- 1The Department of Mechatronics Engineering, The University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan
- 2Graduate School, Mongolian University of Science and Technology, Ulan Bator, Mongolia
- 3The Department of Electrical Engineering, Al Hussein Technical University, Amman, Jordan
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has led to its increasing integration into academic environments, raising critical questions about its educational implications. This study investigates the use of AI tools among university students in Jordan, focusing on platforms such as ChatGPT, Google Bard, Microsoft Bing, and Meta AI. A convergent-parallel mixed-methods design was employed, with quantitative (closed-ended) and qualitative (open-ended) data collected concurrently through an online survey distributed over two months. A total of 337 valid responses were obtained from students across 27 universities. The survey explored demographic characteristics, chatbot awareness and use, perceived benefits and challenges, ethical concerns, and future intentions. Results indicate that ChatGPT is the most recognized (94.3%) and widely used (90.4%) tool, while Meta AI is the least utilized (7.8%). Approximately 89% of students reported using AI tools for academic tasks, and 86.6% perceived them as educationally beneficial. However, only 39.7% believed these tools significantly improved their understanding, while 57.6% reported a positive impact on academic performance. These findings reveal a growing trend of AI integration into student study practices in Jordan, highlighting both its practical advantages and the need for further inquiry into its pedagogical value and ethical use.
1 Introduction
1.1 Motivation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of modern society, influencing various industries and transforming traditional practices. In recent years, AI technologies have made significant strides in the field of education, reshaping the way institutions approach teaching, learning, and research. Scholars studied how AI technologies improve teaching and research based on reinforcing and balancing feedback loops (Katsamakas et al., 2024; Tomaskinova et al., 2024). The findings underscore the significant role of AI in higher education institutions HEIs. AI-powered tools such as intelligent tutoring systems, learning analytics, and AI-driven assessments have provided new opportunities to personalize learning experiences, automate administrative tasks, and improve educational outcomes (Popenici and Kerr, 2017; Crompton and Burke, 2023; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019). These innovations have the potential to streamline operations and improve the quality of education, making AI a critical component of modern educational practices.
One of the most notable developments in the application of AI to education is the emergence of conversational AI tools like ChatGPT. Such tools can significantly alter the way students interact with educational content and engage in academic activities. ChatGPT, in particular, has been praised for its versatility in helping students with tasks such as writing essays, providing instant feedback, and supporting research efforts (Ariyaratne et al., 2023; Pallivathukal et al., 2024; Salvagno et al., 2023). However, while the advantages of these tools are evident, their widespread adoption has sparked a range of ethical concerns, especially regarding data privacy, academic integrity, and the role of AI in promoting or diminishing critical thinking skills (Holmes et al., 2022; Mahrishi et al., 2024; Irfan et al., 2023a).
In the context of higher education, the introduction of AI offers both opportunities and challenges. AI enables institutions to track student progress in real-time and personalize learning on a large scale. For example, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and classification models–such as support vector machines (SVM), Random Forest, and KNN–have been applied to predict student success (Shoaib et al., 2024). In parallel, artificial intelligence-enabled intelligent assistants (AIIAs) support students through adaptive instructional pathways that respond to individual needs (Sajja et al., 2024). On the other hand, concerns about algorithmic bias, unequal access to technology, and potential misuse of AI by students pose significant risks to academic integrity and equity in education (Tsai et al., 2020; El Alfy et al., 2019; Crawford et al., 2023). These developments also prompt deeper inquiry into how AI shapes students' critical engagement with academic content and learning behaviors (Mapletoft et al., 2024; Mujtaba et al., 2024).
While there is a growing body of global research on the role of AI in education, gaps remain in understanding how these technologies are being adopted in specific regional contexts. In countries like Jordan, where educational institutions face challenges related to infrastructure, digital literacy, and equitable access to technology, the integration of AI tools brings both new opportunities and obstacles (Al-Qerem et al., 2023; Mosleh et al., 2023). Addressing these issues is essential for ensuring that the benefits of AI are equitably distributed and that potential drawbacks are mitigated.
1.2 Study aim
Building on the above motivation, the present work investigates the uptake and educational impact of AI-powered chatbots–principally ChatGPT–in Jordanian universities. Employing a convergent-parallel mixed-methods design (Creswell and Plano Clark, 2018), quantitative (closed-ended) and qualitative (open-ended) data were gathered simultaneously via one survey instrument and integrated during interpretation. The study is guided by three research questions:
1. RQ1: To what extent, and for which academic tasks, do Jordanian university students use generative-AI chatbots?
2. RQ2: What benefits, challenges, and ethical concerns do students perceive when engaging with these tools?
3. RQ3: How do usage patterns and perceptions vary across demographic variables such as gender, academic level, and college type?
Clarifying these aims helps situate the subsequent methodology and ensures that the mixed-methods design is explicitly linked to concrete, answerable research questions.
2 Background
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has grown significantly, evolving from theoretical frameworks to practical applications across multiple fields. Since its inception, AI has permeated industries like healthcare, finance, software development, and, most recently, education, transforming traditional methodologies (Beganovic et al., 2023; Rahmaniar, 2024; Tabone and De Winter, 2023). In education, AI tools like ChatGPT, learning analytics, and automated assessments have been applied to transform instructional delivery and assessment models. For example, AI is used to provide instant feedback, adapt content in real time to individual learner progress, automate formative assessment, and generate personalized learning materials that cater to students' specific strengths and weaknesses (Yadav, 2025). AI also offers numerous opportunities to transform traditional teaching and learning methodologies. For instance, in translation pedagogy, AI technologies have been used to reduce assessment time and automate grading systems (Khasawneh and Shawaqfeh, 2024). Another example is the integration of AI in natural language processing (NLP) education, enhancing both instruction and learner engagement (Mishra, 2024).
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has grown significantly, evolving from theoretical frameworks to practical applications across multiple fields. Since its inception, AI has permeated industries like healthcare, finance, software development, and, most recently, education, transforming traditional methodologies (Beganovic et al., 2023; Rahmaniar, 2024; Tabone and De Winter, 2023). In education, AI tools like ChatGPT, learning analytics, and automated assessments have started to reshape teaching and learning practices (Yadav, 2025). AI also offers numerous opportunities to transform traditional teaching and learning methodologies. For instance, in translation pedagogy, AI technologies have been used to reduce assessment time and automate grading systems (Khasawneh and Shawaqfeh, 2024). Another example is the integration of AI in natural language processing (NLP) education, enhancing both instruction and learner engagement (Mishra, 2024).
2.1 AI in higher education
Recent research underscores the growing significance of chatbots in education, noting their scalability and potential to provide personalized support. Key findings indicate that chatbots play important roles in mentoring students, offering tailored feedback, and increasing student engagement through adaptive interactions. Current challenges identified include ensuring chatbot evaluations align with educational goals, effectively utilizing chatbots for mentoring roles, and enhancing their adaptability to individual learner needs (Wollny et al., 2021). AI is increasingly transforming higher education by enhancing instruction, administration, and research productivity. Studies indicate that its integration improves personalized and adaptive learning experiences, as well as overall educational outcomes (Ke Zhang, 2021; Jiahong Su, 2023). Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT have attracted significant attention, particularly in engineering education, with benefits noted for both students and instructors (Qadir, 2023; Eman A. Alasadi, 2023).
AI-powered systems such as intelligent tutoring platforms and adaptive learning environments provide dynamic, real-time feedback and personalized instruction by analyzing student performance data (Crompton and Burke, 2023; Kamalov et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023; Celik, 2023). These tools support mastery of complex topics, early identification of at-risk students, and tailored intervention strategies (Chaudhry et al., 2023; Mackney and Shields, 2019; Embarak and Hawarna, 2024; Sunandar et al., 2024).
In addition to instruction, AI is increasingly used in grading, administrative functions, and student support systems. Learning analytics enables data-driven decision-making by offering insights into student engagement and institutional performance (Ojha et al., 2023; El Alfy et al., 2019; Jones et al., 2020; Shaik et al., 2022; Schönberger, 2023).
Global trends reflect growing scholarly interest in AI's role in higher education. Most publications are concentrated in the United States and China, with a marked increase in output between 2021 and 2022 (Crompton and Burke, 2023). A survey of 311 educators found that using AI in classrooms positively influenced both their perceptions of ease of use and their attitudes toward AI-enhanced instruction (Youmei Wang, 2021).
Beyond teaching and learning, AI tools also support university administration and student care functions (Hannan and Liu, 2023). As AI continues to evolve, its integration into academic processes is expected to expand further, raising important questions around pedagogy, equity, and data ethics (Selwyn, 2022).
2.2 AI in scientific research and writing
In addition to transforming education, AI has significant applications in scientific research. AI tools, such as ChatGPT, assist researchers in drafting, editing, and summarizing academic articles, thus streamlining the scientific writing process (Castillo-Martínez et al., 2024). This automation can reduce the time and effort required to produce research content, potentially enhancing productivity. AI-generated content has been found useful for tasks such as literature reviews, data synthesis, and report generation (Uhlig et al., 2023). However, these benefits come with notable limitations. Concerns around academic integrity, including the risk of plagiarism and overreliance on AI, remain significant (Pallivathukal et al., 2024; Mosleh et al., 2023). Moreover, AI-generated texts may lack the depth, critical analysis, and domain-specific insight expected in scholarly work. As such, while AI can be a supportive tool, its outputs should be carefully reviewed and supplemented by human expertise to maintain academic standards.
In healthcare education, AI-driven tools are used to support decision-making processes, diagnostic simulations, and personalized learning experiences for students in medical and pharmacy disciplines (Al-Qerem et al., 2023; Ajlouni et al., 2023). While these tools show promise in enhancing educational outcomes, they also bring ethical dilemmas related to fairness, data security, and transparency (Dergaa et al., 2023; Crawford et al., 2023).
2.3 Ethical concerns and challenges in AI integration
AI's growing presence in education and research brings several ethical considerations, particularly related to data privacy, algorithmic bias, and academic integrity (Kooli, 2023). The rapid integration of AI technologies into academic environments demands robust frameworks that address these concerns and ensure that AI systems are used responsibly. For instance, the “privacy paradox” in learning analytics, where students are concerned about their data privacy yet benefit from AI systems that rely on personal data, poses an ethical dilemma.
Researchers argue that institutions must develop transparent policies and guidelines to manage the ethical use of AI tools in academia. This includes creating frameworks to ensure that AI-generated content does not hinder critical thinking and creativity (Arman, 2023; Elbanna and Armstrong, 2024). Moreover, the potential bias in AI algorithms and the risk of over-reliance on AI technologies require careful consideration by educators and policymakers (Irfan et al., 2023b; Zeb et al., 2024).
2.4 Challenges and future directions for AI in education
Despite the promising benefits of AI in education, several challenges remain. The technological infrastructure required to support AI-based tools is often lacking in many institutions, particularly in underserved regions. This digital divide limits the potential of AI to deliver equitable learning outcomes across different educational environments (Mahrishi et al., 2024; Dare, 2024). Additionally, educators need to be trained in AI literacy to leverage the benefits of these tools fully (Mapletoft et al., 2024; Mujtaba et al., 2024).
Future research should focus on developing more inclusive AI tools that account for diverse student populations and creating ethical frameworks that guide the responsible use of AI in education and research. As AI continues to evolve, its role in enhancing collaboration, critical thinking, and interactive learning experiences will become increasingly important.
Educators and scholars are calling for a discussion about the future of AI in higher education (Schön, 2023; K.F. Chiu, 2024). The rapid change in the learning attitude of modern students, together with the implementation of AI in higher education, is prompting lecturers and professors to adapt their pedagogical approaches (Shrivastava et al., 2024). Modern students from Generation Z often apply AI tools in higher education and prefer a personalized approach to learning (Bennett and Abusalem, 2024).
2.5 Identifying gaps in the literature
While existing research has addressed AI applications in healthcare education in Jordan, (Al-Qerem et al., 2023; Mosleh et al., 2023) there remains a need to understand how AI tools–particularly generative chatbots–are used across other academic domains. A recent systematic review identified 69 studies on ChatGPT in education, including work in general higher education, engineering, social sciences, and health sciences. However, most of these studies originate from North America, Europe, or Asia, and none examine usage in Jordan or the Arab region more broadly (Ansari et al., 2024).
This study seeks to address that gap by providing one of the first empirical, survey-based investigations into the use of AI-powered chatbots by university students in Jordan. The Jordanian context introduces distinct variables–such as a strong emphasis on academic integrity, varying levels of digital infrastructure, and differing cultural attitudes toward AI-generated content–that may shape usage patterns in ways not captured by existing literature. For example, concerns about plagiarism and mistrust in chatbot-generated information may be more pronounced due to institutional codes of conduct and students' limited exposure to AI-integrated pedagogies.
Although our findings confirm global trends–such as ChatGPT being the most recognized tool and ethical concerns being widely shared–they also suggest that sociocultural and institutional contexts may mediate student experiences. This research thus contributes new insights by grounding AI adoption in a specific underrepresented context and demonstrating how global technological trends intersect with local academic ecosystems.
3 Methodology
This section outlines the research methodology used to investigate the integration and impact of AI-powered chatbots on university students in Jordan. The study uses a mixed methods approach, combining quantitative and qualitative data collection to gain a comprehensive understanding of students' perceptions, experiences, and attitudes toward chatbot technologies, such as ChatGPT, Microsoft Bing AI, Google Bard, and Meta AI, in their academic practices. Using a cross-sectional survey design, this research aims to capture diverse insights from students from various academic disciplines at Jordanian universities. The methodology ensures robust data collection and analysis, allowing the identification of trends, challenges, and opportunities associated with AI integration in education.
3.1 Survey design
This study used a cross-sectional survey to assess the impact of AI-powered chatbots on university students in Jordan. The survey, titled “Survey on the Impact of Using Chatbots in the Educational Process in Jordan”, was designed to gather data on students' experiences, perceptions, and attitudes toward chatbot technologies, such as ChatGPT, Microsoft Bing AI, Google Bard, and Meta AI, in their academic practices. The survey comprised both closed and open-ended questions, divided into sections covering demographic information, knowledge and usage of chatbots, perceived benefits, ethical considerations, and future intentions to use AI tools in both academic and non-academic contexts.
This study employed a convergent-parallel mixed-methods design, in which quantitative (closed-ended) and qualitative (open-ended) data were collected concurrently using the same survey instrument. Each strand was analyzed independently and later integrated during interpretation to enable triangulation of findings (Creswell and Plano Clark, 2018).
3.2 Target population and sampling
The target population consisted of undergraduate and graduate students enrolled in all faculties (scientific, humanities, and health) at Jordanian universities, including public and private institutions. A random sampling method was used to ensure a broad representation of students from various academic disciplines. The survey was distributed electronically using social media platforms (e.g., university student groups) and group emails sent to student bodies. This approach facilitated access to a diverse sample of students representing a wide range of educational backgrounds and experiences with AI technologies.
3.3 Survey instrument
The survey instrument was structured to capture both quantitative and qualitative data and included the following sections:
• Demographic information: participants provided details on their gender, university affiliation, degree level, faculty (scientific, humanities, or health), and year of study.
• Knowledge and usage of chatbots: this section assessed participants' awareness of various AI-powered chatbots, including ChatGPT, and their extent of use for academic purposes. Specific tasks such as finishing homework, coding, writing reports and email drafting were also addressed.
• Perceptions and benefits: participants rated the perceived benefits of using chatbots in their education, including saving time, improving comprehension, and accessing diverse resources. They also rated how these tools affected student-teacher interaction, academic performance, and overall learning.
• Ethical and practical considerations: questions focused on privacy concerns, trust in AI-generated content, and the extent to which students cross-checked the information produced by chatbots. Participants were also asked to rate their level of reliance on these tools for academic tasks.
• Future use and challenges: this section captured participants' intentions regarding the continued use of chatbots in both academic and non-academic settings, as well as an open-ended question about the challenges they faced while using these tools.
3.4 Data collection
Data collection was carried out over a two-month period, during which the survey was distributed via Google Forms to students at Jordanian universities. Participants were recruited through social media platforms (e.g., university Facebook and WhatsApp groups) and group email distributions. The random sampling approach ensured diverse participation, with students from different faculties and academic levels represented in the dataset. To encourage a higher response rate, reminders were sent periodically during the data collection window.
3.5 Data analysis
The data collected were analyzed using both quantitative and qualitative methods to fully understand the students' perceptions and experiences.
3.5.1 Quantitative analysis
Quantitative data from closed-ended questions were analyzed using descriptive statistics, including frequencies, percentages, and means. Likert scale responses, ranging from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”, were used to assess student attitudes and perceptions toward chatbot technologies. These data were further analyzed by demographic variables such as faculty type (scientific, humanities, or health), degree level (undergraduate or graduate) and year of study to examine variations in chatbot usage and perceptions between student groups.
3.5.2 Qualitative analysis
The open-ended responses were subjected to thematic analysis to identify common challenges, benefits, and concerns raised by participants regarding the use of chatbots. The responses were coded into themes such as perceived benefits, ethical concerns (e.g., privacy), and challenges faced while using AI technologies. This qualitative analysis provided deeper insights into students' nuanced experiences and the barriers they encountered when integrating chatbot tools into their academic routines.
3.6 Ethical considerations
The survey followed strict ethical guidelines to protect the rights and privacy of the participants. Informed consent was obtained from all participants, who were informed of the purpose of the study, how their data would be used, and the voluntary nature of their participation. No personally identifiable information was collected, and all responses were anonymized to ensure confidentiality. Data privacy measures were adhered to, ensuring that participant data was securely stored and accessed only by the research team for analysis purposes.
3.7 Limitations
Although the survey used random sampling and reached a broad audience through social media and university channels, reliance on online distribution may have excluded students who are less active on digital platforms or lack consistent internet access. Furthermore, self-reported data may be subject to biases, such as social desirability bias, where participants may provide responses that they perceive as favorable.
4 Results
The survey revealed a nearly even gender distribution among participants, with 49% identifying as female and 51% as male. A substantial proportion of respondents, 25.1%, were affiliated with the University of Jordan, the country's oldest public institution, while 16.1% came from Al-Hussein Technical University, Jordan's newest private university. Overall, the participants represented 27 out of the 30 registered universities in the country.
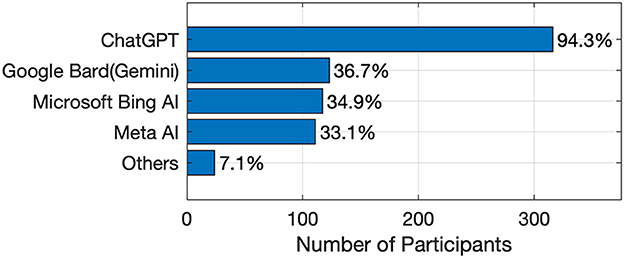
The overwhelming majority of participants, an impressive 94.3%, reported familiarity with ChatGPT, making it by far the most recognized AI tool in the survey. Google Bard (Gemini) followed with 36.7%, while 34.9% of respondents were aware of Microsoft's Bing AI chatbot. Meta AI was also known to 33.1% of participants. A handful of other AI tools, including Microsoft CoPilot, Quillbot, and Plusfinity AI, were recognized by a smaller percentage of the respondents, highlighting the dominance of a few key platforms in the AI landscape. A graph representing these results is shown in Figure 1. Based on these results, it is clear that ChatGPT can be considered the most widely used tool by students due to its ability to understand and generate human-like text, which is consistent with other findings in the literature (Beganovic et al., 2023; Rahmaniar, 2024).
The scientific faculties demonstrate strong recognition of multiple AI tools beyond just ChatGPT. In addition to the near-universal familiarity with ChatGPT (96.6%), a significant proportion of participants are aware of other AI tools such as Google Bard (40.2%), Meta AI (31.4%), and Microsoft Bing AI Chatbot (39.8%). This suggests that students in scientific disciplines are exposed to a wider range of AI technologies, likely due to the technical nature of their studies, which often integrate cutting-edge tools. In contrast, humanities and health faculties exhibit a narrower scope of familiarity with AI tools, with their recognition primarily centered around ChatGPT.
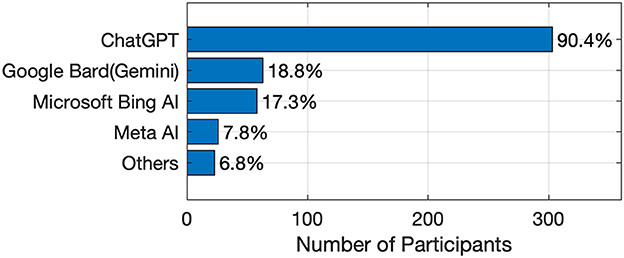
The usage of AI tools reveals that the majority of participants, 90.4%, used on ChatGPT to complete their tasks, making it the most dominant tool in academic settings. This strong preference highlights ChatGPT's versatility and effectiveness in generating human-like text to meet student needs. In contrast, 18.8% used Google Bard (Gemini), 17.3% utilized Microsoft's Bing AI chatbot, and 7.8% employed Meta AI. The limited usage of these alternatives suggests that students find ChatGPT more suitable for their tasks. Other AI tools were used by only a small fraction of participants, indicating that the AI landscape in education remains largely concentrated around a few key platforms, as shown in Figure 2.
A comparison of Figures 1, 2 reveals that although many participants are aware of other prominent AI tools, such as Microsoft Bing AI chatbot, Google Bard (Gemini), and Meta AI, they do not rely on them as heavily as they do on ChatGPT for completing tasks. Several factors may explain this preference: ChatGPT's earlier introduction, which has led to greater familiarity among students; its superior performance and capabilities (Al Mashagbeh et al., 2024); and its more user-friendly interface, which makes it more accessible compared to other tools (Tabone and De Winter, 2023).
When asked whether they had used any AI tools during their studies to solve homework, assignments, or other tasks, 89% of participants responded positively, while only 11% indicated they had not. This high level of usage reflects a major shift in how students approach their academic responsibilities, leveraging AI tools to enhance productivity and optimize learning outcomes. The widespread adoption of these tools signals a transformation in study habits as technology becomes increasingly embedded in the educational experience.
The increasing use of AI tools presents both opportunities and challenges for educators. On the one hand, these technologies can create more personalized, adaptive, and engaging learning experiences that cater to diverse student needs. By integrating AI, educators can make learning more dynamic and accessible. However, there are concerns that excessive reliance on AI could hinder students' ability to think critically and solve problems independently. If students rely on these tools to complete tasks without fully understanding underlying concepts, it may result in superficial learning. Thus, educators face the challenge of incorporating AI in a way that enhances learning while ensuring students continue to develop essential cognitive and problem-solving skills.
The results highlight notable trends in how students integrate AI tools into various tasks. With 73.9% of students using these tools for homework and assignments, it can be inferred that AI tools may support students in improving efficiency and understanding, based on their self-reported usage patterns. Studies such as Bin-Nashwan et al. (2023) have highlighted similar motivations driving the use of AI tools like ChatGPT, including time-saving and academic self-efficacy. The fact that 59.6% use AI for writing projects shows its growing role in complex tasks like essays and reports, suggesting a significant change in traditional academic processes.
The 45% of students utilizing AI for coding highlights its growing role in technical education, where real-time assistance can enhance skill-based learning, as supported by Rohm et al. (2021). However, the 31% of students using AI for online quizzes raises concerns about academic integrity, underscoring the need for careful monitoring of assessments. Additionally, 31.6% of students using AI for writing emails demonstrates the broader application of these tools beyond academic tasks, signaling their expanding influence in everyday communication. The remaining participants, accounting for less than 5%, used these tools for a variety of other tasks including paraphrasing content, translating text, simplifying complex concepts, providing explanations, and verifying solutions. This illustrates the versatility of AI tools, as students are leveraging them not only for traditional academic tasks but also for support in more specialized areas of their studies.
When students were asked about the most useful features of AI tools for educational purposes, responses varied. The majority, 86.6%, indicated that these tools help save time and effort when searching for information. This finding suggests that many students may prioritize efficiency and convenience, potentially focusing more on achieving high grades with minimal time investment rather than deeply engaging in the learning process itself. While AI tools offer significant benefits in streamlining academic tasks, this trend raises questions about whether students are fully exploring the educational value these technologies can offer.
Although AI tools provide access to a vast range of information, there is a risk that the information may be inaccurate or misleading. Additionally, the convenience of these tools may discourage students from using more traditional learning methods, such as studying textbooks or conducting independent research. These methods are essential for developing a stronger knowledge base and fostering a deeper understanding of core concepts. As students increasingly rely on AI, there is a concern that the depth of their learning may be compromised in favor of speed and convenience.
Students were asked, “To what extent do you believe that using AI tools has improved your understanding?” The response scale ranged from 1, representing very low improvement, to 5, representing very high improvement. The results, presented in Figure 3, show that only 19.1% of students felt these AI tools significantly enhanced their understanding of concepts. This suggests that while AI tools may offer convenience and efficiency, their impact on deep learning and conceptual comprehension may be more limited than anticipated.
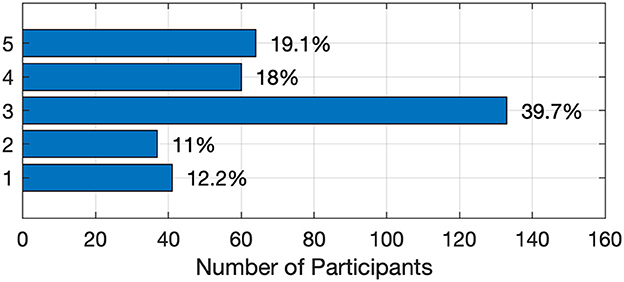
Figure 3. Students' perceptions of the extent to which AI tools have improved their understanding of academic concepts.
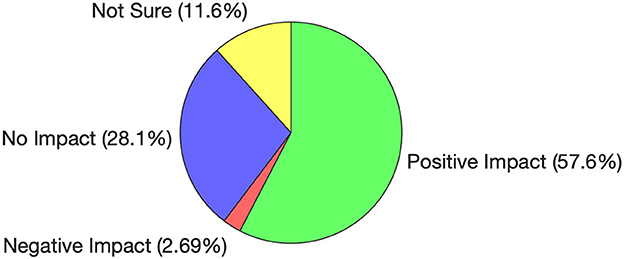
The encouraging news is that when participants were asked whether the use of AI tools had impacted their academic performance, 57.6% responded positively, as shown in Figure 4. Only 2.7% believed these tools had a negative effect, while 28.1% indicated that AI had no impact on their performance. The remaining participants were unsure. While these results are promising, further investigation is needed to determine whether students perceive this positive impact due to an actual improvement in understanding or because AI tools enable them to complete homework and assignments more efficiently, with minimal time investment and potentially without deep comprehension.
Another positive sign emerged when students were asked whether they verified the answers obtained from AI tools. A majority, 78.2%, reported that they checked the accuracy of the answers, a practice essential for meaningful learning. However, 21.8% accepted the AI-provided answers without verification, which raises concerns about potential over-reliance on these tools. This minority may risk diminishing their analytical skills and deep understanding. To mitigate this, educators should encourage cross-verification of AI-generated information and promote a more reflective use of these tools, ensuring that they enhance learning rather than hinder students' educational development.
When asked whether they plan to continue using AI tools in their future education, 86.3% of participants indicated they would, while 13.7% stated they would not. This strong inclination toward continued use suggests that students derive significant benefits from these tools, whether through enhanced productivity, comprehension, or academic performance. Understanding the reasons behind the minority's reluctance to use these tools could provide valuable insights for developers, helping to address any limitations or challenges that may be inhibiting wider adoption. Additionally, as AI becomes more integrated into education, laws and regulations must evolve accordingly, ensuring that these tools are used ethically and effectively in shaping the future of learning.
Figure 5 illustrates the distribution of students' responses regarding their reliance on AI tools, with “1” representing low reliance and “5” representing high reliance. As shown, 42.1% of students reported low reliance on these tools, while 21.2% fell into the high-reliance category. The remaining 36.7% selected “3,” indicating moderate reliance. These results suggest that while a considerable number of students find AI tools somewhat helpful, they do not view them as essential for their academic success.
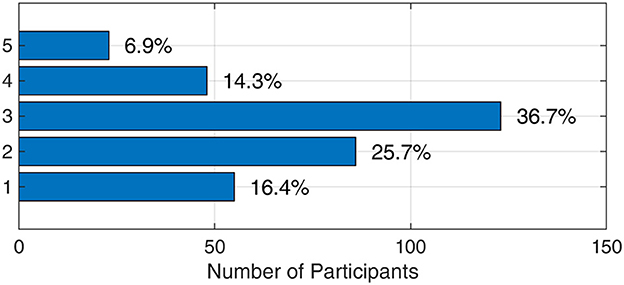
Figure 5. Distribution of students' reliance on AI tools, indicating varying levels of dependence from low to high.
Figure 6 shows the distribution of students' confidence in the accuracy of answers provided by AI tools, where “1” represents low confidence and “5” represents high confidence. The survey results reveal a range of opinions: 26% of students reported low confidence, indicating caution or skepticism, while 29.2% expressed high confidence, suggesting trust in AI-generated results without further validation. The majority, 44.8%, selected “3”, reflecting a moderate level of confidence. These findings suggest that although many students find AI tools useful, they often feel the need to verify the information provided. The distribution highlights both the strengths and perceived limitations of AI tools in delivering accurate information.
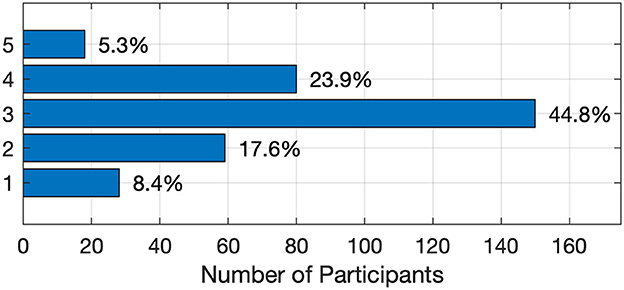
Figure 6. Distribution of students' confidence in the accuracy of answers provided by AI tools, ranging from low to high confidence.
The students were also asked whether they believed that the answers obtained from the AI tools could be better than their own. While 23.3% of students felt that the AI-generated answers could surpass their own, only 16.7% disagreed, expressing confidence in their abilities. Interestingly, 60% of the students were uncertain, indicating uncertainty about the reliability or effectiveness of these tools. This hesitation may arise from a lack of familiarity or trust in AI tools, which aligns with the confidence levels shown in Figure 6.
The majority of students, 77.6%, believe that the use of AI tools positively contributes to the educational process, indicating strong confidence in the role of digital technologies in enhancing learning. This suggests that most students recognize the benefits these tools offer, such as increased efficiency and improved access to information. However, 11.6% of the students expressed skepticism, potentially due to concerns about the risks of overreliance on technology, which could undermine critical thinking and independent problem-solving. The remaining students, who were uncertain, may not have enough experience with these tools to evaluate their impact fully. This uncertainty points to the need for further research to understand whether these tools foster deeper learning or provide surface-level convenience in academic tasks.
Figure 7 presents students' responses regarding their level of concern about security and privacy when using AI tools, with 1 representing low concern and 5 representing very high concern. As indicated, most students exhibit relatively low levels of concern about the security and privacy risks associated with AI tools, with only 19.4% selecting 4 or 5, signaling significant concern. This suggests that most students do not prioritize these risks or may not fully grasp the potential implications of security and privacy when using such technologies. The low level of concern could be attributed to the convenience and perceived usefulness of AI tools, overshadowing their potential risks. Alternatively, it may reflect a lack of awareness about how personal data is collected, stored, and used by AI platforms. This points to the need for greater education on digital security and privacy, ensuring that students are more informed and cautious in their use of these tools. Understanding these risks is essential as AI becomes more integrated into academic and personal activities.
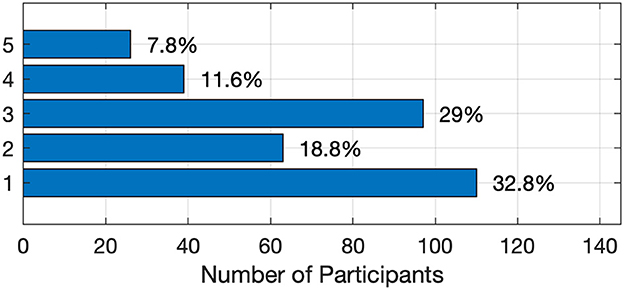
Figure 7. Student responses about their level of concern regarding security and privacy issues when using AI tools.
The results show that 59.1% of the students use AI tools to assist with non-academic tasks, highlighting their broader role in personal productivity beyond education. Meanwhile, 40.9% limit their use of these tools to academic purposes, suggesting varying levels of adoption for everyday activities. This indicates that AI tools are becoming integral to both academic and personal domains for a majority of students.
4.1 Qualitative findings: thematic analysis of challenges
To analyze the open-ended responses regarding challenges faced when using AI tools, we applied Braun and Clarke's (2006) thematic analysis method. Out of 337 participants, 93 provided valid qualitative input. Five major themes emerged:
• Theme 1: accuracy and relevance issues–many students reported receiving vague, inaccurate, or unhelpful responses from AI tools. Several emphasized that the information provided was either off-topic or confusing.
• Theme 2: difficulty in framing questions–respondents noted that how a question is phrased significantly affects the quality of the AI's answer. Some expressed frustration with having to reword their questions multiple times.
• Theme 3: ethical concerns and academic misconduct–a number of students raised concerns about plagiarism and the potential for duplicate responses among peers using the same tools.
• Theme 4: lack of source credibility—several students indicated that AI-generated content often lacked verifiable sources or citations, making it difficult to trust or reference in academic work.
• Theme 5: technical and language limitations—some participants experienced technical issues, such as delayed responses, language mismatches, or the inability to upload images or complex input formats.
These themes provide deeper insight into the practical, ethical, and pedagogical limitations students encounter when using AI tools for academic purposes. Addressing these challenges through institutional policy and digital literacy training may help improve outcomes.
5 Discussion
The results indicate a high rate of adoption and recognition of AI tools–especially ChatGPT–among Jordanian university students. This finding aligns with global patterns observed in prior research (Beganovic et al., 2023; Rahmaniar, 2024), which document ChatGPT's wide popularity due to its accessibility, effectiveness, and human-like response generation. The significant reliance on ChatGPT over other platforms may reflect not only its usability but also a lack of awareness or institutional promotion of alternative tools.
The findings also suggest that students perceive AI tools as beneficial for enhancing academic performance and managing their workload efficiently. This corroborates prior literature (Ke Zhang, 2021; Celik, 2023), which emphasizes the productivity gains and engagement benefits of integrating AI into higher education.
However, the limited proportion of students (only 19.1%) who reported that AI tools significantly enhanced their understanding points to a critical limitation. This aligns with studies that question the depth of learning supported by AI tools (Tabone and De Winter, 2023), indicating that while such technologies can facilitate task completion, they may not necessarily promote conceptual mastery.
Moreover, qualitative findings revealed concerns about the accuracy, ethical implications, and technical constraints of AI tools. These are consistent with challenges noted in previous studies (Jiahong Su, 2023; Hannan and Liu, 2023), especially in relation to academic misconduct, the lack of source credibility, and difficulties in generating contextually accurate outputs. The issue of framing questions effectively was also prominent–underscoring the importance of digital literacy and prompting skills, which should be integrated into university curricula.
Interestingly, while most students reported verifying AI-generated content (78.2%), a significant minority did not, highlighting the risk of over-reliance and the potential erosion of critical thinking skills. This concern has been echoed in literature addressing the unintended consequences of unchecked AI use in academic environments (El Alfy et al., 2019).
These findings illustrate the dual-edged nature of AI in education: its potential to democratize access and enhance efficiency, and its risk of diminishing deep learning and academic integrity. As AI tools become increasingly embedded in student practices, institutions should develop structured guidelines for ethical use and offer support mechanisms that encourage thoughtful, critical engagement with AI technologies.
Ultimately, this study offers valuable insights into student experiences with AI in a developing country context, contributing to the broader discourse on global educational transformation. Future work should consider longitudinal analyses to capture evolving perceptions and learning outcomes, and investigate the differential impacts of AI use across disciplines and demographic segments.
6 Conclusions and future research
6.1 Conclusions
This study provides valuable insights into the adoption of AI tools among university students in Jordan, based on responses from 337 participants. The survey highlights the majority of chatbot technologies, particularly ChatGPT, which emerged as the most recognized and widely used tool for academic tasks. With 90.4% of respondents utilizing ChatGPT, the findings demonstrate its pivotal role in enhancing task efficiency and academic performance. Our finding is aligned with other research in the field. For instance, a study conducted across Germany found that nearly two-thirds of students used AI-based tools in their studies, with ChatGPT or GPT-4 being commonly mentioned by students in engineering, mathematics, and natural sciences, which aligns with our findings on the increasing reliance on AI tools for understanding and explaining subject-specific concepts (Von Garrel and Mayer, 2023). However, only 19.1% of students reported significant improvements in their understanding of academic concepts, suggesting that while AI tools are beneficial for productivity, their contribution to deeper learning remains limited. As noted in the study by Foŝner (2024), while AI tools are increasingly recognized for their efficiency in education, there are concerns about their impact on learning quality and academic integrity, which align with the findings indicated above.
The analysis also revealed differences in AI tool usage across academic disciplines, with students from scientific fields displaying greater familiarity with multiple platforms compared to those in humanities and health disciplines. Additionally, ethical considerations surfaced, as only 19.4% of students expressed significant concern about privacy and data security. This lack of awareness highlights the need to address the potential risks associated with AI technologies and encourage responsible usage practices.
6.2 Future research directions
Future research should investigate the long-term impacts of AI tools on students' academic performance, focusing on critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and conceptual understanding. Studies could explore how AI tools influence diverse learning outcomes across disciplines, addressing the unique needs and challenges of fields such as humanities, sciences, and health education. Additionally, research should examine strategies for effectively integrating AI into curriculum design, ensuring these tools enhance learning processes without fostering over-reliance.
The development of ethical frameworks is another key area for future work, particularly with regard to data privacy, academic integrity, and equitable access to AI technologies. Investigating how AI can address gaps in digital literacy and technology infrastructure, especially in under-resourced regions, remains a crucial focus.
Furthermore, new evaluation models should be developed to assess the benefits of AI adoption in higher education. Such models, incorporating multidimensional criteria, could streamline the analysis of AI's effectiveness in teaching and learning. They would also enable educators to design consistent surveys and compare data across studies, facilitating deeper insights into AI's impact on education.
In addition, future research should explore how sociocultural and institutional factors mediate student engagement with AI tools in diverse regional contexts. Comparative studies between Jordanian and non-Arab university cohorts may reveal how academic norms, technological readiness, and cultural attitudes shape the perceived benefits and ethical concerns associated with AI use. Qualitative investigations–such as interviews or focus groups–could deepen our understanding of how students and educators interpret the role of AI in learning and assessment. Moreover, policy-oriented studies could examine how institutional guidelines on academic integrity and digital conduct influence AI adoption in Middle Eastern education systems.
By extending this line of inquiry, future research can help build a more globally inclusive evidence base and ensure that AI-supported learning is responsive to both universal and context-specific educational needs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
MAM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. UT: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. We would like to acknowledge the assistance of OpenAI's ChatGPT in proofreading parts of this paper. Feedback and suggestions helped refine the clarity and readability of the text.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ajlouni, A., Almahaireh, A., and Whaba, F. (2023). Students' perception of using ChatGPT in counseling and mental health education: the benefits and challenges. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 18, 199–218. doi: 10.3991/ijet.v18i20.42075
Al Mashagbeh, M., Dardas, L., Alzaben, H., and Alkhayat, A. (2024). Comparative analysis of artificial intelligence-driven assistance in diverse educational queries: ChatGPT vs. google bard. Front. Educ. 9:1429324. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1429324
Al-Qerem, W., Eberhardt, J., Jarab, A., Al Bawab, A. Q., Hammad, A., Alasmari, F., et al. (2023). Exploring knowledge, attitudes, and practices towards artificial intelligence among health professions' students in jordan. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 23:288. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02403-0
Ansari, A. N., Ahmad, S., and Bhutta, S. M. (2024). Mapping the global evidence around the use of ChatGPT in higher education: a systematic scoping review. Educ. Inform. Technol. 29, 11281–11321. doi: 10.1007/s10639-023-12223-4
Ariyaratne, S., Iyengar, K. P., Nischal, N., Chitti Babu, N., and Botchu, R. (2023). A comparison of ChatGPT-generated articles with human-written articles. Skeletal Radiol. 52, 1755–1758. doi: 10.1007/s00256-023-04340-5
Arman, H. (2023). Evolving higher education: Challenges and opportunities on the horizon. J. Mod. Educ. Res. 2:13. doi: 10.53964/jmer.2023013
Beganovic, A., Jaber, M. A., and Abd Almisreb, A. (2023). Methods and applications of ChatGPT in software development: a literature review. Southeast Europe J. Soft Comp. 12, 08–12.
Bennett, L., and Abusalem, A. (2024). Artificial intelligence (AI) and its potential impact on the future of higher education. Athens J. Educ. 11, 195–212. doi: 10.30958/aje.11-3-2
Bin-Nashwan, S. A., Sadallah, M., and Bouteraa, M. (2023). Use of ChatGPT in academia: Academic integrity hangs in the balance. Technol. Soc. 75:102370. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2023.102370
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 3, 77–101. doi: 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Castillo-Martínez, I. M., Flores-Bueno, D., Gómez-Puente, S. M., and Vite-León, V. O. (2024). AI in higher education: a systematic literature review. Front. Educ. 9:1391485. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1391485
Celik, I. (2023). Towards intelligent-tpack: an empirical study on teachers' professional knowledge to ethically integrate artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools into education. Comput. Human Behav. 138:107468. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2022.107468
Chaudhry, I. S., Sarwary, S. A. M., El Refae, G. A., and Chabchoub, H. (2023). Time to revisit existing student's performance evaluation approach in higher education sector in a new era of ChatGPT–a case study. Cogent Educ. 10:2210461. doi: 10.1080/2331186X.2023.2210461
Crawford, J., Cowling, M., and Allen, K.-A. (2023). Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). J. Univer. Teach. Learn. Pract. 20:02. doi: 10.53761/1.20.3.02
Creswell, J. W., and Plano Clark, V. L. (2018). Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
Crompton, H., and Burke, D. (2023). Artificial intelligence in higher education: the state of the field. Int. J. Educ. Technol. HIgher Educ. 20, 2–22. doi: 10.1186/s41239-023-00392-8
Dare, R. (2024). “Reimagining academic performance management in the age of AI,” in ARPHA Conference Abstracts (Sofia, Bulgaria: Pensoft Publishers).
Dergaa, I., Chamari, K., Zmijewski, P., and Saad, H. B. (2023). From human writing to artificial intelligence generated text: examining the prospects and potential threats of ChatGPT in academic writing. Biol. Sport 40:615. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2023.125623
El Alfy, S., Marx Gómez, J., and Dani, A. (2019). Exploring the benefits and challenges of learning analytics in higher education institutions: a systematic literature review. Inform. Discov. Delivery 47, 25–34. doi: 10.1108/IDD-06-2018-0018
Elbanna, S., and Armstrong, L. (2024). Exploring the integration of ChatGPT in education: adapting for the future. Managem. Sustainab. 3, 16–29. doi: 10.1108/MSAR-03-2023-0016
Eman, A., and Alasadi, C. R. B. (2023). Generative AI in education and research: Opportunities, concerns, and solutions. J. Chem. Educ. 100, 2965–2971. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00323
Embarak, O. H., and Hawarna, S. (2024). Automated AI-driven system for early detection of at-risk students. Procedia Comput. Sci. 231, 151–160. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2023.12.187
Foŝner, A. (2024). University students' attitudes and perceptions towards AI tools: implications for sustainable educational practices. Sustainability 16:8668. doi: 10.3390/su16198668
Hannan, E., and Liu, S. (2023). AI: new source of competitiveness in higher education. Int. Busin. J 33, 265–279. doi: 10.1108/CR-03-2021-0045
Holmes, W., Porayska-Pomsta, K., Holstein, K., Sutherland, E., Baker, T., Shum, S. B., et al. (2022). Ethics of AI in education: Towards a community-wide framework. Int. J. Arti. Intellig. Educ. 2022, 1–23. doi: 10.1007/s40593-021-00239-1
Irfan, M., Aldulaylan, F., and Alqahtani, Y. (2023a). Ethics and privacy in Irish higher education: a comprehensive study of artificial intelligence (AI) tools implementation at university of limerick. Global Social Sci Rev 8, 201–210. doi: 10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-II).19
Irfan, M., Murray, L., and Ali, S. (2023b). Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Academia: A Case Study of Critical Teaching and Learning in Higher Education. Global Social Sciences Review (GSSR).
Jiahong Su, W. Y. (2023). Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: A framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Rev. Educ. 6, 355–366. doi: 10.1177/20965311231168423
Jones, K. M., Rubel, A., and LeClere, E. (2020). A matter of trust: Higher education institutions as information fiduciaries in an age of educational data mining and learning analytics. J. Assoc. Inform. Sci. Technol. 71:1227–1241. doi: 10.1002/asi.24327
Kamalov, F., Calonge, D. S., and Gurrib, I. (2023). New era of artificial intelligence in education: towards a sustainable multifaceted revolution. Sustainability 15, 12451–12451. doi: 10.3390/su151612451
Katsamakas, E., Pavlov, O. V., and Saklad, R. (2024). Artificial intelligence and the transformation of higher education institutions: a systems approach. Sustainability 16:6118. doi: 10.3390/su16146118
Ke Zhang, A. B. A. (2021). AI technologies for education: Recent research & future directions. Comp. Educ. 21, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.caeai.2021.100025
K. F., and Chiu, T. (2024). Future research recommendations for transforming higher education with generative AI. Comp. Educ. 44:100239. doi: 10.1016/j.caeai.2024.100239
Khasawneh, M. A. S., and Shawaqfeh, A. T. (2024). Breaking traditional boundaries in translation pedagogy; evaluating how senior lecturers have incorporated digital tools to enhance translation teaching. World 14:154. doi: 10.5430/wjel.v14n4p154
Kooli, C. (2023). Chatbots in education and research: A critical examination of ethical implications and solutions. Sustainability 15:5614. doi: 10.3390/su15075614
Mackney, S., and Shields, R. (2019). “Learning analytics for student success at university: trends and dilemmas,” in The Educational Intelligent Economy: Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and the Internet of Things in Education (Leeds: Emerald Publishing Limited), 251–268.
Mahrishi, M., Abbas, A., Radovanović, D., and Hosseini, S. (2024). Emerging dynamics of ChatGPT in academia: a scoping review. J. Univer. Teach. Learn. Pract. 21:13. doi: 10.53761/b182ws13
Mapletoft, N., Price, A., Smith, K., Mapletoft, O., and Elliott, M. (2024). An attempt to cheat using GPT-4: findings, discussion and recommendations for academic staff and students. Enhanc. Teach. Learn. Higher Educ. 1, 52–73. doi: 10.62512/etlhe.11
Mishra, R. (2024). “Embracing a paradigm shift: Transitioning from traditional teaching methods to AI-based nlp education,” in Research and Reviews in Literature, Social Sciences, 75.
Mosleh, R., Jarrar, Q., Jarrar, Y., Tazkarji, M., and Hawash, M. (2023). Medicine and pharmacy students' knowledge, attitudes, and practice regarding artificial intelligence programs: Jordan and west bank of palestine. Adv. Med. Educ. Pract. 2023, 1391–1400. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S433255
Mujtaba, B. (2024). Clarifying ethical dilemmas in sharpening students' artificial intelligence proficiency: dispelling myths about using AI tools in higher education. Busin. Ethics Leaders. 8, 107–127. doi: 10.61093/bel.8(2).107-127.2024
Neumann, M., Rauschenberger, M., and Schön, E.-M. (2023). “We need to talk about ChatGPT”?: The future of AI and higher education,” in 2023 IEEE/ACM 5th International Workshop on Software Engineering Education for the Next Generation (SEENG) (Melbourne: IEEE), 29–32.
Ojha, S., Narendra, A., Mohapatra, S., and Misra, I. (2023). From Robots to Books: An Introduction to Smart Applications of AI in Education (AIED). Singapore: Springer.
Pallivathukal, R. G., Soe, H. H. K., Donald, P. M., Samson, R. S., and Ismail, A. R. H. (2024). ChatGPT for academic purposes: survey among undergraduate healthcare students in Malaysia. Cureus 16:53032. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53032
Popenici, S. A., and Kerr, S. (2017). Exploring the impact of artificial intelligence on teaching and learning in higher education. Res. Pract. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 12:22. doi: 10.1186/s41039-017-0062-8
Qadir, J. (2023). “Engineering education in the era of ChatGPT: Promise and pitfalls of generative AI for education,” in IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) (Kuwait, : IEEE), 1–9.
Rahmaniar, W. (2024). ChatGPT for software development: Opportunities and challenges. IT Prof. 26, 80–86. doi: 10.1109/MITP.2024.3379831
Rohm, A. J., Stefl, M., and Ward, N. (2021). Future proof and real-world ready: the role of live project-based learning in students' skill development. J. Market. Educ. 43, 204–215. doi: 10.1177/02734753211001409
Sajja, R., Sermet, Y., Cikmaz, M., Cwiertny, D., and Demir, I. (2024). Artificial intelligence-enabled intelligent assistant for personalized and adaptive learning in higher education. Inform. 15:596. doi: 10.3390/info15100596
Salvagno, M., Taccone, F. S., and Gerli, A. G. (2023). Can artificial intelligence help for scientific writing? Crit. Care 27:75. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04380-2
Schönberger, M. (2023). “ChatGPT in higher education: the good, the bad, and the university,” in Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Higher Education Advances (HEAd'23) (Valencia: Editorial Universitat Politècnica de València).
Selwyn, N. (2022). The future of AI and education: Some cautionary notes. Eur. J. Educ. 57, 620–631. doi: 10.1111/ejed.12532
Shaik, T., Tao, X., Li, Y., Dann, C., McDonald, J., Redmond, P., et al. (2022). A review of the trends and challenges in adopting natural language processing methods for education feedback analysis. IEEE Access 10, 56720–56739. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3177752
Shoaib, M., Sayed, N., Singh, J., Shafi, J., Khan, S., and Ali, F. (2024). AI student success predictor: Enhancing personalized learning in campus management systems. Comp. Human Behav. 158:108301. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2024.108301
Shrivastava, P., Pawar, M. T., Kumar, S., Gupta, J. K., Kumar, P., and Bale, A. S. (2024). Shaping the future of higher education with AI: Challenges and strategies directions. Library Prog. Int. 44, 9787–9797.
Sunandar, E., Purnama, A., Arribathi, A. H., Yusuf, D. A., Daeli, O. P. M., et al. (2024). “Strategies and consequences of AI-enhanced predictive models for early identification of students at risk,” in 2024 3rd International Conference on Creative Communication and Innovative Technology (ICCIT) (Tangerang: IEEE), 1–6.
Tabone, W., and De Winter, J. (2023). Using ChatGPT for human-computer interaction research: a primer. R. Soc. Open Sci. 10:231053. doi: 10.1098/rsos.231053
Tomaskinova, J., West, L. B., Chircop, T., Judge, J., de Vries, S., Marinescu-Muster, R., et al. (2024). “Shaping the future: Navigating the AI era with an innovative training model,” in EDULEARN24 Proceedings (New York, NY: IATED), 6295–6303.
Tsai, Y.-S., Whitelock-Wainwright, A., and Gašević, D. (2020). “The privacy paradox and its implications for learning analytics,” in Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Analytics & Knowledge (Association for Computing Machinery), 230–239.
Uhlig, R. P., Jawad, S., Sinha, B., Dey, P. P., and Amin, M. N. (2023). “Student use of artificial intelligence to write technical engineering papers-cheating or a tool to augment learning,” in 2023 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition (American Society for Engineering Education).
Von Garrel, J., and Mayer, J. (2023). Artificial intelligence in studies–use of ChatGPT and AI-based tools among students in Germany. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 10, 1–9. doi: 10.1057/s41599-023-02304-7
Wang, Y., Liu, C., and Tu, Y.-F. (2021). Factors affecting the adoption of AI-based applications in higher education: an analysis of teachers perspectives using structural equation modeling. Educ. Technol. Soc. 24, 116–129.
Wang, Z., Ma, Q., Somjit, N., Robertson, I. D., and Chudpooti, N. (2023). “Prospects for artificial intelligence and learning analytics in engineering higher education,” in 2023 Research, Invention, and Innovation Congress: Innovative Electricals and Electronics (RI2C) (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), 23–28.
Wollny, S., Schneider, J., Di Mitri, D., Weidlich, J., Rittberger, M., and Drachsler, H. (2021). Are we there yet? - A systematic literature review on chatbots in education. Front. Artif. Intellig. 4:654924. doi: 10.3389/frai.2021.654924
Yadav, S. (2025). “Reimagining education with advanced technologies: transformative pedagogical shifts driven by artificial intelligence,” in Impacts of Generative AI on the Future of Research and Education (Hershey: IGI Global), 1–26.
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., and Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education-where are the educators? Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 16, 1–27. doi: 10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0
Keywords: artificial intelligence in education (AIeD), learning analytics, large language models (LLMs), chatbots, higher education
Citation: Al Mashagbeh M, Alsharqawi M, Tudevdagva U and Khasawneh HJ (2025) Student engagement with artificial intelligence tools in academia: a survey of Jordanian universities. Front. Educ. 10:1550147. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1550147
Received: 22 December 2024; Accepted: 16 June 2025;
Published: 18 August 2025.
Edited by:
Alyse Jordan, Indiana State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Reham Salhab, Palestine Technical University Kadoorie, PalestineBeverley Pickard-Jones, Bangor University, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Al Mashagbeh, Alsharqawi, Tudevdagva and Khasawneh. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohammad Al Mashagbeh, bS5tYXNoYWdiZWhAanUuZWR1Lmpv; Hussam J. Khasawneh, aC5raGFzYXduZWhAanUuZWR1Lmpv
 Mohammad Al Mashagbeh
Mohammad Al Mashagbeh Malak Alsharqawi
Malak Alsharqawi Uranchimeg Tudevdagva
Uranchimeg Tudevdagva Hussam J. Khasawneh
Hussam J. Khasawneh