- Faculty of Educational Sciences, An-Najah National University, Nablus, Palestine
Student engagement significantly influences academic success, motivating educators to explore innovative technologies to enhance learning environments. This mixed-methods study systematically investigates the impact of Artificial Intelligence, Extended Reality, and their combined usage, compared with traditional learning environments, on high school students' cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social engagement. Utilizing Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory, this research used a convergent parallel design, combining quantitative data from 888 students who took part in rigorous non-parametric analyses and semi-structured interviews with 40 students sampled for qualitative descriptive thematic analysis. Results indicated that the AI-XR environment outperformed all other environments across all four engagement categories. Findings reinforce the synergistic opportunities for learning with AI and XR when applied in educational environments. The XR environment conceptually yielded higher levels of emotional and cognitive engagement through the immersive visualization, while the AI-environment yielded high levels of personalized adaptive learning pathways for students. Meanwhile, traditional learning environments led to the lowest engagement levels, due to their passive and non-interactive teaching nature. These findings reveal the transformative power of combining AI and XR technologies, offering essential implications for teachers, policymakers, and instructional designers committed to fostering deeper and broader student engagement in the context of digitally enriched educational systems.
1 Introduction
Student engagement is an essential element to obtain academic achievement and effective learning experiences. Engagement includes cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social dimensions, and is a predictive factor of academic performance, motivation, efforts, and persistence (Kahu, 2013; Fredricks et al., 2016; Lei et al., 2018). Conventional teaching strategies can lack an inclusive engagement model, specifically for those learners who can best engage in digital formats. In this regard, educational researchers have begun to investigate new technologies, specifically, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Extended Reality (XR), to support the development of more friendly, customized, and stimulating learning environments (Merchant et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2020).
AI technologies, which include adaptive learning systems and intelligent tutors, provide adaptive instructional pathways predicated on learner data, and possibility increasing motivation and deep engagement (Roll and Wylie, 2016; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019; Chiu et al., 2023). In contrast XR technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) provide immersive, and powerful experience-based learning opportunities to enhance emotional and cognitive engagement by placing learners in realistic, interactive scenarios (Radianti et al., 2020; Hamilton et al., 2021; Hmoud et al., 2023). While both AI and XR have demonstrated promise overall in promoting engagement, there remains limited empirical evidence investigating their comparative and combined engagement effects across the multidimensional construct of engagement.
Based on Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory (LTE) (1984), this research explores how AI and XR environments support learner engagement by following the experiential learning cycle: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. Kolb's theory indicates that engaging learning can happen in contexts where learners experience, reflect, and use their knowledge. These principles indicate that immersive and adaptive technologies may fit with and enhance experiential learning methods (Kolb and Kolb, 2017).
To fill this gap, the current study utilized a mixed-methods design to analyze engagement that reflected cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social engagement for high school students in four instructional settings (traditional, AI, XR, and AI-XR). The quantitative strand was to compare the engagement of the four different groups in these four instructional settings, while the qualitative strand sought to determine students' perceptions and lived experiences in the technology-mediated learning environments. The findings of this study will enhance knowledge of how advanced educational technology can support multidimensional engagement. This study will also systematically compare the specific learning environments and afford student voice(s) to advance teacher, designer, and policy-maker decisions, in order to enhance engagement in digitally rich classrooms.
Despite the increasing interest surrounding AI and XR technologies in education, research comparing their individual and combined effects on multidimensional components of student engagement in secondary level settings, remains limited. To address this gap, the present study adopts a mixed methods approach and is guided by the following research questions:
1.1 Overall research question:
How do different learning environments (Traditional, AI, XR, and AI-XR) influence high school students' engagement?
1.2 Quantitative sub-question (RQ1a):
Are there statistically significant differences in cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social engagement among students exposed to Traditional, AI, XR, and AI-XR environments?
1.3 Qualitative sub-question (RQ1b):
How do students describe their engagement experiences within AI, XR, and AI-XR learning environments?
2 Literature review and theoretical framework
2.1 Experiential learning theory
Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory (ELT) describes a holistic process of learning we engage in and reflects on our experiences. Kolb (1984) described learning as a dynamic cycle, reclaimed in four stages: concrete experience (CE), reflective observation (RO), abstract conceptualization (AC), and active experimentation (AE). Learning happens effectively when learners are able to engage in all four learning stages and alternate between action and reflection, through concrete and abstract thinking. Learning through experiences is cyclical in nature and learners create knowledge when experiencing and purposely critically reflecting on those experiences (Kolb, 1984; Kolb and Kolb, 2005, 2017).
Within the field of educational technology, ELT provides a particularly fruitful theoretical framework for understanding how digital tools can deepen engagement. Technologies such as AI and XR are naturally suited for Kolb's stages. For instance, XR environments offer realistic simulations that can be immersive (CE) and prompt students to reflect on relevant situations (RO), infer what to learn, and abstract principles (AC) before applying what they learn through real-world (AE) or interactive experiences (Radianti et al., 2020; Hmoud et al., 2023; Crogman et al., 2025). Likewise, AI will foster active experimentation by adapting tasks to learners' responses and providing feedback in a personalized way that creates iterative learning cycles (Roll and Wylie, 2016; Feijóo-García et al., 2025). These affordances suggest ELT will be a viable lens for analyzing AI and XR while providing a rich view of the multidimensional aspects of engagement (Hamilton et al., 2021).
In addition, ELT informs the present study's inquiry into the role different learning contexts play in cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social engagement. Cognitive engagement is informed by opportunities for abstract conceptualization, emotional engagement by experiences that are meaningful and immersive, behavioral engagement by students actively participating in learning activity, and social engagement by engaging in collaborative reflection and experimenting together (Fredricks et al., 2016; Cárdenas-Sainz et al., 2023). While this study is situated in Kolb's theory, we ensure that student engagement is examined as one psychological or behavioral outcome of learning and also considered as a component of experiential learning processes provided by the innovative educational technologies employed.
2.2 The role of AI and XR in education
A complete revolution in education practice has been provided by Artificial Intelligence through personalized and adaptive learning experiences that reflect the unique cognitive abilities and learning preferences of individual students. Learning systems based on artificial intelligence can analyze extremely large datasets to improve and adjust educational material and teaching practices to optimize levels of engagement and students' learning outcomes (Hmoud et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024; Feijóo-García et al., 2025). AI-based learning systems can also provide time-sensitive feedback, tailored remediation, and purposeful and engaging experiences that enhance the effectiveness of the learning process (Shaik et al., 2022). AI further facilitates next-generation data analytics in education. Educators can quickly and precisely identify learners who are at risk for not being successful and support their learning by providing interventions to improve their learning outcomes (Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019).
Extended Reality, which includes the spectrum of Virtual, Augmented, and Mixed Reality, enhances AI to provide deep immersive interactive environments for students that reach them through experiential learning. XR provides students the opportunity to investigate scenarios and concepts that would be difficult or impossible to realize in the traditional classroom setting and promotes comprehension, critical thinking, and retention (Radianti et al., 2020; Cárdenas-Sainz et al., 2023). For instance, VR simulations enable students to interact with historical events, and/or complex scientific phenomena, to integrate theoretical concepts with past experience (Crogman et al., 2025).
An important benefit of XR is its ability to enhance student engagement in cognitive, emotional, social, and behavioral aspects. Students in XR environments will typically experience an increased amount of curiosity and motivation, which enhances cognitive processing and retention of educational material (Percuku and Minkovska, 2022). XR technologies also foster collaborative learning, i.e., students are able to interact and solve problems together in a virtual environment while working on their social skills and teamwork (Merchant et al., 2014; Chung et al., 2021).
The integration of AI and XR multiplies educational advantages through interactive and individualized immersive learning experiences. AI can enhance the XR environment with Intelligence support systems, permitting adaptive guidance based on student interaction and performance in virtual environments (Reiners et al., 2021). The opportunities this partnership opens permit rapid, personalized feedback, and adaptive learning trajectories, thus increasing students' engagement and satisfaction. As an instance, AI-powered environments with virtual tutors can interact with students in an easy manner within XR environments, guiding students through complex tasks, adjusting the difficulty as students engage, and providing contextualized interactive feedback (Divekar et al., 2021).
While the use of AI and XR has great potential to disrupt traditional modes of education, effective forms of specialists are often more nuanced and challenging in educational contexts. For example, the high costs and technical difficulties of technologies are issues. In addition, educators and institutions must articulate any valuable educational benefit while considering the risks of reliance on technology to promote pedagogy. Finally, data privacy and ethical considerations around the use of some student data are perennial considerations in the application of technology in education (Akgun and Greenhow, 2021; UNESCO, 2021). The successful resolution of these challenges is essential for the successful equitable access to and deployment of AI and XR technologies in diverse settings within education.
2.3 Dimensions of student engagement
Student engagement is a measure of how much motivation students have to be fully involved in the learning process, which is demonstrated through participating and collaboration with each other as well as their professors (Fredricks et al., 2016). Engagement is most frequently defined as the quality of effort that students cognitive commit to learning in the course of participating in their academic activities and in pursuit of the desired educational outcomes (Lewis et al., 2011; Groccia and Buskist, 2018). Christenson et al. (2012) describe engagement as the involvement of the learner in tasks and activities that fosters learning while not engaging in behaviors that inhibit sustained academic learning effort.
Skinner et al. (2009) categorized engagement into three distinct dimensions: behavioral engagement, including consistent learning, focused effort, and attention; emotional engagement, which represents interest and excitement about learning; and cognitive engagement, which includes challenge, autonomy, and actively working on the task. Appleton et al. (2006) also refer to emotional and psychological (cognitive) engagement as similar concepts that can be considered together. These definitions reveal that engagement moves from observable aspects of behavior to cognitive and emotional depths. Engagement also spans all curricular learning activities, such as time on task, effort exerted, and learning strategies, to extracurricular experiences such as community service and attendance at non-academic experiences (Lee et al., 2019).
According to Marks (2000), behavioral engagement consists of observable traits such as effort put into learning and achievement academically. Emotional engagement refers to the emotional reactions of learners toward learning activities such as enjoyment, boredom, or interest. Finn (1989) described a two-factor engagement model with behavioral factors (e.g., participation) and affective factors (e.g., identification) that describe behavioral engagement as action as a participant in learning, such as asking questions and turning in work, and emotional engagement as an individual's belonging and sense of self or identity within the academic environment (Lee et al., 2019).
Moreover, cognitive engagement pertains to the efforts of students to think and implement mental strategies as they become acquainted with, and subsequently learn, a task or academic task (Lewis et al., 2011). Cognitive engagement is associated with academic performance and is typically measured through, for example, confidence in learning and assessment scores (Handelsman et al., 2005). This multifaceted view of engagement distinguishes this component as a critical piece of inquiry into the ways in which students engage with and learn from innovative and emerging learning environments involving AI and XR.
2.4 The effects of AI and XR on student engagement
In recent years, the research community has begun to identify AI and XR as important facilitators of student engagement in education. They are changing the way instruction is delivered and impacting students' experience in terms of cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social engagement during their respective learning processes. AI innovations such as adaptive learning systems, chatbots, and predictive analytics facilitate personalized and responsive learning paths that promote learners' perceptions of relevance, autonomy, and competence (Wang et al., 2024; Feijóo-García et al., 2025). Similarly, XR technologies create emotionally meaningful and physically engaging experiences in immersive simulations and interactive visual worlds that can capture and sustain learners' attention, curiosity, and intrinsic motivation (Radianti et al., 2020; Crogman et al., 2025).
Research shows that AI and XR have the opportunity to promote multiple dimensions of engagement with students. For example, AI-enhanced immersive learning environments have positively influenced behavioral engagement when technology increased the learners' persistence and attention levels through intelligent feedback, anecdotes, and game-based elements (Almufarreh, 2024; Hmoud et al., 2024). Additionally, XR technologies influence emotional and social engagement dimensions through immersiveness, keeping learners engaged with the dynamic experience while also encouraging collaborative empathy, excitement, and peer exchanges (Hamilton et al., 2021; Hmoud et al., 2023). Immersive environments allow learners to participate in simulations or experiences that embody real-world challenges, promoting a deeper reflection and a more authentic learning experience.
When AI and XR are united, they present a synergy of instructional innovation that enhances the engagement in all domains. The use of adaptive intelligence paired with experiential immersion allows for a learning experience that is personalized and deeply engaging. Research shows hybrid environments support higher-order thinking skills, motivation, and collaboration. For instance, in AI-XR environments, students are given personalized prompts or adaptive scaffolding while engaged in immersive tasks that enhance strategic learning and affective involvement. This dual mechanism fosters a profound learning encounter and helps make abstract content more tangible and learning outcomes more meaningful (Reiners et al., 2021; Hirzle et al., 2023; Prada, 2023; Rocca, 2024).
As advanced technology continues to permeate education, understanding how engagement is influenced within AI and XR environments will become ever more essential. This study aims to add to this conversation by examining how AI, XR, and AI-XR learning environments predict engagement in the cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social dimensions of high school students. Findings offer evidence-based lessons about how technology-enhanced instruction may support deeper engagement in learning and better students' academic experience overall.
3 Methods
3.1 Research design
This study employed a convergent parallel mixed-methods design to explore the effects of four learning environments—Traditional, AI, XR, and AI-XR—on high school students' engagement across cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social dimensions. The quantitative component utilized an experimental design with cluster random sampling to support the generalizability of results and reduce selection bias. Simultaneously, the qualitative component incorporated semi-structured interviews to provide contextual depth and insight into students' experiences. This methodological triangulation allowed for the integration of numerical trends and narrative meaning, strengthening the study's overall validity (Teddlie and Tashakkori, 2009; Creswell and Clark, 2017).
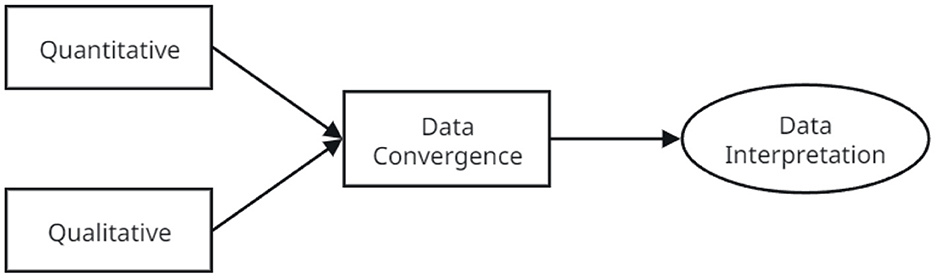
This mixed-methods approach was particularly suitable for addressing the multidimensional nature of engagement and capturing both the measurable outcomes and subjective experiences related to AI and XR technologies. The two data strands were collected, analyzed separately, and then merged during interpretation to cross-validate and enrich the findings. Figure 1 illustrates the convergent parallel mixed-methods design employed in this study, showing the separate collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data, followed by integration during interpretation.
3.2 Participants and sampling
The quantitative sample consisted of 888 students from four high schools in Jerusalem, each randomly assigned to one of the four learning environments. The sample was distributed as follows: traditional (n = 234), AI (n = 225), XR (n = 218), and AI-XR (n = 211). A multistage cluster sampling approach was applied, randomly selecting schools and assigning intact classrooms to one of the four experimental conditions. While randomization was prioritized, care was taken to include a range of schools from different districts and school types to promote diversity across gender, academic performance levels, and geographic locations (Lohr, 2021).
For the qualitative phase, 40 students were selected through purposive sampling, ensuring maximum variation across the four instructional environments, school type, and gender. Ten participants were chosen from each group (n = 10 × 4), and interviews continued until data saturation was reached. This sample size is consistent with qualitative research standards for thematic analysis and ensures sufficient depth without sacrificing manageability (Creswell and Creswell, 2017).
3.3 Intervention design
All participants in this study engaged with the same curricular content in science and humanities subjects; however, the mode of instructional delivery differed across the four experimental groups. The Traditional group received instructor-led lessons using conventional tools such as printed textbooks, whiteboards, and PowerPoint presentations. The AI group learned through intelligent tutoring systems that offered adaptive learning pathways, real-time feedback, and analytics powered by machine learning to personalize instruction. Students in the XR group engaged with content in immersive environments using virtual and augmented reality headsets, allowing them to interact with problem-based scenarios relevant to the curriculum. The AI-XR group experienced a hybrid model that combined adaptive AI features with XR's immersive simulations. This integrated approach followed Kolb's experiential learning cycle by facilitating real-time feedback, reflective engagement, and hands-on learning. The intervention spanned 6 weeks, comprising 18 instructional sessions, with approximately three 45-min weekly lessons. To ensure consistent implementation across conditions, all participating teachers underwent specialized training aligned with the requirements of their respective instructional modality.
3.4 Data collection
3.4.1 Quantitative data collection
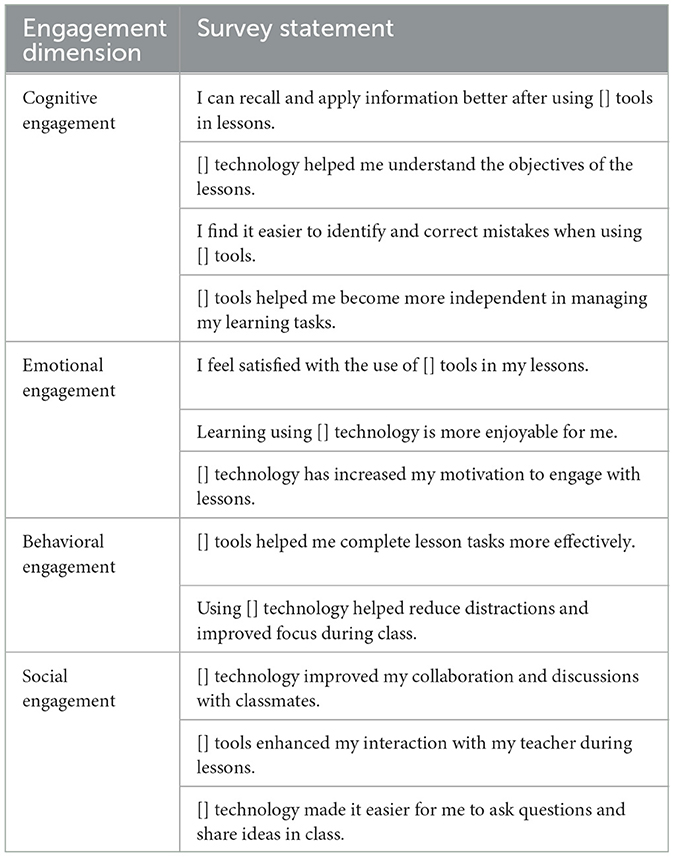
Student engagement was measured using a 12-item multidimensional scale developed and validated by Hmoud et al. (2023), targeting cognitive (4 items), emotional (3 items), behavioral (2 items), and social (3 items) engagement. The Full instrument is provided in Appendix A. Responses were collected on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). A pilot test with 60 students yielded strong reliability (Cronbach's alpha = 0.88 overall; subscales ranged from 0.76 to 0.82).
3.4.2 Qualitative data collection
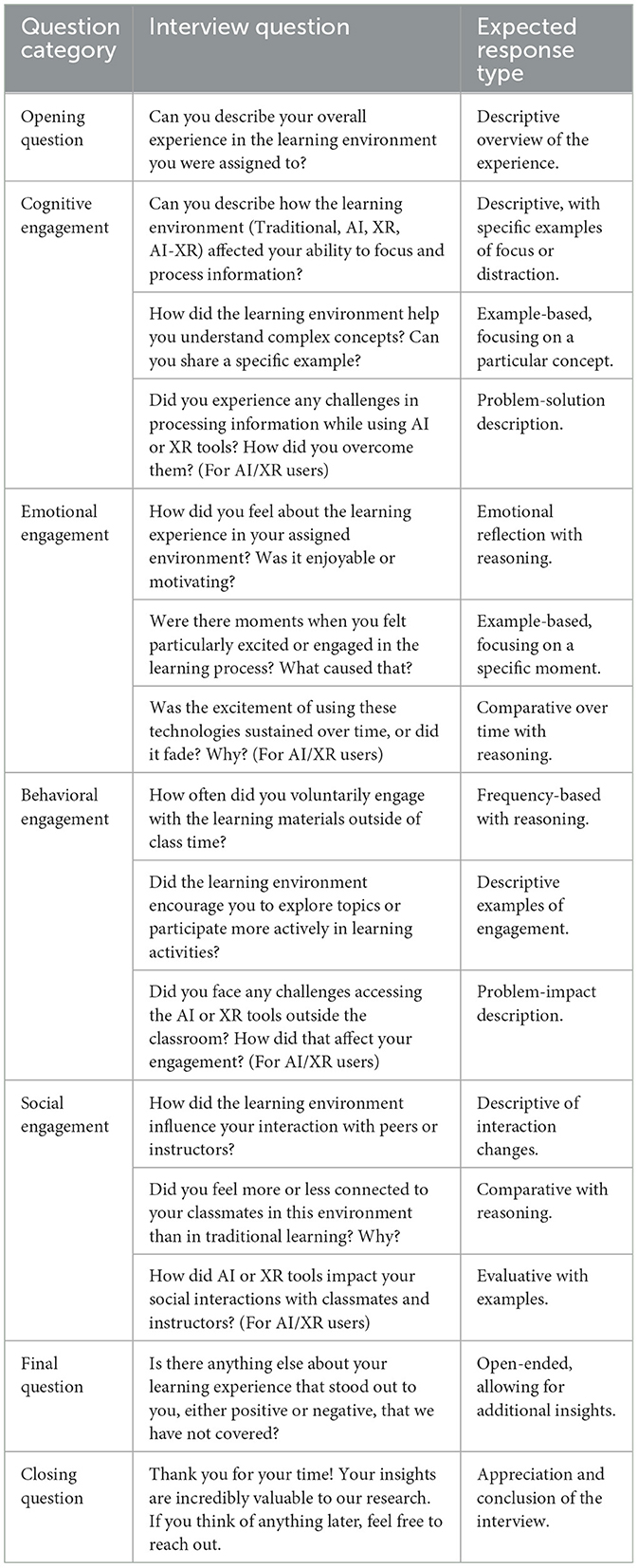
Semi-structured interviews, lasting 25–40 min each, explored students' perspectives on engagement in their respective environments. Interview guides included open-ended questions aligned with the engagement dimensions (see Appendix B). Interviews were conducted in Arabic, recorded, and transcribed verbatim. A professional translator reviewed English translations for accuracy (Behling and Law, 2000).
3.5 Data analysis
3.5.1 Quantitative data analysis
The statistical analysis began with a preliminary check for outliers and assumption testing. Normality and homogeneity of variance assumptions were violated, rendering traditional MANOVA unsuitable. Instead, PERMANOVA (Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance) was selected for its robustness in handling non-parametric multivariate data. It used 9,999 permutations to test group-level differences in overall engagement across the four learning environments (Anderson, 2001). PERMANOVA was followed by pairwise comparisons to determine where specific differences occurred. In addition, Kruskal-Wallis tests were conducted for each engagement dimension individually—cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social—supplemented by Dunn's post-hoc tests with Bonferroni adjustment to control for Type I error (Conover, 2006; Elliott and Hynan, 2011). Descriptive statistics and box plots were also used to illustrate the distribution of engagement scores among the groups.
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS v26 and R v4.4.2, ensuring cross-platform validation of findings. Effect sizes (eta-squared for Kruskal-Wallis and F-values for PERMANOVA) were reported to indicate the practical significance of the results.
3.5.2 Qualitative data analysis
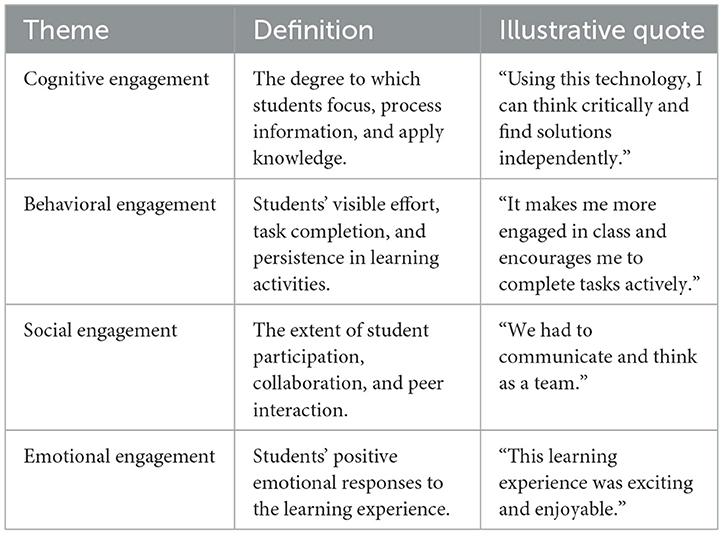
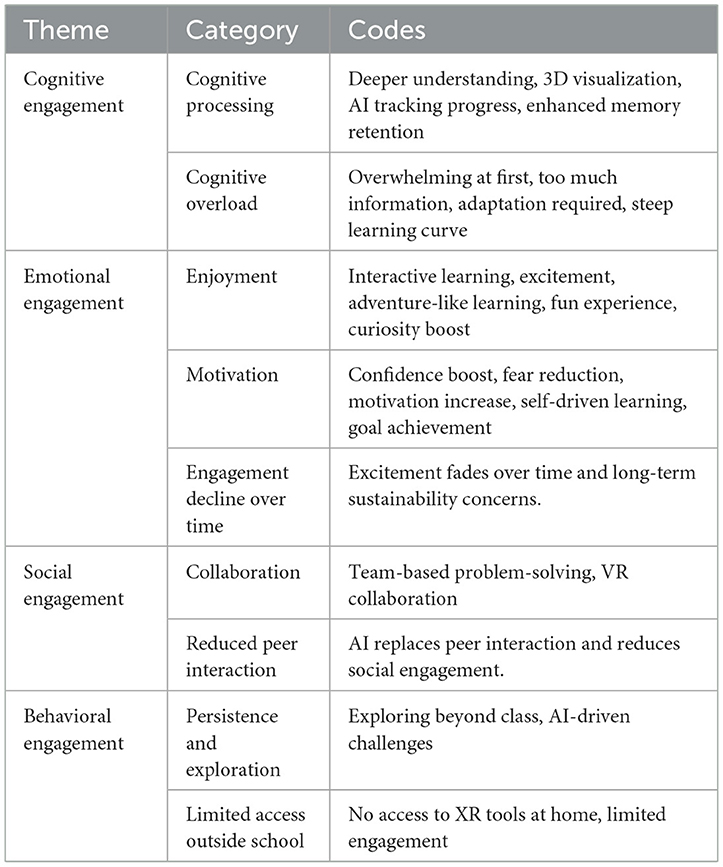
The qualitative strand was analyzed through thematic analysis following Braun and Clarke's (2006) six-phase approach: (1) data familiarization, (2) initial coding, (3) theme generation, (4) theme review, (5) theme definition, and (6) report production. Transcripts were initially coded using an inductive approach, allowing natural patterns and themes to emerge, followed by deductive coding guided by the four predefined engagement dimensions (Hmoud et al., 2023). A codebook was constructed during the initial coding phase to systematically capture emergent codes, their definitions, and representative excerpts. It was refined iteratively through ongoing thematic analysis and collaborative discussions among the research team. Table 1 below summarizes the finalized codes and their alignment with the engagement dimensions.
MAXQDA 2020 supported data coding through its structure, allowing the researcher to recognize the categories and quantify the frequency of emerging concepts. Therefore, the initial coding phase involved assigning codes to emerging concepts that gave shape to categories. Nine engagement categories were established and subsequently structured according to the proposed frameworks. These categories were then reviewed by the researchers' consensus to check for their correspondence with theoretical structures. Following Saldaña's method, data analysis was done in two coding cycles (Saldaña, 2021). The first cycle included transcribing the interviews, in vivo coding, line-by-line coding, and incident-by-incident coding to provide a thorough data-driven analysis. In the second cycle, theoretical coding included association, categorization, and classification, were creating meaningful relationships between codes. The unit of analysis in this study is the “theme,” meaning the analysis of information took place at the phrase or sentence level.
Table 2 outlines this study's themes, categories, and codes. The engagement themes were defined and categorized following Hmoud et al. (2023), the codes and categories were generated through constant comparative analysis, which involved continuously reading and re-reading the interview transcripts to maintain consistency and rigor in the data interpretation.
Findings from the quantitative and qualitative strands were merged during interpretation using joint display tables, which allowed for direct comparison and integration of results across both methods. This process enhanced the explanatory power of the findings and offered a nuanced understanding of how students engaged with different instructional environments (Creswell and Creswell, 2017).
3.6 Trustworthiness
To ensure the rigor and reliability of the qualitative findings, this study followed Lincoln and Guba (1985) four criteria: credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability. Credibility was addressed through triangulation between quantitative and qualitative data, peer debriefing, and independent coding by two researchers. Thick descriptions of the study context, participant characteristics, and instructional settings supported Transferability. Dependability was maintained through a clear audit trail of decisions, use of analytic software, and consistent coding protocols, while confirmability was strengthened through reflexive journaling and external auditing. These procedures collectively reinforced the authenticity and trustworthiness of the qualitative data, ensuring that the findings are grounded in participant experiences and can contribute meaningfully to research on engagement in technology-enhanced learning environments.
4 Results
4.1 Quantitative results
To address RQ1a “Are there statistically significant differences in cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social engagement among students exposed to Traditional, AI, XR, and AI-XR environments?” a series of quantitative analyses were conducted, beginning with descriptive statistics, followed by PERMANOVA and non-parametric post-hoc tests.
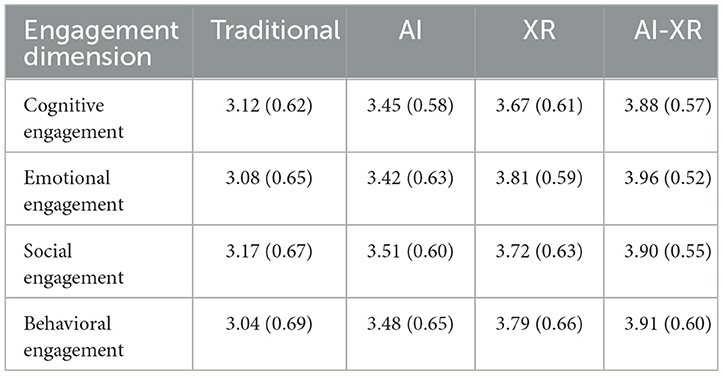
Descriptive analyses revealed that students in the AI-XR group consistently scored higher across all four engagement dimensions, followed by XR, AI, and Traditional groups. Table 3 presents the means and standard deviations for each group.
A one-way PERMANOVA was conducted to examine differences in student engagement dimensions across the four learning environments: traditional, AI, XR, and AI-XR. Results indicated significant differences in overall engagement among the learning environments, F(3, 815) = 78.39, R2 = 0.22, p < 0.001. The model explained ~22.4% of the total variance in the data, while the residual variance accounted for 77.6%.
Pairwise comparisons with Bonferroni correction revealed significant differences between all environment pairs (p < 0.05). As shown in Table 4, the most significant effect was observed between Traditional and AI-XR environments (F = 188.34, R2 = 0.32, p < 0.001), suggesting substantial differences in engagement between these environments. The smallest, though still significant, difference was found between AI and XR environments (F = 9.87, R2 = 0.02, p = 0.012).
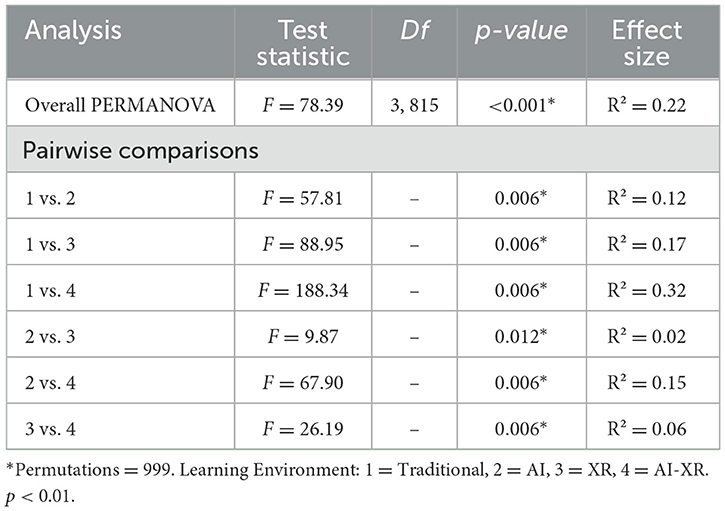
Table 4. Student's engagement PERMANOVA and pairwise comparison results by learning environment types.
The non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plot (Figure 2) visualizes the multivariate differences in student engagement across the four experimental groups by projecting their positions in a two-dimensional space. NMDS is a robust ordination technique that simplifies high-dimensional data by preserving the ranked dissimilarities between data points, thereby offering an intuitive visual representation of group relationships (Kruskal, 1964). The plot revealed a clear and meaningful spatial separation among the four learning environments, further supporting the PERMANOVA findings. The AI-XR cluster was positioned furthest from the Traditional cluster, reflecting a substantial divergence in overall engagement profiles. This suggests that students in the AI-XR condition experienced a uniquely high level of multidimensional engagement compared to those in conventional settings. Notably, the AI and XR clusters were closer together, indicating that their effects on engagement, while distinct, were relatively similar and less pronounced than those produced by the integrated AI-XR approach. These spatial patterns underscore the synergistic impact of combining adaptive AI features with immersive XR elements, providing a richer and more effective learning experience than either technology alone.
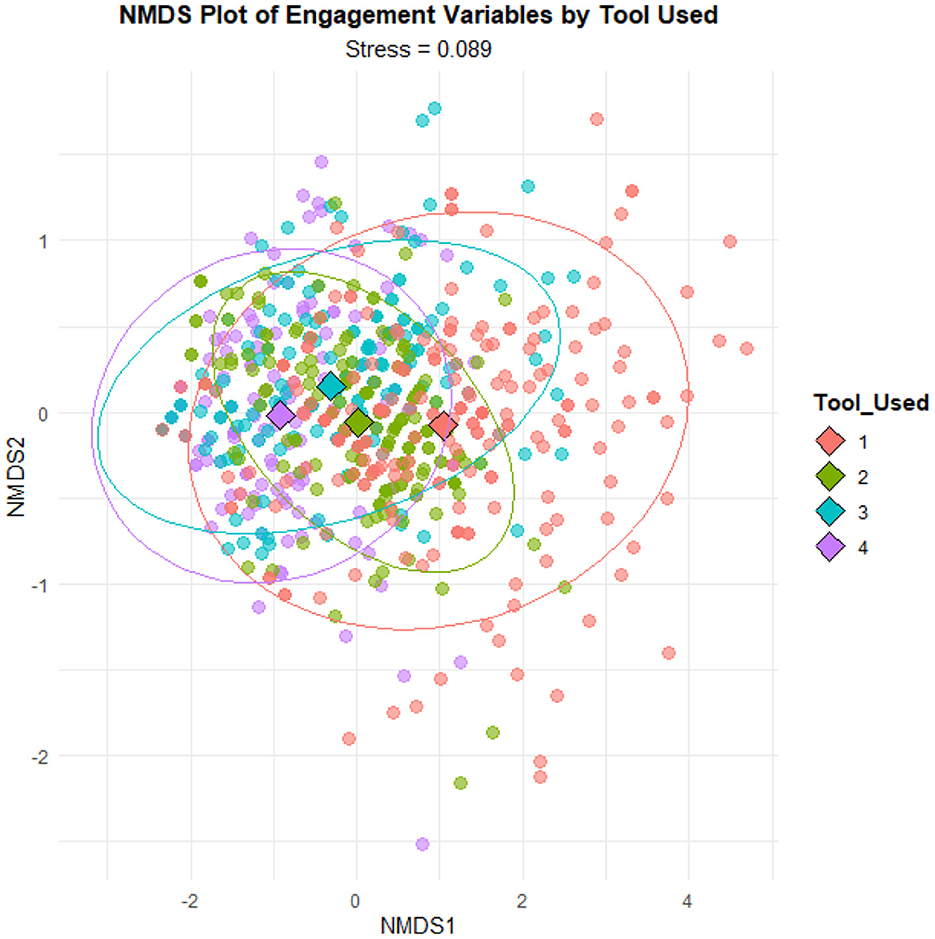
Figure 2. NMDS visualization of student's engagement differences across learning environments. Greater distance between clusters reflects greater dissimilarity in engagement profiles. The AI-XR (4) group is most distinct from Traditional (1), while AI (2), and XR (3) show partial overlap.
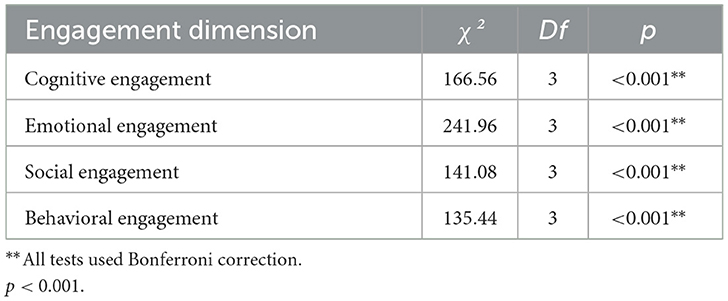
The non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test was conducted to understand how each engagement dimension (cognitive, emotional, social, and behavioral) differed across learning environments. Kruskal-Wallis is appropriate when data are non-normally distributed or heteroscedastic, making it a suitable choice for further analysis (Field, 2018). The results confirm that different learning environments significantly impact all four engagement dimensions (see Table 5).
Since Kruskal-Wallis is based on ranked data rather than raw scores, traditional parametric post-hoc tests like Tukey's HSD or Bonferroni t-tests are unsuitable. Instead, Dunn's test is specifically designed for multiple pairwise comparisons following a Kruskal-Wallis test while controlling for Type I errors using Bonferroni corrections (Dunn, 1964; Elliott and Hynan, 2011).
4.1.1 Cognitive engagement
Dunn's post-hoc comparisons with Bonferroni correction indicated that students in the AI-XR environment (M = 4.27, SD = 0.57) reported significantly higher cognitive engagement than those in the XR (M = 3.79, SD = 0.74), AI (M = 3.81, SD = 0.19), and Traditional (M = 3.40, SD = 0.69) environments. Additionally, the AI and XR environments significantly outperformed the Traditional environment, while no significant difference was observed between AI and XR (p = 0.572).
4.1.2 Emotional engagement
Post-hoc Dunn's test revealed that students in the AI-XR environment (M = 4.32, SD = 0.58) reported significantly higher emotional engagement than those in the XR (M = 4.12, SD = 0.64), AI (M = 3.85, SD = 0.62), and Traditional (M = 3.09, SD = 0.87) environments. XR and AI environments significantly outperformed the Traditional environment, with XR significantly exceeding AI (p = 0.001). The slightest difference, though still significant, was between XR and AI-XR (p = 0.08).
4.1.3 Social engagement
Dunn's post-hoc test showed that students in the AI-XR environment (M = 4.27, SD = 0.65) exhibited significantly higher social engagement than those in the XR (M = 3.98, SD = 0.67), AI (M = 3.72, SD = 0.64), and Traditional (M = 3.45, SD = 0.76) environments. Furthermore, both AI and XR environments significantly outperformed Traditional, while XR also showed significantly higher social engagement than AI (p = 0.001).
4.1.4 Behavioral engagement
Dunn's test indicated that students in the AI-XR environment (M = 4.20, SD = 0.62) exhibited significantly higher behavioral engagement compared to XR (M = 3.87, SD = 0.79), AI (M = 3.74, SD = 0.62), and Traditional (M = 3.22, SD = 0.91) environments. Additionally, AI and XR significantly outperformed the Traditional environment, while XR showed significantly greater behavioral engagement than AI (p = 0.016).
Figure 3 illustrates the Estimated Marginal Means (EMMs) plots for Cognitive, Emotional, Social, and Behavioral Engagement across different learning environments. To enhance clarity, 95% confidence intervals and standard error bars have been added. These allow for a more precise comparison of engagement levels across groups and highlight significant differences. Across all four engagement types, students in the AI-XR learning environment consistently outperformed those in XR, AI, and Traditional learning environments, reinforcing the value of combining immersive and adaptive technologies.
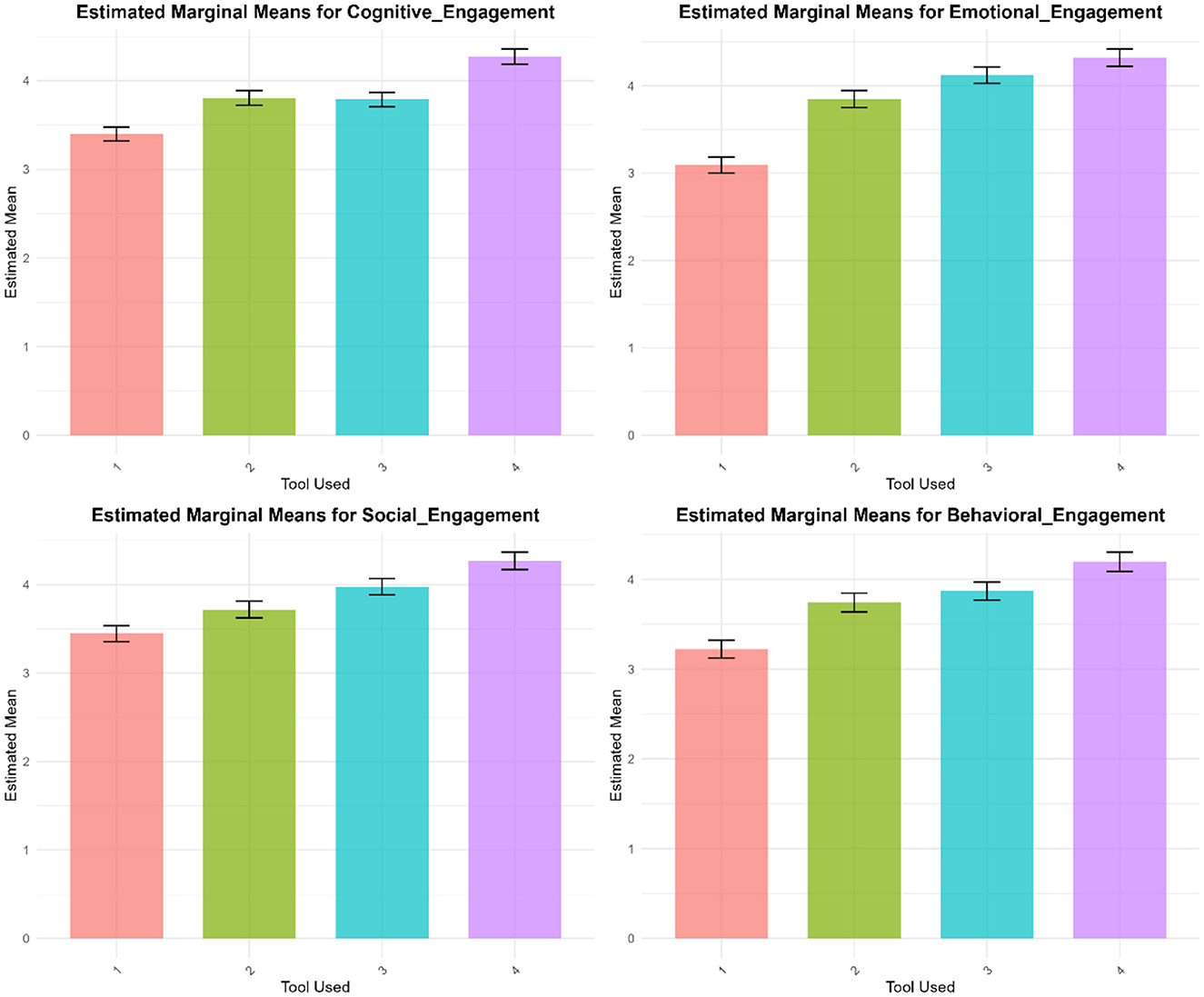
Figure 3. EMMS plots for students engagement dimensions by learning environment. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. AI-XR (4) yielded the highest engagement across all dimensions.
The estimated marginal means for the AI-XR environment were the largest in four groups and consistently remained significant during analysis. Emotional and behavioral engagement scores were the lowest in all cases, and the Traditional environment group (1) scored consistently. Both the AI (2) and XR (3) environments achieved moderate scores, sometimes outscoring the Traditional environment, yet comparable statistically to each other at the same dimension. Error bars in all plots denote confidence intervals and reflect that AI-XR results are more stable and steadily more significant regarding engagement scores.
4.2 Qualitative results
To answer RQ1b “How do students describe their engagement experiences within AI, XR, and AI-XR learning environments?” semi-structured interview data were analyzed thematically. The emerging themes are organized under the four dimensions of engagement. Thematic analysis revealed four significant themes consistent with the engagement framework: cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and social engagement. The word cloud in Figure 4 shows the codes with more frequency in the interviews coding for students' engagement.
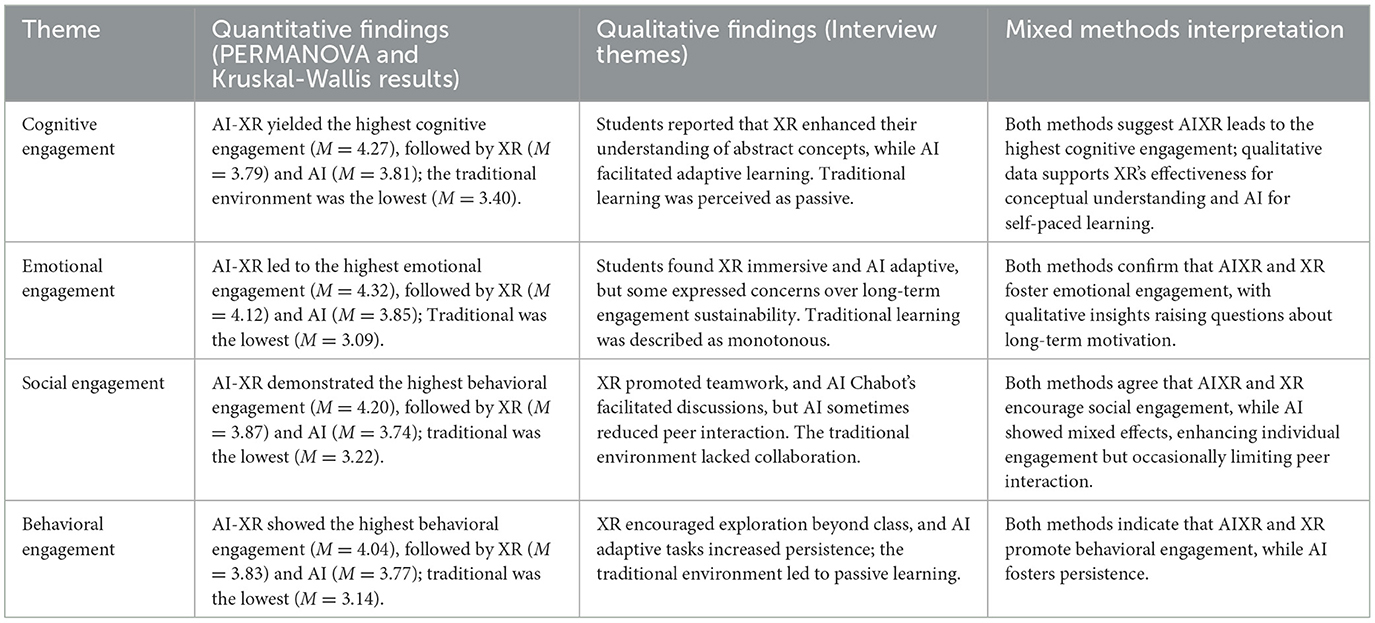
4.2.1 Theme 1: cognitive engagement
Cognitive engagement refers to students' ability to focus, process information, and apply knowledge effectively.
4.2.1.1 Cognitive processing
Students in the XR environment reported a greater comprehension of abstract concepts, attributing it to the technology's immersive and interactive features. “I could see the heart and its chambers in 3D, instead of only viewing flat diagrams in textbooks. This enhanced my ability to remember and explain it later” (Participant 7, XR group) Students mentioned that AI adaptive learning systems enabled them to monitor their progress, rectify mistakes, and manage their learning more efficiently. “With AI, I received immediate feedback on my mistakes and the reasons behind them. I had the opportunity to retry questions until I fully grasped the concepts” (Participant 10, AI group). While XR enhances comprehension via visualization and interactivity, AI fosters self-regulated learning by providing timely, tailored feedback.
4.2.1.2 Cognitive overload
Ensure students do not face cognitive overload when exploring AI and XR environments. The sheer volume of new information and interactive elements created a challenging learning curve. “At first, it felt overwhelming—so much information at once. But after a few lessons, I got used to it” (Participant 2, AI-XR group). Conversely, traditional learners demonstrated reduced cognitive involvement, perceiving their educational experience as passive and lacking interactivity. “It was memorizing facts and attending lectures. It did not feel like I was critically thinking or interacting with the material” (Participant 3, Traditional group). This shows the balance between interactive and passive learning styles. While AI and XR may present initial cognitive challenges, they foster deeper engagement and critical thinking over time. Traditional methods, though more comfortable, can limit active participation, impacting long-term retention, and satisfaction.
4.2.2 Theme 2: emotional engagement
Emotional engagement is defined by students' enthusiasm, motivation, and feelings of connection to the learning material.
4.2.2.1 Enjoyment
Interviewees often credited this to these tools' engaging and hands-on characteristics. “It felt more like an adventure than a lesson. I looked forward to learning every day” (Participant 3, AI-XR group). Students reported that XR-based learning felt more like an adventure than a lesson, making the learning experience enjoyable. “Using XR was like an adventure—it felt like I was inside the body, not just reading about it” (Participant 5, XR group). This shows how XR and AI-XR provide a compelling learning environment to keep learners engaged, encouraging a level of engagement sufficient to ensure motivation for deep participation.
4.2.2.2 Motivation
Students expressed greater confidence and motivation when utilizing AI, as it lowered their fear of failure by enabling them to practice and enhance their skills at their own pace. “AI quizzes were fun because I could keep trying until I got better. I was not afraid of making mistakes” (Participant 8, AI group). It shows confidence and motivation from the AI that develops an even less risky climate for learning.
4.2.2.3 Engagement decline over time
However, although students showed initial excitement, some expressed concerns about sustaining motivation in the long run. “At first, it was exciting, but I wonder if it will still feel this way after months of use” (Participant 2, XR group). Traditional learners, in contrast, expressed lower emotional engagement, describing the learning experience as passive and monotonous. “It was just listening to lectures and taking notes. There was not much to get excited about” (Participant 1, Traditional group). This indicates that although XR arouses initial enthusiasm, sustaining it seems complicated, unlike traditional learning, where emotional engagement does not exist.
4.2.3 Theme 3: social engagement
Social engagement involves collaborative learning and peer interaction.
4.2.3.1 Collaboration
Students in an XR environment participated in collaborative team problem-solving activities, enhancing communication and teamwork. “In VR, we had to work together to solve problems. We had to communicate and think as a team” (Participant 10, XR group). AI Chabot's and AI-based discussion Forums also facilitated a sense of community. “With AI Chabot's and discussion forums in magic school, I felt like I was part of a learning community, not just studying alone” (Participant 9, AI group). This highlights how XR and AI improve collaboration and community, creating a more interactive and socially engaging learning experience.
4.2.3.2 Reduced peer interaction
Some students indicated that AI tools occasionally substituted peer interactions, resulting in unexpected social isolation. “Sometimes I just asked AI instead of my friends, so I talked less to my classmates” (Participant 5, AI group). In contrast, some students in the Traditional group noted a lack of peer interaction, as learning was often individualistic and lecture-based. “There was not much teamwork involved. It was mostly just listening and writing” (Participant 2, Traditional group). This indicates that, although AI boosts learning efficiency, it might lessen peer interaction, akin to the solitary aspect of conventional learning.
4.2.4 Theme 4: behavioral engagement
Behavioral engagement refers to students' participation levels, task completion, and classroom interactions.
4.2.4.1 Persistence and exploration
Students utilizing XR tools exhibited greater self-directed exploration. “I kept exploring different parts of the cell in XR, even after class. It made me wants to learn more” (Participant 6, XR group). Similarly, AI-driven challenges motivated students to continue practicing beyond classroom hours. “AI challenges made me want to keep practicing, even outside of class” (Participant 1, AI group). This emphasizes how XR and AI promote self-directed learning, nurturing curiosity, and prolonged involvement outside the classroom.
4.2.4.2 Limited access outside school
A concern about equity arose regarding students' access to XR tools outside school, impacting their engagement beyond class hours. “I do not have a VR headset at home, so I could not review the lesson later” (Participant 8, XR group). Traditional learners, in contrast, described lower persistence and engagement, often attributing it to a lack of interactivity. “If I did not understand something, I would move on rather than trying to figure it out” (Participant 4, Traditional group). This shows how access barriers can restrict the benefits of XR, whereas conventional learning may hinder persistence because it lacks interactivity.
4.2.5 Mixed-methods results
This was a convergent mixed-method design that used quantitative methods, including PERMANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis Results, and qualitative methods, such as Thematic Analysis, to provide an overall understanding of how different learning environments (Traditional, AI, XR, and AI-XR) influence engagement among students. Combining statistical trends with rich participant narratives enhances these findings' validity, depth, and context. Table 6 summarizes the results.
5 Discussions
Differences across the four learning environments regarding engagement become apparent. In comparison, the traditional classroom yielded the least engagement, owing to the inertness of teaching and low interactivity. In contrast, AI-based learning enhanced engagement moderately through personalized feedback and adaptive pathways, although it remained considerably more limited than extended reality in providing complex social-emotional interaction. In contrast, XR had an immense impact on engagement because of immersive and active engagement of students in an environment that could engage cognitively and emotionally. Most significantly, the AI-XR combined condition provided the most significant engagement as it merged AI with the experiential immersion of XR. AI-XR is the balance of structured guidance for AIE learning and its interactive process.
This research reveals that these engagement models correlate with previous works on XR-based learning environments. These are places for hands-on experimental learning: they make the involvement of students 10 times higher with XR environments (Radianti et al., 2020; Hmoud et al., 2023). Similarly, AI-based adaptive learning may foster cognitive engagement, but it is still far away from the engagement XR brings (Feijóo-García et al., 2025). Furthermore, it was stated in the research that combined AI-based personalization and XR-based immersion contributes most to engagement on various factors (Kluge et al., 2022).
5.1 Cognitive engagement
Cognitive engagement was the strongest in AI-XR and XR conditions; these students had longer attention spans, deep information processing, and more efficient problem-solving when compared to the other conditions. While AI-based learning did provide some structure to cognitive engagement, as the latter helped students stay focused and process information more efficiently, it did not match up with XR conditions. On the other hand, cognitive engagement was the least in the traditional lecture style because passive instruction was usually not interesting enough to catch students' interest in deep learning. Both the quantitative and qualitative results demonstrated that these patterns existed. Statistically, the students in AI-XR exhibited the most significant cognitive engagement scores: Kolb's ELT states that learning occurs best with active experimentation and concrete experience (Kolb, 1984).
Qualitatively, the AI-XR students talked about how they could tinker with information and use it in real-life scenarios. This enabled them to engage with and make sense of the information they were learning interactively. On the other hand, some students in the AI learning environment complained that the structured and guided learning method was functional but limited the students' opportunities to explore topics freely. That sentiment seems consistent with Sweller's Cognitive Load Theory. (Sweller, 2011), which states that over-scaffolding the learners does not allow them to explore freely, thus hindering deep learning as the cognitive load goes beyond capacity.
5.2 Emotional engagement
Emotional engagement followed a similar pattern, peaking in the XR and AI-XR environments and dropping to its lowest in the traditional setting. Students in XR and AI-XR reported significantly higher motivation, excitement, and curiosity, thanks to the immersive and interactive nature of these experiences. AI-based learning provided emotional engagement by offering personalized feedback and adaptive learning paths that could spark interest. However, it did not match the level of immersion and excitement that XR offered. In the traditional environment, many students felt disconnected from the material, resulting in the lowest emotional engagement levels. Differences are discussed under Self-Determination Theory, which explains that there are environments where people tend to become more emotionally committed to their learning because of how autonomous and meaningful the learning becomes (Deci and Ryan, 1985). According to these lines, previous studies indicate that XR plays an important motivating and curious role by letting students engage in interactive learning activities; that is, the emotional part of learning becomes more alive (Kluge et al., 2022; Hmoud et al., 2023; Jayadurga and Rathika, 2023).
Qualitative evidence served further to illustrate these trends. XR-based classes saw students who said they were emotionally connected to the subject matter because they had vividly and interactively simulated real-world situations. On the other hand, the AI-only settings were appreciated for the personalized attention that they gave, yet in many instances, the students did find themselves lacking in the excitement and emotional involvement that one could feel during the actual classes. Hence, AI can, to some extent, make learning enjoyable, although unless we introduce more interactive and experiential components, it will not evoke emotion in students. Cao and Jian (2024) noted that pure AI learning enhances personalized instruction, yet such learning never gives rise to the emotional engagement generated by rich interactive environments.
5.3 Social engagement
Social engagement was also highest in the XR and AI-XR conditions and lowest in the traditional setting. Students in the XR and AI-XR learning environments spend enough time working in collaboration, peer discussions, and group simulations. This helps them feel more engaged and proactive in their learning process. In a nutshell, AI-based learning promotes formal social interaction (like online discussion forums or AI-driven peer feedback). Still, several have commented on how the interaction here felt mechanically and less spontaneous than the traditional XR collaboration. Traditional settings, on the other hand, limit interaction only to lecturing and student assignments. Students have no interaction with their peers and feel ignored and unengaged.
This variation in social engagement aligns with the relatedness component of Self-Determination Theory: learners engage more deeply when they feel a sense of connection and belonging in their learning environment (Deci and Ryan, 1985). Prior studies have supported this notion that interactive, technology-enhanced environments improve peer collaboration and knowledge co-construction (Mayordomo et al., 2022). This variation in social engagement aligns with the relatedness component of Self-Determination Theory: learners engage more deeply when they feel a sense of connection and belonging in their learning environment (Deci and Ryan, 1985). Prior studies have supported this notion that interactive, technology-enhanced environments improve peer collaboration and knowledge co-construction (Mayordomo et al., 2022). Thus, AI-driven virtuality can make virtual social interactions more interactive (Feijóo-García et al., 2025). The qualitative data supported these observations. Students in the XR and AI-XR groups often expressed that collaborative work in the virtual simulations or joint assignments increased their engagement because they got to discuss and solve real-time problems with classmates. Students in an AI learning environment have realized the benefits of AI conversation prompts that guide them to work together online. Still, some of them regretted not being with friends or working in person with a group that allows interaction in its original form. A study by Tang (2024) noted that AI could support teamwork in many respects but would still be less likely to simulate real-life interactions or motivate a group to come together and share ideas.
5.4 Behavioral engagement
Behavioral engagement was most prevalent in XR and AI-XR, but it was almost the opposite in the traditional way. XR and AI-XR environments had high levels of behavioral engagement from students: the students had high motivation. They were engaged in activities, with a more significant time for persistence under problems due to the interactive and exciting character of the problem-solving process. Students were motivated by AI learning as it generated problems adaptively and offered quick feedback on results, so they were prompted to apply them. Nevertheless, it was not as visible as it was in XR settings. On the other hand, the level of engagement in a regular class tended to be low: most students engaged in activities out of necessity rather than volition. This was accompanied by a minimal likelihood of students taking initiative or staying focused without such outside prompts.
The patterns of interactivity and gamification, introduced to boost class participation, have been well-studied in recent years by previous studies (Katyara et al., 2022). Kolb's ELT says interactive learning in a hands-on environment allows students to test, improve, and apply what is learned; therefore, commitment and persistence may rise. The behavior engagement trends among the students, which were strengthened by their reflective statements, were reflected in the findings. Students of the AI-XR group were stimulated by deep engagement with the real-time feedback given by AI plus immersive XR. As a result, students found themselves capable of making choices, pushing through tasks, and not giving up in challenging moments. Students instructed with traditional teaching strategies would express disengagement or motivational feelings; thus, their motivation did not extend beyond surface-level participation. A few AI-XR members mentioned the frustration since sometimes the tech could not respond quickly enough or without smoothness and sometimes got stuck because of a technology failure. Research results proved to highlight the warning word of Hirzle et al. (2023), whereby a combination of AI and XR could enhance behavioral engagement; any technical malfunctions, e.g., lag from the systems or glitching could nullify such motivation if it was not appropriately dealt with.
6 Implications, limitations, recommendations, and conclusions
6.1 Implications of the study
The findings of this study carry important implications for educational theory, instructional design, and policy development, especially in integrating artificial intelligence and extended reality in high school learning environments. The study supports and extends Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory by showing how AI-XR environments can stimulate all stages of experiential learning—concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation—through adaptive, immersive, and personalized features. These results suggest that AI can serve as scaffolding within XR-based experiential learning, promoting reflection, and conceptual understanding through real-time feedback and adaptive pathways.
From a practical standpoint, the study highlights how pairing adaptive AI systems with immersive XR can create engaging and inclusive learning environments. Teachers can personalize instruction through AI while enhancing experiential learning through XR, promoting student-centered and active learning. Educational leaders should prioritize investment in infrastructure, training, and equitable access to ensure effective implementation. Furthermore, the study recommends a user-centered design of educational technologies, incorporating features such as adaptive scaffolding, collaborative tools, and real-time feedback to enhance cognitive and emotional engagement.
6.2 Limitations
While this study provides valuable insights into the potential of AI and XR technologies to enhance student engagement, several limitations must be acknowledged. First, the study was conducted within a specific educational context involving high school students in a single geographic region, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Other regions' cultural, institutional, and socioeconomic factors may yield different outcomes when implementing similar technologies. Second, engagement data were collected shortly after the intervention, raising the possibility of novelty effects, and the lack of a longitudinal follow-up limits understanding of the long-term impact on learning retention and academic performance. Additionally, the study relied on self-reported data for several measures of engagement, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Although qualitative interviews provided rich insights, some participants may have provided favorable responses due to their enthusiasm for the new technology. Technological constraints such as occasional XR hardware glitches and AI responsiveness issues due to network variability also introduced variability in learner experience. Lastly, the study focused on specific learner characteristics. It did not explore other moderating factors such as prior knowledge, subject matter differences, or teacher influence, which may affect engagement outcomes.
6.3 Recommendations
Based on the study's findings, several recommendations are proposed for educators, policymakers, researchers, and technology developers. Educators should adopt a blended approach that leverages AI's adaptive capabilities alongside XR's immersive experiences to foster engagement. Teacher training programs should include strategies for integrating these technologies effectively while minimizing cognitive overload. Policymakers should invest in educational infrastructure to support the adoption of AI and XR, including access to hardware, high-speed internet, and ongoing technical support. Ensuring equitable access for all learners—regardless of socioeconomic background—is essential for maximizing the benefits of these technologies. Researchers should pursue longitudinal studies to examine the sustained impact of AI and XR on student engagement and achievement. Future studies should also explore how these technologies function across different subjects and educational levels and interact with other learner characteristics and instructional strategies. Technology developers are encouraged to design user-centered, inclusive, and adaptable platforms that offer real-time feedback, personalization, and collaborative features that support various engagement dimensions. These efforts will help establish technology-enhanced learning environments that are effective, accessible, and sustainable.
6.4 Conclusions
This mixed-methods research adds to the increasing research into education technology and demonstrates that the use of AI and XR, especially when combined, has a positive and considerable influence on student engagement. This research has implications for theory, practice, and methodology. Theoretically, our results confirm Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory as a valid theoretical framework for understanding different forms of engagement, which advanced technologies can provide in a multidimensional way. Practically, this work has relevance for practitioners and policymakers looking to enhance learning environments using immersive and adaptive technologies. Methodologically, the convergent mixed methods permitted a detailed, triangulated understanding of the engagement outcomes and learning experiences. There are potential avenues for inclusive, interactive, and authentic learning experiences using AI and XR, which simply do not emerge when using traditional approaches alongside revolutionary technology. Looking forward, subsequently research might consider the sustainable, equitable, and scalable implications of AI and XR initiatives, with a view to aiming for diverse contexts implementing these technologies effectively. Recognizing engagement as both an outcome and an experience living in practice is a crucial aspect of the study which highlights the potential AI and XR has to engage learners' thinking and ultimately shape the future of learning.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of An-Najah National University (Fgs/Hum. Feb. 2025/72). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
MH: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Formal analysis, Validation, Methodology, Data curation, Software, Project administration. WD: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Validation, Supervision. AA: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Validation, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Akgun, S., and Greenhow, C. (2021). Artificial intelligence in education: addressing ethical challenges in K-12 settings. AI Ethics 32, 431–440. doi: 10.1007/s43681-021-00096-7
Almufarreh, A. (2024). Determinants of students' satisfaction with AI tools in education: a PLS-SEM-ANN approach. Sustainability 16:5354. doi: 10.3390/su16135354
Anderson, M. J. (2001). A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 26, 32–46. doi: 10.1046/j.1442-9993.2001.01070.x
Appleton, J. J., Christenson, S. L., Kim, D., and Reschly, A. L. (2006). Measuring cognitive and psychological engagement: validation of the student engagement instrument. J. Sch. Psychol. 44, 427–445. doi: 10.1016/j.jsp.2006.04.002
Behling, O., and Law, K. (2000). Translating Questionnaires and Other Research Instruments. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 3, 77–101. doi: 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Cao, F. F., and Jian, Y. (2024). The role of integrating AI and VR in fostering environmental awareness and enhancing activism among college students. Sci. Total Environ. 908:168200. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168200
Cárdenas-Sainz, B. A., Barrón-Estrada, M. L., Zatarain-Cabada, R., and Chavez-Echeagaray, M. E. (2023). Evaluation of eXtended reality (XR) technology on motivation for learning physics among students in mexican schools. Comput. Educ. 3:100036. doi: 10.1016/j.cexr.2023.100036
Chen, L., Chen, P., and Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: a review. IEEE Access 8, 75264–75278. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988510
Chiu, T. K. F., Xia, Q., Zhou, X., Chai, C. S., and Cheng, M. (2023). Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 4:100118. doi: 10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100118
Christenson, S. L., Reschly, A. L., and Wylie, C. (2012). Handbook of Research on Student Engagement. Boston, MA: Springer US.
Chung, C.-Y., Awad, N., and Hsiao, I.-H. (2021). Collaborative programming problem-solving in augmented reality: multimodal analysis of effectiveness and group collaboration. Aust. J. Educ. Technol. 37, 17–31. doi: 10.14742/ajet.7059
Conover (2006). Practical Nonparametric Statistics, 3rd Edn. Wiley India Pvt. Limited. Available online at: https://books.google.com/books?id=UBV2VwCxrMcC
Creswell, J. W., and Clark, V. L. P. (2017). Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research. SAGE Publications. Available online at: https://books.google.co.il/books?id=eTwmDwAAQBAJ
Creswell, J. W., and Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. SAGE Publications. Available online at: https://books.google.co.il/books?id=335ZDwAAQBAJ
Crogman, H. T., Cano, V. D., Pacheco, E., Sonawane, R. B., and Boroon, R. (2025). Virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality in experiential learning: transforming educational paradigms. Educ. Sci. 15:303. doi: 10.3390/educsci15030303
Deci, E. L., and Ryan, R. M. (1985). Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in Human Behavior. New York, NY: Springer.
Divekar, R., Drozdal, J., Chabot, S., Zhou, Y., Su, H., Chen, Y., et al. (2021). Foreign language acquisition via artificial intelligence and extended reality: design and evaluation. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 35, 2332–2360. doi: 10.1080/09588221.2021.1879162
Dunn, O. J. (1964). Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 6, 241–252. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1964.10490181
Elliott, A. C., and Hynan, L. S. (2011). A SAS® macro implementation of a multiple comparison post-hoc test for a Kruskal–Wallis analysis. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 102, 75–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2010.11.002
Feijóo-García, P. G., Wrenn, C., Gomes de Siqueira, A., Ghosh, R., Stuart, J., Yao, H., et al. (2025). Exploring the effects of user-agent and user-designer similarity in virtual human design to promote mental health intentions for college students. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. 22, 1–41. doi: 10.1145/3689822
Field, A. (2018). Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics. SAGE Publications. Available online at: https://books.google.co.il/books?id=JIrutAEACAAJ
Finn, J. D. (1989). Withdrawing from school. Rev. Educ. Res. 59, 117–142. doi: 10.3102/00346543059002117
Fredricks, J. A., Filsecker, M., and Lawson, M. A. (2016). Student engagement, context, and adjustment: addressing definitional, measurement, and methodological issues. Learn. Instr. 43, 1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2016.02.002
Groccia, J. E., and Buskist, W. (2018). Student Engagement: A Multidimensional Perspective. New Jersey: Jossey-Bass.
Hamilton, D., McKechnie, J., Edgerton, E., and Wilson, C. (2021). Immersive virtual reality as a pedagogical tool in education: a systematic literature review of quantitative learning outcomes and experimental design. J. Comput. Educ. 8, 1–32. doi: 10.1007/s40692-020-00169-2
Handelsman, M. M., Briggs, W. L., Sullivan, N., and Towler, A. (2005). A measure of college student course engagement. J. Educ. Res. 98, 184–192. doi: 10.3200/JOER.98.3.184-192
Hirzle, T., Müller, F., Draxler, F., Schmitz, M., Knierim, P., and Hornbæk, K. (2023). “When XR and AI meet - a scoping review on extended reality and artificial intelligence,” in Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (New York, NY: ACM), 1–45.
Hmoud, M., Swaity, H., Hamad, N., Karram, O., and Daher, W. (2024). Higher education students' task motivation in the generative artificial intelligence context: the case of ChatGPT. Information 15:33. doi: 10.3390/info15010033
Hmoud, M., Swaity, H., Karram, O., Shibli, H., Swaity, S., and Daher, W. (2023). High school students' engagement in biology in the context of XR technology. IEEE Access 11, 137053–137066. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3338176
Jayadurga, R., and Rathika, S. (2023). Significance and impact of artificial intelligence and immersive technologies in the field of education. Int. J. Rec. Technol. Eng. (IJRTE) 12, 66–71. doi: 10.35940/ijrte.B7802.0712223
Kahu, E. R. (2013). Framing student engagement in higher education. Stud. High. Educ. 38, 758–773. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2011.598505
Katyara, P., Hussain Dahri, K., and Muhiuddin, G. (2022). Impact of technology on student's engagement in different dimensions: cognitive, behavioral, reflective and social engagement. Webology 19, 3451–3464.
Kluge, M. G., Maltby, S., Keynes, A., Nalivaiko, E., Evans, D. J. R., and Walker, F. R. (2022). Current state and general perceptions of the use of extended reality (XR) technology at the university of Newcastle: interviews and surveys from staff and students. Sage Open 12. doi: 10.1177/21582440221093348
Kolb, A. Y., and Kolb, D. A. (2005). Learning styles and learning spaces: enhancing experiential learning in higher education. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 4, 193–212. doi: 10.5465/amle.2005.17268566
Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential learning: experience as the source of learning and development. Englewood Cliffs: NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Kolb, D. A., and Kolb, A. Y. (2017). The Experiential Educator: Principles and Practices of Experiential Learning, 1st Edn. Hayward, CA: EBLS Press.
Kruskal, J. B. (1964). Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrika 29, 1–27. doi: 10.1007/BF02289565
Lee, J., Song, H.-D., and Hong, A. J. (2019). Exploring factors, and indicators for measuring students' sustainable engagement in e-Learning. Sustainability 11:985. doi: 10.3390/su11040985
Lei, H., Cui, Y., and Zhou, W. (2018). Relationships between student engagement and academic achievement: a meta-analysis. Soc. Behav. Person. Int. J. 46, 517–528. doi: 10.2224/sbp.7054
Lewis, A. D., Huebner, E. S., Malone, P. S., and Valois, R. F. (2011). Life satisfaction and student engagement in adolescents. J. Youth Adolesc. 40, 249–262. doi: 10.1007/s10964-010-9517-6
Lincoln, Y. S., and Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic Inquiry. Newbury Park, CA: SAGE Publications. Available online at: https://books.google.co.il/books?id=2oA9aWlNeooC
Marks, H. M. (2000). Student engagement in instructional activity: patterns in the elementary, middle, and high school years. Am. Educ. Res. J. 37, 153–184. doi: 10.3102/00028312037001153
Mayordomo, R. M., Espasa, A., Guasch, T., and Martínez-Melo, M. (2022). Perception of online feedback and its impact on cognitive and emotional engagement with feedback. Educ. Inf. Technol. 27, 7947–7971. doi: 10.1007/s10639-022-10948-2
Merchant, Z., Goetz, E. T., Cifuentes, L., Keeney-Kennicutt, W., and Davis, T. J. (2014). Effectiveness of virtual reality-based instruction on students' learning outcomes in K-12 and higher education: a meta-analysis. Comput. Educ. 70, 29–40. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2013.07.033
Percuku, A., and Minkovska, D. (2022). “The application of eXtended reality for learning in higher education,” in 2022 10th International Scientific Conference on Computer Science (COMSCI) (Tirana: IEEE), 1–4. doi: 10.1109/COMSCI55378.2022.9912574
Prada, R. (2023). Artificial Intelligence test agents for automated testing of Extended Reality (XR). Open Access Govern. 37, 344–345. doi: 10.56367/OAG-037-10543
Radianti, J., Majchrzak, T. A., Fromm, J., and Wohlgenannt, I. (2020). A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Comput. Educ. 147:103778. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103778
Reiners, D., Davahli, M. R., Karwowski, W., and Cruz-Neira, C. (2021). The combination of artificial intelligence and extended reality: a systematic review. Front. Virtual Real 2:721933. doi: 10.3389/frvir.2021.721933
Rocca, S. (2024). “AI-XR for personalized and experiential learning in DIGICOMPASS,” in DIGICOMPASS (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland), 135–172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-81318-4_6
Roll, I., and Wylie, R. (2016). Evolution and revolution in artificial intelligence in education. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 26, 582–599. doi: 10.1007/s40593-016-0110-3
Saldaña, J. (2021). The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Available online at: https://books.google.co.il/books?id=p6UIzgEACAAJ
Shaik, T., Tao, X., Li, Y., Dann, C., McDonald, J., Redmond, P., et al. (2022). A review of the trends and challenges in adopting natural language processing methods for education feedback analysis. IEEE Access 10, 56720–56739. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3177752
Skinner, E. A., Kindermann, T. A., and Furrer, C. J. (2009). A motivational perspective on engagement and disaffection. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 69, 493–525. doi: 10.1177/0013164408323233
Sweller, J. (2011). Cognitive load theory. https://www.sciencedirect.com/bookseries/psychology-of-learning-and-motivation Psychol. Learn. Motiv. 55, 37–76. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387691-1.00002-8
Tang, K. H. D. (2024). Implications of artificial intelligence for teaching and learning. Acta Pedagog. Asiana 3, 65–79. doi: 10.53623/apga.v3i2.404
Teddlie, C., and Tashakkori, A. (2009). Foundations of Mixed Methods Research: Integrating Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches in the Social and Behavioral Sciences. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications. Available online at: https://books.google.co.il/books?id=c3uojOS7pK0C
UNESCO (2021). AI and education: guidance for policy-makers. Available online at: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000376709 (accessed March 24, 2025).
Wang, S., Wang, F., Zhu, Z., Wang, J., Tran, T., and Du, Z. (2024). Artificial intelligence in education: a systematic literature review. Expert Syst. Appl. 252:124167. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124167
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., and Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education – where are the educators? Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 16:39. doi: 10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0
Appendix A
Appendix B
Keywords: student engagement, experiential learning, artificial intelligence, extended reality, mixed methods, educational technology
Citation: Hmoud M, Daher W and Ayyoub A (2025) From experience to engagement: a mixed methods exploration of learning environments using artificial intelligence and extended reality. Front. Educ. 10:1617132. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1617132
Received: 23 April 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 31 July 2025.
Edited by:
Soon Hin Hew, Multimedia University, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Hiroyuki Obari, Aoyama Gakuin, JapanAli Ateeq, Gulf University, Bahrain
Jialei Jiang, University of Pittsburgh, United States
Copyright © 2025 Hmoud, Daher and Ayyoub. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohammad Hmoud, czEyMTcwMjc4QHN0dS5uYWphaC5lZHU=
 Mohammad Hmoud
Mohammad Hmoud Wajeeh Daher
Wajeeh Daher Abedalkarim Ayyoub
Abedalkarim Ayyoub