximately 36.5% of the T2DM patients of the current study had an abnormal PT test. These results align well with previous studies that reported shortened PT tests in DM patients (64–68). PT abnormalities usually occur due to the impaired balance between fibrinolysis and coagulation processes. DM promotes a procoagulant state. This state is characterized by a significant increase of hypofibrinolysis, activating coagulation factors and platelet activation (64, 65, 69). Hyperglycemia triggers prothrombin synthesis in the liver, which in turn increases thrombin levels and thus prompts a procoagulant state in DM patients (66, 67). Nevertheless, several studies showed no association between DM and PT, while other studies reported prolonged PT in DM patients (65, 70–73). Furthermore, the current study reports an increased PT abnormality in T2DM patients at the age of 71 or more. Admittedly, it is difficult to take into account all the possible factors that could lead to such an observation; however, one of the possible factors that could contribute to this effect is the consumption of anticoagulant medications. Using these medications, a common practice in this age group, could prolong the PT (67, 74). This may explain the significant association of PT abnormalities and older T2DM patients. The current study also reports an increase in ALB and TP abnormalities in older T2DM patients. The impairment of serum protein biosynthesis as a result of aging and DM could explain the elevated ALB and TP abnormalities (75). Previous studies showed a significant decrease in ALB and TP synthesis with aging (76, 77). Other studies showed that DM development could potentially impair serum ALB biosynthesis (78, 79).
The current study investigated the association between LFTs and T2DM and their relation to accompanying diseases. T2DM patients diagnosed with comorbidities, specifically CKD, FLD, stroke, HF, LC, or lymphoma, are more likely to have at least one abnormal LFT. T2DM patients diagnosed with LC tend to have higher TBIL test abnormalities. LC is typically associated with significantly higher TBIL concentrations than the normal level (80–82). However, several studies reported significantly lower TBIL concentrations in pre-DM and new-onset DM than T2DM (83–85). Despite DM’s apparent ameliorating effect on TBIL, this effect seems unable to overcome the increasing abnormality level of TBIL due to LC damages (82). T2DM patients suffering strokes or diagnosed with CKD seem to maintain higher ALB test abnormalities. Previous studies indicated that low serum ALB levels are associated with stroke (86–88). Other studies indicate that serum ALB is commonly lower in CKD patients. These studies suggest that lower serum ALB is one of the indicators of poor renal function (89, 90). T2DM can amplify these risks since it impairs the biosynthesis of serum proteins as previously mentioned (76, 77, 90). The current study also investigated TP and found it to be higher in T2DM patients diagnosed with stroke and lymphoma. A previous study indicated that low serum TP concentrations are associated with stroke. The same study showed that serum protein concentrations increased due to improved nutrition are associated with better stroke outcomes (91, 92). Other researchers attributed the elevated TP test abnormalities in T2DM patients suffering from lymphoma to the overproduction of immunoglobulins (93, 94). The overproduction of these proteins could potentially increase TP in lymphoma patients. The current study also revealed an association between GGT and INR test abnormalities and T2DM patients diagnosed with HF. Several studies indicated the association of high GGT levels and HF (95–99). Many of these studies focused on the association of elevated GGT and oxidative stress and its involvement in glutathione metabolism. Oxidative stress and inflammation are known risk factors for HF and other cardiovascular diseases. INR studies, on the other hand, indicated an inverse correlation between INR levels and HF and other thrombotic events (100, 101). These studies offer a partial explanation of the association between elevated GGT and INR abnormalities and HF in T2DM patients. The current study found that T2DM patients diagnosed with FLD have higher ALT activity abnormalities. These results are in agreement with several studies that indicated a strong correlation between higher ALT activity and FLD (102–105). Several researchers agree that ALT indicates liver cell damage that non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and other conditions cause with high reliability (106–108).
The majority of patients included in the current study are using metformin 500 mg alone for T2DM treatment. The remaining patients either used a higher dosage of metformin, metformin in combination with liraglutide, or liraglutide alone. We observed no association between T2DM medications and LFTs abnormalities except for their effect on the AST test. Generally, metformin is a safe drug that has low toxic effects on the hepatocytes (109, 110). There is no clear effect of metformin or liraglutide on most of the LFTs (111, 112). However, patients who used metformin 500 mg alone had significantly lower AST test abnormalities when compared to patients who received different treatment plans. The observed effect of metformin on AST agrees with several studies that indicated that long-term use of metformin reduces transaminase activities (110, 113, 114). Animal-based model studies showed that metformin treatment prevented or reversed liver cell steatosis. In these models, metformin treatment decreased serum ALT, AST, and ALP levels (115–118). These studies predicted that metformin inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative stress action mediates its effect on liver enzyme synthesis (119). About 5.7% of patients used medications other than those for T2DM. The current study showed that patients receiving medications other than those for T2DM have higher INR and TP test abnormalities. Previous studies showed that allopurinol, amiodarone, and amoxicillin/clavulanate may prolong INR and increase the risk of bleeding (120–123). One study showed that carbamazepine lowers INR and increases the risk of clotting (124). As for the TP test, there is evidence that some of these drugs, like amiodarone and carbamazepine, can bind to serum proteins (125, 126); however, it is not clear how these medications could affect these proteins synthesis and concentrations.
When considering the relatively high prevalence of T2DM in Saudi Arabia, in addition to the significant associations between LFT abnormalities and T2DM revealed in this study, the researchers recommended integrating routine monitoring of liver function into the clinical management of T2DM patients in the health care system of Saudi Arabia. Priority should be given to GGT, PT, AST, ALB, and TP tests. This protocol could improve patient care by early detection of potential liver dysfunction in T2DM patients and reduce the risk of developing severe liver-related complications.
4.2 Strengths and limitations
This study is the first to explore the association between T2DM and LFTs in Saudi Arabia. The access to the MNGHA Best-Care database ensured a robust and wide utilization of large and full data sets that extend over longer periods of time and spread over a wide geographical location throughout Saudi Arabia. This large data set allowed for proper sampling and statistical analyses, which in turn strengthened the validity of the drawn conclusions. Overall, the findings of this study agree with the findings of similar studies investigating other ethnicities and geographical locations; however, there are many factors that could limit the generalizability of the current study. Despite the large size of the MNGHA Best-Care database, some of the records in this study were incomplete. Moreover, this investigation restricted the sample to T2DM patients who had LFT. It is important to highlight that the exclusion of T2DM patients with untested LFTs could cause a selection bias. The current study estimated the effect of many confounding variables; however, it did not consider the effects of residual confounding factors that could affect LFTs (e.g., dietary habits, physical activity, medication adherence). It is important to acknowledge that not taking these factors into account could affect the generalizability of the findings of the current investigation. This observation reveals the need for intervention studies to investigate the association between T2DM and LFT abnormalities while minimizing the effect of confounding factors to a minimum. It is also important to notice that association analysis of LFTs and comorbidities did not adjust for potential confounders such as age, BMI, gender, and diabetes duration. These variables may influence both comorbidities and LFTs abnormalities. Multivariable analysis can give a better understanding of the effect of these factors. Finally, this study used Fisher’s exact test and Pearson’s chi-squared test to infer the significance of observed associations. The study also used the OR method to measure the significance of the associations. In most cases, there was an agreement between the OR method and other methods. However, the OR method showed additional significant associations not detected by other methods (Supplementary Tables S1–S4). We attribute this apparent discrepancy between the different types of association analysis to the very low values of terms used to calculate ORs. These low values could inflate the OR values and widen their confidence interval, which in turn would increase their uncertainty. In these cases, we only relied on the more accurate Fisher’s exact test and Pearson’s chi-squared tests to judge the associations of these variables. Taking a large sample size could potentially resolve these inconsistencies.
5 Conclusions
This study examines the association between T2DM and LFTs abnormalities in Saudi Arabia. The study emphasizes the positive association between T2DM and the incidence of GGT and PT test abnormalities. It reveals the association between T2DM and comorbidities, including CKD, LC, FLD, stroke, HF, and lymphoma, and several LFT abnormalities. Finally, it stresses the association between T2DM and other conditions, medications, and some LFT abnormalities. The findings of this study are in agreement with similar studies investigating various populations. However, the generalizability of the study remains limited due to intrinsic biases and uncontrolled factors. More controlled intervention studies could provide better evidence on these associations. The outcome of this study stresses the importance of monitoring the liver function of T2DM patients, especially those who suffer other comorbidities and consume additional medications besides the traditional T2DM medications.
Data availability statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due KAIMRC policies but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to bWVoeWFybkBrc2F1LWhzLmVkdS5zYQ==.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the King Abdullah International Medical Research Center (KAIMRC) approved this study (Approval No: IRB/1095/22). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
NM: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. ZAlh: Data curation, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MA: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Data curation. ZAla: Methodology, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AA: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology, Data curation. RA: Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank King Abdullah International Medical Research Center for supporting this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcdhc.2025.1617641/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
ALT, Alanine aminotransferase; ALB, Albumin; ALP, Alkaline phosphatase; AST, Aspartate aminotransferase; CKD, Chronic kidney disease; DM, Diabetes mellitus; FLD, Fatty liver disease; GGT, Gamma-glutamyl transferase; INR, International normalized ratio; LC, Liver Cirrhosis; LFT, Liver function test; MNGHA, Ministry of National Guard-Health Affairs; PT, Prothrombin time; TBIL, Total bilirubin; TP, Total serum protein; T2DM, Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
References
1. American Diabetes A. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. (2013) 36 Suppl 1:S67–74. doi: 10.2337/dc13-S067
2. Federation ID. Saudi Arabia 2024. Available online at: https://idf.org/our-network/regions-and-members/middle-east-and-north-africa/members/saudi-arabia/ (Accessed November 11, 2024).
3. Prevention CDC. National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2024. (Atlanta, Georgia, USA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services) (2024).
4. Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Results. Seattle, Washington, USA: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (2021). Available online at: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/ (Accessed November 15, 2024).
5. Robert AA, Al Dawish MA, Braham R, Musallam MA, Al Hayek AA, and Al Kahtany NH. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia: major challenges and possible solutions. Curr. Diabetes Rev. (2017) 13:59–64. doi: 10.2174/1573399812666160126142605
6. Aljulifi MZ. Prevalence and reasons of increased type 2 diabetes in Gulf Cooperation Council Countries. Saudi Med. J. (2021) 42:481–90. doi: 10.15537/smj.2021.42.5.20200676
7. Khalil SA, Azar S, Hafidh K, Ayad G, and Safwat M. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the MENA region: A systematic review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. (2024) 20:71–6. doi: 10.2174/1573399820666230731105704
8. Iglay K, Hannachi H, Howie PJ, Xu JF, Li XY, Engel SS, et al. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. (2016) 32:1243–52. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2016.1168291
9. Garcia-Compean D, Jaquez-Quintana JO, Gonzalez-Gonzalez JA, and Maldonado-Garza H. Liver cirrhosis and diabetes: risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical implications and management. World J. Gastroenterol. (2009) 15:280–8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.280
10. Sakharkar P and Deb S. Examining liver function in adults with diabetes in the United States. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. (2021) 24:317–28. doi: 10.18433/jpps31851
11. Tomic D, Salim A, George J, Magliano DJ, and Shaw JE. Liver disease mortality and hospitalisations among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A population-based study. Liver Int. (2024) 44:508–17. doi: 10.1111/liv.15794
12. Chilay A MN, Misra M, Jatale R, and Ramchandran S. Liver function test and diabetes mellitus: correlation from a laboratory perspective. Indian J. Med. Biochem. (2023) 27:40–4. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10054-0220
13. Wan JY and Yang LZ. Liver enzymes are associated with hyperglycemia in diabetes: A three-year retrospective study. Diabetes Metab. Synd Ob. (2022) 15:545–55. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S350426
14. Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. (2019) 71:793–801. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021
15. Han HS, Kang G, Kim JS, Choi BH, and Koo SH. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp. Mol. Med. (2016) 48:e218. doi: 10.1038/emm.2015.122
16. Giugliano D, Ceriello A, and Esposito K. Glucose metabolism and hyperglycemia. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. (2008) 87:217S–22S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.1.217S
17. Palsamy P, Sivakumar S, and Subramanian S. Resveratrol attenuates hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress, proinflammatory cytokines and protects hepatocytes ultrastructure in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced experimental diabetic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. (2010) 186:200–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.03.028
18. Lucchesi AN, Cassettari LL, and Spadella CT. Alloxan-induced diabetes causes morphological and ultrastructural changes in rat liver that resemble the natural history of chronic fatty liver disease in humans. J. Diabetes Res. (2015) 2015:494578. doi: 10.1155/2015/494578
19. Welt K, Weiss J, Martin R, Dettmer D, Hermsdorf T, Asayama K, et al. Ultrastructural, immunohistochemical and biochemical investigations of the rat liver exposed to experimental diabetes und acute hypoxia with and without application of Ginkgo extract. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. (2004) 55:331–45. doi: 10.1078/0940-2993-00337
20. Mota M, Banini BA, Cazanave SC, and Sanyal AJ. Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. (2016) 65:1049–61. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.02.014
21. McGill MR. The past and present of serum aminotransferases and the future of liver injury biomarkers. Excli J. (2016) 15:817–28. doi: 10.17179/excli2016-800
22. Salmela PI, Sotaniemi EA, Niemi M, and Maentausta O. Liver function tests in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. (1984) 7:248–54. doi: 10.2337/diacare.7.3.248
23. Kunutsor SK, Apekey TA, and Walley J. Liver aminotransferases and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. (2013) 178:159–71. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws469
24. Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Lennon L, and Whincup PH. Hepatic enzymes, the metabolic syndrome, and the risk of type 2 diabetes in older men. Diabetes Care. (2005) 28:2913–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.12.2913
25. Doi Y, Kubo M, Yonemoto K, Ninomiya T, Iwase M, Tanizaki Y, et al. Liver enzymes as a predictor for incident diabetes in a Japanese population: the Hisayama study. Obes. (Silver Spring). (2007) 15:1841–50. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.218
26. Lee DH, Ha MH, Kim JH, Christiani DC, Gross MD, Steffes M, et al. Gamma-glutamyltransferase and diabetes–a 4 year follow-up study. Diabetologia. (2003) 46:359–64. doi: 10.1007/s00125-003-1036-5
27. Ahmed MH BC. Drug treatment and type 2 diabetes: the impact of liver disease. Pract. Diabetes Int. (2007) 24:318–23. doi: 10.1002/pdi.1132
28. Razavizade M, Jamali R, Arj A, Matini SM, Moraveji A, and Taherkhani E. The effect of pioglitazone and metformin on liver function tests, insulin resistance, and liver fat content in nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease: a randomized double blinded clinical trial. Hepat Mon. (2013) 13:e9270. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.9270
29. Andrade RJ, Lucena M, Vega JL, Torres M, Salmeron FJ, Bellot V, et al. Acarbose-associated hepatotoxicity. Diabetes Care. (1998) 21:2029–30. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.11.2029
30. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury. Bethesda (MD). (2012). doi: 10.1097/01.ogx.0000415824.34652.1a
31. Al-Bakr ABAAS and Mohanned A. A Descriptive Study: The Concept of Gross Domestic Product. Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency and King Saud University (2016).
32. Mokdad AH, Tuffaha M, Hanlon M, El Bcheraoui C, Daoud F, Al Saeedi M, et al. Cost of diabetes in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 2014. J. Diabetes Metab. (2015) 6:575. doi: 10.4172/2155-6156.1000575
33. Cicek M, Buckley J, Pearson-Stuttard J, and Gregg EW. Characterizing multimorbidity from type 2 diabetes: insights from clustering approaches. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. (2021) 50:531–58. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2021.05.012
34. Lin PJ, Pope E, and Zhou FL. Comorbidity type and health care costs in type 2 diabetes: A retrospective claims database analysis. Diabetes Ther. (2018) 9:1907–18. doi: 10.1007/s13300-018-0477-2
35. Kim KS, Hong S, Han K, and Park CY. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study. BMJ. (2024) 384:e076388. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-076388
36. Khanna S, Parikh NS, and VanWagner LB. Fatty liver and cerebrovascular disease: plausible association and possible mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. (2022) 33:31–8. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000799
37. Kumar R, Priyadarshi RN, and Anand U. Chronic renal dysfunction in cirrhosis: A new frontier in hepatology. World J. Gastroentero. (2021) 27:990–1005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i11.990
38. Struijs JN, Baan CA, Schellevis FG, Westert GP, and van den Bos GA. Comorbidity in patients with diabetes mellitus: impact on medical health care utilization. BMC Health Serv. Res. (2006) 6:84. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-6-84
39. Cochran WG. The Estimation of Sample Size. Sampling Techniques. New York: John Wiley & Sons (1963) p. 75–6.
40. Hua S, Qi Q, Kizer JR, Williams-Nguyen J, Strickler HD, Thyagarajan B, et al. Association of liver enzymes with incident diabetes in US Hispanic/Latino adults. Diabetes Med. (2021) 38:e14522. doi: 10.1111/dme.14522
41. Bi Y, Yang S, Liu Y, Cao L, Gao M, Liu W, et al. To explore association between gamma-glutamyl transferase and type 2 diabetes using a real-world study and mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). (2022) 13:899008. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.899008
42. Lee DH, Jacobs DR, Gross M, Kiefe CI, Roseman J, Lewis CE, et al. γ-glutamyltransferase is a predictor of incident diabetes and hypertension:: The coronary artery risk development in young adults (CARDIA) study. Clin. Chem. (2003) 49:1358–66. doi: 10.1373/49.8.1358
43. Nakanishi N, Suzuki K, and Tatara K. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in middle-aged Japanese men. Diabetes Care. (2004) 27:1427–32. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.6.1427
44. Nguyen QM, Srinivasan SR, Xu JH, Chen W, Hassig S, Rice J, et al. Elevated liver function enzymes are related to the development of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in younger adults: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Diabetes Care. (2011) 34:2603–7. doi: 10.2337/dc11-0919
45. Xu L, Jiang CQ, Schooling CM, Zhang WS, Cheng KK, and Lam TH. Liver enzymes and incident diabetes in China: a prospective analysis of 10–764 participants in the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health. (2015) 69:1040–4. doi: 10.1136/jech-2015-205518
46. Schneider AL, Lazo M, Ndumele CE, Pankow JS, Coresh J, Clark JM, et al. Liver enzymes, race, gender and diabetes risk: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Diabetes Med. (2013) 30:926–33. doi: 10.1111/dme.12187
47. Vasishta S, Ganesh K, Umakanth S, and Joshi MB. Ethnic disparities attributed to the manifestation in and response to type 2 diabetes: insights from metabolomics. Metabolomics. (2022) 18:45. doi: 10.1007/s11306-022-01905-8
48. Wannamethee SG. Liver enzymes and incident diabetes in China: a prospective analysis of 10–764 participants in the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health. (2015) 69:1031–2. doi: 10.1136/jech-2015-206050
49. Choi SH, Kim BT, Shin J, and Kim KN. Combined effect of serum alanine aminotransferase and gamma-glutamyltransferase on incidence of diabetes mellitus: A longitudinal study. Med. (Baltimore). (2020) 99:e18963. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018963
50. Lonardo A and Ndrepepa G. Concise review: gamma-glutamyl transferase - evolution from an indiscriminate liver test to a biomarker of cardiometabolic risk. Metab. Target Organ D. (2022) 2:17. doi: 10.20517/mtod.2022.20
51. Perry IJ, Wannamethee SG, and Shaper AG. Prospective study of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and risk of NIDDM. Diabetes Care. (1998) 21:732–7. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.5.732
52. Wallace TM, Utzschneider KM, Tong J, Carr DB, Zraika S, Bankson DD, et al. Relationship of liver enzymes to insulin sensitivity and intra-abdominal fat. Diabetes Care. (2007) 30:2673–8. doi: 10.2337/dc06-1758
53. Liang SC and Yang TF. Analysis of the association between changes in the GGT/HDL-C ratio and the risk of diabetes mellitus based on a latent class growth mixed modeling: A longitudinal cohort study of adults in China. Diabetes Metab. Syndrome Obes. (2024) 17:3139–50. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S475067
54. Saxena T AA, Rathore AJ, Rajak N, Naz S, and Shah R. GGT and SGPT - A rising marker in diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. (2014) 7:277–80. doi: 10.13005/bpj/487
55. Fujii H, Doi H, Ko T, Fukuma T, Kadono T, Asaeda K, et al. Frequently abnormal serum gamma-glutamyl transferase activity is associated with future development of fatty liver: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. (2020) 20:217. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01369-x
56. Abu Khadra KM, Bataineh MI, Khalil A, and Saleh J. Oxidative stress and type 2 diabetes: the development and the pathogenesis, Jordanian cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Med. Res. (2024) 29:370. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01906-4
57. Rosen P, Nawroth PP, King G, Moller W, Tritschler HJ, and Packer L. The role of oxidative stress in the onset and progression of diabetes and its complications: a summary of a Congress Series sponsored by UNESCO-MCBN, the American Diabetes Association and the German Diabetes Society. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. (2001) 17:189–212. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.196
58. Dawi J, Misakyan Y, Affa S, Kades S, Narasimhan A, Hajjar F, et al. Oxidative stress, glutathione insufficiency, and inflammatory pathways in type 2 diabetes mellitus: implications for therapeutic interventions. Biomedicines. (2025) 13:18. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010018
59. Matsuoka T, Kajimoto Y, Watada H, Kaneto H, Kishimoto M, Umayahara Y, et al. Glycation-dependent, reactive oxygen species-mediated suppression of the insulin gene promoter activity in HIT cells. J. Clin. Invest. (1997) 99:144–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI119126
60. Eguchi N, Vaziri ND, Dafoe DC, and Ichii H. The role of oxidative stress in pancreatic β Cell dysfunction in diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2021) 22:1509. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041509
61. Nakagawa T, Tuttle KR, Short RA, and Johnson RJ. Hypothesis: fructose-induced hyperuricemia as a causal mechanism for the epidemic of the metabolic syndrome. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. (2005) 1:80–6. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010018
62. Gong SJ, Gan SL, Zhang YH, Zhou HF, and Zhou Q. Gamma-glutamyl transferase to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is a more powerful marker than TyG index for predicting metabolic syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. (2023) 14. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1248614
63. Puukka K, Hietala J, Koivisto H, Anttila P, Bloigu R, and Niemela O. Age-related changes on serum ggt activity and the assessment of ethanol intake. Alcohol Alcohol. (2006) 41:522–7. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agl052
64. Carmassi F, Morale M, Puccetti R, De Negri F, Monzani F, Navalesi R, et al. Coagulation and fibrinolytic system impairment in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Thromb. Res. (1992) 67:643–54. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(92)90206-790206-7
65. Ebrahim H, Asrie F, and Getaneh Z. Basic coagulation profiles and platelet parameters among adult type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients at dessie referral hospital, Northeast Ethiopia: comparative cross-sectional study. J. Blood Med. (2021) 12:33–42. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S287136
66. Park HS, Gu JY, Yoo HJ, Han SE, Park CH, Kim YI, et al. Thrombin generation assay detects moderate-intensity statin-induced reduction of hypercoagulability in diabetes. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. (2018) 24:1095–101. doi: 10.1177/1076029618766254
67. Li X, Weber NC, Cohn DM, Hollmann MW, DeVries JH, Hermanides J, et al. Effects of hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus on coagulation and hemostasis. J. Clin. Med. (2021) 10:2419. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112419
68. Getu F, Aynalem M, Bizuneh S, and Enawgaw B. The prevalence of coagulopathy and associated factors among adult type II diabetes mellitus patients attending the university of gondar comprehensive specialized hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Diabetes Metab. Synd Ob. (2022) 15:579–90. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S349412
69. Bryk-Wiazania AH and Undas A. Hypofibrinolysis in type 2 diabetes and its clinical implications: from mechanisms to pharmacological modulation. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. (2021) 20:191. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01372-w
70. Sauls DL, Banini AE, Boyd LC, and Hoffman M. Elevated prothrombin level and shortened clotting times in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J. Thromb. Haemost. (2007) 5:638–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02366.x
71. Ephraim RK, Awuku YA, Adu P, Ampomah LT, Adoba P, Panford S, et al. High risk of coagulopathy among Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus clients at a municipal hospital in Ghana. Ghana Med. J. (2017) 51:101–7. doi: 10.4314/gmj.v51i3.2
72. Fattah MA, Shaheen MH, and Mahfouz MH. Disturbances of haemostasis in diabetes mellitus. Dis. Markers. (2003) 19:251–8. doi: 10.1155/2004/797458
73. Erem C, Hacihasanoglu A, Çelik S, Ovali E, Ersöz HÖ, Ukinç K, et al. Coagulation and fibrinolysis parameters in type 2 diabetic patients with and without diabetic vascular complications. Med. Prin Pract. (2005) 14:22–30. doi: 10.1159/000081919
74. Liu L, Ying M, Chen S, Li Q, Chen G, Li H, et al. The association between prothrombin time-international normalized ratio and long-term mortality in patients with coronary artery disease: a large cohort retrospective study with 44,662 patients. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. (2022) 22:297. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02619-4
75. Zeng RX, Xu JP, Zhang YZ, Tan JW, Kong YJ, Zhang MZ, et al. Associations of total protein, albumin, and globulin with insulin resistance: an NHANES study. Front. Endocrinol. (2024) 15. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1393137
76. Weaving G, Batstone GF, and Jones RG. Age and sex variation in serum albumin concentration: an observational study. Ann. Clin. Biochem. (2016) 53:106–11. doi: 10.1177/0004563215593561
77. Ignjatovic V, Lai C, Summerhayes R, Mathesius U, Tawfilis S, Perugini MA, et al. Age-related differences in plasma proteins: how plasma proteins change from neonates to adults. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e17213. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017213
78. Chang DC, Xu X, Ferrante AW Jr., and Krakoff J. Reduced plasma albumin predicts type 2 diabetes and is associated with greater adipose tissue macrophage content and activation. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. (2019) 11:14. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0409-y
79. Nicholson JP, Wolmarans MR, and Park GR. The role of albumin in critical illness. Br. J. Anaesth. (2000) 85:599–610. doi: 10.1093/bja/85.4.599
80. Ohkubo A. Bilirubin metabolism in liver cirrhosis. Nihon Rinsho. (1994) 52:138–44. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.196
81. Lee HA, Jung JY, Lee YS, Jung YK, Kim JH, An H, et al. Direct bilirubin is more valuable than total bilirubin for predicting prognosis in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gut Liver. (2021) 15:599–605. doi: 10.5009/gnl20171
82. Li S, Li NM, Li LS, Wang Y, Liu YS, Wang YJ, et al. Association of serum bilirubin levels with macro- and microvascular complications in chinese people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: new insight on gender differences. Diabetes Metab. Syndrome Obes. (2023) 16:597–606. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S403483
83. Wang J, Li Y, Han X, Hu H, Wang F, Li X, et al. Serum bilirubin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from two independent cohorts in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Sci. Rep. (2017) 7:41338. doi: 10.1038/srep41338
84. Vitek L, Hinds TD Jr., Stec DE, and Tiribelli C. The physiology of bilirubin: health and disease equilibrium. Trends Mol. Med. (2023) 29:315–28. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.01.007
85. Wei Y, Liu C, Lai F, Dong S, Chen H, Chen L, et al. Associations between serum total bilirubin, obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. (2021) 13:143. doi: 10.1186/s13098-021-00762-0
86. Xu GH and Zhang J. Stable stratified correlation and linear negative correlation between serum albumin and risk of all-cause death in patients with ischaemic stroke. Artery Res. (2024) 30:9. doi: 10.1007/s44200-024-00054-8
87. Nair R, Radhakrishnan K, Chatterjee A, Gorthi SP, and Prabhu VA. Serum albumin as a predictor of functional outcomes following acute ischemic stroke. J. Vasc. Interv Neurol. (2018) 10:65–8.
88. Shen G, Liu YT, Zhou C, Luo W, Yang YX, Guo S, et al. Associations between neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin ratio level and all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease-cause mortality in diabetes population. BMC Public Health. (2025) 25:401. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20924-9
89. Cheng T, Wang X, Han Y, Hao J, Hu H, and Hao L. The level of serum albumin is associated with renal prognosis and renal function decline in patients with chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. (2023) 24:57. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03110-8
90. Jung CH and Mok JO. Recent updates on vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol. Metab. (2020) 35:260–71. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.260
91. Wang R, Cao L, He Y, Zhang P, and Feng L. Nutrition-associated markers and outcomes among patients receiving enteral nutrition after ischemic stroke: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Neurol. (2024) 24:303. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03812-y
92. Mao YS, Zhu BQ, Wen HQ, Zhong T, and Bian MH. Impact of platelet hyperreactivity and diabetes mellitus on ischemic stroke recurrence: A single-center cohort clinical study. Int. J. Gen. Med. (2024) 17:1127–38. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S450059
93. Maurer MJ, Cerhan J, Katzmann JA, Link B, Micallef IN, Colgan J, et al. Elevation of serum free light chains are common in lymphoma and associated with poor event free and overall survival. Blood. (2010) 116:1683. doi: 10.1182/blood.V116.21.4136.4136
94. de Leval L, Gaulard P, and Dogan A. A practical approach to the modern diagnosis and classification of T- and NK-cell lymphomas. Blood. (2024) 144:1855–72. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023021786
95. Dhingra R, Gona P, Wang TJ, Fox CS, D'Agostino RB Sr, and Vasan RS. Serum gamma-glutamyl transferase and risk of heart failure in the community. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. (2010) 30:1855–60. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.207340
96. Wang Y, Tuomilehto J, Jousilahti P, Salomaa V, Li B, Antikainen R, et al. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and the risk of heart failure in men and women in Finland. Heart. (2013) 99:163–7. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2012-302972
97. Poelzl G, Eberl C, Achrainer H, Doerler J, Pachinger O, Frick M, et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of elevated gamma-glutamyltransferase in chronic heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. (2009) 2:294–302. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.108.826735
98. Ndrepepa G and Kastrati A. Gamma-glutamyl transferase and cardiovascular disease. Ann. Transl. Med. (2016) 4:481. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.12.27
99. Mentz RJ, Brunton SA, and Rangaswami J. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and chronic kidney disease with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus: a narrative review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. (2023) 22:316. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02023-y
100. Nassif ME, LaRue SJ, Raymer DS, Novak E, Vader JM, Ewald GA, et al. Relationship between anticoagulation intensity and thrombotic or bleeding outcomes among outpatients with continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices. Circ. Heart Fail. (2016) 9:e002680. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002680
101. Connors JM. On target: optimum international normalized ratio for left ventricular assist device patients. Circ. Heart Fail. (2016) 9:e003166. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.116.003166
102. Oh SY, Cho YK, Kang MS, Yoo TW, Park JH, Kim HJ, et al. The association between increased alanine aminotransferase activity and metabolic factors in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. (2006) 55:1604–9. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2006.07.021
103. Chen JF, Wu ZQ, Liu HS, Yan S, Wang YX, Xing M, et al. Cumulative effects of excess high-normal alanine aminotransferase levels in relation to new-onset metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in China. World J. Gastroenterol. (2024) 30:1346–57. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1346
104. Liu WX and Liu L. Predictive value of serum alanine aminotransferase for fatty liver associated with metabolic dysfunction. World J. Hepatol. (2024) 16:990–4. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.990
105. Chen ZW, Chen LY, Dai HL, Chen JH, and Fang LZ. Relationship between alanine aminotransferase levels and metabolic syndrome in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Zhejiang Univ Sci. B. (2008) 9:616–22. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B0720016
106. Wang M, Wang M, Zhang R, Zhang L, Ding Y, Tang Z, et al. A combined association of serum uric acid, alanine aminotransferase and waist circumference with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a community-based study. PeerJ. (2022) 10:e13022. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13022
107. Kang Y, Park S, Kim S, and Koh H. Normal serum alanine aminotransferase and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study using data from KNHANES 2010-2015. BMC Pediatr. (2018) 18:215. doi: 10.1186/s12887-018-1202-z
108. Xu JY, Wu LY, Deng J, Yang LB, Wang YT, Tian HY, et al. Population attributable fractions of fatty liver disease for type 2 diabetes Mellitus. BMC Endocr. Disord. (2023) 23:201. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01433-z
109. Cone CJ, Bachyrycz AM, and Murata GH. Hepatotoxicity associated with metformin therapy in treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Pharmacother. (2010) 44:1655–9. doi: 10.1345/aph.1P099
110. Chaudhary S and Kulkarni A. Metformin: past, present, and future. Curr. Diabetes Rep. (2024) 24:119–30. doi: 10.1007/s11892-024-01539-1
111. Farah S, Nguyen T, Kelsberg G, and Safranek S. Metformin for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. Fam Physician. (2019) 99:262–3.
112. Xu YY, Wang X, She YQ, Liu J, and Zhang Q. Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy of liraglutide in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Endocr. J. (2024) 71:881–94. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ24-0168
113. Ratziu V. Novel pharmacotherapy options for NASH. Dig Dis. Sci. (2016) 61:1398–405. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4128-z
114. Nazer RI, Abalhassan MF, and Alburikan KA. Liver enzyme trends in patients taking uninterrupted metformin before and after coronary surgery. Cardiovasc. Diagn. The. (2018) 8:469–79. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2018.05.04
115. Kita Y, Takamura T, Misu H, Ota T, Kurita S, Takeshita Y, et al. Metformin prevents and reverses inflammation in a non-diabetic mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e43056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043056
116. Lin HZ, Yang SQ, Chuckaree C, Kuhajda F, Ronnet G, and Diehl AM. Metformin reverses fatty liver disease in obese, leptin-deficient mice. Nat. Med. (2000) 6:998–1003. doi: 10.1038/79697
117. Saeedi Saravi SS, Hasanvand A, Shahkarami K, and Dehpour AR. The protective potential of metformin against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in BALB/C mice. Pharm. Biol. (2016) 54:2830–7. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1185633
118. Chen H, Huang MS, Zhang D, Wang H, Wang D, Li MW, et al. Metformin's effect on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease through the miR-200a-5p and AMPK/SERCA2b pathway. Front. Pharmacol. (2024) 15. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1477212
119. Vial G, Detaille D, and Guigas B. Role of mitochondria in the mechanism(s) of action of metformin. Front. Endocrinol. (2019) 10. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00294
120. Day R and Quinn D. Adverse interaction between warfarin and indomethacin. Drug Safety. (1994) 11:213–4. doi: 10.2165/00002018-199411030-00006
121. Barry M and Feely J. Allopurinol influences aminophenazone elimination. Clin. Pharmacokinet. (1990) 19:167–9. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199019020-00006
122. Sanoski CA and Bauman JL. Clinical observations with the amiodarone/warfarin interaction - Dosing relationships with long-term therapy. Chest. (2002) 121:19–23. doi: 10.1378/chest.121.1.19
123. Clark NP, Delate T, Riggs CS, Witt DM, Hylek EM, Garcia DA, et al. Warfarin interactions with antibiotics in the ambulatory care setting. JAMA Intern. Med. (2014) 174:409–16. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.13957
124. Mannheimer B, Andersson ML, Järnbert-pettersson H, and Lindh JD. The effect of carbamazepine on warfarin anticoagulation: a register-based nationwide cohort study involving the Swedish population. J. Thromb. Haemost. (2016) 14:765–71. doi: 10.1111/jth.13268
125. Lalloz MR, Byfield PG, Greenwood RM, and Himsworth RL. Binding of amiodarone by serum proteins and the effects of drugs, hormones and other interacting ligands. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. (1984) 36:366–72. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04400.x
126. Dasgupta A and Volk A. Displacement of valproic acid and carbamazepine from protein binding in normal and uremic sera by tolmetin, ibuprofen, and naproxen: Presence of inhibitor in uremic serum that blocks valproic acid-naproxen interactions. Ther. Drug Monit. (1996) 18:284–7. doi: 10.1097/00007691-199606000-00011
Keywords: liver function test, type 2 diabetes mellitus, comorbidities, liraglutide, allopurinol, Saudi Arabia
Citation: Mehyar N, Alhajeri Z, Alosaimi M, Alanazi Z, Alanazi A and Abusaris R (2025) The association between liver function tests abnormalities and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional study. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 6:1617641. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2025.1617641
Received: 24 April 2025; Accepted: 02 July 2025;
Published: 29 July 2025.
Edited by:
Alessando Mattina, IRRCS ISMETT/UPMC Italy, ItalyReviewed by:
Fatma Nişancı Kılınç, Kırıkkale University, TürkiyeThien Le, Flinders University, Australia
Copyright © 2025 Mehyar, Alhajeri, Alosaimi, Alanazi, Alanazi and Abusaris. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nimer Mehyar, bWVoeWFybkBrc2F1LWhzLmVkdS5zYQ==; Raghib Abusaris, U2FyaXNyQGtzYXUtaHMuZWR1LnNh
 Nimer Mehyar
Nimer Mehyar Ziyad Alhajeri2,3
Ziyad Alhajeri2,3