Abstract
A smart home represents an emerging technological revolution. Devices such as smart TVs, smart refrigerators, and smart locks are connected to the Internet to enhance convenience in daily life. However, users contact these smart home devices via public channels, which makes the data being transferred vulnerable to attacks. Ensuring the privacy and data security of home users becomes a significant challenge. As smart home systems become increasingly integrated into our daily routines, securing them is crucial. This study presents a lightweight authentication scheme for smart homes. It combines biometric data (OTIC) with cryptographic techniques. The goal is to achieve robust security while maintaining minimal computational overhead. The scheme allows mutual authentication among users, gateways, and devices. A formal security analysis is conducted using the Real-or-Random (RoR) model. The results demonstrate the scheme’s resilience against polynomial-time adversaries. The scheme is efficient, robust, and resistant to common attacks, making it a practical solution for securing smart home networks. In the informal analysis, the proposed scheme was compared to other smart home authentication schemes. The comparison addressed various security features, including eavesdropping attacks, fault analysis attacks, and other security aspects. Finally, the performance analysis shows that the scheme performs well in terms of computation cost (memory = 332.2916 bits, CPU = 6.8299%, and Time = 1.5341 ms), as well as communication cost of 2,400 bits. These results demonstrate that the scheme offers lightweight performance with enhanced security.
1 Introduction
In today’s world, the fast development of IoT technology has resulted in the emergence of smart homes. Smart homes are environments in which equipment and appliances are interconnected and can be managed remotely (Hasan et al., 2024) or via automation, often through a central system. IoT technology typically includes a smart gateway and resource-constrained smart devices (Ashrif et al., 2024), where various interconnected devices and systems enable automation, convenience, and improved quality of life for residents. One crucial aspect of securing smart home systems is the implementation of robust authentication mechanisms (Rajeh et al., 2024).
Due to the unconventional manufacturing of IoT devices and the vast amount of data they handle, there is a constant threat of cyber-attacks. Smart homes face numerous security and privacy threats. For example, hacking into the security cameras of the smart home can compromise user privacy and access sensitive information, such as health data, photos, and videos (Mohammad et al., 2021). Such violations and unauthorized access can lead to critical and dangerous consequences (Qashlan et al., 2021).
While smart homes provide useful services such as temperature management, home monitoring, and daily activity support, they remain vulnerable to malicious attacks since all communications are transmitted through insecure channels. Furthermore, as security measures improve, hackers continuously develop new techniques to bypass them; smart homes face significant security challenges, such as: (1) Most IoT devices transmit sensitive data (e.g., camera feeds, health metrics) over the internet, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, spoofing, and man-in-the-middle attacks (Mohammad et al., 2021). (2) Traditional security techniques are not enough for the developed IoT devices used in smart homes (Alasmary and Tanveer, 2023). (3) Weak authentication mechanisms, which means many existing schemes fail to resist common attacks such as offline password guessing (OPG), impersonation, and insider threats (Zahary and Al-Nbhany, 2025). (4) Most of their schemes have various security weaknesses that can impair the smart home’s control and monitoring operation.
This article supports the use of IoT in smart home environments by building a more trustworthy authentication scheme. Authentication is the process of verifying the identification of an entity, which might be a person, a software application, or a physical item. It acts as the primary defensive mechanism in a smart environment since it is a prerequisite for other security measures, such as intrusion detection, access control, and audit logs (Mohammad et al., 2021). If the authentication process is not implemented, the system may be vulnerable to security threats.
The proposed scheme follows the widely accepted network model outlined in the typical smart home architecture shown in Figure 1. The smart devices connect to the public Internet via the gateway (GW). Users (Ui) and smart devices (SD) must be registered with the registration authority RA before being able to operate in the network.
Figure 1
The main objective of this study is to develop a secure and lightweight biometric-driven authentication scheme to enhance the security of smart home environments with IoT devices. This objective is achieved through some sub-objectives. (1) To design and implement an iris-based biometric encoding mechanism that ensures secure and lightweight user authentication. (2) To develop a secure authentication protocol for smart home IoT environments integrating biometric and cryptographic techniques. (3) To evaluate the proposed authentication scheme in terms of security features, computation costs, and communication costs.
Protecting users’ login data is critical; to overcome these vulnerabilities, this scheme introduces a dynamic One-Time Iris Code (OTIC). The OTIC generates one-time authentication biometric data by applying a lightweight transformation to the user’s original iris features. The process utilizes a combination of a pseudo-random number, a rotation parameter, and a current timestamp. Moreover, the code is changeable for every session that protects the underlying real biometric, ensuring that even if intercepted, it cannot be reused, thereby enhancing both security and user privacy (see Iris encoding process in section V).
The main contributions of this study include:
Develop a secure authentication scheme for a smart home environment. This scheme facilitates strong mutual authentication between the user, gateway, and smart device. This is achieved through a series of message exchanges that leverage the OTIC and an encrypted nonce to establish a secure session key. The protocol’s design ensures that all communicating parties are authenticated, providing a higher level of trust and security than solutions that only authenticate one party.
The authentication scheme with biometrics utilizes a strong, lightweight iris encoding model, generates a One Time Iris Code (OTIC) for every user authentication, using a pseudo-random number generator, a timestamp, and a rotation parameter. This is a distinct advantage over more complex biometric systems that require significant processing power and memory.
The proposed scheme shows the resistance against various potential attacks in a smart home environment, through the formal security analysis using the Real-or-Random model as well as informal security analysis.
A comparative analysis of the proposed scheme and most related schemes is conducted in terms of security features, computation costs, and communication costs.
The rest of the study is structured as follows: Section II provides background on smart home environments. Section III reviews related study. Section IV discusses the Methodology. The proposed scheme is presented in Section V. Section VI presents the results and dissection details the security analysis—both formal and informal, as well as the performance analysis. The conclusion and future study are presented in Section VII.
2 Background
2.1 Smart home environment
A smart home is any residence equipped with one or more interconnected home automation or entertainment devices that are web-enabled and can be remotely controlled (Lazaroiu et al., 2024). Smart homes are one of the most prominent applications of IoT (Zahary and Al-Nbhany, 2025), allowing authorized users to remotely access their smart devices and easily manage home automation (Sarbishaei et al., 2024). Moreover, the smart home equipment gets data from families to execute their duties, part of which contains personal and family information (Yang and Sun, 2022). Different communication technologies, such as KNX, Ethernet, WiFi, BLE, Zigbee, LoRa, EnOcean, Mioty, and Z-Wave, provide various connectivity options for automation.
Smart homes rely on the wireless sensor system, which forms the central component of a smart home system (Zhu et al., 2024). The system detects environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, and light. Sensors can monitor changes in the home environment in real-time (Islam et al., 2022). The wide variety of available systems presents a challenge, as they differ in terms of functionality, device and protocol support, and the general quality and maturity of the software (Setz et al., 2021).
However, this very interconnectivity and reliance on ubiquitous data collection create a broad and complex attack surface. The conventional security model of a perimeter defense is ineffective in a smart home, where devices are inside the home but communicate externally. This directly impacts authentication, as attackers can no longer be assumed to be external entities; compromised devices within the network can become launchpads for attacks against other devices and users (Maodah et al., 2024). The following security concerns arise due to the increased connectivity and interdependence of devices within public networks (Bhardwaj et al., 2024; Yang and Sun, 2022; Abohatem et al., 2023).
Physical breaches: when unauthorized people access IoT devices, they can often extract long-term secrets (e.g., embedded keys, credentials), completely bypassing any network-based authentication protocol.
Encryption breaches happen when attackers intercept and capture data from unencrypted IoT systems.
Denial of service (DoS) attacks can render authentication gateways unavailable, locking out legitimate users and disrupting the smart home’s functionality—a direct attack on availability, a core security tenet.
Man-in-the-middle (MITM): an attack can allow a hacker to intercept and alter communication between a user and a smart device, making it impossible to establish a secure, mutually authenticated connection.
Ransomware encrypts files, preventing access until the attacker provides a decryption key.
Eavesdropping attacks occur when hackers intercept network traffic between IoT devices.
Privilege escalation and unauthorized access occur due to weak authentication mechanisms. If an attacker compromises a low-privilege device (e.g., a smart bulb), weak authentication protocols may allow them to leverage that access to impersonate a user or gain control of a more critical device (e.g., a smart lock; Can et al., 2023).
2.2 Authentication
Authentication is the procedure for confirming an application end user’s identification before allowing them to access a system or application (Basavala and Kumar, 2012). It involves the verification and validation of the identity of users, devices, and services seeking access to the smart home ecosystem. Furthermore, authentication can take various forms, depending on the level and suitability of security required for a web application.
In the context of a smart home, authentication is the critical gatekeeper that determines if a command to unlock a door or view a camera feed is legitimate. However, the resource-constrained nature of many IoT devices often means they cannot support complex, traditional authentication schemes. This has led to a proliferation of weak implementations, such as hard-coded passwords or weak key agreement protocols, making them vulnerable to the threats listed above. Therefore, a fundamental research challenge is designing lightweight yet strong authentication that is suitable for this environment.
In general, the types of authentication include (Basavala and Kumar, 2012; Padm and Srinivasan, 2017):
Knowledge possessed by the user, such as passwords, PINs, and phone numbers.
A thing the user owns, such as tokens, driver’s license, or smart cards.
Something the user is, such as fingerprints, hand geometry, facial image, iris, retina, voice, or signature patterns.
Each factor type has weaknesses: passwords can be guessed or stolen, tokens can be lost, and biometrics can be replicated if stored statically. The shortcomings of single-factor authentication are especially pronounced in smart homes. This justifies the need for a multi-factor authentication (MFA) scheme that combines these elements to create a more robust defense-in-depth strategy, which is the focus of this study.
2.3 Biometrics
Biometrics refers to the measurement and statistical analysis of individuals’ distinctive physical and behavioral traits. Biometric authentication was developed to identify individuals and manage system access. It provides a robust authentication method based on specific human characteristics (Yusuf et al., 2020). In this study, iris recognition is used to support the authentication system in a smart home.
Iris recognition: involves authentication by verifying the unique features surrounding the eye’s pupil (Padm and Srinivasan, 2017). This technique has garnered significant attention due to its high level of accuracy. It excels at distinguishing individuals by analyzing the complex patterns within the iris, making it highly suitable for various security applications (Maghrabi et al., 2024).
Using biometrics (like an iris scan) for login is very secure. However, the biggest problem is if the stored copy of your iris data is stolen. Since you cannot change your iris like a password, it would be stolen forever. Therefore, a good system should not store the actual iris scan. Instead, it should use a special, disguised version of the data that changes every time you log in. This is exactly the reason this scheme creates One-Time Iris Code (OTIC), it turns iris into a unique code for each login session. This way, even if a hacker steals the code, it becomes useless immediately after, protecting your biometric identity.
This research aims to fill a critical gap in smart home security by combining strong mutual authentication with a secure, iris-based encryption scheme. While mutual authentication ensures that users, gateways, and devices all verify each other’s identities, it often relies on weaker factors like passwords alone. Our scheme strengthens this process by integrating a dynamic One-Time Iris Code (OTIC). This means the powerful, unique properties of a user’s iris are not just used for identification, but are actively encrypted and used as a key component in securing the entire authentication handshake. This fusion creates a far more robust barrier against attacks. On the other hand, biometrics like fingerprints and facial recognition present specific challenges for smart home authentication. Fingerprints can be difficult to capture reliably on small sensors and can be affected by everyday wear, while facial recognition can struggle with changing lighting conditions or angles in a home environment.
3 Related study
The smart home application presents several challenges due to its multi-user and multiple-device nature. Sharing smart devices between smart home users causes many conflicts in terms of users. Authentication in smart homes is the process of identifying and authenticating the identification of individuals or devices before providing them access to the smart home’s devices, systems, and data. Therefore, home automation systems deal with highly sensitive data in terms of privacy, which should be managed with care (Setz et al., 2021). This section has reviewed many authentication schemes for a smart home environment, as mentioned next.
Cho et al. (2022) have examined Zou et al.’s approach, which provided two-factor authentication and key agreement in smart home situations utilizing elliptic curve cryptography (ECC). They demonstrated that their technique is vulnerable to forgery, ephemeral secret leaking, and session key disclosure attacks. To address the security issues in Zou et al.’s system, they suggested a secure user authentication scheme based on physical unclonable functions. Furthermore, they employed the Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and Applications (AVISPA) program to test their scheme’s resistance to security threats.
Alasmary and Tanveer (2023) propose an efficient and lightweight authentication framework for a smart home environment based on the properties of an authenticated encryption scheme and the “ESCI-AKA” hash function. ESCI-AKA authenticates the user at the local device and exchanges three messages between the user, gateway, and smart embedded device to establish a secure channel for indecipherable communication by setting a session key. They confirmed the security of the established session key using the random oracle model and informal security analysis.
Qashlan et al. (2021) offer an authentication technique that combines attribute-based access management, smart contracts, and edge computing to provide a secure basis for IoT devices in smart home systems. The edge server increases system scalability by offloading heavy processing activities and using a differential privacy method to safely and secretly gather data in the cloud. They illustrate the efficiency of their proposed system by extensively evaluating its security and privacy goals in terms of confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Das et al. (2021) studied Rana et al.’s scheme, which suggested a smart card-based remote user authentication system that uses a user password. They discovered that their plan is vulnerable to a number of serious attacks, such as privileged insider attacks, password change attacks, user impersonation attacks, stolen smart card attacks, and Ephemeral Secret Leakage (ESL) attacks. In order to address these issues, they provide a few solutions that might help in creating a user authentication system that is more secure and efficient to utilize while protecting IPv6 infrastructure.
Dey and Hossain (2019) study examines a safe and lightweight session key setup approach for smart home networks, including the Diffie Hellman (DH) key exchange as a backup technique. To establish a public key between a smart device and the home gateway, a trusted service provider gives the devices the algorithm parameters. Security Protocol Animator for AVISPA is used to officially assess the suggested plan (SPAN).
Ashraf et al. (2023) provides a lightweight remote authentication system for the upcoming generation of Internet of Things-based smart homes. They use the AVISPA tool’s formal and informal security evaluations to gage how reliable their suggested plan is. The analysis and comparison of related studies are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1
| Scheme (Year) | Key contribution(s) | Primary limitation(s) | Future direction(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sarbishaei et al. (2024) | Proposes a new lightweight multi-factor authentication protocol | Lacks formal security verification (e.g., RoR model); performance metrics not quantified. | Integration with intrusion detection systems (IDS); context-aware access policies. |
| Cho et al. (2022) | Identifies vulnerabilities in a prior scheme; proposes a PUF-based solution. | Lacks formal verification; no quantitative network performance analysis (e.g., delay, throughput). | Adapting the scheme for broader IoT environments. |
| Alasmary and Tanveer (2023) | Uses lightweight crypto (ASCON); validated with Random Oracle Model (ROM). | A performance benchmark for comparison is lacking. | Using lightweight crypto for blockchain-based access control. |
| Qashlan et al. (2021) | Integrates blockchain and differential privacy for data privacy. | A performance benchmark for comparison is lacking. | Using lightweight crypto for blockchain-based access control. |
| Dey and Hossain (2019) | Proposes a session key setup using DH key exchange; formally verified with AVISPA/SPAN. | Relies on a trusted service provider; performance costs are not quantified. | Not specified. |
| Ashraf et al. (2023) | Provides a lightweight authentication scheme; uses AVISPA for formal verification. | Lacks quantitative performance analysis (computation/communication costs). | Not specified. |
Related study analysis and comparison.
4 Methodology
The development of this study followed a clear, four-stage process to ensure a thorough and effective solution.
Analysis of Related Study and Gap Identification
The first step involved an examination of recently published authentication schemes for smart homes. This review aimed to understand the current state of the art, not just to summarize it, but to critically identify recurring weaknesses and limitations.
Design of the One-Time Iris Code (OTIC)
The next stage focused on creating a more secure and private biometric method. Traditional static biometric templates are risky; if stolen, they are compromised forever. The solution was to design a dynamic One-Time Iris Code (OTIC). This mechanism takes a user’s unique iris features and applies a lightweight transformation for every single login attempt. The transformation uses a combination of a fresh pseudo-random number (from the gateway), a current timestamp, and a rotation parameter. This process ensures the generated code is unique to each session and protects the original biometric data.
Designing the Authentication Protocol
The third stage involved building the full authentication protocol. The goal was to create a seamless process for mutual authentication between the three main actors: the user, the gateway, and the smart device. The protocol was carefully structured into clear phases: registration, login, and authentication. The OTIC was integrated with established, lightweight cryptographic operations like cryptographic hashing and symmetric encryption. The design prioritizes a minimal number of message exchanges and uses the unique OTIC in place of static passwords or keys to verify identities securely and efficiently.
Analysis of the Proposed Scheme
The final stage was a comprehensive evaluation to validate the proposed scheme. This analysis was conducted on two key fronts: security and performance. For security, a formal verification was performed using the Real-or-Random (RoR) model to provide mathematical proof of the scheme’s strength. This was supplemented by an informal, logical analysis of how the scheme defends against a detailed list of common attacks, like replay and impersonation. For performance, the computational and communication costs were calculated and then directly compared to those of the recent schemes analyzed in the first stage. This comparison demonstrates the scheme’s practical advantage in real-world IoT environments.
5 The proposed scheme
The proposed scheme starts with reviewing various authentication schemes that have recently been proposed for authentication in smart homes (Lazaroiu et al., 2024; Sharma and Dhiman, 2024; Kamarainen et al., 2006; Qashlan et al., 2021; Attard et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2022; Barpanda et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2023; Kaur and Kumar, 2021; Banerjee et al., 2020; Padm and Srinivasan, 2017; Fakroon et al., 2022; Sarbishaei et al., 2024; Yu et al., 2021; Wazid et al., 2020). To overcome security issues, a new lightweight user authentication scheme is proposed.
This scheme has a registration authority, several smart sensing devices, a gateway node (GW), and several users. The process starts with secure offline registration of each smart device and legal users. The users need to register at the registration authority, providing his/her necessary information. Each user has a smartphone, which is capable of reading the credential information, such as the user’s identity, password, and biometric. The biometric used in this scheme is iris, which is considered the most reliable biometric for authentication. The steps of using biometrics are mentioned below. The following section provides a description of the proposed scheme in detail.
5.1 Notations
The following abbreviations (notations) are used in this scheme (Table 2).
Table 2
| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| OIC | The original iris code |
| TS | timestamp |
| RN | random number |
| RA | matrix rotation |
| EIC | encoded iris code |
| Ui | The i-th user |
| IDi | Identity of user |
| HIDi | Hash identity |
| PWi | User’s password |
| PIDi | Pseudo identity of user |
| RE | The registration authority |
| X | RE’s secret key |
| GW | The gateway |
| PIDk | GW’s pseudo identity |
| Dj | The j-th smart device |
| SIDj | Dj ‘s identity |
| PIDj | Dj ‘s pseudo identity |
| SKij, SKji | The session key |
Notations used in this scheme.
5.2 Biometrics using iris encoding
Biometrics using iris encoding goes through several steps will be mentioned below.
5.2.1 Iris feature extraction (generating image matrix)
The process begins with choosing an image of an iris, which is subsequently preprocessed to isolate the iris region. The preprocessing function converts the image to grayscale, as in Figure 2, facilitating iris segmentation through thresholding. This method identifies the largest contour to effectively isolate the iris. Finally, the iris region is resized to a 64×64 pixel image.
Figure 2
To enhance the precision of iris recognition, a Gabor filter (Mehrotra et al., 1992; Kamarainen et al., 2006) is utilized in the image preprocessing stage, prior to the execution of the wavelet transformation. This approach allows for pixel-level analysis of images, facilitating detection irrespective of their direction (Attard et al., 2018). Following preprocessing, a Haar wavelet transform is applied to the preprocessed iris image. The Haar wavelet (Guo et al., 2022; Barpanda et al., 2019) transform decomposes the image into approximation and detail coefficients (LL, LH, HL, HH). The approximation coefficients (LL) are resized to an 8×8 matrix and binarized based on the mean value of the coefficients. The resulting 8×8 binary matrix represents the iris features (original iris code OIC), the process is as in Figure 3. The following is an example of an 8×8 iris code.
Figure 3
5.2.2 Iris encoding process
The received 8×8 matrix of the iris consists of 64 bits. Initially, the matrix is rotated in five directions—Clockwise 90°, Anti-Clockwise 90°, Clockwise 270°, Anti-Clockwise 270°, and Clockwise 180°—based on a randomly chosen rotation parameter. Subsequently, the rotated 8×8 matrix is converted into a linear 64-bit array. In this linear 64-bit matrix, an XOR key is provided to perform a bitwise XOR operation between the 64-bit flattened iris code and the 64-bit XOR key, ensuring that the XOR key is exactly 64 bits long. A 33-bit timestamp generated during each transaction is divided into four octets, which are then inserted into any five-bit positions of the Iris Code. The specific bit positions for inserting the timestamp information are determined using four random numbers. This process results in a 97-bit encoded information, to which a 3-bit rotation parameter is appended. Finally, a 100-bit encoded iris code matrix (EIC) is produced. The process in detail is illustrated in Figure 4 and Table 2.
Figure 4
5.2.3 Iris decoding process
The 100-bit EIC received from the Ui will be decoded on the server by extracting five octets using random numbers. This process involves reverse rotating the data with the rotation bit provided by the Ui, ultimately restoring it to its original form as a 64-bit Iris Code. As shown in Table 3.
Table 3
| Encoding Iris Input:
Encode Steps (OIC, TS, RN, XOR_Key): 1. Rotate the Original Iris Code
2. Flatten the Rotated Matrix
3. XOR Operation
4. Divide Timestamp
5. Divide Original Iris Code
6. Concatenate Parts for Encoded Iris Code
7. Validation
8. Return EIC Decode Iris Input
Output
Decode Steps (EIC, RN, XOR_Key): 1. Extract Rotation Parameter:
2. Remove Rotation Parameter and Timestamp Bit
3. Extract Timestamps
4. Extract Encoded Iris Code Parts
5. Combine Parts for Linear Original Iris Code:
6. Apply Anti-XOR Operation
7. Reverse Rotation
8. Reconstruct Matrix
|
Iris encoding and decoding algorithm.
5.3. Smart home authentication system
After reviewing various authentication schemes that have been proposed for authentication in smart homes recently (Sharma and Dhiman, 2024; Wu et al., 2023; Kaur and Kumar, 2021; Banerjee et al., 2020; Fakroon et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2021; Wazid et al., 2020; Shuai et al., 2019; Huszti et al., 2022; Dey and Hossain, 2019; Cho et al., 2022; Alshahrani and Traore, 2019; Sarbishaei et al., 2024; Xia et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022), a new scheme has been proposed in this study, “a smart homes authentication scheme with a biometric–driven approach.”
5.3.1 Registration phase
During this phase, smart devices and users register as a legal entity with the gateway, and all registration data is sent via a secure channel. Figure 5 shows the proposed smart home system network model.
User registration phase
Figure 5
Ui select IDi, PWi, and biometric OIC (iris for recognition). The GW receives the registration information form Ui, then generates a fixed ai value based on IDi and PWi, computes HIDi= h(IDi || ai), and sends it to Ui. The Ui receives the HIDi, then encodes the OIC to generate EIC 100-bit compute Authi= h(IDi || PWi || EIC). Last, Ui store {Authi, HIDi, EIC} in the mobile device as shown in Table 4.
Smart device registration phase
Table 4
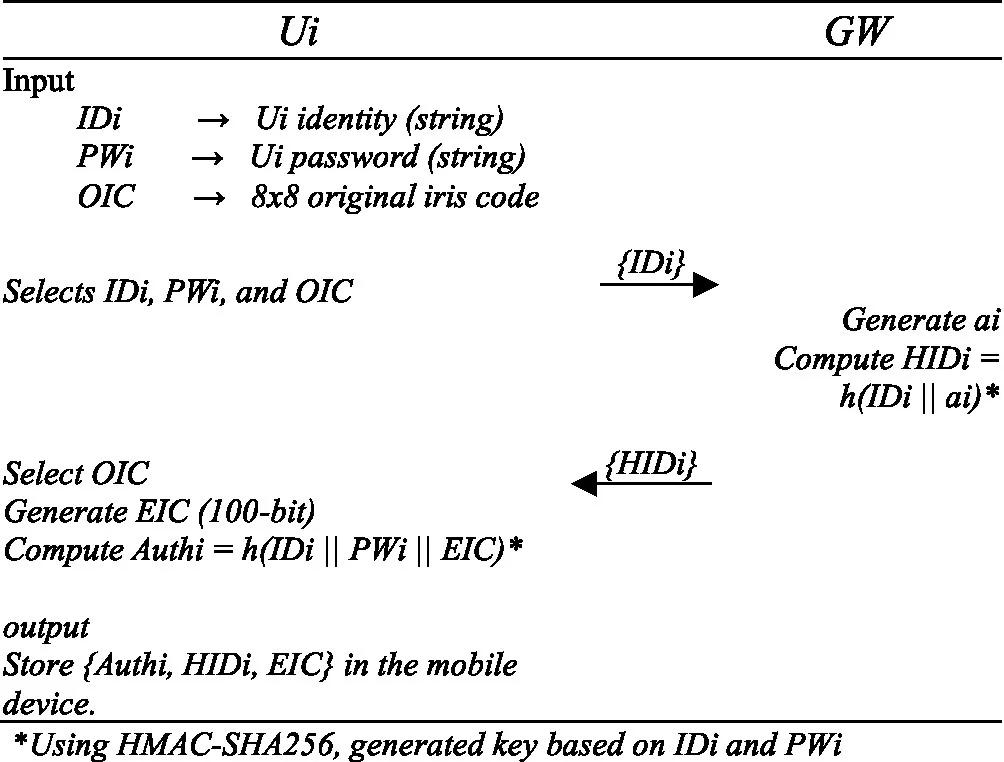 |
User registration phase.
*Using HMAC-SHA256, generated key based on IDi and PWi.
Dj selects identity SIDj and sends it to the GW; The GW selects random number rj and computes PIDj= h(SIDj || rj). GW stores PIDj in memory. Finally, it sends PIDj to Dj. Dj stores PIDj in its own memory, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5
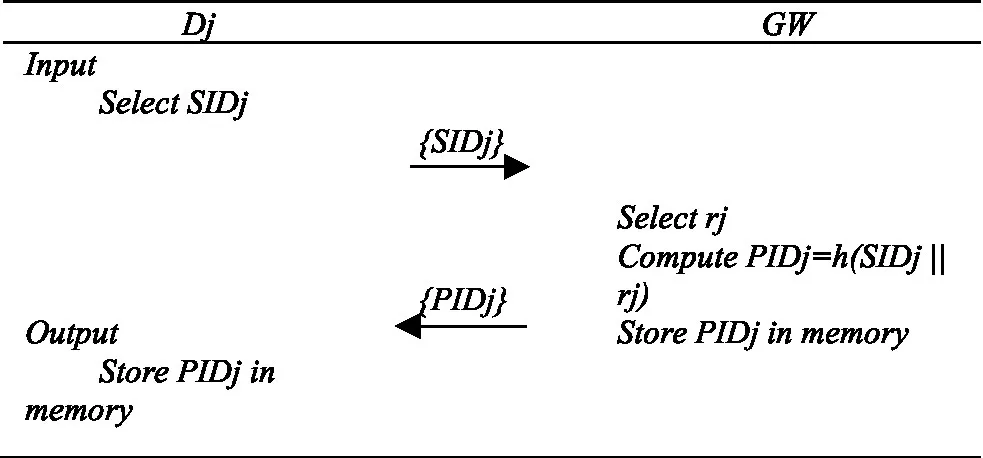 |
Smart device registration phase.
5.3.2 Login and authentication phase
Step 1: User (Ui) enters IDi, PWi, and biometric (OIC), the system encodes the OIC to generate the EIC using TS, RN, RA, and XOR_Key. Combine IDi, PWi, and EIC to compute Authi’, then verify Authi’ =? Authi (generated in registration phase). If the Authi’ passes the verification, this means that the Ui is valid; else, terminate the process. After verification, Ui generates random values d1, d2, shared parameter x, and uses system timestamp TS1. Then, Ui compute C1= d1 * x, C2 = C1 * x, C3 = d2 ⊕ C2 ⊕ SIDj, and C4= IDi ⊕ h(SIDj || d2) Using HMAC-SHA256 the key generated based on IDi and PWi. Finally, Ui transmits the message M1= {PIDk, PIDj, C1, C3, V1, TS1, C4}.
Step 2: GW receives M1, validates TS1, and sends PIDj, PIDk to SGX Match SIDj, x according PIDj, PIDk. If correct, GW compute C2’= x * C1, d2’ = C3 ⊕ C2’ ⊕ SIDj. Recover User ID (IDi) and compute h(SIDj || d2’), IDi= C4 ⊕ h(SIDj || d2’). GW computes V1’= h(C2’ || IDi || T1) and verities V1’ =? V1. If correct, GW generates message M2, computes TS2= current TS, C5 = IDi ⊕ d2’ ⊕ h(SIDj || T2), and V2 = h(SIDj || d2’ || T2). Then sends the M2 = {C5, V2, T2}.
Note: for hashing, HMAC-SHA256 is used; the key is generated based on IDi and PWi.
Step 3: Dj receives M2, validates TS2. If correct, computes d2= C5 ⊕ h(SIDj || T2) ⊕ IDi, V2’= h(SIDj || d2 || TS2), then verities V2’ =? V2 if correct Dj generates TS3 = current TS, d3 = random, and computes SKji = h(SIDj || d3 || IDi ⊕ d2). Last step, Dj generates M3: C6= d3 ⊕ h(IDi ⊕ d2 || SIDj), V3= h(SIDj || T3), V4= h(SKji || d3 || SIDj), and construct M3= {C6, V3, TS3, V4, d3, d2}.
Step 4: Upon the received message M3, GW validates TS3, after that, GW computes V3’= h(SIDj || T3), then verifies if V3’! = V3, if correct, that proves this device is legitimate, then the device computes M4. The M4 consists of TS4= current TS, and includes C6, V4, and T4 from M3. M4= {C6, V4, T4, d3, d2}.
Step 5: Ui receives the last message M4. First, validate TS4, then compute d4, SKij, and V4’. d4= C6 ⊕ h(IDi ⊕ d3 || SIDj), Kij= h(SIDj ⊕ d4 || IDi ⊕ d4), V4’= h(SKij || d3 || SIDj). Verifies V4’ =? V4 if correct, Store SKij for future communication. The process in detail is shown in Table 6.
Table 6
 |
Login and authentication phase.
5.3.3 Password and biometric update phase
To update the password and/or biometric, a registered user Ui performs the following steps:
Input Existing data
Ui inputs their identity IDi, existing password PWi, and imprints their existing biometric Bi.
Authentication
Ui logs in using steps similar to the login and authentication phase (as described in Section 2).
The system verifies Ui's data by computing Authi′ = h(IDi∣∣PWi∣∣Bi), and comparing it with the stored Authi
If Authi′ = Authi, the authentication is successful, and Ui is allowed to update their data.
Provide new registration data
Ui provides a new password PWi* and imprints a new biometric (iris) Bi*.
Recalculate new registration date
The system computes the following updated values:
eic∗ = Encode(Bi∗): Generate a new encoded iris code eic∗ from the new biometric Bi∗.
Authi∗ = h(IDi∣∣PWi∗∣∣eic∗): Update Authi using the new password and encoded iris code.
HIDi∗ = h(IDi∣∣ai∗): Update HIDi using the new password, where ai∗ is derived from IDi and PWi*
Replace Stored data
replaces the old credentials Authi, HIDi, and eic with the updated credentials Authi∗, HIDi∗, and eic∗.
The updated data are stored in the user’s mobile device.
The mobile device now contains the updated data Authi∗, HIDi∗, and eic∗.
5.3.4 Security considerations for the update phase
Update Frequency: It is recommended that updates be performed periodically, for instance, every 3 to 6 months, or immediately following any suspicion of credential compromise.
Securing the Update Process: The entire update phase is executed under the same secure mutual authentication protocol that is used for a standard login. Initiation of the update process is protected from unauthorized access by the requirement that authentication must first be successfully completed using the old credentials.
Handling Lost or Stolen Devices: The risk associated with a lost device is inherently minimized by the scheme’s design. Plaintext credentials are not stored on the mobile device; only hashed and derived values are retained.
6 Results and discussion
6.1 Formal security analysis “Real or Random model (RoR)”
Real or Random model (Abdalla et al., 2005) is commonly used for key agreement and authentication security analysis (Sireesha and Amaravathi, 2021). The RoR model is utilized to analyze the proposed scheme formally.
It simulates the chance of an attacker breaking the scheme in polynomial time using various rounds of games and determines the security of the proposed scheme based on the attacker’s ability to compute the session key.
6.1.1 Adversary’s capabilities
In the RoR model, the adversary (A) can perform the following queries:
Execute(O): A can eavesdrop on messages exchanged between entities (Ui, GW, Dj).
Send(O, Mi): A can send a message Mi to an entity O and receive a response.
Hash(string): A can compute the hash of any string.
CorruptDevice(O): A can extract long-term secrets stored on a device (e.g., key, x).
Test(O): A can attempt to distinguish between the real session key and a random key.
6.1.2 Security theorem
The objective is to prove that the advantage of A in breaking the scheme is negligible. Let:
Hash: Range space of the hash function.
AdvECDHP: Advantage of solving the Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Problem (ECDHP).
qs: Number of Send queries.
l: Bit length of biometric information.
D: Size of the password dictionary.
The theorem is given by Equation 1:
where:
qh: Number of hash queries.
AdvECDHP: Adversary’s advantage in solving ECDHP
Game-Based Proof.
Four games are defined (GM0-GM3) to simulate the adversary’s attack process.
GM0: Real Attack
This game simulates the real-world attack where A interacts with the protocol.
A selects a bit cc and tries to guess the session key.
The advantage of A is defined by Equation 2:
GM1: Execute Query
A eavesdrops on messages (M1, M2, M3, M4) exchanged between Ui, GW, and Dj.
A cannot compute the session key SKij because it requires knowledge of d2 and d3, which are ephemeral and not revealed in the messages.
The probability of success in GM1 is the same as in GM0, as shown in Equation 3:
GM2: Send and Hash Queries
A attempts to tamper with messages and compute hashes.
The authentication values (V1, V2, V3, V4) are based on hash functions and random numbers, making collisions unlikely.
A cannot compute C2 = x * C1 without knowing x, which is protected by ECDHP.
The difference between GM1 and GM2 is bounded by the advantage of solving ECDHP and the hash function’s security, as in Equation 4:
GM3: Corrupt-Device Query
A extracts long-term secrets (e.g., key, x) from a compromised device.
A can guess the password using a dictionary attack, but the biometric key (Bi) adds entropy.
The probability of guessing the correct password and biometric key is bounded by Equation 5:
6.1.3 Final step
In the final game, A guesses the bit c through the Test query. The probability of success is given by Equation 6:
6.1.4 Combining the games
Combining the results from GM0-GM3 yields Equation 7:
Therefore, from Equations 2–7, the final is obtained the security bound expressed in Equation 8:
6.1.5 Interpretation
The advantage of A in breaking the scheme depends on:
The security of the hash function .
The hardness of ECDHP .
The entropy of the password and biometric key (qs2lD2lDqs).
If the hash function is secure, ECDHP is hard, and the password/biometric entropy is high, the advantage of A is negligible.
6.2 Informal security analysis
The following section demonstrates the proposed scheme’s security against various known attacks.
6.2.1 User anonymity and untraceability
The scheme ensures user anonymity by not revealing the user’s real identity (IDi) in plaintext during communication. Instead, it uses derived values such as Authi = h(IDi || PWi || EIC), C4 = IDi ⊕ h(SIDj || d2), and SKij = h(SIDj ⊕ d4 || IDi ⊕ d4) to authenticate the user without exposing IDi. The use of random numbers (d1, d2, d3) and timestamps (T1, T2, T3, T4) ensures that each session is unique, making it difficult for an attacker to trace the user across different sessions. Moreover, the iris biometric encoding process further enhances anonymity by transforming the biometric data into a 100-bit encoded iris code (eic), which cannot be easily reverse-engineered to reveal the original biometric data.
6.2.2 Fault analysis attacks
The scheme is resistant to fault analysis attacks because it uses cryptographic hashing (HMAC-SHA256) to protect sensitive data. Even if an attacker introduces faults into the system, the hashed values (Authi, V1, V2, V3, V4) cannot be easily reverse-engineered to reveal the original inputs. Furthermore, the iris biometric encoding process adds another layer of protection. Faults introduced during the encoding process would result in an invalid encoded iris code (eic), which would fail authentication. The use of random numbers (d1, d2, d3) ensures that each session is independent. Even if an attacker successfully introduces a fault in one session, it would not compromise other sessions.
6.2.3 Resist mobile device loss attack
The scheme does not store sensitive information (e.g., IDi, PWi, or the iris biometric) directly on the mobile device. Instead, it uses derived values such as Authi, eic, and key for authentication. Even if the mobile device is lost, an attacker cannot easily extract IDi or PWi because Authi is derived using a hash function (HMAC-SHA256), which is computationally irreversible. The use of timestamps and random numbers ensures that even if an attacker captures previous session data, they cannot reuse it to impersonate the user.
6.2.4 Impersonation attacks
First, the scheme uses multi-factor authentication (MFA) combining password (PWi), iris biometric (eic), and cryptographic keys {key, SKij}. This makes it extremely difficult for an attacker to impersonate a user without knowing all three factors. Also, the iris biometric encoding process ensures that even if an attacker steals IDi and PWi, they cannot generate a valid Authi without the user’s biometric data. More, the use of random numbers (d1, d2, d3) and timestamps ensures that each session is unique, preventing replay attacks that could be used for impersonation. And finally, the gateway and device verify the authenticity of messages (M1, M2, M3, M4) using hash values (V1, V2, V3, V4) where, V1 = h(C2 || IDi || TS1), V2 = h(SIDj || d2’ || TS2), V3 = h(SIDj || TS3), V4 = h(SKji || d3 || SIDj), which are derived from session-specific data. This ensures that only legitimate parties can generate valid messages.
6.2.5 Resist Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack
The scheme uses cryptographic hashing (HMAC-SHA256) to protect the integrity of exchanged messages (M1, M2, M3, M4). Any tampering by a MITM attacker would invalidate the hash values (V1 = h(C2 || IDi || TS1), V2 = h(SIDj || d2’ || TS2), V3 = h(SIDj || TS3), V4 = h(SKji || d3 || SIDj)), causing the authentication to fail. The session key (SKij = h(SIDj ⊕ d4 || IDi ⊕ d4)) is derived using a combination of random numbers (d2, d3) and shared secrets {SIDj, IDi}. This ensures that even if an attacker intercepts messages, they cannot derive the session key without knowing the random numbers and secrets. Moreover, the use of timestamps prevents replay attacks, which are a common tactic in MITM attacks.
6.2.6 Eavesdropping attack
The scheme does not transmit sensitive information (e.g., IDi, PWi, or biometric data) in plaintext. Instead, it uses derived values such as Authi = h(IDi || PWi || EIC), C4 = IDi ⊕ h(SIDj || d2), and SKij = h(SIDj ⊕ d4 || IDi ⊕ d4), which are protected by cryptographic hashing. The iris biometric encoding process ensures that even if an attacker intercepts the encoded iris code (eic), they cannot reverse-engineer it to obtain the original biometric data. And, the session key (SKij = h(SIDj ⊕ d4 || IDi ⊕ d4)) is derived using random numbers and shared secrets, making it computationally infeasible for an eavesdropper to derive the key without knowing the random numbers.
6.2.7 Forward/Backward secrecy
The scheme ensures forward secrecy by deriving the session key (SKij = h(SIDj ⊕ d4 || IDi ⊕ d4)) using random numbers (d2, d3) that are unique to each session. Even if an attacker compromises the long-term secrets (IDi, PWi, SIDj, x), they cannot derive past session keys. Moreover, the scheme ensures backward secrecy by using new random numbers (d2, d3) for each session. If an attacker compromises the current session key, they cannot derive future session keys without knowing the new random numbers.
6.2.8 User credentials attack
The scheme protects user credentials {IDi, PWi} by not transmitting them in plaintext. Also, using a hash function (HMAC-SHA256) to derive the key from IDi and PWi. This ensures that even if an attacker intercepts the key, they cannot reverse-engineer it to obtain IDi and PWi. And storing only derived values (Authi = h(IDi || PWi || EIC), HIDi = h(IDi || ai)) instead of the actual credentials. Furthermore, the use of iris biometrics adds an additional layer of security. Even if an attacker steals IDi and PWi, they cannot authenticate without the user’s biometric data.
6.2.9 Smart device capture attack
The scheme does not store sensitive information directly on the smart device. Instead, it uses derived values such as {Authi, key} for authentication. So, even if the smart device is captured, an attacker cannot easily extract IDi or PWi because Authi is derived using a hash function (HMAC-SHA256), which is computationally irreversible. Furthermore, the iris biometric encoding process adds another layer of protection. Even if the smart device is compromised, the attacker cannot reverse-engineer the encoded iris code (eic) to obtain the original biometric data.
6.2.10 Offline password guessing attack
The scheme protects against offline password guessing attacks by:
Using a hash function (HMAC-SHA256) to derive the key from {IDi, PWi, eic}. This ensures that even if an attacker obtains the key, they cannot reverse-engineer it to guess PWi.
Incorporating iris biometrics as an additional authentication factor. Even if an attacker guesses PWi, they cannot authenticate without the user’s biometric data.
Using random numbers (d1, d2, d3) and timestamps to ensure that each session is unique. This prevents attackers from reusing captured data to guess passwords.
The scheme also enforces strong password policies (e.g., minimum length, complexity) to reduce the likelihood of successful password guessing.
6.2.11 Replay attack
First, the scheme uses timestamps (T1, T2, T3, T4) to ensure that each session is unique and time-bound. If an attacker attempts to replay a captured message, the timestamp validation will fail if the message is outside the allowed time window (delta_t). Moreover, the use of random numbers (d1, d2, d3) ensures that each session is independent. Even if an attacker captures a valid message, they cannot reuse it in a different session because the random numbers will not match. Additionally, the hash values (V1 = h(C2 || IDi || TS1), V2 = h(SIDj || d2’ || TS2), V3 = h(SIDj || TS3), V4 = h(SKji || d3 || SIDj)) are derived from session-specific data (e.g., random numbers, timestamps, and shared secrets). This ensures that replayed messages will fail verification because the hash values will not match.
6.2.12 Privileged insider attack
The scheme protects against privileged insider attacks by derived values such as Authi and key, which are protected by cryptographic hashing. And using iris biometrics as an additional authentication factor. Even if a privileged insider obtains IDi and PWi, they cannot authenticate without the user’s biometric data. In addition, deriving the session key (SKij = h(SIDj ⊕ d4 || IDi ⊕ d4)) using random numbers (d2, d3) and shared secrets. This ensures that even a privileged insider cannot derive the session key without knowing the random numbers. The scheme also enforces role-based access control to limit the privileges of insiders. For example, only authorized personnel can access certain parts of the system.
Table 7 compares the security features of the proposed scheme with the other most related ones.
Table 7
| Security features | Wu et al. (2023) | Kaur and Kumar (2021) | Banerjee et al. (2020) | Fakroon et al. (2022) | Yu et al. (2021) | Wazid et al. (2020) | Shuai et al. (2019) | Sharma and Dhiman (2024) | Proposed scheme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anonymity and Untraceability | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fault analysis attacks | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Mobile Device Loss Attack | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Impersonation Attacks | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Resist (MITM) Attack | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Eavesdropping Attack | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Forward/Backward Secrecy | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| User Credentials Attack | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Smart Device Capture Attack | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Offline Password Guessing | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Replay Attack | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Privileged Insider Attack | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
Security attributes comparison.
6.3 Performance analysis
This section compares the proposed scheme with related existing schemes of Mengxia Shuai et al., Tsu-Yang Wu et al., Moneer Fakroon et al., Mohammad Wazid et al., Soumya Banerjee et al., and Sungjin Yu during the login and authentication phases. Since the registration phase is not repeated, the costs involved in this phase are not discussed.
6.3.1 Computation cost (time, CPU, and memory cost)
The computation cost tested in this scheme is the computation time, CPU usage, and memory usage. The computation time for user TUi requires one message M1. The gateway (TGW) requires two messages (M2, M4) ≃ 2TGW, and the computation time for device TD requires one message (M4). For more clarification, the whole system requires TUi + 2TGW + TD. The time cost is 1.4909 + 2 × 0.0035 + 0.0362 ≈ 1.5341. Seem when testing the CPU cost CPUUi + 2CPUGW + CPUD → 2.5732 + 2 × 0.00 + 3.2566 ≈ 6. 829%. Moreover, analyzing memory cost for the three participants: user Ui, gateway GW, and smart device D. The memory (ME) usage is MEUi + 2MEGW + MED ≈ 332.2916 bits. This scheme has been tested more than 30 times to take the average of the authentication process with different user IDs, pw, and biometrics. Table 8 shows the average use of computation cost for this scheme. 1.5341.
Table 8
| Factors | Ui | GW | D | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory | 332.1614 bits | 0.00 bits | 0.1302 bits | 332.2916 bits |
| CPU | 2.5732% | 0.00% | 3.2566% | 6.8299% |
| Time | 1.4909 ms | 0.007 ms | 0.0362 ms | 1.5341 ms |
Computation cost.
6.3.2 Computation cost comparison
The following Table 8 uses the notation Texp, Th, TED, and TM to denote the computational time for modular exponentiation operation, Hash function, Symmetric encryption or decryption, and point scalar multiplication. The bitwise XOR operation execution time is negligible and is not considered a performance evaluation parameter. The existing experimental values of these operations are given as follows: 0.003300 ms, 0.116800 ms, 0.001900 ms, and 0.002000. The execution time for the generation of fuzzy extractor 𝑇𝑓𝑒 is assumed to be equal to 𝑇𝑒xp as given in (Soumya Banerjee), (Damandeep Kaur), (SUNGJIN YU). The following Table 9 shows the value of the computation cost of complex operations.
Table 9
| Crypto-operations | Symbol | Execution time |
|---|---|---|
| modular exponentiation operation | Texp | 0.0033 ms |
| Hash function | Th | 0.1168 ms |
| Symmetric encryption or decryption | TED | 0.0019 ms |
| Point scalar multiplication | TM | 0.002 ms |
Computation cost of complex operations.
These operations are acquired based on a used laptop with Windows 10, CPU is Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-10510U CPU @ 1.80GHz 2.30, and 16.0 memory. Moreover, the software development environment was implemented using Python. The proposed scheme was compared in terms of computation cost (time cost) in milliseconds with some other related schemes. Table 9 shows the comparison of the proposed scheme and seven others. It is noticed that the proposed scheme has a good performance in terms of execution time. It takes almost 1.5341 ms, which shows better performance than many others shown in Table 10 and Figure 6. It is also noticed that the scheme of Fakroon et al. performs a lighter performance, but this is obvious due to using only a hash function without combining it with other operations such as encryption/decryption or exponentiation operation, which led to security issues.
Table 10
| Scheme | Total cost | Execution time |
|---|---|---|
| Wu et al. (2023) | 18th + 3TM | 2.1084 ms |
| Kaur and Kumar (2021) | 16th + 3Texp | 1.8787 ms |
| Banerjee et al. (2020) | 24th + 1Texp | 2.8065 ms |
| Fakroon et al. (2022) | 10th | 1.168 ms |
| Yu et al. (2021) | 29th + 1Texp + 1Ted | 3.3924 ms |
| Wazid et al. (2020) | 22th + 4TED + Texp | 2.5805 ms |
| Shuai et al. (2019) | 3Texp + 16th | 1.8787 ms |
| Sharma and Dhiman (2024) | 42th + 2TE + 2TD | 4.9132 ms |
| Proposed scheme | 3Texp + 13th + 2TED + 1TM | 1.5341 ms |
Comparison of computation cost.
Figure 6
6.3.3 Communication cost
This section compares the communication cost between the proposed scheme and other related schemes. The communication cost of the scheme depends upon the sum of bits transferred in messages between the user node, GW, and smart device (Dj). Assuming the communication costs of the following parameters, the length of timestamp, random nonce, hash function, identity, and pseudo-identity, symmetric encryption/decryption, ECC point multiplication, and secret key are 32 bits, 160 bits, 160 bits, 128 bits, 256 bits, 320 bits, and 160 bits, respectively. The proposed scheme has 4 messages, in message1(user to GW), the total communication cost is 320 + 320 + 160 + 32 + 160 = 992 bits, total communication cost of M2 (GW to Dj), M3 (Dj to GW), and M4 (GW to User) as follows: 160 + 160 + 32 = 352 bits, 160 + 32 + 160 + 128 + 128 = 608 bits, 160 + 32 + 128 + 128 = 448 bits. The total cost of the four messages is 2,400 bits. Compared to other related schemes, the proposed scheme shows a better and lighter performance in the communication cost than others. Table 11 illustrates the comparison process. Figure 7 compares the communication cost of each message, and Figure 8 compares the total communication cost
Table 11
| Node | Wu et al. (2023) | Kaur and Kumar (2021) | Banerjee et al. (2020) | Fakroon et al. (2022) | Yu et al. (2021) | Wazid et al. (2020) | Shuai et al. (2019) | Sharma and Dhiman (2024) | Proposed scheme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User to GW | 1,248 bits | 1,600 bits | 1,056 bits | 896 bits | 672 bits | 480 bits | 1,280 bits | 992 bits | 992 bits |
| GW to Dj | 352 bits | 1,120 bits | 640 bits | 480 bits | 768 bits | 448 bits | 736 bits | 1,248 bits | 352 bits |
| Dj to GW | 672 bits | 704 bits | 800 bits | 448 bits | 352 bits | 512 bits | 480 bits | 512 bits | 608 bits |
| GW to User | 512 bits | 992 bits | 928 bits | 736 bits | 640 bits | 640 bits | 608 bits | 1,024 bits | 448 bits |
| Total | 2,784 bits | 4,416 bits | 3,424 bits | 2,560 bits | 2,432 bits | 2080 bits | 3,104 bits | 3,776 bits | 2,400 bits |
Comparison of communication costs.
Figure 7
Figure 8
7 Limitation and future work
The current authentication protocol provides a strong security layer for conventional smart home environments. However, its architecture suggests two major avenues for future research that could significantly enhance its utility and scope.
The current analysis remains based on a simulated environment. Future study will involve developing a hardware implementation of the proposed scheme using embedded systems, such as Arduino or Raspberry Pi, to test performance in a real-world setting under network variability and interference. Additional research will explore extending the protocol to larger IoT ecosystems, such as smart cities and vehicular networks, and investigating resilience against physical side-channel attacks.
Integration with Behavioral Analytics
While the protocol effectively validates user identity, it currently operates independently of modern intelligent systems. A crucial next step involves integrating the authentication layer with AI-driven behavioral analytics engines. Future studies should focus on enabling the authentication system to work in concert with a behavioral analytics engine. This convergence would establish a more dynamic and context-aware security posture, moving beyond mere credential verification.
Scaling to Large IoT Ecosystems
The protocol is designed to secure the initial gateway to connected devices, but it does not directly manage the subsequent massive data flows generated by these devices. Scaling this solution to larger-scale Internet of Things (IoT) environments, such as smart cities, introduces significant big data challenges. Future efforts must explore additional strategies to pair the authentication mechanism with privacy-preserving data analysis techniques.
8 Conclusion
This study presented an approach to enhancing authentication security within IoT-based smart home environments. The proposed solution is a novel, lightweight authentication scheme utilizing a dynamic One-Time Iris Code (OTIC) to establish robust mutual authentication among users, gateways, and smart devices. Formal security verification with the Real-or-Random (RoR) model, supplemented by informal analysis, confirms the scheme’s resilience against a wide range of prevalent attacks, including impersonation, privileged insider, and offline password guessing. Performance evaluations further demonstrate the scheme’s superior security posture alongside reduced computation and communication costs compared to recent state-of-the-art schemes (Lazaroiu et al., 2024; Sarbishaei et al., 2024; Yang and Sun, 2022). These attributes make the proposed scheme highly suitable for resource-constrained IoT devices.
This study contributes to lightweight cryptography by offering a viable model for integrating dynamic biometrics into cryptographic protocols. The OTIC mechanism provides a blueprint for moving beyond static credentials, enabling non-linkability and forward secrecy. For industry adoption, the scheme’s efficiency and security address key barriers to developing more secure consumer IoT products. Reduced computational overhead allows for integration into existing device hardware without costly upgrades, facilitating a path toward more secure smart homes without compromising performance or affordability. Finally, the core design principles—such as dynamic session-specific credentials and lightweight operations—could inform the development of future IoT security standards and best practices, encouraging more resilient security architectures by default.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
ZR: Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SA: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. FT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. KM: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declared that financial support was not received for this work and/or its publication.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared that this work was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declared that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. To paraphrase some statements in this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
AbdallaM.FouqueP.-A.PointchevalD., “LNCS 3386 - password-based authenticated key exchange in the three-party setting,” (2005). Available online at: https://www.di.ens.fr/users/mabdalla,fouque,pointche (Accessed January 2025).
2
AbohatemA. Y.Ba-AlwiF. M. M.Al-KhulaidiA. A. G. (2023). View of suggestion cybersecurity framework (CSF) for reducing cyber-attacks on information systems. Sana’a University J. Applied Sci. Technol.1:248.
3
AlasmaryH.TanveerM. (2023). ESCI-AKA: enabling secure communication in an IoT-enabled smart home environment using authenticated key agreement framework. Mathematics11:3450. doi: 10.3390/math11163450
4
AlshahraniM.TraoreI. (2019). Secure mutual authentication and automated access control for iot smart home using cumulative keyed-hash chain. J. Inf. Secur. Appl.45, 156–175. doi: 10.1016/j.jisa.2019.02.003
5
AshrafZ.SohailA.HameedA.FarhanM.AlotaibiF. A.AlnfiaiM. M. (2023). Robust and lightweight remote user authentication mechanism for next-generation IoT-based smart home. IEEE Access11, 137899–137910. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3336763
6
AshrifF. F.SundararajanE. A.AhmadR.HasanM. K.YadegaridehkordiE. (2024). Survey on the authentication and key agreement of 6LoWPAN: open issues and future direction. US: Academic Press.
7
AttardL.DebonoC. J.ValentinoG.Di CastroM. (2018). Tunnel inspection using photogrammetric techniques and image processing: a review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens.144, 180–188. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.07.010
8
BanerjeeS.OdeluV.DasA. K.ChattopadhyayS.ParkY. (2020). An efficient, anonymous and robust authentication scheme for smart home environments. Sensors20, 1–31. doi: 10.3390/s20041215,
9
BarpandaS. S.MajhiB.SaP. K.SangaiahA. K.BakshiS. (2019). Iris feature extraction through wavelet mel-frequency cepstrum coefficients. Opt. Laser Technol.110, 13–23. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.03.002
10
BasavalaS. R.KumarN. (2012). Authentication: an overview, its types and integration with web and Mobile applications. Coimbatore, India: IEEE.
11
BhardwajA.BharanyS.AbulfarajA. W.Osman IbrahimA.NagmeldinW. (2024). Fortifying home IoT security: a framework for comprehensive examination of vulnerabilities and intrusion detection strategies for smart cities. Egyptian Informatics J.25, 1–21. doi: 10.1016/j.eij.2024.100443
12
CanO.ThabitF.AljahdaliA. O.Al-HomdyS.AlkhzaimiH. A. (2023). A comprehensive literature of genetics cryptographic algorithms for data security in cloud computing. Cybern. Syst.56, 413–447. doi: 10.1080/01969722.2023.2175117
13
ChoY.OhJ.KwonD.SonS.LeeJ.ParkY. (2022). A secure and anonymous user authentication scheme for IoT-enabled smart home environments using PUF. IEEE Access10, 101330–101346. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3208347
14
DasA. K.BeraB.WazidM.JamalS. S.ParkY. (2021). On the security of a secure and lightweight authentication scheme for next generation IoT infrastructure. IEEE Access9, 71856–71867. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3079312
15
DeyS.HossainA. (2019). Session-key establishment and authentication in a smart home network using public key cryptography. IEEE Sens. Lett.3, 1–4. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2019.2905020
16
FakroonM.AlshahraniM.GebaliF.TraoreI. (2022). Secure remote anonymous user authentication scheme for smart home environment. Internet Things (Neth.)9, 1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2020.100158
17
GuoT.ZhangT.LimE.Lopez-BenitezM.MaF.YuL. (2022). A review of wavelet analysis and its applications: challenges and opportunities. IEEE Access10, 58869–58903. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3179517
18
HasanM. K.WeichenZ.SafieN.AhmedF. R. A.GhazalT. M. (2024). A survey on key agreement and authentication protocol for internet of things application. IEEE Access12, 61642–61666. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3393567
19
HusztiA.KovácsS.OláhN. (2022). Scalable, password-based and threshold authentication for smart homes. Int. J. Inf. Secur.21, 707–723. doi: 10.1007/s10207-022-00578-7
20
IslamR.RahmanM. W.RubaiatR.HasanM. M.RezaM. M.RahmanM. M. (2022). LoRa and server-based home automation using the internet of things (IoT). J. King Saud University - Computer Information Sci.34, 3703–3712. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.12.020
21
KamarainenJ. K.KyrkiV.KälviäinenH. (2006). Invariance properties of Gabor filter-based features - overview and applications. IEEE Trans. Image Process.15, 1088–1099. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.864174,
22
KaurD.KumarD. (2021). Cryptanalysis and improvement of a two-factor user authentication scheme for smart home. J. Inf. Secur. Appl.58, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jisa.2021.102787
23
LazaroiuA. C.RosciaM.DancuV. S.BalabanG. (2024). Social impact of decarbonization objectives through smart homes: survey and analysis. Renew. Energy230, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2024.120872
24
LiuZ.LiZ.ZhangQ.DongS.LiuJ.ZhaoY. (2022). Two-factor authentication and key agreement schemes for smart home fingerprint characteristics. Mob. Inf. Syst.2022, 1–10. doi: 10.1155/2022/4184433
25
MaghrabiL. A.AltwijriM.BinyaminS. S.AlallahF. S.HamedD.RagabM. (2024). Secure biometric identification using Orca predators algorithm with deep learning: retinal Iris image analysis. IEEE Access12, 18858–18867. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3360871
26
MaodahK. A.AlhomdyS. A.ThabitF., “A comprehensive survey on automotive hacking,” In 1st international conference on emerging Technologies for Dependable Internet of things, ICETI 2024, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., (2024).
27
MehrotraR.NamuduriK RRanganathanN.Gabor filter-based edge detection. Oxford, United Kingdom: Pergamon Press, Elsevier (1992).
28
MohammadZ. N.FarhaF.AbuassbaA. O. M.YangS.ZhouF., “Access control and authorization in smart homes: a survey,” (2021). Available online at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9449335 (Accessed December, 2021).
29
PadmP.SrinivasanS. (2017). 2 a survey on biometric based authentication in cloud. Coimbatore, India: IEEE.
30
QashlanA.NandaP.HeX.MohantyM. (2021). Privacy-preserving mechanism in smart home using Blockchain. IEEE Access9, 103651–103669. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3098795
31
RajehZ. M.AlhomdyS. A.ThabitF., “Secure authentication in smart home environment using SGX and biometrics: survey,” In 1st international conference on emerging Technologies for Dependable Internet of things, ICETI 2024, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., (2024).
32
SarbishaeiG.ModarresA. M. A.JowshanF.KhakzadF. Z.MokhtariH. (2024). Smart home security: an efficient multi-factor authentication protocol. IEEE Access12, 106253–106272. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3437294
33
SetzB.GraefS.IvanovaD.TiessenA.AielloM. (2021). A comparison of open-source home automation systems. IEEE Access9, 167332–167352. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3136025
34
SharmaN.DhimanP. (2024). “Privacy in smart homes with remote user authenticated key establishment protocol” in Procedia computer science. International Conference on Recent Trends in Advanced Computing (ICRTAC) 2023. (Netherland: Elsevier B.V), 119–128.
35
ShuaiM.YuN.WangH.XiongL. (2019). Anonymous authentication scheme for smart home environment with provable security. Comput. Secur.86, 132–146. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2019.06.002
36
SireeshaK.AmaravathiP.ROR model based formal security analysis and informal security analysis. New York, USA: AIP Publishing (American Institute of Physics) (2021)
37
WazidM.DasA. K.OdeluV.KumarN.SusiloW. (2020). Secure remote user authenticated key establishment protocol for smart home environment. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput.17, 391–406. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2017.2764083
38
WuT. Y.MengQ.ChenY. C.KumariS.ChenC. M. (2023). Toward a secure smart-home IoT access control scheme based on home registration approach. Mathematics11, 1–22. doi: 10.3390/math11092123
39
XiaY.QiR.JiS.ShenJ.MiaoT.WangH. (2022). PUF-assisted lightweight group authentication and key agreement protocol in smart home. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput.2022, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2022/8865158
40
YangJ.SunL. (2022). A comprehensive survey of security issues of smart home system: ‘spear’ and ‘shields,’ theory and practice. IEEE Access10, 124167–124192. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3224806
41
YuS.JhoN.ParkY. (2021). Lightweight three-factor-based privacy- preserving authentication scheme for IoT-enabled smart homes. IEEE Access9, 126186–126197. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3111443
42
YusufN.MarafaK. A.ShehuK. L.MammanH.MaidawaM. (2020). A survey of biometric approaches of authentication. Int. J. Advanced Computer Res.10, 96–104. doi: 10.19101/ijacr.2019.940152
43
ZaharyA. T.Al-NbhanyW. (2025). View of Blockchain-IoT healthcare applications and Trends_ review. Sana’a University J. Applied Sci. Technol.3, 113–128.
44
ZhuJ.WangD.ZhaoY. (2024). Design of smart home environment based on wireless sensor system and artificial speech recognition. Measurement: Sensors33:101090. doi: 10.1016/j.measen.2024.101090
Summary
Keywords
smart home environment, authentication, biometric, Iris, encoding
Citation
Rajeh ZM, Alhomdy SA, Thabit F and Maodah KA (2026) A secure authentication scheme for smart home environments: a biometric-driven approach. Front. Comput. Sci. 8:1669659. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2026.1669659
Received
20 July 2025
Revised
10 October 2025
Accepted
12 January 2026
Published
27 February 2026
Volume
8 - 2026
Edited by
Rajkumar Saini, Luleå University of Technology, Sweden
Reviewed by
Sahar Zahiri, Oxford Brookes University, United Kingdom
Mohammed Balfaqih, Jeddah University, Saudi Arabia
Dhruv Parikh, Emory University, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2026 Rajeh, Alhomdy, Thabit and Maodah.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zahra M. Rajeh, z.rajeh22@gmail.com
† Present address: Fursan Thabit, Department Computer Engineering, Ege University, Izmir, Türkiye
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.