- 1College of Nursing, Public Authority for Applied Education and Training, Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 2International Observatory on End of Life Care, Division of Health Research, Faculty of Health and Medicine, Lancaster University, Lancaster, United Kingdom
- 3Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Department of Nursing Science, Bayero University Kano, Kano, Nigeria
- 4Department of Nursing Sciences, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria
- 5College of Business and Economics, American University of Kuwait, Safat, Kuwait
- 6Department of Medical-Surgical Nursing, North Private College of Nursing, Arar, Saudi Arabia
- 7Faculty of Medical Sciences, Department of Nursing, Al-Aqsa University, Gaza, Palestine
- 8Faculty of Medical Sciences, Department of Nursing, Gaza University, Gaza, Palestine
Introduction: This study investigates the factors influencing the adoption and behavioral intention toward eLearning models in nursing education, using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with Partial Least Squares (PLS) analysis.
Methods: A structured questionnaire was administered to a sample of 65 participants, examining constructs such as Digital Literacy, Information Literacy, Perceived Usefulness, Feasibility of Adopting eLearning, and Performance Expectancy.
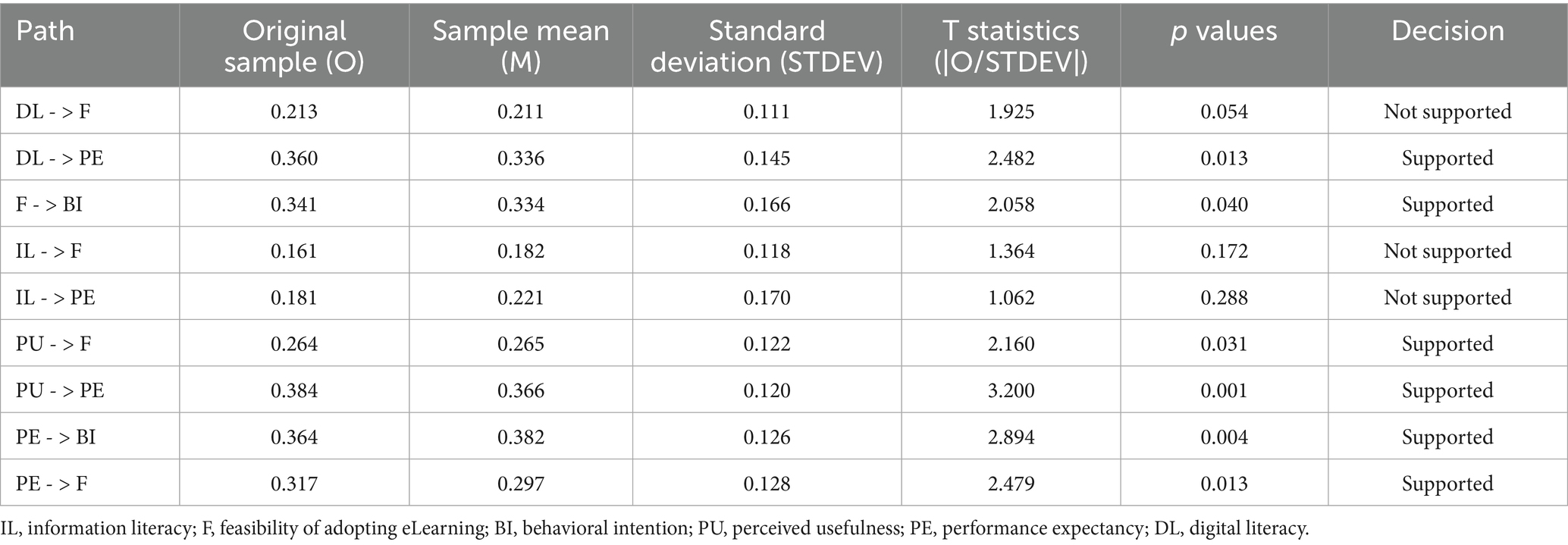
Results: Reveal that Perceived Usefulness has a significant direct effect on Performance Expectancy (β = 0.384, t = 3.200, p = 0.001) and Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (β = 0.264, t = 2.160, p = 0.031), and indirectly affects Behavioral Intention through Performance Expectancy (β = 0.140, t = 1.967, p = 0.049). Performance Expectancy also significantly influences Behavioral Intention (β = 0.364, t = 2.894, p = 0.004) and Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (β = 0.317, t = 2.479, p = 0.013). However, Information Literacy showed limited influence, with non-significant pathways to both Feasibility (β = 0.161, t = 1.364, p = 0.172) and Performance Expectancy (β = 0.181, t = 1.062, p = 0.288).
Discussion: These findings underscore the importance of perceived usefulness and performance expectations as key predictors of eLearning adoption, with implications for enhancing digital literacy and support frameworks in educational settings.
1 Introduction
The advent of the internet has significantly transformed healthcare delivery and the education system on a global scale. Since before the COVID-19 pandemic, e-learning has been campaigned as the new champion of teaching and learning environment (Al-alak and Alnawas, 2011). These authors argued that the traditional didactic method of teaching may have limitations to the positive outcomes and impact on learners. Xhaferi and Xhaferri (2021) portray e-learning simply as a method that use technology to assist in student learning. As such it might be safe to say that e-learning has revolutionized how course content is shared, enabling learners to access and engage with educational materials and resources online. This means that learners can now interact with educators and peers in ways that may be previously challenging. Most of the changes noted with e-learning transcends both from learning content development, the delivery process and the assessment and feedback through various platforms such as Learning Management Systems (LMS) (Bhardwaj et al., 2015; Harandi, 2015). Despite the technology utilization in each stage, the lecturer/faculty member still retains their role as an important stakeholder in the learning environment (Xhaferi and Xhaferri, 2021).
As a fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic, higher education institutions (HEIs) across the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region like others across the globe closed their campuses and implemented online learning programs to maintain continuity of education. In Kuwait, private HEIs adapted swiftly, enabling students to attend regular online classes within weeks. Their access to technological resources and prompt decision-making minimized disruptions to the academic calendar. In contrast, public educational institutions faced challenges and were slower to transition to online learning (Alshaboul et al., 2024).
A key goal of Kuwait educational strategic plan 2013–2017 was to enhance faculty teaching skills through e-learning, fostering better student-teacher interaction and improved outcomes (Al-Sharhan, 2018). However, implementation has lagged due to insufficient infrastructure highlighting a research gap on the effectiveness of e-learning and the adequacy of government efforts to support it (Alhouti, 2020). A thorough literature indicates a lack of studies, and this research is one of the very few papers to examine the digital literacy, readiness of faculty/ academics and their behavioral intentions specifically in nursing faculty in Kuwait.
Due to the numerous positives echoed by the use of e-learning across institutions, various researchers have attempted to examine its adoption by lecturers/faculty (Al-alak and Alnawas, 2011; Shin and Yunus, 2021; Wasserman and Migdal, 2019; Xhaferi and Xhaferri, 2021). Arguably a deductive approach that investigates core areas of this technology adoption will be key in examining what drives faculty members to incorporate this technology in their teaching environment. As such, the technology acceptance model (TAM) was selected so serve as a framework to critically assess its core constructs in line with e-learning adoption by faculty members. The TAM developed by Venkatesh and Davis (1996) has been used extensively in the literature that examines adoption of technology across various disciplines including nursing (Ladan et al., 2018). Within the context of this paper, a modified TAM was utilized with emphasis on the derived constructs of perceived usefulness, performance expectancy, behavioral intention, digital literacy and information literacy.
Perceived usefulness is described as the extent to which an individual user believes that adopting new technology will significantly enhance their work performance (Davis, 1989). With the emergence of new technologies, they garner user interest when individuals recognise the advantages, especially in terms of efficiently and effectively accomplishing tasks. Perceived usefulness serves as a crucial factor influencing the adoption of user-friendly and liberating innovative technologies (Pikkarainen et al., 2004). Therefore, the increased perceived usefulness of e-learning systems translates into more favorable attitudes and intentions to utilize them. Research has identified a direct correlation between perceived usefulness and the intention to adopt e-learning systems (Al-Fraihat et al., 2020; Al-Rahmi et al., 2018; Tarhini et al., 2017).
Perceived ease of use is one of the primary factors influencing the intention to use, perceived ease of use, which is characterized by the user’s belief that employing a new technological system will involve minimal effort (Davis, 1989). The ease of use of a technology, together with its user-friendly aspects, can boost participation and adoption rates. Essentially, a higher perceived ease of use regarding an e-learning system fosters more favorable intentions toward its adoption and can alter users’ perceptions of the system’s usefulness (Davis, 1989; Mohammadi, 2015). Previous research has shown that perceived ease of use significantly affects both the intention to use (Chang et al., 2017; Tarhini et al., 2017) and perceived usefulness (Mohammadi, 2015; Salloum et al., 2019).
In this study, Perceived behavioral control over eLearning adoption, herein referred to as ‘Feasibility of Adopting eLearning,’ reflects the perceived ease and capacity to implement eLearning, encompassing the availability of resources, skills, and institutional support, aligned with constructs such as perceived behavioral control in the Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1991; Mousa et al., 2020) and adoption readiness in TAM extensions (Venkatesh and Davis, 2000).
2 Review of the literature
Davis (1989) defined perceived usefulness as the degree to which users believe that using a specific system will enhance their job performance and productivity, such as by providing timely information. Theoretically, TAM posits that individuals form intentions before taking action, with perceived usefulness and attitudes toward the technology serving as key determinants of behavioral intention. On the other hand, perceived ease of use refers to the expected level of effort required to learn or operate a technological tool (Al-alak and Alnawas, 2011). Venkatesh and Morris (2000) argue that perceived ease of use depends on users’ evaluation of the effort required to learn a system. By reducing uncertainty, ease of use fosters technology adoption (Elliott and Fu, 2008). However, Porter and Donthu (2006) note that perceived difficulty and risk can deter users from engaging with new technologies.
Furthermore, Howard (1986) asserts that sufficient digital literacy / knowledge contributes to favorable attitudes. In e-learning contexts, educators’ fear of using computers may negatively impact their intention to adopt e-learning, while those with adequate technological knowledge are more likely to embrace such systems. Thus, assessing these key variables are pertinent in the assessment of behavioral intention to adopt e-learning.
Alkhaldi et al. (2024), suggests that to enhance the extensive utilization of e-learning platforms in education, there remains a need for further research on the application of the TAM to comprehend the factors that influence the adoption of eLearning as well as the behavioral intention of such platforms and their impact on students’ learning. Although some studies have applied TAM to investigate the adoption of e-learning platforms, but most of them have focused on factors related to the technology itself, such as its perceived usefulness and ease of use (Teo and Noyes, 2011). Also, In Kuwait, Al-Shamali et al. (2022), used a quantitative survey to examine the impact of Organisational culture on academics’ readiness and behavioral intention to implement eLearning changes within educational institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study confirms the mediating role of academics’ readiness for eLearning changes in the relationship between Organisational culture and behavioral intention. Additionally, a recent study (Nurse-Clarke and Joseph, 2022) use a descriptive-correlational online survey tool to explore factors related to technology acceptance among nursing faculty teaching online for the first time during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study’s findings highlighted a general satisfaction with online teaching, including confidence in teaching abilities and ease with using technology. However, the results also revealed challenges, such as difficulties in managing workload, less effective interactions with students, and a need for greater support. The literature revealed that none of such studies have been conducted specifically in nursing institutions in Kuwait, and it is important to acknowledge the existence of relevant global investigations in this domain. Studies in different countries: Germany by Holzmann-Littig et al. (2023), Iraq by Yudhana et al. (2022), Japan by Al-Azawei et al. (2017) Saudi Arabia by Alamri et al. (2020), and Alyoussef (2021), Jordan by Almaiah et al. (2020), Amarin (2022), Malaysia by Ana et al. (2020), Palestine by Qashou (2021) and Romania by Dimulescu (2023) have explored factors influencing eLearning adoption during the COVID-19 pandemic. These studies reveal various moderator effects such as technological readiness, platform efficacy, and institutional support and highlight cultural and infrastructural differences that shape acceptance and resistance toward to eLearning. However, comparable data from Kuwaiti nursing students, particularly regarding the usability of the Arabic language platform and the adaptation of clinical training, remain absent from the literature, justifying the focus of this study. Given this context, the current study is geared using the TAM model to assess the behavioral intentions to eLearning adoption for nursing education in Kuwait. This focus aims to fill the identified gap and offer culturally and linguistically relevant insights into eLearning acceptance in Kuwait’s nursing sector.
2.1 Objectives
1. To describe the extent of e-learning model usage among teachers in the College of Nursing.
2. To assess teachers’ perceptions of the effectiveness of the e-learning model in improving teaching quality, student engagement, and learning achievement, and measure their levels of satisfaction with the e-learning resources, technology tools, and support systems used.
3. To identify teachers experiences about the utilization of e-learning model in nursing education.
4. To assess the main barriers/obstacles hindering the integration of e-learning into nursing education.
5. To assess the facilitators enabling the integration of e-learning into nursing education.
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Study design, period, and setting
A survey was done to examine the behavioral intentions to eLearning adoption among faculty members departments of nursing institutions in Kuwait. The period for data collection was between from September to November 2024.
3.2 Study participants
Conveniently, 65 nursing faculty members in nursing institutions in Kuwait. Participants had varying qualifications and utilized eLearning that encompassed the diverse views of faculty members engaged in nursing education were included in the study. Completion of the survey tool implied consent to voluntarily participate in this study.
3.3 Measurement instrument
A survey was done to examine the behavioral intentions to eLearning adoption among faculty members departments of nursing institutions in Kuwait. Specifically, the questionnaire employed established Likert-type scales, ranging from 1 (Strongly Disagree) to 5 (Strongly Agree), which are commonly used in Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)-based research. The items were adapted and modified from validated instruments in prior studies (e.g., Davis, 1989; Venkatesh and Davis, 1996; Teo and Noyes, 2011; Al-alak and Alnawas, 2011), ensuring theoretical alignment and content validity for constructs such as Perceived Usefulness (PU), Performance Expectancy (PE), Behavioral Intention (BI), Digital Literacy (DL), and Information Literacy (IL).
Additionally, a pilot test was conducted with 12 nursing faculty members to evaluate the clarity and relevance of the instrument in the Kuwaiti academic context. Feedback from the pilot led to minor wording adjustments for clarity.
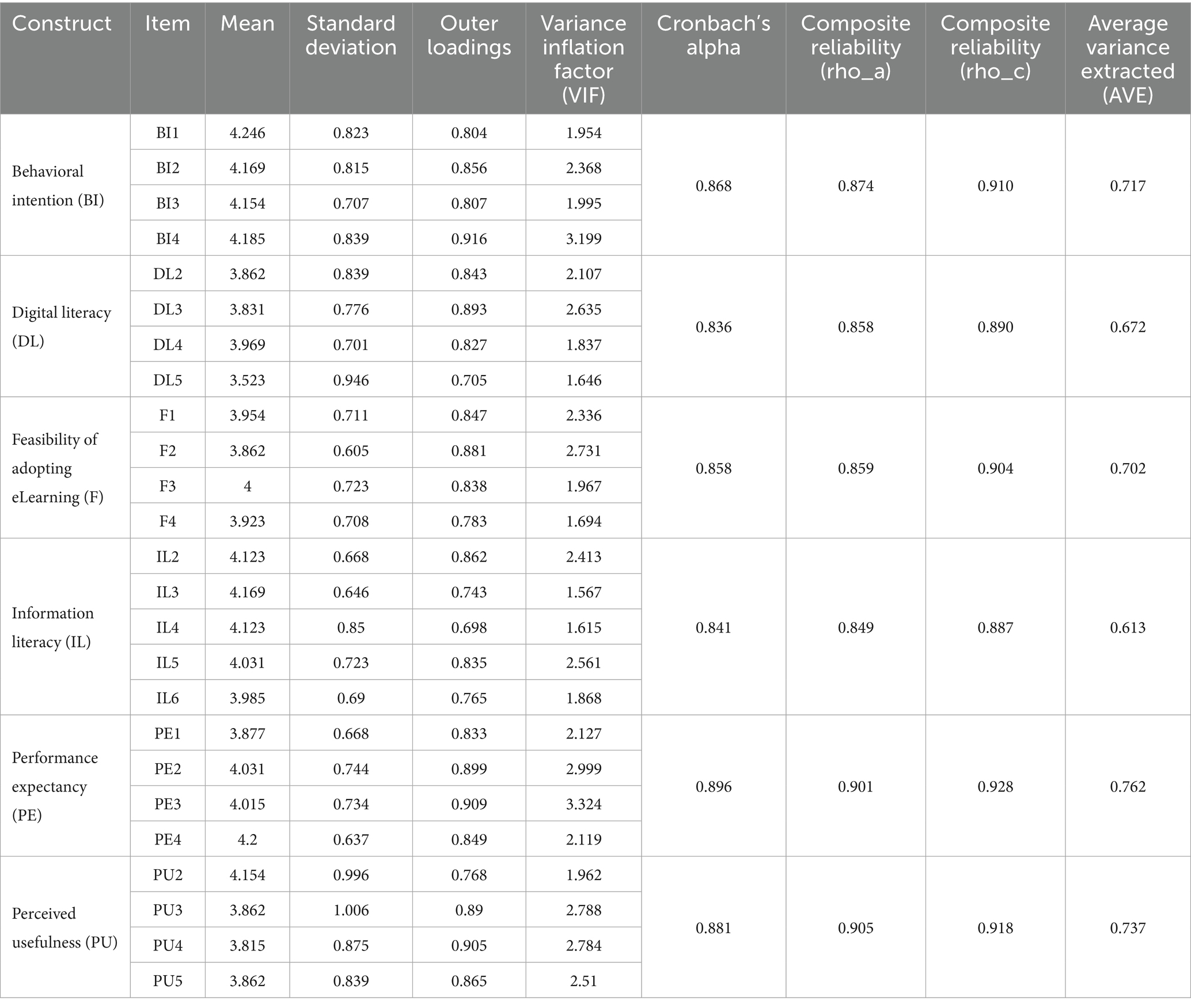
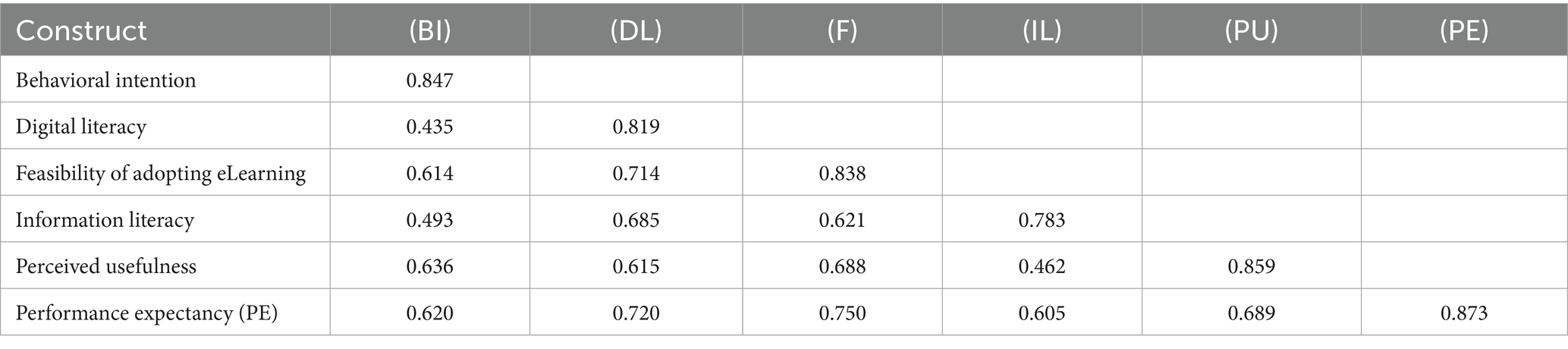
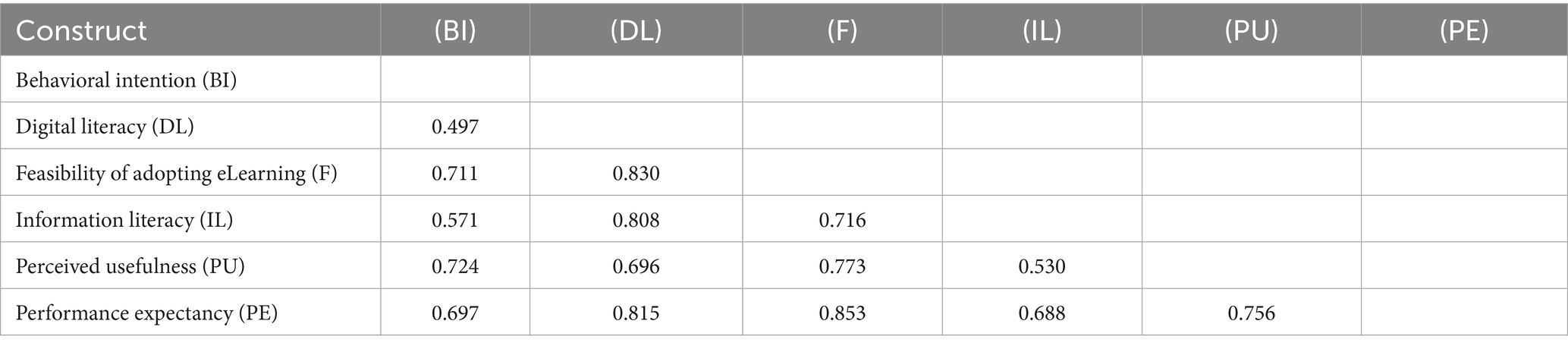
In the main study, reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha and Composite Reliability (CR), with all constructs exceeding the recommended threshold of 0.70. Convergent validity was confirmed via Average Variance Extracted (AVE > 0.50), and discriminant validity was verified using both the Fornell-Larcker criterion and HTMT ratio, as detailed in Tables 1–3. These evaluations align with widely accepted standards in SEM analysis (Hair et al., 2017; Fornell and Larcker, 1981).
3.4 Data analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with Partial Least Squares (PLS), an approach that is well-suited for exploratory studies involving complex models and smaller sample sizes. SEM allows for the simultaneous analysis of multiple dependent relationships among latent and observed variables. Data analysis was performed using Smart-PLS software, which supports robust PLS-SEM estimation. The outer measurement model was evaluated for reliability and validity, utilizing Cronbach’s alpha, Composite Reliability (CR), Average Variance Extracted (AVE), and discriminant validity measures, including the Fornell-Larcker criterion and Heterotrait-Monotrait (HTMT) ratio. Additionally, the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) was calculated to check for multicollinearity among predictor variables. The reliability of constructs was confirmed through composite reliability and Cronbach’s alpha, with values exceeding the threshold of 0.70, while convergent validity was established with AVE values above 0.50. These values support the robustness of the measurement model, ensuring reliable and valid interpretation of the structural model’s relationships.
Path coefficients were assessed to examine direct and mediating effects among constructs. Bootstrapping with 5,000 resamples was employed to determine the significance of the paths, producing t-statistics and p-values for each relationship.
3.5 Ethical considerations
Ethical approval was obtained from the Research Ethic Committee of the Public Authority for Applied Education and Training, College of Nursing, State of Kuwait, (Ethical Approval No. CoN: 10/23). Written informed consent was obtained from each of the faculty members in nursing institutions in Kuwait prior to the study.
4 Results
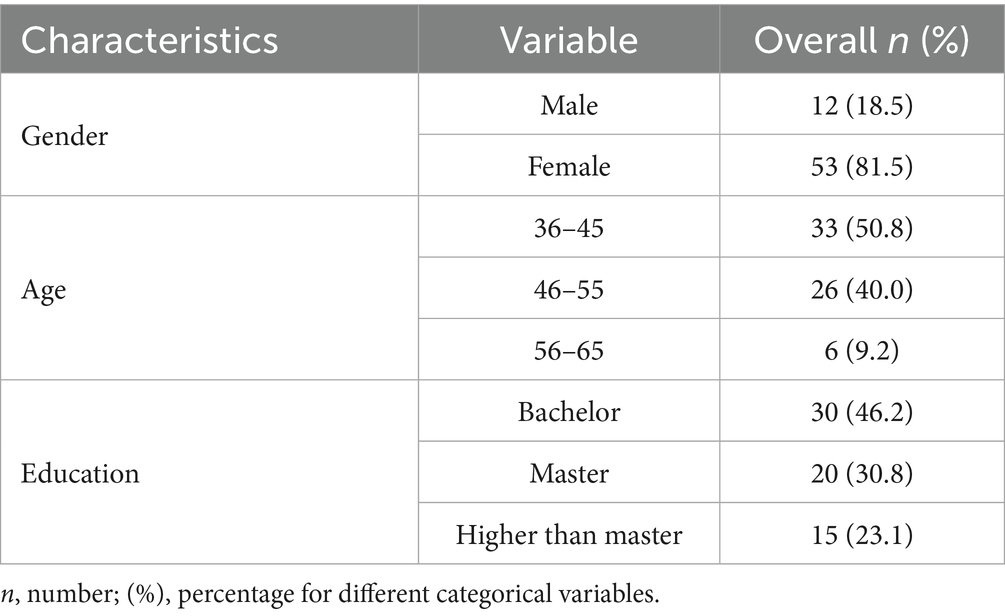
The demographic characteristic of the participants is shown in Table 4. The study sample consisted of 65 participants, with a notable gender imbalance: females comprised 81.5% (n = 53), while males represented 18.5% (n = 12) of the sample. The age distribution was concentrated in the middle age ranges. Specifically, 50.8% (n = 33) of participants were aged 36–45, followed by 40.0% (n = 26) in the 46–55 age range. Only a small proportion, 9.2% (n = 6), fell within the 56–65 age group, suggesting that the sample primarily includes individuals aged 36–55. Regarding educational attainment, 46.2% (n = 30) of participants held a bachelor’s degree, while 30.8% (n = 20) had a master’s degree, and 23.1% (n = 15) reported educational qualifications higher than a Master’s degree. This distribution indicates a relatively high educational level within the sample (Table 4).
4.1 Structure equation modeling
Figure 1 presents a simplified conceptual framework of the modified Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) used in this study. The model illustrates the relationships among perceived ease of use (PEOU), perceived usefulness (PU), attitude toward use, and behavioral intention, incorporating the added constructs according to the modifications. The relationships hypothesized within this framework were tested using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) using Smart-PLS. SEM is a comprehensive statistical technique that enables the analysis of complex relationships among observed and latent variables, allowing for the testing of both direct and indirect effects (Bauldry, 2020; Shah and Goldstein, 2006).
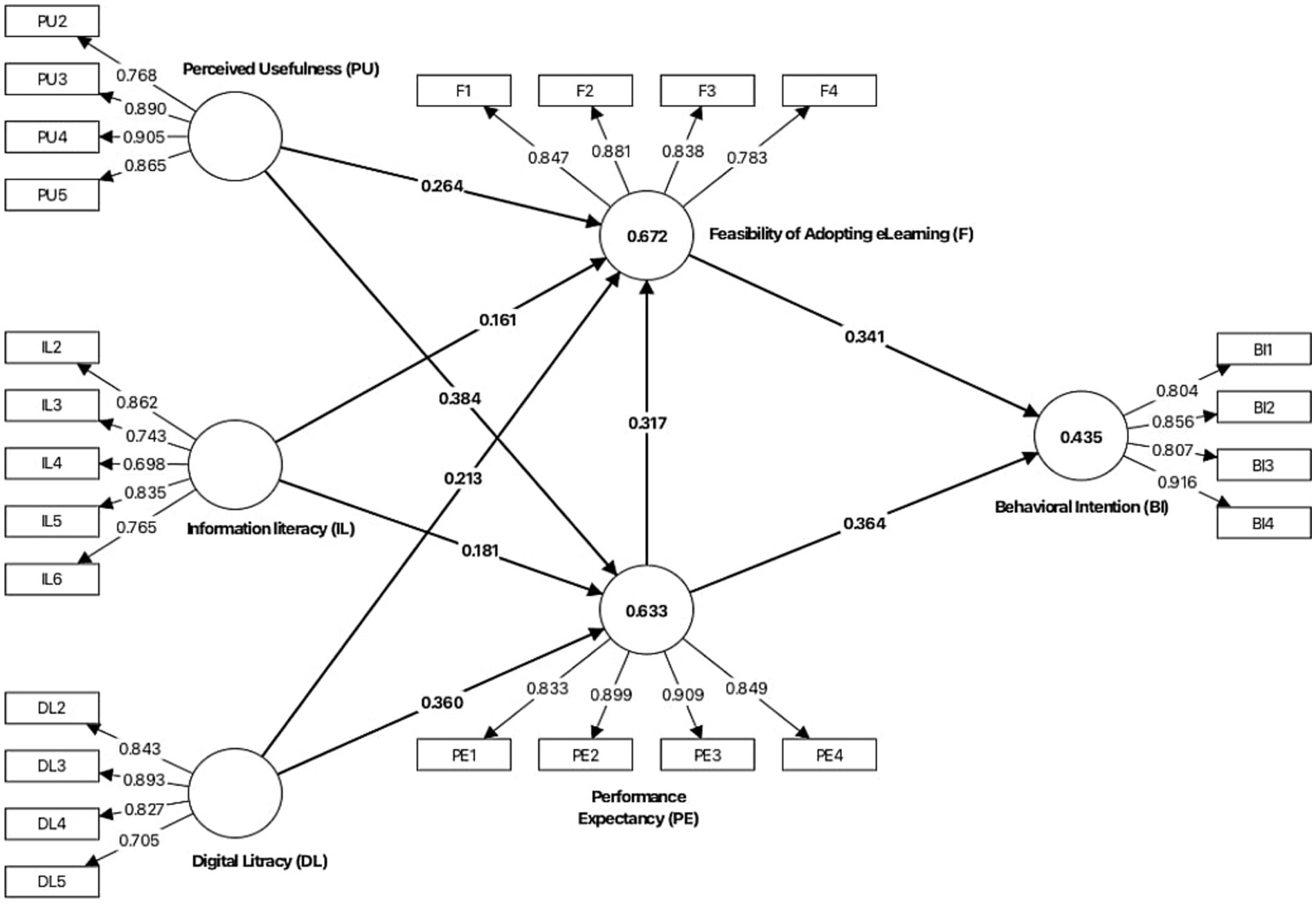
Figure 1. Node diagram for the PLS-PM model with loadings. IL, information literacy; F, feasibility of adopting eLearning; BI, behavioral intention; PU, perceived usefulness; PE, performance expectancy; DL, digital literacy.
4.2 Measurement model assessment
The outer measurement model is used to assess the reliability, internal consistency, and validity of both observed (questionnaire-based) and latent variables (Ho, 2013). The results of measurement model analysis are shown in Table 1. To evaluate consistency, both Cronbach’s alpha and Composite Reliability (CR) are employed. Unlike Cronbach’s alpha, which assumes equal weighting of all items, Composite Reliability takes standardized loadings into account, providing a more precise measure of internal consistency (Fornell and Larcker, 1981). Discriminant validity is assessed through cross-loadings and the Fornell-Larcker criterion, helping ensure that constructs are distinct (Ali et al., 2018; Hair et al., 2017).
The items display mean values ranging from 3.5 to 4.2, suggesting a generally positive response across constructs. Moderate standard deviations (0.7–1.2) indicate some variability in participant responses, reflecting a favorable overall disposition toward the constructs under study and consistent support across items.
Outer loadings for all items surpass the recommended threshold of 0.70, demonstrating the reliability of these items as indicators of their respective constructs (Hair et al., 2017). High loadings are observed in items such as BI4 (0.92), PE2 (0.90), and PE3 (0.91), underscoring their strong representation of underlying constructs. Although a few items, such as IL4 (0.70), have slightly lower loadings, they remain within acceptable limits for exploratory analysis (Hair et al., 2010; Malhotra et al., 2006).
Multicollinearity was evaluated using Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) values, which range from 1.57 to 3.32, remaining well within the acceptable < 5 (Hair et al., 2010). This suggests that each item offers unique information for its construct, reinforcing the structural integrity of the model.
The reliability analysis, shown in Table 1, is based on CR and Cronbach’s alpha. Both measures exceed the accepted threshold of 0.7, indicating satisfactory reliability across constructs. For convergent validity, item loadings are expected to > 0.70, while Average Variance Extracted (AVE) values should be > 0.50 (Hair et al., 2010). As illustrated in Table 1, all factor loadings and AVE values meet these criteria, confirming the model’s convergent validity and further supporting the constructs for structural analysis (Table 1).
Discriminant validity was assessed to indicate that the construct is distinct from other constructs and accurately captures its intended variable (Sarstedt et al., 2014). To establish discriminant validity, a construct should correlate more strongly with its own indicators than with those of other constructs (Hair et al., 2017). In this study, discriminant validity was assessed using two approaches: The Fornell-Larcker criterion and the HTMT ratio.
The Fornell-Larcker criterion was used to assess the discriminant validity of the constructs in the measurement model (Table 2). This method compares the square root of the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) for each construct with the correlations between that construct and all other constructs. For discriminant validity to be confirmed, the square root of AVE (displayed on the diagonal) should be higher than any of the inter-construct correlations in the same row and column (Fornell and Larcker, 1981).
In this analysis, each construct’s square root of AVE exceeds its correlations with other constructs. These results confirm that each construct shares more variance with its items than with other constructs, satisfying the Fornell-Larcker criterion and indicating adequate discriminant validity in the model (Table 2).
The Heterotrait-Monotrait (HTMT) ratio of correlations was employed to assess discriminant validity among the constructs (Table 3). The HTMT approach, as proposed by Henseler et al. (2015), provides a stringent criterion for determining whether constructs in a model are sufficiently distinct. A widely accepted threshold is an HTMT value < 0.85. In this study, all construct pairs exhibit HTMT values below the conservative threshold of 0.85, indicating satisfactory discriminant validity (Table 3).
4.3 Structural model assessment
Structural model assessment is a crucial step in Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) that evaluates the relationships between latent variables in the hypothesized model. It involves examining the path coefficients for strength and significance. The results of the direct path analysis are shown in Table 5.
The path analysis reveals a range of significant relationships between constructs. Digital Literacy (DL) demonstrates a positive impact on Performance Expectancy (PE) (β = 0.36, t = 2.48, p = 0.013*), indicating that greater digital literacy corresponds with higher expectations for improved performance. The relationship between Digital Literacy and Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (F) is also positive, with a path coefficient of 0.21 (t = 1.93, p = 0.054), though this falls just above the threshold for statistical significance, suggesting a more limited association.
Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (F) significantly influences Behavioral Intention (BI), with a path coefficient of 0.34 (t = 2.06, p = 0.040*). This result implies that perceptions of eLearning feasibility contribute positively to individuals’ intentions to adopt eLearning technologies. Information Literacy (IL), however, does not show significant effects on either Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (β = 0.16, t = 1.37, p = 0.172) or Performance Expectancy (β = 0.18, t = 1.06, p = 0.288), indicating that information literacy may have a limited direct role in influencing these outcomes.
Perceived Usefulness (PU) exhibits a strong positive relationship with both Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (β = 0.26, t = 2.16, p = 0.031*) and Performance Expectancy (β = 0.38, t = 3.20, p = 0.001***). These significant results suggest that perceived usefulness is an influential predictor of both the feasibility of eLearning adoption and the expected performance outcomes.
Additionally, Performance Expectancy (PE) positively impacts Behavioral Intention (BI), as evidenced by a path coefficient of 0.36 (t = 2.89, p = 0.004**), which indicates that higher expectations of performance improvements enhance intentions to engage with eLearning. Performance Expectancy also significantly predicts Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (β = 0.32, t = 2.48, p = 0.013*), underscoring the importance of anticipated performance benefits in shaping perceptions of eLearning feasibility (Table 5).
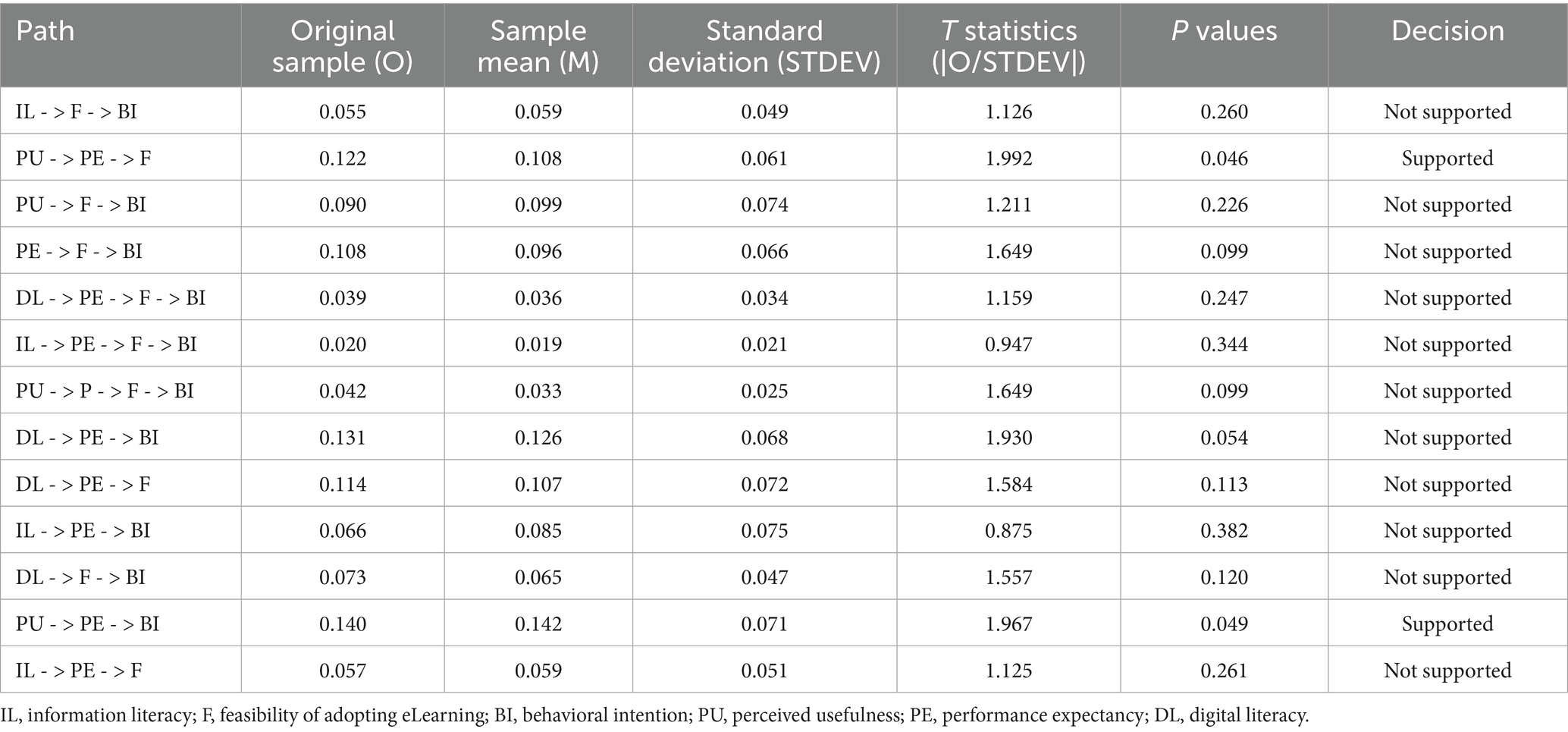
The analysis of indirect effects reveals several significant pathways (Table 6). The pathway from Perceived Usefulness (PU) to Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (F), mediated through Performance Expectancy (PE), is significant with a path coefficient (β) of 0.12 (t = 1.99, p = 0.046*). This indicates that perceived usefulness indirectly enhances the feasibility of adopting eLearning by increasing performance expectancy. Similarly, Perceived Usefulness also shows a significant indirect effect on Behavioral Intention (BI) through Performance Expectancy, with a path coefficient of 0.14 (t = 1.97, p = 0.049*), suggesting that perceived usefulness positively influences behavioral intention via enhanced expectations of performance.
In contrast, several pathways did not achieve statistical significance. For instance, Information Literacy (IL) does not significantly affect Behavioral Intention (BI) through Feasibility of Adopting eLearning (F) (β = 0.05, t = 1.13, p = 0.260) or through Performance Expectancy (PE) and Feasibility (β = 0.02, t = 0.96, p = 0.34). The pathway from Digital Literacy (DL) to Behavioral Intention (BI) through Performance Expectancy (PE) and Feasibility (F) also fails to reach significance (β = 0.04, t = 1.16, p = 0.247). Additionally, Digital Literacy (DL) shows an indirect effect on Behavioral Intention (BI) through Performance Expectancy (PE) (β = 0.13, t = 1.93, p = 0.054) and Performance Expectancy to Behavioral Intention through Feasibility (β = 0.10, t = 1.65, p = 0.099), both approaching significance but not meeting the conventional threshold (p < 0.05) (Table 6).
5 Discussion
This study assessed the behavioral intentions to eLearning adoption for nursing education using Technology Acceptance Model. The demographic characteristics of the respondents highlight conspicuous patterns, particularly gender imbalance, age concentration, and high educational attainment. These patterns provide a rich context for analysing the implications of the adoption and acceptance of e-learning systems. This pattern corroborates with earlier studies research on technology adoption and user behaviors in education (Garrido-Gutiérrez et al., 2023; Khan et al., 2023), the high proportion of female participants (81.5%) supports with patterns observed in previous studies, which suggest that women tend to be more engaged in educational and professional development opportunities, especially online (Al-Maroof et al., 2021) with implication on the use e-learning platforms (Al-Shamali et al., 2022).
The demographic profile of the respondents reveals notable implications for the adoption of technology, particularly with regard to gender and age. Most of the respondents (81.5%) were females, which is consistent with the findings of (Ekaimi et al., 2024) that highlight gender as a significant factor influencing technology utilization. This gender skew warrants attention, as existing research suggests that gender differences can indeed shape perceptions and acceptance of digital health technologies, potentially affecting the generalizability of results across broader populations. Additionally, more than half of the respondents (50.8%) were aged between 36–45 years, which has implications for their readiness to adopt new learning technologies. Wijaya and colleagues (Wijaya et al., 2022) have indicated that adults in this age group are often balancing professional responsibilities with lifelong learning needs, hence might be more receptive to eLearning which could fit within their schedules. Furthermore, the high educational attainment of the participants, with 76.9% holding at least a master’s degree, could be the reason for them as adopters of innovative educational tools, given their familiarity with structured learning processes and their tendency to value self-directed learning opportunities (Toprak and Aslan, 2020).
5.1 Measurement model
The assessment of the measurement model demonstrates robust reliability and validity, underscoring the structural soundness of the constructs examined. Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability exceed the acceptable thresholds, aligning with prior findings that emphasize the importance of internal consistency for effective e-learning model evaluations (Khan et al., 2023). High outer loadings further indicate that the constructs used in the study, such as perceived usefulness and behavioral intention, are well-represented, a key criterion for ensuring meaningful insights into technology adoption behaviors (Garrido-Gutiérrez et al., 2023).
However, the variability in certain item loadings, such as IL4, which marginally meets the threshold, suggests that specific aspects of the constructs may require refinement to better capture user perceptions. This aligns with Toprak and Aslan’s (Toprak and Aslan, 2020) assertion that construct development must account for contextual and cultural nuances, especially in cross-disciplinary studies. The use of the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the HTMT ratio to confirm discriminant validity demonstrates rigorous adherence to methodological standards, ensuring that the constructs measured are distinct and meaningful (Al-Maroof et al., 2021).
The assessment of the structural model reveals several significant relationships among the constructs, offering valuable insights into the factors influencing eLearning adoption.
5.2 Structural model
The structural model assessment shows significant relationships among the constructs analyzed, providing valuable insights into the dynamics of eLearning adoption.
Perceived usefulness emerges as a critical predictor, significantly influencing both feasibility (β = 0.26, p = 0.031*) and performance expectancy (β = 0.38, p = 0.001*). This aligns with existing literature emphasizing perceived usefulness as a primary driver in technology acceptance models.
Digital literacy also shows a significant positive relationship with performance expectancy (β = 0.36, p = 0.013*), highlighting the important role of digital competencies in shaping teachers’ expectations of e-learning’s benefits. Although digital literacy shows only a marginal relationship with feasibility (β = 0.21, p = 0.054) suggests that digital literacy alone may not fully address the perceived barriers to e-learning, necessitating additional support mechanisms, such as user-friendly interfaces and targeted training programs. This finding resonates with research by Park and Shea (2020), which identified digital literacy as a pivotal factor in eLearning adoption.
In contrast, information literacy does not exhibit significant direct effects on feasibility or performance expectancy, diverging from expectations. This may imply that information literacy influences e-learning adoption indirectly or plays a less immediate role compared to digital literacy. As suggested by (Prior and Wilson, 2016), the impact of information literacy might be mediated through other constructs such as organization support or resource availability.
The structural model evaluation highlights several significant relationships, shedding light on the complex interplay of variables influencing e-learning adoption. For instance, the positive impact of digital literacy on performance expectancy aligns with the findings of Wijaya et al. (2022), who emphasize the foundational role of digital competence in shaping user expectations of technology. Similarly, the strong influence of perceived usefulness on both performance expectancy and behavioral intention underscores its pivotal role as a determinant of technology adoption, a pattern well-documented in studies using the UTAUT framework (Garrido-Gutiérrez et al., 2023; Khan et al., 2023).
Interestingly, the non-significant effects of information literacy on key outcomes, such as feasibility and performance expectancy, suggest that other factors may mediate these relationships. Al-Shamali et al. (2022) propose that organisational culture and resource availability often outweigh individual competencies in determining technology adoption, a perspective that could contextualize these findings. The significant indirect effects of perceived usefulness on behavioral intention, mediated through performance expectancy, also align with the broader literature, indicating that the perceived value of e-learning systems enhances user engagement (Al-Maroof et al., 2021).
6 Implications for practice
The findings provide useful lessons for improving e-learning adoption. These are: Firstly, the strong relationship between digital literacy and performance expectancy suggests the need for targeted interventions to enhance digital skills among learners, particularly those from underrepresented groups Khan et al. (2023). Therefore, Universities or teaching institutions could prioritize digital literacy workshops. With such knowledge from the workshops and its subsequent integration into instructional methodologies could reduce potential resistance to e-learning platforms (Toprak and Aslan, 2020).
The second implication for practice is the importance of perceived usefulness of eLearning that underscores the need for a user-centred design in e-learning systems. As found in the work of Wijaya et al. (2022), eLearning platforms that align with user needs and offer clear benefits are more likely to gain acceptance. This also has implications for eLearning developers and educators in designing learning that meets the practical learning objectives of learners taking into account their unique needs and preferences.
Thirdly, the findings of this study point to the need to integrate feedback mechanisms for users of the eLearning platform to periodically adjust to user preferences. This will address the ever-changing users’ needs to further improve the perceived usefulness of eLearning systems (Garrido-Gutiérrez et al., 2023).
The fourth implication for practice is the need and role of institutions to support in facilitating e-learning adoption. As indicated by de Souza Rodrigues et al. (2021), fostering a culture of innovation and providing adequate resources can significantly enhance the feasibility of adopting new technologies. This also has implication on how institutions should be investing, training, and providing technical support, and infrastructure that enables an environment for e-learning adoption, acceptance and usage (Khan et al., 2023).
6.1 Strengths and limitations
The main limitation relates to the sample size of our study and therefore any generalization of the current study must be done with care. Secondly, conditions in which eLearning systems are employed may differ from country to country, and thus the styles and model in the study can be used in other studies, but the results obtained may be different from our study. Thirdly, not all the factors determining the relinquishment of eLearning systems were explored in the study, we recommend that nursing institutions develop a policy framework and a readiness checklist to facilitate the effective adoption of eLearning systems. Such a framework should include assessments of digital and information literacy levels among staff, infrastructure capacity, and organisational support mechanisms to enhance acceptance and utilization of eLearning tools. Additionally, future study will therefore examine the moderating impact of technological structure, cost of internet pack, and leadership commitment on the espousal of eLearning systems. Moreover, the study will also try to explore the agreement effect of perceived utility and perceived ease of use in the model estimated in this paper.
7 Conclusion
This study contributes to the growing body of literature on eLearning adoption by identifying key factors influencing user behavior and highlighting areas for intervention. The integration of advanced statistical techniques, such as SEM, strengthens the validity of the findings, while the contextual insights provided by the demographic analysis offer a nuanced understanding of the challenges and opportunities in this field.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethical approval was obtained from the Research Ethic Committee of the Public Authority for Applied Education and Training, College of Nursing, State of Kuwait, (Ethical Approval No. CoN: 10/23). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)’ legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YS: Conceptualization, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BA: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ML: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. AA: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SA: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the nursing faculty in the nursing institutions in Kuwait, as they paved the way for the study by giving approval and agreed to take part in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 50, 179–211. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
Al-alak, B. A., and Alnawas, I. A. (2011). Measuring the acceptance and adoption of e-learning by academic staff. Knowledge management e-learning 3:201. doi: 10.34105/j.kmel.2011.03.016
Alamri, M. M., Almaiah, M. A., and Al-Rahmi, W. M. (2020). Social media applications affecting Students’ academic performance: A model developed for sustainability in higher education. Sustain. For. 12:6471. doi: 10.3390/su12166471
Al-Azawei, A., Parslow, P., and Lundqvist, K. (2017). Investigating the effect of learning styles in a blended e-learning system: An extension of the technology acceptance model (TAM). Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 33. doi: 10.14742/ajet.2741
Al-Fraihat, D., Joy, M., Masa'deh, R. E., and Sinclair, J. (2020). Evaluating e-learning systems success: An empirical study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 102, 67–86. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2019.08.004
Alhouti, I. (2020). Education during the pandemic: the case of Kuwait. J. Professional Capital Community 5, 213–225. doi: 10.1108/JPCC-06-2020-0050
Ali, F., Rasoolimanesh, S. M., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., and Ryu, K. (2018). An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) in hospitality research. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 30, 514–538. doi: 10.1108/IJCHM-10-2016-0568
Alkhaldi, A., Malik, S., Alhaimer, R., Alshaheen, A., and Lytras, M. D. (2024). Translating a value-based framework for resilient e-learning impact in post COVID-19 times: Research-based Evidence from Higher Education in Kuwait. Heliyon 10:e24271. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24271
Almaiah, M. A., Al-Khasawneh, A., and Althunibat, A. (2020). Exploring the critical challenges and factors influencing the e-learning system usage during COVID-19 pandemic. Educ. Inf. Technol. 25, 5261–5280. doi: 10.1007/s10639-020-10219-y
Al-Maroof, R. S., Alhumaid, K., Alhamad, A. Q., Aburayya, A., and Salloum, S. (2021). User acceptance of smart watch for medical purposes: an empirical study. Future Internet 13:127. doi: 10.3390/fi13050127
Al-Rahmi, W. M., Alias, N., Othman, M. S., Alzahrani, A. I., Alfarraj, O., Saged, A. A., et al. (2018). Use of e-learning by university students in Malaysian higher educational institutions: A case in Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. IEEE Access 6, 14268–14276. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2802325
Alshaboul, Y. M., Alazaizeh, M. A., Sellami, A. L., Abu-Tineh, A. M., Ghamrawi, N., and Shal, T. (2024). The perceived challenges to online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: A nationwide study of K-12 parental perspectives (Arab and other parents) in Qatar. Heliyon 10:e28578. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28578
Al-Shamali, S., Al-Shamali, A., Alsaber, A., Al-Kandari, A., AlMutairi, S., and Alaya, A. (2022). Impact of organizational culture on academics’ readiness and behavioral intention to implement eLearning changes in Kuwaiti universities during COVID-19. Sustain. For. 14:15824. doi: 10.3390/su142315824
Al-Sharhan, S. (2018). Kuwait. E-Learning Middle East North Africa Region, 193–224. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-68999-9_9
Alyoussef, I. Y. (2021). E-Learning acceptance: The role of task–technology fit as sustainability in higher education. Sustain. For. 13:6450. doi: 10.3390/su13116450
Amarin, N. Z. (2022). The future of blended learning in Jordanian universities post-Covid 19. Kıbrıslı Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi 17, 4114–4125. doi: 10.18844/cjes.v17i11.7572
Ana, A., Minghat, A. D., Purnawarman, P., Saripudin, S., Muktiarni, M., Dwiyanti, V., et al. (2020). Students' Perceptions of the Twists and Turns of e-learning in the Midst of the Covid 19 Outbreak. Rom. J. Multidimensional Education Revista Românească pentru Educaţie Multidimensională 12. doi: 10.18662/rrem/12.1sup2/242
Bhardwaj, A., Nagandla, K., Swe, K., and Abas, A. (2015). Academic staff perspectives towards adoption of e-learning at melaka manipal medical college: has e-learning redefined our teaching model? Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. 13, 12–18. doi: 10.3126/kumj.v13i1.13746
Chang, C.-T., Hajiyev, J., and Su, C.-R. (2017). Examining the students’ behavioral intention to use e-learning in Azerbaijan? The general extended technology acceptance model for e-learning approach. Comput. Educ. 111, 128–143. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2017.04.010
de Souza Rodrigues, M. A., Chimenti, P., and Nogueira, A. R. R. (2021). An exploration of eLearning adoption in the educational ecosystem. Educ. Inf. Technol. 26, 585–615. doi: 10.1007/s10639-020-10276-3
Dimulescu, C. (2023). E-learning platform usage and acceptance of technology after the covid-19 pandemic: The case of transilvania university. Sustain. For. 15:16120. doi: 10.3390/su152216120
Ekaimi, S., Utomo, P., Gunawan, D., Jimmy, S. Y., and Christian, M. (2024). Examining the factors influencing teleconsultation adoption during the pandemic using the tam model. Global Business Finance Rev. 29, 149–160. doi: 10.17549/gbfr.2024.29.3.149
Elliott, M. T., and Fu, F. Q. (2008). Consumer acceptance of technology products: the impact of tactical selling approaches. Mark. Manag. J. 18, 47–64.
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 18, 39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104
Garrido-Gutiérrez, P., Sánchez-Chaparro, T., and Sánchez-Naranjo, M. J. (2023). Student Acceptance of e-Learning during the COVID-19 outbreak at Engineering universities in Spain. Education Sciences 13:77. doi: 10.3390/educsci13010077
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., and Tatham, R. (2010). Multivariate Data Analysis: Pearson Education. New Jersey: Upper Saddle River.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., and Thiele, K. O. (2017). Mirror, mirror on the wall: a comparative evaluation of composite-based structural equation modeling methods. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 45, 616–632. doi: 10.1007/s11747-017-0517-x
Harandi, S. R. (2015). Effects of e-learning on Students’ Motivation. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 181, 423–430. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.04.905
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Marketing Sci. 43, 115–135.
Ho, R. (2013). Handbook of univariate and multivariate data analysis with IBM SPSS. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press, A division of Taylor & Francis Group.
Holzmann-Littig, C., Jedlicska, N., Wijnen-Meijer, M., Liesche-Starnecker, F., Schmidt-Bäse, K., Renders, L., et al. (2023). Design and transition of an emergency e-learning pathology course for medical students—evaluation of a novel course concept. European J. Investigation Health Psychology Education 13, 112–129. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe13010008
Howard, A. (1986). College experiences and managerial performance. J. Appl. Psychol. 71, 530–552. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.71.3.530
Khan, M. J., Reddy, L. K. V., Khan, J., Narapureddy, B. R., Vaddamanu, S. K., Alhamoudi, F. H., et al. (2023). Challenges of e-learning: behavioral intention of academicians to use e-Learning during COVID-19 crisis. J. Personalized Medicine 13:555. doi: 10.3390/jpm13030555
Ladan, M. A., Wharrad, H., and Windle, R. (2018). Towards understanding healthcare professionals’ adoption and use of technologies in clinical practice: using Q-methodology and models of technology acceptance. J. Innov. Health Inform. 25, 027–037. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v25i1.965
Malhotra, N. K., Kim, S. S., and Patil, A. (2006). Common method variance in IS research: A comparison of alternative approaches and a reanalysis of past research. Manag. Sci. 52, 1865–1883. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.1060.0597
Mohammadi, H. (2015). Investigating users’ perspectives on e-learning: An integration of TAM and IS success model. Comput. Hum. Behav. 45, 359–374. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.07.044
Mousa, A. H., Aldeen, Z. N., Nasir, I. S., and Hamdi, R. S. (2020). Measuring readiness of higher education institutes towards adopting e-learning using the technology acceptance model. Context 4. doi: 10.24507/icicel.14.07.731
Nurse-Clarke, N., and Joseph, M. (2022). An exploration of technology acceptance among nursing faculty teaching online for the first time at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Prof. Nurs. 41, 8–18. doi: 10.1016/j.profnurs.2022.04.002
Park, H., and Shea, P. (2020). A Review of Ten-Year Research through Co-citation Analysis: Online Learning, Distance Learning, and Blended Learning. Online Learning 24, 225–244. doi: 10.24059/olj.v24i2.2001
Pikkarainen, T., Pikkarainen, K., Karjaluoto, H., and Pahnila, S. (2004). Consumer acceptance of online banking: an extension of the technology acceptance model. Internet Res. 14, 224–235. doi: 10.1108/10662240410542652
Porter, C. E., and Donthu, N. (2006). Using the technology acceptance model to explain how attitudes determine Internet usage: The role of perceived access barriers and demographics. J. Bus. Res. 59, 999–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2006.06.003
Qashou, A. (2021). Influencing factors in M-learning adoption in higher education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 26, 1755–1785. doi: 10.1007/s10639-020-10323-z
Salloum, S. A., Al-Emran, M., Habes, M., Alghizzawi, M., Ghani, M. A., and Shaalan, K. (2019). “Understanding the impact of social media practices on e-learning systems acceptance,’’ in International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics. (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 360–369.
Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., Henseler, J., and Hair, J. F. (2014). On the emancipation of PLS-SEM: A commentary on Rigdon (2012). Long Range Plan. 47, 154–160. doi: 10.1016/j.lrp.2014.02.007
Shah, R., and Goldstein, S. M. (2006). Use of structural equation modeling in operations management research: Looking back and forward. J. Oper. Manag. 24, 148–169. doi: 10.1016/j.jom.2005.05.001
Shin, J. L. K., and Yunus, M. M. (2021). A Systematic Review of e-learning in Teaching And Learning of Speaking Skills. Int J. Academic Research Business Social Sciences 11, 725–740. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v11-i4/9245
Tarhini, A., Hone, K., Liu, X., and Tarhini, T. (2017). Examining the moderating effect of individual-level cultural values on users’ acceptance of e-learning in developing countries: a structural equation modeling of an extended technology acceptance model. Interact. Learn. Environ. 25, 306–328. doi: 10.1080/10494820.2015.1122635
Teo, T., and Noyes, J. (2011). An assessment of the influence of perceived enjoyment and attitude on the intention to use technology among pre-service teachers: A structural equation modeling approach. Comput. Educ. 57, 1645–1653. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2011.03.002
Toprak, A., and Aslan, M. (2020). Transcultural adaptation and validity of the Nurse Competence Scale. Int. J. Caring Sci. 13, 1135–1147.
Venkatesh, V., and Davis, F. D. (1996). A model of the antecedents of perceived ease of use: Development and test. Decis. Sci. 27, 451–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5915.1996.tb01822.x
Venkatesh, V., and Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Manag. Sci. 46, 186–204. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.46.2.186.11926
Venkatesh, V., and Morris, M. G. (2000). Why don't men ever stop to ask for directions? Gender, social influence, and their role in technology acceptance and usage behavior. MIS Q. 24, 115–139. doi: 10.2307/3250981
Wasserman, E., and Migdal, R. (2019). Professional Development: Teachers' Attitudes in Online and Traditional Training Courses. Online Learning 23, 132–143. doi: 10.24059/olj.v23i1.1299
Wijaya, T. T., Cao, Y., Weinhandl, R., Yusron, E., and Lavicza, Z. (2022). Applying the UTAUT model to understand factors affecting micro-lecture usage by mathematics teachers in China. Mathematics 10:1008. doi: 10.3390/math10071008
Xhaferi, B., and Xhaferri, G. (2021). STUDENTS’INTERACTION IN ONLINE CLASSES DURING COVID 19 PANDEMIC IN NORTH MACEDONIA. Folia Linguistica et Litteraria XII, 333–350. doi: 10.31902/fll.36.2021.19
Yudhana, A., Riadi, I., and Abe, T. (2022). Measuring The Success of e-learning In Universities Using The Technology Acceptance Model. INTENSIF 6, 167–183. doi: 10.29407/intensif.v6i2.17509
Glossary
AVE - Average Variance Extracted
BI - Behavioral Intentions
CR - Composite Reliability
DL - Digital Literacy
FC - Facilitating Conditions
F - Feasibility of Adopting eLearning
GCC - Gulf Cooperation Council
HTMT - Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio of correlations
HEIs - Higher Education Institutions
IL - Information literacy
LMS - Learning Management Systems
O - Original sample
PLS - Partial Least Squares
PU - Perceived Usefulness
PE - Performance Expectancy
M - Sample Mean
STDEV or “SD” - Standard Deviation
SEM - Structural Equation Modeling
UTAUT - Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology
VIF - Variance Inflation Factor
Keywords: e-learning adoption, nursing education, technology acceptance model, information literacy, Kuwait
Citation: Alshammari M, Salifu Y, Alwadaany B, Ladan MA, Abdul HM, Alsaber A and Abu El-Kass SM (2025) E-learning adoption in nursing education: feasibility analysis using the technology acceptance model with a focus on digital and information literacy. Front. Educ. 10:1632298. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1632298
Edited by:
Muhammad Khalilur Rahman, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Mostafa Aboulnour Salem, King Faisal University, Saudi ArabiaSaurabh Chaturvedi, King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2025 Alshammari, Salifu, Alwadaany, Ladan, Abdul, Alsaber and Abu El-Kass. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Muna Alshammari, bWEuYWxzaGFtbWFyaUBwYWFldC5lZHUua3c=
†ORCID: Muna Alshammari, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7286-3556
Yakubu Salifu, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5523-3010
Bader Alwadaany, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8529-9272
Muhammad Awwal Ladan, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6372-6349
Halima Musa Abdul, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7382-5420
Ahmad Alsaber, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9478-0404
Sae’d M. Abu El-Kass, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5593-2038
 Muna Alshammari
Muna Alshammari Yakubu Salifu
Yakubu Salifu Bader Alwadaany1†
Bader Alwadaany1† Ahmad Alsaber
Ahmad Alsaber Sae’d M. Abu El-Kass
Sae’d M. Abu El-Kass