- 1Institute for Educational Technology, National Research Council, Genova, Italy
- 2Hybrid Intelligence, Capgemini Engineering, Milan, Italy
The increasing complexity of career decision-making, shaped by rapid technological advancements and evolving job markets, highlights the need for more responsive and data-informed post-diploma guidance. Machine learning (ML), a core component of artificial intelligence, is gaining attention for its potential to support personalized educational and career decisions by analyzing academic records, individual preferences, and labor market data. Despite growing interest, research in this field remains fragmented and methodologically diverse. This scoping review maps the application of ML in post-diploma guidance by examining the types of models used, data sources, reported outcomes, and ethical considerations related to fairness, privacy, and transparency. A systematic search of Scopus and Web of Science was conducted, with the final search completed on December 31, 2023. Twenty-one studies met the inclusion criteria, primarily employing supervised or mixed-method ML techniques to develop recommendation systems or predictive models. While several contributions report positive technical performance, evidence on educational effectiveness and user impact is limited. Ethical concerns such as bias, opacity, and limited explainability are acknowledged but not consistently addressed. The findings point to the need for more rigorous empirical research, greater methodological transparency, and the integration of educational perspectives to ensure that ML-based systems for career guidance are used responsibly and with clear added value.
1 Introduction
1.1 Rationale
The rapid evolution of technology and the shifting demands of the labor market have made career decision-making increasingly complex for students. The 21st-century job landscape is characterized by the decline of traditional occupations and the emergence of new professions, raising concerns about students’ ability to make informed educational and professional choices (Rojewski and Hill, 2017). Unequal access to higher education opportunities further compounds these challenges, particularly for students with limited access to career guidance resources (Billett et al., 2022).
Despite ongoing efforts to improve career decision-making frameworks, students often lack structured pathways to guide their post-diploma choices, underscoring the need for more effective support systems (McKenzie et al., 2017). Machine learning (ML) has emerged as a promising tool in this context, offering data-driven, personalized career guidance. By analyzing academic records, sociodemographic data, and personal preferences, ML models have demonstrated their ability to support decision-making processes in education, particularly in personalizing learning experiences and predicting academic success (Basu et al., 2019; Fernandes et al., 2023; Rusdi et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2020). However, research on the application of ML in post-diploma guidance remains fragmented, necessitating a systematic exploration of existing studies to understand its role, limitations, and potential impact.
This scoping review systematically maps the existing literature on ML applications in post-diploma guidance. It identifies the types of models employed, the data sources used, and the outcomes achieved while also addressing ethical and practical challenges such as fairness, privacy, and transparency in automated guidance systems. By analyzing current research and identifying gaps in the field, this review aims to inform the development of ML-driven career guidance tools and highlight key considerations for their responsible implementation.
Given the emerging nature of this field and the diversity of methodologies employed in existing studies, a scoping review was selected as the most appropriate approach. Unlike systematic reviews, which focus on assessing the quality of evidence, scoping reviews provide a broad overview of a research area, making them particularly suited to topics with evolving methodologies and interdisciplinary applications (Tricco et al., 2018). By synthesizing available knowledge, this review offers insights for researchers, educators, and policymakers, supporting future research and the responsible adoption of ML in career guidance.
1.2 Objectives
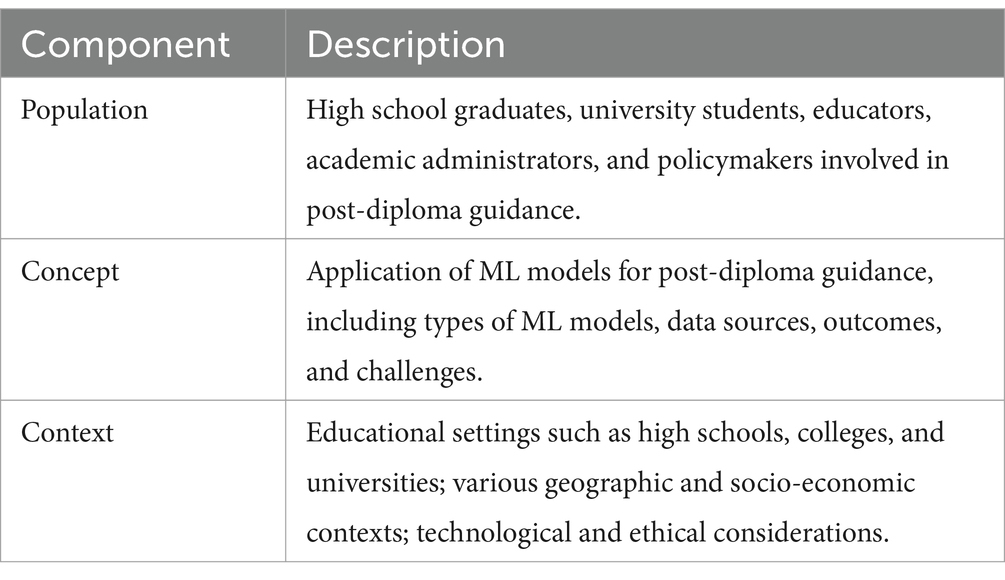
The research questions for this scoping review were structured using the Population, Concept, and Context (PCC) framework (Peters et al., 2020; Pollock et al., 2023) to ensure a systematic and comprehensive approach. In line with Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) guidelines, this framework refined the objectives and established clear eligibility criteria. It provided a structured basis for defining the review focus, guiding the search strategy, and determining inclusion and exclusion criteria, ensuring a transparent and replicable methodology.
The PCC framework is particularly suited for scoping reviews, as it enables a structured yet flexible formulation of research questions, essential for mapping broad and heterogeneous fields (Arksey and O’Malley, 2005; Levac et al., 2010). Unlike systematic reviews, which require narrowly defined questions and strict inclusion criteria, scoping reviews aim to capture the breadth of existing literature, identify gaps, and inform future research (Westphaln et al., 2021). The PCC framework supports this goal by explicitly delineating key study dimensions. Table 1 summarizes its primary elements as applied to this study, while Table 2 provides a detailed breakdown of each component.
By categorizing the research question into population, concept, and context, the study ensured methodological coherence and clear eligibility criteria. This scoping review systematically mapped the research landscape, analyzed the role of machine learning (ML) in post-diploma guidance, and identified knowledge gaps. The following research questions were formulated based on the PCC framework:
• RQ 1: What types of ML models are used in post-diploma guidance, and what are their specific applications? This question explores various ML models, such as neural networks, decision trees, and support vector machines, and their uses in personalized educational and career guidance.
• RQ 2: What data sources are utilized in ML models for post-diploma guidance? This question identifies data sources like academic records, sociodemographic information, personal preferences, and standardized test scores, and their contributions to model effectiveness.
• RQ 3: What outcomes have been reported in studies applying ML models for post-diploma guidance? This question assesses outcomes such as improved decision-making, prediction of academic success, career path optimization, and personalized recommendations to evaluate ML model effectiveness.
• RQ 4: What challenges and ethical considerations are associated with using ML models in post-diploma guidance? This question explores challenges like data quality, ethical issues, model transparency, privacy concerns, and adaptability to local contexts in educational settings.
2 Methods
2.1 Protocol and registration
The protocol for this scoping review was developed in advance following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) framework (Tricco et al., 2018) which ensures methodological transparency and consistency across eligibility criteria, search strategy, data extraction, and synthesis. The protocol guided the systematic mapping of ML applications in post-diploma career guidance and supports the identification of key themes and gaps in the literature. It was registered using the Generalized Systematic Review Registration Form on Open Science Framework (OSF) and is publicly available at: https://osf.io/vxyzg.
2.2 Eligibility criteria
To ensure the relevance and methodological rigor of this scoping review, a set of clearly defined inclusion and exclusion criteria was established in alignment with the research focus. These criteria were developed to guarantee that the selected studies were consistent with the objective of investigating ML applications in post-diploma educational and career guidance, while maintaining academic reliability.
Studies were included if they examined the use of artificial intelligence techniques, specifically ML, deep learning, or neural networks, in support of career guidance, university selection, or related decision-making processes. The focus had to be explicitly on post-diploma guidance, particularly in relation to transitions toward higher education or professional pathways. Eligible studies targeted high school graduates, university students, educators, or policymakers involved in post-secondary decision-making. To ensure scholarly quality, only peer-reviewed journal articles, book chapters, conference proceedings, and review papers were considered.
Studies were excluded if they did not specifically address AI or ML in the context of educational or career guidance. Articles unrelated to decision-making processes in education, non-peer-reviewed sources, and those not published in English were also excluded.
2.3 Information sources
The search strategy for this scoping review was conducted using two academic search engines, Scopus and Web of Science (All Database). These databases were selected due to their comprehensive indexing of peer-reviewed literature across multiple disciplines, ensuring broad coverage of relevant studies on machine learning applications in post-diploma career guidance.
To maximize inclusivity, no time frame restrictions were applied, allowing the review to capture all pertinent studies published to date. The last search was conducted on December 31, 2023, ensuring that the review reflects the most recent research available at the time of data collection.
The literature search was limited to published, peer-reviewed sources and did not include grey literature, direct author contacts, or manual searches of reference lists. This decision was made to maintain a focus on rigorously vetted academic contributions while ensuring consistency in methodological quality.
2.4 Search strategy
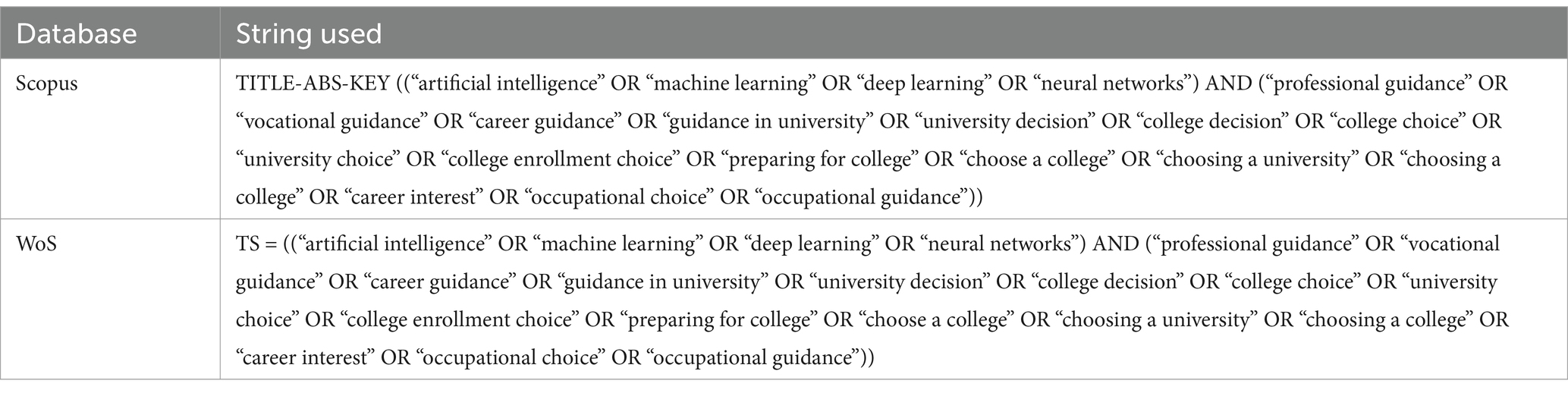
To ensure transparency and reproducibility, a structured search strategy was implemented across two academic databases: Scopus and Web of Science (WoS).
For Scopus, the TITLE-ABS-KEY field was used to retrieve studies containing relevant keywords in the title, abstract, or keywords section. The search string combined terms related to artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks with those associated with career guidance, university selection, and post-secondary decision-making.
For WoS, the TS (Topic Search) field was applied, ensuring that both titles and abstracts were searched for the same set of keywords, maintaining consistency between databases and optimizing retrieval of relevant literature while minimizing irrelevant results.
No filters or language restrictions were applied to maximize inclusivity. The full search strategy, including exact search strings and the number of records retrieved from each database, is provided in Table 3 to allow for full replication of the search process.
2.5 Selection of sources of evidence
The bibliographic search conducted in Scopus and Web of Science (WoS) retrieved 144 and 39 records, respectively. Following the completion of database searches, all records were exported in CSV format and compiled into a shared Microsoft Excel document for screening.
To ensure a rigorous and standardized selection process, duplicate entries were identified and removed, leaving 148 unique records for initial assessment. A team of four researchers independently screened the titles and abstracts of each article based on the predefined eligibility criteria. A calibration exercise was conducted before screening began to ensure consistency in the selection process. Studies were retained if they received at least 75% favorable votes from the reviewers. In cases of disagreement, inclusion decisions were resolved through discussion and consensus among the research team. This process resulted in a selection of 50 studies for full-text evaluation.
2.6 Data charting process
A data charting form was developed in Microsoft Excel to systematically extract information relevant to the research questions. The form was designed to capture key study characteristics, including publication details, study design, data collection methods, sample characteristics, ML methodologies, and study focus.
To ensure consistency and reliability, a calibration exercise was conducted before full data extraction, allowing the research team to refine the form based on an initial set of studies. Four researchers independently charted the data from each study, and any discrepancies were resolved through discussion and consensus.
The charting process was iterative, with periodic team discussions to address inconsistencies, clarify categorizations, and refine the extraction framework. Revisions to the charting form were made as needed to improve clarity and ensure all relevant variables were consistently recorded.
The final consolidated dataset provided a structured and comprehensive foundation for analysis, ensuring that key insights on the application of machine learning in post-diploma guidance were systematically captured and reported.
2.7 Data items
To systematically map the scope of ML applications in post-diploma guidance, data were extracted on key study characteristics. Publication details included author, year of publication, and country of origin. Study characteristics encompassed research design, methodological approach, and the primary focus of the study.
Information on data collection methods was recorded, identifying the types of data sources used, such as surveys, academic records, digital footprints, user interaction data, and qualitative sources, including interviews and focus groups. Population characteristics were documented, including sample size and participant profiles, to provide insights into the scope and representativeness of each study.
The primary focus of each study was classified based on its application within post-diploma career guidance. Additionally, details on ML methodologies were extracted, distinguishing between supervised, unsupervised, and mixed-method approaches, as well as specific algorithmic techniques applied in the studies.
2.8 Critical appraisal of individual sources of evidence
A formal quality assessment was not conducted, as this scoping review aimed to map the existing literature rather than evaluate study validity or risk of bias (Tricco et al., 2018). Given the emerging nature of ML in post-diploma guidance, prioritizing breadth over appraisal ensured the inclusion of diverse sources, including conference proceedings, which often capture cutting-edge developments. Applying strict quality criteria could have excluded relevant exploratory studies, limiting the review’s scope. Instead, transparency in selection and methodology was maintained to provide a comprehensive overview of current research and gaps in the field.
However, a descriptive reflection on the methodological features of the included studies was carried out to support the interpretation of findings. This reflection was informed by dimensions inspired by established evaluation frameworks such as the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (Wells et al., 2000), including the representativeness of the study sample, clarity in the documentation of data sources and preprocessing, consistency and appropriateness of evaluation procedures, and the extent to which studies controlled for relevant variables or reported interpretability measures.
The results of this reflection are presented in the section describing the critical appraisal within sources of evidence and are intended to support future methodological improvements in this area of research.
2.9 Synthesis of results
To systematically analyze and categorize the findings of this scoping review, we employed a qualitative content analysis approach (Elo and Kyngäs, 2008). A deductive framework was applied, structuring data extraction around eight predefined categories aligned with the PCC framework.
The extracted data were synthesized based on key dimensions of ML applications in post-diploma guidance, including the types of ML models used, their methodological characteristics, and their specific applications in career and university decision-making. Additionally, data on dataset types, impact on student choices, emerging trends, and challenges (including ethical considerations) were documented.
To ensure consistency and transparency, we also recorded publication details (author, year, country), study characteristics (design, data collection methods), and population characteristics (sample size, degree level).
The results are presented using a structured narrative synthesis, supported by Table 4, which maps the analyzed categories to each research question. This structured approach enhances clarity and facilitates the identification of patterns and gaps in the literature.
3 Results
3.1 Selection of sources of evidence
A total of 183 records were retrieved through database searches (144 from Scopus and 39 from Web of Science). After removal of duplicates, 148 unique records remained for screening.
During title and abstract screening, 98 studies were excluded for not meeting the eligibility criteria, leaving 50 full-text articles for further assessment. At this stage, 29 studies were excluded due to reasons such as lack of direct relevance to ML in post-diploma guidance, insufficient methodological detail, or focus on non-educational contexts. No studies were excluded due to lack of accessibility, as all full texts were available.
To further clarify how these criteria were applied at this stage, we include several illustrative examples of excluded studies. These include works that, while addressing educational or vocational guidance using AI-related or data-driven methods, did not meet the operational definition of machine learning adopted in this review. For example, Lahoud et al. (2023) proposed a hybrid recommender system based on ontologies and case-based reasoning, but without any form of model training or adaptive learning. Paterson and Guerrero (2023) focused on student retention using traditional statistical methods such as logistic regression and discriminant analysis, with only superficial references to ML. Tenison et al. (2023) applied structural topic modeling for college recommendation, a probabilistic approach that does not fall within the scope of machine learning. Finally, Kleshinski et al. (2009) used neural networks to predict medical exam performance, but in a context unrelated to post-diploma educational or career transitions. These examples illustrate how the inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied to ensure consistency in both methodological and thematic scope.
The final selection comprised 21 studies, forming the core body of evidence for this scoping review. Figure 1 presents a PRISMA flow diagram, outlining the full study selection process, including the number of records retrieved, screened, assessed for eligibility, and excluded at each stage, along with the reasons for exclusion. This structured approach ensures transparency and reproducibility in study selection.
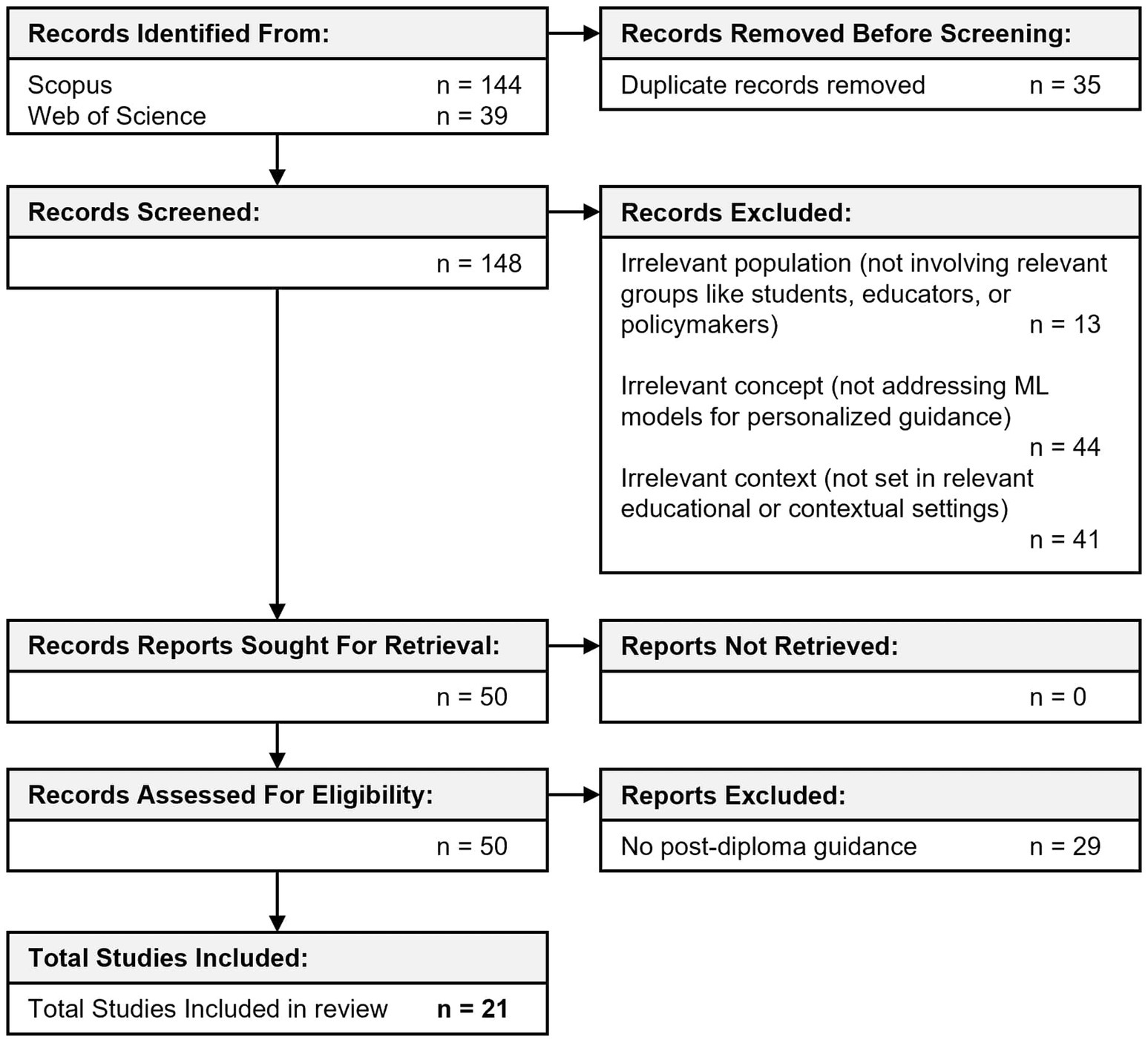
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram outlining the screening process, including reasons for exclusions and final sources of evidence.
3.2 Characteristics of sources of evidence
Key characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Supplementary Table 1, providing an overview of the methodological approaches, data sources, and ML applications in post-diploma guidance. The table details each study’s author, year of publication, country of origin, research design, data collection methods, sample characteristics, ML techniques, and study focus to ensure a comprehensive synthesis of the literature.
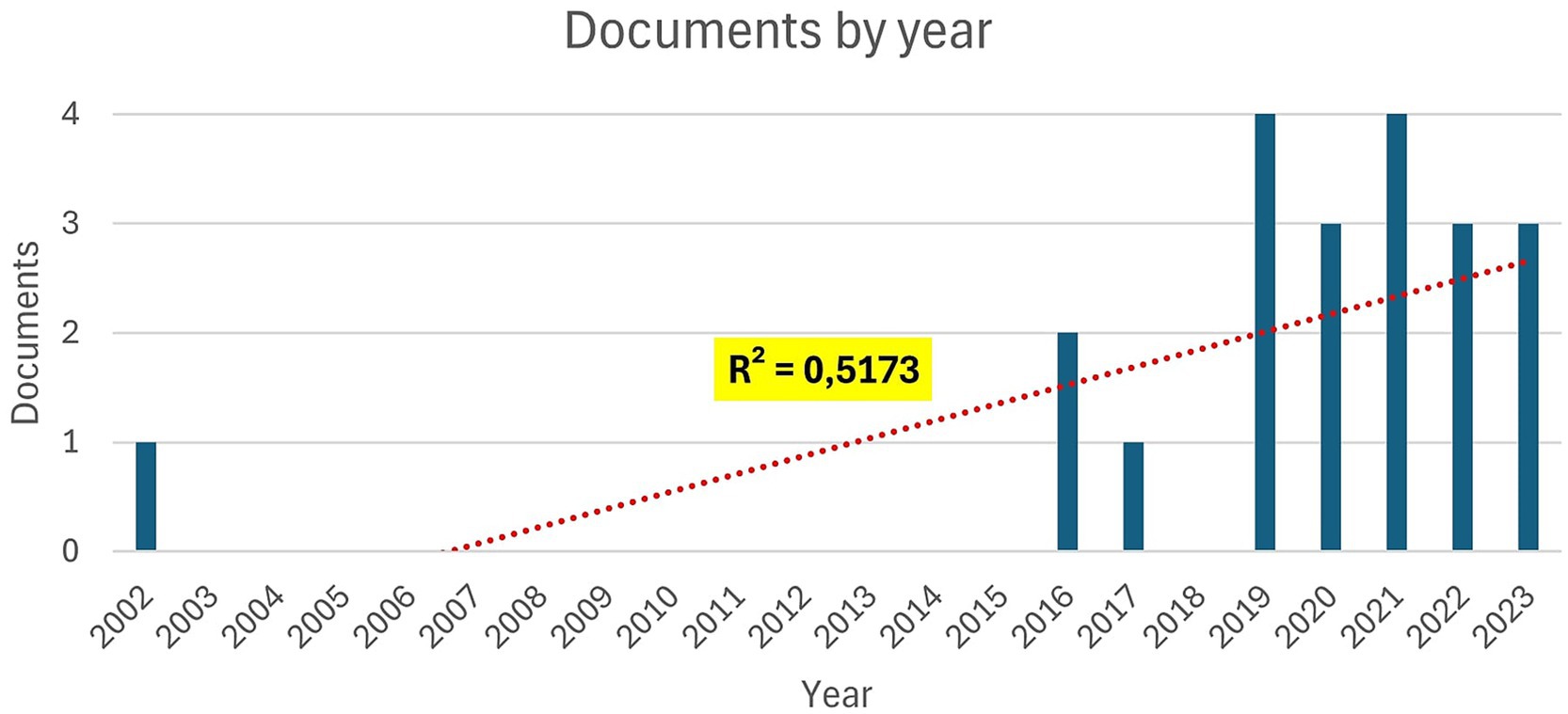
The temporal distribution of the included studies is illustrated in Figure 2. The earliest study dates to 2002 (González and DesJardins, 2002), with a gradual increase in publications observed from 2016 onward (e.g., Gupta et al., 2016; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016). A more consistent presence appears between 2019 and 2023 (e.g., Alghamdi et al., 2019; Kiselev et al., 2020a; Dawson et al., 2021; Chekalev et al., 2022; José-García et al., 2023), although the overall number of studies remains relatively limited. Despite some variability across years, the linear trend (R2 = 0.5173) indicates a moderate upward trajectory in research activity. This pattern reflects a growing, albeit still emerging, interest in AI-supported and immersive technologies applied to post-diploma educational and career guidance.
The dominant study design involved the development and evaluation of AI-based systems, with the majority of studies focusing on system implementation and effectiveness (e.g., Alghamdi et al., 2019; Goyal et al., 2023; Kiselev et al., 2020a; Kolhe et al., 2023; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019). One study conducted a comparative analysis of ML methods applied to student application data (González and DesJardins, 2002). Two studies proposed theoretical models for the application of AI in guidance (El Haji and Azmani, 2020; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019). Additionally, one study reported on the development and implementation of a decision support system (Chekalev et al., 2022), while another presented an implementation and validation study (Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016). A further study employed a multi-method and mixed-method approach to explore AI support in study planning (Westman et al., 2021), illustrating the methodological diversity within the field.
Data collection methods varied across studies. Surveys and questionnaires were employed in several studies, including those by Sapare and Beelagi (2021), Alghamdi et al. (2019), and José-García et al. (2023), highlighting the importance of user feedback in evaluating guidance systems. Academic and performance records were used by Lutfiyani and Arifin (2019), Vignesh et al. (2021), and Gupta et al. (2016) to inform predictive models. Digital footprint and user interaction data were applied in studies such as Kolhe et al. (2023), Kiselev et al. (2020a, 2020b), and Suvon et al. (2022). Data from educational platforms were utilized in Peker et al. (2017) and Dawson et al. (2021). Interviews and focus groups were employed in Najdi and Er-Raha (2016) and Westman et al. (2021), offering qualitative insights into system implementation and user perception.
The studies exhibited varied sample sizes, ranging from small cohorts, such as 64 university and high school students (José-García et al., 2023), to large datasets, including over 25,000 students with approximately 150,000 applications (Gupta et al., 2016) and more than 8 million job advertisements (Dawson et al., 2021). This variation reflects different research scopes, where large-scale datasets support broader generalizability, while smaller samples allow for more context-specific or exploratory analysis.
Regarding ML applications, eleven studies focused on university and career recommendation systems (e.g., Alghamdi et al., 2019; Chekalev et al., 2022; El Haji and Azmani, 2020; Goyal et al., 2023; Huang, 2022; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; Kiselev et al., 2020a; Kiselev et al., 2020b; Kolhe et al., 2023; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019; Peker et al., 2017). Two studies examined the prediction of admission to academic programs (Gupta et al., 2016; Suvon et al., 2022), while one investigated job retention using labor market data (Dawson et al., 2021). One study assessed the likelihood of student application to specific institutions (González and DesJardins, 2002), and another addressed academic performance prediction (Sapare and Beelagi, 2021). Additional studies focused on skill-market compatibility (José-García et al., 2023), student clustering (Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016), and study planning support (Westman et al., 2021). Finally, one study classified career guidance questions based on Holland’s typology (Zahour et al., 2019).
Mixed ML approaches, combining supervised and unsupervised techniques, were employed in nine studies (e.g., Alghamdi et al., 2019; Chekalev et al., 2022; Goyal et al., 2023; Kolhe et al., 2023; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019; Vignesh et al., 2021). Supervised learning was used in eight studies (e.g., Dawson et al., 2021; González and DesJardins, 2002; Gupta et al., 2016; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; Kiselev et al., 2020a, 2020b; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021; Suvon et al., 2022). Unsupervised learning was identified in three studies (José-García et al., 2023; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016; Peker et al., 2017). These results suggest a prevalent reliance on hybrid approaches to benefit from the strengths of both predictive accuracy and pattern discovery.
These findings highlight the diversity of ML applications, methodological approaches, and data sources employed in the context of post-diploma guidance. Supplementary Table 1 provides a detailed overview of each study, ensuring transparency and supporting comparative analysis. In particular, the columns “ML algorithm families” and “Target” allow for a clear mapping between the types of machine learning models adopted and their specific educational or guidance-related applications.
3.3 Critical appraisal within sources of evidence
A descriptive reflection on the methodological quality of the included studies revealed substantial variability across key dimensions. In terms of sample representativeness, several studies relied on large and well-documented datasets, such as González and DesJardins (2002), who analyzed ACT score senders from cohorts exceeding 20,000 students, and Gupta et al. (2016), who processed over 150,000 graduate applications. In contrast, other contributions such as Alghamdi et al. (2019) and Chekalev et al. (2022) used small-scale or pilot data with unclear recruitment procedures, and some, like El Haji and Azmani (2020), did not involve empirical samples at all.
Regarding data source transparency, most studies clearly described their inputs and variables, particularly those using institutional records (e.g., José-García et al., 2023; Suvon et al., 2022) or publicly available corpora. However, several system prototypes and student-led implementations (e.g., Goyal et al., 2023; Vignesh et al., 2021) reported their datasets only partially or lacked detail on data origin and structure.
Preprocessing procedures were also unevenly reported. While advanced studies such as Dawson et al. (2021) and Kiselev et al. (2020b) implemented structured pipelines involving normalization, feature engineering, and dataset balancing, others provided little to no information on preprocessing (e.g., Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021), limiting reproducibility and model transparency.
Evaluation methods ranged from basic internal performance metrics to sophisticated validation protocols. For example, Gupta et al. (2016) and Zahour et al. (2019) employed multiple models, cross-validation, and statistical comparisons, whereas several conceptual contributions (e.g., Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019; El Haji and Azmani, 2020) did not report any model evaluation or implementation results.
Control for potential confounding variables was limited overall. Some studies incorporated demographic or academic controls to improve robustness (e.g., González and DesJardins, 2002; José-García et al., 2023), but most, particularly those using unsupervised or rule-based systems (e.g., Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016; Kolhe et al., 2023), did not address this aspect.
Finally, model interpretability remains an underexplored dimension. Although a few contributions discussed feature importance (e.g., Suvon et al., 2022) or visual outputs (e.g., José-García et al., 2023), the majority of studies relied on black-box algorithms without explaining decision processes (e.g., Goyal et al., 2023; Kiselev et al., 2020a), raising concerns about the transparency and accountability of ML systems applied to educational guidance.
3.4 Synthesis of results from sources of evidence
The analysis of the 21 contributions included in the final corpus reveals a common interest in the development and application of ML algorithms and AI techniques in career and academic guidance. The corpus showcases a variety of approaches and methods employed to tackle the challenges associated with choosing an educational path or professional career.
Many studies focus on the development of recommendation systems, fuzzy logic, and ML techniques to assist students in making informed decisions about university courses and career paths. These systems integrate factors such as students’ interests, competencies, and previous educational achievements, as well as unconventional sources like social media profiles. For example, Peker et al. (2017) discuss a fuzzy logic-based career guidance system called WEB-CGS, while Lutfiyani and Arifin (2019) propose a rule-based expert system based on the Case-Based Reasoning method. In Vignesh et al. (2021), the authors develop a decision-support tool using clustering algorithms based on students’ skill assessments.
Other studies explore predictive analysis and supervised ML models to forecast academic success, course admissions, or career choices. These models utilize historical data and latent variables to offer personalized predictions and guidance based on student profiles. For instance, González and DesJardins (2002) use artificial neural networks to predict application behavior, while Suvon et al. (2022) employ decision tree and random forest models to predict the likelihood of Bangladeshi students gaining admission to foreign universities. Similarly, Kolhe et al. (2023) experiment with synthetic datasets to model employability scenarios and optimize recommendation performance.
Several contributions examine the enhancement of the educational experience through AI and ML, including the development of intelligent chatbots and the integration of AI in student training. For instance, José-García et al. (2023) present a career guidance system using ML and network visualization, while Goyal et al. (2023) develop an AI-powered conversational assistant tailored to Indian students transitioning from school to university. In another case, Jimenez-Raygoza et al. (2019) propose a digital guidance ecosystem incorporating predictive models and student profiling, although it remains at the conceptual stage.
Additionally, some studies focus on analyzing demographic factors and external influences on educational choices, such as gender, social background, and labor market trends. For example, the study by Gupta et al. (2016) examined how student profiles and institutional features influenced admission decisions, explicitly including demographic factors such as socioeconomic background and country of origin. Dawson et al. (2021) used labor market data and national skills surveys to model the alignment between graduate competencies and employer demands, thus integrating external socioeconomic trends into their ML approach. Similarly, Kiselev et al. (2020b) analyzed digital footprints and personality typologies to support value-based identity development among Russian students.
The following sections provide a detailed overview of the results, organized according to the four review questions and the corresponding categories used for analysis. Each section addresses specific aspects of the application of ML models in post-diploma guidance, including the types of models used, the data sources utilized, the reported outcomes, and the challenges and ethical considerations associated with their use. This structured approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of the current state of research in this field.
4 Types of ML models for post-diploma guidance
4.1 Mapping the use of ML in predicting post-diploma choices
From the analysis of 21 studies in the corpus, a significant trend emerges in leveraging the power of data and ML to guide and predict students’ post-diploma choices in higher education.
From the point of view of the final objective of the individual applications, the following main categories could be identified:
• Classification of career guidance questions,
• Compatibility between skills and market demand,
• Identification of student clusters,
• Prediction of academic performance,
• Prediction of admission to academic programs,
• Prediction of job retention,
• Probability of student application to specific institutions,
• Recommendation of university or career choices,
• Support for study planning.
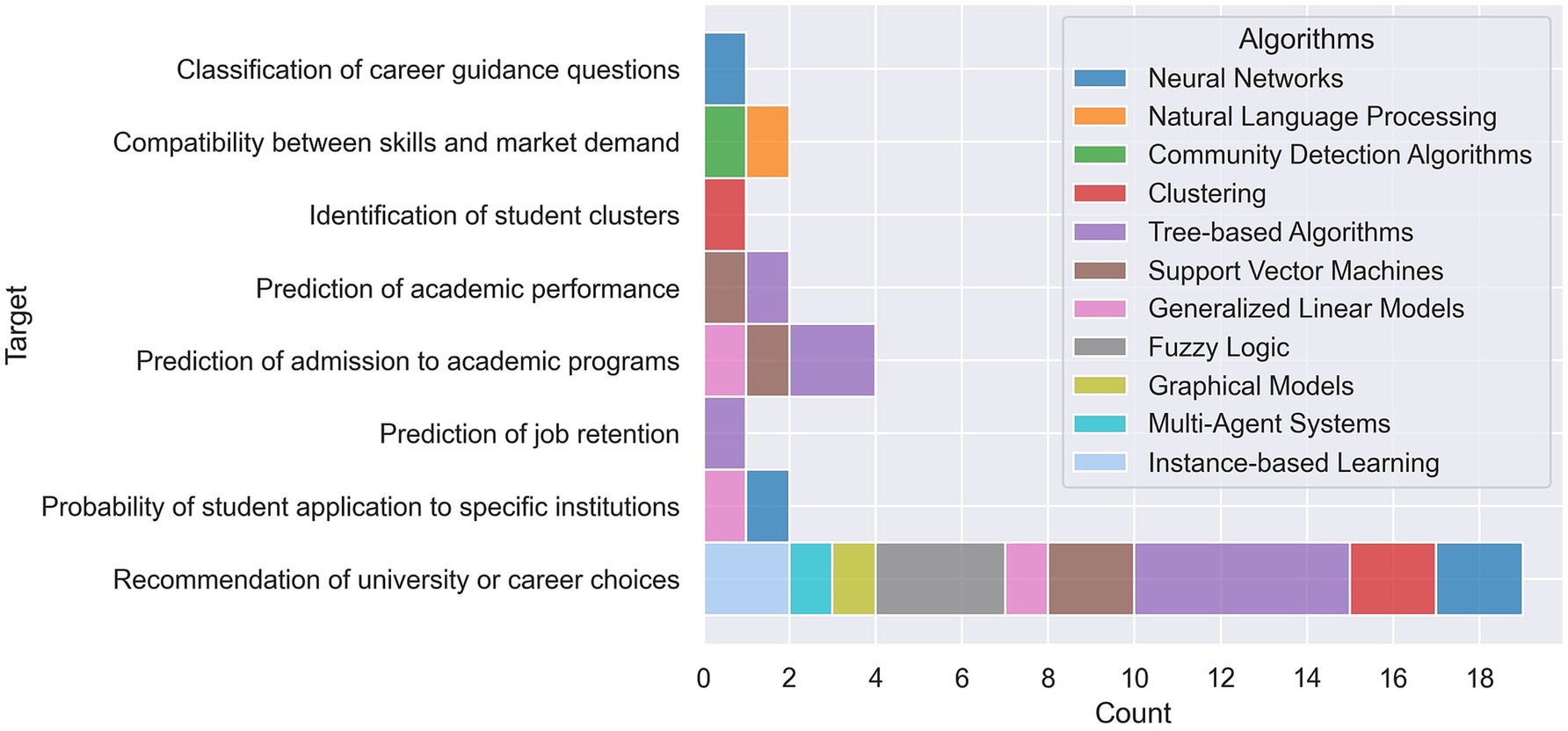
The stacked bar chart in Figure 3 visualizes the frequency of different ML methods used for various research targets. Each bar represents a target, with sections indicating the frequency of ML methods (Supervised, Unsupervised, Mixed). A combination of Supervised and Unsupervised approaches (indicated as Mixed methods) is mainly used for the challenging task of providing “Recommendation of university or career choices,” while supervised methods are common for “Prediction of academic performance,” “Prediction of job retention,” and “Classification of career guidance questions.” Unsupervised methods are used for “Identification of student clusters” and “Compatibility between skills and market demand.” Cases where the ML paradigm was not specified were excluded from the graphical representation.
Most of the studies analyzed aim for the challenging goal of providing students with a suitable recommendation towards academic and professional paths. For example, Peker et al. (2017) present a fuzzy logic-based career guidance system. Similarly, Vignesh et al. (2021), Chekalev et al. (2022), and Jimenez-Raygoza et al. (2019) describe the development of ML-based decision support systems to optimize the choice of study paths and professional careers. In this context, an interesting trend is the integration of AI with civic education, as illustrated in Huang (2022), where a career guidance system for university students integrates artificial intelligence and civic education.
Another large set of studies focuses on a different and more specific task, that is predicting students’ (or professionals’) behavior and performance in specific contexts – being it their applications to institutions or their academic or professional career. These types of tasks are well-suited to be tackled with supervised ML models trained with historical data. For example, González and DesJardins (2002), models trained on students’ performance records to predict student behavior in the university application process. Similarly, studies like Gupta et al. (2016) and Suvon et al. (2022) explore different SML models trained on similar data help applicants evaluate their chances of admission to graduate programs. Another task suited for supervised ML is the classification of survey questions within the well-known RIASEC categories defined by Holland (Nauta, 2010). Two studies (Kiselev et al., 2020b; Zahour et al., 2019) address this task with tree-based algorithms (Catboost) and neural networks, respectively.
Other studies focus on more unsupervised types of tasks, such as evaluating the level of match between skills and market demand (José-García et al., 2023), or the identification of student clusters with similar academic behavior (Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016).
Finally, a few studies, such as Peker et al. (2017) and Westman et al. (2021), explore the use of AI to provide timely and integrated guidance in daily learning activities.
4.2 Analysis of ML methodologies used
The 21 studies analyzed demonstrate a wide use of ML or, more broadly, data-driven techniques and algorithms to guide students’ decisions regarding higher education.
Among supervised learning algorithms, tree-based algorithms represent the most widely used algorithm family, in many cases due to the intuitive logic behind their decision process, which makes them among the most explainable models within the SML panorama. In particular, the basic Decision Tree (DT) algorithm emerged as the most frequently utilized method, appearing in six studies. Random Forest (RF) followed with four occurrences, while more powerful boosting approaches such as XGBoost, CatBoost and Adaboost appear in total in 5 studies. The latter methods are widely appreciated for the combination of explainability and prediction performance. Dawson et al. (2021), for instance, demonstrate the effectiveness of XGBoost to accurately predict occupational transitions based on labor market data, after training on historic examples of occupational transitions.
Another widely employed class of algorithms is the family of Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), and in particular fully connected architectures (often referred to as Multilayer Perceptrons, MLP), appearing in four studies. This indicates a growing interest in neural network approaches, due to their ability to obtain accurate predictions on complex classification or regression tasks, when provided with large numbers of training examples. In the work of Huang (2022), for instance, neural networks are used to design the recommendation module for employment units, helping to match students with suitable job opportunities.
Support Vector Machines (SVM), featuring in four studies, and Generalized Linear Models such as Logistic Regression, are often presented in parallel to other supervised approaches (RF, ANN, etc.). It is indeed common practice within a ML development pipeline to test several models, usually starting from the simplest ones, and select those performing best in the specific task at hand. For example, González and DesJardins (2002) use artificial neural networks to predict student behavior and academic performance, demonstrating the superiority of these techniques over more traditional statistical methods, such as logistic regression. Gupta et al. (2016), compare the performance of Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Adaboost and SVMs with different kernel functions in predicting admission to higher education programs.
Unsupervised approaches appear to be used especially for the identification of groupings within data, with K-Means Clustering featuring in two studies, and Louvain Community Detection Algorithm used in one study (José-García et al., 2023) to detect subcommunities within a wider network.
Fuzzy Logic was used in three studies, often combined with other techniques like graphical models or clustering, highlighting its versatile application in knowledge representation and reasoning. Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) and Nearest Neighbor Algorithm were noted in mixed approaches, emphasizing instance-based learning’s role in these studies.
Figure 4 illustrates the frequency of different ML algorithm families employed across various targets in the 21 studies analyzed. The stacked bar chart showcases a diverse range of ML algorithms, highlighting the tailored approaches researchers take to address specific problems within educational and career guidance systems.
4.3 Impact on university decision-making processes
Many studies (Alghamdi et al., 2019; Chekalev et al., 2022; Dawson et al., 2021; El Haji and Azmani, 2020; González and DesJardins, 2002; Goyal et al., 2023; Gupta et al., 2016; Huang, 2022; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; Kiselev et al., 2020a; Kiselev et al., 2020b; Kolhe et al., 2023; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016; Peker et al., 2017; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021; Suvon et al., 2022; Vignesh et al., 2021; Westman et al., 2021; Zahour et al., 2019) indicate how ML can be used to optimize the admission process and student guidance. Institutions can leverage these technologies to provide more accurate and personalized recommendations, thereby improving student experience and satisfaction.
ML algorithms enable universities to analyze large datasets to identify trends and patterns in student behavior. This can help institutions predict future needs and plan resources and services more effectively. For example, studies like González and DesJardins (2002), Zahour et al. (2019), José-García et al. (2023), and Kiselev et al. (2020a) demonstrate the utility of ML in understanding student preferences and behaviors, which can inform strategic planning and policy development.
The analysis of student data through ML allows universities to tailor educational offerings to the preferences and needs of students. This can increase the effectiveness of education and improve student success and retention rates. Studies such as Peker et al. (2017), Vignesh et al. (2021), and Chekalev et al. (2022) highlight how personalized recommendations and predictive analytics can enhance student outcomes by aligning educational pathways with individual aspirations and abilities.
5 Data sources in ML applications
5.1 Datasets used in the structured learning of an ML algorithm
The analysis of the 21 studies regarding the types of data (i.e., datasets) used in the structured learning of ML algorithms reveals the heterogeneity and complexity of the datasets employed, as well as their significance in influencing the learning and effectiveness of the models.
Various studies, such as Chekalev et al. (2022), El Haji and Azmani (2020), Goyal et al. (2023), Gupta et al. (2016), Huang (2022), Jimenez-Raygoza et al. (2019), Kiselev et al. (2020b), Kolhe et al. (2023), Sapare and Beelagi (2021), and Suvon et al. (2022), use detailed data on students that include academic aspects, sociodemographic information, career preferences, and standardized test performances. These data allow ML algorithms to learn and predict students’ post-diploma choices with greater accuracy. For example, Sapare and Beelagi (2021) and Suvon et al. (2022) employ academic records and admission exam scores. In the latter case, the authors report that data cleaning, normalization, SMOTE oversampling, and feature selection were essential to improve classification performance and reduce bias in predictions.
Some studies, such as Alghamdi et al. (2019), Dawson et al. (2021), González and DesJardins (2002), José-García et al. (2023), Kiselev et al. (2020a), Lutfiyani and Arifin (2019), Najdi and Er-Raha (2016), Peker et al. (2017), Vignesh et al. (2021), and Zahour et al. (2019), focus on specific data such as academic evaluations, skills, career interests, and digital footprints. These data are essential for providing personalized recommendations and effectively training ML models. For example, González and DesJardins (2002) use information on 40,000 students, including scores and course preferences, while José-García et al. (2023) analyze data from job advertisements and the O*NET database to connect student skills with labor market demands.
In the study by Gupta et al. (2016), the authors emphasize that the performance of the applied models, including ensemble learning and EM-based clustering, improved significantly when training was conducted on data that had been thoroughly preprocessed. Their dataset of over 150,000 applications was cleaned, normalized, and structured to maximize predictive accuracy and ensure generalizability across different institutional profiles.
The effectiveness of ML models in educational and career guidance is therefore strongly influenced by the availability and quality of structured data. When such data are incomplete, unbalanced, or poorly documented, the accuracy and reliability of the recommendations generated may be compromised, with potential implications for equity and relevance.
6 Reported outcomes of ML models
6.1 Evaluation of the impact of ML on student decisions
ML has a significant impact on the educational and professional decisions of students. While these technologies offer advanced predictive analytics and personalized guidance, it is essential to consider the importance of student autonomy and balance between data-driven advice and individual choices.
Numerous studies (Alghamdi et al., 2019; Chekalev et al., 2022; El Haji and Azmani, 2020; Goyal et al., 2023; Gupta et al., 2016; Huang, 2022; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; José-García et al., 2023; Kiselev et al., 2020a; Kiselev et al., 2020b; Kolhe et al., 2023; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019; Peker et al., 2017; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021; Vignesh et al., 2021) reveal a positive impact of ML on student decisions. These technologies provide personalized recommendations based on in-depth analysis of students’ skills, interests, and preferences, thus facilitating more informed and strategically advantageous decisions. For example, Chekalev et al. (2022) use recommender systems to help students choose appropriate academic and professional paths. Additionally, José-García et al. (2023) and Kiselev et al. (2020b) provide a visual representation of how students’ skills align with job roles in the IT sector, enhancing awareness of their abilities.
Some studies, such as Dawson et al. (2021), González and DesJardins (2002), Najdi and Er-Raha (2016), Suvon et al. (2022), Westman et al. (2021), and Zahour et al. (2019), do not provide a direct assessment of the impact of ML technologies on student choices but imply that such technologies can play a useful role in providing targeted and personalized guidance.
However, some studies also highlight potential negative implications, such as the possibility of excessive reliance on ML predictions, which could limit students’ spontaneity and freedom of choice (Kiselev et al., 2020b; Kolhe et al., 2023). This aspect requires a balance between the use of ML technologies and the ability to make autonomous decisions based on personal and contextual considerations.
6.2 Identification of trends and prospects
The exploration of trends and prospects for the use of ML in post-diploma guidance reveals an evolving landscape, with potential innovative applications and significant impacts on students and educational institutions.
Studies such as Chekalev et al. (2022) and Kiselev et al. (2020a) suggest a shift towards more integrated and complex ML systems that can handle heterogeneous and high-dimensional data. This indicates a trend towards more sophisticated and personalized recommendation and guidance systems.
Peker et al. (2017), Vignesh et al. (2021), Westman et al. (2021), and Kolhe et al. (2023) highlight the growth potential of ML in career guidance. An increase in the use of these systems is expected to personalize guidance and tailor educational paths to individual student needs.
As discussed in Zahour et al. (2019), there is potential for integrating ML with sentiment analysis from social media. This can enhance the classification of questions and student interests, offering more targeted and personalized guidance.
According to José-García et al. (2023), ML could evolve to analyze the skills required in the labor market, helping students visualize personalized career paths. This approach is crucial for aligning education with labor market needs.
Many studies (Alghamdi et al., 2019; Dawson et al., 2021; El Haji and Azmani, 2020; Goyal et al., 2023; Gupta et al., 2016; Huang, 2022; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; Kiselev et al., 2020b; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021; and Suvon et al., 2022) indicate that there will be an expansion in the use of advanced ML techniques such as neural networks, deep learning, and more sophisticated clustering methods. These methods can lead to more accurate predictions and personalized advice.
7 Challenges and ethical considerations in ML usage
7.1 Exploration of challenges and limitations
While ML offers potential benefits in guiding students in their educational and professional choices, it is essential to address technical, ethical, and practical challenges to ensure that such systems are effective, fair, and respectful of student privacy and autonomy.
Some studies (Alghamdi et al., 2019; Chekalev et al., 2022; Dawson et al., 2021; El Haji and Azmani, 2020; Goyal et al., 2023; Gupta et al., 2016; Huang, 2022; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; José-García et al., 2023; Kiselev et al., 2020a; Kolhe et al., 2023; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021; Suvon et al., 2022) highlight the need to manage large amounts of data and the complexity of ML models such as neural networks. Challenges like the cold-start problem (impacting recommender systems during their initial phase), and data sparsity (poorly populated datasets) are common. The necessity to continuously update models with new data to maintain their relevance and accuracy (Alghamdi et al., 2019; Huang, 2022; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; José-García et al., 2023; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021) is an ongoing challenge. Managing heterogeneous datasets and ensuring data reliability (Kiselev et al., 2020b; Kolhe et al., 2023; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016; Suvon et al., 2022) are additional complications.
The need to adapt ML systems to the specific needs of students and local contexts (Dawson et al., 2021; El Haji and Azmani, 2020; Peker et al., 2017; Vignesh et al., 2021; Westman et al., 2021) presents practical challenges. Some studies (González and DesJardins, 2002; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019) do not specifically address ML challenges but imply the need to consider the adaptability and applicability of models in different contexts.
Understanding and interpreting ML models (González and DesJardins, 2002; Gupta et al., 2016) is often complex, particularly when dealing with “black box” models that do not offer transparency in their decisions. The lack of a uniform definition of variable importance and sensitivity to initial choices in models (Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016) limits the effectiveness and reliability of predictions.
7.2 Ethical and social considerations
The reflection on ethical and social considerations in the use of ML technologies for post-diploma guidance is crucial. Many studies (Alghamdi et al., 2019; Chekalev et al., 2022; Dawson et al., 2021; El Haji and Azmani, 2020; González and DesJardins, 2002; Goyal et al., 2023; Gupta et al., 2016; Huang, 2022; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; José-García et al., 2023; Kiselev et al., 2020a; Kiselev et al., 2020b; Kolhe et al., 2023; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016; Peker et al., 2017; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021; Suvon et al., 2022; Vignesh et al., 2021; Westman et al., 2021; Zahour et al., 2019) highlight the need to ensure that ML models are free from prejudices and biases, especially when used for decisions that influence students’ academic and professional futures. The representativeness and impartiality of the data are crucial to ensure fairness in the recommendations provided. In this regard, algorithmic fairness emerges as a central concern. Models trained on non-representative datasets risk reinforcing existing inequalities, particularly when sensitive variables such as gender, socioeconomic status, or geographical location are not adequately considered.
Transparency in ML models is fundamental to ensuring the trust of users and stakeholders. These studies emphasize the importance of accountability in decisions generated by ML systems, particularly when they influence significant life paths. The absence of explainability mechanisms in black-box systems may limit users’ understanding of how outcomes are produced, which in turn can affect the perceived legitimacy of automated recommendations. This becomes especially critical when ML-based systems are deployed among vulnerable groups, such as students from underrepresented backgrounds or those with limited access to human guidance services.
The management of students’ personal data and their privacy is a critical ethical concern. Many studies (Alghamdi et al., 2019; Chekalev et al., 2022; Dawson et al., 2021; El Haji and Azmani, 2020; González and DesJardins, 2002; Goyal et al., 2023; Gupta et al., 2016; Huang, 2022; Jimenez-Raygoza et al., 2019; José-García et al., 2023; Kiselev et al., 2020a; Kiselev et al., 2020b; Kolhe et al., 2023; Lutfiyani and Arifin, 2019; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016; Peker et al., 2017; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021; Suvon et al., 2022; Vignesh et al., 2021; Westman et al., 2021; Zahour et al., 2019) discuss the need to protect sensitive information, ensuring that data use complies with privacy regulations and ethics. Privacy and responsible use of student data (Alghamdi et al., 2019; Chekalev et al., 2022; Sapare and Beelagi, 2021) are primary concerns. Ethical issues also arise from potential biases in ML models (Kiselev et al., 2020b; Kolhe et al., 2023; Suvon et al., 2022), which could negatively affect the representativeness and fairness of the recommendations.
The distinction between simple models with deterministic training and more complex models incorporating stochastic elements helps clarify how different approaches impact interpretability and reliability. Deterministic models may offer more transparency but lack flexibility in capturing complex student profiles, while models with greater predictive power may sacrifice explainability. Balancing these dimensions is essential to ensure that AI-based guidance systems support students effectively and equitably.
8 Discussion
The domain of ML in post-diploma guidance is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advances and growing awareness of the need for more personalized educational and career support. This discussion synthesizes findings from the review of 21 studies, highlighting thematic areas such as the evolution of research in the field, design and methodological trends, contributions to educational practice, future research directions, and the challenges and limitations that persist.
The integration of ML into educational guidance marks a transition from conventional models toward data-informed, adaptive systems. Initial work often concentrated on prediction and rule-based recommendations. More recent studies, however, demonstrate an expanded focus on real-time interaction, hybrid systems, and intelligent decision support. For example, José-García et al. (2023) describe a career guidance system that combines ML with network visualization tools to map compatibility between student skills and job profiles. Similarly, Kolhe et al. (2023) develop a multi-model pipeline to simulate employability outcomes using synthetic datasets, reflecting a growing emphasis on scalability and experimentation.
Methodologically, the landscape is highly diverse. A number of studies adopt supervised learning approaches for tasks such as admission prediction (e.g., Suvon et al., 2022) or academic performance estimation (Sapare and Beelagi, 2021), while others employ unsupervised or hybrid methods, including clustering and fuzzy logic systems (Peker et al., 2017; Najdi and Er-Raha, 2016). These methodological choices are closely tied to the nature of the available data, the intended outcome of the guidance system, and the level of interpretability required by users and institutions.
One of the most frequently cited benefits of ML in post-diploma guidance is its ability to deliver personalized recommendations. By integrating academic records, career preferences, and contextual information, ML models can generate tailored suggestions that support more informed student choices. For instance, Kiselev et al. (2020a) leverage digital footprints and psychometric data to develop a typological framework for aligning student values and identity with academic and career paths. In the same vein, Gupta et al. (2016) use large-scale application data and ensemble learning to build models that adapt to the specific characteristics of student profiles and institutional contexts.
In addition to academic recommendations, several systems incorporate broader behavioral and contextual indicators. For example, Goyal et al. (2023) present a chatbot interface designed to simulate human conversation and emotional responsiveness in guidance interactions. These approaches underscore the potential of ML to enrich the student experience, especially when integrated into multi-modal environments that include both digital and human support.
Nonetheless, significant challenges remain in the implementation of ML in educational guidance. A recurring issue concerns the quality and structure of the training data. As demonstrated by Suvon et al. (2022) and Gupta et al. (2016), the effectiveness of predictive models relies heavily on preprocessing steps such as normalization, balancing, and variable selection. Poor data quality may not only reduce model performance but also lead to biased or misleading recommendations.
Ethical considerations are central to this field. Several studies highlight the risks of algorithmic opacity and the potential for bias in ML-driven systems. Kiselev et al. (2020b) and Kolhe et al. (2023) emphasize the need to audit models for fairness and ensure that demographic variables such as gender or socioeconomic status do not inadvertently skew results. Transparency and accountability are also critical, particularly in contexts involving high-stakes decisions. Jimenez-Raygoza et al. (2019) stress the importance of building trust in AI-based systems through explainability and human-centered design, especially when guidance is offered to students from underrepresented or disadvantaged backgrounds.
8.1 Future research directions
The field of ML in post-diploma guidance is poised for further growth, with several promising research directions. The integration of more sophisticated AI techniques, such as deep learning and natural language processing, could enhance the predictive capabilities of these systems. Additionally, there is a growing interest in exploring the potential of real-time data analytics and adaptive learning systems, as suggested by Huang (2022).
Future research should also focus on developing more robust frameworks for the ethical use of ML in education. This includes creating standardized guidelines for data management, ensuring transparency in algorithmic decision-making, and addressing the broader social implications of AI-driven guidance systems.
The findings of this review have relevant implications for both institutional practices and educational policy. The increasing use of ML-based systems for university and career guidance reflects a shift toward more data-informed and personalized support mechanisms. Educational institutions could adopt these tools to complement the role of human advisors, especially in settings with limited guidance resources. Furthermore, the range of applications identified, from admission prediction to labor market alignment, demonstrates the adaptability of these systems across different educational and regional contexts.
At the policy level, ML systems may inform strategies aimed at reducing early school leaving, improving orientation processes, and strengthening the match between educational offerings and labor market demand. However, successful implementation requires careful attention to data availability, model transparency, and equity of access. Future initiatives should be accompanied by governance mechanisms that promote responsible use, including clear validation procedures, ethical safeguards, and alignment with human-centered educational practices.
8.2 Limitations
This review acknowledges several limitations that must be considered. Firstly, the use of multiple terms in the literature to describe ML models and their applications may have led to the exclusion of some relevant sources despite comprehensive search strategies. The rapidly evolving nature of AI technology implies that a review conducted in 5 years might present significantly different findings and trends than those discussed here. Additionally, some commercially available AI-driven guidance systems may still be under development and not yet documented in the academic literature, indicating a gap in our current understanding.
Another limitation is the variability in data quality and the heterogeneity of datasets used across studies, which can affect the generalizability and comparability of findings. The ethical concerns surrounding data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and potential biases in ML models also present significant challenges that warrant further investigation.
Despite these limitations, this review provides a valuable overview of current research activities and serves as a foundational resource for future studies. It highlights the critical need for ongoing research to keep pace with technological advancements and to ensure that ML applications in educational guidance remain relevant, effective, and ethically sound. Future research should aim to address these limitations by refining search strategies, exploring emerging AI technologies, and developing robust ethical frameworks for the deployment of AI-driven guidance systems.
9 Conclusion
This scoping review provides a structured overview of current research on the application of ML in post-diploma guidance. While the integration of ML into educational and career decision-making processes is a growing area of interest, the evidence remains fragmented and inconsistent in both methodological approaches and reported outcomes. Many contributions describe experimental systems or prototypes without clear validation of their educational effectiveness.
Although several studies present innovative models and technical architectures, few address how these tools perform in real-life settings or how they impact student outcomes. Evaluation often relies on internal performance metrics rather than independent measures of decision quality or user benefit. The link between model outputs and meaningful educational or career trajectories is not always made explicit.
Important challenges persist in terms of data quality, representativeness, and documentation. Many studies do not report how data were selected, cleaned, or balanced. Models are often tested on small or synthetic datasets, limiting the generalizability of findings. The heterogeneity of study contexts and the lack of common reporting standards make it difficult to compare results or synthesize best practices.
Ethical concerns such as algorithmic bias, opacity of model decisions, and the protection of student data are acknowledged but rarely examined in detail. Few studies propose concrete strategies to address fairness, inclusiveness, or accountability in the design and deployment of ML-based guidance systems.
Future research should engage more deeply with educational theory and incorporate interdisciplinary perspectives. Stronger empirical designs, longitudinal studies, and user-centered evaluations are needed to assess the actual contribution of ML to post-diploma decision-making. Greater attention should also be paid to the role of institutional and policy frameworks in shaping the adoption and governance of these technologies.
Author contributions
FM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. ER: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AV: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. GB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study presented in this paper has been carried out within the project ITAVER5O -Intelligent 5G-Technology-Assisted Virtual Experiences for Robust Student Orientation, co-funded by the Ministry of Enterprises and Made in Italy -MIMIT (CUP: B53C23004710004). The project involves the participation of eight partners: the Institute for Educational Technology of the Italian National Research Council (ITD-CNR), the University of Rome Tor Vergata, Capgemini Engineering, Vodafone Italia, HYPEX, SATIS Centro Clinico di Psicologia, PRODEA Group, and Digivox.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2025.1578979/full#supplementary-material
References
Alghamdi, S., Alzhrani, N., and Algethami, H. (2019). Fuzzy-based recommendation system for university major selection. IJCCI, 317–324. doi: 10.5220/0008071803170324
Arksey, H., and O’Malley, L. (2005). Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 8, 19–32. doi: 10.1080/1364557032000119616
Basu, K., Basu, T., Buckmire, R., and Lal, N. (2019). Predictive models of student college commitment decisions using machine learning. Data 4:65. doi: 10.3390/data4020065
Billett, S., Dymock, D., Hodge, S., Choy, S., and Le, A. H. (2022). “Shaping young People’s decision-making about post-school pathways: institutional and personal factors” in The standing of vocational education and the occupations it serves: Current concerns and strategies for enhancing that standing (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 103–136.
Chekalev, A. A., Khlobystova, A. O., and Tat’yana, V. T. (2022). “Applicant’s decision support system for choosing the direction of study” in In 2022 XXV international conference on soft computing and measurements (SCM) (St. Petersburg, Russia: IEEE), 226–228.
Dawson, N., Williams, M. A., and Rizoiu, M. A. (2021). Skill-driven recommendations for job transition pathways. PLoS One 16:e0254722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254722
El Haji, E., and Azmani, A. (2020). Proposal of a digital ecosystem based on big data and artificial intelligence to support educational and vocational guidance. Int. J. Modern Educ. Computer Sci. 12, 1–11. doi: 10.5815/ijmecs.2020.04.01
Elo, S., and Kyngäs, H. (2008). The qualitative content analysis process. J. Adv. Nurs. 62, 107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.x
Fernandes, C. W., Rafatirad, S., and Sayadi, H. (2023). “Advancing personalized and adaptive learning experience in education with artificial intelligence” in In 2023 32nd annual conference of the European Association for Education in electrical and information engineering (EAEEIE) (Eindhoven, The Netherlands: IEEE), 1–6.
González, J. M. B., and DesJardins, S. L. (2002). Artificial neural networks: a new approach to predicting application behavior. Res. High. Educ. 43, 235–258. doi: 10.1023/A:1014423925000
Goyal, R., Chaudhary, N., and Singh, M. (2023). “Machine learning based intelligent career counselling Chatbot (ICCC)” in 2023 international conference on computer communication and informatics (ICCCI) (Coimbatore, India: IEEE), 1–8.
Gupta, N., Sawhney, A., and Roth, D. (2016). “Will I get in? Modeling the graduate admission process for American universities” in In 2016 IEEE 16th international conference on data mining workshops (ICDMW) (Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain: IEEE), 631–638.
Huang, L. (2022). The establishment of college student employment guidance system integrating artificial intelligence and civic education. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 1–9. doi: 10.1155/2022/3934381
Jimenez-Raygoza, L. I., Medina-Vazquez, A. S., and Perez-Torres, G. (2019). “Proposal of a computer system for vocational guidance with data mining” in In 2019 IEEE international conference on engineering Veracruz (ICEV), vol. 1 (Veracruz, México: IEEE), 1–5.
José-García, A., Sneyd, A., Melro, A., Ollagnier, A., Tarling, G., Zhang, H., et al. (2023). C3-IoC: a career guidance system for assessing student skills using machine learning and network visualisation. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 33, 1092–1119. doi: 10.1007/s40593-022-00317-y
Kiselev, P., Feshchenko, A., Matsuta, V., and Bogdanovskaya, I. (2020a). “Career robot for managing college major choice” in INTED2020 proceedings (Valencia, Spain: IATED), 3925–3931.
Kiselev, P., Kiselev, B., Matsuta, V., Feshchenko, A., Bogdanovskaya, I., and Kosheleva, A. (2020b). Career guidance based on machine learning: social networks in professional identity construction. Procedia Computer Sci. 169, 158–163. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2020.02.128
Kleshinski, J., Khuder, S. A., Shapiro, J. I., and Gold, J. P. (2009). Impact of preadmission variables on USMLE step 1 and step 2 performance. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 14, 69–78. doi: 10.1007/s10459-007-9087-x
Kolhe, H., Chaturvedi, R., Chandore, S., Sakarkar, G., and Sharma, G. (2023). “Career path prediction system using supervised learning based on users’ profile” in Computational intelligence: Select proceedings of InCITe 2022 (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore), 583–595.
Lahoud, C., Moussa, S., Obeid, C., Khoury, H. E., and Champin, P. A. (2023). A comparative analysis of different recommender systems for university major and career domain guidance. Educ. Inf. Technol. 28, 8733–8759. doi: 10.1007/s10639-022-11541-3
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., and Obrien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement. Sci. 5, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-5-69
Lutfiyani, A., and Arifin, F. (2019). Case based reasoning: recommendations of high school student program. J. Physics 1413:012022. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1413/1/012022
McKenzie, S., Coldwell-Neilson, J., and Palmer, S. (2017). Informing the career development of IT students by understanding their career aspirations and skill development action plans. Aust. J. Career Dev. 26, 14–23. doi: 10.1177/1038416217697972
Najdi, L., and Er-Raha, B. (2016). “Implementing cluster analysis tool for the identification of students typologies” in In 2016 4th IEEE international colloquium on information science and technology (CiSt) (Tangier-Asilah, Morocco: IEEE), 575–580.
Nauta, M. M. (2010). The development, evolution, and status of Holland’s theory of vocational personalities: reflections and future directions for counseling psychology. J. Couns. Psychol. 57, 11–22. doi: 10.1037/a0018213
Paterson, K., and Guerrero, A. (2023). Predictive analytics in education: considerations in predicting versus explaining college student retention. Res. High. Educ. J. 44, 1–12. Available at: https://aabri.com/manuscripts/233654.pdf
Peker, M., Gürüler, H., Şen, B., and İstanbullu, A., (2017). A new fuzzy logic based career guidance system: WEB-CGS. Tehnički vjesnik 24, 6, 1863–1868. doi: 10.17559/TV-20151105201325
Peters, M. D., Marnie, C., Tricco, A. C., Pollock, D., Munn, Z., Alexander, L., et al. (2020). Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Synthesis 18, 2119–2126. doi: 10.11124/JBIES-20-00167
Pollock, D., Peters, M. D., Khalil, H., McInerney, P., Alexander, L., Tricco, A. C., et al. (2023). Recommendations for the extraction, analysis, and presentation of results in scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Synthesis 21, 520–532. doi: 10.11124/JBIES-22-00123
Rojewski, J. W., and Hill, R. B. (2017). A framework for 21st-century career-technical and workforce education curricula. Peabody J. Educ. 92, 180–191. doi: 10.1080/0161956X.2017.1302211
Rusdi, M. R., Enrico, T. G., Salomo, A. O., Gaol, F. L., and Matsuo, T. (2023). “February” in The model of personalized machine learning to enhance students’ achievements. In international conference on intelligent sustainable systems (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore), 701–712.
Sapare, N. S., and Beelagi, S. M. (2021). “Comparison study of regression models for the prediction of post-graduation admissions using machine learning techniques” in In 2021 11th international conference on cloud computing, Data Science & Engineering (confluence) (Uttar Pradesh, India: IEEE), 822–828.
Suvon, I., Siam, S. C., Ferdous, M., Alam, M., and Khan, R. (2022). Masters and doctor of philosophy admission prediction of Bangladeshi students into different classes of universities. IAES Int. J. Artif. Intelligence 11, 1545–1553. doi: 10.11591/ijai.v11.i4.pp1545-1553
Tenison, C., Ling, G., and McCulla, L. (2023). Supporting college choice among international students through collaborative filtering. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 33, 659–687. doi: 10.1007/s40593-022-00307-0
Tricco, A. C., Rios, P., Zarin, W., Cardoso, R., Diaz, S., Nincic, V., et al. (2018). Prevention and management of unprofessional behaviour among adults in the workplace: a scoping review. PLoS One 13:e0201187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201187
Vignesh, S., Priyanka, C. S., Manju, H. S., and Mythili, K. (2021). “An intelligent career guidance system using machine learning” in In 2021 7th international conference on advanced computing and communication systems (ICACCS), vol. 1 (Coimbatore, India: IEEE), 987–990.
Wells, G. A., Shea, B., O’Connell, D., Peterson, J., Welch, V., Losos, M., et al. (2000). The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Available online at: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (Accessed January 21, 2025).
Westman, S., Kauttonen, J., Klemetti, A., Korhonen, N., Manninen, M., Mononen, A., et al. (2021). Artificial intelligence for career guidance – current requirements and prospects for the future. IAFOR J. Educ. 9, 43–62. doi: 10.22492/ije.9.4.03
Westphaln, K. K., Regoeczi, W., Masotya, M., Vazquez-Westphaln, B., Lounsbury, K., McDavid, L., et al. (2021). From Arksey and O’Malley and beyond: customizations to enhance a team-based, mixed approach to scoping review methodology. MethodsX 8:101375. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2021.101375
Wu, J. Y., Hsiao, Y. C., and Nian, M. W. (2020). Using supervised machine learning on large-scale online forums to classify course-related Facebook messages in predicting learning achievement within the personal learning environment. Interact. Learn. Environ. 28, 65–80. doi: 10.1080/10494820.2018.1515085
Keywords: machine learning, post-diploma guidance, educational guidance, career guidance, predictive analytics, scoping review
Citation: Manganello F, Rasca E, Villa A, Maddalena A and Boccuzzi G (2025) Machine learning for post-diploma educational and career guidance: a scoping review in AI-driven decision support systems. Front. Educ. 10:1578979. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1578979
Edited by:
Kiran Deep Singh, Chitkara University, IndiaReviewed by:
Laura-Diana Radu, Alexandru Ioan Cuza University, RomaniaJenniffer Sobeida Moreira-Choez, State University of Milagro, Ecuador
Copyright © 2025 Manganello, Rasca, Villa, Maddalena and Boccuzzi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Flavio Manganello, ZmxhdmlvLm1hbmdhbmVsbG9AY25yLml0
 Flavio Manganello
Flavio Manganello Elisa Rasca2
Elisa Rasca2