- 1Department of Primary School Teacher Education, Universitas Sulawesi Barat, Majene, Indonesia
- 2Department of Early Childhood Education, Universitas Terbuka, Jakarta, Indonesia
- 3Department of Political Science, Universitas Sulawesi Barat, Majene, Indonesia
- 4Department of Government Studies, Universitas Muhammadiyah Makassar, Makassar, Indonesia
Introduction: This study investigates the critical factors influencing the successful implementation of Smart Education in Majene Regency, with particular attention to trust, communication, commitment, educational foundations, educational pillars, and educational benefits. The initiative responds to the growing need for digital transformation in education, particularly in remote areas.
Methods: A quantitative research design was employed, involving 345 respondents selected through purposive sampling from institutions that actively implement Smart Education. Data were collected using a structured questionnaire consisting of 57 items measured on a 5-point Likert scale. The data were analysed using Structural Equation Modeling–Partial Least Squares (SEM-PLS), a technique suitable for moderate sample sizes, complex models, and non-normal data distributions.
Results: The analysis identified trust as the most dominant factor influencing Smart Education adoption, surpassing communication, commitment, and service quality. A strong educational foundation and the tangible benefits of education—such as upskilling and employment opportunities—significantly enhanced stakeholder perceptions and service quality. In contrast, the educational pillar and communication variables showed limited direct effects but functioned as catalysts when combined with trust and educational foundations.
Discussion: The findings highlight the central role of trust and stakeholder engagement in supporting the digital transformation of education in peripheral regions. While commitment plays a supportive role, its limited influence underscores the importance of long-term sustainability and institutional dedication. The minimal impact of communication and service quality as standalone factors suggests that their effectiveness is maximised when embedded within a broader trust-based strategy. Moreover, aligning educational benefits with local labour market demands reinforces the strategic relevance of Smart Education initiatives. Overall, the study underscores that the harmonisation of trust, commitment, and strong educational foundations is crucial for sustaining Smart Education transformations in geographically remote areas.
Introduction
Due to the continuous advancement of information technology, smart education has emerged as a new frontier for the development of education (Kang, 2023), driven by technological advancements and increasing recognition of the need for educational reform in the digital era (Cebrián et al., 2020). Smart education represents a shift from the traditional education model to a more interactive and learner-centered approach that integrates information and communication technology (ICT; Gafiatulina et al., 2020).
Smart education initiatives have a significant impact in improving learning outcomes through the transformation of traditional teaching methods into more interactive and engaging (Joshi and Koirala, 2023). The use of digital resources and online platforms not only strengthens students' understanding of theory, but also narrows the gap between academic concepts and their application in the real world (Urbanus, 2024). Additionally, the flexibility and accessibility of digital education allows for personalized learning experiences, which play a crucial role in supporting students with special needs and disabilities (Funan, 2024; Layachi and Pitchford, 2024). As such, smart education contributes to educational inclusion and equity, expanding its impact beyond simply improving access. Despite these successes, the implementation of smart education in remote areas, especially in developing countries such as Indonesia, is still limited. Regions such as Majene Regency face different challenges that hinder the adoption of smart education systems, making it difficult for learners to reap the full benefits of digital advancements.
Majene Regency, located on the western coast of Sulawesi Island and forming part of West Sulawesi Province, Indonesia, is marked by unique geographical and social characteristics. With a coastline stretching approximately 125 kilometers, the region is largely defined by hilly terrain and coastal zones, which directly influence the distribution of infrastructure and public services, including access to education. Although Majene is endowed with abundant natural resources and holds considerable potential in tourism development, recent studies have identified persistent social challenges, especially in the domain of educational inequality across remote and underserved areas (Nur Adyla et al., 2022). Known as the educational center of West Sulawesi—due to the presence of several higher education institutions such as the University of West Sulawesi and STAIN Majene—the regency's reputation has not translated into widespread educational equity. In rural districts such as Tammeroddo and Pamboang, residents continue to encounter multifaceted barriers—geographical, economic, and socio-cultural—that limit access to quality educational services (Evawati et al., 2024).
Moreover, research conducted in Majene reveals that stunting and malnutrition remain prevalent, further underscoring systemic weaknesses in the dissemination of knowledge, the reach of educational information, and the delivery of foundational educational programs, particularly for marginalized communities. These conditions reflect not only the structural limitations in service provision but also the need for more contextual and inclusive educational strategies. In this regard, the findings of Evawati et al. (2024) emphasize the strategic importance of integrating local wisdom into educational and health interventions. Their study highlights how the utilization of locally sourced food in the preparation of complementary feeding (MP-ASI) serves as a culturally relevant and nutritionally effective approach to strengthening child health outcomes and supporting broader community resilience in Majene (Evawati et al., 2024).
In addition, Majene is also an area affected by multiple disasters, namely the earthquake and the COVID-19 pandemic simultaneously in 2021. This incident worsened economic conditions and social infrastructure, including educational services. Post-disaster recovery efforts require financial governance and adaptive policies, including community capacity building through digital-based education innovations.
This district is one of the areas that experiences education disparities due to geographical isolation, limited technological infrastructure, and socio-economic factors. Previous research has identified that, while urban areas are rapidly adopting smart education systems, rural and remote areas are left behind, further exacerbating educational inequalities (Liu, 2022; Zhang, 2024). In Majene, the traditional education system, which relies heavily on face-to-face teaching and printed materials, remains the dominant mode of learning, despite government efforts to promote digital literacy and integrate technology into the classroom.
One of the major gaps in the existing literature is the lack of focus on the specific needs of remote areas when implementing smart education. Most studies on smart education concentrate on urban and suburban contexts where infrastructure and resources are more available (Akter, 2024; Liu, 2022). Digital learning platforms provide flexible access to educational resources, which is especially beneficial for students in remote areas and helps reduce the educational gap with students in urban areas (Muslimin and Indrawati, 2024; Vivi et al., 2024). However, the implementation of smart education in remote areas is faced with challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, uneven distribution of teachers, and low digital literacy (Firdaus and Ritonga, 2024; Siti, 2024). Therefore, policy interventions that focus on infrastructure development and capacity building of educators are essential to create inclusive and sustainable education systems in remote areas. As a result, little attention has been paid to the unique challenges faced by remote areas, such as limited internet access, teacher readiness, and lack of collaboration between key stakeholders. In addition, while there is substantial research on the benefits of smart education in general, there is little research exploring how these initiatives can be adapted to specific socio-economic and geographical conditions in remote areas such as Majene.
This research aims to fill this gap by investigating the barriers to smart education in Majene Regency and proposing collaborative strategies that can help address these challenges. The purpose of this study is to develop a stakeholder collaboration model that can facilitate the successful implementation of smart education in remote areas. By engaging with local governments, educational institutions, private technology providers, and community members, the study seeks to create a framework that ensures the sustainability and inclusivity of smart education initiatives. The findings of this study highlight the importance of infrastructure development, digital literacy programs, and multi-stakeholder collaboration as key components of the success of smart education in remote areas.
Literature review
Smart education in remote areas
Rapid global digitalization has driven the adoption of technology in education, triggering the birth of a smart education model that emphasizes personalization, digital integration, and data analytics. This model emerged as an answer to the demands of more flexible and effective education, especially in countries with mature technological infrastructures. Smart education is now the dominant approach in improving the quality of learning through the use of information and communication technology that is in line with modern pedagogical methods. The main dimension of smart education is seen in Figure 1 (Demir, 2021).
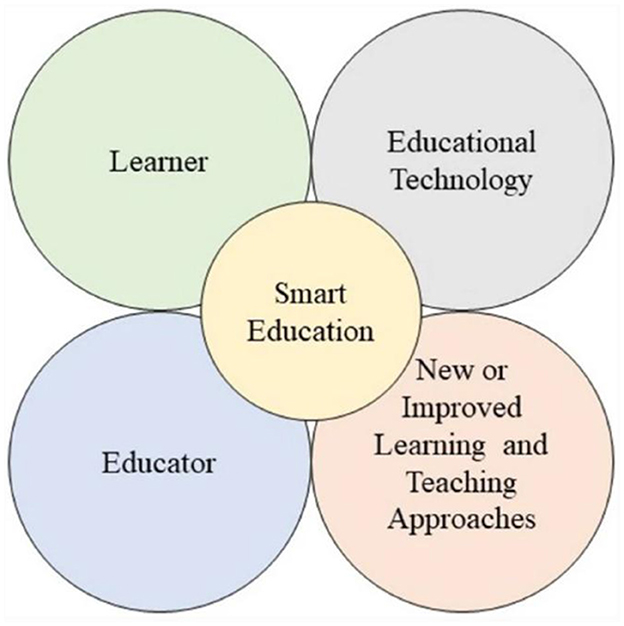
Figure 1. Dimensions of smart education. Source: Adapted from Demir (2021).
Smart education is an education system that allows students to learn using the latest technology (Bajaj and Sharma, 2018). In order to be able to learn with a variety of materials based on their talents and intellectual level (Kumar et al., 2023). This is inevitable and is an important development of educational trends in the Information Age (Guo et al., 2021), as well as a “panacea” that can solve various educational problems (Lee and Lee, 2023). In addition, smart education is a form of education in which educators build a smart educational environment by relying on a new generation of information technology.
Smart education Figure 2 (Guo et al., 2021) is a basic element of smart educational activities (Zhu et al., 2016). The improvement of technology and its continuous integration into formal education settings is challenged to operationalize and regulate systems that combine pedagogy and technology (Morgado et al., 2021).
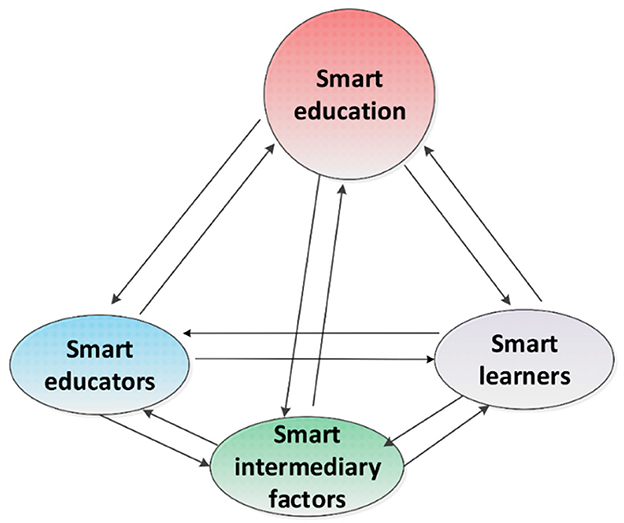
Figure 2. Intelligent education theory framework. Source: Adapted from Zhu et al. (2016).
Framework stakeholder collaboration
Stakeholder Collaboration is operationally defined as a stakeholder participation strategy that encourages cooperation, improves resource sharing, encourages unity, increases collective responsibility and encourages joint efforts among education stakeholders (Aina et al., 2021; Ouko et al., 2020). Stakeholder engagement in education programs to ensure the effective use of smart technology (Mathane, 2023), and participate in a variety of programs that will improve school and student achievement (Chang and Huang, 2022). So that it can improve the teaching and learning process, efficiency in school management, increase motivation and commitment among staff, and encourage collaboration and open communication with various actors (Khadija, 2022). The relationship between stakeholders is driven by relationship governance on trust, communication, commitment, and service quality (Figure 3) (Jain et al., 2022).
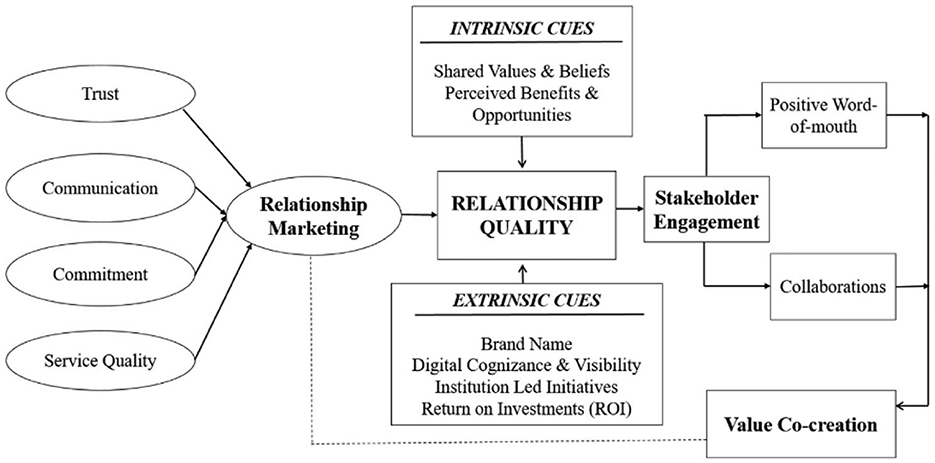
Figure 3. Stakeholder collaboration framework model. Source: in the formulation of Jain et al. (2022).
Collaboration among stakeholders has been an important factor in addressing complex issues, especially in sectors such as education, where many entities are involved. The collaborative framework, in this study, refers to a structured approach that brings together a variety of stakeholders—government agencies, educational institutions, private sector organizations, community leaders, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs)—to achieve common goals. In smart education, this framework is essential to address challenges that no single entity can handle independently. Stakeholders must pool their resources, expertise, and authority to create effective and scalable solutions for education in remote areas.
Education city framework
The idea of “Education City” is one of the tools we can use to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 4, “Quality Education,” whose goal is to “guarantee inclusive and equitable quality education and encourage lifelong learning opportunities for all” (Hirju and Georgescu, 2023). The success of an education city lies in its ability to foster cooperation among different social and educational agents in society (Gabriel et al., 2022). Urban development, which places learning as a top priority in its policies and strategies, has become an important phenomenon around the world (Shvindina et al., 2022). The Cities of Education initiative developed by the UNESCO Institute for Lifelong Learning defines cities of education as follows (Figure 4) (Kaewhanam et al., 2023):
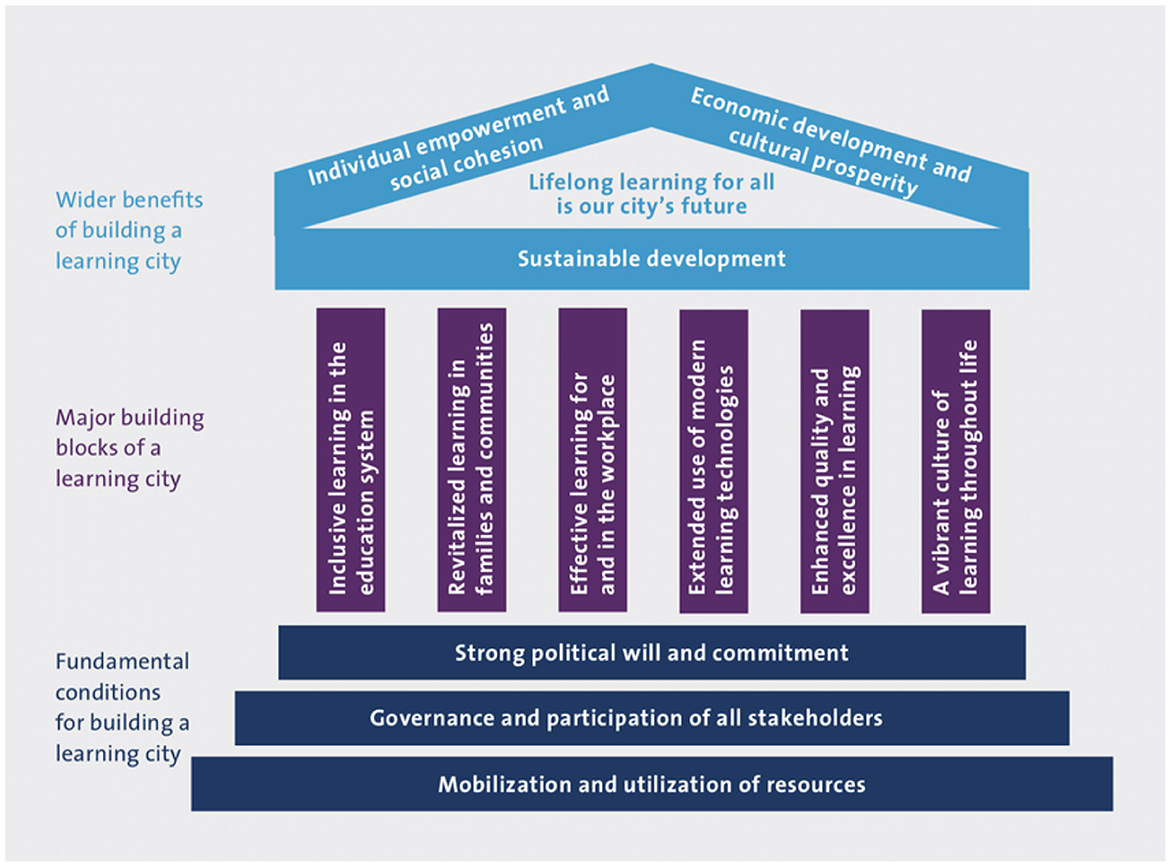
Figure 4. Education city framework. Source: in the formulation of Kaewhanam et al. (2023) and Nemeth (2019).
The concept of “City of Education” has received increasing attention in the global discourse around education reform and sustainable urban development (Kameni and Tekouabou Koumetio, 2023). An education city refers to a city that puts education at the heart of its development strategy, creates an environment where learning is accessible, integrated into the fabric of the community, and designed to encourage lifelong learning for all citizens (Fang and Liu, 2023). The idea of an education city is in line with UNESCO's Education 2030 Agenda, which emphasizes the importance of ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education and promoting lifelong learning opportunities for all (Shulla et al., 2020). The concept integrates various elements of urban planning, infrastructure, governance, and technology to create a learning ecosystem that goes beyond the classroom (Ma, 2022).
The development of educational cities is driven by the recognition that learning is not limited to formal educational institutions such as schools and universities, but must also be carried out in public spaces, workplaces, and through community interaction (Ma, 2022). By promoting education as a key aspect of urban development, cities can better prepare their residents to face the challenges of the 21st century, including economic shifts, technological advancements, and social change (Kutto and Erastus, 2025).
Despite the growing interest in education cities, there is still a significant gap in the literature on how this model can be adapted to the needs of remote or developing areas such as Majene Regency. Most research on education cities focuses on developed urban centers, where infrastructure, governance, and economic resources are more available. There is a need for further research exploring how the principles of the education city model can be applied in areas where resources are limited, and socio-economic disparities are more pronounced.
Methodology and hypothesis
This study employed a quantitative approach to systematically examine the relationships among variables that influence the implementation of smart education, including trust, commitment, communication, and service quality. The primary research instrument was a structured questionnaire comprising 57 items derived from 19 indicators, each measured using a five-point Likert scale ranging from “Strongly Disagree” to “Strongly Agree.” The instrument was designed to capture respondents' perceptions regarding various dimensions of smart education. Prior to full-scale data collection, a pilot test was conducted with 30 participants possessing similar characteristics to the target population, to ensure clarity and consistency of the items. Content validity was assessed through expert evaluation by three scholars specializing in education and research methodology. Construct validity was examined using Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) within the framework of Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). Reliability analysis indicated that all constructs had Cronbach's alpha values exceeding 0.70 and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) values above 0.50, confirming that the instrument met the criteria for both reliability and convergent validity.
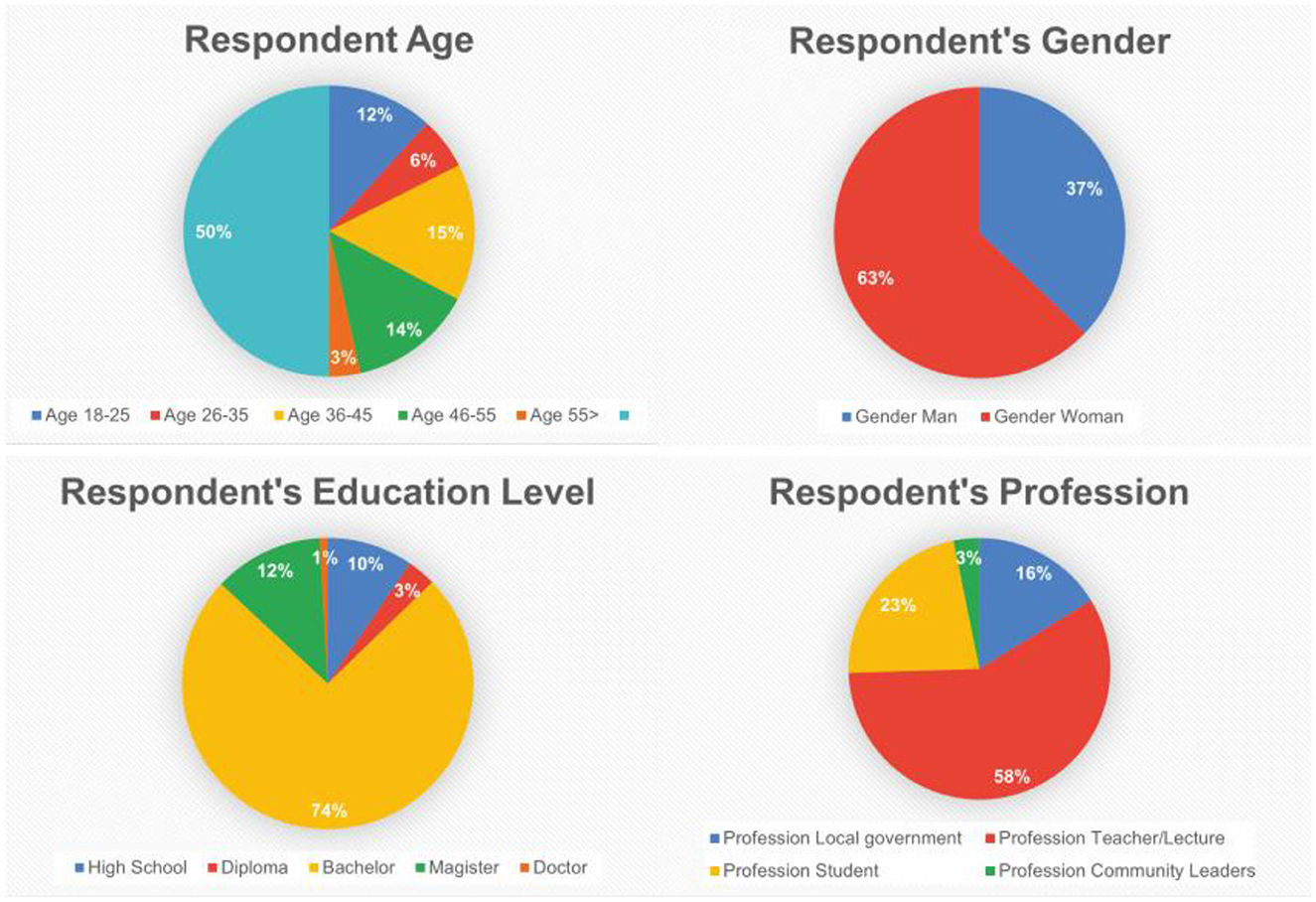
A total of 345 respondents were selected through purposive sampling based on specific inclusion criteria, namely, active involvement in educational institutions that have adopted smart education principles. Participants who submitted incomplete responses were excluded from the final analysis. The sample size was determined in accordance with SEM-PLS standards, requiring a minimum of ten respondents per indicator for the largest construct, and was further supported by power analysis conducted using G*Power software, which confirmed that the sample size was statistically adequate. To minimize sampling bias, the questionnaire was distributed online to a diverse group of respondents representing various ages, genders, educational backgrounds, and professional roles (Figure 5). Moreover, anonymity was ensured throughout the data collection process to reduce the risk of social desirability bias. The collected data were analyzed using the SEM-PLS technique, which is well-suited for evaluating complex models and handling non-normally distributed data. The analysis was conducted using SmartPLS version 4.0 to evaluate the measurement model's validity and reliability, and to test the hypothesized relationships among constructs in the proposed theoretical framework.
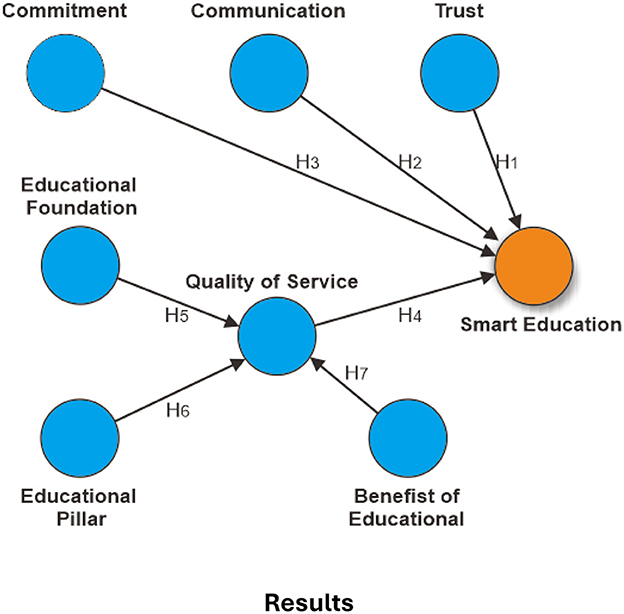
The hypothesis model (Figure 6) outlines the factors influencing the implementation of Smart Education. Trust, communication, and commitment serve as the primary drivers, represented by hypotheses H1, H2, and H3. Service quality (H4), the educational pillar (H5), and the benefits of education (H6 and H7) further support this framework. Achieving optimal Smart Education requires enhancing these factors and reinforcing the foundational elements, pillars, and benefits of the education system. The details of the seven hypotheses are as follows:
H1: Trust has a positive and significant effect on Smart Education.
H2: Communication has no significant effect on Smart Education.
H3: Commitment has a positive and significant effect on Smart Education.
H4: Quality of Service does not have a significant effect on Smart Education.
H5: Educational Foundation has a positive and significant effect on the Quality of Service.
H6: Educational Pillar does not have a significant effect on Quality of Service.
H7: Benefits of Education have a positive and significant effect on Quality of Service.
Results
This study aims to assess the challenges and opportunities for the implementation of smart education in Majene Regency through a quantitative approach. The results of this study provide a measurable and objective picture of the perception and involvement of stakeholders in supporting technology-based education initiatives.
Data reliability
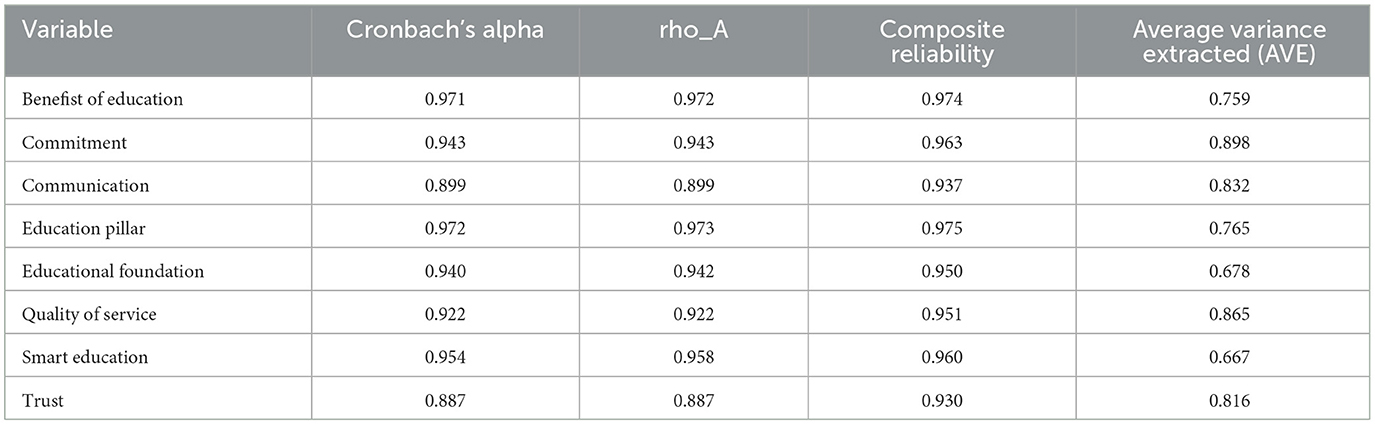
Table 1 shows the results of the reliability and validity analysis of the constructs used in the study. It appears that all the variables analyzed have a good level of reliability and validity, with some variables showing higher performance than others. By considering the relationship between variables, this table provides a solid foundation to explain the influence of certain factors on the desired outcomes, especially in the context of smart education and educational services.
Variabel Benefit of Education menunjukkan reliabilitas dan validitas konvergen yang sangat tinggi, menegaskan bahwa manfaat pendidikan terukur secara konsisten dan sepenuhnya merepresentasikan konstruk yang dikembangkannya. Peran sentral variabel ini dalam meningkatkan Quality of Service mengindikasikan bahwa persepsi positif terhadap kualitas layanan berbanding lurus dengan tingkat manfaat pendidikan yang dirasakan.
On the other hand, Commitment with an AVE of 0.898 shows a significant contribution to the success of Smart Education, where strong commitment from individuals and institutions is the main motor in supporting the implementation of technology and educational innovation. Although Communication has good reliability and validity performance (AVE 0.832), its influence on the success of intelligent education appears to be weaker than that of Commitment and Trust, reflecting that effective communication needs to be combined with continued trust and dedication to produce greater impact.
The dimensions of the Education Pillar and Educational Foundation with high reliability provide a solid foundation in strengthening the quality of education services, where the conceptual framework and educational infrastructure play a direct role in shaping a positive user experience. Quality of Service which has strong validity (AVE 0.865) is an important link in the Smart Education system, although its contribution to overall success is still inferior to the Trust variable, whose AVE reaches 0.816 and serves as the main catalyst in building user confidence in the technology-based education system.
So, it appears that the relationship between the variables in this table shows that the development of smart education not only requires technology but also basic elements such as educational benefits, commitment, communication, and trust. The strong interaction between these variables provides the foundation for creating a more effective and innovative education system.
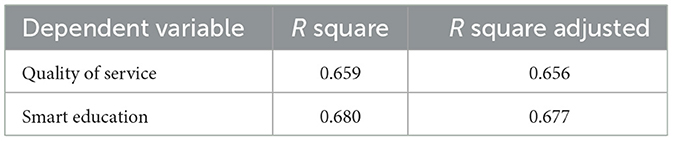
Based on Table 2, the R Square value for Quality of Service is 0.659 with an Adjusted R Square of 0.656, indicating that the model can account for about 65.6% variation in service quality. This indicates that the factors used in the model have a strong contribution in predicting service quality. Meanwhile, Smart Education has an R Square value of 0.680 and an R Square Adjusted of 0.677, which means that about 67.7% of the variation in the success of the implementation of smart education can be explained by the model used. The R Square Adjusted value, which is only slightly lower than R Square indicates that the model is not overfitting and remains consistent despite the adjustment of the number of variables. Overall, these results confirm that the regression model applied has good predictive power in analyzing the factors that affect the quality of services and the success of technology-based education.
Results on SEM-PLS
This study analyzes the relationship between variables in the conceptual model to identify factors that affect the implementation of Smart Education. A total of 345 respondents were selected through a sampling method according to the inclusion criteria, namely involvement in educational institutions that have adopted Smart Education. Data was collected through a questionnaire consisting of 57 questions and 19 indicators, using a 5-point Likert scale to measure variables such as Trust, Communication, Commitment, Educational Foundation, Educational Pillars, Educational Benefits, Service Quality, and the implementation of Smart Education.
The results of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) in this Figure 7 show the complex relationship between latent variables that affect the implementation of Smart Education. The latent variables analyzed include Commitment, Communication, Trust, Educational Foundation, Education Pillar, Quality of Service, and Benefit of Education. Each of these variables is measured by a number of indicators, which are reflected in the loading factor listed in each relationship.
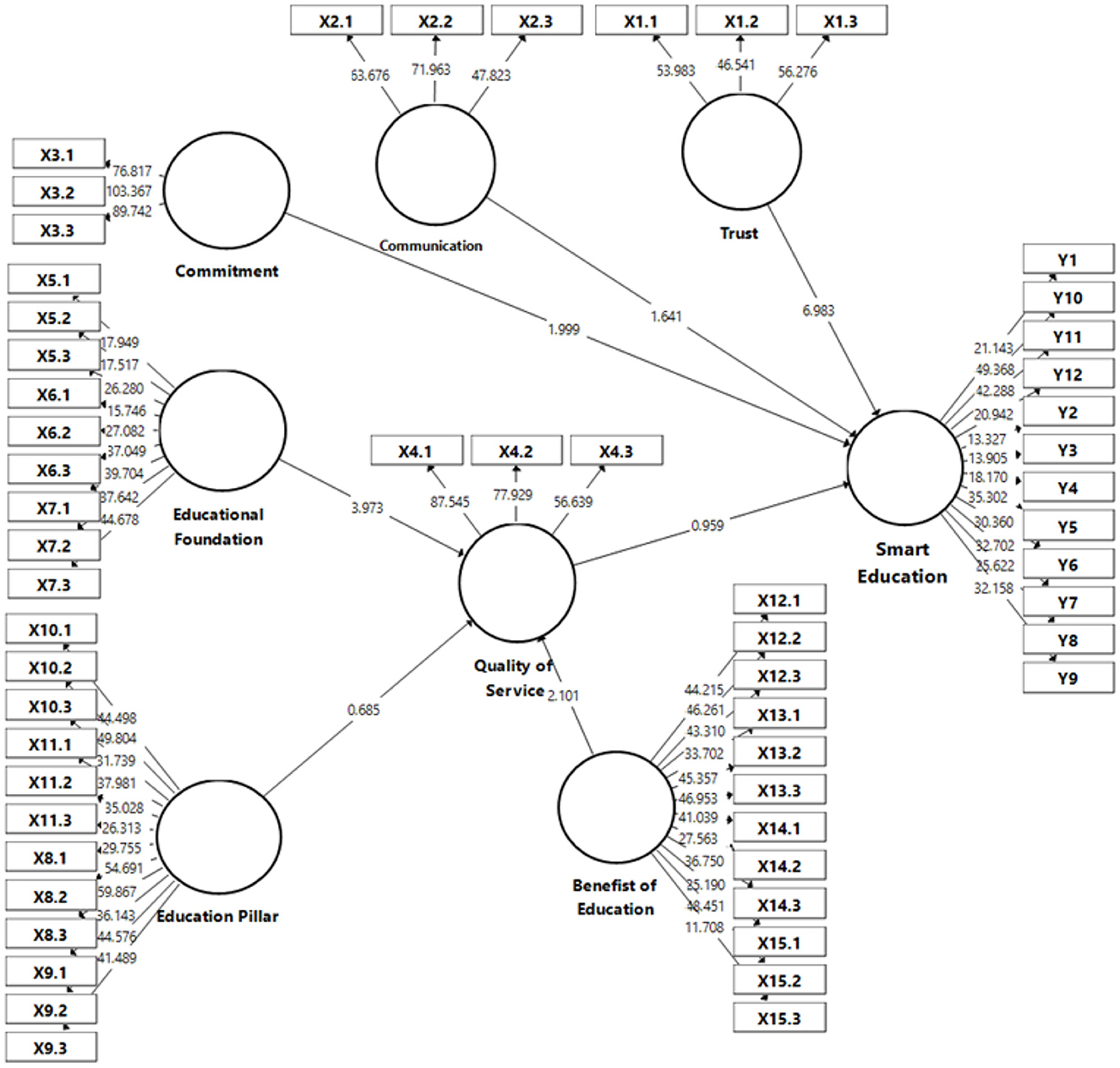
Figure 7. SEM-PLS structural model for analysis of factors influencing smart education. Source: SEM-PLS processing results.
This model shows that Communication has a significant direct influence on Smart Education with a track weight of 1,999, while Trust contributes with a weight of 1,641. Education Foundations had a strong relationship with Quality of Service (2.101), which then significantly affected Smart Education with a weight of 0.959. The Education Pillar also contributes to the Benefits of Education, which has a direct impact on Smart Education with a track weight of 1,685.
These results indicate that the main factors driving the success of Smart Education are Communication, Trust, and Service Quality. The Foundation and Pillar of Education act as supporting factors that strengthen the Quality of Services and Benefits of Education. Therefore, to improve the implementation of Smart Education, educational institutions need to strengthen communication between stakeholders, build trust, and improve the quality of education services. Thus, broader educational benefits can be achieved, driving the success of a smarter and more responsive education system.
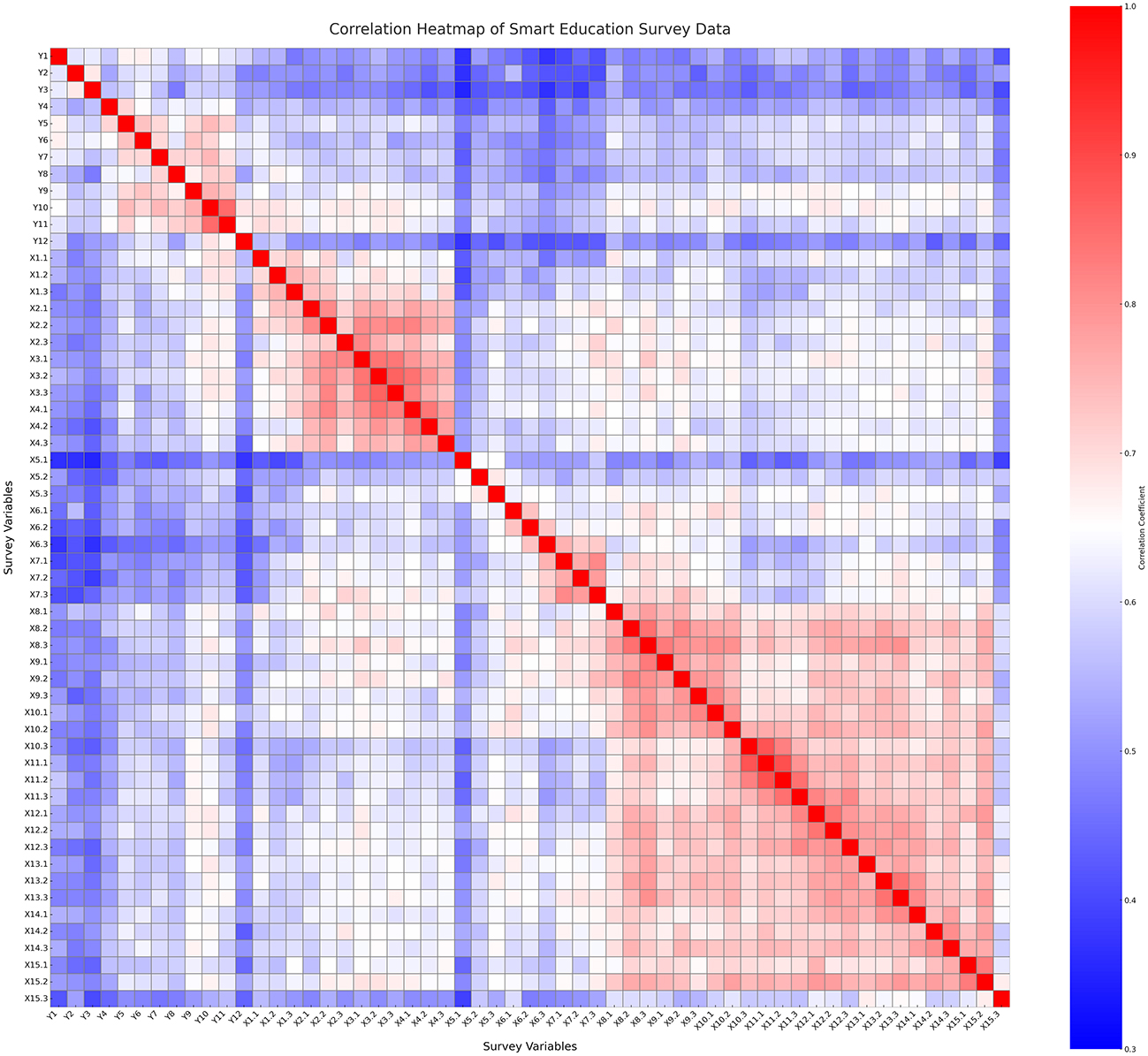
Figure 7 displays a visualization of the correlation between 57 survey indicators using the Pearson method. The colors on the heatmap represent the strength and direction of the linear relationship between variables. It can be seen that indicators in the same group (e.g., X1.1 to X1.3) show a high positive correlation, indicating internal consistency in the measurement construct. More moderate correlations between groups of variables indicate potential links between factors and the measured outcomes. This visualization provides an important initial overview for further analysis such as validity testing, regression, or dimensional exploration.
Figure 8 presents a heatmap illustrating the correlations among the survey variables. It shows that variables within the same cluster exhibit strong correlations, whereas correlations across clusters tend to be relatively weak.
Testing hypotheses
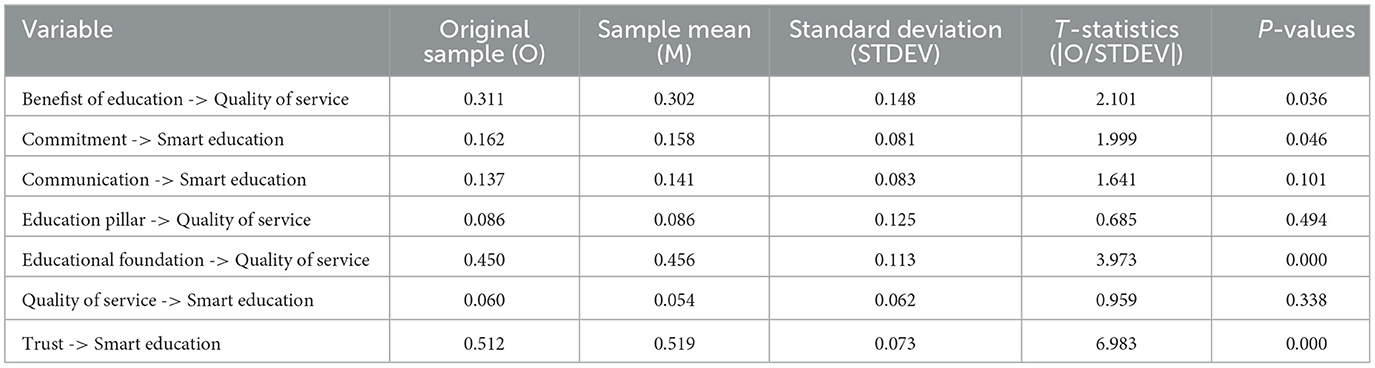
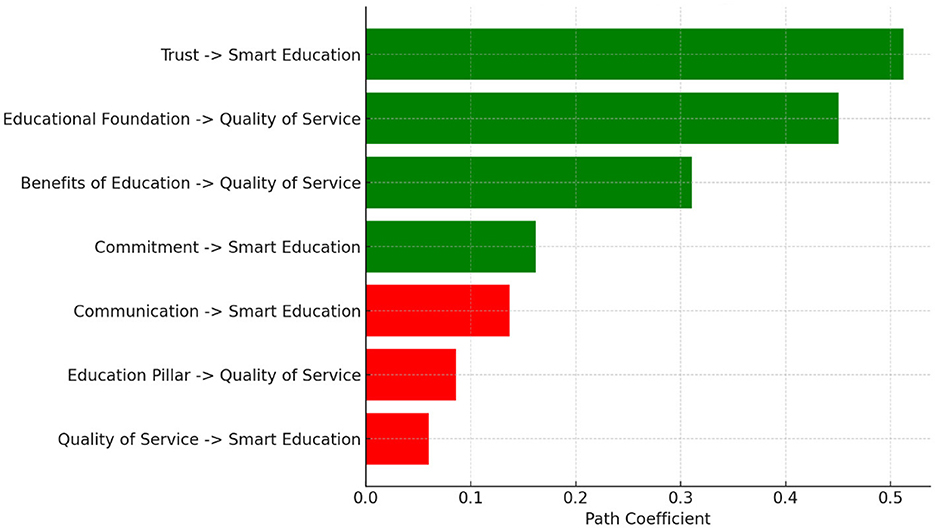
Based on the SEM results, the total impact of each process dimension shows the complex relationship between latent variables that affect the implementation of Smart Education in Majene district is calculated and presented in Table 3. Path Coefficients are normalized and displayed for easy comparison. Figure 9 illustrates the path coefficients representing the relationships between various constructs and their impact on Quality of Service and Smart Education. The analysis reveals that Trust exerts the strongest and most statistically significant influence on Smart Education (coefficient = 0.512, p < 0.001), followed by Educational Foundation, which significantly affects Quality of Service (coefficient = 0.450, p < 0.001). Additionally, Benefits of Education and Commitment demonstrate statistically significant yet comparatively weaker relationships with Quality of Service and Smart Education, respectively. In contrast, the paths from Communication, Education Pillar, and Quality of Service to Smart Education are not statistically significant, as indicated by p-values exceeding the 0.05 threshold. These findings highlight the pivotal role of trust and a strong educational foundation in enhancing service quality and advancing smart education initiatives.
The significant effect of trust on smart education (H1)
The connection between trust and smart education plays a key part in facilitating the effective integration of technology and innovation in educational settings. A coefficient of 0.512 indicates that trust plays a crucial role in shaping the acceptance and involvement of diverse stakeholders, including students, teachers, parents, and institution managers. A strong level of trust fosters the adoption of new technologies and innovations in education, while also enhancing digital management systems. Consequently, it is essential for educational institutions to focus on establishing trust by ensuring transparency, fostering effective communication, and providing concrete evidence of the advantages of smart education. The absence of trust will impede the success of smart education, regardless of the quality of services and dedication involved.
The lack of influence of communication on smart education (H2)
The relationship between communication and smart education shows a coefficient of 0.137 with a T-statistics value of 1.641 and a P-value of 0.101, indicating that this relationship is not significant at the 95% confidence level. While communication plays a role in conveying the purpose and benefits of technology to stakeholders, the data shows that its influence on the success of smart education is weak. Effective communication can help reduce resistance and increase understanding, but without the support of other factors such as trust and commitment, its contribution is limited. Therefore, educational institutions need to combine communication with other strategies to ensure optimal adoption of smart education.
The positive impact of commitment on smart education (H3)
The relationship between commitment and smart education showed significance at the 95% confidence level, with a coefficient of 0.162, T-statistics of 1.999 and a P-value of 0.046. This result confirms that commitment has a real, albeit relatively moderate, positive influence on the successful implementation of smart education. Dedication from stakeholders, such as institutions, educators and students, contributes to adopting educational technologies and innovation strategies. Commitment includes technology integration, consistency in the implementation of digital strategies and allocation of resources that support smart education goals. Although influential, these results suggest that other factors, such as trust or service quality, may have a greater impact, so commitment needs to be strategically directed to maximize the potential of technology in education.
The insignificance of quality of service on smart education (H4)
The relationship between service quality and smart education showed insignificance at the 95% confidence level, with a coefficient of 0.060, T-statistics of 0.959 and P-value of 0.338. While service quality is expected to contribute to the success of smart education, the data indicate that the effect is relatively small and not strong enough. Service quality reflects the provision of facilities, learning support and access to educational resources. In smart education, good services can create a conducive environment, but factors such as trust and commitment seem to have a greater influence. Therefore, educational institutions need to ensure consistency in service quality while strengthening other more impactful factors to increase the adoption and success of technology-based education.
The contribution of educational foundation to quality of service (H5)
The correlation between educational foundations and service quality showed high significance at the 99% confidence level, with a coefficient of 0.450, T-statistics of 3.973, and P-value of 0.000. A strong educational foundation contributes greatly to enhancing positive perceptions of educational service quality. Fundamental elements such as infrastructure, learning systems, institutional policies and technological support play an important role in the delivery of quality education. When these foundations are well-established, the quality of service perceived by students, educators and stakeholders improves significantly. Therefore, strengthening educational foundations should be an institutional priority to ensure educational services are consistent, relevant and in line with user needs. A solid educational foundation is a key cornerstone in driving success and positive experiences in the educational environment.
The limitations of educational pillar on quality of service (H6)
The relationship between the education pillar and service quality shows insignificance, with a coefficient of 0.086, T-statistics of 0.685, and P-value of 0.494. These results indicate that education pillars do not have a strong direct influence on perceived service quality. The education pillar includes basic principles, core values, and macro policies that support the sustainability of education, but its influence on service quality tends to be indirect. To improve service quality, educational institutions need to focus more on operational elements that have a direct impact, such as infrastructure, technology and communication. The integration of educational pillars with other more applicable factors is key in creating optimal service quality and in accordance with user needs.
The benefits of education in improving quality of service (H7)
The relationship between educational benefits and service quality showed significance at a confidence level of 95%, with a coefficient of 0.311, T-statistics 2.101, and P-value 0.036. These results indicate that the benefits of education have a moderate influence on the perception of service quality. Educational benefits, such as skill enhancement, personal development, and career opportunities, contribute to shaping a positive perception of the quality of services provided by the institution. When these benefits are felt in real terms, the assessment of service quality increases, indicating that the relevant educational experience affects user satisfaction. Therefore, educational institutions need to focus on developing a curriculum that suits market needs and provides supportive training and career opportunities. This approach will strengthen positive perceptions and encourage continuous improvement in service quality.
Discussions
Trust in smart education
The findings of this study highlight the pivotal role of trust in driving the success of smart education initiatives (H1). Trust functions as a social adhesive that binds diverse stakeholder groups toward collective action, which is essential for the development of inclusive, adaptive, and technologically driven learning environments. Without a sufficient level of trust, it becomes increasingly difficult to foster stakeholder engagement and create a collaborative learning culture that supports innovation and digital transformation in education (Kanaris and Mujtaba, 2023).
Trust reduces perceived uncertainty and perceived risk, thereby increasing the likelihood of technology acceptance among students, educators, and institutional leaders (Al-Abdullatif, 2023). These findings align with trust theory, which posits that individuals' beliefs and values are foundational in shaping educational environments and teaching practices (Burak Ayçiçek, 2022). In smart education, trust becomes a determining factor in how learners and institutions navigate change, manage digital platforms, and sustain participation in dynamic digital learning ecosystems.
The successful implementation of smart education depends on three key pillars that together foster trust: transparency, consistent communication, and demonstration of tangible benefits. Transparency—particularly when enhanced by technologies such as blockchain—ensures the integrity, immutability, and accountability of educational records, thus mitigating concerns about data manipulation or credential falsification (Kishor, 2023; Saravanan, 2022). Effective and ongoing communication also serves to bridge the gap between educators and students, facilitating mutual understanding, clarifying expectations, and cultivating an environment of psychological safety (Sidhu et al., 2023; Sneesl et al., 2022). Trust is further strengthened when stakeholders are exposed to the tangible benefits of smart education systems, such as increased academic performance, personalized learning paths, and reward systems based on engagement and merit (Gloria et al., 2023; Liu S. et al., 2024).
These three pillars operate not in isolation, but in a mutually reinforcing manner, establishing a foundation upon which smart education systems can thrive. Trust, therefore, must be viewed not merely as a precursor to system implementation, but as a strategic asset that determines long-term sustainability and system adaptability in dynamic educational contexts. In rural and underdeveloped regions like Majene Regency, where digital inequality persists, the establishment of trust is especially crucial to overcome sociocultural resistance, increase stakeholder buy-in, and maintain system resilience under resource-constrained conditions.
This emphasis on trust is supported by previous studies. For example, Kilinç et al. (2021) found that trust in school leadership significantly influences teachers' willingness to adopt instructional technology (Kilinç et al., 2021). Similarly, Polatcan et al. (2024) showed that digital trust mediates the relationship between perceived usefulness of educational technologies and students' sustained engagement (Polatcan et al., 2024). These findings reinforce the current study's assertion that trust is not only a catalyst for initial adoption but a stabilizing force that enables long-term participation and digital growth.
Building trust among educational stakeholders—through clear communication, visible accountability, and demonstrated value—is essential for the long-term success and institutionalization of smart education, particularly in peripheral regions facing systemic educational gaps. Future interventions must, therefore, integrate trust-building mechanisms into the design and deployment of smart education initiatives to enhance their legitimacy, functionality, and impact.
The influence of communication on smart education
Contrary to expectations, this study found that communication (H2), although conceptually significant, did not exhibit a strong direct effect on the success of smart education initiatives in Majene Regency. While communication is often regarded as a vital enabler in any educational reform, its impact may become indirect or mediated in the context of digitally driven environments. This suggests that communication alone—without being embedded in trust-based interactions or supported by pedagogical alignment—may not substantially influence stakeholder engagement or learning outcomes.
However, the broader literature continues to assert the foundational role of communication in education. Özdogru et al. (2024) emphasizes that effective communication, alongside social intelligence and intercultural sensitivity, significantly contributes to teacher performance and classroom efficiency (Özdogru et al., 2024). Likewise, Hrytsenko et al. (2024) and Sharkov et al. (2022) argue that the integration of AI in smart education strengthens communication channels between students and educators by personalizing interactions and enabling responsive feedback mechanisms (Hrytsenko et al., 2024), (Sharkov et al., 2022). In addition, Mihus and Nakonechna (2022) view communication as an inseparable component of an educator's social competence, reinforcing its essential place in fostering relational quality within smart classrooms.
Nonetheless, Chen et al. (2024) cautions against an overreliance on technological mediation, warning that such dependence may inadvertently reduce human connection and diminish the effectiveness of traditional pedagogical discourse. This concern is particularly relevant in underdeveloped contexts, where digital literacy gaps, limited infrastructure, and cultural preferences for face-to-face interaction may hinder the full potential of digital communication tools (Chen et al., 2024).
Commitment to smart education
The study identifies commitment as a key determinant of the success of smart education (H3). The success of smart education is greatly influenced by the level of commitment from various stakeholders, including educators, students, and educational institutions, which directly determines the effectiveness of technology implementation in learning (Mardin et al., 2024). This commitment includes a willingness to adopt as well as integrate smart technology and pedagogy into the existing educational framework (Mardin et al., 2024). Research shows that testability and observability factors in smart education programs have a crucial role in driving these commitments, as they allow institutions to evaluate the benefits of technology before full implementation. Schools that are given the opportunity to test technology gradually tend to have a higher success rate in adopting smart education initiatives, as confidence in the results achieved increases (Mardin et al., 2024).
Additionally, personalization in smart education contributes greatly to increased student engagement and commitment, by creating learning experiences tailored to individual needs (Aggarwal et al., 2024). Technology's ability to adapt to diverse learning styles allows students to develop at their own pace, which has a direct impact on their motivation and willingness to actively participate in the learning process (Aggarwal et al., 2024). Studies Ma et al. (2024) affirming that students' perception of a supportive and responsive learning environment significantly increases their engagement levels, suggesting that an adaptive environment plays an important role in strengthening students' commitment to education.
The integration of smart technology in the curriculum also plays an important role in building commitment, especially because of the direct benefits that students feel in the teaching-learning process (Hu et al., 2024). However, the implementation of smart technology in vocational education environments often faces various challenges, including limited resources and the need for intensive training for teachers. This shows that institutional commitment is indispensable to overcome these obstacles and ensure the success of smart education programs (Wang and Wang, 2023).
Other factors that play an important role in strengthening student commitment are the quality of the relationship between teachers and students and the effectiveness of communication in a smart learning environment (Hou, 2024). The teacher's immediacy and the quality of interaction with students not only increase engagement but also form an emotional bond that reinforces the commitment to learning (Hou, 2024).
In Majene's case, the relatively high level of stakeholder commitment observed can be attributed to the local relevance of the smart education programs, where the perceived benefits—such as improved access, digital literacy, and employability—align with community aspirations. However, the challenge remains in maintaining this commitment over time. Continuous institutional support, transparent progress monitoring, and inclusive stakeholder engagement are essential to prevent attrition and sustain momentum.
Commitment in smart education should be viewed not as a static trait, but as a dynamic process that must be cultivated, reinforced, and renewed (Liu L. et al., 2024). Future initiatives should embed mechanisms that promote shared ownership, reflective practice, and contextual alignment to ensure that stakeholder commitment evolves in tandem with system maturity (Ramos et al., 2023). This approach will be particularly vital for rural and remote regions, where sustained commitment is both a prerequisite and a product of transformative educational change.
The cultural identity of the Majene Regency community is shaped by a combination of historical, social, and economic influences that contribute to its distinctive local character. A defining feature of this community is the central role of traditional customs and collective participation in the development of social norms and practices. Local wisdom is particularly significant in everyday life, especially in dietary habits that emphasize health and wellbeing. This cultural orientation is further reflected in the educational sphere, where institutions actively promote a reading culture through initiatives such as the School Literacy Movement, which has become an integral component of Majene's educational landscape. This movement not only seeks to enhance students' reading proficiency but also aims to cultivate a culture of lifelong learning within the broader community (Awaru et al., 2022). In addition, educational efforts in Majene are reinforced by the local government's initiatives to strengthen human resource management and elevate teacher professionalism, indicating a systemic commitment to improving the quality of both community-based and formal education (Erwin et al., 2023).
Compared to Majene, Polewali Mandar Regency—its neighboring district—demonstrates a distinct emphasis on enhancing language literacy among students, which has been identified as a key educational priority (Hamzah et al., 2022). This focus on linguistic development is closely associated with improved learning outcomes (Yusuf and Arif, 2022), underscoring a targeted and structured educational environment oriented toward language proficiency. Moreover, the district has implemented systematic efforts to advance teacher professional development as a means of strengthening pedagogical competence (Amaliah et al., 2023). These institutional strategies are further complemented by findings that highlight the significant influence of metacognitive skills, self-efficacy, and student confidence on academic performance, suggesting that individual cognitive development plays a critical role in shaping broader educational achievements (Rahmawati et al., 2024). Collectively, these initiatives reflect a comprehensive and integrative approach to education in Polewali Mandar, where both institutional capacity and individual learner attributes contribute to sustained academic progress.
Quality of service in smart education
Despite its intuitive importance, the present study finds that quality of service (QoS) does not exert a significant direct effect on the perceived success of smart education in Majene Regency (H4). While service quality remains a critical dimension in conventional education and public service delivery, its influence in digital learning environments may be more complex and indirect, especially in underserved or transitional contexts.
The statement that service quality does not affect intelligent education can be studied through various studies that highlight the complex relationship between service quality and educational outcomes in intelligent learning environments. While some studies emphasize the importance of quality of services in improving the educational experience, others suggest that the impact may not be as important as traditionally perceived (Ritonga and Desrani, 2022).
Similarly, research by Yan highlights that service quality, particularly in smart classroom settings, significantly drives customer loyalty, implying that high service quality can improve user satisfaction and engagement in an educational context (Yan and Trisakhon, 2024). Hal ini menunjukkan bahwa meskipun kualitas layanan merupakan komponen pendidikan pintar, hal itu mungkin tidak secara tunggal menentukan keberhasilan pendidikan. Selain itu, penelitian oleh Wang et al. mengidentifikasi berbagai faktor yang memengaruhi kualitas layanan di komunitas pintar, yang menunjukkan bahwa kompleksitas pemberian layanan di lingkungan pendidikan dapat melemahkan dampak langsung kualitas layanan pada hasil pendidikan (Wang et al., 2021).
Moreover, it is imperative to view service quality through the lens of educational justice and inclusion. Ensuring equal access to reliable, high-quality services across different socio-economic and geographic segments reinforces the broader goals of smart education as a transformative and democratizing force. In this sense, quality of service becomes a foundation for digital equity, rather than merely a customer satisfaction metric.
While service quality may not emerge as a dominant factor in statistical models, its strategic relevance remains. It operates as a structural enabler, shaping the conditions under which trust, satisfaction, and long-term engagement can flourish. Future research should explore its interaction effects and mediating pathways, particularly in contexts like Majene where foundational infrastructure and digital culture are still evolving.
Educational foundation to quality of service
The findings of this study indicate that educational foundations—including institutional management, regulatory frameworks, and infrastructure—play a significant role in shaping the perceived quality of education services in smart learning environments (H5). Unlike service quality, which often functions as a surface-level metric of user experience, foundational elements underpin the systemic functionality and long-term sustainability of digital education systems. In the case of Majene Regency, where infrastructural and organizational disparities persist, the strength of the educational foundation becomes an essential factor in ensuring equitable access and reliable service delivery.
The quality of education services is influenced by various factors such as institutional management, regulatory framework, and stakeholder satisfaction, which together determine the effectiveness of the education process (Leonova et al., 2020). The relationship between service quality and student satisfaction is a major focus, where quality improvement in higher education institutions is proven to improve the learning experience (Dugenio-Nadela et al., 2023). Managerial approaches, including the use of balanced scorecards and information systems, play a crucial role in ensuring quality and improving the performance of educational institutions (Abd El- hamed et al., 2023; Rosana, 2022). In addition, public administration also contributes to improving the quality of services at the primary school level, creating a positive impact on the development of the education system at large (Mahardhani, 2023). This is in line with institutional theory that highlights the role of established structures, policies, and infrastructure in shaping organizational outcomes (Muluk et al., 2025).
The influence of educational foundations extends beyond institutional capacity—it also affects stakeholder confidence and engagement. When students and parents perceive schools as organized, transparent, and well-managed, their trust in the educational process increases, which in turn enhances their satisfaction with services received. This dynamic is especially critical in rural regions like Majene, where communities may harbor skepticism toward externally imposed innovations unless supported by visible institutional commitment and clarity of purpose.
Limitations of the education pillar on service quality
While educational foundations serve as a critical backbone for the development of smart education, this study identifies notable limitations of the education pillar in enhancing perceived service quality (H6). These limitations are rooted not only in infrastructural or administrative weaknesses, but also in systemic constraints that inhibit the translation of foundational strength into tangible improvements in user experience.
The limitations of the educational pillar in improving service quality in educational institutions are caused by inconsistent measurements, the complexity of the relationship between service quality and student satisfaction, as well as the role of leadership and organizational culture (Mishra et al., 2024). Non-uniform quality measurements often hinder the identification of areas that need improvement, while generic approaches are not always effective in local contexts (Nguyen et al., 2024). Institutions' failure to implement continuous service improvement exacerbates the problem, despite continuous evaluation being shown to improve student satisfaction (Al-Yozbakey and Esmaeel, 2024). Lack of understanding of the service quality dimension causes the strategies implemented not to be in accordance with the needs of students (Widayanthi et al., 2024).
Additionally, leadership and organizational culture play an important role in determining service quality, but a lack of institutional support often hampers its effectiveness (Budur et al., 2024). Student loyalty is influenced by trust and satisfaction, which mediates the impact of service quality on institutional retention and reputation (Widayanthi et al., 2024). Thus, improving the quality of education services requires an integrated approach that includes the adjustment of assessment strategies, sustainable practices, and institutional commitments to create a responsive educational environment (Qie and Quan, 2024).
In addition, institutional rigidity and bureaucratic inaction limit the capacity of the education system to integrate continuous improvement mechanisms. Many schools in remote areas lack the organizational maturity to conduct internal service audits, track performance indicators, or implement data-driven decision-making. As a result, service quality tends to stagnate, and the gap between user expectations and actual experience widens over time.
Ultimately, strengthening the pillars of education requires more than just technical improvements—it needs a cultural and systemic transformation that empowers institutions to become learning organizations. In Majene, where educational challenges are exacerbated by geographical isolation and resource scarcity, overcoming the institutional limitations of the education pillar is essential to unlock the full potential of smart education and provide equitable quality of services to all segments of society.
Benefits of education on service quality
This study reaffirms that education plays a pivotal role in enhancing service quality, not only within the education sector itself but across broader public and community services (H7). In smart education ecosystems, education functions both as an input and an outcome—improving users' capacity to engage with technology, interpret information, and demand quality, while simultaneously shaping institutional accountability and responsiveness.
Education has a crucial role in improving the quality of services in various sectors, especially in educational institutions and service delivery frameworks (Zheng and Ouyang, 2023). The availability of quality educational resources and the professionalism of educators significantly affect the perception and outcomes of services, which requires institutions to prioritize resource and faculty development (Zheng and Ouyang, 2023). In addition, customer education contributes to more effective participation, thereby improving the quality of services in various sectors (Shah et al., 2023).
Customer satisfaction, which is influenced by the educational experience, plays a role in shaping values and loyalty, strengthening the reputation of the educational institution (Cahyono et al., 2023). This relationship is reinforced by the institution's positive image, which reflects public trust and user satisfaction (Ramadina, 2024). In the context of early childhood education, quality services also have a positive impact on the wellbeing and work preferences of parents, demonstrating the far-reaching effects of education on social and economic aspects (Nkechi et al., 2023).
Additionally, educational experiences influence values, expectations, and perceptions of service quality, particularly among students and parents. When users are equipped with critical thinking, digital literacy, and problem-solving skills, their engagement with service providers becomes more discerning and collaborative. This has been supported by studies such as Martini et al. (2023), which demonstrate that education increases “participation efficacy” and improves alignment between service delivery and user needs (Martini et al., 2023).
In early childhood and primary education contexts, improved service quality contributes not only to child development outcomes but also to family wellbeing and workforce participation, particularly among mothers. In Majene, where many households rely on informal employment and subsistence livelihoods, accessible and high-quality educational services can reduce care burdens and open new economic opportunities, reinforcing education's role as a multiplier of social equity.
Education is not merely a beneficiary of quality service—it is a catalyst for elevating the standards, accountability, and equity of service systems as a whole. In the context of Majene, where smart education intersects with broader challenges of underdevelopment and social disparity, maximizing the transformative impact of education on service quality represents a strategic pathway toward inclusive and sustainable development.
Conclusion
This study reveals that trust is the main determinant in encouraging the implementation of smart education in Majene Regency, Indonesia. These findings highlight the importance of stakeholder engagement and acceptance as a fundamental prerequisite for the transformation of technology-based education. Commitments from various parties also contribute positively, albeit with a lower intensity, indicating the need to strengthen consistency and dedication in the development of the digital ecosystem.
On the other hand, communication and service quality did not show a significant direct influence on the success of smart education, confirming that these factors require interaction and synergy with elements of trust and educational foundations. A strong educational foundation proved to be a catalyst in improving the perception of service quality, emphasizing the importance of infrastructure, policies, and the integration of holistic learning systems.
The education pillar does not have a substantial direct contribution to the perception of service quality, so that service optimization is more effective through an operational approach oriented to improving facilities and technology. In addition, the benefits of education in the form of upskilling and career opportunities have a significant positive impact on the perception of service quality, indicating that the relevance of education to the needs of the local job market has strategic implications.
Thus, this study emphasizes that the success of smart education in Majene Regency lies in the harmonization between trust, commitment, and a strong educational foundation, with other supporting factors as catalysts that strengthen the sustainability of digital education transformation at the local level.
Research implications
The findings of this study offer significant implications for both policy and practice in advancing smart education, particularly in geographically disadvantaged regions. The central role of trust and commitment suggests that successful implementation of digital learning initiatives cannot rely solely on technological infrastructure; instead, it requires deliberate efforts to foster social capital, institutional credibility, and stakeholder engagement. Policymakers should prioritize the development of inclusive digital governance frameworks that embed transparency, feedback mechanisms, and user-centered design. For practitioners, the results underscore the need to invest in professional development that enhances educators' digital pedagogical skills, communication strategies, and adaptive capacities in low-resource environments. Furthermore, strengthening foundational aspects of education—such as institutional leadership, policy coherence, and local stakeholder participation—will be essential in building a sustainable ecosystem for smart education that promotes equity, resilience, and long-term innovation.
Ensuring the sustainability of smart education in Majene requires a clear implementation roadmap, beginning with short-term teacher training and infrastructure preparation, followed by mid- to long-term integration of digital systems into educational policy. A structured monitoring and evaluation framework should be established, using indicators such as digital tool usage and learning outcomes to guide improvements. Additionally, a resource needs assessment—including funding, technical support, and policy alignment—is essential. Sustainable implementation depends on multi-stakeholder collaboration to secure commitment and continuity.
Suggestions for future research
Future research should explore the longitudinal effects of trust-building and commitment-enhancing strategies on the sustainability of smart education systems in rural and underserved areas, particularly in contexts with limited digital infrastructure and administrative capacity. Comparative studies across diverse regions or countries are also encouraged, as they would offer valuable insights into how cultural, institutional, and infrastructural variations influence the adoption, adaptation, and outcomes of smart education models. To enrich contextual understanding, future studies should adopt mixed-methods or participatory action research designs, enabling deeper exploration of community-level dynamics, stakeholder engagement, and learner experiences in digital learning environments. Incorporating educational theories—such as constructivism, socio-cultural theory, or connectivism—into future investigations could provide a more grounded framework for evaluating the pedagogical impact of smart education initiatives. Moreover, with the rapid advancement of technology, future research should critically examine the role of emerging digital innovations (e.g., artificial intelligence, blockchain, and adaptive learning systems) in developing equitable, inclusive, and culturally responsive smart education ecosystems. Importantly, such research should explicitly align with the goals of SDG 4 (Quality Education) by contributing to evidence-based strategies that promote inclusive, equitable, and lifelong learning opportunities for all, especially those in geographically and socially marginalized settings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the [patients/participants OR patients/participants legal guardian/next of kin] was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SU: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was financially supported by the Directorate of Research, Technology, and Community Service (DRTPM), Directorate General of Higher Education, Research, and Technology (DITJEN DIKTIRISTEK), Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology (KEMDIKBUDRISTEK), Republic of Indonesia. Grant Numbers: Master Contract Number: 091/E5/PG.02.00.PL/2024 dated June 11, 2024, Derivative Contract Number: 195/UN55. C/PG/2024 dated June 19, 2024.
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to the educators, government officials, and technology providers in Majene Regency who participated in this study. This research was made possible by the support of the Indonesian Ministry of Education and Culture.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author (s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abd El- hamed, A., Khalefa, M., Mohamed, A., and Zaher, M. D. (2023). Using the environmental perspective of the balanced scorecard to improve the quality of education service. J. Environ. Sci. 52, 89–109. doi: 10.21608/jes.2023.215616.1541
Aggarwal, D., Sharma, D., and Saxena, A. B. (2024). Smart education: an emerging teaching pedagogy for interactive and adaptive learning methods. J. Learn. Educ. Policy 44, 1–9. doi: 10.55529/jlep.44.1.9
Aina, A. N., Siswidyanto, S., and Hayat, A. (2021). Analysis on education provision policy in frontier, outermost, and underdeveloped regions to improve national security in Sebatik island, Indonesia. J. Contemp. Govern. Public Policy 2, 1–12. doi: 10.46507/jcgpp.v2i1.34
Akter, S. (2024). Digitalization of education in rural schools: a study of access, utilization, and impact toward digitalization in Bangladesh. Am. Int. J. Multidiscipl. Sci. Res. 15, 1–9. doi: 10.46281/aijmsr.v15i1.2205
Al-Abdullatif, A. M. (2023). Modeling students' perceptions of chatbots in learning: integrating technology acceptance with the value-based adoption model. Educ. Sci. 13:1151. doi: 10.3390/educsci13111151
Al-Yozbakey, E. A., and Esmaeel, R. I. (2024). The role of educational service quality in enhancing student satisfaction / an exploratory study of the opinions of a sample of students of the Department of Industrial Management. J. Port Sci. Res. 7, 523–544. doi: 10.36371/port.2024.special.41
Amaliah, N., Nur, S., Firman, F., Rahman, S. R., and Sainab, S. (2023). Peningkatan Profesionalisme Guru Polewali Mandar melalui Pelatihan Tindakan Kelas (PTK). Jurnal Interaktif 3, 10–15. doi: 10.29303/interaktif.v3i1.65
Awaru, O. T., Said Ahmad, M. R., Putra Agustang, A. D. M., and Sugeng, H. H. (2022). Literacy movement in junior high schools to form students' reading habits. SHS Web Conf. 149:01026. doi: 10.1051/shsconf/202214901026
Bajaj, R., and Sharma, V. (2018). Smart education with artificial intelligence based determination of learning styles. Proc. Comput. Sci. 132, 834–842. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.05.095
Budur, T., Demir, A., and Ahmed, N. S. (2024). Does empowerment work? The role of education in service quality. Glob. Bus. Org. Excell. 43, 20–31. doi: 10.1002/joe.22249
Burak Ayçiçek, Ç. T. (2022). The predictive role of reasons for choosing the teaching profession as a career on the educational beliefs of teachers. Int. J. Contemp. Educ. Res. 7, 300–310. doi: 10.33200/ijcer.713412
Cahyono, T., Herdinata, C., Harianto, E., and Olasode, T. (2023). Implementation of resource-based theory on the relationship of intellectual capital and smes performance with innovation ability as a medium. J. Aplikasi Manaj. 21:9. doi: 10.21776/ub.jam.2023.021.1.09
Cebrián, G., Palau, R., and Mogas, J. (2020). The smart classroom as a means to the development of ESD methodologies. Sustainability 12:3010. doi: 10.3390/su12073010
Chang, H. B., and Huang, W.-J. (2022). Stakeholder workshops as a pedagogical method for experiential learning in collaborative planning education. Plann. Pract. Res. 37, 427–445. doi: 10.1080/02697459.2021.2019523
Chen, Y., Li, B., and Huang, Z. (2024). Journalism and communication education enabled by artificial intelligence: reflections on the construction of majors and professional groups. J. New Media Econ. 1, 85–89. doi: 10.62517/jnme.202410315
Demir, K. A. (2021). Smart education framework. Smart Learn. Environ. 8, 1–36. doi: 10.1186/s40561-021-00170-x
Dugenio-Nadela, C., Cañeda, D. M., Tirol, S. L., Samillano, J. H., Pantuan, D. J. M., Piañar, J. C., et al. (2023). Service quality and student's satisfaction in higher education institution. J. Hum. Resour. Sustain. Stud. 11, 858–870. doi: 10.4236/jhrss.2023.114049
Erwin Mas'ud, A. A., Dj, A. A., and Sumarsih (2023). The role of human resource management in enhancing the professionalism of educators. Manag. Dev. Appl. Res. J. 6, 49–56. doi: 10.31605/mandar.v6i1.3362
Evawati, E., Jafar, N., Hidayanty, H., Natsir, S., Thaha, R., Amiruddin, R., et al. (2024). Analysis of the giving of Mp-Asi through food based on majene's local wisdom for stunting prevention. Pharmacogn. J. 16, 372–377. doi: 10.5530/pj.2024.16.57
Fang, Y., and Liu, X. (2023). Urban higher education development with Chinese characteristics–the case of Shenzhen. Int. J. Chin. Educ. 12:4731. doi: 10.1177/2212585X221144731
Firdaus, K., and Ritonga, M. (2024). Peran Teknologi Dalam Mengatasi Krisis Pendidikan di Daerah Terpencil. Jurnal Kepemimpinan Dan Pengurusan Sekolah 9, 43–57. doi: 10.34125/jkps.v9i1.303
Funan, F. (2024). The role of educational technology in improving access in rural areas: a case study of YPPK ST. Educ. J. Hist. Human. 7, 489–495. doi: 10.24815/jr.v7i2.37919
Gabriel, M. H., de Vieira, A. P., and Castral, P. C. (2022). Educating cities and cultural heritage: theoretical approach. Rev. Nacl. Gerenciamento Cidades 10:223184. doi: 10.17271/23188472107620223184
Gafiatulina, N., Shishova, N., Volkova, D., and Topchiy, I. (2020). Applying of information and communication technologies in the education process. E3S Web Conf. 175:15031. doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202017515031
Gloria, M. D., Lubis, A. N., and Sembiring, B. K. F. (2023). Investigating the determinants of students' trust in Budi Utomo Binjai Vocational, Indonesia. J. Madani Soc. 2, 116–127. doi: 10.56225/jmsc.v2i2.253
Guo, X.-R., Li, X., and Guo, Y.-M. (2021). Mapping knowledge domain analysis in smart education research. Sustainability 13:13234. doi: 10.3390/su132313234
Hamzah, H., Muna, W., Z, H., and Zainuddin, Z. (2022). “A case study on the development of Arabic students in the arabic language education study program at IAI DDI Polewali Mandar, West Sulawesi, Indonesia,” in Proceedings of the 6th Batusangkar International Conference, BIC 2021, 11 - 12 October, 2021 (Batusangkar-West Sumatra).
Hirju, I., and Georgescu, R.-I. (2023). The concept of learning cities: supporting lifelong learning through the use of smart tools. Smart Cities 6, 1385–1397. doi: 10.3390/smartcities6030066
Hou, G. (2024). Correlation among teacher ICT teaching, teacher immediacy behaviors, teacher–student rapport, and student engagement in smart classroom teaching. Sustainability 16:9592. doi: 10.3390/su16219592
Hrytsenko, V., Tkachenko, A., Podolyan, O., Dieiev, K., and Ilyn, L. (2024). The role of artificial intelligence in personalisation of the learning process. Revista EDaPECI 24, 152–165. doi: 10.29276/redapeci.2024.24.320987.152-165
Hu, Y., Fang, C., He, X., and Wu, J. (2024). Implementing and assessing a teaching mode based on smart education in english literature teaching. Int. J. Web Based Learn. Teach. Technol. 19, 1–18. doi: 10.4018/IJWLTT.336484
Jain, V., Mogaji, E., Sharma, H., and Babbili, A. S. (2022). A multi-stakeholder perspective of relationship marketing in higher education institutions. J. Market. High. Educ. 0, 1–19. doi: 10.1080/08841241.2022.2034201
Joshi, B. M., and Koirala, P. (2023). Enhancing economics education through digital resources and online learning. Pragyaratna 5, 183–195. doi: 10.3126/pragyaratna.v5i1.59287
Kaewhanam, K., Kaewhanam, P., Pongsiri, A., Intanin, J., Kamolkat, S., Sirisuwan, A., et al. (2023). UNESCO building factors Thailand's Kalasin learning city and citizenship. Int. J. Eval. Res. Educ. 12:771. doi: 10.11591/ijere.v12i2.24715
Kameni, E. D., and Tekouabou Koumetio, S. C. (2023). The role of inclusive educational technologies in transforming african cities into inclusive smart cities. E3S Web Conf. 418, 03003. doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202341803003
Kanaris, M. E., and Mujtaba, B. G. (2023). Trust shaping the social relationship of diverse learners in the online education environment. Environ. Soc. Psychol. 9, 1–21. doi: 10.54517/esp.v9i2.2197
Kang, X. (2023). Strategies for promoting regional smart education. J. Contemp. Educ. Res. 7, 27–31. doi: 10.26689/jcer.v7i,8.5183
Khadija, H. (2022). Stakeholders in education. Econ. Sci. 31, 425–435. doi: 10.47535/1991AUOES31(1)040
Kilinç, A. Ç., Bellibaş, M. S., and Bektaş, F. (2021). Antecedents and outcomes of teacher leadership: the role of teacher trust, teacher self-efficacy and instructional practice. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 35, 1556–1571. doi: 10.1108/IJEM-04-2021-0148
Kishor, R. (2023). smart contract based fraud degree detection system. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Manag. 7:30. doi: 10.55041/IJSREM25030
Kumar, R., Sexena, A., and Gehlot, A. (2023). “Artificial intelligence in smart education and futuristic challenges,” in 2023 International Conference on Disruptive Technologies (ICDT) (Greater Noida), 432–435.
Kutto, N., and Erastus, M. (2025). Equity and social inclusion in higher education. Afr. J. Tech. Vocat. Educ. Train. 9, 20–27. doi: 10.69641/afritvet.2024.91189
Layachi, A., and Pitchford, N. J. (2024). Formative evaluation of an interactive personalised learning technology to inform equitable access and inclusive education for children with special educational needs and disabilities. Technol. Knowl. Learn. doi: 10.1007/s10758-024-09739-0
Lee, S., and Lee, K. (2023). Smart teachers in smart schools in a smart city: teachers as adaptive agents of educational technology reforms. Learn. Media Technol. 22:7143. doi: 10.1080/17439884.2023.2207143
Leonova, V. P., Vasileva, L. A., Povorina, E. V., and Volkov, D. V. (2020). Theoretical aspects of the quality of educational services provided. Uchenye Zapiski RGSU 19, 113–121. doi: 10.17922/2071-5323-2020-19-4-113-121
Liu, J. (2022). Research on challenges and solutions in elementary schools' STEAM education promotion in rural China. BCP Soc. Sci. Human. 19, 401–407. doi: 10.54691/bcpssh.v19i.1637
Liu, L., Liu, P., Yang, H., Yao, H., and Thien, L. M. (2024). The relationship between distributed leadership and teacher well-being: the mediating roles of organisational trust. Educ. Manag. Administr. Leadersh. 52, 837–853. doi: 10.1177/17411432221113683
Liu, S., Liu, Z., Zhu, X., Pan, X., and Chen, B. (2024). Incentive mechanism of online leaning based on blockchain. ITM Web Conf. 60:00005. doi: 10.1051/itmconf/20246000005
Ma, A. S. (2022). Assessing the effects of university reputation and city image on international student destination choice: evidence from a flagship university in Taipei. Educ. Urban Soc. 54, 992–1009. doi: 10.1177/00131245211013844
Ma, Y., Zuo, M., Gao, R., Yan, Y., and Luo, H. (2024). Interrelationships among college students' perceptions of smart classroom environments, perceived usefulness of mobile technology, achievement emotions, and cognitive engagement. Behav. Sci. 14:565. doi: 10.3390/bs14070565
Mahardhani, A. J. (2023). The role of public administration in improving the quality of education services in primary schools. Indo-MathEdu Intellect. J. 4, 1370–1381. doi: 10.54373/imeij.v4i2.363
Mardin, N. F. R. H., Haning, M. T., and Syahribulan, S. (2024). Exploring the effectiveness of smart school program as a policy innovation in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Edelweiss Appl. Sci. Technol. 8:3639. doi: 10.55214/25768484.v8i6.3639
Martini, M., Rollero, C., Rizzo, M., Di Carlo, S., De Piccoli, N., and Fedi, A. (2023). Educating youth to civic engagement for social justice: evaluation of a secondary school project. Behav. Sci. 13:650. doi: 10.3390/bs13080650
Mathane, T. P. (2023). “Stakeholder involvement and Institutionalisation of smart cities applications: a case study in the City of Tshwane,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management (Istanbul), 4980–4980.
Mihus, I., and Nakonechna, N. (2022). The role of communicative competence in the structure of social intelligence of teachers of higher education institutions. Public Administr. Law Rev. 4, 75–86. doi: 10.36690/2674-5216-2022-4-75
Mishra, R., Mishra, A., Tiwari, V., and Jain, R. K. (2024). Effect of institute and LMS service quality on HEI brand equity: an empirical investigation. Qual. Assur. Educ. 33, 124–139. doi: 10.1108/QAE-01-2024-0022
Morgado, J. C., Lencastre, J. A., Freires, T., and Bento, M. (2021). Smart education as empowerment: outlining veteran teachers' training to promote digital migration. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 26, 897–916. doi: 10.1007/s10758-021-09494-6
Muluk, M. R. K., Novita, A. A., and Wiswayana, W. M. (2025). Collaborative strategies for community empowerment: a narrative study on thematic village development in Malang, Indonesia. J. Contemp. Govern. Public Policy 6, 23–38. doi: 10.46507/jcgpp.v6i1.649
Muslimin, M., and Indrawati, R. (2024). Digitalization and education equity in remote areas: challenges and strategic solutions. J. Educ. Human. Soc. Sci. 7, 376–383. doi: 10.34007/jehss.v7i2.2356
Nemeth, B. (2019). Learning cities: participatory-focused community development in adult and lifelong education. Sisyphus 7, 9–23. doi: 10.25749/sis.17702
Nguyen, H. V., Vu, T. D., Saleem, M., and Yaseen, A. (2024). The influence of service quality on student satisfaction and student loyalty in Vietnam: the moderating role of the university image. J. Trade Sci. 12, 37–59. doi: 10.1108/JTS-12-2023-0032
Nkechi, M. M., Christy, O., and Abimbola, O. (2023). Impact of early childhood education service delivery on working class parents. Int. J. Res. Innovat. Soc. Sci. VII 65–73. doi: 10.47772/IJRISS.2023.70507
Nur Adyla, S., Muhammad, A., Nurlaela, N., Abdullah, M. A., and Mulawarman, A. (2022). Study on development potency of coastal tourist object in Majene District, West Sulawesi, Indonesia. Pusaka 4, 91–98. doi: 10.33649/pusaka.v4i1.124
Ouko, N. G., Abuya, I. O., and Amolo, P. O. (2020). Stakeholder collaboration and resources mobilization for science activities in early years education programme in Kisumu West Sub-County, Kenya. J. Res. Method. 10, 24–35.
Özdogru, M., Çevik, M. N., and Çevik, M. S. (2024). Investigation of communication, social intelligence and intercultural sensitivity competencies of teacher candidates in sustainable education by structural equation modeling. Sustainability 16:9282. doi: 10.3390/su16219282
Polatcan, M., Özkan, P., and Bellibaş, M. S. (2024). Cultivating teacher innovativeness through transformational leadership and teacher agency in schools: the moderating role of teacher trust. J. Prof. Capital Commun. 9, 227–242. doi: 10.1108/JPCC-01-2024-0008
Qie, L., and Quan, C. (2024). Relationship between the educational service quality, student satisfaction, school trust, and student loyalty among Chinese University Students. Kor. Assoc. Learn. Cent. Curric. Instruct. 24, 478–491. doi: 10.22251/jlcci.2024.24.23.478
Rahmawati, R., Daud, F., and Bahri, A. (2024). The correlation between self-efficacy, self-confidence, and metacognitive skills on biology learning outcomes of student's high school. Biosfer Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi 17, 473–484. doi: 10.21009/biosferjpb.43918
Ramadina, E. (2024). Supervisi manajerial untuk meningkatkan mutu penyelenggaraan pendidikan sekolah dasar di era society 5.0. Jurnal Manajemen Pendidikan 9, 34–43. doi: 10.34125/jmp.v9i1.363
Ramos, L., Sanchez, S., Scyner, L., and Amigon, R. (2023). Teacher adaptability to change in special education: creativity and commitment to the institution. Can. J. Educ. Soc. Stud. 3:131. doi: 10.53103/cjess.v3i2.131
Ritonga, A. W., and Desrani, A. (2022). Framework of smart learning technology in supporting quality of higher education in Indonesia. Int. J. Multidiscipl. Res. Growth Eval. 283–289. doi: 10.54660/anfo.2022.3.6.11
Rosana, E. (2022). The role of school operators in data and information system management and service to improve school quality. Indones. J. Educ. 3, 216–225. doi: 10.54443/injoe.v3i2.27
Saravanan, D. S. K. (2022). A block-chain based framework for educational domain and its benefits. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 10, 336–341. doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2022.39819
Shah, S. A. A., Jajja, M. S. S., and Chatha, K. A. (2023). Antecedents and consequences of effective customer participation: the role of customer education and service modularity. J. Serv. Theory Pract. 33, 697–720. doi: 10.1108/JSTP-08-2022-0171
Sharkov, F. I., Abisheva, V. T., Luchina, M. A., Potapchuk, V. A., and Ramazanova, Z. S. (2022). New communication trends in education: digital technologies and artificial intelligence. Communicology 10, 67–86. doi: 10.21453/2311-3065-2022-10-3-67-86
Shulla, K., Filho, W. L., Lardjane, S., Sommer, J. H., and Borgemeister, C. (2020). Sustainable development education in the context of the 2030 Agenda for sustainable development. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 27, 458–468. doi: 10.1080/13504509.2020.1721378
Shvindina, H., Petrushenko, Y., and Balahurovska, I. (2022). Global experience of establishing new standards in education: the case of global network of learning cities and perspectives for Ukraine. Educ. Anal. Ukraine 5, 106–118. doi: 10.32987/2617-8532-2022-5-106-118
Sidhu, A., Singh, A., Qazi, S., and Bhalla, P. (2023). Social media, social capital, and knowledge sharing: Impact and implications for the higher education governance. Corp. Bus. Strat. Rev. 4 (4, special issue), 227–234. doi: 10.22495/cbsrv4i4siart3
Siti, H. (2024). Tantangan dalam Pendidikan MIPA dan Solusinya untuk Pendidikan Inklusif. Polygon : Jurnal Ilmu Komputer Dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam 3, 11–17. doi: 10.62383/polygon.v3i1.339
Sneesl, R., Jusoh, Y. Y., Jabar, M. A., and Abdullah, S. (2022). Revising technology adoption factors for IoT-based smart campuses: a systematic review. Sustainability 14:4840. doi: 10.3390/su14084840
Urbanus, U. (2024). Use of Digital Technology in Education at The State Institut of Christiany Palangka Raya. Journal of Learning and Technology 3, 29–37. doi: 10.33830/jlt.v3i1.9732
Vivi, S., Annisa Harahap, M., Yusri Ali, L., and Sahkholid, N. (2024). Tantangan dan Peluang Pembelajaran Bahasa Arab di Era Digital. Mutiara 3, 76–86. doi: 10.59059/mutiara.v3i1.1969
Wang, F., Zhang, J., and Zhang, P. (2021). Influencing factors of smart community service quality: evidence from China. Tehnicki Vjesnik - Technical Gazette 28:94941. doi: 10.17559/TV-20210429094941
Wang, L., and Wang, Y. (2023). Design and implementation of STEAM programs in vocational schools in a smart education environment. Contemp. Educ. Teach. Res. 4, 677–684. doi: 10.61360/BoniCETR232015491212
Widayanthi, D. G. C., Yudana, I. M., Agung, A. A. G., and Ariawan, I. P. W. (2024). Effect of workplace spirituality and servant leadership on service quality in higher education: a mediation model of job satisfaction. Glob. Bus. Finan. Rev. 29, 57–67. doi: 10.17549/gbfr.2024.29.3.57
Yan, L., and Trisakhon, C. (2024). the impact of corporate brand competitiveness and service quality on customer loyalty in using smart classroom products: a case of Beijing Oriental Zhongyuan Digital Technology Co., Ltd. RMUTT Global Bus. Account. Finan. Rev. 8, 32–45. doi: 10.60101/gbafr.2024.276325
Yusuf, M., and Arif, M. (2022). Implementation of interactive multimedia to improve understanding of Arabic Rules in Jar and Athaf Letters. ELOQUENCE 1, 138–152. doi: 10.58194/eloquence.v1i3.386
Zhang, Y. (2024). An investigation of the differences in education between China's urban and rural areas from the standpoint of educational equity. Lect. Notes Educ. Psychol. Public Media 39, 142–147. doi: 10.54254/2753-7048/39/20240700
Zheng, C.-Q., and Ouyang, H. (2023). Factors influencing quality of transnational education: evidence from a Sino-UK MA program. Front. Psychol. 13:1099359. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1099359
Keywords: smart education, remote regions, stakeholder collaboration, digital literacy, educational infrastructure
Citation: Sapiah S, Ulfah SM, Saputra AN and Hardi R (2025) Smart education in remote areas: collaborative strategies to address challenges in Majene Regency, Indonesia. Front. Educ. 10:1552575. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1552575
Received: 28 December 2024; Accepted: 12 June 2025;
Published: 04 July 2025.
Edited by:
Paitoon Pimdee, King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, ThailandReviewed by:
Unik Hanifah Salsabila, Universitas Ahmad Dahlan, IndonesiaMuhammad Luthfi Hamzah, State Islamic University of Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Sapiah, Ulfah, Saputra and Hardi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sitti Sapiah, c2l0dGlzYXBpYWhAZ21haWwuY29t
 Sitti Sapiah
Sitti Sapiah St. Maria Ulfah2
St. Maria Ulfah2 Rudi Hardi
Rudi Hardi