- 1Institute of Germplasm Resources and Biotechnology, Tianjin Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Tianjin, China
- 2College of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture, Tianjin Agricultural University, Tianjin, China
To investigate the expression of micro RNAs (miRNA) at the transcriptome level in interactions between maize (Zea mays) and the Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis), four miRNA libraries were constructed based on four groups of samples: fresh, uneaten maize leaves; maize leaves eaten by Asian corn borer larvae; Asian corn borer larvae that had eaten maize leaves; and Asian corn borer reared on an artificial diet). Through second-generation sequencing technology, 810 known miRNAs and 132 new miRNAs were identified and analyzed. In specific miRNA comparisons, five new plant-derived miRNAs were found in the Asian corn borer larvae, of which one was differentially expressed because of its diet. Expression levels of all differentially expressed miRNAs were validated using qRT PCR. Because of biotic stress and differences in food types, miRNAs with cross-kingdom transfer were regulated by their target genes to express metabolic factors such as transcription factors (e.g., growth hormone response factors (ARF6, ARF8), inorganic phosphate transporters (Pht10), and phosphate transporters (Pht7, Pht9)). We improve understanding of the roles of microRNAs in plant–insect interactions, and establish a foundation upon which new maize varieties with resistance to Asian corn borer larvae can be developed through genetic engineering.
1 Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of endogenous single stranded non coding small RNA molecules of approximate length 20–22 nucleotides (nt). As important post transcriptional gene expression regulators, these miRNAs play roles in various biological processes, and they are key regulatory factors in plant and insect development and physiological processes (Reinhart et al., 2002; Sarma Bordoloi and Agarwala, 2021), such as seeds, roots. The development, phase transition, and response to biotic and abiotic stresses of stems and flowers (Li and Yu, 2021) regulates insect development, reproduction, metamorphosis, immunity, and insecticide resistance (Zhang et al., 2021). Many reports of miRNA regulatory mechanisms in interactions between plants and insects exist. For example, 68 differentially expressed (DE) miRNAs were identified and 324 new miRNAs were discovered in a comparison of healthy tea tree leaves and those affected by the tea geometrid (Ectropis obliqua), indicating that miRNAs are involved in plant defense responses against herbivorous insects (Jeyaraj et al., 2017). MiR-998-3p regulated resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis (hereinafter Bt) in three Lepidoptera pest species (cotton bollworm, beet armyworm, and diamondback moth), which manages Cry1Ac resistance by targeting ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 2 (ABCC2) (Zhu et al., 2019). Cross-border transportation of miRNAs has also been demonstrated. For example, miRNAs derived from mulberries can enter multiple silkworm tissues, but feeding silkworms with synthesized miR166b causes no phenotypic change (Jia et al., 2015). Studies using plant leaves to feed insects have found plant-derived miRNAs, including miR168a, within insect tissues that did not feed on monocotyledonous plants (Zhang et al., 2012).
Study of maize at the transcriptome level (https://magic.novogene.com/customer/main#/homenew/de1e649f1982fa3ca5e212a72bd31022).
There are few reports of interactions between maize (Zea mays) and the Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis) on the miRBase website (http://www.mirbase.org/). To August 31, 2023, 174 precursor sequences and 325 mature sequences had been reported for corn, but relevant information for Asian corn borer was lacking. Feeding Bt corn to European corn borer (O. nubilais) larvae resulted in differential expression of 35 miRNAs in susceptible and resistant larvae. Bioinformatics predicted some of these miRNAs to be associated with targeted Bt resistance genes, such as cadherin and aminopeptidase N (APN) (Carrière and Crowder, 2010; Yu et al., 2018). In antiCryECB, the miRNA regulating the APN gene is up-regulated, decreasing APN levels. Downregulation of miRNA onu novol-29, which regulates the cadherin gene, leads to an increase in Cry potent binding protein levels. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are putative targets of these miRNAs (Belles, 2016). As the major Lepidopteran pest affecting corn yield, studying their interaction is essential to provide data support for breeding high−quality insect−resistant varieties.
The function of factors regulating gene expression in the interaction between corn and Asian corn borer is imperfectly known. To reveal the mechanism of action at the transcriptome level, we begin with miRNAs and explore their regulatory characteristics in interactions between corn and Asian corn borer via high-throughput sequencing, bioinformatics analysis, and qRT PCR. In doing so improve on understanding of plant–insect interaction in general, and more specifically for a commercially important crop and an important pest species, and provide a foundation upon which new corn varieties with resistance to corn borer can be developed through genetic engineering.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Test materials
Plant and insect test materials were sourced from the Institute of Germplasm Resources and Biotechnology, Tianjin Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The purity, germination rate, and other qualities of plant materials (corn variety Xianyu 335) meets or exceeds Chinese standards (GB4404.1) for Grade II corn seeds. Asian corn borer larvae were raised indoors (26–28°C, relative humidity 70%–80%, light/dark cycle 16/8) until the 4th instar. They were then starved for 24 h until their intestines were evacuated of fecal material (without contacting any plant materials, they were withheld from feeding for 24 h to allow the test insects to expel residual feces on their own), and were subsequently inoculated onto corn leaf cores at the V3 leaf stage. Each maize plant was inoculated with 10 borer larvae.
Corn plants and larvae were monitored. After the fourth corn leaf had fully unfolded it was collected. Leaf tissues that had been eaten were labeled “ymy,” and borer larvae that had fed on them were labeled “ymmy.” The fourth new and uneaten leaf represented a maize control and was labeled “ymx.” Fourth instar borer larvae that had been raised on artificial feed, starved (24 h) to evacuate gut contents, represented a larval control and were labeled “ymms.” Two sets of borer samples were dissected to remove the digestive tract and head tissue. After collecting four sets of samples, each treatment was repeated three times, with more than 800 mg of corn leaf tissue and more than 500 mg of corn borer tissue obtained per replicate. The samples were separately ground in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C.
2.2 miRNA prediction
Samples were entrusted to Beijing Nuohe Zhiyuan Technology Co., Ltd., for Solexa sequencing. Four sets of small RNA libraries were constructed by high-throughput sequencing (Illumina HiSeq 2000/MiSeq). Raw image data files were transformed into original Sequenced Reads by CASAVA base calling analysis. Base calling accuracy, measured by the Phred quality score (Q score), was used to assess the accuracy of Illumina (version 1.8) sequencing; the quality of original sequencing data corresponding to each sample was analyzed. After filtering original sequencing data, clean reads were obtained and re-screened to observe the proportion of consistent and unique sequences between samples. The screened sRNAs were then aligned to the reference genome using Bowtie, and the distribution of sRNAs on the genome was analyzed. Alignment and annotation of all sRNAs with various RNAs were summarized.
2.3 Differential gene expression analysis and target gene function prediction and pathway analysis
Expression levels of known and new miRNAs in each sample obtained from sequencing were statistically analyzed; expression levels have been normalized using transcripts per million (TPM) (Zhou et al., 2010). After processing, the TPM density distribution of miRNAs and correlations between miRNA expression levels in different samples were tested. For read-count data obtained from miRNA expression level analysis, DE gene analysis was performed using DESeq2 (Love et al., 2014). The overall distribution of miRNAs was evaluated based on fold changes and corrected significance levels. Because samples contained biological replicates, the screening condition to identify differential miRNAs used a Benjamini–Hochberg adjusted p-value (padj) < 0.05.
MiRanda and psRobot software was used to predict target genes for the miRNA, and to obtain corresponding relationships between miRNA and target genes. According to this relationship, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses were performed on the set of target genes for which miRNA was differentially expressed in each sample group for biological function prediction. The biological DataBase network (bioDBnet) (https://biodbnet-abcc.ncifcrf.gov/db/db2db.php) was used for Gene Symbol conversion, and to analyze the differential gene protein interaction network based on the STRING protein-interaction database.
2.4 RNA extraction and qRT PCR validation
Samples from each group were replicated three times. After grinding, RNA was extracted using a TransZol Up (TRAN Version 2.0) extraction kit, and cDNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA using TransScript ALL in One First Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix for qPCR (One Step gDNA Removal). For maize leaves, miR397a was used as an internal reference gene (Jiang et al., 2015); for Asian corn borer, actin-1 was used an internal reference gene (Liu et al., 2017). Forward primers were designed using Primer Premier3 software; reverse primers were provided by the miRcut Plus miRNA qPCR kit (SYBR Green) (Tiangen FP210831).
To examine relative changes in gene expression, qRT-PCR data were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCT method. The Cycle Threshold (CT) method was used to calculate relative expression levels of miRNAs (Li et al., 2010). GraphPad Prism (Prism9) was used to prepare images.
3 Results
3.1 miRNA sequencing data processing and comparative analysis
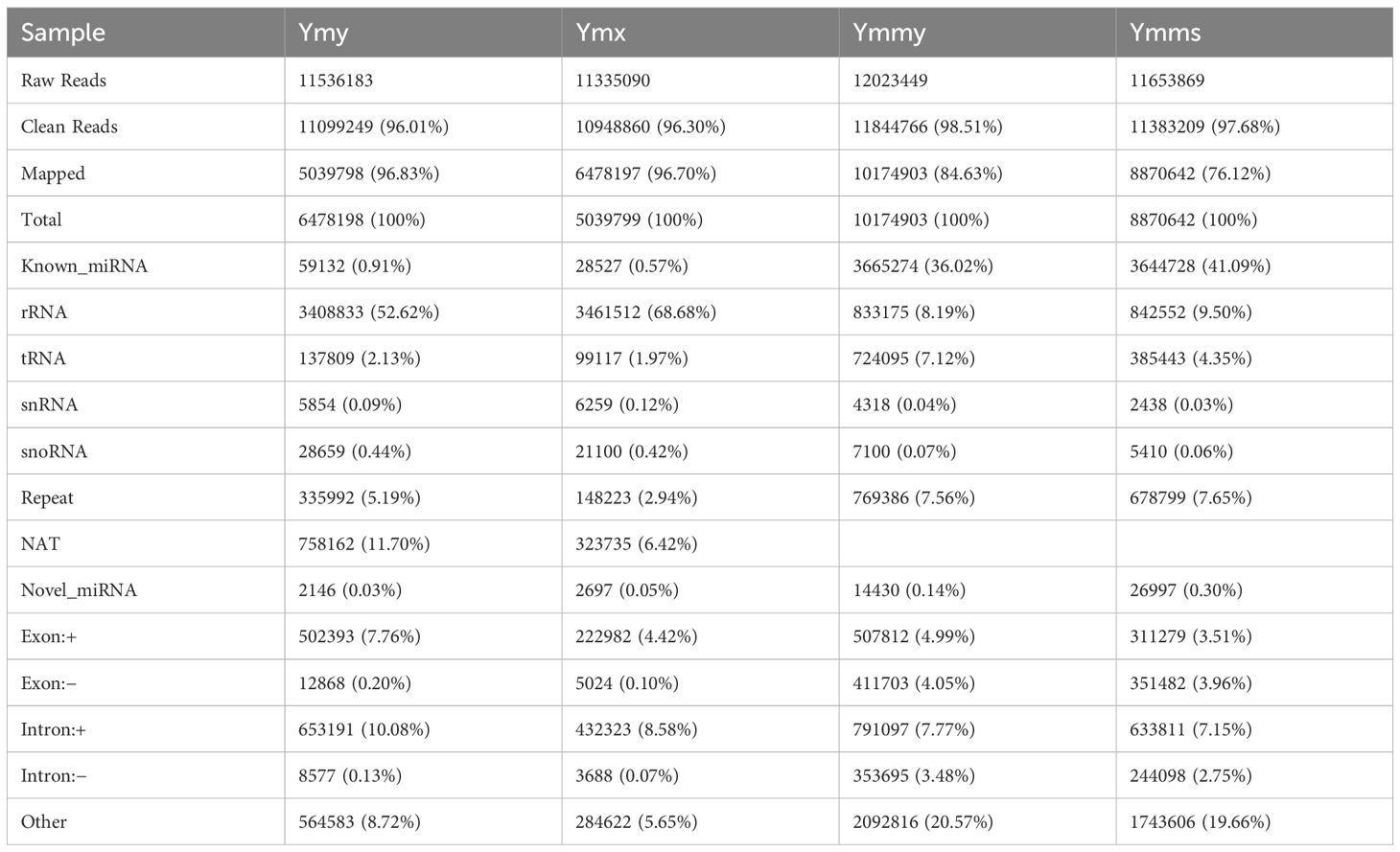
Four small RNA libraries were established by high-throughput sequencing of four sets of samples, for which 11,536,183 (ymy), 11,335,090 (ymx), 12,023,449 (ymmy), and 11,653,869 (ymms) original sequences were generated. After removing low non-compliant reads, clean reads for miRNA prediction numbered 11,099,249 (ymy), 10,948,860 (ymx), 11,844,766 (ymmy), and 11,383,209 (ymms). There were 5,039,798 (96.83%), 6,478,197 (96.70%), 10,174,903 (84.63%), and 8,870,642 (76.12%) successfully matched genome readings, respectively. A summary of the alignment and annotation of small RNAs with various RNA types is provided in Table 1.
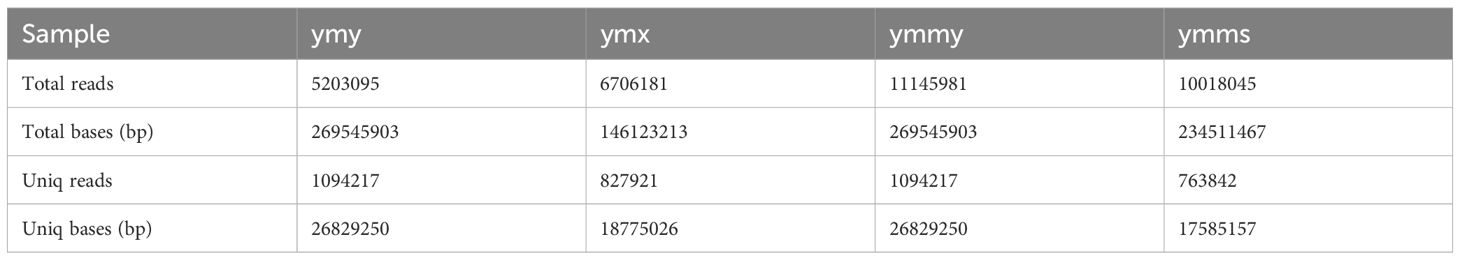
Animal sRNA length ranges 18–35 nt, while that of plants ranges 18–30 nt. The peak length of miRNA occurs between 21 and 22 nt, and siRNA at 24 nt, indicating that all samples met the requirements. Samples within treatments and controls were compared pairwise to observe the proportion of consistent and unique sRNA sequences between them (Table 2; Figure 1).
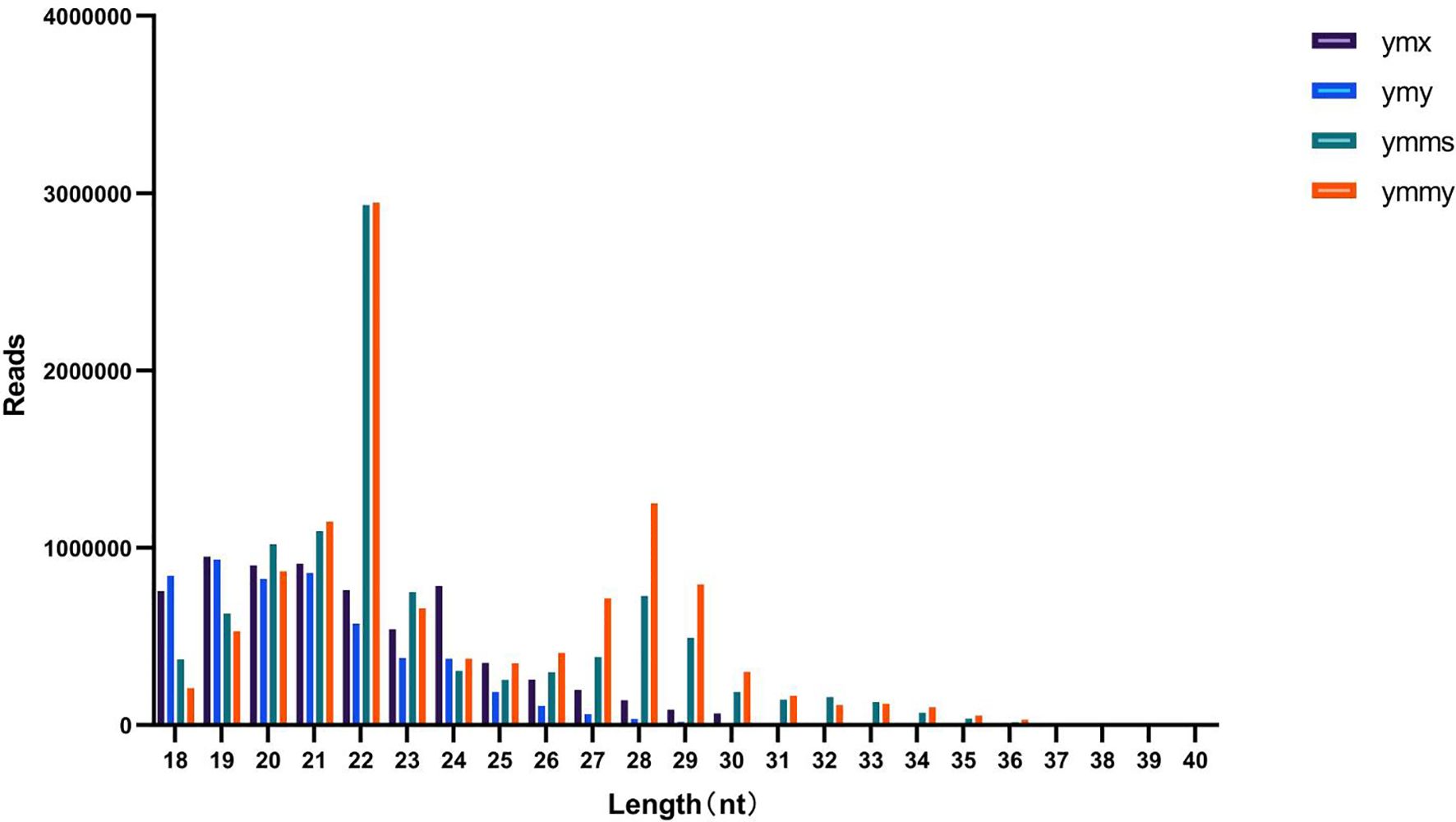
Figure 1. Size distribution and abundances of sRNAs in sample libraries for leaves eaten by Asian corn borer (ymy), uneaten fresh maize leaves (ymx), Asian corn borer larvae that had eaten maize leaves (ymmy), and Asian corn borer larvae fed an artificial feed (ymms).The majority of sequence lengths in the four libraries are distributed between 21–23 nt, with the densest length being 22 nt.
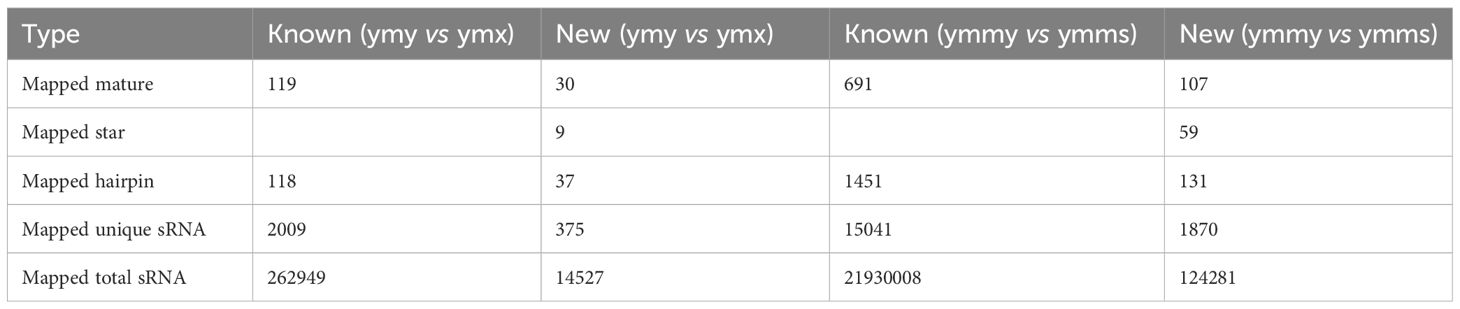
Known miRNA prediction. By aligning clean reads with specified range sequences in the miRBase database, a total of 810 known miRNAs belonging to 133 families (30 families in plants and 103 families in animals) were identified in the four libraries. Among them, 105 known miRNAs were detected in ymy samples and 110 in ymx samples; 618 and 580 miRNAs were detected in ymmy and ymms samples, respectively (Table 3; Figures 2, 3).
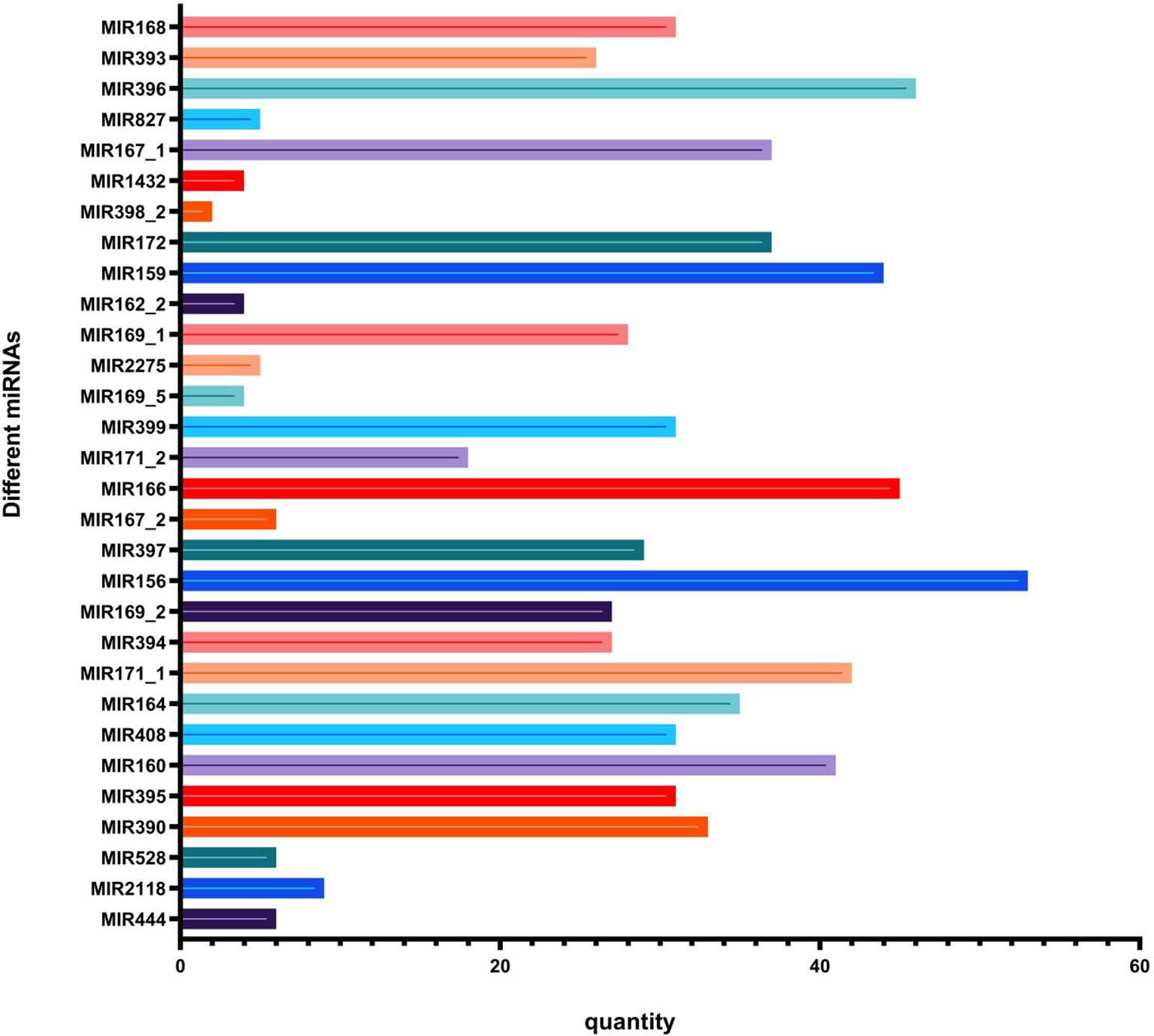
Figure 2. Comparison of miRNA precursors in the miRNA family in maize leaves.The horizontal axis represents the quantity collected, while the vertical axis represents the name of the miRNA family to which it belongs.
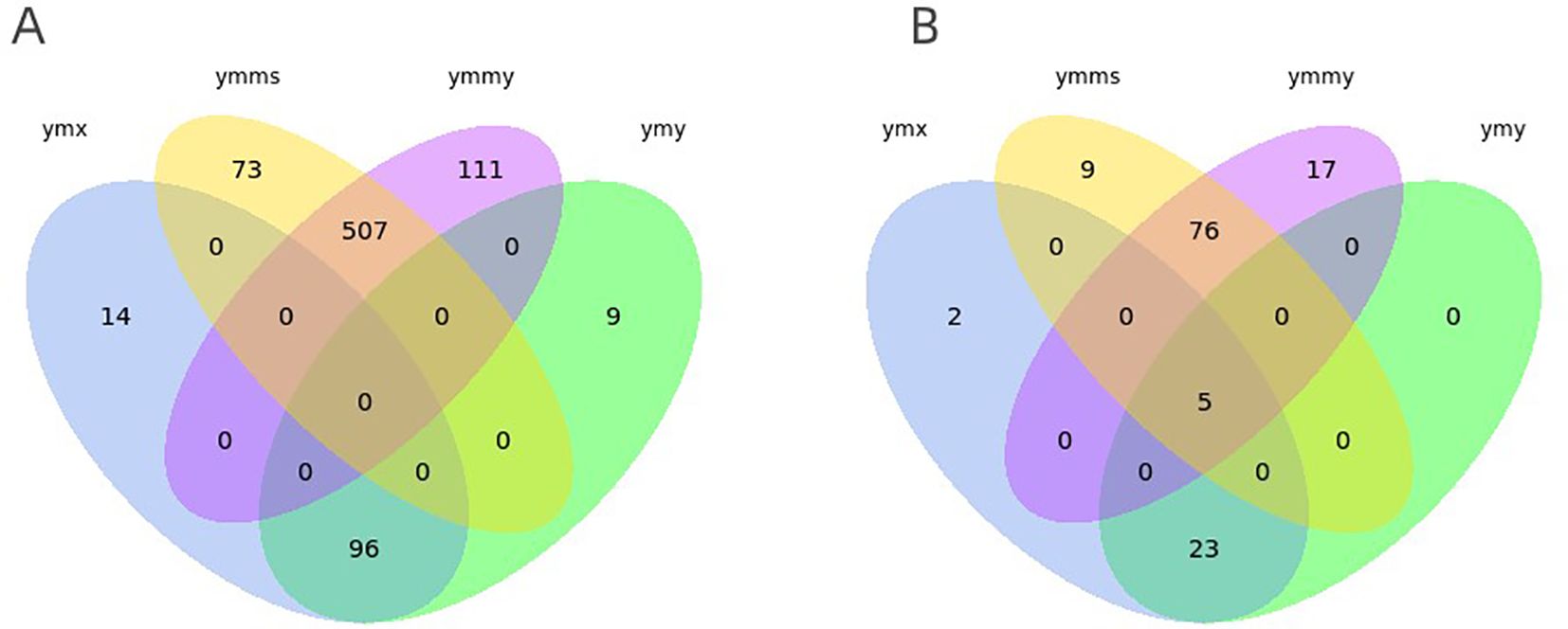
Figure 3. Venn diagrams depicting numbers of conserved (A) and new (B) miRNAs expressed in leaves eaten by Asian corn borer (ymy), uneaten fresh maize leaves (ymx), Asian corn borer larvae that had eaten maize leaves (ymmy), and Asian corn borer larvae fed an artificial feed (ymms).
New miRNA identification. For sequence fragments for which no match was found in the miRBase database, new miRNA analysis was performed using miREvo and mirdeep2 miRNA prediction software. A total of 132 new miRNAs were identified in the four libraries, with 28 and 30 new miRNAs detected in ymy and ymx samples, and 98 and 90 new miRNAs detected in ymmy and ymms samples, respectively (Table 3; Figures 2, 3).
3.2 Differential expression analysis of miRNA
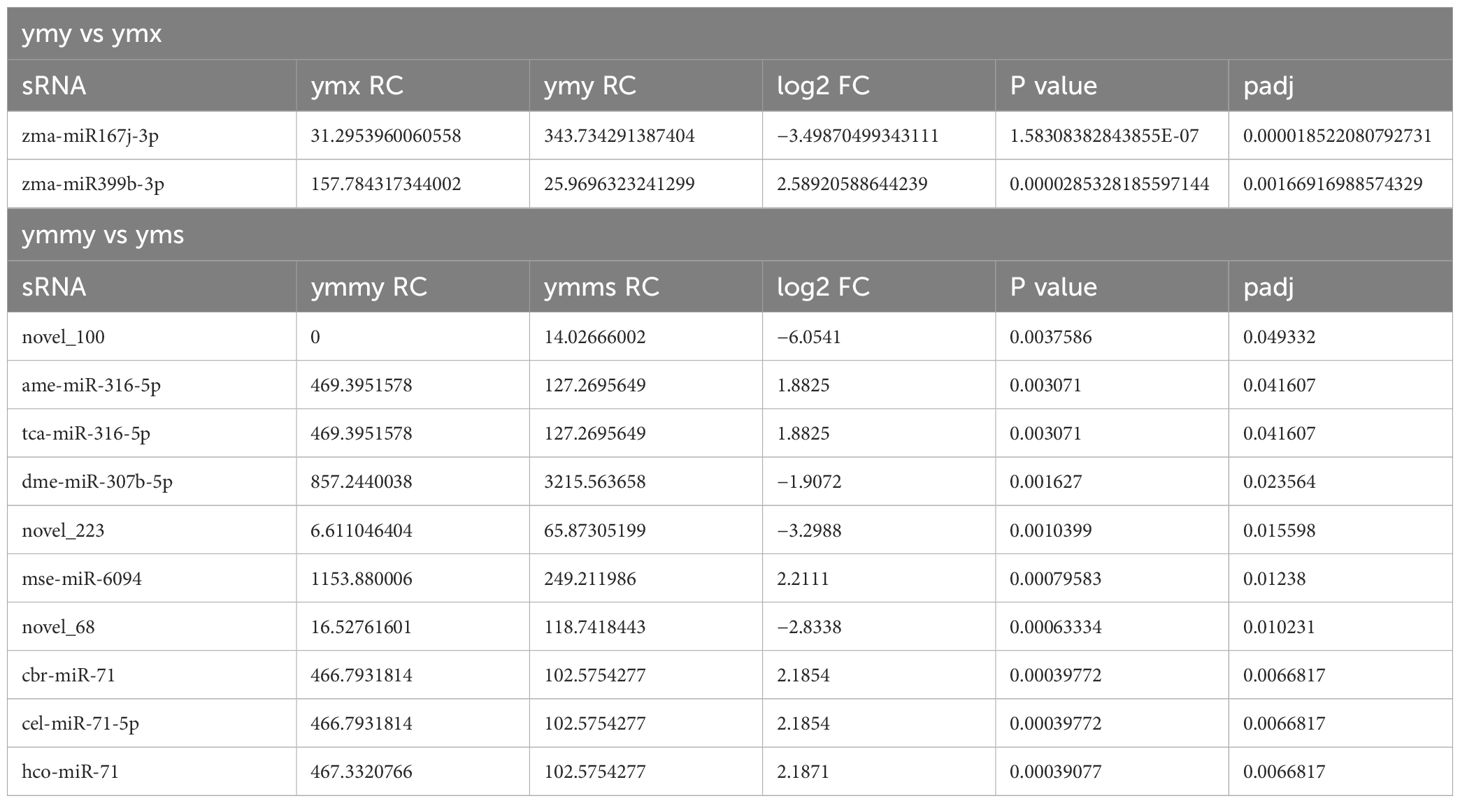
To investigate the effect of Asian corn borer feeding on endogenous miRNA expression in maize, expression levels of miRNAs were normalized using sequencing samples from ymx and ymy libraries (fresh leaves, and those eaten by Asian corn borer). Two miRNAs (one upregulated) were differentially expressed (padj < 0.05 and | log2FoldChange | > 1) (Table 4; Figure 4).
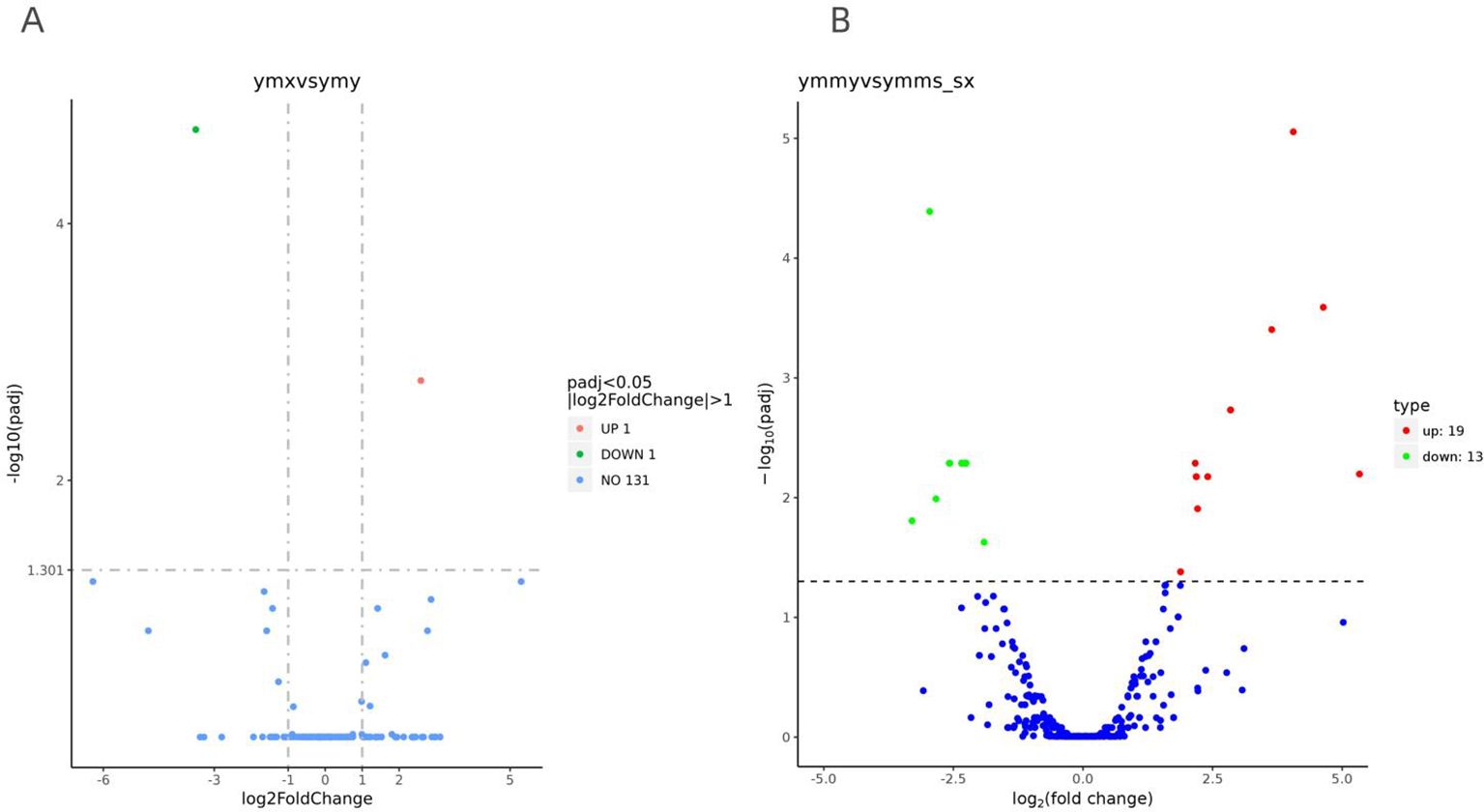
Figure 4. Cluster volcano plot of differentially expressed miRNAs in the interaction between corn and corn borer. The figure (A) shows the effect of Asian corn borer feeding on endogenous miRNA expression in maize, and the expression levels of miRNA were standardized using sequencing samples ymx and ymy libraries (fresh leaves and leaves consumed by Asian corn borer). (B) shows the effect of maize miRNA on Asian corn borer, and miRNA expression levels were standardized using ymmy and ymms libraries (Asian corn borer larvae that have eaten maize leaves and larvae that have eaten artificial food). MiRNA (an upregulated) differential expression (padj<0.05 andlog2FoldChange |>1).
To investigate the effect of maize miRNA on Asian corn borer, the expression levels of miRNAs were normalized using sequencing samples from ymmy and ymms libraries (Asian corn borer larvae that had eaten maize leaves, and larvae that had eaten artificial food). A total of 32 miRNAs (19 upregulated) were differentially expressed (padj < 0.05 and | log2FoldChange | > 1) (Table 4; Figure 4).
3.3 Target gene prediction
The prediction of animal miRNA target genes used the miRanda (miRanda-3.3a) and RNAhybrid (RNAhybrid v2.0) databases, and that for plants used psRobot (psRobot_v1.2). Among predicted target genes, two DE genes (zma miR167j-3p and zma miR399b-3p) in ymy and ymx samples were known miRNAs, and 36 potential target miRNA genes were predicted, belonging to 16 potential target genes, which may play roles in the biotic stress response of maize to Asian corn borer. Among the 32 DE genes in the ymmy and ymms sample comparison, 25 were known miRNAs and 7 were new, and 3619 potential target genes were predicted, which may play roles in regulating insect growth and development (Table 4).
In the analysis of specific and common miRNAs, four datasets shared five new miRNAs (novel_39, novel_52, novel_68, novel_73, and novel_91). The artificial feed is a corn-based mixed feed primarily composed of plant tissue (referring to a feed consisting of corn grits, yeast powder, soybean grits, microbial C-sheets, multidimensional glucose, sorbic acid, nipagin, and agar powder mixed together and sterilized at high temperature [121°C for 20 minutes], followed by the addition of sterile water and formaldehyde), supporting the conclusion that these five novel miRNAs detected in corn borers fed on both corn leaves and artificial feed are plant-derived. We speculate that these miRNAs enter the body of the Asian corn borer during feeding. As these are newly discovered miRNAs, the next step will be to validate the expression of their target genes at the transcript or protein level, with the aim of verifying their origin from plants. A comparison of the base composition of these five miRNAs with previously reported plant miRNAs revealed no evidence that miRNAs with higher guanine-cytosine (GC) content are more capable of stable cross-border transport (Figure 5).
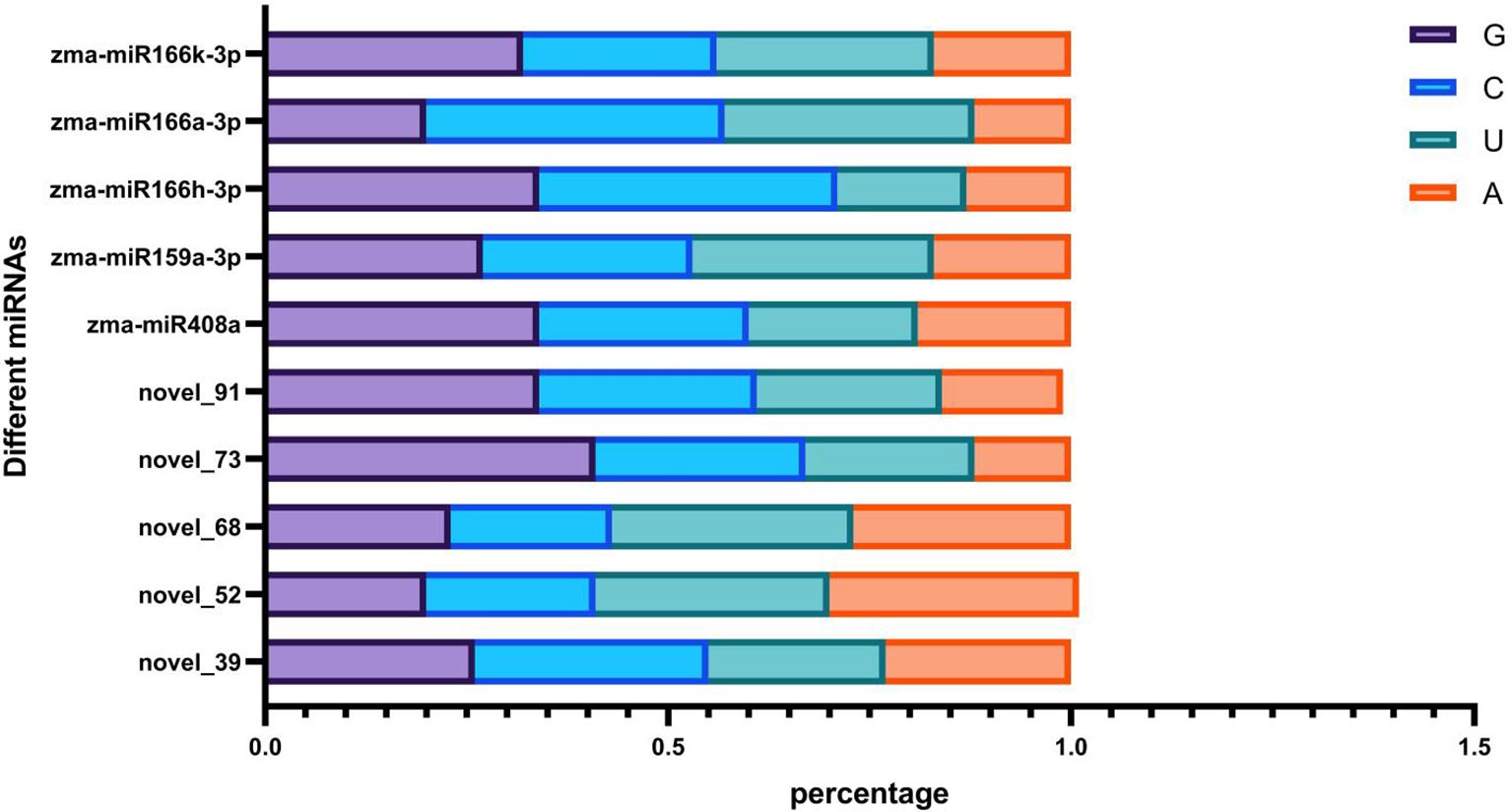
Figure 5. Base expression in miRNA.The horizontal axis represents the proportion of G/C/U/A bases, and the vertical axis represents the miRNA name.Comparing the base characteristics of these five miRNAs with previously reported plant miRNAs, it was not found that miRNAs with lower guanine cytosine (GC) ratios could stably transport across borders.
Target genes enriched in 225 GO terms and 7 KEGG pathways were compared between ymy and ymx leaf samples. differentially expressed miRNAs target genes were mainly enriched in functions such as intracellular protein transport and macromolecular metabolism, and involved in regulating pathways such as ABC transport, plant hormone signal transduction, transcription factors, and transmembrane transport. Target genes were enriched in 762 GO terms and 115 KEGG pathways in the comparison between ymmy and ymms larval samples. Target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs were mainly enriched in functions such as nucleus, transferase activity, cytoplasm, microtubule motility, and small molecule catabolism, and participated in regulating pathways such as ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum protein processing, endocytosis, and oxidative phosphorylation (Figure 6).
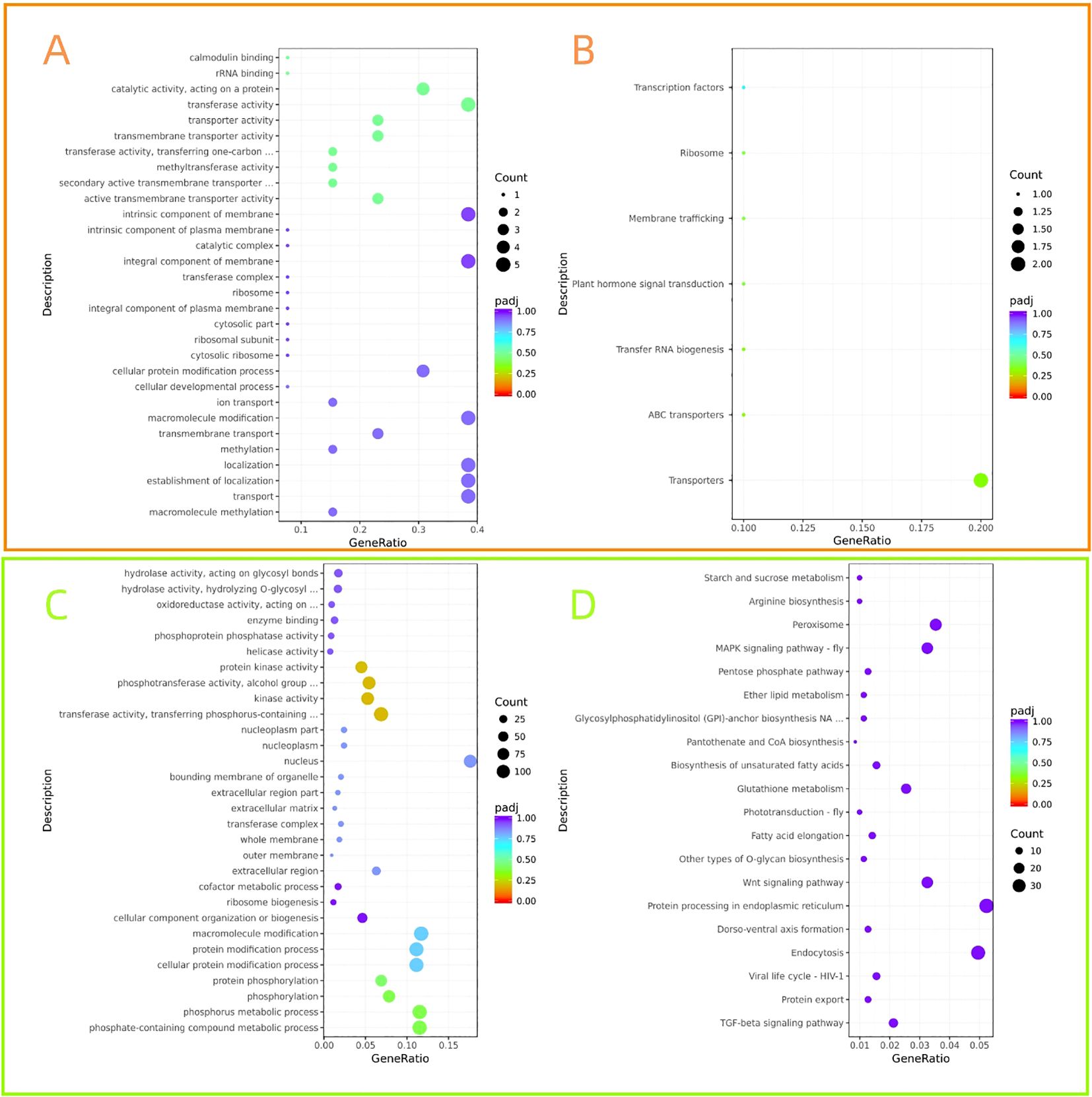
Figure 6. Functional prediction and pathway analysis of target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs.The orange box represents the GO enrichment analysis scatter plot, and the green box represents the KEGG enrichment scatter plot of candidate target genes. (A, C) showed the effect of feeding by Asian corn borer on endogenous miRNA expression in maize. Sequencing samples from ymx and ymy libraries (fresh leaves and leaves consumed by Asian corn borer) were used, and target genes were enriched in 225 GO terms and 7 KEGG pathways. (B, D) is the effect of maize miRNA on Asian corn borer. Using the ymmy and ymms libraries (Asian corn borer larvae that have eaten corn leaves and larvae that have eaten artificial food), the target genes were enriched in 762 GO projects and 115 KEGG pathways.
Using the STRING protein–protein interaction database for protein–protein interaction network analysis, we predicted that the regulatory factors of target genes encoding transcription factors for differentially expressed genes included growth hormone response factors (ARF6, ARF8), inorganic phosphate transporters (Pht10), and phosphate transporters (Pht7, Pht9) (Figure 7).
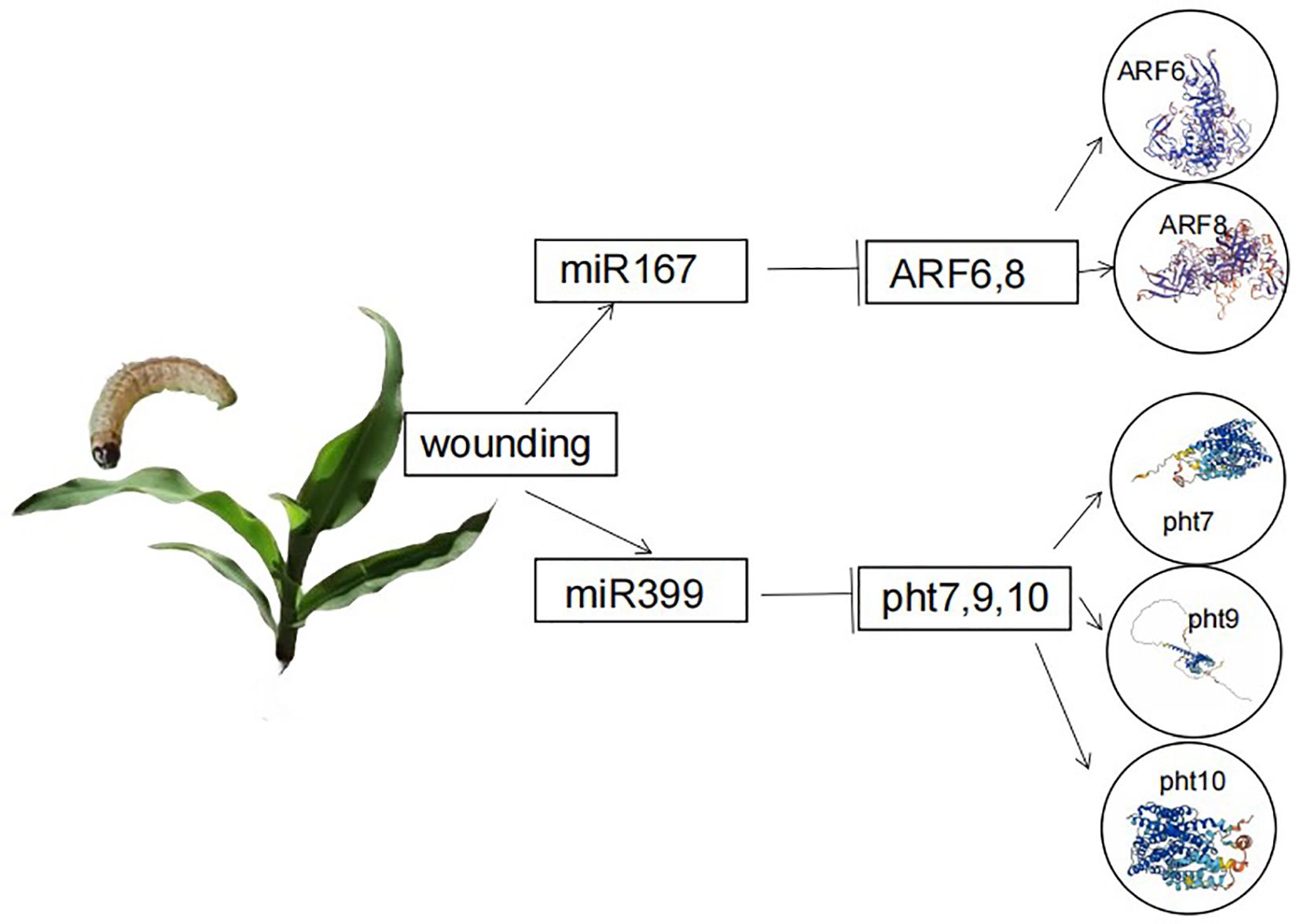
Figure 7. Protein–protein interaction diagram.which obtained gene data through bioinformatics analysis using the bioDBnet database network (https://biodbnet-abcc.ncifcrf.gov/db/db2db.php) Used for gene symbol conversion and analyzing differential gene protein interaction networks based on STRING protein interaction database. Then, by determining the protein name in NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) After searching on the website, obtain a protein map.
3.4 qRT PCR validation
We selected two differentially expressed maize miRNA genes, while the six insect miRNAs were representative members of six previously reported families supported by robust experimental data. Differential expression levels of miRNAs analyzed by bioinformatics were verified by qRT PCR. Two differentially expressed genes (zma-miR167j-3p, zma-miR399b-3p) were identified between ymy and ymx samples, with relative expression levels of 0.68 (zma-miR167j-3p) and 2.02 (zma-miR399b-3p). These results are consistent with high-throughput sequencing. Of 32 differentially expressed genes compared between ymmy and ymms samples, 6 genes (bmo-miR-1b-3p, cbr-miR-71, sfr-miR-13a-5p, dmemiR-307b-5p, ame-miR-316-5p, novel_68) were selected. The highest and lowest relative expression levels were 1.20 and 11.45, respectively, consistent with high-throughput sequencing results (Figure 8).
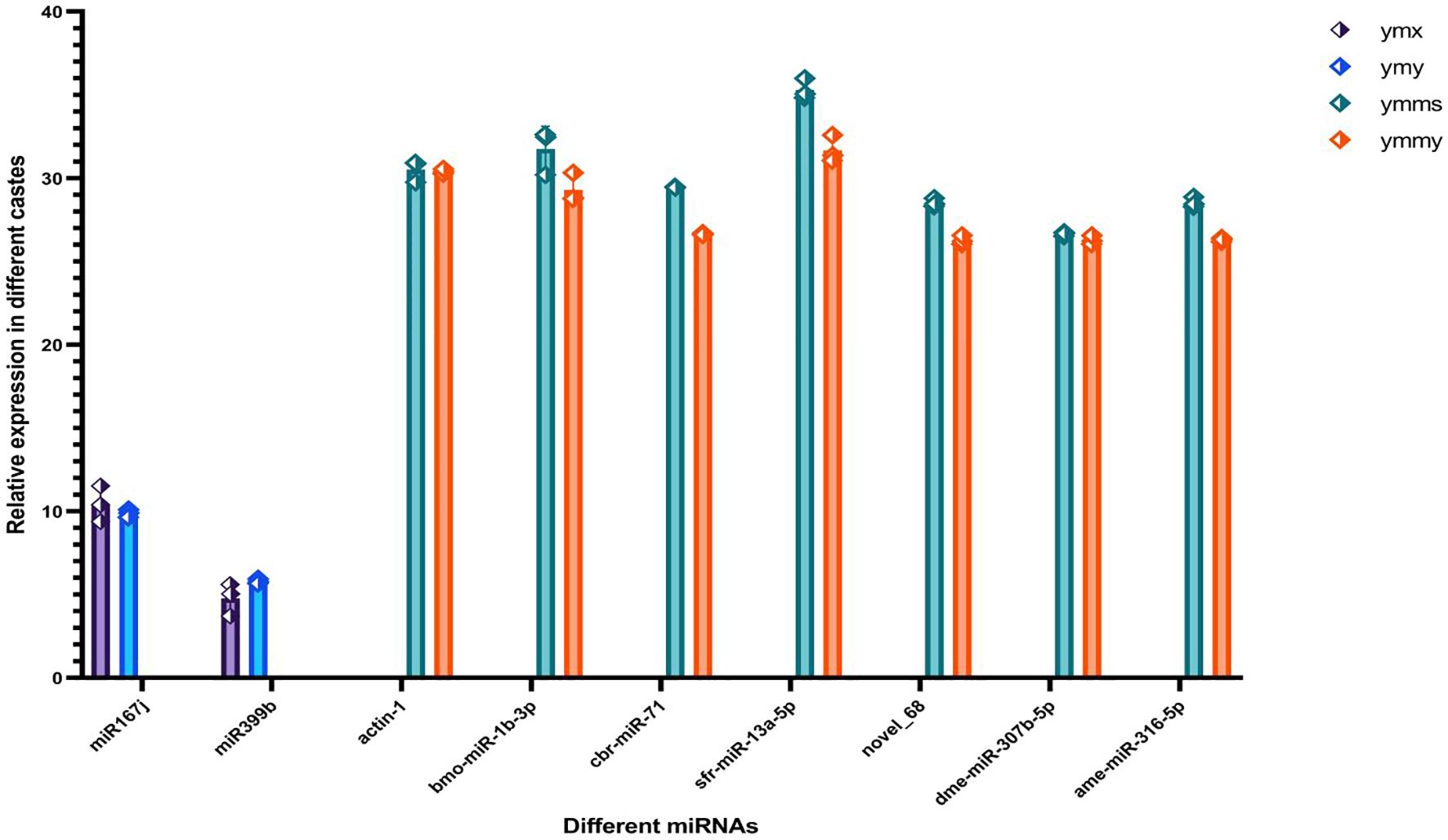
Figure 8. Verify the significant differential expression of miRNAs in the interaction between corn and corn borer. The sample consists of three biological replicates per sample. This figure shows the relative expression levels of two differentially expressed maize miRNA genes and six different families of insect miRNAs. Plants use miR397a as an internal reference gene, while insects use actin-1 as an internal reference gene. The relative expression levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method.
4 Discussion
Insects can easily become vectors that carry various pathogens such as fungi, bacteria, and viruses when chewing and piercing their food (Kortbeek et al., 2018). Plants, while attracting insect pollinators and beneficial insects, trigger molecular and hormonal signaling pathways to prevent destructive damage from insect herbivores and pathogens, leading to direct or indirect defense at transcriptional and metabolic levels (Zhu-Salzman et al., 2005; Lucas-Barbosa et al., 2016; Aljbory and Chen, 2018; Li et al., 2018). miRNAs play roles in defending plants against insect invasion and regulating plant genes during invasion, and provide an epigenetic tool for plant immunity in response to biotic stresses (Aljbory and Chen, 2018; Sarma Bordoloi and Agarwala, 2021).
We explored the regulatory role of miRNAs in interactions between maize and Asian corn borer. Four small RNA libraries were constructed in four sample groups: those expressed in leaves eaten by Asian corn borer, uneaten fresh maize leaves, Asian corn borer larvae that had eaten maize leaves, and Asian corn borer larvae that had only fed on artificial feed. Using bioinformatic techniques, 810 known miRNAs and 132 new miRNAs were identified.
In the comparison of fresh maize leaves and those that had been fed on by Asian corn borer, expression of zma miR167j-3p was downregulated and zma miR399b-3p was upregulated. Similar results have been reported previously, with upregulation of miR160, miR167, and miR393 after aphids fed on chrysanthemums and melons; target gene prediction revealed that these were potential targets for auxin response factors (ARFs) and transport inhibitor response 1 (TIR1) (Sattar et al., 2012; Xia et al., 2015). The abundance of miR167 increased in tobacco consumed by Manduca sexta, indicating a decrease in transcriptional abundance of ARF6 and ARF8, which inhibited auxin signaling (Bozorov et al., 2012).
The defense response of plants against pest attacks can be induced by mechanical injury and/or oral secretion. It is inferred that miR160, miR167, and miR396 are induced by mechanical injury stress rather than stimulation of oral secretion in insect herbivores (Khraiwesh et al., 2012; Sarma Bordoloi and Agarwala, 2021). We report expression of zma miR167j-3p (in the miR167 family) to be downregulated in leaves fed on by Asian corn borer. We speculate that after being fed by these larvae, maize leaves may experience a decrease in abundance of endogenous zma miR167j-3p because of mechanical injury stress, leading to an increase in ARF6 and ARF8 transcripts, enhancing auxin signaling to enhance plant defense and resist insect damage.
MiR399 targets the gene encoding ubiquitin binding enzyme (UBC24), partially controlling phosphate homeostasis, which is a limiting nutrient for plant growth necessary to synthesize nucleic acids and membrane lipids (Jones-Rhoades and Bartel, 2004; Sunkar et al., 2006). Similarly, in a study on plant responses to hypoxia and oxidative stress, Zm-miR399 was induced in early immersed seedlings (Zhang et al., 2008). In a study of symbiotic relationships between maize and arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, certain members of the miR399 and miR397 families were involved in controlling fatty acid metabolism and promoting lipid transfer from plants to the fungi; it was inferred that the miR399 family should conservatively regulate AM symbiosis in different plant lineages (Xu et al., 2018). We report the expression of zma miR399b-3p (in the miR399 family) to be upregulated in leaves fed on by the Asian corn borer, indicating that this family was induced under biotic stress. It can be inferred that the miR399 family is activated in plant defense responses under biotic stress, regulating plant growth.
In the comparison of Asian corn borer larvae that had fed on maize leaves and those that had only been given an artificial feed, 32 differentially expressed genes were screened, of which 19 genes were upregulated. Taking miR-71, miR307, and miR-316 as examples, Liang et al. (2013) used high-throughput sequencing on different developmental stages (egg, larval instar stages 1–4, pupae, and adult) of Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella. Because miR-71 (miR-71 family) was highly expressed in both egg and pupal stages, it was speculated that miR-71 had a specific function in regulating egg hatching and larval metamorphosis development in these moths. The miR307 family exhibited high levels of expression in both pupae and adults, possibly related to pupal metamorphosis and development. Mir-1a and mir-307 exhibit high levels of identity with other insects in the mature and complementary regions, respectively (Liang et al., 2013). In locusts, miR-71 and miR-263 respectively regulate chitin synthase 1 and chitin synthase 10, jointly controlling chitin metabolism and molting. Through reverse validation using injection manipulation of agomirs or antagonists, it was found that expression of miR-71 and miR-263 caused molting defects (Yang et al., 2016). The miR-2 cluster (miR-2, miR-13a, miR-13b, and miR-71) synergistically targets Notch and, together with let-7 and miR-278, regulates kr-h1 to control oogenesis. Reverse validation through injection manipulation revealed a significant reduction in vitellogenin transcripts and inhibition of oocyte maturation, ultimately blocking ovarian development (Song et al., 2018; Song et al., 2019).
From this, it can be inferred that feeding stimulates the resistance mechanism of maize, while Asian corn borer resists this by regulating its metabolic (e.g., through accelerating metamorphosis and development, and improving its detoxification ability).
5 Conclusion
Changing the feed formula or corn variety may also lead to different experimental outcomes. For example, feeding rice engineered to express miR-14 (targeting Spook and EcR) to larvae of the rice stem borer resulted in high mortality and developmental defects (He et al., 2019). Feeding genetically modified CSU-Novel-260 rice to the rice stem borer resulted in significant lethality and growth retardation, and the efficacy of CSU-Novel-260 rice in controlling the stem borer has been confirmed in field trials (Wamiq and Khan, 2018; Zheng et al., 2021).
We report that after being eaten by Asian corn borer larvae, biotic stress on maize leaves induces expression of endogenous miRNAs, and activates and regulates plant defense responses, regulating plant growth and development through a series of targeted genes to resist insect infestations. However, consuming different foods can promote or reduce the expression of conserved miRNAs in Asian corn borers, regulate the development, reproduction, metamorphosis, immunity, and insecticidal resistance of individual insects, and ultimately alter gene expression in populations eating a certain diet. We detected plant miRNAs in insects and speculate that plant−derived miRNAs are capable of being transported under harsh biotic and abiotic conditions. In doing so, we demonstrate that microRNAs can play roles in plant-insect interactions and provide a foundation for developing new maize varieties with resistance to corn borer through genetic engineering.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
R-XZ: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. XZ: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. NL: Software, Writing – review & editing. R-HL: Validation, Writing – review & editing. J-JY: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. CX: Resources, Writing – review & editing. XQ: Resources, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Writing – review & editing. Y-SW: Writing – review & editing. Q-KL: Writing – original draft. YW: Writing – original draft. Y-PC: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Major national R&D projects Development and Application Support System Construction of Molecular Feature Security Detection Technology 2022ZD04020. We thank the Institute of Germplasm Resources and Biotechnology, Tianjin Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Tianjin Agricultural University for research funding.
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the time, suggestions, and feedback provided by reviewers of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aljbory Z. and Chen M. S. (2018). Indirect plant defense against insect herbivores: A review. Insect Sci. 25. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12436
Belles X. (2016). MicroRNAs and the evolution of insect metamorphosis. Annu. Rev. Entomology 62, 111–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-031616-034925
Bozorov T., Baldwin I., and S. -G. (2012). Identification and profiling of miRNAs during herbivory reveals jasmonate-dependent and -independent patterns of accumulation in Nicotiana attenuata. BMC Plant Biol. 12, 209. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-209
Carrière Y. and Crowder D. (2010). Evolutionary ecology of insect adaptation to Bt crops. Evolutionary Appl. 3, 561–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-4571.2010.00129.x
He K., Xiao H. M., Sun Y., Ding S. M., Situ G. M., and Li F. (2019). Transgenic microRNA-14 rice shows high resistance to rice stem borer. Plant Biotechnol. J. 17, 461–471. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12990
Jeyaraj A., Liu S., Zhang X., Zhang R., Shangguan M., and Wei C. (2017). Genome-wide identification of microRNAs responsive to Ectropis oblique feeding in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.). Sci. Rep. 7, 1–16. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13692-7
Jia L., Zhang D., Xiang Z., and He N. (2015). Nonfunctional ingestion of plant miRNAs in silkworm revealed by digital droplet PCR and transcriptome analysis. Sci. Rep. 5, 12290. doi: 10.1038/srep12290
Jiang T., Su Q., and An L. J. (2015). Screening and validation of reference genes of qPCR in maize under multiple stresses. Plant Physiol. J. 51, 1457–1466. doi: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2015.0140
Jones-Rhoades M. and Bartel D. (2004). Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol. Cell 14, 787–799. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.05.027
Khraiwesh B., Zhu J., and Zhu J. (2012). Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress response of plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gene Regul. Mech. 1819, 137–148. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.05.001
Kortbeek R., van der Gragt M., and Bleeker P. (2018). Endogenous plant metabolites against insects. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 154, 1–24. doi: 10.1007/s10658-018-1540-6
Li P., Peng J., Hu J., Xu Z., Xie W., and Yuan L. (2010). Localized expression pattern of miR-184 in Drosophila. Mol. Biol. Rep. 38, 355–358. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0115-1
Li C., Wong A., Wang S., Jia Q., Chuang W., Bendena W., et al. (2018). miRNA-mediated interactions in and between plants and insects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3239. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103239
Li M. and Yu B. (2021). Recent advances in the regulation of plant miRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 18. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1899491
Liang P., Feng B., Zhou X., and Gao X. (2013). Identification and developmental profiling of microRNAs in diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.). PloS One 8, e78787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078787
Liu N., Zhang T. S., Li Z. Z., Duan L. J., Li S. Q., Dong H., et al. (2017). Selection of the reference genes in Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) under diapause and different insect states. J. Environ. Entomology 39, 611–617. doi: 10.39691/j.issn.1674-0858.2017.03.16
Love M. I., Huber W., and Anders S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15, 550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Lucas-Barbosa D., Sun P., Hakman A., van Beek T., van Loon J., and Dicke M. (2016). Visual and odour cues: Plant responses to pollination and herbivory affect the behaviour of flower visitors. Funct. Ecol. 30, 431–441. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12509
Reinhart B. J., Weinstein E. G., Rhoades M. W., Bartel B., and Bartel D. P. (2002). MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev. 16, 1616–1626. doi: 10.1101/gad.993502
Sarma Bordoloi K. and Agarwala N. (2021). MicroRNAs in plant insect interaction and insect pest control. Plant Gene 26, 100271. doi: 10.1016/j.plgene.2021.100271
Sattar S., Song Y., Anstead J., Sunkar R., and Thompson G. (2012). Cucumis melo microRNA expression profile during aphid herbivory in a resistant and susceptible interaction. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 25, 839–848. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-09-11-0252
Song J. S., Li W. W., Zhao H. H., Gao L. L., Fan Y. N., Zhou &, et al. (2018). The microRNAs let-7 and miR-278 regulate insect metamorphosis and oogenesis by targeting the juvenile hormone early-response gene Kru¨ppel-homolog 1. Dev. 145, dev170670. doi: 10.1242/dev.170670
Song J. S., Li W. W., Zhao H. H., and Zhou S. T. (2019). Clustered miR-2, miR-13a, miR-13b and miR-71 coordinately target Notch gene to regulate oogenesis of the migratory locust Locusta migratoria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 106, 39–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2018.11.004
Sunkar R., Kapoor A., and Zhu J.-K. (2006). Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell 18, 2051–2065. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.041673
Wamiq G. and Khan J. A. (2018). Overexpression of ghr-miR166b generates resistance against Bemisia tabaci infestation in Gossypium hirsutum plants. Planta 247, 1175–1189. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2951-1
Xia X., Shao Y., Jiang J., Du X., Sheng L., Fang W., et al. (2015). MicroRNA expression profile during aphid feeding in chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium). PloS One 10, e0143720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.00143720
Xu Y., Zhu S., Liu F., Wang W., Wang X., Han G., et al. (2018). Identification of arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi responsive microRNAs and their regulatory network in maize. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3201. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103201
Yang M., Wang Y., Jiang F., Song T., Wang H., Liu Q., et al. (2016). miR-71 and miR-263 jointly regulate target genes chitin synthase and chitinase to control locust molting. PloS Genet. 12, e1006257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006257
Yu T., Li X., Coates B., Zhang Q., Siegfried B., and Zhou X. (2018). microRNA profiling between Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab-susceptible and -resistant European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner): miRNA survey in Ostrinia nubilalis. Insect Mol. Biol. 27, 279–294. doi: 10.1111/imb.12376
Zhang Q., Dou W., Taning C., Smagghe G., and Wang J.-J. (2021). Regulatory roles of microRNAs in insect pests: Prospective targets for insect pest control. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 70, 158–166. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2021.05.002
Zhang Z., Wei L., Zou X., Tao Y., Liu Z., and Zheng Y. (2008). Submergence-responsive microRNAs are potentially involved in the regulation of morphological and metabolic adaptations in maize root cells. Ann. Bot. 102, 509–519. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn129
Zhang Y., Wiggins B. E., Lawrence C., Petrick J., Ivashuta S., and Heck G. (2012). Analysis of plant-derived miRNAs in animal small RNA datasets. BMC Genomics 13, 381. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-381
Zheng X. X., Weng Z. J., Li H., Kong Z. C., Zhou Z. H., Li F., et al. (2021). Transgenic rice overexpressing insect endogenous microRNA csu-novel-260 is resistant to striped stem borer under field conditions. Plant Biotechnol. J. 19, 421–423. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13504
Zhou L., Jiahao C., Li Z., li X., Hu X., Huang Y., et al. (2010). Integrated profiling of microRNAs and mRNAs: MicroRNAs located on Xq27.3 associate with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PloS One 5, e15224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015224
Zhu B., Sun X., Nie X., Pei L., and Gao X. (2019). MicroRNA-998-3p contributes to Cry1Ac-resistance by targeting ABCC2 in lepidopteran insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 117, 103283. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2019.103283
Keywords: Asian corn borer, maize, microRNAs, high-throughput sequencing, interaction
Citation: Zhang R-X, Zhao X, Liu N, Li R-H, Yao J-J, Xu C, Qi X, Zhang C, Wang Y-S, Lan Q-K, Wang Y, Cheng Y-P and Wang C (2025) Characteristics analysis of microRNAs in the interaction between maize and Ostrinia furnacalis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 13:1623560. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2025.1623560
Received: 06 May 2025; Accepted: 04 August 2025;
Published: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Ruiqi Li, University of Colorado Boulder, United StatesReviewed by:
Keon Mook Seong, Chungnam National University, Republic of KoreaHonglong Chu, Qujing Normal University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhao, Liu, Li, Yao, Xu, Qi, Zhang, Wang, Lan, Wang, Cheng and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: You-Pu Cheng, Y2hlbmd5b3VwdUAxNjMuY29t; Cheng Wang, d2FuZ2NoZW5nODgwNjI1QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Rui-Xue Zhang1,2†
Rui-Xue Zhang1,2† Xin Qi
Xin Qi You-Pu Cheng
You-Pu Cheng