- Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, Tufts University, Boston, MA, United States
Periodontitis, a chronic inflammatory disease of the periodontium, has well-established links to systemic metabolic conditions, particularly diabetes and obesity. Recent research suggests a novel interaction between periodontitis and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) pathways, both of which regulate glucose metabolism and inflammation. In this review, we examine the potential bidirectional relationships between periodontitis and GLP-1 signaling and evaluate the therapeutic implications of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in periodontal disease. A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library identified 52 studies published between 1990 and 2025, ranging from in vitro and animal studies to human clinical and observational research. Findings indicate a multifaceted relationship between GLP-1 pathways and periodontal disease. Periodontitis may impair GLP-1 signaling and exacerbate glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity in individuals with diabetes or obesity. Several periodontopathic bacteria, notably Porphyromonas gingivalis, produce DPP-4-like enzymes that degrade GLP-1 and potentially disrupt glucose regulation. GLP-1 RAs, such as liraglutide and exendin-4, demonstrated anti-inflammatory, osteoprotective, and regenerative effects in preclinical models. Additionally, studies identified host and microbial DPP-4 activity as key mechanistic links between periodontal inflammation and systemic insulin resistance. This review highlights a novel and clinically relevant intersection between periodontitis and GLP-1 biology. GLP-1 RAs and DPP-4 inhibitors may offer dual benefits for metabolic control and periodontal health. Further research is needed to define delivery strategies, assess efficacy across patient populations, and explore the therapeutic targeting of DPP-4 activity in both host and microbial contexts.
Introduction
Periodontitis, a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the supporting structures of the teeth—including the gingiva, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone—is one of the leading causes of tooth loss worldwide. It is increasingly recognized for its systemic health implications. Its pathogenesis involves dysbiosis that triggers a persistent host inflammatory response, leading to destruction of periodontal tissues, including the alveolar bone. Beyond local effects, periodontitis is strongly associated with systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease and obesity and it has an established bidirectional relationship with diabetes, underscoring the interconnectedness of oral and systemic health (1, 2).
A previous scoping review has highlighted emerging evidence of a potential interplay between periodontitis and the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a key regulator of glucose metabolism with anti-inflammatory properties. The novelty of this review is its focus on GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), widely used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. GLP-1 RAs have shown promise in reducing systemic inflammation and promoting tissue regeneration (3, 4). Because type 2 diabetes and obesity share similar GLP-1 pathways of metabolic dysregulation, this review considers how these pathways may be leveraged in managing inflammatory conditions such as periodontitis.
A key aspect of this relationship is the role of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), the enzyme responsible for degrading GLP-1. Notably, certain periodontopathic bacteria, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, exhibit DPP-4–like enzymatic activity, which may disrupt GLP-1 signaling and glucose homeostasis (5–7). This mechanism suggests a bidirectional interaction between periodontitis and GLP-1 pathways, in which periodontal inflammation could exacerbate systemic metabolic dysfunction and vice versa.
Preclinical studies have further explored the therapeutic potential of GLP-1 RAs, such as liraglutide, in mitigating periodontitis. These agents have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects and promoted bone regeneration in experimental models, suggesting a dual benefit for managing both metabolic and periodontal health (8–10). However, the direct mechanistic links and clinical relevance of these findings remain under investigation.
Given the shared inflammatory and metabolic pathways underlying periodontitis, diabetes, and obesity, understanding the interactions between these conditions and GLP-1 pathways is critical. Unlike prior reviews (e.g., 11), which emphasized the periodontitis–diabetes axis, this review takes a broader perspective that integrates obesity-related evidence and highlights therapeutic implications across both populations.
This review addresses the following four specific objectives applied throughout the manuscript:
1. To evaluate population-specific variations in periodontal outcomes associated with GLP-1 RAs among individuals with type 2 diabetes.
2. To evaluate population-specific variations in periodontal outcomes associated with GLP-1 RAs among individuals with obesity but without diabetes.
3. To examine the role of DPP-4 activity in periodontitis and its interaction with GLP-1 signaling.
4. To synthesize evidence on the therapeutic effects of GLP-1 RAs—including anti-inflammatory, bone-preserving, and tissue-regenerative actions—in periodontal disease.
Materials and methods
This scoping review was conducted to synthesize and evaluate existing evidence on the interplay between GLP-1 RAs and periodontitis. The review aimed to investigate the therapeutic potential and underlying mechanisms of GLP-1 RAs in the context of periodontal health, focusing on outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes, those with obesity but without diabetes, and mixed populations. The methodological framework was guided by the five-step process described by Arksey and O’Malley, with refinements, and was further informed by recommendations by Levac et al. to enhance rigor and transparency in scoping reviews.
Identification of the research question
The central research question was the following:
“What is the role of GLP-1 pathways in linking metabolic dysregulation and periodontal disease, and how might GLP-1 receptor agonists contribute to periodontal therapy across diabetic and obese populations?”
This question emerged from an exploratory literature review that revealed emerging evidence of GLP-1 RAs modulating inflammatory pathways, bone metabolism, and periodontal tissue healing.
Literature search strategy
A comprehensive literature search was performed using PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library to identify relevant studies. The search strategy incorporated combinations of Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and keywords, including the following:
● Interventions: “semaglutide, “ “Ozempic, “ “Rybelsus, “ “Wegovy, “ “GLP-1 receptor agonist, “ “Glucagon-like peptide-1, “ “dulaglutide, “ “exenatide, “ “liraglutide, “ “lixisenatide, “ “DPP-4, “ “Dipeptidyl peptidase-4, “ “linagliptin, “ “sitagliptin, “ “alogliptin.”
● Disease context: “periodontitis, “ “periodontal disease.”
These agents and trade names were chosen because they represent widely studied and clinically approved GLP-1 RAs and DPP-4 inhibitors for diabetes and obesity management. Including both generic names and trade names ensured a comprehensive capture of relevant studies across clinical and translational research.
The search included peer-reviewed studies published in English between January 1990 and January 2025. Bibliographies of selected articles were also manually screened for additional relevant studies.
Study selection
Inclusion criteria were the following:
● Investigated the effects of GLP-1 RAs or DPP-4 inhibitors on periodontitis or related biological pathways.
● Examined outcomes such as periodontal inflammation, bone metabolism, tissue regeneration, or systemic effects of periodontitis.
● Included diabetic populations, obese populations, or otherwise healthy controls.
● Were original peer-reviewed articles, encompassing randomized controlled trials, observational studies, in vitro experiments, or scoping and systematic reviews where relevant.
Exclusion criteria were the following:
● Non-English publications.
● Studies without accessible full texts.
● Articles not directly evaluating the interaction between GLP-1 RAs and periodontal health.
Screening was performed in two phases: title and abstract review, followed by full-text review for eligibility.
Data charting and synthesis
Data from the selected studies were extracted and charted using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corporation, United States). Key variables included:
● Study characteristics: author(s), publication year, study design, and population demographics.
● Methodological details: interventions (e.g., GLP-1 RAs or DPP-4 inhibitors), outcomes measured, and analytic approaches.
● Key findings: effects of GLP-1 RAs on inflammation, bone preservation, and periodontal regeneration, stratified by population (diabetic, obese, or mixed).
Charted data were synthesized into descriptive summaries to highlight emerging patterns and gaps in the literature.
Reporting and analysis
The findings are presented as a narrative synthesis organized around four objectives:
1. Impact of Periodontitis on GLP-1 Levels and Glucose Metabolism in Diabetes
2. Interplay Among Periodontitis, GLP-1 Pathways, and Dyslipidemia in Obesity
3. Role of DPP-4, Periodontopathic Bacteria, and Molecular Pathways in Periodontitis
4. Therapeutic Potential of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Periodontal Inflammation and Regeneration
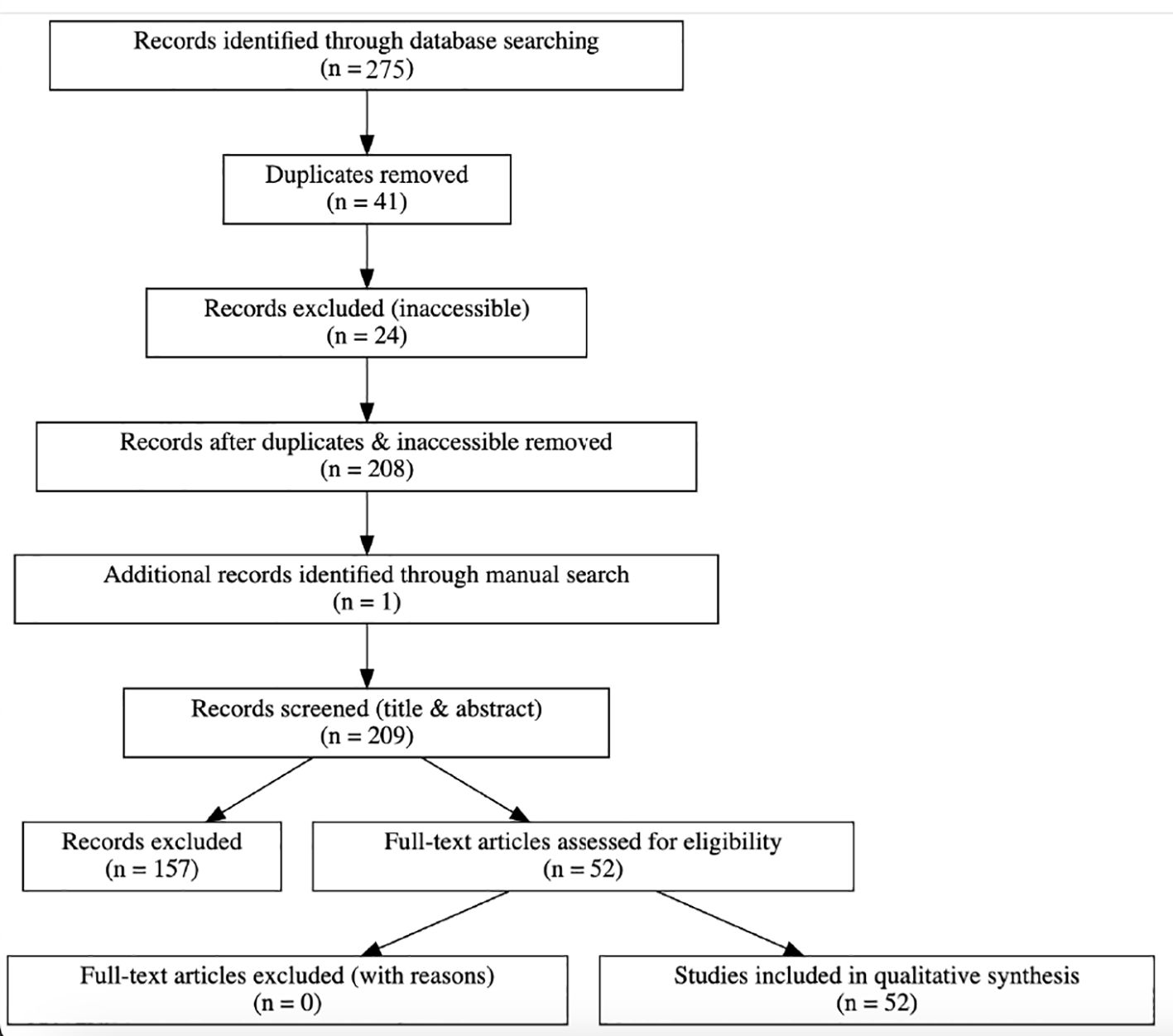
The review process and study selection followed PRISMA-ScR guidelines, with a revised PRISMA flow diagram provided.
Results
Search results and study selection
A total of 275 records were identified through electronic database searches (PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane). After removing 41 duplicates and excluding 24 inaccessible articles, 208 unique records remained for title and abstract screening. One additional study was identified through manual searching. After screening and conducting full-text reviews, 52 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in the final synthesis (Figure 1: PRISMA Flow Diagram).
Thematic synthesis of evidence
Impact of periodontitis on GLP-1 levels and glucose metabolism in diabetes
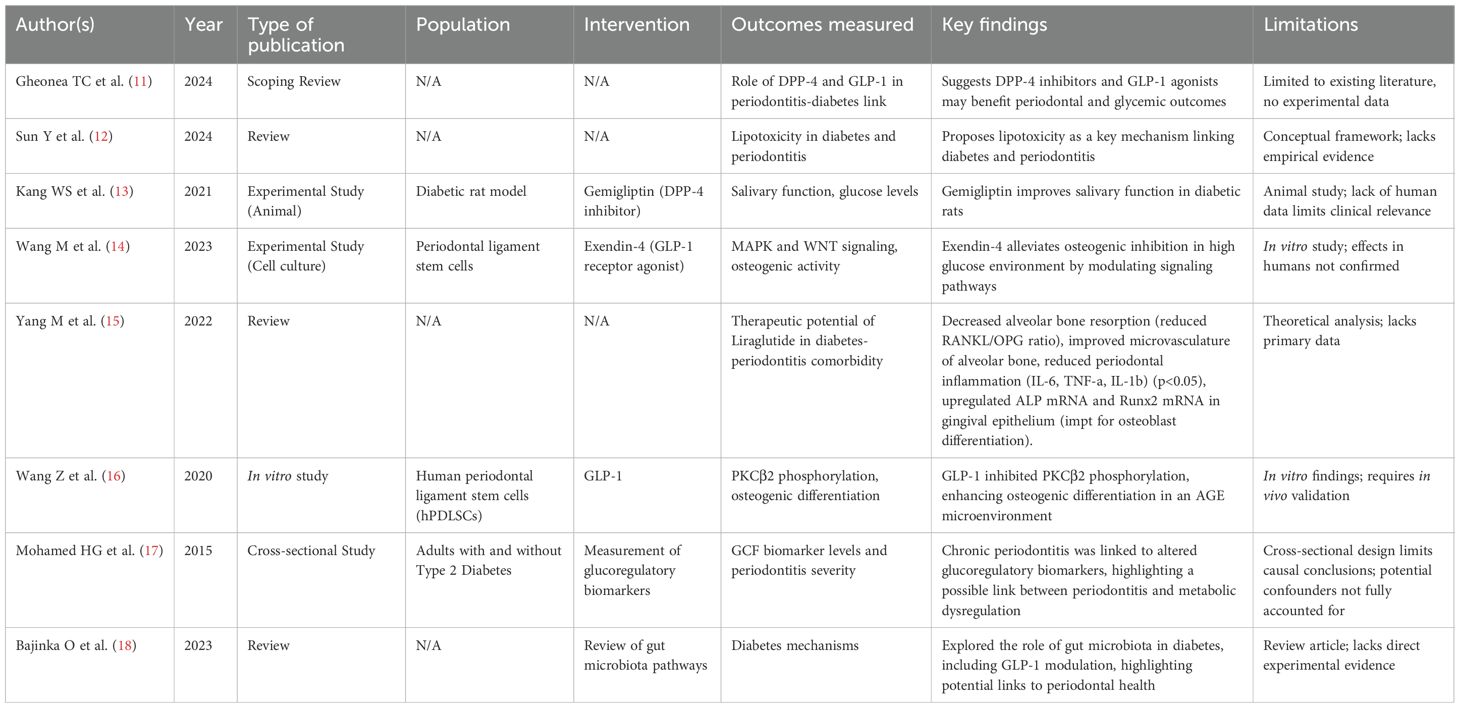
Eight studies investigated how periodontitis influences GLP-1 activity, glucose metabolism, and related pathways under glucotoxic and lipotoxic conditions, particularly in the context of diabetes (Table 1).
● Narrative reviews (11, 12, 15) underscored the theoretical link between GLP-1 pathways and the periodontitis–diabetes axis. Gheonea et al. highlighted potential dual benefits of DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 RAs for periodontal and glycemic outcomes. Sun et al. proposed lipotoxicity as a shared mechanism aggravating both diabetes and periodontal inflammation. Yang et al. summarized experimental evidence that liraglutide reduces alveolar bone resorption, improving bone microvasculature, and downregulates inflammatory mediators (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β), while enhancing osteoblast differentiation markers (ALP and Runx2).
● Experimental studies demonstrated protective roles of GLP-1 signaling under hyperglycemic stress. Kang et al. (13) showed that the DPP-4 inhibitor gemigliptin improved salivary function and glycemic control in diabetic rats. Wang et al. (14) reported that Exendin-4 alleviated osteogenic inhibition in periodontal ligament stem cells exposed to high glucose via MAPK and WNT pathway modulation. Similarly, Wang et al. (16) found that GLP-1 enhanced osteogenic differentiation in AGE-rich environment by inhibiting PKCβ2 phosphorylation.
● Clinical evidence remains limited. Mohamed et al. (17) reported altered glucoregulatory biomarker levels in gingival crevicular fluid in type 2 diabetes patients with periodontitis, suggesting metabolic dysregulation associated with periodontal inflammation.
● Microbiome-related mechanisms were highlighted by Bajinka et al. (18), who reviewed how gut microbiota-mediated modulation of GLP-1 could link diabetes and periodontal health.
Together, these studies support a bidirectional link between periodontal inflammation and impaired glucose metabolism, mediated partly by GLP-1 pathways.
Interplay among periodontitis, GLP-1 pathways, and dyslipidemia in obesity
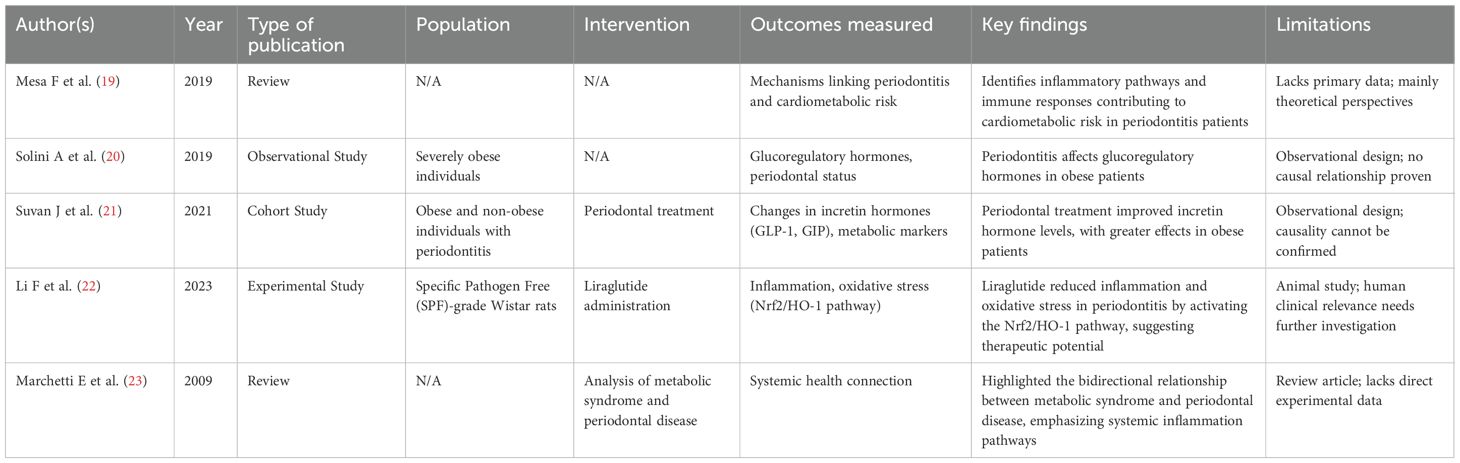
Five studies examined links among periodontitis, GLP-1 pathways, and dyslipidemia or lipotoxicity in obesity and metabolic syndrome (Table 2).
● Narrative reviews (19, 23) emphasized the systemic burden of chronic low-grade inflammation as a shared feature of periodontal disease and metabolic syndrome, though without primary data.
● Human studies provided preliminary evidence: Solini et al. (20) showed that periodontitis negatively affected incretin hormone profiles in severely obese individuals, whereas Suvan et al. (21) reported that periodontal treatment improved GLP-1 and GIP levels and metabolic markers, with stronger effects in obese patients.
● Animal evidence (22) suggested that liraglutide mitigated periodontal inflammation and oxidative stress by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, pointing to a mechanistic role for GLP-1 in obesity-related periodontal disease.
These findings suggest that GLP-1 modulation may represent a shared therapeutic pathway for obesity, metabolic dysregulation, and periodontal disease.
Role of DPP-4, periodontopathic bacteria, and molecular pathways in periodontitis
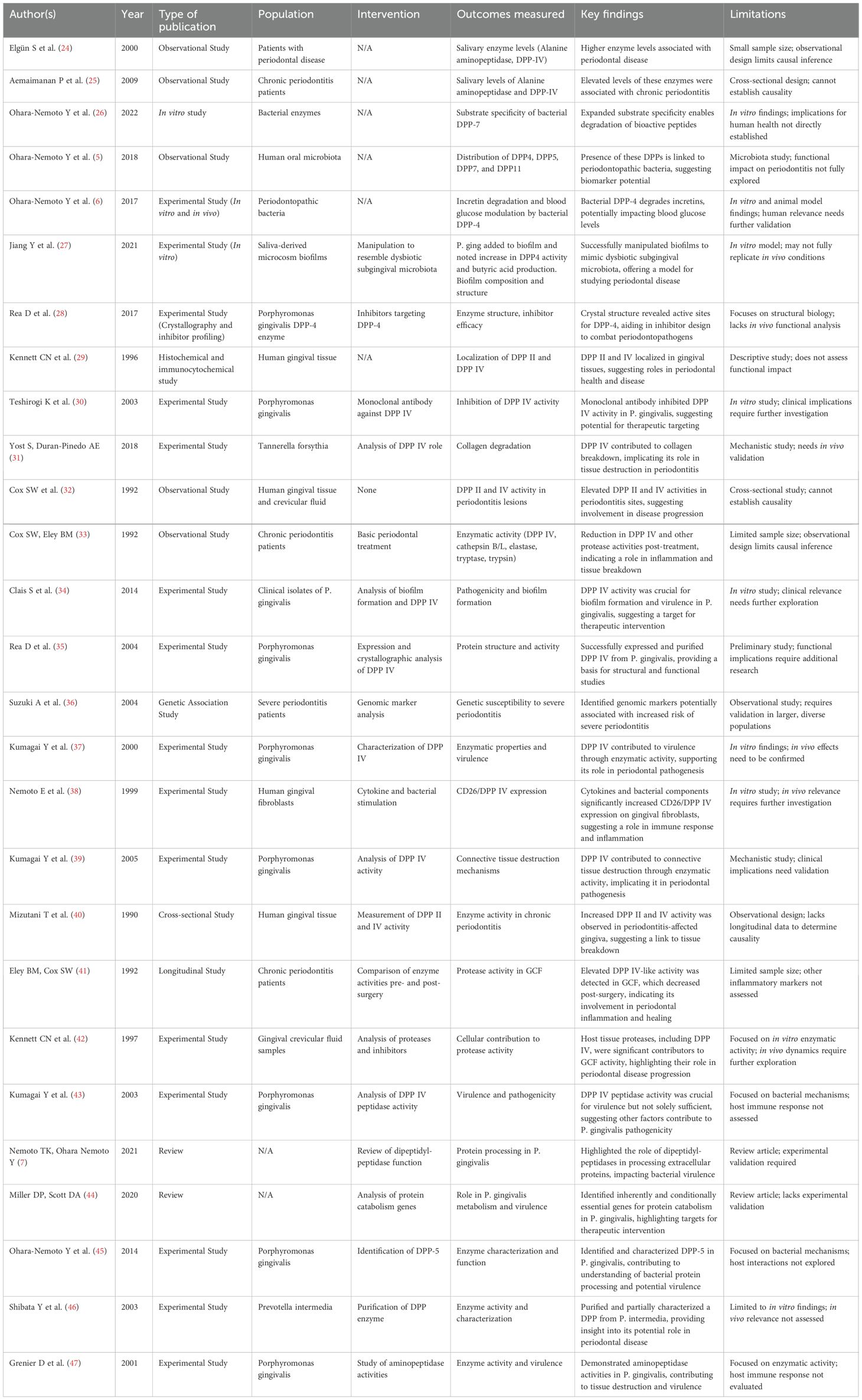
Twenty-seven studies have explored the contributions of DPP-4 activity, bacterial proteases, and host–microbe interactions to periodontal pathogenesis (Table 3).
● Host-derived DPP-4 activity: Multiple observational studies (24, 25, 33, 40) consistently reported elevated DPP-4 levels in saliva, gingival crevicular fluid, and gingival tissues in periodontitis patients. Longitudinal work showed that periodontal treatment reduced DPP-4-like protease activity, linking enzyme activity with disease progression.
● Bacterial proteases: Studies on Porphyromonas gingivalis and other pathogens (28, 34, 35, 37, 39, 43) demonstrated that bacterial DPPs degrade collagen and bioactive peptides, facilitate biofilm formation, and increase virulence. In vitro biofilm models (26, 27) showed that bacterial DPPs expand substrate specificity and degrade incretins, potentially impacting systemic glucose regulation.
● Therapeutic targeting: Monoclonal antibody inhibition of bacterial DPP-IV reduced P. gingivalis activity (30), whereas structural studies (28) provided potential frameworks for targeted drug design.
● Genomic and review insights (36, 44) underscored the multifactorial nature of disease, highlighting host genetic susceptibility and bacterial protein catabolism genes.
Together, these studies identify host–microbe enzymatic interactions as key drivers of periodontal tissue destruction and possible systemic effects.
Therapeutic potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in periodontal inflammation and regeneration
Twelve studies investigated GLP-1 receptor agonists and related incretin-based therapies for periodontal inflammation, osteoprotection, and regeneration (Table 4).
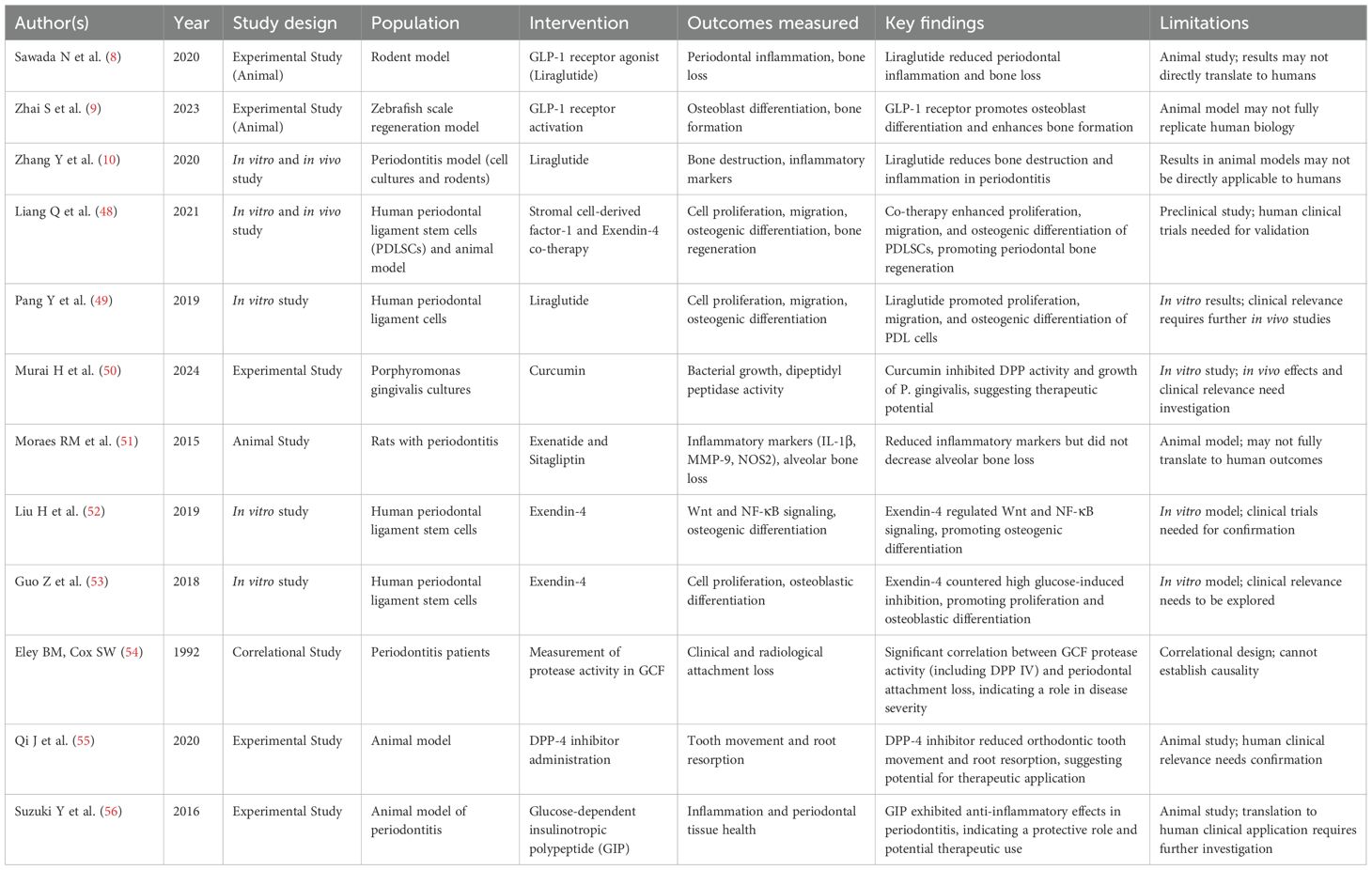
Table 4. Therapeutic potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in periodontal inflammation and regeneration.
● Anti-inflammatory and bone-protective effects: Animal studies consistently showed that GLP-1 RAs reduce periodontal inflammation and bone loss (8, 10). Moraes et al. (51) found reduced inflammatory mediators with exenatide and sitagliptin, though without significant bone preservation. Qi et al. (55) showed DPP-4 inhibitors reduced orthodontic root resorption.
● Osteogenic and regenerative capacity: In vitro and in vivo evidence demonstrated that GLP-1 RAs stimulate periodontal ligament cell proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation (49, 52, 53). Zhai et al. (9) and Liang et al. (48) further supported regenerative potential, including synergistic effects with SDF-1.
● Complementary mechanisms: Suzuki et al. (56) reported that GIP exerted anti-inflammatory effects in periodontitis. Murai et al. (50) showed curcumin inhibited bacterial DPP activity, suggesting adjunctive antimicrobial potential.
● Clinical correlations: Classic work by Eley & Cox (41, 54) linked protease activity in gingival fluid with periodontal attachment loss, reinforcing the relevance of protease modulation.
Taken together, these findings suggest that GLP-1 RAs exert multifaceted benefits in periodontitis by reducing inflammation, protecting alveolar bone, enhancing osteogenesis, and potentially modulating microbial virulence.
Discussion
This scoping review highlights a complex, interdependent network linking periodontitis, diabetes, and systemic metabolic dysfunction, with inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid metabolism, and microbial dysbiosis serving as central mediators. Elevated dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) activity and disturbances in glucoregulatory hormones—particularly in gingival environment—connect periodontal inflammation with impaired glycemic control. Evidence increasingly supports the role of GLP-1 and its analogues, such as exendin-4 and liraglutide, in not only improving glycemic outcomes but also enhancing bone regeneration, mitigating oxidative damage, and reducing local inflammatory responses. These effects are particularly relevant for diabetic patients, in whom lipotoxicity and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) exacerbate periodontal tissue destruction, but may be attenuated by agents including metformin, omega-3 fatty acids, and GLP-1 analogues. Moreover, gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to systemic inflammation and insulin resistance, while natural compounds such as resveratrol may help restore microbial and immune balance—underscoring the value of integrated therapeutic approaches.
Overall, the reviewed studies have reinforced the bidirectional relationship between periodontitis and cardiometabolic disorders. Periodontitis is more prevalent among individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes, while also contributing to disease progression through chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and dysregulation of the incretin axis. In severely obese populations, periodontitis correlates with elevated glucagon and GIP levels alongside reduced GLP-1, suggesting a mechanistic pathway that exacerbates glucose dysregulation. Notably, periodontal therapy has been shown to restore GLP-1 and GIP levels even in non-diabetic populations, although systemic markers such as hs-CRP often remain elevated in obese individuals, indicating an attenuated systemic response.
The therapeutic relevance of GLP-1 RAs is particularly compelling. Liraglutide demonstrated anti-inflammatory and bone-preserving effects in experimental periodontitis models through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 oxidative stress pathway. GLP-1 receptor signaling also enhanced osteoblast differentiation in human dental pulp–derived stem cells via the LINC00968/miR-3658/Runx2 axis, sustaining osteogenesis even in hyperglycemic conditions. Similarly, exendin-4 reversed LPS-induced suppression of osteogenic differentiation in periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) by modulating NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Combined therapies, such as SDF-1 with Ex-4, further synergized to enhance PDLSC activity and bone regeneration in vivo, supporting the potential of stem cell–based regenerative approaches in periodontology.
The enzymatic role of DPPs, particularly DPP IV, emerges as another critical node at the intersection of microbial virulence and host systemic health. Elevated DPP IV activity in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid correlates with periodontitis severity and with the presence of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Since P. gingivalis relies heavily on DPP4, DPP5, DPP7, and DPP11 for nutrient acquisition in its asaccharolytic environment, inhibiting these enzymes disrupts its growth and pathogenicity. Strikingly, bacterial DPP IV mimics its human counterpart, degrading GLP-1 and thereby potentially worsening systemic insulin resistance. Host cells, including macrophages and fibroblasts, also upregulate DPP IV expression during inflammation, reinforcing its centrality at the host–pathogen interface. The structural similarities between bacterial and human DPP IV enzymes highlight opportunities to repurpose or redesign existing DPP-4 inhibitors for both systemic and periodontal applications.
Adjunctive approaches demonstrate potential. Curcumin, for instance, disrupts amino acid metabolism in P. gingivalis and inhibits DPP activity, causing nutrient deprivation stress. Human leukocyte elastase (HLE) has shown anti-inflammatory effects by downregulating CD40 on gingival fibroblasts, thereby impairing cytokine signaling central to periodontal tissue inflammation.
Together, these findings underscore the incretin axis and proteolytic enzyme systems as key regulatory nodes linking periodontal inflammation and systemic metabolic dysfunction. Targeting these pathways presents promising opportunities to develop dual-benefit therapies for both periodontal disease and cardiometabolic conditions.
Future directions
Animal studies and clinical translation
Future preclinical studies should use long-term and disease-complex models that better mimic chronic diabetes-associated periodontitis, including aged, obese, or genetically modified rodents. Studies of localized delivery systems for GLP-1 RA or DPP-4 inhibitors (e.g., biodegradable gels or microspheres) may clarify the feasibility of site-specific periodontal therapies with minimized systemic exposure. Moreover, animal models can clarify the impact of incretin-based therapies on the oral microbiome, oxidative stress, and immune-cell dynamics (e.g., M1/M2 macrophage polarization). Gene knockout or CRISPR-based modulation of bacterial and host DPP activity could further reveal mechanistic drivers of disease progression and resolution.
Clinical trials
Translation to human trials is the next critical step. Early-phase studies should assess GLP-1 receptor agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors as adjuncts to conventional periodontal therapy, particularly in patients with metabolic comorbidities. Non-diabetic or prediabetic populations with moderate-to-severe periodontitis may be ideal initial cohorts. Primary endpoints may include clinical attachment gain, inflammatory biomarkers, and systemic measures such as GLP-1 levels, HbA1c, and lipid profiles.
Randomized controlled trials
Comparisons of administration routes (oral, injectable, and localized delivery) and patient subgroups (e.g., obese vs. non-obese) will provide valuable insight into personalized therapy. Incorporating microbiome profiling and biomarker analysis may further reveal systemic and microbial shifts associated with treatment. Such translational trials will be essential to validate the dual periodontal and metabolic benefits of incretin-based therapies and protease inhibitors.
Conclusion
In summary, preclinical and observational evidence provides a strong rationale for exploring GLP-1 receptor agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors as novel adjunctive therapies in periodontology. Although preliminary data are promising, well-controlled human trials—conducted with careful ethical oversight and interdisciplinary collaboration—will be key to advancing these therapies into clinical practice. By targeting shared pathways of metabolic and periodontal dysfunction, incretin-based therapies hold potential to transform periodontitis management within the broader landscape of cardiometabolic health.
Author contributions
NJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Graves DT, Li J, and Cochran DL. Inflammation and uncoupling as mechanisms of periodontal bone loss. J Dent Res. (2011) 90:143–53. doi: 10.1177/0022034510385236.
2. Preshaw PM, Alba AL, Herrera D, Jepsen S, Konstantinidis A, Makrilakis K, et al. Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship. Diabetologia. (2012) 55:21–31. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2342-y.
3. Drucker DJ. The Cardiovascular Biology of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. (2016) 24:15–30. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.06.009.
4. Trujillo JM, Nuffer W, and Smith BA. GLP-1 receptor agonists: an updated review of head-to-head clinical studies. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. (2021) 12:2042018821997320. doi: 10.1177/2042018821997320.
5. Ohara-Nemoto Y, Shimoyama Y, Nakasato M, Nishimata H, Ishikawa T, Sasaki M, et al. Distribution of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP) 4, DPP5, DPP7 and DPP11 in human oral microbiota-potent biomarkers indicating presence of periodontopathic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2018) 365. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fny221
6. Ohara-Nemoto Y, Nakasato M, Shimoyama Y, Baba TT, Kobayakawa T, Ono T, et al. Degradation of incretins and modulation of blood glucose levels by periodontopathic bacterial dipeptidyl peptidase 4. Infect Immun. (2017) 85:e00277–17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00277-17
7. Nemoto TK and Ohara-Nemoto Y. Dipeptidyl-peptidases: Key enzymes producing entry forms of extracellular proteins in asaccharolytic periodontopathic bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis. Obes Rev. (2021). doi: 10.1111/omi.12317
8. Sawada N, Adachi K, Nakamura N, Miyabe M, Ito M, Kobayashi S, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide ameliorates the development of periodontitis. J Diabetes Res. (2020) 2020:8843310. doi: 10.1155/2020/8843310
9. Zhai S, Liu C, Vimalraj S, Subramanian R, Abullais SS, Arora S, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor promotes osteoblast differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and bone formation in a zebrafish scale regeneration model. Peptides. (2023) 163:170974. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2023.170974
10. Zhang Y, Yuan X, Wu Y, Pei M, Yang M, Wu X, et al. Liraglutide regulates bone destruction and exhibits anti-inflammatory effects in periodontitis in vitro and in vivo. J Dent. (2020) 94:103310. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103310
11. Gheonea TC, Șurlin P, Nicolae FM, Gheorghe DN, Popescu DM, and Rogoveanu I. Dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 and glucagon-like-peptide-1, a link in the connection between periodontitis and diabetes mellitus-what do we know so far?-A scoping review. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:903. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030903
12. Sun Y, Yin Y, Yang S, Ai D, Qin H, Xia X, et al. Lipotoxicity: The missing link between diabetes and periodontitis? J Periodontal Res. (2024) 59:431–45. doi: 10.1111/jre.13242
13. Kang WS, Jung WK, Park SB, Kim HR, and Kim J. Gemigliptin suppresses salivary dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. BioMed Pharmacother. (2021) 137:111297. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111297
14. Wang M, Liu M, Zheng J, Xiong L, and Wang P. Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment. Open Med (Wars). (2023) 18:20230692. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0692
15. Yang M, Pang Y, Pei M, Li Y, Yuan X, Tang R, et al. Therapeutic potential of liraglutide for diabetes-periodontitis comorbidity: killing two birds with one stone. J Diabetes Res. (2022) 2022:8260111. doi: 10.1155/2022/8260111
16. Wang Z, Wang X, Zhang L, Wang B, Xu B, and Zhang J. GLP-1 inhibits PKCβ2 phosphorylation to improve the osteogenic differentiation potential of hPDLSCs in the AGE microenvironment. J Diabetes Complications. (2020) 34:107495. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2019.107495
17. Mohamed HG, Idris SB, Mustafa M, Ahmed MF, Åstrøm AN, Mustafa K, et al. Impact of chronic periodontitis on levels of glucoregulatory biomarkers in gingival crevicular fluid of adults with and without type 2 diabetes. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0127660. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127660
18. Bajinka O, Tan Y, Darboe A, Ighaede-Edwards IG, and Abdelhalim KA. The gut microbiota pathway mechanisms of diabetes. AMB Express. (2023) 13:16. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01520-3
19. Mesa F, Magan-Fernandez A, Castellino G, Chianetta R, Nibali L, and Rizzo M. Periodontitis and mechanisms of cardiometabolic risk: Novel insights and future perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2019) 1865:476–84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.12.001
20. Solini A, Suvan J, Santini E, Gennai S, Seghieri M, Masi S, et al. Periodontitis affects glucoregulatory hormones in severely obese individuals. Int J Obes (Lond). (2019) 43:1125–9. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0253-4
21. Suvan J, Masi S, Harrington Z, Santini E, Raggi F, D’Aiuto F, et al. Effect of treatment of periodontitis on incretin axis in obese and nonobese individuals: A cohort study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2021) 106:e74–82. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa757
22. Li F, Huang Y, and Li F. Liraglutide ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress of periodontitis through activating nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. (2023) 37:102. doi: 10.23812/j.biol.regul.homeost.agents.20233702.102
23. Marchetti E, Monaco A, Procaccini L, Mummolo S, Gatto R, Tetè S, et al. Periodontal disease: The influence of metabolic syndrome. BMC Oral Health. (2009) 9:88. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-88
24. Elgün S, Ozmeriç N, and Demirtaş S. Alanine aminopeptidase and dipeptidylpeptidase IV in saliva: the possible role in periodontal disease. Clin Chim Acta. (2000) 298:187–91. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(00)00282-5
25. Aemaimanan P, Sattayasai N, Wara-aswapati N, Pitiphat W, Suwannarong W, Prajaneh S, et al. Alanine aminopeptidase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV in saliva of chronic periodontitis patients. J Periodontol. (2009) 80:1809–14. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090233
26. Ohara-Nemoto Y, Shimoyama Y, Ono T, Sarwar MT, Nakasato M, Sasaki M, et al. Expanded substrate specificity supported by P1’ and P2’ residues enables bacterial dipeptidyl-peptidase 7 to degrade bioactive peptides. J Biol Chem. (2022) 298:101585. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101585
27. Jiang Y, Brandt BW, Buijs MJ, Cheng L, Exterkate RAM, Crielaard W, et al. Manipulation of saliva-derived microcosm biofilms to resemble dysbiotic subgingival microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2021) 87:e02371–20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02371-20
28. Rea D, Van Elzen R, De Winter H, Van Goethem S, Landuyt B, Luyten W, et al. Crystal structure of Porphyromonas gingivalis dipeptidyl peptidase 4 and structure-activity relationships based on inhibitor profiling. Eur J Med Chem. (2017) 139:482–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.024
29. Kennett CN, Cox SW, and Eley BM. Histochemical and immunocytochemical localization of dipeptidyl peptidases II and IV in human gingiva. J Periodontol. (1996) 67:846–52. doi: 10.1902/jop.1996.67.9.846
30. Teshirogi K, Hayakawa M, Ikemi T, and Abiko Y. Production of monoclonal antibody inhibiting dipeptidylaminopeptidase IV activity of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Hybrid Hybridomics. (2003) 22:147–51. doi: 10.1089/153685903322286557
31. Yost S and Duran-Pinedo AE. The contribution of Tannerella forsythia dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV in the breakdown of collagen. Mol Oral Microbiol. (2018) 33:407–19. doi: 10.1111/omi.12244
32. Cox SW, Gazi MI, and Eley BM. Dipeptidyl peptidase II- and IV-like activities in gingival tissue and crevicular fluid from human periodontitis lesions. Arch Oral Biol. (1992) 37:167–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(92)90086-n
33. Cox SW and Eley BM. Cathepsin B/L-, elastase-, tryptase-, trypsin- and dipeptidyl peptidase IV-like activities in gingival crevicular fluid. A comparison of levels before and after basic periodontal treatment of chronic periodontitis patients. J Clin Periodontol. (1992) 19:333–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1992.tb00655.x
34. Clais S, Boulet G, Kerstens M, Horemans T, Teughels W, Quirynen M, et al. Importance of biofilm formation and dipeptidyl peptidase IV for the pathogenicity of clinical Porphyromonas gingivalis isolates. Pathog Dis. (2014) 70:408–13. doi: 10.1111/2049-632X.12156
35. Rea D, Lambeir AM, Kumagai Y, De Meester I, Scharpé S, and Fülöp V. Expression, purification and preliminary crystallographic analysis of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from Porphyromonas gingivalis. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. (2004) 60:1871–3. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904017639
36. Suzuki A, Ji G, Numabe Y, Ishii K, Muramatsu M, and Kamoi K. Large-scale investigation of genomic markers for severe periodontitis. Odontology. (2004) 92:43–7. doi: 10.1007/s10266-004-0035-4
37. Kumagai Y, Konishi K, Gomi T, Yagishita H, Yajima A, and Yoshikawa M. Enzymatic properties of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV produced by the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis and its participation in virulence. Infect Immun. (2000) 68:716–24. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.2.716-724.2000
38. Nemoto E, Sugawara S, Takada H, Shoji S, and Horiuch H. Increase of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV expression on human gingival fibroblasts upon stimulation with cytokines and bacterial components. Infect Immun. (1999) 67:6225–33. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.12.6225-6233.1999
39. Kumagai Y, Yagishita H, Yajima A, Okamoto T, and Konishi K. Molecular mechanism for connective tissue destruction by dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV produced by the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect Immun. (2005) 73:2655–64. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.2655-2664.2005
40. Mizutani T, Mizutani H, Kaneda T, Hagihara M, and Nagatsu T. Activity of dipeptidyl peptidase II and dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human gingiva with chronic marginal periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. (1990) 35:891–4. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90068-l
41. Eley BM and Cox SW. Cathepsin B/L-, elastase-, tryptase-, trypsin- and dipeptidyl peptidase IV-like activities in gingival crevicular fluid: a comparison of levels before and after periodontal surgery in chronic periodontitis patients. J Periodontol. (1992) 63:412–7. doi: 10.1902/jop.1992.63.5.412
42. Kennett CN, Cox SW, and Eley BM. Investigations into the cellular contribution to host tissue proteases and inhibitors in gingival crevicular fluid. J Clin Periodontol. (1997) 24:424–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1997.tb00207.x
43. Kumagai Y, Yajima A, and Konishi K. Peptidase activity of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV produced by Porphyromonas gingivalis is important but not sufficient for virulence. Microbiol Immunol. (2003) 47:735–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03443.x
44. Miller DP and Scott DA. Inherently and conditionally essential protein catabolism genes of porphyromonas gingivalis. Trends Microbiol. (2020) 28:902. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.09.002
45. Ohara-Nemoto Y, Rouf SMA, Naito M, Yanase A, Tetsuo F, Ono T, et al. Identification and characterization of prokaryotic dipeptidyl-peptidase 5 from Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:10285–95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.527333
46. Shibata Y, Miwa Y, Hirai K, and Fujimura S. Purification and partial characterization of a dipeptidyl peptidase from Prevotella intermedia. Oral Microbiol Immunol. (2003) 18:211–7. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-302X.2003.00057.x
47. Grenier D, Gauthier P, Plamondon P, Nakayama K, and Mayrand D. Studies on the aminopeptidase activities of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. (2001) 16:203–9. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-302X.2001.160403.x
48. Liang Q, Du L, Zhang R, Kang W, and Ge S. Stromal cell-derived factor-1/Exendin-4 cotherapy facilitates the proliferation, migration and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro and promotes periodontal bone regeneration in vivo. Cell Prolif. (2021) 54:e12997. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12997
49. Pang Y, Yuan X, Guo J, Wang X, Yang M, Zhu J, et al. The effect of liraglutide on the proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. (2019) 54:106–14. doi: 10.1111/jre.12607
50. Murai H, Kuboniwa M, Kakiuchi M, Matsumura R, Hirata Y, and Amano A. Curcumin inhibits growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis by arrest of bacterial dipeptidyl peptidase activity. J Oral Microbiol. (2024) 16:2373040. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2024.2373040
51. Moraes RM, Lima GM, Oliveira FE, Brito AC, Pereira RC, Oliveira LD, et al. Exenatide and sitagliptin decrease interleukin 1β, matrix metalloproteinase 9, and nitric oxide synthase 2 gene expression but does not reduce alveolar bone loss in rats with periodontitis. J Periodontol. (2015) 86:1287–95. doi: 10.1902/jop.2015.150278
52. Liu H, Zheng J, Zheng T, and Wang P. Exendin-4 regulates Wnt and NF-κB signaling in lipopolysaccharide-induced human periodontal ligament stem cells to promote osteogenic differentiation. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 75:105801. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105801
53. Guo Z, Chen R, Zhang F, Ding M, and Wang P. Exendin-4 relieves the inhibitory effects of high glucose on the proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. (2018) 91:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.03.014
54. Eley BM and Cox SW. Correlation of gingival crevicular fluid proteases with clinical and radiological measurements of periodontal attachment loss. J Dent. (1992) 20:90–9. doi: 10.1016/0300-5712(92)90112-p
55. Qi J, Kitaura H, Shen W-R, Ogawa S, Ohori F, Noguchi T, et al. Effect of a DPP-4 inhibitor on orthodontic tooth movement and associated root resorption. Hindawi. (2020) 2020:7189084. doi: 10.1155/2020/7189084
Keywords: GLP-1, periodontitis, oral-systemic association, diabetes mellitus, obesity
Citation: Jeong N, Chuang L-H and Ho Y (2025) Periodontitis and GLP-1 pathways: a new frontier in oral-systemic health connections —a scoping review. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 6:1679511. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2025.1679511
Received: 04 August 2025; Accepted: 13 October 2025;
Published: 11 November 2025.
Edited by:
Thomas E. Van Dyke, The Forsyth Institute, United StatesReviewed by:
Jinmei Zhang, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaDongfang Li, The Forsyth Institute, United States
Copyright © 2025 Jeong, Chuang and Ho. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Natalie Jeong, bmF0YWxpZS5qZW9uZ0B0dWZ0cy5lZHU=
 Natalie Jeong
Natalie Jeong Lin-Hsin Chuang
Lin-Hsin Chuang Yolanda Ho
Yolanda Ho