- 1Department of Foreign Language, Inner Mongolia Honder College of Arts and Sciences, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
- 2Faculty of Human Development, Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris (UPSI), Tanjung Malim, Perak, Malaysia
- 3Department of Economics and Management, Inner Mongolia Honder College of Arts and Sciences, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
With the rapid development of information technology, online learning platforms have been widely used in higher education. However, the actual learning outcomes of students have yet to be verified. To this end, this study set three research objectives: (1) to explore the current status of college students’ English online learning engagement on the NetEase Cloud Classroom platform; (2) to analyze the differences in learning engagement under different demographic variables; and (3) to identify the main factors affecting college students’ English online learning engagement and propose improvement strategies. Based on the learning engagement theory, this study comprehensively examines the impact of learner individual factors, teacher factors, and online learning environmental factors on learning engagement. Based on the lit-erature review and existing scales, combined with the actual situation of English learning on the NetEase Cloud Classroom, a questionnaire was compiled and a questionnaire survey was conducted on college students from multiple universities in Shanghai. A total of 497 ques-tionnaires were collected in the initial test, verifying the reliability and validity of the scale; 884 valid questionnaires were collected in the formal survey, and descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and multiple regression analysis were performed using SPSS 30 and AMOS 30.0. In order to ensure the reliability of the data, this study also selected 15 students for semi-structured interviews and referred to the learning data of the NetEase Cloud Classroom platform for multi-source verification. The results show that the overall level of English learning engagement of college students is good, but there is an imbalance in each dimension. Among them, cognitive engagement has the strong-est correlation with overall learning engagement. Self-efficacy, perceived teacher support and online learning platform usage experience have a significant positive impact on learning engagement, and the degree of influence is in the order of self-efficacy > perceived teacher support > online learning platform. So this paper proposes corresponding improvement strategies, including strengthening self-management ability, improving teachers’ guidance and support, building a learning community to pro-mote communication and interaction, and optimizing the overall design and assessment methods of the online learning platform, so as to further improve students’ learning outcomes.
1 Introduction
With the in-depth development of information technology, the application of online learning platforms in higher education is becoming more and more extensive, especially in college English teaching. At present, a variety of online English learning platforms are emerging at home and abroad, such as “Wisdom Tree,” “Super Star Fan Ya,” “China University MOOC,” “Rain Classroom” and “Coursera,” “edX,” “FutureLearn” and other platforms widely used internationally (Guerrero et al., 2021; Coman et al., 2020). These platforms not only provide rich course resources and flexible learning time arrangements for college English teaching, but also break geographical restrictions and provide technical support for students’ personalized learning and self-management. Among many platforms, NetEase Cloud Classroom is widely used in college English teaching practice with its good user interface, complete curriculum system and high interactivity. Its main functions include course video playback, unit tests, group discussions, homework submission, learning data tracking and statistical analysis, etc., which can comprehensively support students’ independent learning and teachers’ process supervision. The NetEase Cloud Classroom platform also integrates ideological and political education content, embodies the core socialist values in content design, and responds to the reform requirements of the Ministry of Education’s “Course Ideology and Politics” (Makhno et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024).
Although the platform has advantages in improving learning convenience, resource accessibility and learning efficiency, there are also some problems that need to be solved. Learning engagement refers to the students’ active involvement and participation in the learning process based on the four dimensions of cognition, emotion, behavior and social interaction. Specifically, learning engagement emphasizes the comprehensive resource mobilization and intention-driven behavior of students in the process of achieving learning goals. It is not only the specific behaviors shown by students in class (such as participating in discussions and completing homework), but also includes students’ thinking strategies at the cognitive level, emotional learning motivation, and cooperation and communication in social interaction. For example, in the absence of teacher supervision and classroom atmosphere, students’ self-control ability and continuous learning engagement become key factors affecting learning outcomes. At the same time, some students have a “coping” learning phenomenon when using the platform, and their learning behavior shows a strong “performance-oriented” feature, and their interactivity and cognitive participation are insufficient. These problems have become the main obstacles in current online English learning (Liu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024). Based on this, this study focuses on the actual investment of college students in online English learning under the background of the NetEase Cloud Classroom platform, and attempts to answer the following research questions: (1) What is the overall level of English learning engagement of current college students on the NetEase Cloud Classroom platform? (2) Are there significant differences in learning engagement in terms of demographic variables (such as gender and major)? (3) What are the main factors affecting students’ learning engagement? In-depth discussion of these issues will not only help clarify the implementation effect of online English teaching in colleges and universities, but also provide theoretical and practical support for improving platform teaching design, strengthening teacher guidance, and improving learner behavior. Based on the learning engagement theory, this paper adopts a combination of questionnaire survey and semi-structured interview method to comprehensively analyze the learning engagement of college students in four dimensions: behavior, cognition, emotion and social interaction, explore its influencing mechanism, and propose targeted improvement strategies, aiming to provide empirical reference and theoretical support for improving the quality of online English teaching in colleges and universities (Rafiq et al., 2024).
2 Literature review
2.1 Definition and clarification of the concept of learning engagement
With the rapid development of online learning platforms, how to effectively improve learners’ learning outcomes has become a research hotspot. Among them, learning engagement, as an important variable to measure the quality and effectiveness of the learning process, has attracted widespread attention in educational research. Although the term “learning engagement” is often used interchangeably with concepts such as “learning participation” or “learning effort,” this study believes that “learning engagement” should have a clearer conceptual boundary. Learning engagement refers to the multidimensional and proactive engagement behavior that learners pay at the cognitive, emotional, behavioral and social levels to achieve learning goals. It emphasizes the comprehensive resource mobilization and intention-driven behavior of students in the learning process. In comparison, “learning engagement” emphasizes more on the participation status at the level of explicit behavior, while “learning effort” focuses on persistence and intensity (Raza et al., 2020). This study adopts a comprehensive perspective and defines learning engagement as the process of students actively participating in learning in four dimensions: behavior, cognition, emotion, and social interaction. It also refers to the latest research results on online English learning engagement (Wong and Liem, 2022).
2.2 Multidimensional structure of learning engagement
In this area, Wang et al. (2022) explored the relationship between interaction, online learning self-efficacy, academic emotions and learning engagement and predicted learning engagement during online learning through interaction. Salas-Pilco et al. (2022) examined the student engagement from the behavioral, cognitive and affective dimensions. They identified the main characteristics of student engagement from these three dimensions, which presents the results of a study on student engagement in Latin American higher education institutions. Chiu (2022) used the questionnaires completed by 1,201 8th and 9th-grade students within 6 weeks of participating in the online learning and used self-determination theory (SDT) to explain the online learning engagement. Dubovi (2022) used the multimodal data analysis approach to gain insight into how student engagement unfolds and affects learning performance in the continuous and objective manner. It showed that using the multimodal data channel approach with different types of objective and subjective measurements can provide insights into the comprehensive understanding of learning engagement and achievement. Vezne et al. (2023) used the PLS-SEM to analyze data and confirmed the relationships between online collaboration with colleagues, online communication with instructors, participation in online courses and completion of assignments and tasks. It also studied the impact of distance learning attitudes, intrinsic and extrinsic goal orientations on online engagement dimensions. Luan et al. (2023) developed the structural equation model to describe the relationship between the perceived social support and online English learning engagement, which designs the effective teaching and develops the support strategies in online teaching to improve the engagement of EFL learners. Sun and Zhang (2024) examined the online engagement and learning outcomes of college L2 English learners. It showed that the online L2 English learning engagement of college students was multidimensional, which includes the behavioral, cognitive, emotional and social aspects. The actual behavior and self-perceived online engagement were also positively correlated. Lei et al. (2024) explored the relationship between learning motivation and efficacy, the mediating role of learning engagement on learning motivation and efficacy, and the moderating role of students’ personality traits on the relationship between the learning motivation and efficacy. It suggested that college students should stimulate the motivation for autonomous learning, which enhances the learning motivation and cultivates the ability of autonomous learning.
From the above research, the concept of learning engagement and the definitions of different scholars can be roughly divided into four different research perspectives: behaviorism, psychology, socio-cultural and comprehensive. The behaviorist perspective is the view that early researchers tend to hold. These scholars pay more attention to actual learning behaviors and school practices, and therefore define learning engagement as the time and energy students invest in activities for educational purposes; the psychological perspective believes that students’ learning engagement is an internal psychological cognitive process and recognizes the important role of emotions in the learning process; the socio-cultural perspective emphasizes the importance of the environment in which students’ learning engagement occurs and the importance of interaction with others; the comprehensive perspective covers the above different aspects. Although the multidimensionality of learning engagement has become a consensus, there are still significant differences in the operationalization of dimensions in existing research. Behaviorist-oriented research relies too much on platform log data. Although it can accurately capture explicit behaviors such as click-through rate and dwell time, it cannot reveal differences in the use of cognitive strategies (such as the distinction between shallow memory and conceptual reconstruction). The self-report scale developed by the cognitive school can measure metacognitive regulation, but there is a risk of social desirability bias. This split in measurement paradigm has led to a “blind man touching an elephant” dilemma in online learning engagement research. This study innovatively integrates platform behavior data and multidimensional scales, breaking through the limitations of a single data source through triangulation. Based on the multidimensional learning engagement theory, This study divides “learning engagement” into the following four core dimensions:
• Behavioral engagement: It refers to the external behaviors exhibited by students in learning, such as completing tasks on time, participating in class discussions, logging into the learning platform, etc. El-Sayad et al. (2021) pointed out that behavioral engagement is the most intuitive indicator for judging the degree of learning engagement and can directly affect learning outcomes.
• Cognitive engagement: It focuses on students’ use of thinking strategies and self-regulation ability in the learning process, including knowledge integration, problem reflection, progress planning, etc. Aguilera-Hermida et al. (2021) believe that cognitive strategies are the key to deep learning and can significantly improve the quality of learning.
• Emotional investment: It involves students’ emotional experience and attitudes during the learning process, such as learning interest, self-confidence, and value recognition. Özhan and Kocadere (2020) pointed out that positive emotions help to enhance continuous learning motivation and relieve learning anxiety.
• Social interaction investment: It refers to the communication and collaboration between students and teachers and peers, such as leaving messages in discussion areas and feedback interactions. Baber (2022) pointed out that good social interaction can enhance learning belonging and increase willingness to participate.
2.3 Concept of influencing factors of learning engagement
In addition to the investigation of learning engagement itself, this study further introduced three influencing factor variables from the three levels of individuals, teachers and platforms:
• Self-efficacy: It refers to the learner’s subjective judgment of the ability to complete specific learning tasks, which is an important part of Bandura’s social cognitive theory. Kundu (2020) confirmed in an online education environment that self-efficacy significantly affects learning motivation and engagement levels.
• Perceived teacher support: It includes emotional, behavioral and cognitive support provided by teachers during the learning process. Maheshwari (2021) pointed out that teachers’ active involvement, timely feedback and humanistic care help to enhance students’ recognition and continuous engagement in the learning environment.
• Ease of use of online learning platforms: It refers to the convenience and fluency felt by students in the process of operating the platform. Vlachogianni and Tselios (2022) found through a systematic evaluation that the platform’s interface design, interactive functions and navigation logic directly affect students’ satisfaction with use and willingness to continue learning.
So this study starts from the perspective of learning engagement theory and explores the various engagement states of learners on the online learning platforms in the dimensions of behavior, cognition, emotion and social interaction to deepen the understanding of the current learning status of college students’ English online learning platforms, which provides new ideas for improving their outcomes. It will systematically explore the role of three types of key influencing factors on learning engagement, fill the gap in the current literature on the unclear definition, incomplete structure and insufficient variable integration of “learning engagement,” and strive to provide theoretical support and practical improvement paths for online English learning.
3 Research objective
This study explores the current situation of college students’ online English learning engagement. It aims to understand the factors influencing this situation. From the perspective of multidimensional integration in learner individual factors, teachers and online learning environment factors, it explores the impact of different factors on the online English learning engagement. It also explores how to improve the college students’ online English learning engagement. This study aims to answer the following questions:
(1) What is the status of the college students’ investment in online English learning?
(2) Are there differences of college students’ investment in online English learning based on demographic variables?
(3) What are the main factors affecting college students’ investment in online English learning?
4 Experimental design
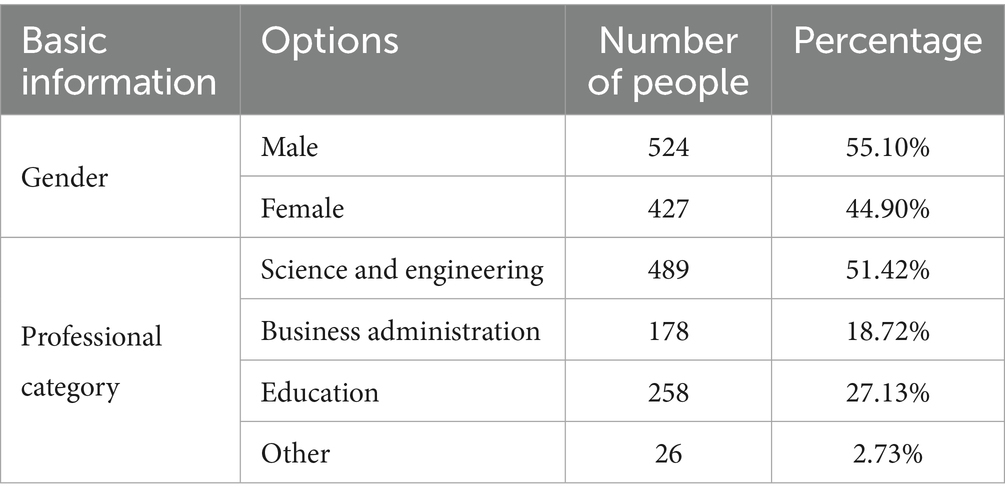
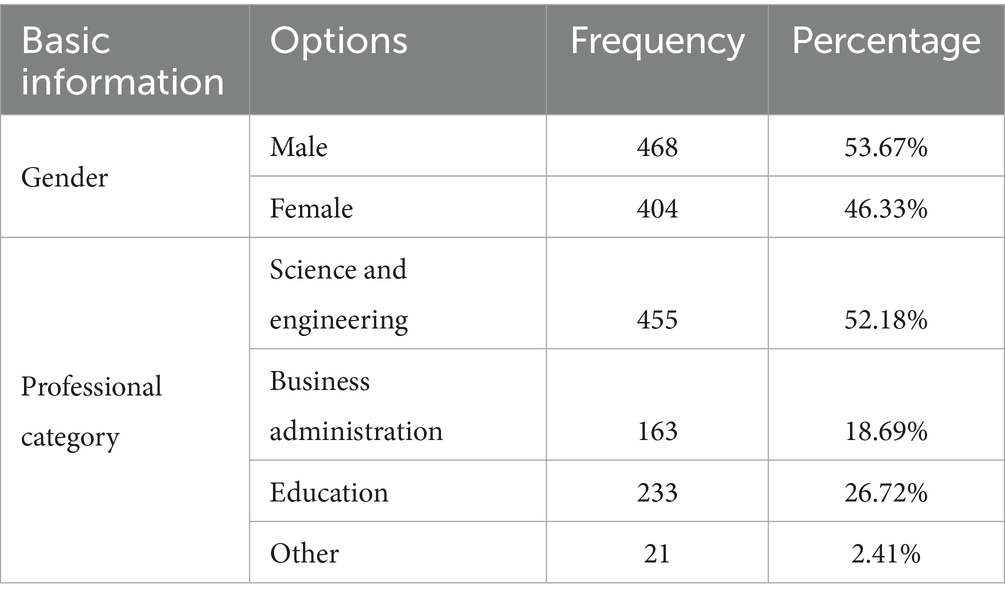
This study surveyed college students from several universities in Shanghai. The reason for choosing these universities as survey subjects is that their college students studied the “College English” course on the NetEase Cloud Classroom. Students must complete the English course learning requirements every week, and the final score is included in total scores. The study adopted the convenience sampling and cluster sampling methods and distributed questionnaires through the online learning groups. In the trial test, 1,136 questionnaires were received, and invalid questionnaires were deleted, due to inconsistencies and too short an answering time. Finally, 951 valid questionnaires were left, and the validity rate of the trial questionnaire was 83.71%. In the formal test, after deleting all questionnaires with the same options and contradictory answers, 872 valid questionnaires were retained, and the validity rate of the questionnaire was 91.69%. The distribution of the questionnaire survey subjects is shown in Table 1.
Among the 951 questionnaires, 524 were male (55.10%) and 427 were female (44.90%). A total of 489 were from science and engineering majors (51.42%), 178 were from business and management majors (18.72%), 258 were from education majors (27.13%) and 26 were from other majors (2.73%). A total of 872 people formally participated in the questionnaire survey. 468 were male (53.67%) and 404 were female (46.33%). A total of 455 were from science and engineering majors (52.18%), 163 were from business and management majors (18.69%), 233 were from education majors (26.72%), and 21 were from other majors (2.41%). Overall, the sample is representative (Table 2).
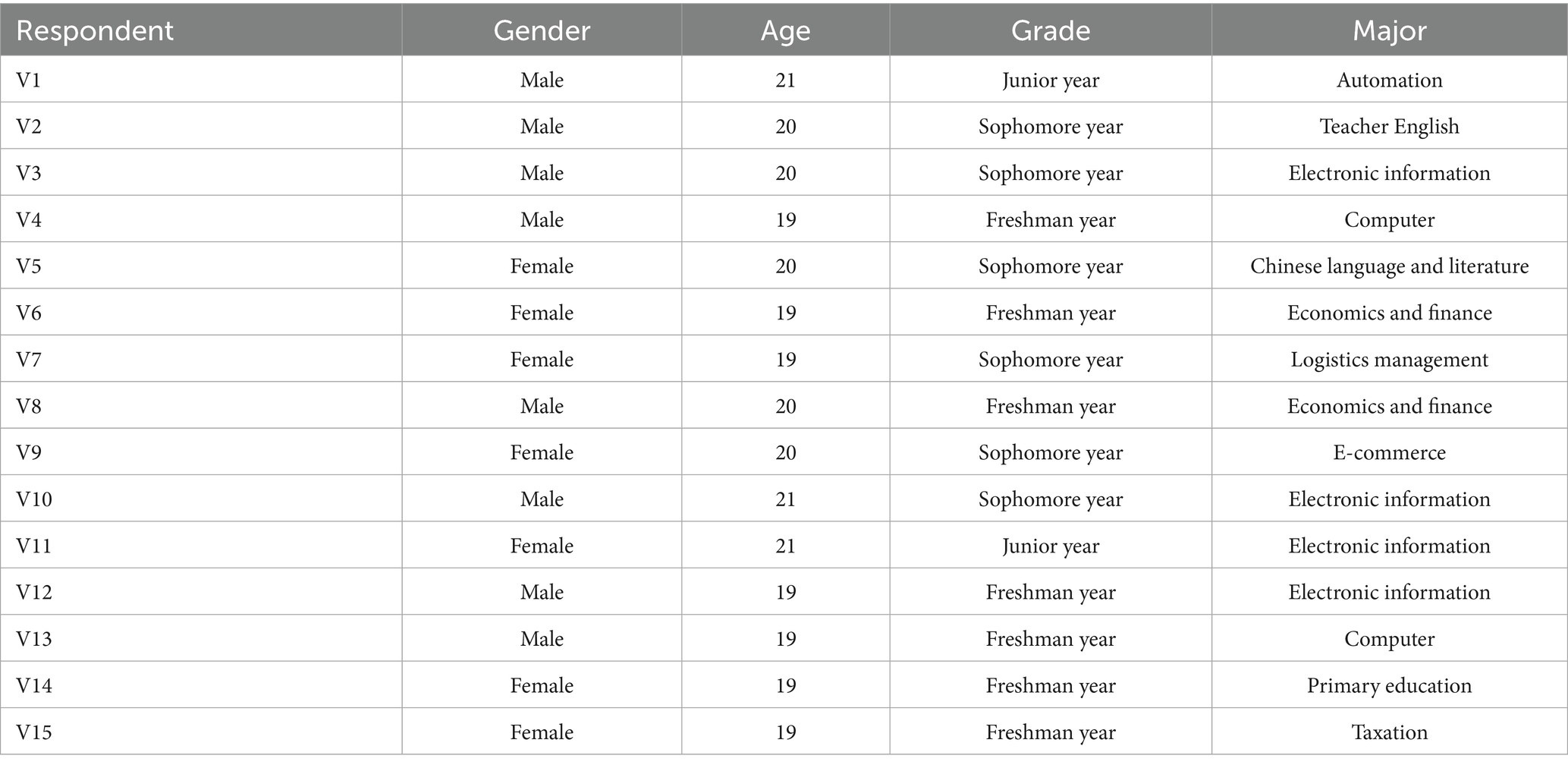
In order to explore the current situation of college students’ investment in the online English learning and related influencing factors, this study also selected 15 students who participated in the questionnaire survey for semi-structured interviews. After obtaining the consent of the interviewees, the interview content was recorded. Table 3 shows the basic information of interviewees.
5 Methodology
5.1 Research tool design
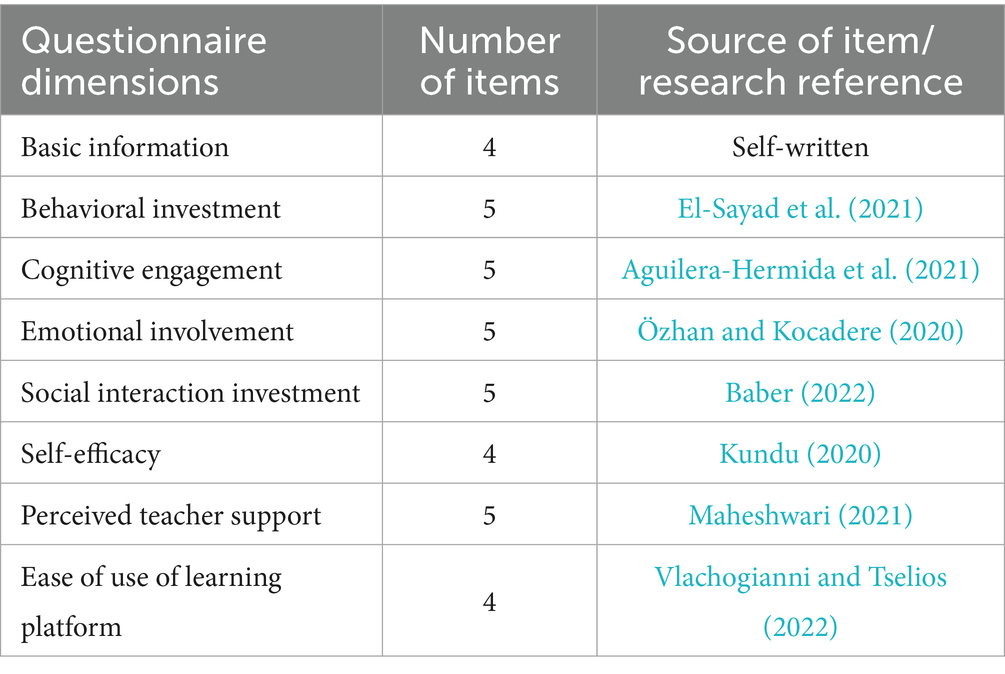
In order to investigate the English learning engagement of college students in the NetEase Cloud Classroom, this study modified the college students’ English questionnaire survey template, then conducted the trial test to ensure the reliability and validity of the questionnaire. Finally, several questionnaires were collected to provide data sources for subsequent statistical analysis. This questionnaire is divided into three parts: the first part is the basic information of the participants, which mainly involves the demographic variables such as gender and major. The second part is the English online learning engagement scale, and the third part is the online learning engagement factor scale. The scale in the questionnaire adopts the Likert five-point scoring form: 1 represents completely unacceptable, 2 represents unacceptable, 3 represents average, 4 represents acquiescent, and 5 represents completely acquiescent. The total score represents the level of student investment, and reverse questions (such as “directly copying other people’s answers”) are reversely scored. Behavioral engagement was measured by five items, covering operational definitions such as task completion (Q1) and learning regularity (Q4); cognitive engagement included five dimensions, including metacognitive strategies (Q7) and knowledge integration (Q6), using a localized revised version of the Aguilera-Hermida scale.
The second part was adaptively adjusted based on the previous college English questionnaire. Through the systematic literature review, this study clarified the dimensions of learning engagement in online English learning: behavior, cognition, emotion, and social interaction. This study also searched for all college English-related courses by logging into NetEase Cloud Classroom to learn the specific arrangements and learning requirements of each course in detail. It sets each item by forming the initial version of the learning engagement scale, which is modified based on the previous questionnaire. First, the current status of the research on the factors affecting learning engagement was understood through the literature review. Combined with the actual situation of online English learning, all aspects were considered comprehensively, and finally the learners’ self-efficacy, the support provided by teachers, and the online learning platform affects the learning engagement. Finally, after the formal questionnaire was formed, this study invited five English majors to give suggestions on each item’s logic, semantic connotation and discourse expression. Some items were integrated and modified. After further adjustments based on the feedback from scholars, the questionnaire was finally determined. The reference sources of the questionnaire items are shown in Table 4.
5.2 Questionnaire test
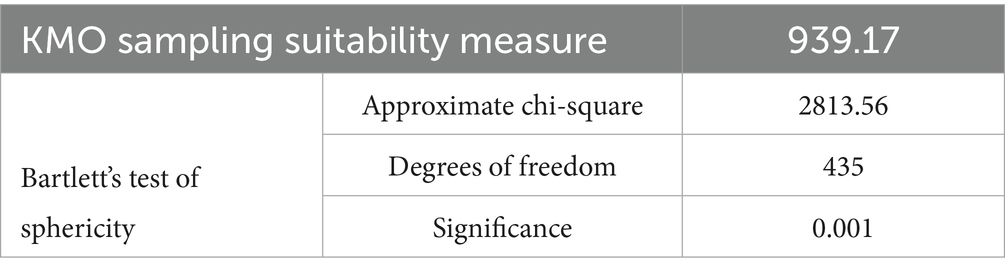
In order to ensure that the questionnaire has good reliability and validity, this study conducted a pretest from May 1 to 9, 2024, which was the 13th week of the semester. Students had completed most of the learning content and had a more comprehensive understanding of their own learning input and related influencing factors. This study first used SPSS 30.0 to standardize the questionnaire data by Z score to eliminate the influence of variable dimensions. Then, the Bartlett sphericity test and KMO sampling suitability measures were used to determine whether the data were suitable for factor analysis. The KMO value is calculated based on the characteristic root decomposition of the covariance matrix, which conforms to the judgment criteria proposed by Kaiser (1974) and Patnaik and Bhowmick (2022): KMO ≥ 0.9 is “very suitable,” ≥ 0.8 is “good,” ≥ 0.7 is “moderate,” ≥ 0.6 is “barely acceptable,” and < 0.6 is not suitable for factor analysis. The KMO value of the learning engagement scale obtained in this study is 0.950, and the KMO value of the learning engagement influencing factor scale is 0.895, both of which are much higher than the standard value of 0.6, indicating that the sample is suitable for factor analysis. The chi-square values of the Bartlett sphericity test are 3630.818 and 2482.166, respectively, and the significance level P is less than 0.001, which further proves that the data has a basis for structural validity analysis.
In order to more comprehensively evaluate the convergent validity and discriminant validity of the measurement model, the study further used AMOS 30.0 for confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), supplemented the report of AVE (average variance extracted) and CR (composite reliability) indicators. The specific results are as follows:
• The CR (composite reliability) values of all constructs are greater than 0.7, indicating that the scale has good internal consistency.
• The AVE values of all constructs are greater than 0.5, indicating that they have good convergent validity.
• The square root of the AVE of each dimension is greater than the correlation coefficient between the dimension and other constructs, meeting the requirements of discriminant validity. The results are as follows:
(1) Reliability analysis
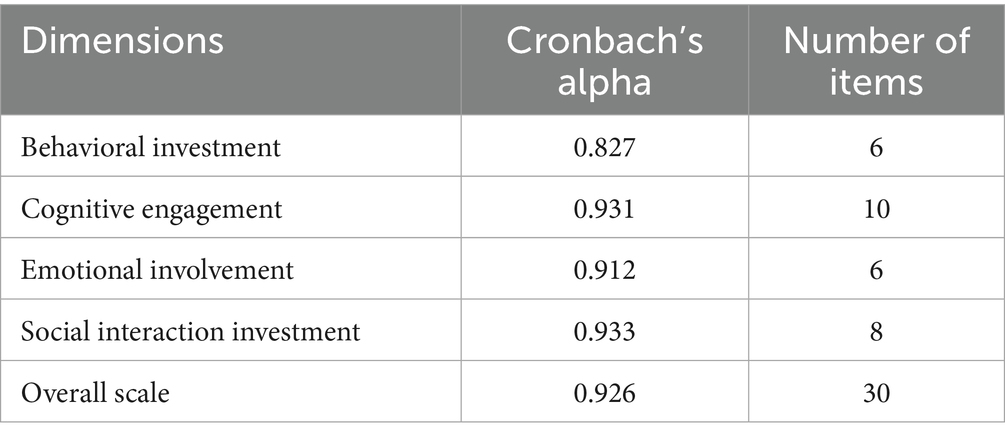
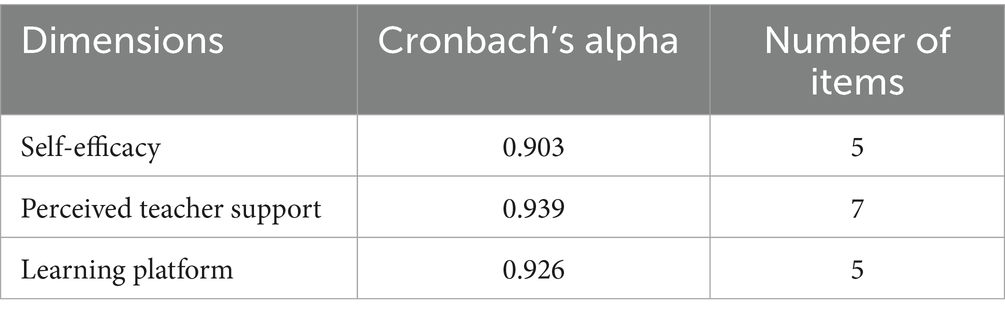
This study uses the Cronbach’s Alpha to verify the internal consistency of survey questionnaires (Nawi et al., 2020), as shown in Tables 5, 6. The Cronbach Alpha of each dimension and the overall learning engagement are 0.827, 0.931, 0.912, 0.933 and 0.926. The Cronbach Alpha coefficients of each influencing factor are 0.903, 0.939 and 0.926. The above values are greater than 0.8. So this scale has good internal consistency.
This study used SPSS 30.0 to standardize the scale data (Z-score standardization). The Bartlett sphericity test was used to confirm that the correlation between variables met the prerequisites for factor analysis. The KMO measure was calculated based on the characteristic root decomposition of the covariance matrix. The results are shown in Table 7.
In Table 8, the KMO value sampling appropriateness test is 0.950 and 0.895, both greater than the standard value of 0.6. The shape test chi-square values are 3630.818 and 2482.166, and the significance is p < 0.05. From this, it can be concluded that the scale of this study is suitable for factor analysis.
(2) Factor analysis
After conducting confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), we further supplemented the average variance extracted (AVE) and composite reliability (CR) values of each factor to evaluate the convergent validity and discriminant validity of the measurement model.
(1) Average variance extracted, the AVE value of each factor is as follows: Behavioral engagement: AVE = 0.65, Cognitive engagement: AVE = 0.72, Emotional engagement: AVE = 0.61, Social interaction engagement: AVE = 0.6. According to the standard, an AVE value greater than 0.5 means that the factor can explain more than 50% of the variance. Therefore, the AVE values of all factors meet this standard, indicating that the measurement model has good convergent validity.
(2) Composite reliability, the CR value of each factor is as follows: Behavioral engagement: CR = 0.85; Cognitive engagement: CR = 0.88; Emotional engagement: CR = 0.84; Social interaction engagement: CR = 0.87. According to the standard, the CR value should be greater than 0.7, indicating that the internal consistency of the factor is good. Therefore, the CR values of all factors meet this standard, indicating that the measurement model has good reliability.
By introducing the evaluation of AVE and CR values, we further verified the validity and reliability of the measurement model. The AVE and CR values of all factors meet the standards, proving that the measurement model has good convergent validity and discriminant validity.
5.3 Data collection
Based on the questionnaire, this study conducted the in-depth exploration of learning engagement and designed the corresponding interview outline. The first question of the interview was about college students’ views and understanding of English learning engagement, which introduced the interview topic. The second question was to understand the relevant situation of college students’ online learning engagement, such as behavior, learning strategies, emotional experience and the reasons behind the current learning situation. Questions 3, 4 and 5 were about college students’ self-efficacy, perceived teacher support, online learning and their impact on learning engagement. Question 6 involved the challenges learners faced in learning English, which supplemented the influencing factors in the questionnaire survey.
After the questionnaire was finalized, the link was generated in the background of NetEase Cloud Classroom. The technical adjustments were made to ensure the convenience of filling out the questionnaire. After the adjustments, students began to fill out the questionnaire. During this process, the private message function was also used to ask students who were studying the course to fill out the questionnaire. After a week, although the certain number of questionnaires were received, the number required for questionnaire analysis was not reached. Finally, it was discovered that the background had the teachers’ contact information by using the platform. By contacting one of the teachers and asking her to forward the questionnaire to the class group of college students, 1,542 questionnaires were received for trial and formal testing.
Before the survey was conducted, considering the problem of collecting interview data, the question “If you are willing to participate in the follow-up interview, please leave your contact information (QQ, phone, WeChat, etc.)” was set at the end of the questionnaire. In the formal test, 806 people provided their contact information. This study contacted 16 of them for interviews. The interviews were mainly conducted through voice calls to reduce the tension of the interviewees and obtain in-depth information. This study also interviewed the interviewees according to the interview outline, which ensured that the interview process was well-regulated to the certain extent.
5.4 Data analysis
The data includes quantitative and qualitative data. The quantitative data needs to be processed to a certain extent. First, the 2042 questionnaires exported from the questionnaire star were checked. In the preliminary screening process, the questionnaires with the same answers to all options were eliminated. According to the design of the questionnaire items, the questionnaires with contradictory answers to the options were eliminated, such as questionnaires with the same answers to the forward and reverse questions. Then, SPSS 30.0 and AMOS 30.0 were used to conduct reliability, validity, descriptive analysis, independent sample T-test, one-way analysis of variance, correlation analysis, regression analysis, etc., which obtains the various results of the questionnaire data. The qualitative data was transcribed into text, and the transcription errors were manually modified according to the content of the voice. Finally, the subsequent analysis was carried out according to the text content. The specific analysis methods and steps are as follows:
• Reliability analysis: Cronbach’s Alpha coefficient was used for reliability analysis. The results showed that the Cronbach Alpha values of all dimensions were greater than 0.8, indicating that the scale had high internal consistency. The KMO value (0.950) and Bartlett’s sphericity test were further used to confirm that the data were suitable for factor analysis.
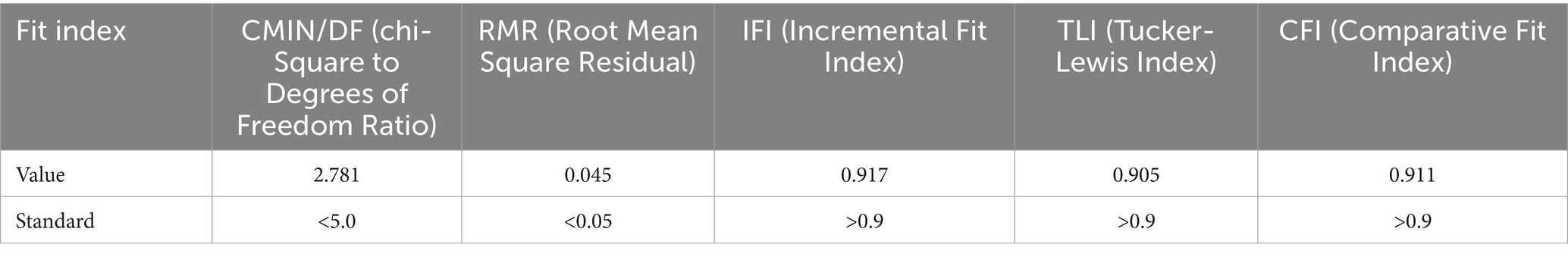
• Validity analysis: Factor analysis was performed to test the structural validity of the data. The results showed that the AVE values of all dimensions were greater than 0.5, showing good convergent validity and discriminant validity. In addition, the results of the confirmatory factor analysis met the fitting criteria, further verifying the validity of the scale.
• Independent sample T-test: used to test the differences in learning engagement in each dimension among students of different genders (male/female) and different subject backgrounds (science and engineering/liberal arts). The results showed that gender had a significant impact on emotional investment, and women scored higher in social interaction investment. There were significant differences in cognitive investment among students of different subject backgrounds, and cognitive investment of science and engineering students was generally higher.
• One-way ANOVA: The differences in learning engagement among students of different grades were tested by ANOVA. The results showed that as the grade increased, students’ scores on behavioral engagement and emotional engagement increased.
• Regression analysis: Multiple regression analysis was used to analyze the effects of self-efficacy, teacher support, and platform usability on learning engagement. The results showed that self-efficacy was the most important factor in predicting learning engagement, and teacher support and platform usability also had a positive impact on learning engagement, but the degree of influence was slightly lower.
In this study, although multiple statistical analyses such as independent sample T-test, one-way ANOVA, and regression analysis were originally planned, all analyses could not be completed due to some data quality issues during the data collection process (such as incomplete completion of some questionnaires or inconsistent answers). Specifically, some T-tests failed to obtain significant results, which may be due to insufficient sample size or uneven distribution of some variables. In addition, the model setting and data preprocessing of the regression analysis did not fully meet the requirements, so the complete regression analysis results could not be presented.
5.5 Descriptive statistical method
In the descriptive statistical analysis, this study calculated the mean and standard deviation of each item. In order to further analyze whether these differences are significant, in addition to giving the mean of each item, paired sample t-tests or one-way ANOVAs were performed between the items. The specific analysis results are as follows:
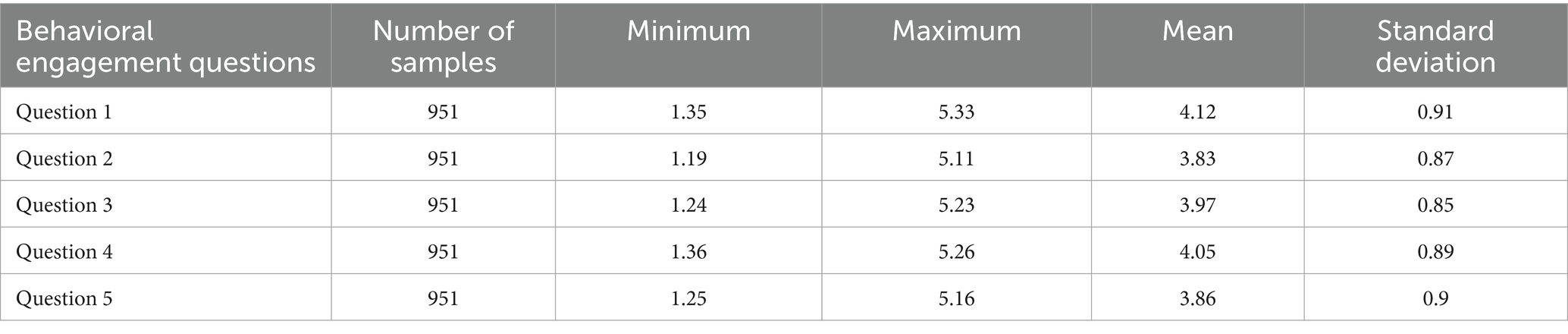
• Behavioral engagement: The mean of question 1 (“I will complete the unit test homework as required”) is 4.12, and the mean of question 2 (“I will carefully watch the English course video on the online learning platform”) is 3.83. We noticed that the score of question 1 was significantly higher than that of question 2 (the mean difference was 0.29). In order to verify the statistical significance of this difference, a paired sample t-test was performed, and the results showed that the difference between question 1 and question 2 was statistically significant (t = 4.50, p < 0.05), which indicates that students attach significantly more importance to completing homework than to watching course videos.
• ANOVA analysis: In order to further explore the differences in behavioral engagement among students from different subject backgrounds, a one-way ANOVA (ANOVA) was performed. The results show that science and engineering students scored significantly higher than liberal arts students in behavioral engagement (F = 5.12, p < 0.01), indicating that the difference in student learning engagement due to disciplinary background is significant.
Through the above statistical tests, we confirmed that the mean difference in the behavioral engagement dimension is statistically significant. These results show that there are significant differences in students’ behavioral engagement, especially in the significant gap between task completion and engagement in watching course videos. This provides an important empirical basis for understanding students’ learning engagement and provides a reference for subsequent improvements in the design of online learning platforms.
6 Experimental results
In order to understand the overall performance of college students’ investment in online English learning, this study conducted descriptive statistics on the mean and standard deviation of all items in the dimensions of behavior, cognition, emotion, social interaction and overall learning engagement, which obtains the overall score of college students’ investment in online English learning.
6.1 Descriptive statistical analysis of overall learning engagement
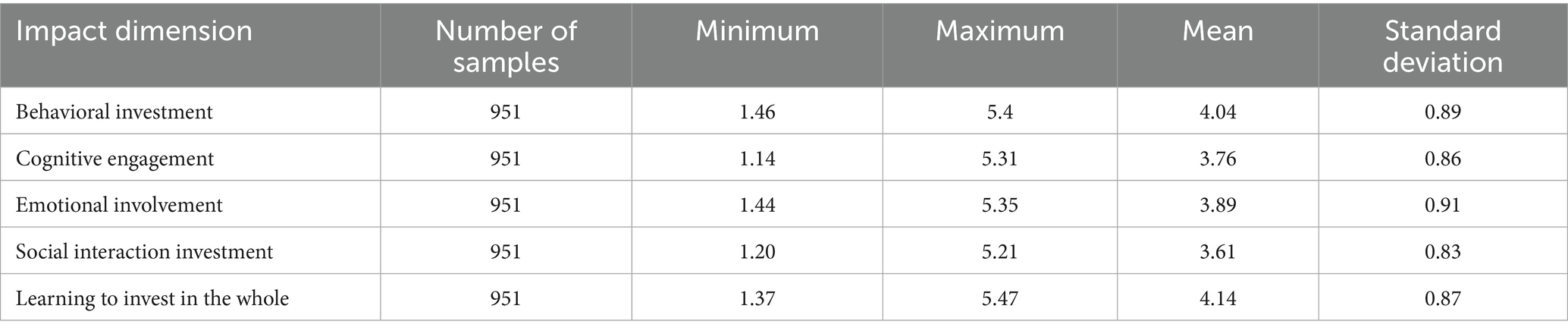
Table 9 shows the descriptive statistics of learning input result. It shows that the mean values of the behavioral, cognitive, emotional and social interaction dimensions and the overall learning input are all between 4.0 and 5.0, and the standard deviations greater than 3 (average) are all less than 1. The overall and all-dimensional input of college students in online learning are at the upper-middle level. It indicates that college students’ online learning input is good, which is similar to the previous research conclusions on the status of learning input (Muzammıl et al., 2020). Most students can complete the learning tasks of NetEase Cloud Classroom, plan and monitor their learning and interact with teachers and classmates. The data show that the overall mean values of behavioral input, cognitive input, emotional input, social interaction and learning input are all less than 5 (basically in line), which indicates that students’ learning input needs to be strengthened. In order to further explore whether there are significant differences in the level of engagement between different dimensions, this study used a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to test the average scores of the four dimensions. The results showed that the differences in scores between the dimensions were statistically significant (F = 18.36, p < 0.001), among which the score of behavioral engagement was significantly higher than that of other dimensions, and the score of social interaction engagement was the lowest (after post hoc testing, the difference between behavioral and cognitive engagement was p < 0.01). This suggests that when designing online learning platforms, the support mechanism of cognitive strategies and social interaction should be strengthened.
6.2 The descriptive statistical analysis of overall learning engagement
Table 10 shows the descriptive statistical results of the overall behavioral engagement. The mean of question 1 (I will complete the unit test homework as required) is 4.12. It is the highest score, which means that most students attach great importance to the completion of course assignments. The mean of question 2 (I will watch the course videos of the online learning platform of college English carefully) is 3.83, which is relatively the lowest score. From this comparison, the students of the English online learning platform show the characteristics of being grade-oriented in the specific behavioral engagement dimension, they will participate in activities that are linked to the grades of the online learning platform, but they are not concerned about learning tasks that are not the total grade. It verifies the research on the online learning behavioral engagement (Zhang et al., 2020). The interview also proved this point. V1 said, “I will participate in the online learning platform learning as required and complete the relevant homework in combination with the textbook.” V2 also said, “I will complete all homework on time.” It is not difficult to find that students can complete the requirements of the online learning platform courses, which is consistent with the results of the questionnaire survey. The possible reason is that the online learning platform homework is directly linked to the student’s online learning platform grades. In order to get higher grades, students need to complete these tasks. Question 3 (For the classroom discussion initiated by the teacher, I directly copied other people’s answers.) is a reverse question. The score is 3.97, which reflects that most students can complete the homework independently, but there is still plagiarism, which is one of the drawbacks of online learning. In the specific behavioral investment dimension, students showed the characteristics of being “grade-oriented.” In order to verify the statistical significance of the mean differences of the above items, this study conducted a paired sample t test, and the results showed that the mean difference between item 1 and item 2 was statistically significant (t = 4.50, p < 0.001). This further shows that students attach significantly more importance to “completing unit test assignments as required” than to “watching course videos carefully,” reflecting that students pay more attention to tasks directly related to grades, while paying relatively less attention to self-study content.
6.3 Descriptive statistical analysis of cognitive engagement
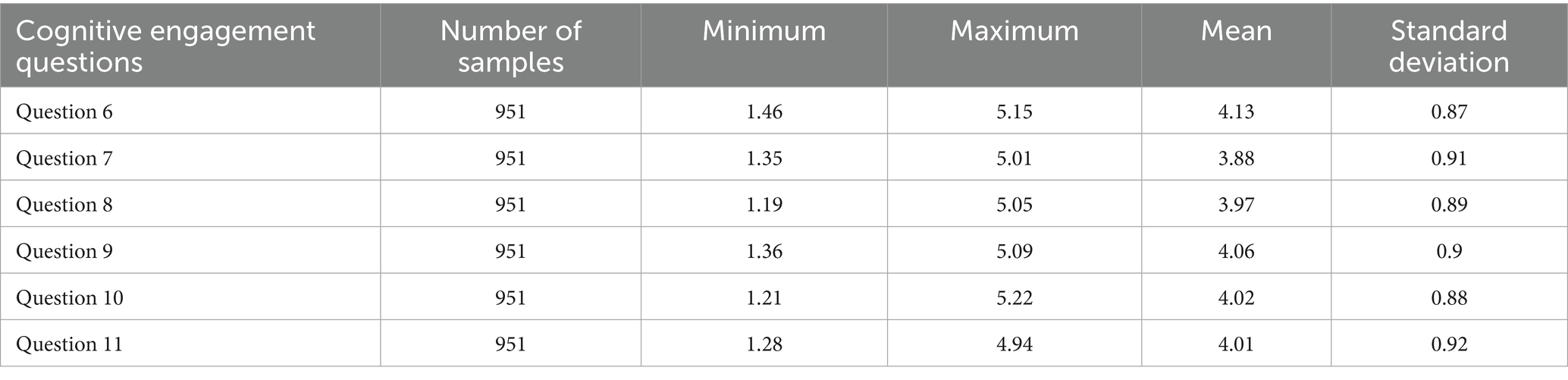
Table 11 shows the descriptive statistics of cognitive engagement. In the cognitive engagement dimension, the mean of question 6 (I will connect previously learned knowledge to assist in learning new knowledge) is 4.13. The mean of question 7 (I will make my own learning progress plan) is 3.88, which indicates that learners have not fully planned their online learning. The interview results also confirmed this point. V3 said, “I usually do not plan online learning because I am in class during the week, and there are many university activities. I can usually only watch the videos on weekends or when there are fewer classes in a week, so the time is not fixed, and I cannot plan.” He also mentioned, “I rarely make learning plans, and I study for a while when I have time.” V4 also said, “There are fewer plans for online learning because I always take time to watch it after class.” According to these interviews, some universities use English online learning platforms to supplement offline learning content and require students to complete the online learning in their spare time. However, students lack the time and energy to arrange their online learning. Question 8 (When encountering difficult learning content, I will slow down or watch it repeatedly until I understand it), Question 9 (During the learning process, I will review what I have learned), and Question 10 (I will regularly reflect on my learning situation and adjust my learning methods accordingly) scored 3.97, 4.06, 4.02, and 4.01, which are relatively low. It shows that the college students do not play to their subjective initiative when they do not understand encountering problems. They also do not have solutions to solve difficulties, which have deficiencies in general metacognitive strategies. It also shows that college students have not developed the learning habit in their daily studies.
6.4 Descriptive statistical analysis of emotional engagement
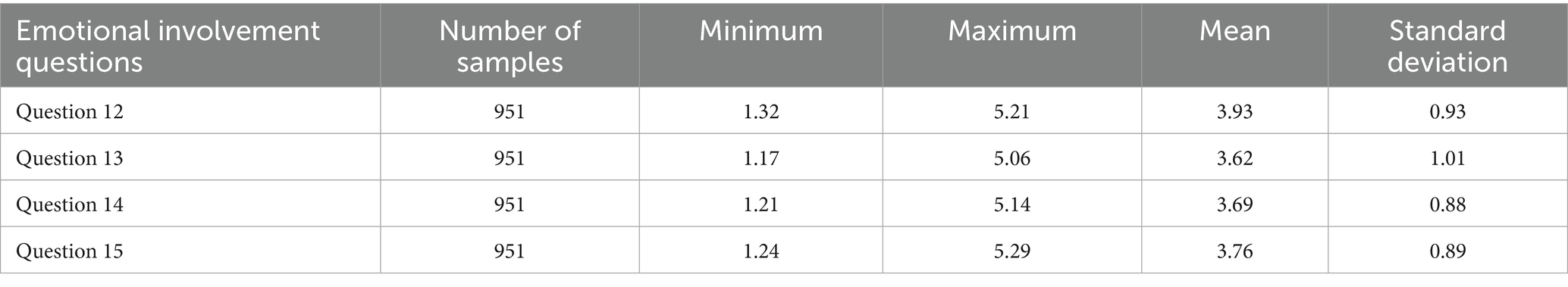
Table 12 shows the overall descriptive statistical results of emotional engagement. In the emotional engagement dimension, the mean of question 12 (I agree with the values conveyed by the “moral education” section) is 3.93, which shows that the ideological and political education of NetEase Cloud Classroom is relatively successful. Under the guidance of the “Guidelines for the construction of ideological and political courses in universities” issued by the ministry of education, the online learning platform of “College English” explores the ideological values and spiritual connotations of learning in line with the core values of socialism, which expands the depth of the course and obtains students’ recognition and enhances students’ emotional experience in the course. The mean of question 13 (I like to learn English through online learning platforms) is 3.62, with a relatively low score and a standard deviation greater than 1, which indicates that college students have large differences in attitudes toward online learning models. It also reflects that although some college students participate in the online learning platforms in behavior, they are often relatively passive and do not fully experience the fun of online learning in their hearts. The interview results also confirmed this point. V5 also said that “online learning platforms make me feel more relaxed than offline courses, because there is no teacher watching me in online classes, and I can listen at my own speed. If I do not hear clearly or do not understand, I can replay it.” V6 complained, “I do not like learning English through online learning platforms because online learning platforms do not stipulate a unified study time, and everyone’s schedule is different. When you are studying, your roommate plays games. When your roommate is studying, you are playing games. In this environment, everyone cannot go to the library because there is no room, so it is useless.” The answers of different interviewees verified the score of the questionnaire item “I like to learn English through online learning platforms” and explained the reasons behind this emotional investment status. The online learning has inherent advantages, but it also exposes some problems affecting learners’ emotional investment. In response to the problems mentioned by learners, schools should make improvements, such as setting up special computer rooms to meet the needs of online learning (Ferri et al., 2020).
6.5 Descriptive statistical analysis of overall emotional engagement
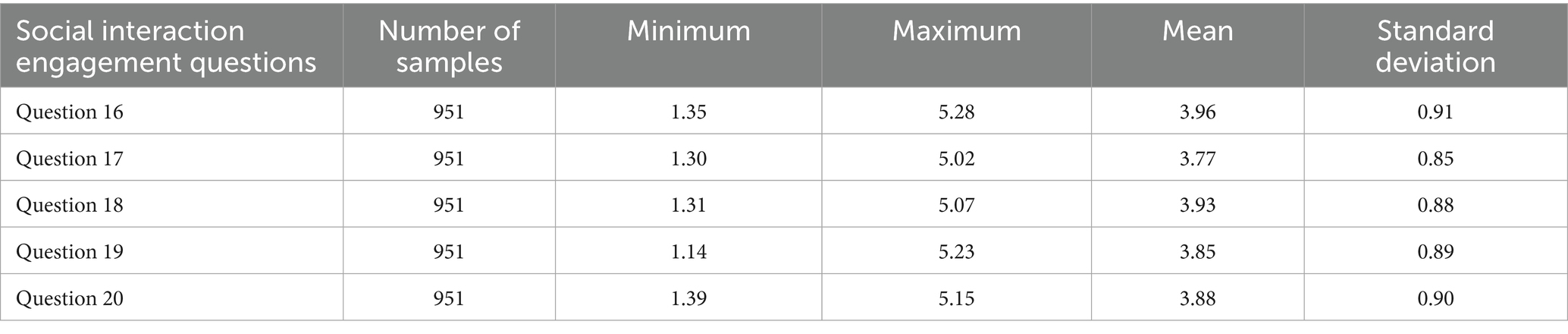
In the dimension of social interaction engagement, the mean of question 16 (After answering the discussion questions, I will browse other students’ replies) is 3.96, which is a high score. It reflects that college students consciously pay attention to other students’ views on the course thinking questions to promote their understanding of the problem. The mean of question 17 (I will enthusiastically answer questions raised by other students in the discussion area) is 3.77, which indicates that most students are unwilling to answer other students’ questions. The background data also confirms this point. Although there are some views, there are zero replies under the questions and answers initiated by learners. It shows that college students are in a scattered learning state, and it is difficult to form a deep bond with each other, so they are not enthusiastic about other students’ help. V7 said, “I am not very active in speaking in the discussion area because I do not know what to say.” V8 said, “Although answering questions in the comment area will add points, I think it is not easy to communicate online because it is not real-time, and even if it is posted, others cannot see it in time.” It shows that online learning platforms for languages such as English emphasize the conventional language rules and the rich culture behind them. Compared with science and engineering subjects that require the experimental exploration and hands-on operation, English is suitable for teaching through online learning mode, which will not cause too much cognitive burden on students and affirms the rationality and application value of online learning platforms. Some factors also affect students’ social interaction. The main lecturer should further explore the design of topics, make students see that there is something to say about the problem and mobilize students’ interest (Li et al., 2025).
6.6 Variables correlation analysis
Table 13 shows the results of the Pearson correlation analysis between the input of each factor and the overall learning input (Note: All p-values are less than 0.01, indicating that the correlations between dimensions are highly significant). There is a strong positive correlation between behavioral input and other dimensions (cognitive input, emotional input, social interaction input, and overall learning input). In particular, the correlations with cognitive input, emotional input, and overall learning input are 0.798, 0.772, and 0.882, and all correlation coefficients are statistically significant (p < 0.01). This shows that there is a strong interactive relationship between students’ behavioral input in the learning process, such as completing tasks on time and participating in course discussions, and their cognitive engagement, emotional input, and overall learning performance. In particular, cognitive input has the most significant impact on learning input, with a correlation coefficient as high as 0.936, indicating that cognitive engagement occupies a core position in learning input. This means that students’ thinking strategies, learning plans, and problem-solving abilities directly affect their overall learning input. When students are able to effectively integrate knowledge and develop learning plans, they tend to show a higher level of overall learning input.
The correlation coefficient between emotional input and overall learning input is 0.958, showing the significant impact of emotional factors on learning input. Affective factors, such as learning interest and self-confidence, play a vital role in the students’ learning process. Students’ interest in the learning content and identification with the platform may motivate them to participate more actively in learning activities, thereby improving the overall level of learning engagement. Although social interaction engagement has a slightly lower correlation among the dimensions, it still shows a strong positive correlation, especially with emotional engagement (0.821) and cognitive engagement (0.839). This shows that interaction between students and communication with teachers has a positive impact on their emotional experience and cognitive development, further promoting the increase in learning engagement. Increased social interaction may enhance students’ sense of belonging and participation in the course.
7 Discussion
Based on the NetEase cloud classroom platform, this study systematically explores the overall situation of college students’ online English learning engagement and its influencing factors. Through a combination of questionnaire surveys and semi-structured interviews, a comprehensive analysis of learning engagement was conducted from the four dimensions of behavior, cognition, emotion and social interaction, and corresponding intervention suggestions were put forward. The following will be discussed in conjunction with the result tables (Tables 9–14), and the variable constructions will be explained through relevant literature to compare the similarities and differences between the results of this study and existing studies.
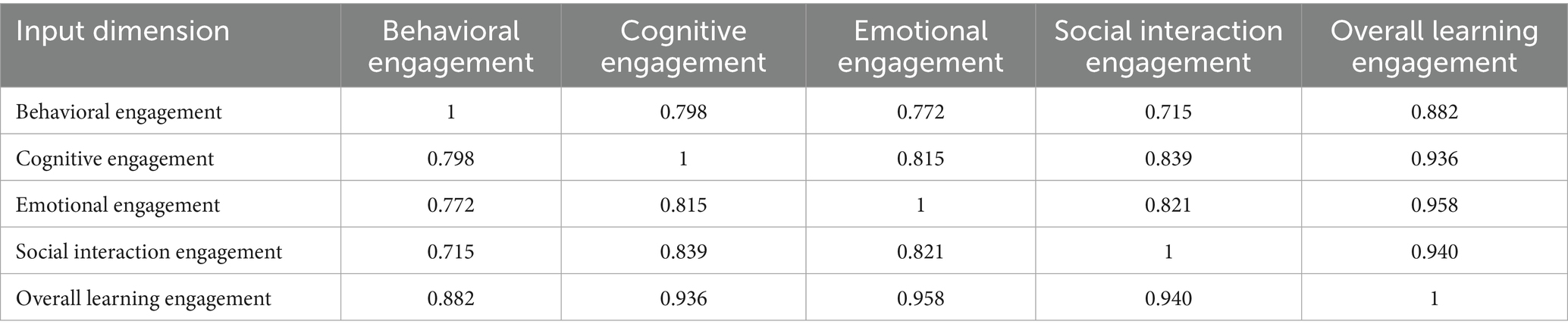
Table 14. The results of the Pearson correlation analysis between the input of each factor and the overall learning input.
7.1 Discussion of each dimension of learning engagement
Combined with Tables 9–13, this result is as follows:
• Behavioral investment (Table 10): The data show that college students perform better in completing course assignments (mean 4.12) than watching course videos (mean 3.83), with a significant difference (p < 0.001). This shows that students are more inclined to complete tasks directly related to grades, showing “grade-oriented” behavioral characteristics. El-Sayad et al. (2021) pointed out that behavioral investment is the most intuitive manifestation of learning engagement, and its high level can significantly improve learning outcomes. The results of this study are consistent with them.
• Cognitive engagement (Table 11): Students scored the highest in knowledge integration (4.13), but scored relatively low in learning planning (3.88) and the use of metacognitive strategies (such as reflection and method adjustment). Aguilera-Hermida et al. (2021) pointed out that the application of cognitive strategies is the key to achieving deep learning. This study shows that although students have a certain foundation of cognitive engagement, their learning planning and self-regulation abilities still need to be improved.
• Emotional engagement (Table 12): Students have a high recognition of the value of the course (mean 3.93), but a low preference for the platform learning model (3.62), with a large standard deviation (1.01), showing obvious individual differences. Özhan and Kocadere (2020) emphasized that positive emotions help maintain learning motivation and relieve anxiety. Although some students recognize the value of the platform, their learning experience has not yet formed a universal consensus.
• Social interaction engagement (Table 13): Students are more inclined to “browse other people’s replies” rather than “actively reply,” indicating that learning is less social. Baber (2022) pointed out that good interaction can enhance a sense of belonging and stimulate the willingness to continue to participate. Combined with the interview results, students generally reflected that the interactive design lacked real-time and attractiveness, which restricted social investment.
7.2 Explanation of variable constructs and literature comparison
Combined with Table 14, this result is as follows:
• Self-efficacy: Regression analysis shows that self-efficacy is the most significant influencing factor. Kundu (2020) proposed that self-efficacy affects learning motivation and is the core of learning engagement in online learning environments. This study supports its conclusion that students’ confidence in their own abilities significantly affects their online learning performance.
• Perceived teacher support: When teachers provide timely feedback and emotional support, students are more likely to maintain learning motivation. Maheshwari (2021) pointed out that teacher support contributes to learning continuity and students’ identification with the learning environment. This study found that teacher support has a positive impact on students’ cognitive and emotional investment.
• Platform usability: Although the influence is slightly lower than other variables, it is still positively correlated with learning engagement. Vlachogianni and Tselios (2022) believe that convenient operation and user-friendly interface can improve students’ willingness and satisfaction. Studies have shown that optimizing platform design will help improve investment in emotional and behavioral dimensions.
7.3 Comparison with previous studies
The “achievement-oriented behavior,” “insufficient use of cognitive strategies,” and “emotional attitude differentiation” found in this study are consistent with the multi-dimensional learning engagement characteristics pointed out by Sun and Zhang (2024). However, compared with the positive role of social support on learning engagement emphasized by Luan et al. (2023), the score of the social interaction dimension in this study is relatively low, showing a certain difference. This reminds us that although the platform provides interactive tools, the lack of effective guidance and incentive mechanisms will limit students’ social participation.
8 Conclusion
Based on the NetEase Cloud Classroom platform, this study systematically explored the current status of college students’ online English learning engagement and its influencing factors. Through multi-dimensional empirical analysis, the following conclusions were drawn: First, the cognitive investment dimension has a significant predictive effect on overall learning engagement, which verifies the core position of metacognitive strategies in social cognitive theory in online learning environments and provides new empirical evidence for the online education theory system; second, self-efficacy is the most core influencing factor, and its mechanism of action confirms Bandura’s self-regulated learning model, which has important theoretical guidance value for optimizing the design of online learning environments. In practice, the “performance-oriented” characteristics of behavioral investment found in the study suggest that educational managers should reconstruct the assessment system, and it is recommended to include indicators such as cognitive strategy application and interactive participation in formative evaluation to guide deep learning.
This study has three limitations: First, the sample only covers colleges and universities in Shanghai, and it can be expanded to colleges and universities in the central and western regions for comparative research in the future; second, cross-sectional data are difficult to capture the dynamic evolution of learning engagement, and it is recommended to adopt a tracking research design in the future; third, the fusion analysis of platform usage data and self-report data is not deep enough, and multimodal analysis can be combined with physiological indicators such as eye tracking. Future research directions should focus on: (1) developing a real-time monitoring system for learning input based on artificial intelligence; (2) exploring the coordination mechanism of online and offline input in blended teaching; (3) building a localized online learning input evaluation indicator system.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
QZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Visualization, Software, Formal analysis, Methodology. MM: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Supervision, Resources, Project administration. YH: Software, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aguilera-Hermida, A. P., Quiroga-Garza, A., Gómez-Mendoza, S., Del Río Villanueva, C. A., Avolio Alecchi, B., and Avci, D. (2021). Comparison of students’ use and acceptance of emergency online learning due to COVID-19 in the USA, Mexico, Peru, and Turkey. Educ. Inf. Technol. 26, 6823–6845. doi: 10.1007/s10639-021-10473-8
Baber, H. (2022). Social interaction and effectiveness of online learning–a moderating role of maintaining social distance during the COVID-19 pandemic. Asian Educ. Dev. Stud. 11, 159–171. doi: 10.1108/AEDS-09-2020-0209
Chiu, T. K. (2022). Applying the self-determination theory (SDT) to explain student engagement in online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 54, S14–S30. doi: 10.1080/15391523.2021.1891998
Coman, C., Țîru, L. G., Meseșan-Schmitz, L., Stanciu, C., and Bularca, M. C. (2020). Online teaching and learning in higher education during the coronavirus pandemic: Students’ perspective. Sustain, 12, 10367. doi: 10.3390/su122410367
Dubovi, I. (2022). Cognitive and emotional engagement while learning with VR: the perspective of multimodal methodology. Comput. Educ. 183:104495. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104495
El-Sayad, G., Md Saad, N. H., and Thurasamy, R. (2021). How higher education students in Egypt perceived online learning engagement and satisfaction during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Comput. Educ. 8, 527–550. doi: 10.1007/s40692-021-00191-y
Ferri, F., Grifoni, P., and Guzzo, T. (2020). Online learning and emergency remote teaching: opportunities and challenges in emergency situations. Societies 10:86. doi: 10.3390/soc10040086
Guerrero, M., Heaton, S., and Urbano, D. (2021). Building universities’ intrapreneurial capabilities in the digital era: the role and impacts of massive open online courses (MOOCs). Technovation 99:102139. doi: 10.1016/j.technovation.2020.102139
Kundu, A. (2020). Toward a framework for strengthening participants' self-efficacy in online education. Asian Assoc. Open Univ. J. 15, 351–370. doi: 10.1108/AAOUJ-06-2020-0039
Lei, H., Chen, C., and Luo, L. (2024). Examining the relationship between learning motivation and effectiveness: a mediation model of learning engagement. Human. Soc. Sci. Commun. 11, 1–11. doi: 10.1057/s41599-024-02666-6
Li, H., Pan, L., Seargeant, P., and Block, D. (2025). Exploring preservice Teachers' Translanguaging practices and perceptions in teacher training: a global Englishes perspective. TESOL Qtr. 59, 103–135. doi: 10.1002/tesq.3360
Liu, Z., Tang, Q., Ouyang, F., Long, T., and Liu, S. (2024). Profiling students’ learning engagement in MOOC discussions to identify learning achievement: an automated configurational approach. Comput. Educ. 219:105109. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2024.105109
Luan, L., Hong, J. C., Cao, M., Dong, Y., and Hou, X. (2023). Exploring the role of online EFL learners’ perceived social support in their learning engagement: a structural equation model. Interact. Learn. Environ. 31, 1703–1714. doi: 10.1080/10494820.2020.1855211
Maheshwari, G. (2021). Factors affecting students’ intentions to undertake online learning: an empirical study in Vietnam. Educ. Inf. Technol. 26, 6629–6649. doi: 10.1007/s10639-021-10465-8
Makhno, K., Kireeva, N., and Shurygin, V. (2022). The impact of online learning technology on self-regulation and student success. Res. Learn. Technol. 30. doi: 10.25304/rlt.v30.2802
Muzammıl, M., Sutawıjaya, A., and Harsası, M. (2020). Investigating student satisfaction in online learning: the role of student interaction and engagement in distance learning university. Turkish online journal of. Distance Educ. 21, 88–96. doi: 10.17718/tojde.770928
Nawi, F. A. M., Tambi, A. M. A., Samat, M. F., and Mustapha, W. M. W. (2020). A review on the internal consistency of a scale: the empirical example of the influence of human capital investment on Malcom Baldridge quality principles in TVET institutions. Asian People J. 3, 19–29. doi: 10.37231/apj.2020.3.1.121
Özhan, Ş. Ç., and Kocadere, S. A. (2020). Flow, emotional engagement, and motivation affect success in a gamified online learning environment. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 57, 2006–2031. doi: 10.1177/0735633118823159
Patnaik, J., and Bhowmick, B. (2022). Determining appropriateness for management of appropriate technology: an empirical study using factor analysis. Tech. Anal. Strat. Manag. 34, 125–137. doi: 10.1080/09537325.2021.1890013
Rafiq, S., Iqbal, S., and Afzal, A. (2024). The impact of digital tools and online learning platforms on higher education learning outcomes. Al-Mahdi Res. J. 5, 359–369.
Raza, S. A., Qazi, W., and Umer, B. (2020). Examining the impact of case-based learning on student engagement, learning motivation and learning performance among university students. J. Appl. Res. Higher Educ. 12, 517–533. doi: 10.1108/JARHE-05-2019-0105
Salas-Pilco, S. Z., Yang, Y., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Student engagement in online learning in Latin American higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 53, 593–619. doi: 10.1111/bjet.13190
Sun, P. P., and Zhang, L. J. (2024). Investigating the effects of Chinese university students’ online engagement on their EFL learning outcomes. Asia Pac. Educ. Res. 33, 747–757. doi: 10.1007/s40299-023-00800-7
Vezne, R., Yildiz Durak, H., and Atman Uslu, N. (2023). Online learning in higher education: examining students' online engagement predictors. Educ. Inf. Technol. 28, 1865–1889. doi: 10.1007/s10639-022-11171-9
Vlachogianni, P., and Tselios, N. (2022). Perceived usability evaluation of educational technology using the system usability scale (SUS): a systematic review. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 54, 392–409. doi: 10.1080/15391523.2020.1867938
Wang, Y., Cao, Y., Gong, S., Wang, Z., Li, N., and Ai, L. (2022). Interaction and learning engagement in online learning: the mediating roles of online learning self-efficacy and academic emotions. Learn. Individ. Differ. 94:102128. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2022.102128
Wang, F., Zhu, X., Pi, L., Xiao, X., and Zhang, J. (2024). Patterns of participation and performance at the class level in English online education: a longitudinal cluster analysis of online K-12 after-school education in China. Educ. Inf. Technol. 29, 1–23. doi: 10.1007/s10639-024-12556-8
Wong, Z. Y., and Liem, G. A. D. (2022). Student engagement: current state of the construct, conceptual refinement, and future research directions. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 34, 107–138. doi: 10.1007/s10648-021-09628-3
Zhang, Z., Li, Z., Liu, H., Cao, T., and Liu, S. (2020). Data-driven online learning engagement detection via facial expression and mouse behavior recognition technology. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 58, 63–86. doi: 10.1177/0735633119825575
Keywords: online learning engagement, English language learning, online learning platforms, cognitive investment, behavioral investment, emotional engagement, social interaction in learning
Citation: Zhang Q, Masran MNB and Hou Y (2025) Research on exploring college students’ online English learning performance through NetEase cloud classroom. Front. Educ. 10:1606014. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1606014
Edited by:
Enrique H. Riquelme, Temuco Catholic University, ChileReviewed by:
Fitra Delita, State University of Medan, IndonesiaHyein Chong, Chungnam National University, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Masran and Hou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanghong Hou, d2luZWFib3V0QDE2My5jb20=
 Qi Zhang1
Qi Zhang1 Yanghong Hou
Yanghong Hou