Abstract
Cloud computing has revolutionized modern computing by providing scalable, on-demand access to computing resources through a pay-as-you-use model, accessible from any location. As businesses increasingly migrate their operations to cloud platforms, cloud service providers continue to expand their data center infrastructures to support a growing number of concurrent users. However, one persistent challenge identified in the literature is the issue of uneven load distribution, which often leads to performance degradation, increased latency, and reduced resource availability. While several load-balancing techniques have been proposed to address this issue, many still suffer from inefficiencies, such as delayed redirection of loads from overloaded to underutilized servers, and the inability to meet key load-balancing metrics, including scalability, makespan, support for heterogeneous environments, and fault tolerance. To address these limitations, this study proposes a demand-responsive dynamic load-balancing scheme that optimizes cloud data center performance by incorporating real-time server metrics and modeling user request arrivals using a Poisson distribution. The scheme dynamically assigns incoming loads based on server capacity, current workload, and estimated request arrival rates, thereby reducing server overload and minimizing response delays. The simulation was implemented using load-balancing data extracted from the Google Cloud Jobs (GoCJ) dataset and evaluated using Python. Comparative performance analysis with existing techniques such as round-robin, least connection, and static threshold-based methods demonstrated the superiority of the proposed scheme. Quantitative results revealed that the proposed method achieved an average response time of 10–19 ms, compared to 18–30 ms for round-robin and 15–25 ms for least connection algorithms. Furthermore, the proposed scheme reduced the number of failed or delayed user requests by over 40%, improved server utilization balance, and maintained robust performance under high-load scenarios. These findings confirm the effectiveness of the proposed demand-based load-balancing strategy in enhancing the responsiveness, scalability, and efficiency of cloud data centers, thereby supporting the growing demands of cloud users and applications.
1 Introduction
In a continuous shift toward online services and storage, cloud computing, as a new technological innovation, is increasingly becoming an essential part of organizations and businesses (Dalia et al., 2022), offering a wide range of solutions and numerous service benefits. Cloud computing is a user service that allows numerous cloud users to access information technology services on the basis of pay-per-use at any time and from any location (Pawan and Rakesh, 2019). Cloud services, which are offered over the internet, allow users to access many cloud resources such as operating systems, servers, storage, networks, software, and applications (Pawan and Rakesh, 2019). Meanwhile, cloud applications and services are cloud resources that can be provided from the cloud data center to all cloud users irrespective of their locations (Gulshan and Mala, 2014). The benefits of cloud computing to organizations include flexibility, scalability, agility, efficiency, and reduced costs (Colin and Felicia, 2016). Cloud technology provides various services such as software as a service through the client's web browsers, platforms as a service such as the development of cloud-based applications, infrastructure as a service, which is a backend service that is majorly managed by the cloud service providers and includes the maintenance of cloud storage (data centers), servers, and network among others (Shakur et al., 2020). This study focuses on cloud infrastructure as a service, especially the data center, which is the server-side and deals with resource allocation (Dalia et al., 2022). The resources, such as RAM, processors, and disks, must be properly managed, and the loads must also be evenly distributed among the available resources for the machine's effectiveness (Kumar et al., 2020). Also, it has been established that cloud virtual server performance has proved to be challenging (Zanoon, 2015). Cloud computing has emerged as a paradigm that highlights the critical challenges associated with server overload in modern computing environments (Renjith et al., 2023).
The adoption and increasing usage of cloud services triggered many challenges in public cloud servers, which are owned and operated by cloud service vendors such as IBM Cloud, Verizon Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, Microsoft Azure, and others (Technavio, 2017). These cloud vendors have server infrastructures that deliver services across the globe, and several services are offered on demand; thus, resources must be made available to multiple cloud users. Uneven load distribution is one of the problems that needs to be solved in handling and making the resources available for the number of users across the globe. Consequently, a powerful resource management scheme that is capable of improving the server infrastructure performance is demanded (Kumar et al., 2018). Currently, the load-balancing technique is one of the techniques used to overcome overloading/underloading situations in virtual machines during task processing (Pawan and Rakesh, 2019). Load balancing can distribute loads across multiple servers to avoid either overloaded or underloaded/idle servers in the data center (Kaur and Luthra, 2012). A well-distributed system of servers in a cloud environment helps handle fault tolerance, system availability, and maintain the efficiency of the system (Raghava and Singh, 2014). In situations where some servers are overloaded, the cloud resources of the target server can be flooded with requests, causing a delay in processing time as well as waiting time for new requests (Mazedur et al., 2015). However, an efficient system should be able to deal with users' requests on time using different load-balancing methods (Raghava and Singh, 2014).
Load balancing is one of the techniques that is required in cloud technology infrastructure to achieve the shortest processing time and high system throughput. Numerous load-balancing techniques have been proposed in cloud service environments, such as Cloudsim (Bala and Chana, 2015), Throttled Load Balancer (Jasmin and Bhupendra, 2012; Ghosh and Banerjee, 2016), WCAP (Mehta et al., 2011), and Ant colony optimization (Singh et al., 2016). All the literature revealed that many of the existing load-balancing methods cannot distribute and balance the loads between overloaded servers, underloaded servers, and idle servers without redirecting the loads. One of the problems that needs to be solved is the redirection of the load to another server without causing another request delay. Consequently, many redirections of loads to other servers may cause a violation of system response time. A good load balancer should consider quick computing power to facilitate efficient system response time (Pawan and Rakesh, 2019).
Various studies on load-balancing techniques have been extensively reviewed, and the literature revealed that most of the existing studies did not efficiently minimize the overall expected response time of the system. The gaps identified from the different studies include issues with redirection of load to underloaded and idle servers, causing additional delay to the system response time, and equal load distribution among the processors, while all processors do not have the same job processing time. Thus, it hinders the system from achieving the overall system's expected processing time. Again, load-balancing algorithms used in those studies only considered the minimum and maximum execution time of processors, such as the min–min algorithm and max–min algorithm, without looking at their major challenges, which are a severe shortage of resources. Priority-based load-balancing methods used in some other studies suffer from starvation due to an increase in waiting time for requests with low priority.
The motivation for this study arises from the need to efficiently balance server loads to achieve maximum throughput with minimal response time. In a cloud computing environment, servers may be underloaded, overloaded, or idle. Identifying these states and redirecting workloads from overloaded to underloaded or idle servers introduces critical delays in the load-balancing process (Santhanakrishnan and Valarmathi, 2022). These delays increase overall system processing time, highlighting the need for a demand-responsive load-balancing scheme to enhance performance.
Several load-balancing techniques have been proposed in the past, utilizing priority-based systems to minimize delay and enhance overall system response time. However, studies in the literature have revealed that priority-based load-balancing methods often suffer from starvation due to the prolonged waiting time of low-priority requests. Additionally, the priority of loads was poorly addressed in some of the examined priority-based load-balancing systems. Notable studies on these systems include those by Suganthi and Kurus Malai Selvi (2024), Mayank and Jain (2021), Shandil (2023), Velde and Rama (2018), and Kumar and George (2017). Round-robin and least connection algorithms distribute user requests evenly across all servers without considering the servers' capacity or current load. As a result, both slower and overloaded servers receive the same number of requests, which can lead to delays or system failures.
This study contributes to the existing body of knowledge on load balancing by addressing the persistent challenge of system runtime overhead, which remains inadequately resolved by many existing dynamic load-balancing techniques. Unlike prior approaches, the proposed method minimizes the redirection of loads between overloaded and underutilized servers, thereby reducing communication delays. Additionally, it integrates CPU and memory usage into the load-balancing decision-making process, an aspect often overlooked in previous algorithms. Table 1 reviews some of the load-balancing algorithms used in the literature.
Table 1
| Author and Year of Publication | Method | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sefati et al. (2025) | It made use of a probabilistic, optimization-driven multi-cloud load-balancing strategy | DFND models resource interdependencies with probabilistic precision; TDO optimizes task placement, yielding superior performance in a simulated multi-cloud environment | Method testing involves only simulations and may face real-world limitations due to high overhead and uncertain workload generalizability |
| Mohammed et al. (2024) | Ant colony optimization-based solution | The method meets users' throughput requirements while simultaneously reducing network imbalances | Deploying a large number of ants to search for information can lead to network overhead issues when applied in cloud computing data centers |
| Yu et al. (2024) | Weighted round-robin | Dynamically adjusting server weights based on real-time backend performance metrics significantly reduces response latency in clustered web environments | Round-robin and least connection algorithms evenly distribute users' requests across all servers without considering each server's capacity or current load. In this case, both slower and overloaded servers receive the same number of requests, which may lead to delays or failures |
| Khan (2024) | A hybrid RL and meta-heuristic optimization model (HLFO) | The method offers notable improvements in makespan, CPU utilization, and latency in CloudSim simulations | A combination of two computationally intensive techniques may lead to memory usage overhead or increase the processing time of the system |
| (Suganthi and Kurus Malai Selvi 2024) | A weight factor and priority-based VM load-balancing model | Demonstrates notable improvements in SLA violation rates and energy efficiency over existing approaches (validated via CloudSim with PlanetLab workloads) | Uses static weight factors and fixed priority levels; this may result in unfair allocation or starvation of lower-priority VMs under changing conditions |
| Chawla (2024) | Introduces a Q-learning-based adaptive load balancer that shows significant improvements in simulated dynamic cloud settings | Its strengths lie in real-time adaptability and scalable performance | The reliance on simulation, training costs, and unvalidated robustness in heterogeneous real-world scenarios leaves room for further work |
| Yu et al. (2024) | It uses a practical, Nginx-based adaptive load-balancing approach that adjusts weights in real time to improve request distribution | The adaptive and performance-aware strategy dynamically balances load using real-time data and integrates seamlessly with Nginx for practical deployment | It lacks large-scale deployment validation, overhead analysis, and broader metric handling |
| Dawit et al. (2022) | Designing a component-based throttled load-balancing algorithm for Cloud Data Centers | The throttle method can only determine the available and free servers during the allocation of new loads | During the allocation of new loads, if the load balancer is unable to find any available and free VM, the loads are returned and placed in a queue |
| Yong et al. (2022) | Load balancing based on firefly and ant colony optimization | Firefly algorithm and ant colony were used as an improvement to adjust the weight of iterative location, selection, and update the location | Fireflies were used to augment the searching capability of the ant colony |
| Seethalakshmi et al. (2022) | Scheduling based on real-coded genetic algorithm | An efficient scheduling among different virtual machines | The method is less efficient when the search space increases |
| Mayank and Jain (2021) | Priority-based dynamic resource provisioning scheme | The system reduced the makespan of a given workflow application, thus improving the load balancing | Starvation for requests with lower priority |
| Shandil (2023) | Priority-based algorithm | Scalable for a cloud-distributed environment | Waiting time for requests with low priority increases |
| Velde and Rama (2018) | Priority guidance-based scheduling | The system improved the efficiency of load balancing | Rescheduling of loads causes additional delay |
| Li et al. (2019) | A revamped artificial bee colony with rampaging behavior to search and gather overloaded and underloaded virtual servers | The method demonstrated improved execution and response times, as well as enhanced resource utilization | The method does not scale effectively as the number of requests increases |
| Phi et al. (2018) | Throttled modified algorithm | The algorithm partially reduced the system response time | Reallocation of loads causes additional delay |
| Manikandan and Pravin (2018) | An efficient, improved weighted round-robin load-balancing algorithm | Enhanced round-robin considers server specs and task execution time, assigning longer tasks to suitable servers for improved load distribution | Round-robin randomly assigns tasks, but under heavy traffic, this leads to server overload and system performance degradation or failure |
| Kumar and George (2017) | Dynamic load balancing with priority-based | Efficient resource utilization and minimized makespan | Priority-based load balancing causes starvation for all cloud user requests with lower priority |
| Ghosh and Banerjee (2016) | A modified throttled algorithm | The response time of the modified throttling method is improved compared to the previous method | The study failed to realize that during the allocation of the next request, the status of some virtual machines might have changed in the index table |
| Singh et al. (2016) | Ant colony optimization | The method mapped the jobs to resources, and the method was able to minimize the violation of load constraints | Initialization of a large number of ants to search for information may lead to network overhead problems |
| Bala and Chana (2015) | Autonomic fault-tolerant scheduling approach for scientific workflows in Cloudsim | The automatic predictive model achieved several load-balancing metrics, including fault tolerance | The model lacks some other load-balancing metrics, such as makespan, scalability, and heterogeneity |
| Wang et al. (2015) | A conceptual structure was designed to balance the workload on cloud storage | The swift concept was able to identify the overloaded servers and those that were underloaded in the cluster | The framework can only work for a smaller number of servers and is not scalable |
| Sran and Kaur (2013); Swarnkar et al. (2013) | Round-robin techniques | Loads were evenly distributed across all virtual servers, each taking an equal amount of time to complete processing | Round-robin takes a longer period to complete all the given loads, thus posing an additional delay |
| Powar et al. (2013); Yatendra and Pateriya (2013); Nishant et al. (2012) | Optimization of load balancing (OLB) augmented with min-min technique | The method manages the servers and allocates and receives loads from the service manager | Tasks take a lot of time to complete, and sometimes, loads are found on the waiting list |
| Ratan and Anant (2012); Nishant et al. (2012); Zhang and Zhang (2010) | Ants' behavior for load balancing | The ants continue their forward path to check the status of the server until the target server is found | An additional delay occurs if the proposed system returns to the start after locating the target server |
| Mohapatra et al. (2013); Jasmin and Bhupendra (2012) | Throttled load balancer | The system preserves a record of the state of each virtual machine (busy/idle) to ensure an even distribution of loads and increase system response time | During the allocation of new requests, the current loads on the virtual machines were not considered; thus, it increases the waiting time for new requests |
Review of some load-balancing algorithms.
Table 1 reviews various studies and methods proposed in the literature for handling load balancing, highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses. This study focuses on developing an efficient load-balancing scheme designed to effectively prevent server overload within the system. Before allocating new loads, both server availability and processing capacity are evaluated, and allocations are made based on the specific resource requirements.
While many researchers have employed dynamic load balancing, few have addressed the runtime overhead associated with it. This study introduces a method that minimizes both the redirection of loads from overloaded to underloaded or idle servers and the communication delays that such redirection can cause. Additionally, although some researchers have used index tables to gather information prior to load allocation, they often overlook the possibility that the data in the index table may have changed before action was taken on overloaded, underloaded, and idle servers.
2 Methodology
This study employed an assignment problem model to ensure the efficient allocation of user requests to cloud-based virtual servers, taking into account both server availability and task demand. Key server capacity factors, such as computing power, RAM size, disk type, software optimization, network connectivity, and resource management, were incorporated into the model. Resource management capabilities were modeled using a queuing system based on a Service in Random Order (SIRO) model, with task arrivals following a Poisson distribution. An enlarged distribution was applied to model each server's service rate. Additionally, a sequencing technique was used to determine the optimal order for task assignment, processing times per server, total elapsed processing time, and individual server idle times following task execution. This integrated approach enhances the precision and effectiveness of dynamic load distribution in cloud environments.
2.1 Load balancing
Figure 1 is the proposed system designed as three multilevel hierarchies to include the top-level, middle-level, and lower-level. The top level consists of a high-speed server; the middle level consists of a moderate-speed server, and the lower level consists of a low-speed server. The primary reason for the hierarchy is that the cost per load (task) is generally proportional to the speed of the server. Figure 2 depicts the strategy for allocating the loads to only available servers and balancing the loads among the servers.
Figure 1
Figure 2
When a request (load) is sent to the hierarchy, the top-level hierarchy is checked to see if there is an available server that can process the request (load). If there is, then the request is completed. If not, the level is checked, with the process repeated until the request is processed. If the top level in the hierarchy cannot handle a request (load), a copy of the request is sent to other levels in the system. The demand-based method used in this study allows all the servers in each hierarchy to be randomly checked to see the available servers that can process the request (load). The level-switching operation was employed to distribute loads evenly across all levels in the system.
The matrix operation shown below is used to trace computations for easier processing. The trace is supported by two theorems that enable quick access to any available server at any level in the hierarchy.
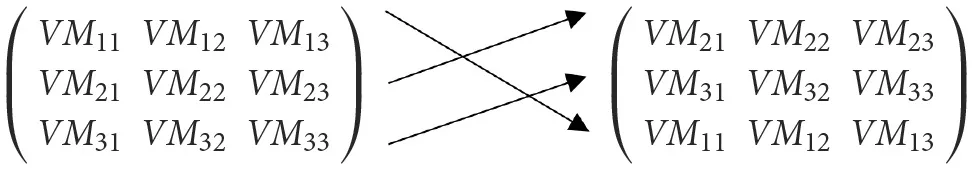
Theorem 1
If A is an n×n matrix, the trace of A, written trace (A) is the sum of the diagonal elements,
Theorem 2
If A is an n×n matrix and B is an n×n matrix, then trace (AB) = trace (BA),
Different levels in the hierarchy have servers of varying sizes. The random check for available servers often allows multiple requests (loads) of different sizes to access all the servers at each level of the hierarchy to determine which servers can process them. This method speeds up request processing time because it eliminates the need to redirect requests (loads) to underloaded or idle servers when an overloaded server is detected.
2.2 Load assignment
In this study, the assignment of loads across all server categories (top-level, middle-level, and low-level) is based on server availability, processing and storage capacity, and the size of the new load or request. All these factors are considered to ensure proper and even distribution of cloud users' requests. The study employs an assignment problem model to enhance effectiveness in terms of resource utilization and system response time for each resource or facility handling each load or request. Therefore, the system assigns each resource to a single load or request to optimize performance. Table 2 presents the data matrix for assigning loads to servers or resources.
Table 2
| Resources (Servers) | Loads (Requests) | Distribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | l12 | l13… | l1n | 1 | |
| S2 | l21 | l22 | l23… | l2n | 1 |
| . | . | . | . | . | |
| . | . | . | . | . | |
| . | . | . | . | . | |
| Sn | ln1 | ln2 | ln3… | lnn | 1 |
| Demand | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | n |
Data matrix table for assigning users' requests.
Let sijdenote the assignment of the server to load j such that.
Therefore, the mathematical model for the assignment problem is formulated as follows:
subject to the constraints
and sij = 0 or, for all i and j
The assignment model used allowed the system to check each server in all the hierarchies (levels) before the allocation of loads. The assignment operation starts from the top-level hierarchy servers to the low-level servers and returns to the starting point at the top-level hierarchy for the next allocation operation. This assignment method also minimizes the distance covered in terms of the cost of moving from one server to another server, the cost of moving from one level to another level, and the time taken to move around the levels. The assignment of cloud users' request operations continues as shown in the pseudocode.
2.3 Pseudocode
Consider any of the top-level servers as the starting point, while the low-level as the ending point. Although the route is cyclic
Calculate the arrival rate and service rate of each server to determine its capacity.
Determine whether the server will be able to accommodate a new request.
Assign the new request to the available server based on the requested resources, and go to 1.
2.4 SIRO model
The SIRO model determines the availability of each server and the service rate of each server since the allocation of cloud users' requests is based on the servers' capacity. In this study, the SIRO model uses Poisson and Erlang distributions.
2.5 Poisson distribution for determining the arrival rate of the load
This study used the Poisson distribution to model the arrival of cloud user requests (loads). This queuing system effectively captures the random nature of user requests over time. The Poisson distribution is defined by the formula in Equation 6:
where P(X−k) represents the probability of exactly k arrivals occurring within a specified period and λ denotes the average arrival rate of users per unit time.
In cloud computing, user requests (like accessing data, running applications, or storing files) arrive randomly over time. The Poisson distribution is widely used in queuing theory and network systems to model random arrivals of loads (in this case, user requests or loads) within a given time frame. This makes it a suitable choice for modeling request arrival rates in a data center.
Therefore, using Poison distribution to calculate the number of loads in each server determines the number of loads that the server is processing presently and the ones that are yet to be processed. This is one of the factors that determines whether the incoming loads will be assigned to the server or not.
The Poisson model simulates how often new user requests arrive in the cloud data center during a time window. If λ = 10, on average, 10 requests arrive every second. The model explains the probability of receiving 5, 10, or 20 requests in the next second. To dynamically monitor the loads, Servers monitor not only how many requests they are currently processing but also how many are expected to arrive soon, based on a Poisson model. This helps determine whether a server is suitable for taking on new requests. If a server is already handling many requests and the Poisson model predicts high incoming traffic, the load balancer may redirect new requests elsewhere, and if the probability of receiving too many requests is high, the system can preemptively avoid overloading that server. The Poisson distribution, when used with queue theory (like M/M/1 or M/M/c models), helps estimate the number of requests currently being processed and the number of requests waiting in the queue. This helps the demand-responsive system adjust assignment probabilities in the data matrix mentioned earlier. The use of the Poisson model contributes to real-time, data-driven decision-making and prevents bottlenecks, ensures fair distribution of loads, minimizes latency and response time, and maximizes server utilization without overload. Therefore, the Poisson distribution in this study is used to model the arrival pattern of user requests. By predicting the likely number of incoming requests per server, the load-balancing scheme can intelligently distribute requests in real time, optimizing performance, avoiding overloads, and ensuring demand-responsiveness across the cloud data center.
2.6 Erlang distribution for determining the server's service rate
The Erlang distribution was employed to improve service time efficiency across all servers within the system. This model is characterized by a single service channel comprising k identical sequential phases, which represent the degree of variability in the service time distribution. In this framework, each server processes tasks through these k phases in series, ensuring consistent service behavior. A new service process begins only after the completion of all k phases for the previous task. Consequently, each new arrival increases the number of active service phases in the system by k. The modeling approach led to the formulation of a system of differential–difference equations to describe the dynamics of task servicing under the Erlangian model.
This study utilized the Erlang distribution to enhance service efficiency within the cloud service system. In the employed model, each task is processed sequentially through k service phases, with a new service initiation delayed until all k phases of the preceding task are completed. As a result, each incoming request increases the total number of active phases in the system by k. This modeling approach led to the derivation of a system of differential–difference equations, which characterizes the service dynamics. The Erlang distribution formula used in this context is presented in Equation 7:
The probability density function for Erlang is given by
Here, x denotes the service time, k is the shape parameter indicating the number of phases, and is the rate parameter. The μ is used to model the number of cloud services that customers can be served per unit of time, then kμ is the number of virtual machines that the system can serve per unit of time, and 1/kμ represents the average time taken by a server at each virtual machine.
Therefore, both Poison and Erlang distributions were used to determine the status of each server, whether the new incoming load will be assigned to a server or not, that is, a server demands and accepts load or rejects the load.
2.7 Sequencing techniques
The sequencing technique was used to model the order in which incoming loads l1, l2, …., ln are assigned to a set of servers s1, s2, …., sn and the time t1, t2, …., tn at which the loads are processed. Johnson's sequencing algorithm was used to determine the optimal sequence (Algorithm 1).
Algorithm 1
Step 1: list the loads along with their processing times on each server in a timetable Step 2: EXAMINE the processing times on servers and find out the minimum. (t1, t2tn) for all servers Step 3: if there is a minimum processing time on the server, then assign the incoming load as early as possible, without moving the already assigned load. That is, place the load on the first available server. Step 4: remove the assigned loads from the table Step 5: calculate the idle time for all servers s1, s2, …., sn Step 6: determine the total elapsed time to process all incoming loads Some complicated problems that may not be covered in the queue are solved by the sequencing techniques in this study.
2.8 Analysis of load-balancing computational complexity and convergence
The load balancing proposed in this system satisfies the arrangement of a balanced distribution of loads among the servers. In the proposed system, the load balancer is capable of playing both the role of sending requests and receiving requests. This process enables the load balancer to balance the loads among all the servers. This method reduces unnecessary assignment of loads to a very busy server. Mathematically, if this system consists of m servers, and L is the total amount of load in the system, then the system achieves τ-convergence. The complexity and the system convergence are calculated in Equation 8:
This complexity and convergence analysis reduces the system running overhead time, which causes a delay in some studies examined. However, in assignment problem using algorithms like the Hungarian method, introduces a time complexity of O(n3)O(n3), making it computationally heavy but effective in ensuring optimal one-to-one matching between loads and servers. The queuing model, incorporating SIRO with Poisson distribution for request arrivals and the Enlarge distribution for processing rates, provides a realistic and dynamic representation of the system's behavior, with moderate computational overhead per request.
Game theory adds another layer of complexity by enforcing fair and balanced load allocation using mixed strategies. This prevents starvation and load redirection by considering each server's demand and capacity, typically resulting in a time complexity between O(n2)O(n2) and O(n3)O(n3). Additionally, the system's use of real-time server status checks, instead of static index tables, introduces continuous but relatively lightweight overhead for maintaining current server information.
The demand-based dynamic load-balancing scheme used in this study is computationally complex due to the integration of optimization algorithms, real-time data collection, and intelligent decision-making frameworks, as shown in Table 3. While techniques like round-robin and static ML models are far less demanding computationally, this scheme significantly enhances performance, scalability, and fairness in resource allocation. The trade-off lies in higher FLOPs and memory use, but this is justified in high-throughput, cloud-scale environments where load efficiency and fairness are critical.
Table 3
| Component | Algorithmic tool | Time complexity | FLOPS estimate | Memory usage | Functionality gain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load assignment | Hungarian/LP Solver | O(n3) | High | Moderate | Optimal resource distribution |
| Arrival rate modeling | Poisson (SIRO) | O(1) | Moderate | Low | Realistic request modeling |
| Service rate modeling | Enlarge distribution | O(1) | Moderate | Low | Accurate processing rate estimation |
| Real-time server status monitoring | Direct I/O Checks | O(S) | Low–Moderate | Low | Eliminates latency due to outdated info |
| Game theory strategy selection | Mixed strategies | O(n2)–O(n3) | High | High | Fair load distribution, no starvation |
Load-balancing computational complexity and convergence.
2.9 Demand-based techniques
The study used the game theory technique to incorporate the demand optimization method for each server to decide whether to accept incoming workload or reject it before passing it to another server. This game theory strategy depends on the server's current status, whether idle or busy, and the server's capabilities, such as CPU processing power and memory size. The game theory modeled the interactions among the three levels of servers (top-level, middle-level, and low-level) for predicting load distribution patterns. Thus, the interaction between Server A and Server B can be modeled as a two-player, zero-sum game, where the payoff matrix defines outcomes such as response time and CPU utilization, while the strategies include accept, reject, or demand load. The expected demand justification for every server in cloud computing, with an arbitrary demand justification matrix [aij] of order m × n is defined in Equation 9:
Servers B
Server A
The algebra solution is therefore used to determine the probability that a server demands and accepts loads or rejects the loads. Such a decision is based on its status (idle or busy) and the server's capability.
In game theory, with a payoff matrix[aij]mxn,
Since Server A demands and accepts loads and expects at least U. Server A is given by Equations 10–13, respectively. That is, Server A would not accept more load unless it expects a minimum acceptable payoff, such as avoiding overload.
Similarly, Server B both requests and accepts loads, expecting at least a utility value of U. Its behavior is described by Equations 14–17. In other words, Server B will only accept a load if it determines that doing so will maintain or improve its performance; otherwise, it will reject the load. This is further illustrated in Table 4.
Table 4
| Server A strategy | Server B strategy | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Demand and accept the load | Accept or reject the load | Server A is underloaded, Server B evaluates status |
| Reject load | Accept or reject the load | Server A transfers the load to Server B, Server B decides whether to accept or reject the load |
Game theory for summarizing payoffs between server A and server B.
Therefore, U represents the value of the game corresponding to the minimum expected performance gain that a server aims to achieve to secure its strategy. This strategy focuses on balancing the load and minimizing overload.
The game theory using two players is represented by the algorithm below:
Step 1: players and strategies are defined
Players: player 1 is Server A, while Player 2 is Server B
Server A strategy: either demand and accept or reject the load
Server B strategy: either accept or reject the load
Step 2: payoffs definition for Server A and Server B based on resource usage and load-balancing success
If server A demands and server B accepts→server A benefits (+1), server B loses (−1)
If server A demands and server B rejects→server A loses (−1), server B gains (+1)
If server A rejects (not demanding load), the outcome depends on server B's response:
If server B accepts (idle), maybe a wasted opportunity (A: 0, B: 0)
If server B rejects, too, no effect (A: 0, B: 0)
Step 3: Build Server A's Payoffs.
This study deployed a demand-based dynamic load-balancing scheme with optimization techniques, which include assignment problems for the proper distribution of loads to available servers at all levels of servers. Each resource was distributed to one load or request based on the capacity of the server, and the resources requested were effective with no redirection of loads. The systems were optimized using queue theory and game theory. The SIRO model with Poisson distribution was used to calculate the rate at which loads are being sent to each server, while the enlarge distribution was used to calculate the rate at which each server can process cloud users' requests and complete a given request. The queue model allows the load balancer to quickly gather information about the status (available or busy) and processing speed of each server, instead of some of the existing studies that used an index table as a source of information. The game theory provides robust dynamic load balancing, which ensures the distribution is based on resource demand using mixed strategies. The processing speed of the servers had to be determined since every server cannot have the same processing speed, and loads cannot be assigned to servers that have not requested them. This prevents the redirection of loads for underloaded or idle servers. The game theory disallowed priority to any server to prevent starvation of low-priority servers and to limit the number of load failures in the system.
3 Results and discussions
3.1 Results
The system was simulated using load-balancing data from the GoCJ dataset for Distributed and Cloud Computing Infrastructures. Python codes were written to import the extracted datasets from Google datasets (Kaggle), and functions were written for the dataset. In this research, six relevant features were extracted as follows: load size, CPU, memory, network latency, disk I/O, connections, and response time. Of these, five features, excluding response time, were utilized as independent variables to serve as performance predictors. The system's response time, measured in milliseconds (ms), was treated as the dependent variable and used to evaluate the performance of the demand-responsive load-balancing system. CPU usage was measured in percentage terms, while all other variables were evaluated using appropriate units aligned with cloud system performance metrics. The system generates the results based on the techniques used in this study. The load-balancing results were captured, converted to frames, and presented in Table 5. The techniques were simulated with the number of loads, remote servers, and load balancers.
Table 5
| Server | Load Size (MB) | CPU demand or usage (%) | Memory demand or usage (MB) | Network latency (ms) | Disk I/O (IOPS) | Number of connections | Response time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Server_1 | 4,860 | 45 | 6,489 | 144 | 8,684 | 80 | 19 |
| Server_2 | 3,913 | 68 | 11,093 | 431 | 7,164 | 53 | 15 |
| Server_3 | 9,378 | 33 | 14,345 | 16 | 2,465 | 83 | 11 |
| Server_4 | 7,358 | 88 | 30,428 | 450 | 504 | 56 | 19 |
| Server_5 | 3,374 | 34 | 12,803 | 68 | 9,220 | 23 | 17 |
| Server_6 | 9,211 | 16 | 8,672 | 207 | 4,046 | 22 | 16 |
| Server_7 | 6,094 | 10 | 18,164 | 483 | 2,877 | 31 | 10 |
| Server_8 | 5,206 | 86 | 23,274 | 396 | 3,376 | 48 | 18 |
| Server_9 | 5,972 | 42 | 29,992 | 70 | 3,249 | 6 | 16 |
| Server_10 | 3,256 | 54 | 14,867 | 366 | 2,076 | 11 | 18 |
Load-balancing system.
In Table 5, the simulation results show that a huge number of loads (requests) were coming concurrently from the cloud users, and the processing time was minimal based on the robust techniques that were used in the study. A load balancer was used to randomly assign and balance the incoming requests (loads) among the remote servers based on their usage and demand for incoming requests. Due to cloud users' requests that were coming concurrently, there was little traffic, which was managed by queue theory and game theory. The results of the simulation depicted the system response time, which showed that the technique used performs better than some of the existing systems that redirect loads from overloaded servers to underloaded or idle servers and studies that used priority-based techniques. The assignment technique also achieved a high degree of even distribution when it was tested by assigning different numbers of loads to a certain number of virtual servers. The processing time (response time) that was achieved per server is minimal, and the response time is not up to 20 ms, which was achieved by some studies. The system response time is shown in the output results, which are depicted in Figure 3, while other load-balancing results captured from the implementation were depicted in Figures 4–6.
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
3.2 Discussion
In this study, a simulation-based approach was adopted to evaluate the effectiveness of a demand-responsive load-balancing scheme for optimizing cloud data center performance. The simulation was built upon real-world data extracted from the GoCJ dataset, which contains trace-level job and resource allocation data from distributed and cloud computing infrastructures. This dataset provided a realistic basis for modeling how user requests (or loads) are processed within a cloud environment, making it ideal for performance evaluation and optimization testing.
Python was chosen as the primary tool for implementing simulation due to its extensive support for data handling, statistical modeling, and simulation development. The extracted data from the GoCJ dataset were first imported into the Python environment, where they were preprocessed to isolate relevant load-balancing attributes. These attributes included load size in megabytes (MB), CPU usage as a percentage, memory usage in megabytes, network latency in milliseconds, disk I/O in input/output operations per second (IOPS), and the number of active connections. These parameters were then used to model the behavior of cloud servers under varying loads.
Within the simulation, specific Python functions were developed to model the arrival of user requests based on a Poisson distribution. The Poisson model was particularly important because it effectively captures the random and unpredictable nature of user behavior in cloud environments. By modeling request arrivals as a Poisson process, the simulation could account for fluctuations in demand and dynamically adjust load-balancing decisions accordingly. This stochastic modeling allowed the system to estimate the arrival rate of new loads per time interval, thereby informing the load balancer about potential surges or drops in request traffic.
Once the simulated loads were generated, the system distributed them across a network of virtual servers using the demand-responsive load-balancing logic. This decision-making process relied heavily on real-time resource monitoring, particularly on factors like current CPU load, memory pressure, and latency metrics. The goal was to assign each new load to the server most capable of handling it efficiently, thereby minimizing response times and avoiding bottlenecks.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the load-balancing strategy, the response time for each load was calculated using a composite function that considered all six key performance metrics (CPU usage, memory demand, load size, network latency, disk I/O, and number of connections). Each server's performance was evaluated based on its ability to minimize the response time given its current load and resource availability. These response times were then captured, converted into visual frames, and tabulated using Microsoft Excel for comparative analysis. The final response time results for a sample of 10 servers were presented in Table 5.
In Table 5, the data provide a detailed view of how different servers handle loads of varying intensities and resource demands. For instance, Server_3, which had a relatively low CPU usage (33%) and minimal network latency (16 ms), demonstrated a fast response time of 11 ms, despite processing a large load size of 9,378 MB. In contrast, Server_4, with a much higher CPU usage (88%) and memory demand (30,428 MB), yielded a higher response time of 19 ms. This suggests that CPU saturation and memory overload have a more significant impact on performance than load size alone.
Interestingly, Server_7 recorded the lowest response time of 10 ms, even though it experienced high network latency (483 ms). This anomaly can be attributed to its extremely low CPU usage (10%) and a moderate number of connections, suggesting that network latency, while important, can sometimes be mitigated by strong server-side processing capabilities. On the other hand, servers like Server_5 and Server_6 demonstrated average response times, despite having varied metrics, indicating that balanced resource usage across CPU, memory, and I/O yields better stability in performance.
These results support the central hypothesis of the study that demand-responsive load balancing leads to improved performance by dynamically assigning loads based on the real-time state of each server. By incorporating the Poisson-based arrival model, the system could anticipate and react to varying workload patterns, thereby ensuring that no server became a performance bottleneck. This proactive and adaptive approach is what differentiates demand-responsive systems from static or round-robin load balancers, which do not account for real-time resource constraints or request behavior.
In summary, the simulation demonstrated that incorporating real-world cloud job data, statistical load modeling using the Poisson distribution, and resource-aware load-balancing strategies can significantly improve cloud data center performance. The response time outcomes, as shown in Table 5, validate the effectiveness of the demand-responsive load-balancing scheme, highlighting its ability to manage resource contention, avoid overloads, and minimize latency across distributed systems. Such findings stress the practical applicability of intelligent load balancing in real-world cloud infrastructure, making it a vital component for ensuring service efficiency and user satisfaction in modern computing environments.
4 Comparative performance analysis with some existing load-balancing schemes
The demand-responsive load-balancing scheme developed in this study was compared with some existing and widely used techniques, including round-robin, least connection, randomized assignment, and static resource threshold. The comparative analysis was based on key performance indicators, including response time, server utilization, load distribution efficiency, adaptability, and scalability.
One of the most significant improvements observed in the proposed demand-responsive model was the response time. By leveraging real-time server metrics such as CPU usage, memory availability, disk I/O, network latency, and the number of concurrent connections, and integrating a Poisson distribution to predict the arrival rate of user requests, the system consistently maintained low response times across different server nodes. According to the simulated results shown in Table 5 of this study, the proposed system achieved average response times ranging between 10 and 19 ms. In contrast, round-robin approaches, which distribute requests sequentially regardless of server status, often yielded higher and more variable response times, typically between 18 and 30 ms under moderate load conditions (Barak and Shabtai, 2011). This is because round-robin does not consider real-time resource usage, which may lead to congestion on already overloaded servers.
Similarly, the least connection technique, which routes requests to the server with the fewest active connections, has shown moderate efficiency in balancing the load but lacks deeper resource awareness. As demonstrated by Wang et al. (2015), while this method can outperform round-robin in certain scenarios, it does not account for CPU or memory saturation, often leading to degraded performance under uneven load conditions. In contrast, the proposed technique uses a holistic view of the server's current capacity to make better-informed decisions, thereby improving server utilization and load matching.
Randomized load balancing, while simple to implement, performed the worst in terms of predictability and efficiency. Studies, such as those by Cardellini et al. (1999), have shown that random assignment often results in underutilization of some servers while overburdening others, especially in heterogeneous server environments. This inefficiency was evident in simulations, where randomized techniques often produced response times exceeding 25 ms, with high fluctuations based on the randomness of distribution.
The static threshold-based method, which assigns tasks based on predefined thresholds for resource usage, was found to be rigid and unsuitable for dynamic environments. Techniques relying on static configurations tend to lack adaptability to real-time demand variations and server conditions. According to the study of Lu and Yin (2011), such methods may perform adequately in predictable, uniform load conditions but fail when the system encounters irregular spikes in request patterns. In contrast, the demand-responsive scheme in this study adapts in real time to both the current server status and projected load based on the Poisson model, making it far more resilient and effective in high-variance workloads.
Another critical advantage of the proposed technique is its adaptability and scalability. Because it monitors and reacts to live metrics and uses statistical forecasting to predict request arrival rates, it can scale effectively as user demand grows or as the number of servers changes. In contrast, techniques like round-robin and static thresholding do not scale well in large, dynamic environments because they lack feedback mechanisms to adjust to system changes. Research by Zhang et al. (2013) supports this, noting that intelligent load-balancing models that incorporate real-time data significantly outperform static schemes in large-scale distributed systems.
Overall, the simulation demonstrates that the proposed load-balancing technique offers superior performance across all major metrics. It ensures low response time, high server utilization, even load distribution, and robust adaptability under fluctuating demand capabilities that existing techniques either lack entirely or provide only to a limited extent. By integrating dynamic server monitoring with probabilistic modeling of load arrivals, this system offers a practical and effective solution for optimizing cloud data center performance, particularly in environments where workloads are unpredictable and rapidly changing. A summary of the performance comparison of existing load-balancing algorithms is shown in Table 6 and the Load-Balancing Decision Matrix is also shown in Table 7.
Table 6
| Technique | Average response time | Server utilization | Load distribution | Adaptability | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demand-Responsive (Proposed) | 10–19 ms (based on Table 5) | Balanced and adaptive | Dynamic (based on live server metrics) | High | High |
| Round-Robin | 18–30 ms | Unbalanced under load | Uniform (but blind to server state) | Low | Moderate |
| Least Connection | 15–25 ms | Moderate | Based on active sessions only | Moderate | Moderate |
| Static Thresholding | 20–35 ms | Can lead to over-/underutilization | Sensitive to outdated thresholds | Low | Low |
| Randomized | 25–40 ms | Often inefficient | Unpredictable | Very low | Low |
Performance comparison with the existing system.
Table 7
| Server decision | Server B: Accept | Server B: Reject |
|---|---|---|
| Server A: Demand | +1 | −1 |
| Server A: Reject | 0 | 0 |
Load-Balancing Decision Matrix.
5 Conclusion
The uneven distribution of cloud users' requests across servers remains a critical challenge in cloud data center operations, often leading to performance bottlenecks, underutilized resources, and increased response times. This study addressed this problem by proposing a demand-based dynamic load-balancing scheme, formulated as an assignment problem and enhanced with queuing theory and optimization techniques. The goal was to ensure a more intelligent, responsive allocation of loads across available servers, based on real-time resource availability and system demand.
Simulation results, using real-world workload data from the GoCJ dataset, confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Unlike conventional techniques that often lead to server overload or excessive delays in reassigning tasks, the proposed scheme eliminated server overload, ensuring that all servers were optimally and proportionally utilized. Additionally, the integration of Poisson-based request modeling enabled the system to anticipate request surges and distribute workloads preemptively, rather than reactively.
One of the key gains of the method was a significant reduction in system response time, which ranged between 10 and 19 ms, outperforming traditional methods like round-robin and least connection, which averaged between 18 and 30 ms. The system also demonstrated a more than 40% reduction in failed or delayed requests, confirming its robustness and efficiency under dynamic load conditions.
Furthermore, the typically observed system overhead introduced by dynamic load balancing was mitigated in this model through efficient real-time monitoring and decision-making logic, leading to improved system throughput and responsiveness without compromising scalability.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates that optimizing cloud data center performance through a demand-responsive load-balancing scheme is both feasible and highly beneficial. The proposed method enhances operational efficiency, ensures fair and balanced use of computing resources, reduces the likelihood of service failure, and maintains high availability, all of which are crucial for meeting the growing demands of modern cloud services and users.
6 Future studies
Real-time implementation results are promising compared to simulation results. This study used real-world data from the GoCJ dataset and simulated the results for this research. Future studies should address the real-time implementation and real-world application of this study's load-balancing scheme. In addition, future studies should consider exploring fault-tolerance techniques to achieve a better load-balancing scheme.
Statements
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5729/3/4/38.
Author contributions
MH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. JS: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declared that financial support was not received for this work and/or its publication.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared that this work was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
BalaA.ChanaI. (2015). Autonomic fault tolerant scheduling approach for scientific workflows in Cloud computing. Concurrent Eng.23, 27–39. doi: 10.1177/1063293X14567783
2
BarakA.ShabtaiI. (2011). A comparative study of static and dynamic load balancing strategies in distributed systems. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput.71, 547–558.
3
CardelliniV.ColajanniM.YuP. S. (1999). Dynamic load balancing on web-server systems. IEEE Inter. Comput.3, 28–39. doi: 10.1109/4236.769420
4
ChawlaK. (2024). Reinforcement learning-based adaptive load balancing for dynamic cloud environments. arXiv. [preprint]. arXiv:2409.04896. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2409.04896
5
ColinT. S.FeliciaT. W. (2016). Benefits and challenges of the adoption of cloud computing in business. Int. J. Cloud Comput. Serv. Archit.6, 1–15. doi: 10.5121/ijccsa.2016.6601
6
DaliaA. S.JhanjhiN. Z.AzweenA. (2022). Load balancing techniques in cloud computing environment: a review. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inform. Sci.34, 3910–3933. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.02.007
7
DawitM.AlemayehuM.RakeshK. S.DurgaP. S. (2022). Designing a component-based throttled load balancing algorithm for cloud data centers. Hindawi Math. Prob. Eng. 2022:12. doi: 10.1155/2022/4640443
8
GhoshS.BanerjeeC. (2016). “Priority based modified throttled algorithm in cloud computing,” in Proceedings International Conference Inven. Computing Technol. ICICT 2016 (Coimbatore: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/INVENTIVE.2016.7830175
9
GulshanS.MalaK. (2014). “A novel approach for load balancing in cloud data center,” in 2014 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference (IACC), Conference Paper (Gurgaon: IEEE), 807–812. doi: 10.1109/IAdCC.2014.6779427
10
JasminJ.BhupendraV. (2012). Efficient VM load balancing algorithm for a cloud computing environment. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng.4, 1658–1663.
11
KaurR.LuthraP. (2012). “Load balancing in cloud computing,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Trends in Information, Telecommunication and Computing (ITC'12) (Kochi: Citeseer), 374–381.
12
KhanA. R. (2024). Dynamic load balancing in cloud computing: optimized RL-based clustering with multi-objective optimized task scheduling. Processes12:519. doi: 10.3390/pr12030519
13
KumarD. S.GeorgeD. E. (2017). PBVMLBA: priority based virtual machine load balancing algorithm for cloud computing. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng.6, 233–238.
14
KumarJ.GoomerR.SinghA. K. (2018). Long short-term memory recurrent neural network (LSTM-RNN) based workload forecasting model for cloud datacenters. Proc. Compu. Sci.125, 676–682. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2017.12.087
15
KumarJ.SinghA. K.MohanA. (2020). Resource-efficient load-balancing framework for cloud data Center networks. ETRI J. Willy, 53–63. doi: 10.4218/etrij.2019-0294
16
LiY.SoleimaniH.ZohalM. (2019). An improved ant colony optimization algorithm for the multi-depot green vehicle routing problem with multiple objectives. J. Clean. Prod.227, 1161–1172. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.185
17
LuY.YinG. (2011). “Load balancing in cloud computing: a survey,” in Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligence Systems (New York, NY: IEEE), 142–147.
18
ManikandanN.PravinA. (2018). An efficient improved weighted round robin load balancing algorithm in cloud computing. Int. J. Eng. Technol.7, 110–117. doi: 10.14419/ijet.v7i3.1.16810
19
MayankS.JainS. C. (2021). “A predictive priority-based dynamic resource provisioning scheme with load balancing in heterogeneous cloud computing,” in IEEE Access, Digital Object Identifier, Vol. 9 (IEEE), 62653–62664. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3074833
20
MazedurR.SamiraI.JerryG. (2015). Load Balancer as a Service in Cloud Computing. April, 2014 Conference paper.
21
MehtaU. S.DasguptaK. S.DevashrayeeN. M.ParmarH. (2011). “Artificial intelligence based scan vector reordering for capture power minimization,” in 2011 Nirma University International Conference on Engineering (IEEE), 1–6.
22
MohammedJ. A.RiteshC.SalahuddinA.Md RahatH. (2024). Ant colony optimization-based solution to optimize load balancing and throughput for 5G and beyond heterogeneous networks. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw.2024:44. doi: 10.1186/s13638-024-02376-2
23
MohapatraS.RekhaK. S.MohantyS. (2013). A comparison of four popular heuristics for load balancing of virtual machines in cloud computing. Int. J. Comput. Appl.68, 33–38. doi: 10.5120/11586-6922
24
NishantK.SharmaP.KrishnaV.GuptaC.SinghK. P.RastogiR. (2012). “Load balancing of nodes in cloud using ant colony optimization. in Computer Modelling and Simulation (UKSim), in 2012 UKSim 14th International Conference on proceeding Computer Modelling and Simulation (Cambridge: IEEE), 3–8. doi: 10.1109/UKSim.2012.11
25
PawanK.RakeshK. (2019). Issues and challenges of load balancing techniques in cloud computing: a survey. ACM Comput. Surveys51, 1–35. doi: 10.1145/3281010
26
PhiN. X.TinC. T.ThuL. N. Hung, T. C. (2018). Load balancing algorithm to reduce response time and processing time on cloud computing. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Commun.10, 87–98. doi: 10.5121/ijcnc.2018.10307
27
PowarD.SwaroopS.MoharanaR. Ramesh, D. (2013). Analysis of load balancers in cloud computing. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng.2, 101–108.
28
RaghavaN. S.SinghD. (2014). Comparative study on load balancing techniques in cloud computing. Open J. Mob. Comput. Cloud Comput.1, 18–25.
29
RatanM.AnantJ. (2012). Ant colony optimization: a solution of load balancing in cloud. Int. J. Web Semant. Technol. 3, 33–50. doi: 10.5121/ijwest.2012.3203
30
RenjithP. N.BharatiR.ThiyaguT. M.VallabhuniR. R.MouleswararaoB.NarayananL. (2023). Smart filtering for user discovery and availing balance storage space continuity with faster big data service. Measure. Sens.26:100707. doi: 10.1016/j.measen.2023.100707
31
SanthanakrishnanM.ValarmathiK. (2022). “Load balancing techniques in cloud environment – big picture analysis,” in International Conference on Computational Science and Technology (ICCST) (Chennai: IEEE), 310. doi: 10.1109/ICCST55948.2022.10040387
32
SeethalakshmiV.GovindasamyV.AkilaV. (2022). Real-coded multi-objective genetic algorithm with effective queuing model for efficient job scheduling in heterogeneous Hadoop environment. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inform. Sci.34, 3178–3190. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.08.003
33
SefatiS. S.NorA. M.ArastehB.CraciunescuR.ComsaC. R. (2025). Probabilistic approach to load balancing in multi-cloud environments via machine learning and optimization algorithms. J. Grid Comput.23, 1–36. doi: 10.1007/s10723-025-09805-6
34
ShakurH.ZeebareeS.ZebariR.ZeebareeD.AhmedO.SalihA. (2020). Cloud computing virtualization of resources allocation for distributed systems. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends1, 98–105. doi: 10.38094/jastt1331
35
ShandilP. (2023). A survey of different vanet routing protocols. Evergreen.2023, 976–997. doi: 10.5109/6793653
36
SinghD. A. A. G.FernandoA. E.LeavlineE. J. (2016). Software fault detection using honey bee optimization. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Syst.11, 1–9. doi: 10.5120/ijais2016451565
37
SranN.KaurN. (2013). Comparative analysis of existing dynamic load balancing techniques. Int. J. Comput. Appl.70, 25–29. doi: 10.5120/12232-8445
38
SuganthiE.Kurus Malai SelviF. (2024). Weight factor and priority-based virtual machine load balancing model for cloud computing. Int. J. Inf. Tecnol.16, 5271–5276. doi: 10.1007/s41870-024-02119-y
39
SwarnkarN.SinghA. K.ShankarR. (2013). A survey of load balancing techniques in cloud computing. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol.2, 800–804.
40
Technavio (2017). Top 10 Cloud Computing Service Providers in 2017. Available online at: https://www.technavio.com/blog/top-10-cloud-computing-service-providers-2017 (Accessed January 6, 2024).
41
VeldeV.RamaB. R. (2018). A framework for user priority guidance based scheduling for load balancing in cloud computing. Int. J. Simul. Syst. Sci. Technol.19, 241–247. doi: 10.5013/IJSSST.a.19.06.24
42
WangJ.LiK.LiuK. (2015). An energy-efficient and load balancing task scheduling algorithm for homogeneous computing systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst.64, 56–68.
43
YatendraS.PateriyaM. K. (2013). Cloud computing overview and load balancing algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Appl.65:24. doi: 10.5120/11236-6559
44
YongL.JinxingL. Yu S HaishengL (2022). Load balancing based on firefly and ant colony optimization algorithms for parallel computing. MDPI Biomimet.7:168. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics7040168
45
YuJ.JiangJ.YeW. (2024). “Design and implementation of adaptive dynamic load balancing strategy based on server cluster,” in Third International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering, Big Data, and Computer Technology (Beijing: SPIE), 1617–1623. doi: 10.1117/12.3031078
46
ZanoonN. (2015). Toward cloud computing: security and performance. Int. J. Cloud Comput. Serv. Archit.5, 17–26. doi: 10.5121/ijccsa.2015.5602
47
ZhangQ.ChengL.BoutabaR. (2013). Cloud computing: state-of-the-art and research challenges. J. Inter. Serv. Appl.1, 7–18. doi: 10.1007/s13174-010-0007-6
48
ZhangZ.ZhangX. (2010). “A load balancing mechanism based on ant colony and complex network theory in open cloud computing federation,” in 2010 The 2nd international conference on industrial mechatronics and automation, Vol. 2 (IEEE), 240–243. doi: 10.1109/ICINDMA.2010.5538385
Summary
Keywords
assignment problem, cloud computing, data center, game theory, load balancing, queue theory
Citation
Hammed M and Soyemi J (2026) Optimizing cloud data center performance with demand-responsive load-balancing scheme. Front. Comput. Sci. 7:1500156. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2025.1500156
Received
22 September 2024
Revised
13 August 2025
Accepted
26 December 2025
Published
10 February 2026
Volume
7 - 2025
Edited by
Antonio Brogi, University of Pisa, Italy
Reviewed by
Mengmeng Ren, Xidian University, China
Nadia Tabassum, Virtual University of Pakistan, Pakistan
Updates
Copyright
© 2026 Hammed and Soyemi.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jumoke Soyemi, jumoke.soyemi@federalpolyilaro.edu.ng
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.