- 1Department of Statistics, Government College University Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
- 2Department of Statistics, College of Science, Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, Oman
- 3Mathematics and Sciences Department, Prince Sultan University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
This study was designed to investigate the impact of inappropriate housing on the emotional wellbeing and academic performance of university students. The cognitive development, mental health outcomes, and educational achievements of children are significantly influenced by the quality of their housing conditions. A cross-sectional study was conducted with a sample of 211 undergraduate and graduate university students. The primary aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of inadequate housing and mental health on students' academic performance, using a validated survey tool. Findings from the structural equation model show that inadequate housing is significantly associated with poorer mental health among students, highlighting housing quality as a critical social determinant of student wellbeing in Pakistan. Additionally, mental health is positively associated with academic performance, with findings suggesting that poor housing is related to lower academic performance through its association with poorer mental health.
1 Introduction
Higher education institutions play a crucial role in producing skilled individuals with the expertise required to address practical challenges faced by communities (Idris et al., 2012). Education serves as a powerful catalyst for transformation, enhancing wellbeing and economic sustainability while fostering societal cohesion. At the individual level, a positive correlation exists between higher education attainment and improved living standards, primarily due to enhanced productivity (Tan, 2014). Among the numerous factors influencing students' long-term academic success, housing plays a vital role in their wellbeing, character development, and academic performance (Khan et al., 2019; Bene et al., 2021). Given the profound importance of the residential environment for human beings, it is essential to investigate the potential impact of housing on individuals' mental wellbeing. There is a prevailing belief that students may gain greater academic benefits from residing in suitable housing located within or near their educational institution (Sotomayor et al., 2022). Inappropriate housing affects not only students' academic performance but also their mental and physical health (Solari and Mare, 2012). Such housing is typically characterized by issues including overcrowding, poor maintenance, limited living space, high occupancy, lack of security, and inadequate access to basic amenities such as electricity, sanitation, and running water (Raymond et al., 2011; Solari and Mare, 2012). It has been noted that certain features of housing have the capacity to exert an influence on the mental wellbeing of individuals (Kan et al., 2022). Poor mental health encompasses several different issues, such as negative affect, psychological distress, and psychiatric conditions, all of which, in turn, negatively impact students' academic performances.
In contemporary society, attaining a college degree is essential for both personal and professional success. However, the academic trajectory of college students is impacted by various factors beyond classroom instruction. Among these, housing quality and mental health status have emerged as significant contributors to students' overall academic performance. The primary objective of this study was to examine the impact of inadequate housing conditions and mental health disorders on the academic achievement of college students. When combined, insufficient housing and mental health issues can create a complex set of pressures that may hinder students' ability to fully engage in their academic pursuits properly. This study aimed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms linking housing quality and mental health to variations in academic performance by investigating their interdependent relationship. Accordingly, the following research objectives were established:
1. To examine the association between substandard housing conditions and the academic performance of university students.
2. To assess the association between inadequate housing conditions and mental health outcomes.
3. To assess the association between academic performance and the mental health of university students.
2 Literature review
Several studies have found that housing plays a crucial role in fulfilling the occupants' bodily requirements, such as air, water, food, and shelter, as well as their psychological and social wellbeing. Housing is commonly seen as the primary financial outlay for a household (Olsen, 2003). The provision of secure housing safeguards individuals within a family unit against potential harm stemming from exposure to various environmental hazards, including but not limited to chemicals and allergens (Weitzman et al., 2013; Bonnefoy, 2007). Additionally, it serves as a preventive measure against unintentional accidents (Jacobs, 2011). The provision of healthy housing has the potential to facilitate the wellbeing of individuals across many life phases by fostering physical health and safety, as well as promoting mental and emotional wellbeing (Kent and Thompson, 2014). On the other hand, it is essential to note that substandard housing conditions are a contributing factor to the prevalence of infectious and chronic diseases as well as injuries and can affect the development of children (Shaw, 2004; Bonnefoy, 2007). The presence of moisture in the ceiling and walls of an enclosed space can lead to reduced air quality and contribute to the development of respiratory ailments, such as asthma and allergies, potentially resulting in suffocation inside the indoor environment (Lee et al., 1996). Inadequate living conditions have the potential to subject students to a range of risks, such as the presence of mold and moisture, as well as suboptimal indoor air quality. Extended exposure to these conditions may result in the development of respiratory ailments and other related illnesses (Krieger and Higgins, 2002).
Raymond et al. (2011) characterized inadequate housing by its essential architectural composition and infrastructure, whereas unhealthy housing is distinguished by its susceptibility to pollutants and various environmental elements. The term inadequate housing refers to a housing unit that is currently occupied but has significant physical problems, including flaws in sanitation, heating, electrical systems, hallways, and overall maintenance (Ranson et al., 1988). The study conducted by the Department of Community Health Sciences at Aga Khan University in Karachi, Pakistan, in 1997 (D'souza, 1997) and further supported by Shafi et al. (2019) elucidates the correlation between housing conditions and physical health outcomes. Engaging in physical activity enhances an individual's emotional wellbeing, facilitates weight management, mitigates the likelihood of disease onset or progression, fortifies musculoskeletal structures, and enhances overall functional capacity for daily tasks (Lawton et al., 2017). Substandard housing can contribute to adverse physical health effects. The body's capacity to control its internal temperature can be affected by frequent fluctuations in indoor temperature. Additionally, it is linked to disrupted sleep patterns, impaired cognitive development, and heightened susceptibility to cardiovascular ailments at subsequent stages of life (Flynn et al., 2000). Jackson et al. (2019) in a study to assess the impact of inadequate housing conditions on the quality of sleep, concluded that students residing in impoverished housing situations encounter challenges in achieving adequate sleep due to disruptions caused by varying schedules, heightened noise levels, and uncomfortable sleeping arrangements. The impact of sleep disruption on students encompasses various aspects, including their physical and emotional wellbeing and their overall quality of life (Szentkirályi et al., 2009). The presence of poor amenities and insufficient maintenance in student housing might undermine the standards of cleanliness and sanitation (Matte and Jacobs, 2000). Consequently, this may heighten the susceptibility of students to various health issues, including infectious diseases, skin infections, and gastrointestinal problems, thereby negatively impacting their physical wellbeing (Khoshaim, 2017; Shafi et al., 2019). The association between physical fitness and mental health and its impact on student academic performance has been thoroughly studied by Chigozie et al. (2021).
Furthermore, students who maintain good physical fitness are less susceptible to illnesses, resulting in fewer absences from school (Lawton et al., 2017). Similarly, optimal mental health equips students with the resilience and coping mechanisms necessary to effectively manage academic pressures and challenges (Kornbluh et al., 2022). In addition to physical fitness and mental health, the quality of housing in which students reside also exerts a significant influence on their overall wellbeing, both mentally and physically (Kan et al., 2022; Ahmad et al., 2022). Inappropriate housing conditions have been found to affect individuals' mental health detrimentally, leading to decreased confidence levels and diminished productivity and creativity (Weitzman et al., 2013). However, prolonged exposure to substandard housing conditions can have a detrimental effect on students' cognitive capacities, encompassing memory, attention, and problem-solving proficiency (Bonnefoy, 2007). According to Friedman (2010), this phenomenon not only negatively impacts students' academic achievement but also undermines their total potential. Similarly, Adeyemi et al. (2024) explored a strong correlation between inadequate living conditions and diminished moral discipline, concentration, and learning outcomes. For a detailed systematic review of the impact of housing conditions on students' physical, mental, and emotional wellbeing, we refer to Franzoi et al. (2023).
2.1 Theoretical foundation
This study is based on a solid theoretical foundation and is in line with several previous studies, a selection of which will be examined and debated. Taking into account variables related to poverty and low socioeconomic status (Contreras Guajardo et al., 2019) attempted to determine whether overcrowding affects students' academic performance, using data from 15 Latin American countries' international SERCE tests. Evidence from several specifications and robustness tests showed that overcrowding negatively and statistically impacts a child's academic performance more than certain levels of maternal education. Barnes et al. (2013) examined the impact of inadequate housing and below-standard living circumstances on the physical and emotional wellbeing of students and found that a significant proportion of children reside in housing situations that fail to meet the basic standards necessary for their wellbeing. The long-term effect of inadequate living conditions on individual health outcomes was examined by Pevalin et al. (2017) using 13 yearly waves of the British Household Panel Survey spanning from 1996 to 2008. They examined whether facing poor housing conditions, even for one year, affects mental health. Furthermore, Pillay (2017) conducted a study that examined the impact of accommodation on children's academic performance and revealed a significant association between the quality of housing and academic achievement. The cohort study was done by Hansen et al. (2021) to investigate the association between overcrowding and health with a cohort of 1,282 participants from Greenland. It was concluded that individuals residing in poor housing are more prone to encountering health issues compared to those residing in suitable housing. Hence, the following conceptual framework showing the relationship of variables was developed for testing in our case.
2.2 In-depth contextual analysis
When Pakistan gained independence in 1947, there were only a few educational institutions, including two universities. In Pakistan, only a few madaris existed, having male-dominated students. Similarly, the University Grant Commission (UGC) existed, which was later replaced by the Higher Education Commission (HEC). HEC started to work as a governing body for higher education in Pakistan. Currently, there are more than Degree Awarding Institutions (DAIs). Similarly, the notion of male dominance in schools, colleges, and universities has also been reversed with female dominance. However, the country has faced economic crises for the last decade, and higher education institutions have no exemption. As a result, fees were raised and students faced different issues, including mental health, which resulted in a negative effect on academic performance. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic also added to lockdowns and the closure of educational institutions in Pakistan.
3 The data and methods
3.1 Design, sample, and sampling technique
The study design is cross-sectional with a population of university students enrolled in public and private sector universities in the Punjab province. A total of 211 students were sampled through a convenience sampling technique due to the unavailability of a sampling frame and time constraints.
3.2 Instrument and measures
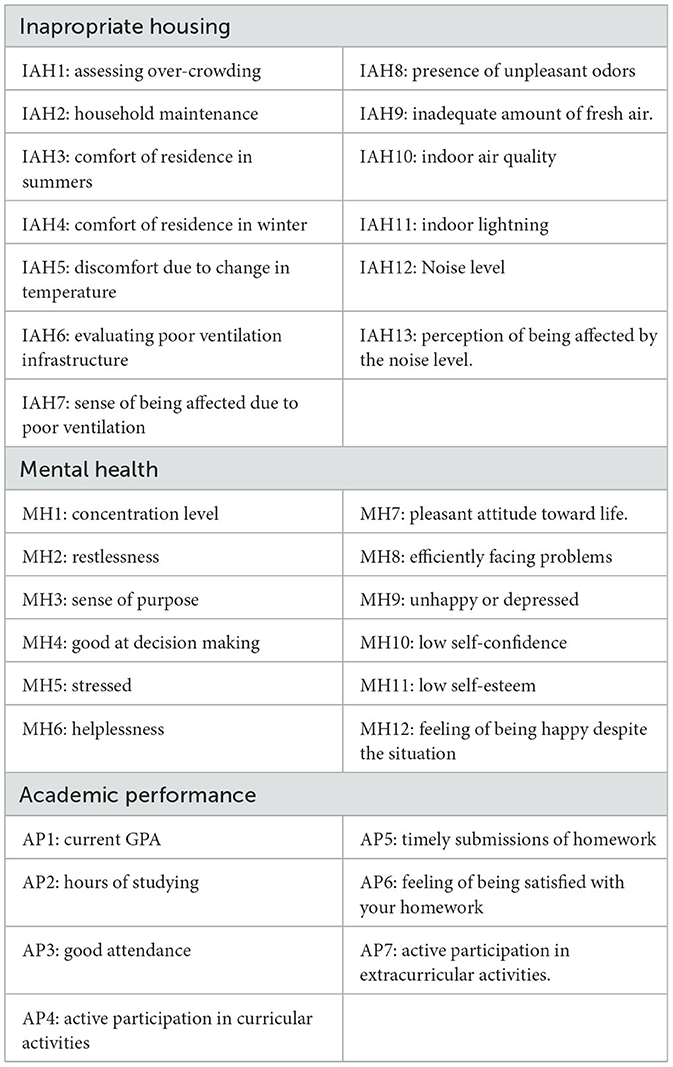
A well-structured questionnaire was used to collect quantitative data on housing situations, mental health state, and academic performance. Inappropriate housing was measured by evaluating specific factors identified through a comprehensive literature review (Zuhaib et al., 2018). The 13-point questionnaire was carefully designed to measure inappropriate housing, including questions to assess overcrowding and indoor environment quality (IEQ). The mental health of students was measured by a valid instrument called GHQ-12 (del Pilar Sánchez-López and Dresch, 2008). It is a widely used self-reported screening instrument for evaluating the mental health and general wellbeing of individuals. The GHQ-12 is a 12-item questionnaire that gathers data on a range of mental health topics, including general psychological distress, anxiety, depression, and social functioning. Finally, students' academic performance considers their academic, curricular, and extracurricular participation, such as questions about GPA, timely submissions, and sports participation. Table 1 further elaborates the three factors and their underlying variables.
3.3 Reliability analysis
The reliability of data collected through a designed questionnaire is checked using Cronbach's alpha, whose value is higher than 0.6, which is acceptable to determine the reliability of data (George, 2011). For this study, the range is 0.6–0.7, as shown in Table 2 for various constructs of the questionnaire.
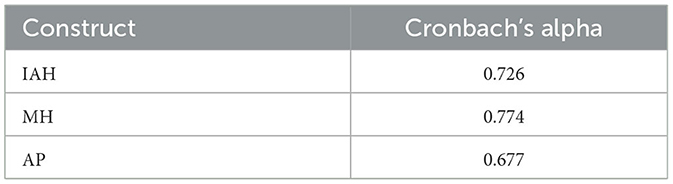
Table 2. Cronbach's alpha for inappropriate housing (IAH), mental health (MH), and academic performance (AP).
3.4 Statistical analysis techniques
The study employs a range of statistical analyses, encompassing descriptive statistics, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation modeling. The confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) is a multivariate technique used to test, based on collected data, how well the considered scale measures the unobserved constructs such as inappropriate housing, mental health, and academic performance for students. Mathematically, the CFA model is defined by
where Y is a p×1 matrix of observed variables, ξ is a vector of k×1 unobserved latent constructs, M is a p×k weight matrix, and ϵ is an error term. The primary estimation procedure for such models is the maximum likelihood method. For more details on CFA, we refer the reader to Collier (2020).
After implementing the CFA, the following step is to establish a structural equation model (SEM). The SEM model here is used to identify the structural relationship between unobserved constructs, namely, inappropriate housing, mental health, and academic performance, considering observed variables of these constructs. Different criteria are available in the literature to assess the goodness of fit of the SEM. For more details of SEM and goodness-of-fit criteria, we refer the readers to Kline and Santor (1999) and Browne and Cudeck (1992). Finally, we have used IBM SPSS 27 software for data entry, preparation, and descriptive analysis; STATISTICA 10.0 for the CFA; and AMOS 24 to employ structural equation modeling.
3.5 Data sensitivity
This study addresses a crucial topic, sparking a debate about the impact of housing and mental illness on students' academic performance. The data have been collected, and the measurement tool has also been pretested. Further, this study also employed CFA and SEM techniques to measure the direct and indirect effects of the proposed model. The results have been interpreted in a very simple way. Researchers believe that this study will be a new contribution to the existing body of literature. It will also provide a roadmap for forthcoming scholars in terms of employing CFA and SEM based on the nature and sensitivity of the data.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Descriptive statistics
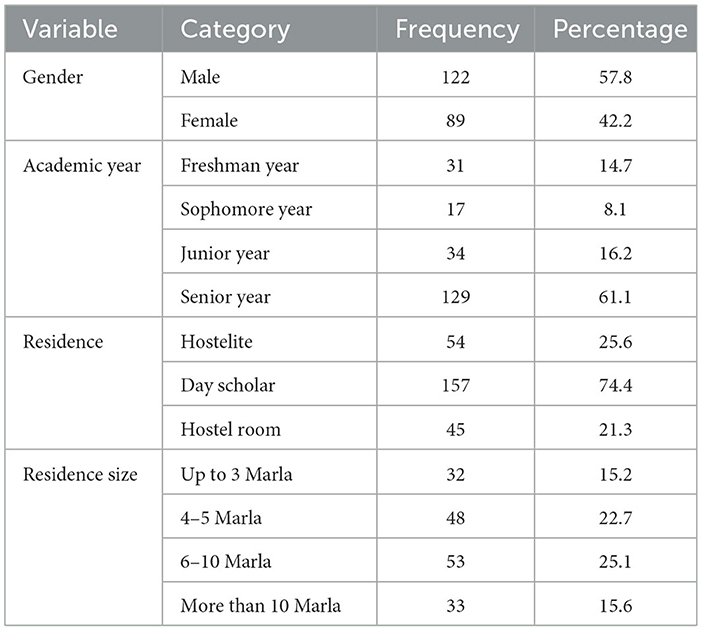
Upon receiving a dataset, the initial course of action entails a thorough examination and exploration of its diverse variables. To perform descriptive statistics, the collected data from the questionnaire, after coding, were explored from various angles using statistical techniques and tools. These tests were conducted with the help of the widely used statistical software SPSS 23. The descriptive statistics of the overall data are as follows: The sample size taken for the underlying study was 211 participants, of whom 122 were men and 89 were women. No non-responses were observed in the collected data. Moreover, the maximum and minimum ages of the participants were 16 and 34 years, respectively. The majority of candidates who participated were 22 years old. The majority of students were in their senior year (129). Out of the 211 total participants, 54 of them resided in a hostel and 157 were day scholars. The family members ranged from a minimum of 2 to a maximum of 25 members living in their respective houses. Furthermore, the majority of participants had a living space of 6–10 Marla. The detailed results are shown in Table 3.
4.2 Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA)
In order to confirm the manifest variables of unobserved constructs such as inappropriate housing, mental health, and academic performance, the confirmatory factor analysis was conducted using statistical software STATISTICA 10.0. The hypothesis to be tested is
H0: The underlying observed variable is not significant
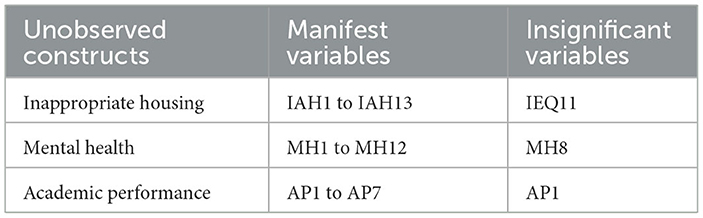
The CFA in STATISTICA 10.0 highlighted final decisions about the hypothesis through the p-values. The universally adopted criterion is used to reject the H0, i.e., reject H0 when the p < 0.05 or t>1.965. The results on unobserved constructs IAH, MH, and AP are shown in Table 4. We observed that all the manifest variables in the IAH model, except IEQ11, exhibited statistical significance based on the requirements of a probability value < 0.05 and a t-statistic more than 1.965. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude IEQ11 during the development of a model to get a good model fit. Similarly, for the case of mental health, the CFA confirmed all the considered variables except MH8, which is also excluded during the process of constructing an SEM model. Finally, by the criterion of a probability value < 0.05 and a t-statistic of more than 1.965, the results of the CFA indicated that AP1 of the construct academic performance should not be incorporated into the development of the SEM model.
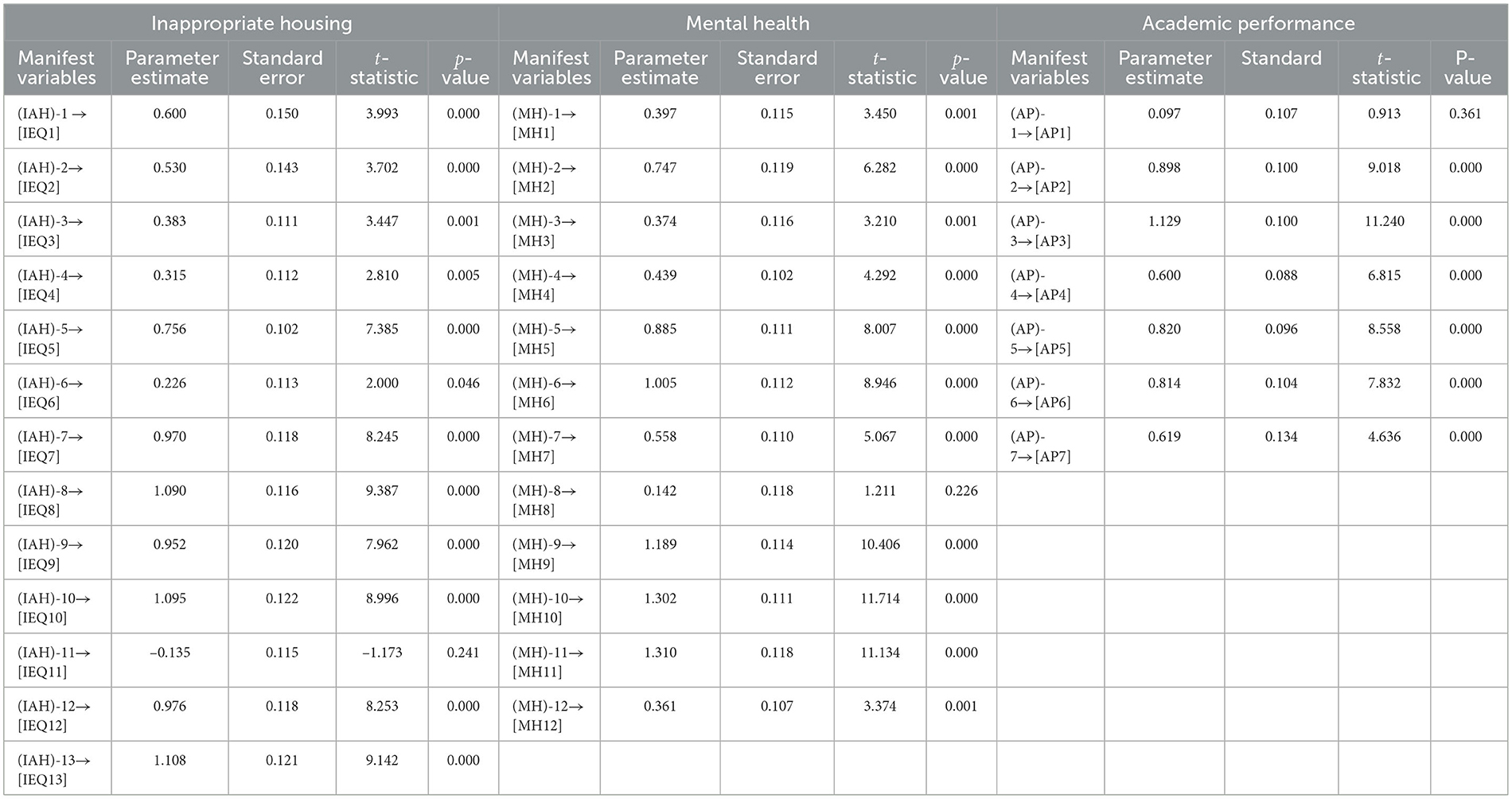
Table 4. The CFA for manifest variables of inappropriate housing, mental health and academic performance.
4.3 Structure model of inappropriate housing, mental health, and academic performance
The conceptual framework employed encompasses a set of constructs and manifest variables, as shown in Table 5 and Figure 1.
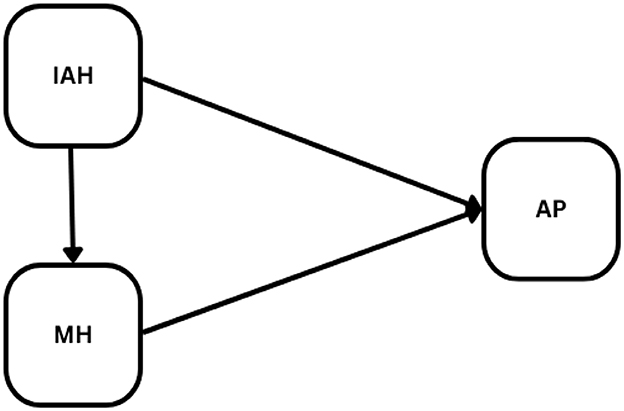
Figure 1. Conceptual framework of the study. IAH, inappropriate housing; MH, mental health; AD, academic performance.
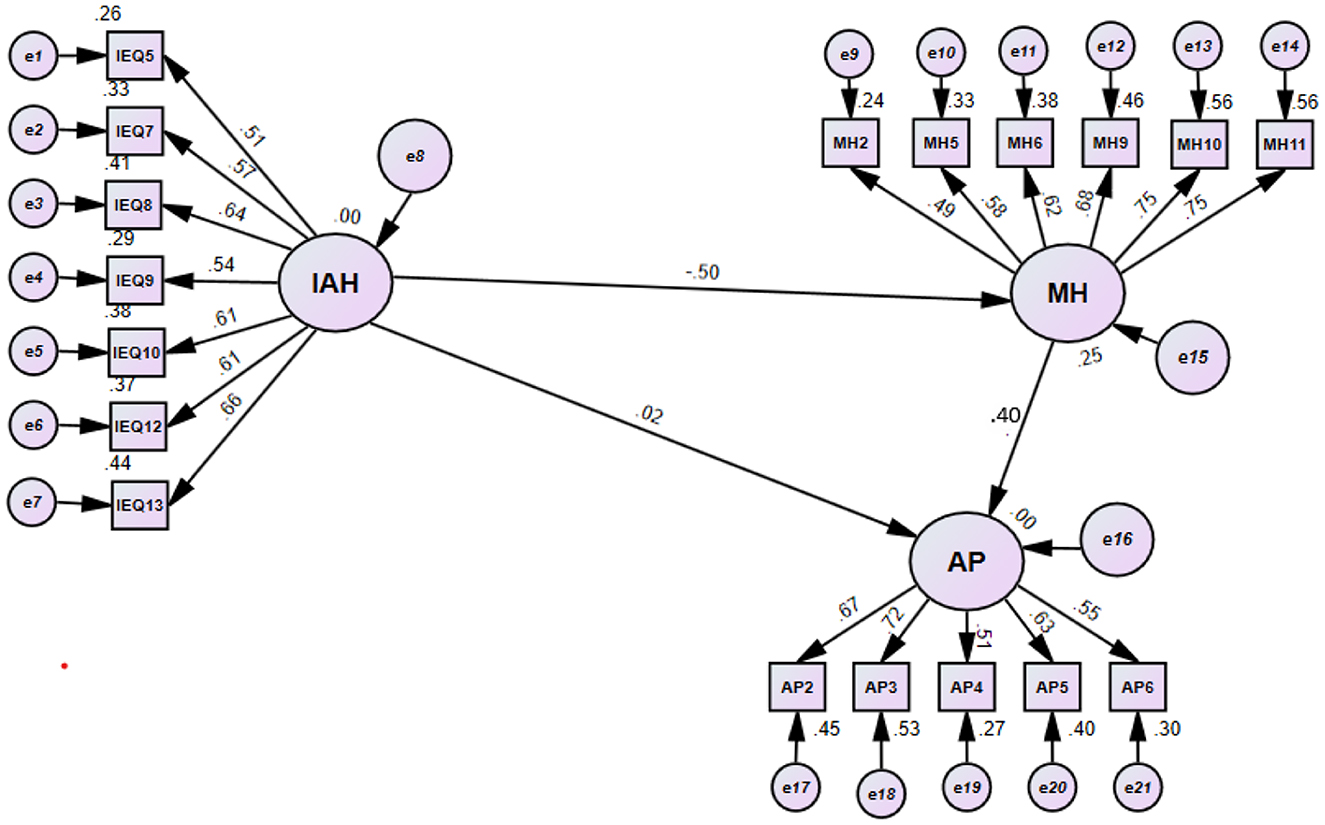
The initiation of an SEM investigation involves the establishment of a model, thereby classifying it as a confirmatory approach rather than an exploratory one. For this study, the SEM was developed using SPSS and Amos 24 (2017). In the model, IAH is specified as the independent variable, whereas AP and MH are included as the dependent variables. The output provided by the software shows both standardized and unstandardized estimates. Both estimates are employed to assess the magnitude of association between independent and dependent variables in the regression model. To decide which one to use, Goyal (2021) suggested that the unstandardized coefficients cannot be used to rank predictors, as it does not eradicate the unit of measurement. Therefore, standardized estimates can be used to draw conclusions and comparisons about the exogenous variables in the model. There are various criteria to decide what manifest variables to add to the model, based on the standardized factor loadings. In this study (Spencer, 2013), the criterion was used to remove the non-significant manifest variables from the model. For a small sample size of 211, any variable having a factor loading < 0.4 was omitted from the model. Thus, the manifest variables to be removed are IAH1, IAH2, IAH3, IAH4, and IAH6 from the construct IAH; MH1, MH3, MH4, MH7, and MH12 from the construct MH; and AP7 from the construct AP. The fitted model after the eradication of these variables is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 comprises solely the manifest variables that are accountable for generating a statistically meaningful distinction in the constructs. Furthermore, fit indices are employed to assess the overall importance of the model. Fit indices are statistical measurements that assess the extent to which a model is a suitable fit for the data that has been provided or collected. The interpretation of these values may vary depending on the specific fit index employed; nevertheless, there is significant variation in the criteria used to determine what qualifies as a satisfactory match. The overall model fit indices demonstrate statistical significance according to their respective threshold levels. Table 6 presents a reference table for fit indices together with the corresponding obtained values. The output of indices of the fitted model is also provided in Table 6 Based on these indices, we clearly see that the fit is satisfactory. This indicates that the model confirms the existence of the structural relationship between inappropriate housing, mental health, and students' academic performance.
A closer examination of the model reveals a substantial relationship between inappropriate housing and students' mental health (factor loading = 0.5), indicating that students living in compromised housing have a higher likelihood of developing mental health issues compared to those living in proper, well-structured accommodations. These findings highlight the importance of housing quality as a critical social determinant of mental health. This observation from our study aligns with previous research (Pevalin et al., 2017; Morganti et al., 2022; Kan et al., 2022; Franzoi et al., 2023). which consistently finds that individuals exposed to persistent poor housing conditions had significantly worse mental health trajectories over time. D'souza (1997) found that poor housing, contaminated water, and inadequate sanitation were associated with an increased risk of diarrhea and respiratory infections in children. However, this is the first study to explore the impact of poor housing on the mental health of students in Pakistan. Given the growing challenges related to urban housing, population density, and economic challenges, these findings underscore an urgent need for policymakers to consider housing quality as part of broader student wellbeing strategies.
The fitted model has also shown a moderately positive association between students' mental health and academic performance, as evident by the factor loading of 0.4. This highlights the importance of good mental health in supporting good academic output. This observation aligns with international research (Eisenberg et al., 2009) as well as with findings from Pakistan reported by Mohamad et al. (2018) and Tabassum et al. (2024).
Interestingly, the model also reveals that there is a very weak direct relationship between poor housing conditions and academic performance. This suggests that substandard housing environments may diminish students' academic success not by directly affecting study habits or learning environments alone, but primarily through the stress, anxiety, and psychological strain they induce. Several aspects of living conditions, including hygiene and sanitation, access to electricity and water, and population density, have a substantial impact on the academic performance of students, according to the study's findings. The subsequent factors with a strong correlation are thermal comfort, which may be attributable to overpopulation, privacy, indoor air quality, safety, and visual comfort.
The findings of this study highlight the need for government intervention to address the poor housing conditions in different areas of Punjab, as inadequate living environments have been shown to adversely affect students' academic performance and mental wellbeing. A key priority should be improving access to clean water, uninterrupted electricity, adequate ventilation, proper sanitation facilities, and reducing overcrowding. These improvements are essential for establishing a stable and healthy home environment that fosters effective learning and cognitive development.
Furthermore, there is a pressing need to enhance community-based mental health outreach programs in collaboration with educational institutions, local health facilities, and non-governmental organizations. These initiatives should aim to provide students and their families with access to qualified mental health professionals. Promoting emotional wellbeing through such interventions is crucial for supporting students in low-income households, enabling them to thrive both academically and personally.
4.4 Limitations and future directions
This study is limited to students residing in Punjab, an economically more developed province relative to other regions of Pakistan, such as Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and interior Sindh. Consequently, the findings may not fully reflect the experiences of students from less developed areas. Future research should consider expanding the geographic scope by including samples from other provinces, allowing for a more comprehensive and contextually diverse understanding of the phenomena under investigation. Such an expansion would also increase the sample size, thereby enhancing both the statistical power and the generalizability of the findings. In light of the gender-based differences observed in this study, further investigation into the moderating role of gender in the relationship between housing conditions, mental health, and academic performance is needed. Moreover, geographically focused studies should be conducted to identify hotspot areas where this issue is most severe, facilitating targeted interventions by government organizations. Finally, longitudinal research designs are recommended to examine the long-term effects of these factors.
5 Conclusion
The study concludes that insufficient housing arrangements and compromised mental wellbeing exert a significant influence on students' academic achievement. The findings confirmed a notable association, indicating that as housing quality declines, students' academic performance also deteriorates. A similar pattern was observed in the correlation between students' mental health and their academic achievement. Several aspects of living conditions, including hygiene and sanitation, access to electricity and water, and population density, were found to have a substantial impact on students' academic performance. Moreover, a negative relationship between inappropriate housing and mental health was identified, indicating that students living in compromised housing are more likely to develop mental health issues than those living in proper, well-structured accommodations.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (REC) of Government College University Lahor. Written informed consent from the participants was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
MM: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal analysis, Software. MF: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Supervision. MI: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Software. MA: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. NF: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors would like to thank the support of Prince Sultan University for paying the Article Processing Charges (APC) of this publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adeyemi, B. A., Ademakinwa, O. O., and Adeyemi, I. (2024). Housing as a stimulus to students' academic deliverables: a Study of Federal University of Technology, Akure. Int. J. Res. Innov. Appl. Sci. 9, 493–505. doi: 10.51584/IJRIAS.2024.90345
Ahmad, S., El-Affendi, M. A., Anwar, M. S., Iqbal, R., et al. (2022). Potential future directions in optimization of students' performance prediction system. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022:6864955. doi: 10.1155/2022/6864955
Barnes, M., Cullinane, C., Scott, S., and Silvester, S. (2013). People Living in Bad Housing: Numbers and Health Impacts.
Bene, K., Lapina, A., Birida, A., Ekore, J. O., and Adan, S. (2021). A comparative study of self-regulation levels and academic performance among stem and non-stem university students using multivariate analysis of variance. J. Turk. Sci. Educ. 18, 320–337. doi: 10.36681/tused.2021.76
Bonnefoy, X. (2007). Inadequate housing and health: an overview. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 30, 411–429. doi: 10.1504/IJEP.2007.014819
Browne, M. W., and Cudeck, R. (1992). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. Sociol. Methods Res. 21, 230–258. doi: 10.1177/0049124192021002005
Chigozie, O. H., Okoye, L. U., Ezeji, F. N., Omankhanlen, A. E., et al. (2021). Environmental factors affecting students' academic performance in public senior secondary schools in Anambra State, Nigeria. ATBU J. Sci. Technol. Educ. 9, 270–285.
Collier, J. (2020). Applied Structural Equation Modeling Using AMOS: Basic to Advanced Techniques. London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781003018414
Contreras Guajardo, D., Delgadillo, J., and Riveros, G. (2019). Is home overcrowding a significant factor in children's academic performance? Evidence from Latin America. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 66, 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijedudev.2019.01.006
del Pilar Sánchez-López, M., and Dresch, V. (2008). The 12-Item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12): reliability, external validity and factor structure in the Spanish population. Psicothema 20, 839–843.
D'souza, R. M. (1997). Housing and environmental factors and their effects on the health of children in the slums of Karachi, Pakistan. J. Biosoc. Sci. 29, 271–281. doi: 10.1017/S002193209700271X
Eisenberg, D., Golberstein, E., and Hunt, J. B. (2009). Mental health and academic success in college. BE J. Econ. Anal. Policy 9:2191. doi: 10.2202/1935-1682.2191
Flynn, E., Matz, P., Woolf, A., and Wright, R. (2000). “Indoor air pollutants affecting child health,” in A Project of the American College of Medical Toxicology, 1–201.
Franzoi, I. G., Carnevale, G., Sauta, M. D., and Granieri, A. (2023). Housing conditions and psychological distress among higher education students: a systematic literature review. J. f Furth. High. Educ. 47, 229–241. doi: 10.1080/0309877X.2022.2102416
George, D. (2011). SPSS for Windows Step by Step: A Simple Study Guide and Reference, 17.0 Update, 10/e. Noida: Pearson Education India.
Hansen, C. B., Larsen, C. V., Bjerregaard, P., and Riva, M. (2021). The effect of household crowding and composition on health in an Inuit cohort in Greenland. Scand. J. Public Health 49, 921–930. doi: 10.1177/1403494820929496
Idris, F., Hassan, Z., Ya'acob, A., Gill, S. K., and Awal, N. A. M. (2012). The role of education in shaping youth's national identity. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 59, 443–450. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.09.299
Jackson, C. L., Duncan, D., Kawachi, I., and Redline, S. (2019). Housing conditions as environmental and social determinants of sleep health. Soc. Epidemiol. Sleep 373. doi: 10.1093/oso/9780190930448.003.0014
Jacobs, D. E. (2011). Environmental health disparities in housing. Am. J. Public Health 101, S115–S122. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2010.300058
Kan, Z., Kwan, M.-P., Ng, M. K., and Tieben, H. (2022). The impacts of housing characteristics and built-environment features on mental health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:5143. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095143
Kent, J. L., and Thompson, S. (2014). The three domains of urban planning for health and well-being. J. Plan. Lit. 29, 239–256. doi: 10.1177/0885412214520712
Khan, F. N., Begum, M., and Imad, M. (2019). Relationship between students' home environment and their academic achievement at secondary school level. Pak. J. Distance Online Learn. 5, 223–234.
Khoshaim, H. B. (2017). High school graduates' readiness for tertiary education in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Instr. 10, 179–194. doi: 10.12973/iji.2017.10312a
Kline, R. B., and Santor, D. A. (1999). Principles &practice of structural equation modelling. Can. Psychol. 40:381. doi: 10.1037/h0092500
Kornbluh, M., Wilking, J., Roll, S., and Donatello, R. (2022). Exploring housing insecurity in relation to student success. J. Am. College Health 72, 680–684. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2022.2068016
Krieger, J., and Higgins, D. L. (2002). Housing and health: time again for public health action. Am. J. Public Health 92, 758–768. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.92.5.758
Lawton, E., Brymer, E., Clough, P., and Denovan, A. (2017). The relationship between the physical activity environment, nature relatedness, anxiety, and the psychological well-being benefits of regular exercisers. Front. Psychol. 8:1058. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01058
Lee, T. G., De Biasio, D., and Santini, A. (1996). “Health and the built environment: indoor air quality,” in Vital Signs Curriculum Materials Project, Health and the Built Environment (Calgary, AB: The University of Calgary), 58.
Matte, T. D., and Jacobs, D. E. (2000). Housing and health—current issues and implications for research and programs. J. Urban Health 77, 7–25. doi: 10.1007/BF02350959
Mohamad, M. H., Baidi, N., Asshidin, N. H. N., Mohamad, M. S., and Subhi, N. (2018). “The relationship between mental health, stress and academic performance among college student,” in Interdisciplinary Sustainability Perspectives: Engaging Enviromental, Cultural, Economic and Social Concerns, vol 44. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences, eds. N. Nadiah Ahmad, N. Raida Abd Rahman, E. Esa, F. Hanim Abdul Rauf, and W. Farhah (Edinburgh: Future Academy), 562–572. doi: 10.15405/epsbs.2018.07.02.60
Morganti, A., Brambilla, A., Aguglia, A., Amerio, A., Miletto, N., Parodi, N., et al. (2022). Effect of housing quality on the mental health of university students during the COVID-19 lockdown. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:2918. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19052918
Olsen, E. O. (2003). “Housing programs for low-income households,” in Means-tested Transfer Programs in the United States (Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press), 365–442. doi: 10.7208/chicago/9780226533575.003.0007
Pevalin, D. J., Reeves, A., Baker, E., and Bentley, R. (2017). The impact of persistent poor housing conditions on mental health: a longitudinal population-based study. Prev. Med. 105, 304–310. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2017.09.020
Pillay, J. (2017). The relationship between housing and children's literacy achievement: Implications for supporting vulnerable children. S. Afr. J. Educ. 37:1268. doi: 10.15700/saje.v37n2a1268
Ranson R. P. World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe (1988). Guidelines for Healthy Housing. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe.
Raymond, J., Wheeler, W., Brown, M. J., and Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDC) (2011). Inadequate and unhealthy housing, 2007 and 2009. CDC Health Disparities and Inequalities Report—United States. MMWR Suppl. 60:21.
Shafi, K., Arif, F., Haroon, S., and Balagamwala, M. (2019). Impact of housing conditions on psycho-social health of residents. J. Psychiatry Behav. Sci. 2:1029.
Shaw, M. (2004). Housing and public health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 25, 397–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.25.101802.123036
Solari, C. D., and Mare, R. D. (2012). Housing crowding effects on children's wellbeing. Soc. Sci. Res. 41, 464–476. doi: 10.1016/j.ssresearch.2011.09.012
Sotomayor, L., Tarhan, D., Vieta, M., McCartney, S., and Mas, A. (2022). When students are house-poor: urban universities, student marginality, and the hidden curriculum of student housing. Cities 124:103572. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2022.103572
Spencer, N. H. (2013). Essentials of Multivariate Data Analysis. Boca Raton, FL: CRC press. doi: 10.1201/b16344
Szentkirályi, A., Madarász, C. Z., and Novák, M. (2009). Sleep disorders: impact on daytime functioning and quality of life. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 9, 49–64. doi: 10.1586/14737167.9.1.49
Tabassum, R., Kashif, M. F., and Jamil, M. (2024). Impact of mental health &well-being on academic performance of university students. J. Soc. Res. Dev. 5, 37–48. doi: 10.53664/JSRD/05-03-2024-04-37-48
Tan, E. (2014). Human capital theory: a holistic criticism. Rev. Educ. Res. 84, 411–445. doi: 10.3102/0034654314532696
Weitzman, M., Baten, A., Rosenthal, D. G., Hoshino, R., Tohn, E., Jacobs, D. E., et al. (2013). Housing and child health. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 43, 187–224. doi: 10.1016/j.cppeds.2013.06.001
Keywords: inappropriate housing, mental health, academic performance, confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation model
Citation: Maqbool M, Farooq M, Imran M, Alghafli M and Fatima N (2025) Mental health and academic performance of students at tertiary level: the role of housing. Front. Educ. 10:1627192. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1627192
Received: 12 May 2025; Accepted: 31 July 2025;
Published: 26 August 2025.
Edited by:
Shaini Suraj, Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaReviewed by:
Maryam Bojulaia, Prince Mohammad bin Fahd University, Saudi ArabiaDuverly Incacutipa, Universidad Nacional del Altiplano, Peru
Copyright © 2025 Maqbool, Farooq, Imran, Alghafli and Fatima. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Muhammad Farooq, bS5mYXJvb3FAc3F1LmVkdS5vbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Menaal Maqbool
Menaal Maqbool Muhammad Farooq
Muhammad Farooq Madiha Imran1†
Madiha Imran1† Nahid Fatima
Nahid Fatima