- 1Electrical Engineering, The University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, United States
- 2Engineering Pathways, The University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, United States
Background: Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as transformative tools in engineering, offering capabilities that streamline complex processes and support decision-making across diverse disciplines. Despite notable advancements in applications such as robotics task planning, autonomous driving, program repair, and technical documentation, challenges persist concerning ethical considerations, transparency, and accountability in safety-critical systems.
Purpose: This study aims to conduct a systematic literature review (SLR) on the applications, challenges, and ethical implications of LLMs in engineering. The objective is to synthesize existing knowledge and identify research gaps to guide future investigations.
Method: A comprehensive review of peer-reviewed publications from 2014 to 2024 was conducted, resulting in the selection of 23 relevant articles. These articles were classified into five thematic categories: automation of complex engineering tasks, knowledge generation and discovery, enhancing engineering education, ethical considerations and challenges, and integration with real-world engineering practices.
Results: The review highlighted (i) increasing interest in LLM applications across multiple engineering domains, (ii) a growing emphasis on ethical and regulatory concerns related to LLM adoption, (iii) significant potential for enhancing productivity and fostering innovation, and (iv) a critical need for interdisciplinary collaboration to address reliability and scalability challenges.
Conclusions: LLMs hold considerable promises for advancing engineering practices by automating tasks, facilitating knowledge discovery, and supporting education. However, ensuring ethical deployment, transparency, and model reliability remains essential. Future research should focus on developing frameworks for responsible AI adoption and fostering interdisciplinary efforts to overcome existing limitations.
Introduction
Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as transformative tools capable of revolutionizing engineering practices by automating complex tasks and enhancing decision-making across diverse fields. These models, which can process vast datasets and generate human-like text, are increasingly being explored in a range of engineering fields including robotics, program repair, autonomous systems. For instance, LLMs are being integrated into robotic systems to improve task planning and human-robot interactions, with significant advancements made in autonomous driving systems (Zhang et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). Recent studies show that LLMs can also automate software repair tasks, such as generating code patches from review comments, helping to reduce deployment time by up to 30% in some cases (Zhang Q. et al., 2024). Furthermore, LLMs are also advancing the automation of complex tasks in autonomous driving, with studies demonstrating an increase in decision-making efficiency by 20% in simulation-based environments (Zhang Q. et al., 2024).
Despite these advancements, integrating LLMs into engineering practices is accompanied by several challenges, particularly around ethical concerns and model transparency. One of the main challenges is the potential for bias in LLM outputs, which can reproduce or even amplify biases inherent in training data, particularly in sensitive applications like robotics and autonomous systems. These biases can have significant implications for the fairness and equity of AI-generated solutions. Moreover, the lack of interpretability in many LLMs raises concerns about their reliability and accountability, especially in safety-critical systems such as autonomous driving and robotic task execution (Zhang Q. et al., 2024). Studies in robotics and program repair have highlighted that while LLMs can assist in automating repetitive tasks, human oversight is still required to ensure the quality and correctness of the output, particularly when models are unable to produce contextually appropriate solutions (Buck et al., 2014; Rahman et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024).
This study aims to answer a specific overall research question: what are the current states, trends and future directions for the use of Large Language Models in engineering education? This study also aims to assess the current state of research on LLMs in engineering (Austin et al., 2021), with a focus on their applications, ethical implications, and integration challenges. In addition to synthesizing findings from studies on LLM applications in robotics, software repair, and autonomous systems. The review identifies research gaps and proposes future directions for LLM integration, focusing on the need for greater transparency, reduced bias, and enhanced reliability in engineering applications. The findings from this study will help inform both research and practice by offering actionable insights into the responsible adoption and application of LLMs in engineering.
Methods
We employed the PRISMA framework to guide our systematic literature review (SLR) process, ensuring transparency and methodological rigor throughout the research. The process followed three main phases: (1) identification, wherein relevant articles were retrieved from multiple databases using targeted search terms; (2) screening, involving the application of predefined exclusion criteria to abstracts and full texts; and (3) inclusion, during which the final articles were thoroughly analyzed to address the study's research questions. The PRISMA framework was selected for its structured approach, facilitating a comprehensive and replicable review process.
To identify relevant studies, we used seven databases: IEE Xplore, Google Scholar, Web of Science, Science Direct, Wiley Online Library, Engineering Village, and Education Resources Information Center (ERIC). Search terms specifically included “Large Language Models in engineering.” Initially, we also had briefed over a few other search terms such as “LLMs in robotics,” “LLMs in program repair,” etc. Based on the preliminary review, we shifted our focus only on the search term “Large Language Models in engineering” to capture entirely the cumulative information and challenges related to ethical considerations and high-stakes applications.
Data collection
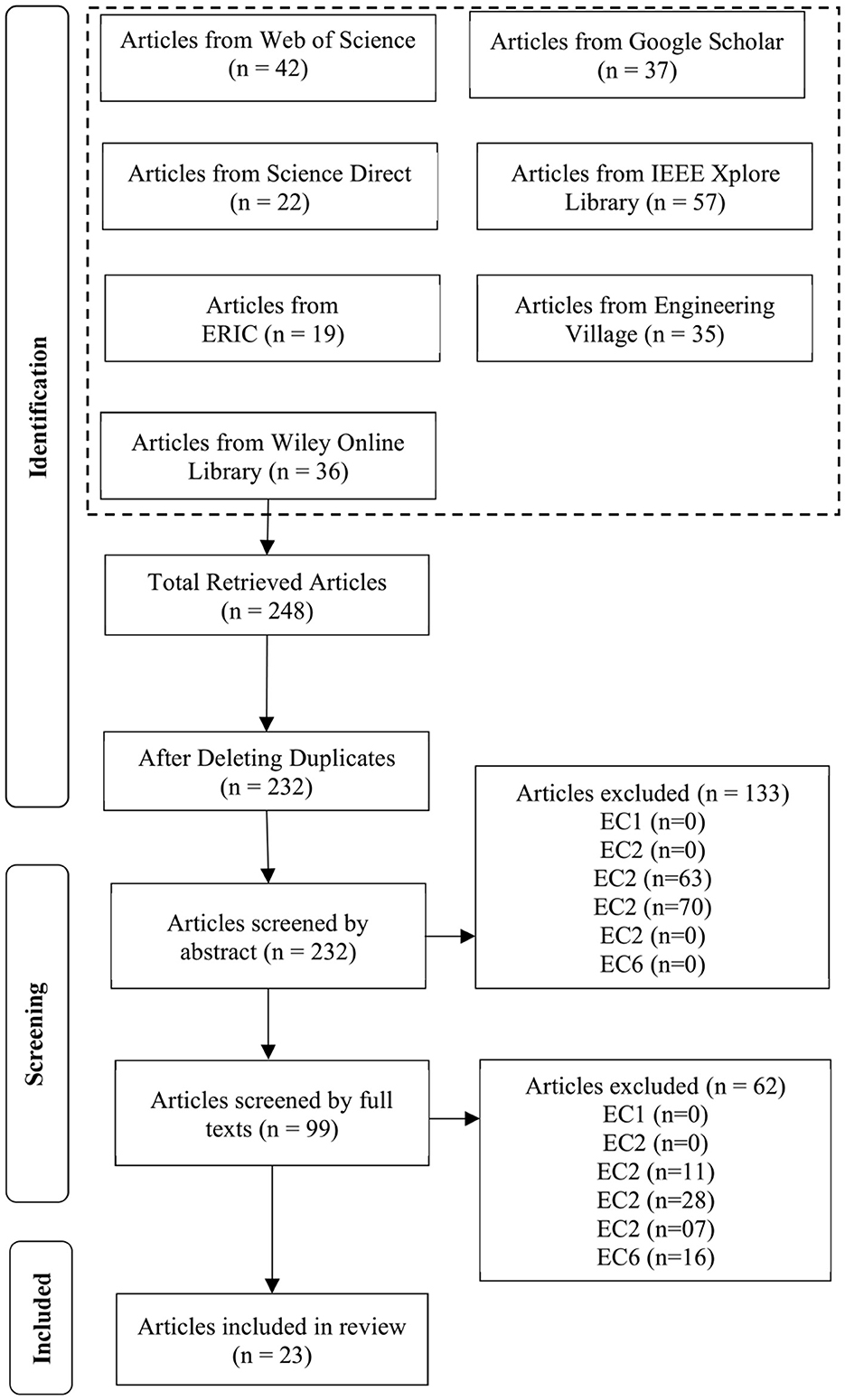
The complete article selection process for this systematic literature review (SLR) is outlined in Figure 1. Articles were excluded if they met any of the following six exclusion criteria (EC): EC1) published before 2014; EC2) not published in English; EC3) did not focus on LLMs; EC4) did not focus on engineering; EC5) were classified as work-in-progress or short papers; or EC6) did not offer full-text availability. These criteria were applied to ensure the review included only high-quality, relevant articles aligned with the research objectives.
A total of 234 articles were retrieved using our search term across seven databases. To complete the identification phases, duplicates among the retrieved articles were removed, followed by a preliminary screening of abstracts to exclude studies that clearly met one or more of the exclusion criteria. Articles that passed this initial screening were then reviewed in full to ensure they aligned with the study's objectives and did not meet any predefined exclusion criteria.
The remaining articles were independently evaluated for inclusion by the first author. Later, the lead author reassessed the remaining articles against the exclusion criteria, ensuring methodological rigor and consistency. Discrepancies regarding inclusion of certain articles were resolved through discussion to ensure a consensus-driven approach. As a result, 23 articles were included in the final synthesis phase, providing the foundation for a comprehensive examination of applications, challenges, and ethical considerations associated with LLMs in engineering.
Data analysis
With the final 23 articles identified, the review followed a structured process to synthesize and extract meaningful insights from the publications. First, the first author independently read and summarized each article, recoding key information including the year of publication, publication type (e.g., conference proceeding vs. journal publication) and publication outlet, engineering field or application discussed, country affiliation of the first author, theoretical frameworks used, research foci and research methods applied, study populations and participant demographics, sampling methods and range of sample sizes, methodologies used and research findings. These summaries were carefully reviewed to ensure consistency and completeness.
Second, the authors collaboratively developed an inductive coding framework to identify common themes and patterns across the articles. This process resulted in the creation of five primary codes: automation, knowledge generation and discovery, engineering education, ethical considerations, and active integration. Each code was carefully defined, and examples from reviewed articles were mapped to these categories to refine the framework further.
Third, the remaining articles were reviewed using the established codebook. The first reviewer captured similar summarizing information as before and assigned articles to the predefined codes. If an article did not align with an existing code, new sub-codes were proposed and incorporated into the framework after discussion and consensus.
In the fourth step of the analysis, the codes developed in earlier steps were further analyzed and grouped into five emergent themes: automation of complex tasks, knowledge generation and discovery, enhancing engineering education, ethical considerations, and real-world integration. These themes were refined to ensure they encompassed the primary focus areas identified across the 23 articles.
In the final step, the articles were assigned to one or more of the five identified themes, ensuring that all relevant aspects of the articles were consistently recorded. Any findings that did not initially align with the predefined themes were carefully reevaluated and, when necessary, subjective accommodations were made to ensure the validity of the analysis.
Data analysis is presented in two parts in this paper. The first part uses descriptive statistics to examine publication trends in the 23 articles retained for final investigation (i.e., distribution of publication years, engineering disciplines, and geographic representation.) The second part presents a qualitative analysis of the articles, organized around the five identified themes.
Strengths and limitations
This SLR offers a comprehensive overview of the current applications of LLMs in engineering, covering a wide range of fields, including robotics, program repair, and system optimization. By categorizing the findings into clear thematic areas-such as applications, ethical considerations, and technical challenges-this review provides actionable insights that can guide both researchers and practitioners in the field. The SLR methodology ensures a rigorous and transparent process, which helps expand the understanding of how LLMs are being used in engineering. Notably, this study identifies research gaps and offers suggestions for future work, helping to shape the direction of LLM-related research in engineering. This is one of the SLR's specifically focused on LLMs within the engineering domain, setting a foundation for future research and practice in this emerging field.
Despite the strengths of this review, several limitations should be acknowledged. The inclusion of articles was based on predefined exclusion criteria, which did not account for the quality or uniqueness of the information within the articles. While this SLR used seven reputable databases such as IEEE Xplore, Google Scholar, Web of Science, Science Direct, Wiley Online, Engineering Village and Education Resources Information Center, there may be relevant studies published in other databases or sources (such as technical reports and books) that were not included in the review. This selection of search terms focused on LLMs and engineering, which may have excluded other relevant studies that did not specifically address these keywords. Furthermore, this SLR was limited to articles published between 2014 and 2024, meaning that older or newer studies and emerging trends in LLM applications may not have been referenced. Additionally, the review exclusively included English-language publications, which may have overlooked important global research and perspectives on the topic.
Findings
We first present a descriptive summary of trends in research and practice related to the integration of LLMs in engineering, based on publications from 2014 to 2024. Following this, the findings are organized around five identified themes through analysis. Then we provide descriptions, exemplary studies, and research and practice implications for the five themes synthesizing the final 23 articles.
Descriptive findings related to publication trends
Publications per year
Over the past decade, from 2014 to 2024, research on the applications of LLMs in engineering has seen a marked increase. This surge in scholarly activity reflects a growing recognition of the transformative potential of LLMs across various engineering disciplines, such as robotics, program repair, and autonomous systems. The intensified interest highlights how academics and industry professionals are increasingly keen to leverage these models for innovative applications and operational optimization. This continuous growth in research publications underscores the expanding role of LLMs in advancing engineering solutions and their increasing integration into practical engineering workflows.
Publication type and publication outlet
Among the 23 articles reviewed for this study, 78% were published as conference proceedings and 22% as journal articles. Most conference papers were presented at notable organizations such as the 2024 IEEE/ACM First International Conference on AI Foundation Models and Software Engineering (Forge; Macedo et al., 2024), 2024 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI; Ananthajothi et al., 2024), 2024 IEEE International Conference of Young Professionals in Electron Devices and Materials (EDM; Lina and Aksyonov, 2024), with the remaining papers distributed across other engineering and AI-focused conferences. Further, the journal articles sampled in this study appeared in the following journal outlets: IEEE Xplore Digital Library (43%), MDPI Journals such as Applied Sciences and Information (17%), Proceedings of the Design Society via Cambridge Core (13%), ScienceDirect journals including The Potential of LLMs in Hardware Design (13%), and arXiv Preprint Server (13%). These outlets highlight a diverse range of platforms where research on LLMs in engineering is disseminated, emphasizing both peer-reviewed studies and cutting-edge preprints.
Country affiliation of first author
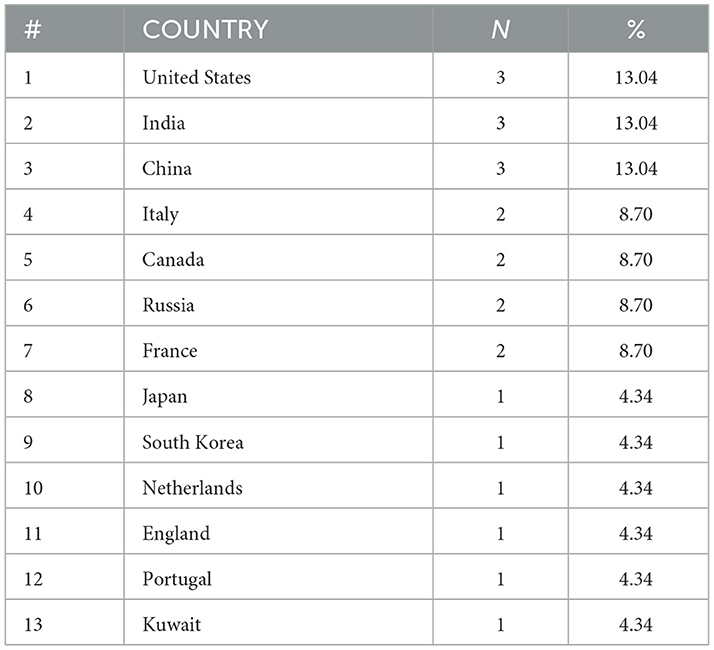
Table 1 reveals that the articles included in this review were authored by researchers from thirteen different countries, reflecting the global interest in research related to LLMs. The United States, India, and China each accounted for 13.04% of first authors, demonstrating their leadership on this field. Italy, Canada, France and Russia followed, each contributing 8.70% of the first authors. Other countries, including Japan, South Korea, the Netherlands, England, Portugal and Kuwait, represented 4.34% each. This distribution highlights a significant concentration of LLM research within the United States, India, and China, likely driven by substantial investments in AI and engineering research in these regions. However, the broad representation of other nations emphasizes the global nature of innovation in LLM applications, showcasing how researchers worldwide contribute to advancements in this area. The findings also suggest potential influences such as the accessibility of English-language publications and varying levels of research support across countries, which could shape the observe patterns.
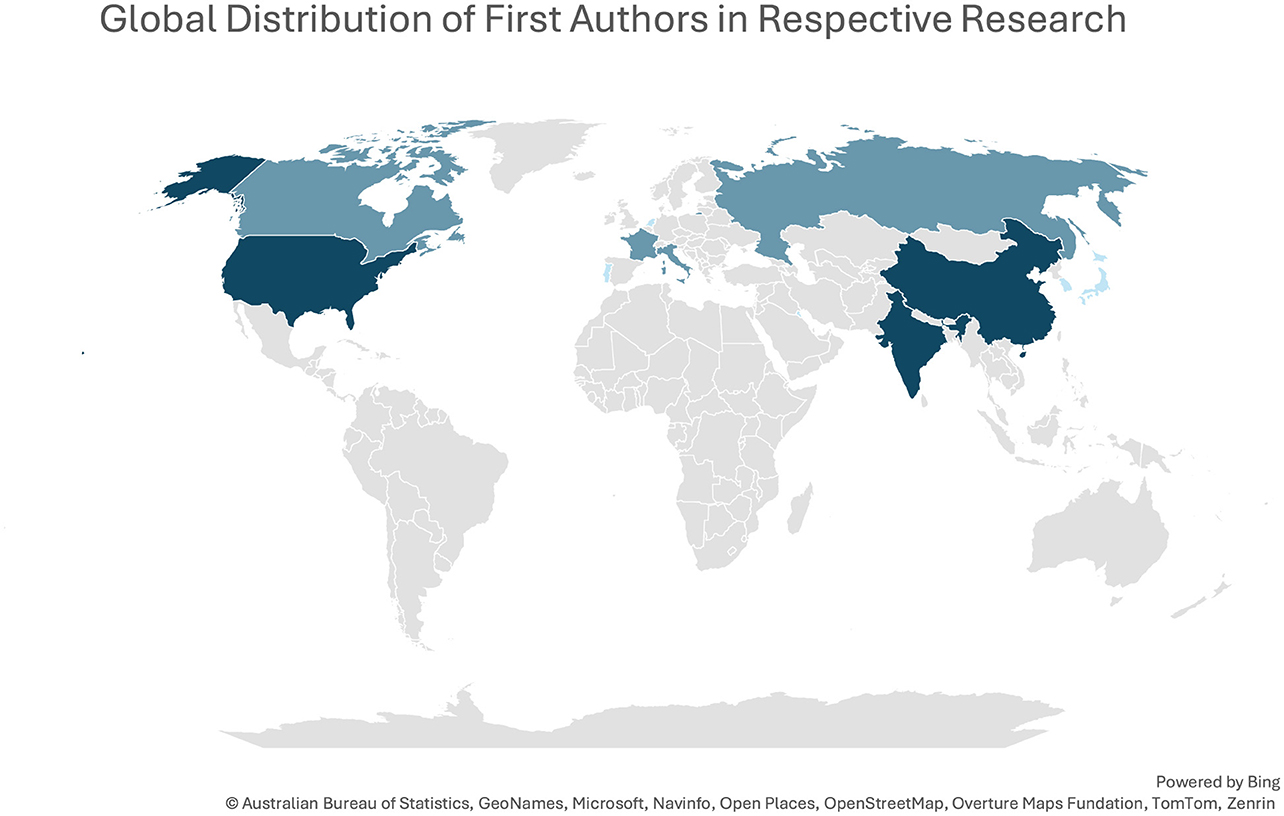
Figure 2 below illustrates the geographical distribution of first authors from the research articles reviewed in our study on the applications of LLMs in engineering. The country affiliations for the global distribution map were determined based on the first author's affiliation. Countries are shaded differently to indicate the relative concentration of contributions from each location, with darker shades representing high frequencies of first authors. This visualization highlights the global impact and interest in LLM technologies within engineering disciplines, showcasing widespread engagement and diverse international insights into this evolving field from 2014 to 2024.
Engineering programs and courses
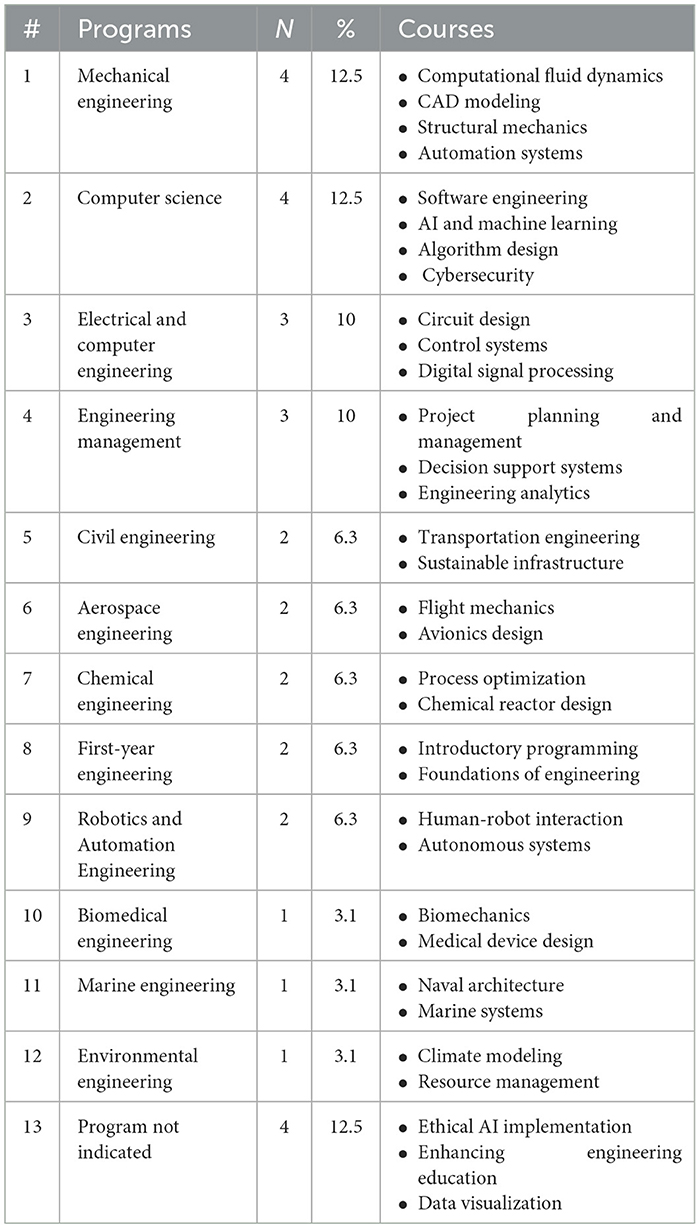
Table 2 below outlines the engineering programs and courses studied in the context of integrating LLMs into engineering practices. Across various disciplines, Mechanical Engineering (12.5%) and Computer Science (12.5%) were the most studied programs, followed by Electrical Engineering (10%), Engineering Management (10%), and other specialized fields. The courses mentioned span both undergraduate and graduate levels, incorporating theoretical, practical, and interdisciplinary applications. These findings reflect the adaptability and potential of LLMs in diverse engineering contexts. It is important to note that some articles referenced multiple engineering programs or courses, indicating the broad applicability and interdisciplinary nature of LLMs in engineering education and practice.
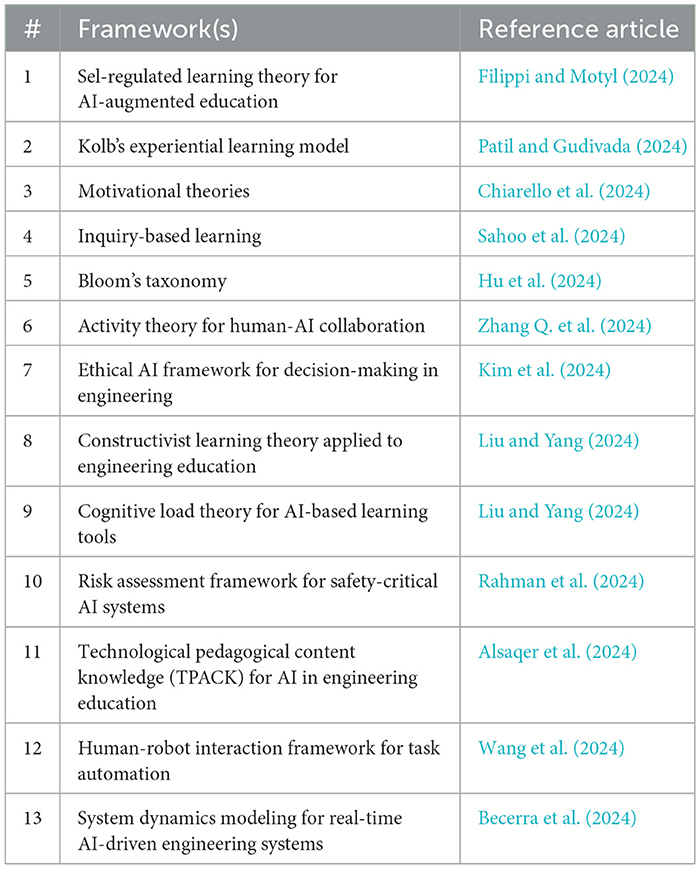
Theoretical frameworks
Ten articles utilized a theoretical framework, seven used a conceptual framework grounded in literature, and the remaining six did not employ a framework in their study. For the articles that adopted a theoretical framework, the frameworks applied are summarized in Table 3. Interestingly, none of the frameworks were repeated across these studies, suggesting a diverse range of theoretical perspectives being employed in the engineering and LLM integration context. This diversity highlights the ongoing exploration of how LLMs interact with various engineering paradigms and learning environments.
While the frameworks themselves were distinct, several studies emphasized shared themes such as improving human-AI collaboration, addressing ethical considerations in engineering design, and optimizing learning processes using LLMs. Four of the six articles that did not use a framework were literature reviews or discussions where a formal framework was not typically employed or applied. The remaining articles focused on exploratory applications of LLMs in novel engineering domains, emphasizing experimentation over theoretical grounding.
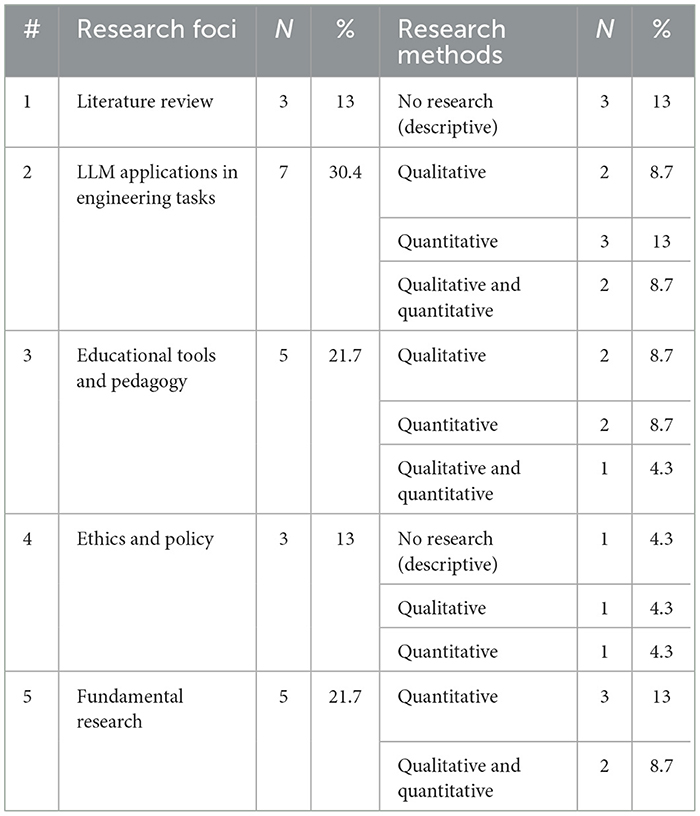
Research foci and research methods
Table 4 summarizes the various research foci and methods utilized in the 23 sample articles examining the impact of LLMs in engineering. Five primary categories of articles emerged: literature reviews (13.0%), LLM applications in engineering tasks (30.4%), educational tools and pedagogy (21.7%), ethics and policy (13.0%), and fundamental research that transcends specific courses or programs (21.7%). Studies labeled as “no research” in Table 4 were descriptive in nature and did not include original data collection or analysis.
Three studies focused on literature reviews, summarizing the existing applications of LLMs in engineering. Topics covered included the automation of repetitive engineering tasks (Zhang Q. et al., 2024), ethical challenges associated with AI-driven systems (Rahman et al., 2024), and integration of LLMs in engineering education (Filippi and Motyl, 2024). These studies were descriptive, synthesizing prior research to identify gaps and opportunities for future investigations.
Seven articles explored how LLMs are applied to real-world engineering tasks, such as automating program repair, optimizing system designs, and improving predictive maintenance. Two of these studies used qualitative methods, focusing on case studies and user feedback (Rahman et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). Three employed quantitative methods, analyzing tasks performance metrics and efficiency improvements (Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Ananthajothi et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024). The remaining two utilized mixed methods, combining survey data with task outcomes to assess effectiveness comprehensively (Biadsy et al., 2014; Brown et al., 2020).
Five articles explored the use of LLMs in engineering education, particularly for personalized learning, automated grading, and interactive problem-solving tools. Two studies used qualitative methods, collecting feedback from students and educators on their experiences (Chiarello et al., 2024; Patil and Gudivada, 2024). Two more employed quantitative approaches to measure the impact of LLM-driven tools on learning outcomes, such as grades and engagement (Liu and Yang, 2024; Alsaqer et al., 2024). One mixed-methods study combined qualitative feedback with quantitative performance data for deeper insights (Filippi and Motyl, 2024).
Three studies address ethical and policy considerations in the adoption of LLMs in engineering (Kim et al., 2024; Patil and Gudivada, 2024; Hu et al., 2024). Topics included bias in AI outputs, privacy concerns, and accountability in AI-driven decision-making. One study was descriptive, offering a framework for ethical implementation. Another used qualitative methods through expert interviews, while the third applied quantitative analysis to survey stakeholder perceptions.
Lastly, five articles explored fundamental questions about LLMs, such as developing new frameworks for their integration into engineering workflows, improving algorithmic reliability, and ensuring transparency in safety-critical systems. Three studies relied on quantitative methods, applying advanced statistical techniques to evaluate LLM reliability and scalability (Marques et al., 2024; Sahoo et al., 2024; Liang and Xiao, 2024). Two used mixed methods, combining technical evaluations with user studies to explore how LLMs could be better integrated into engineering practices (Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Alsaqer et al., 2024).
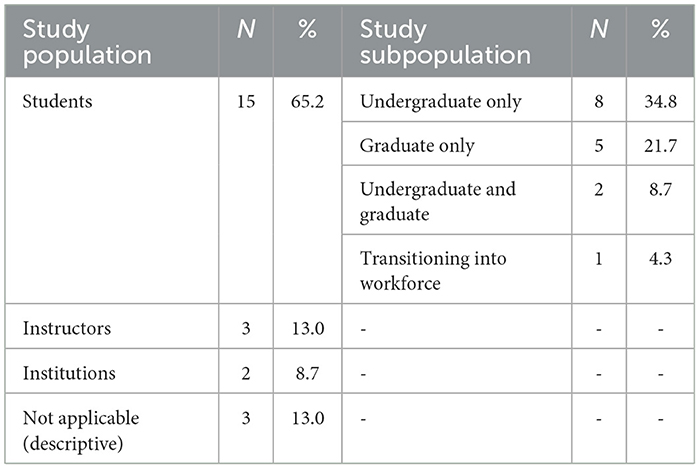
Study populations and participants demographics
Table 5 provides an overview of the study populations included in the 23 articles on the use of LLMs in engineering. The majority of studies (65.2%) focused on student populations, with eight studies (34.8%) targeting undergraduate students, five (21.7%) targeting graduate students, and two (8.7%) including both groups. One study (4.3%) examined students transitioning into the workforce. Additionally, three studies (13.0%) focused on instructors, two (8.7%) targeted institutional adoption of LLMs, and five studies (21.7%) were descriptive works with no specific participant data.
Out of the 15 studies focusing on students, six (40%) reported demographic information. Four studies (26.7%) reported students' gender identities, two (13.3%) detail racial or ethnic data, and three (20%) included information about students' ages. The remaining nine studies (60%) did not report any demographic data. Among the studies targeting instructors, none reported demographic data such as age or teaching background. Similarly, the studies examining institutions provided no details about the types or profiles of the organizations involved.
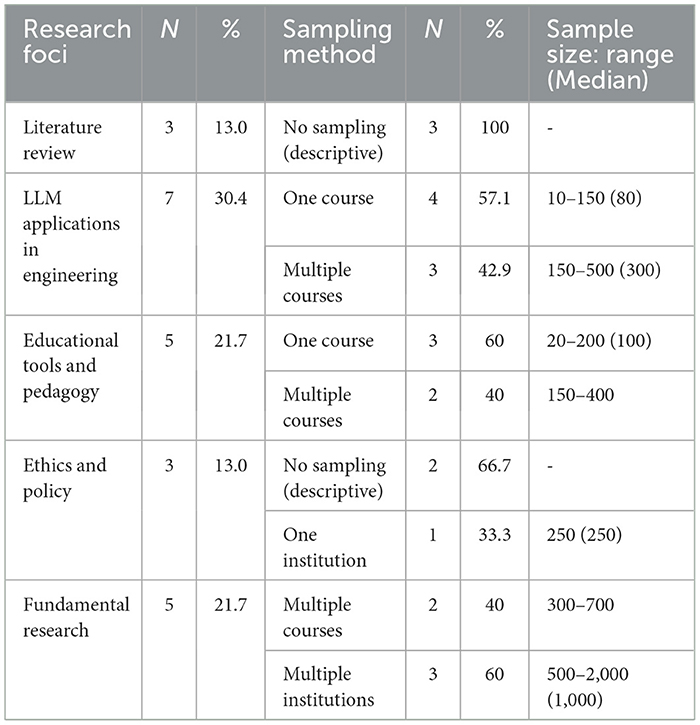
Sampling approaches and sample sizes
Table 6 presents the sampling methods and sampling methods and sample sizes for the studies referenced in the analysis of LLMs in engineering, categorized by research foci (refer to Table 4). Sample size ranges in Table 6 are based on studies where sample sizes were explicitly provided. The findings reveal that studies on LLM applications in engineering tasks and educational tools predominantly rely on smaller samples drawn from individual courses or specific groups. Conversely, fundamental research studies often draw data from multiple institutions or courses, enabling broader and more generalizable findings.
The observations underscore the potential to enhance the generalizability of LLM-focused studies by incorporating data from diverse sources, including multiple institutions or courses. This approach is particularly valuable for replication and extension studies, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of LLM impacts in engineering education and practice.
Thematic analysis: descriptions, exemplars, and implications
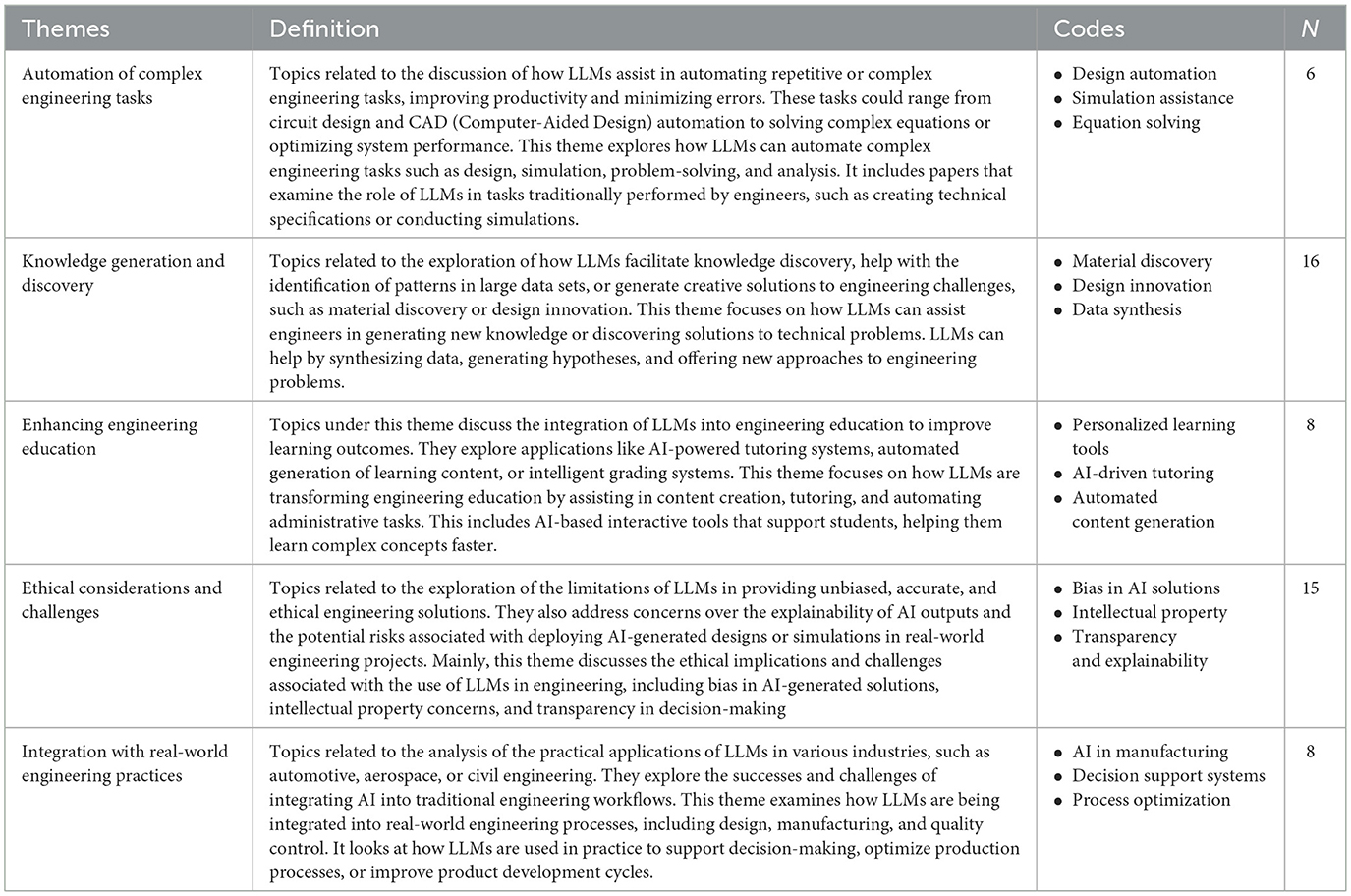
This section examines five themes identified themes (automation of complex tasks, knowledge and generation and discovery, enhancing engineering education, ethical considerations, and real-world integration) in depth. Each theme is introduced, its relevance explained, exemplar studies are highlighted, and implications for future research and practice are discussed. Table 7 defines the themes, their associated codes, and the number of papers categorized under each theme. All the codes, their descriptions, and exemplars are shown in Appendix A.
The evolution of themes related to LLMs in engineering over the past decade reflects shifts in research and practical priorities. Since 2014, the theme of Enhancing Engineering Education has consistency received considerable attention, highlighting the persisten focus on leveraging LLMs to improve educational methodlogies and outcomes. Over time, there has been a notable increase in the exploration of Knowledge Generation and Discovery, as well as Automation of Compex Tasks. These themes have become increasingly prominent, indicating a growing recognition of the potential for LLMs to revolutionize traditional engineering practices by enabling more efficient and innovative solutions. In the recent years, the themes of Ethical Considerations and Real-World Integration have also begun to gain traction. This rising interest underscores the field's acknowledgment of the need to address the ethical complexities and practical challenges that arise as LLMs become more embedded in real-world engineering applications.
Theme 1. Automation of complex engineering tasks
Eight articles addressed the elements of the application of technology, particularly involving the advanced algorithms and systems of LLMs, to perform engineering tasks that are typically complex and labor-intensive (Wang et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024; Rahman et al., 2024; Ananthajothi et al., 2024; Becerra et al., 2024; Brown et al., 2020; Buonamici et al., 2020). These articles directly discuss the use of LLMs to automate complex engineering tasks, which target several components such as 1) the efficiency of processes i.e., debugging and repairing, interpreting and enabling LLM methods to understand context and developer preferences, circuit design, code optimization, and structural analysis in fields such as civil engineering, aerospace and automotive industries, etc.; the automation targets tasks that are repetitive, intricate, or require precision that might be difficult to achieve consistently by humans; 2) reduction of errors, efforts and time due to human interventions to enhance productivity, and training in engineering disciplines i.e., extensive testing and ability to revise results provided by integrating LLMs with robotics and autonomous systems for engineers and technicians who are tasked with managing and optimizing AI-powered systems. Table 8 lists the sampled articles categorized under this theme.
Exemplar studies
Research in LLMs has enabled automation in tasks ranging from computer-aided design (CAD) automation to complex problem-solving in engineering. Studies (e.g, Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Rahman et al., 2024) have highlighted their application in circuit design and system performance optimization, where they assist in automating design iterations and stimulating different configurations without manual intervention.
Zhang Q. et al. (2024) provides a comprehensive review of the use of LLMs in automating program repair (APR), a complex and traditionally manual task in software engineering. The study examines various methodologies implemented within LLMs, such as the use of sequence-to-sequence models to automatically suggest fixes for buggy code by outlining 1) zero-shot learning, which utilizes LLMs without additional training, relying on their pre-trained knowledge; 2) fine-tuning, which adapts LLMs to specific APR tasks by training them on relevant datasets; 3) few-shot learning, which provides LLMs with a few examples to guide their repair process. It also explores the effectiveness of different LLM architectures and training datasets on the performance of automated program repair systems. Furthermore, it delves into the comparison of LLM outcomes with traditional software repair tools, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of LLM in this context. Ultimately, Zhang Q. et al. (2024) analyzes the application of LLMs in automated program repair from 2020 to 2024 while highlighting the use of models like CodeBERT and Codex (Chen et al., 2021), which are deployed through strategies like fine-tuning and few-shot learning to address various repair scenarios, including fixing semantic bugs and security vulnerabilities,
Another key area is the use of LLMs in automating technical documentation and specifications, which effectively streamlines processes that traditionally require extensive human effort. Additionally, LLMs are utilized in conducting complex simulations, such as those required in the automotive and aerospace industries, where they can predict outcomes based on varying parameters, significantly reducing design time and cost. Rahman et al. (2024) investigates the application of LLMs in generating patch sets from code review comments, which is a novel approach in automating responses to human-generated feedback on software development. This study outlines how LLMs can interpret the intent behind code review comments and automatically suggest corresponding modifications in the codebase. It details the methods used to train LLMs on historical code review data, enabling them to understand context and developer preferences effectively. The study also discusses the challenges in achieving high accuracy in code transformation suggestions and measures the performance of these models against manual patch creation. By automating this aspect of software development, the study highlights a significant shift toward more AI-integrated processes in software engineering. Moreover, Rahman et al. (2024) demonstrates that LLMs, such as GPT-4 and CodeBERT, can effectively generate code patches based on code review comments with varying levels of accuracy. This research shows that when the generated patches closely match the historical patch sets (with an 80% match threshold), the LLMs can automate code repairs, reducing manual workload.
Research implications
This theme pushes forward the boundaries of what can be automated, requiring robust algorithms and safety protocols. Additionally, it prompts questions about machine learning interpretability and reliability.
The growing capabilities of LLMs necessitate ongoing research into their ability to understand and generate complex engineering knowledge. This includes improving their accuracy and reliability in simulation and design tasks. There is also a need for research into the integration of LLMs with other AI technologies like machine learning and neural networks (Brown et al., 2020) to enhance their problem-solving capabilities. Zhang Q. et al. (2024) prompt several research implications when it comes to the integration of LLMs. First, the study challenges researchers to improve the accuracy and reliability of LLM outputs to either match or exceed traditional automated repair tools. Additionally, there presents a need to explore how different training datasets and model architectures affect the performance of LLMs in understanding and fixing complex code bugs. Regardless, the study does raise questions about the scalability of these models and their ability to generalize across different programming languages and coding styles. The researchers highlight the necessity for ongoing evaluation of bias and fairness in the solutions proposed by LLMs, ensuring they do not perpetuate existing coding discrepancies.
In addition, the integration of LLMs in robotics and autonomous systems presents both opportunities and challenges for future research. Several studies, such as Wang et al. (2024) and Ananthajothi et al. (2024), highlight the potential for LLMs to significantly enhance decision-making, task planning, and interaction in real-world environments. However, as LLMs can sometimes produce unexpected or incorrect outputs, these technologies encounter multiple obstacles in terms of reliability and predictability. In conclusion, there demands a need for robust evaluation frameworks to assess the accuracy and functionality of LLM-generated solutions.
Under Kim et al. (2024), the potential for LLMs to automate complex tasks, such as robotic task planning and human-robot interaction were underlined. Further research is suggested on multimodal learning, where robots leverage both language and visual data for task completion. This research should focus on improving the robustness of these systems in unpredictable real-world settings, where the combination of different sensory inputs can lead to unexpected results.
Ethical and security aspects of automating engineering tasks with LLMs, particularly in fields like aerospace and biomedical engineering, which involve the sensitive nature of tasks where consequences of errors or unethical decisions can have significant real-world impacts, such as threats to human life or national security, need thorough exploration to ensure safety and compliance with regulatory standards. Of course, this does not exclude the need for ethical and security considerations in other fields. In fact, other engineering domains, such as automotive, civil, energy, and manufacturing engineering, also require thorough examination of ethical implications, especially as LLMs become more integrated into critical decision-making processes in these sectors. In the study that Rahman et al. (2024) did, there presents a critical need to address such implications of automating such tasks, particularly regarding the transparency of the model's decision-making process and its ability to handle sensitive information. Additionally, the study prompts further exploration into the integration of multimodal inputs, such as combining code metrics with textual feedback to enhance accuracy.
Practice implications
The implementation of automated systems that are being powered by LLMs—specifically when LLMs are used to automate tasks such as code generation, task planning, and decision-making in robotics (Wang et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024), program repair, and autonomous systems (Zhang Q. et al., 2024)—can lead to increased efficiency and safety (Ananthajothi et al., 2024; Becerra et al., 2024) but also requires re-skilling of the workforce. Industries need to prepare for a shift in job roles and the potential for reduced human intervention.
From a practical standpoint, incorporating LLMs into computer program repair can significantly enhance the efficiency of the software development process by reducing the time and human effort required for debugging. It also offers the potential for more consistent and continuous code quality improvements across projects (Rahman et al., 2024). However, the deployment of such technology requires substantial training for software teams to adapt to AI-driven tools effectively. There is an imperative need for establishing robust testing and validation frameworks to ensure the safety and reliability of auto-generated code repairs before their integration into production environments. Moreover, the economic impact of automating these tasks could lead to shifts in job roles, necessitating a reevaluation of skills and education in the software engineering workforce.
Additionally, automation poses challenges in terms of model training and integration into existing development pipelines. Organizations would need to invest in infrastructure and training to effectively utilize these AI capabilities. While automation of engineering tasks can enhance productivity, questions regarding the future role of human reviewers and the potential for decreased personal interaction in processes, often valuable for team cohesion and mentoring, drastically skyrocket.
Theme 2. Knowledge generation and discovery
We categorized 21 articles under knowledge generation and discovery theme in the context of engineering involving technology, particularly LLMs. These articles synthesize vast amounts of information, identify patterns, generate hypotheses, and create innovative solutions to engineering challenges (Wang et al., 2024; Patil and Gudivada, 2024; Alsaqer et al., 2024; Donaj and Kačič, 2017; Fan et al., 2023; Filippi, 2023). All articles encompass methods that enhance our understanding of complex systems, enable material discovery, and foster innovation (Sahoo et al., 2024; Chiarello et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Kodali et al., 2024; Rahman et al., 2024; Lina and Aksyonov, 2024; Macedo et al., 2024; Al-Kaswan et al., 2024; Arnautov and Akimov, 2024; Hu et al., 2024; Liu and Yang, 2024; Liang and Xiao, 2024; Osborne et al., 2014) by using data-driven insights to tackle technical problems. Table 9 lists the sampled articles categorized under this theme.
Exemplar studies
LLMs have played a transformative role in material discovery, where they help predict new materials with desired properties faster than traditional experimental methods. Chiarello et al. (2024) examines how generative LLMs can be used in engineering design to foster innovation and generate novel solutions. It delves into the potential of LLMs to assist engineers by suggesting creative approaches to common design problems, thus facilitating knowledge discovery through generative processes. The article provides examples of using LLMs to generate alternative design options and iterate on complex problems, particularly in fields where design constraints are fluid and solutions are not always straightforward. It also discusses the use of these models to interpret and propose modifications in design frameworks, adding new dimensions to traditional design methods. Overall, the study offers insights into how LLMs can function as creative aids in the engineering design space, promoting discovery and creativity in ways that traditional computational tools do not.
In design innovation, LLMs contribute by generating creative solutions to engineering challenges, significantly speeding up the innovation cycle in industries such as consumer electronics and automotive. Their ability to synthesize large datasets into actionable insights has revolutionized fields like environmental engineering and sustainability studies. They enable accurate forecasting and planning e.g., in Chiarello et al. (2024), the researchers offer insights on how LLMs contribute to knowledge generation in engineering design, proposing new solutions and innovations.
Wang et al. (2024) discuss how LLMs can be used in robotics to enhance knowledge generation and decision-making processes through advanced AI capabilities. Additionally, they examine how LLMs can be used to interpret complex data from sensors and other robotic inputs to facilitate decision-making in real-time. For example, LLMs are employed to create detailed action plans for robots based on natural language instructions and sensor feedback, allowing for a higher level of autonomy. The study highlights successful implementations of LLMs in improving robotic navigation and handling complex obstacles, showcasing the ability of these models to generate actionable insights for real-world applications. This research is pivotal in understanding how LLMs can extend beyond traditional robotic programming to enable more adaptive, intelligent systems.
Ultimately, Chiarello et al. (2024) and Wang et al. (2024) explore how LLMs can enhance decision-making, task planning, and human-robot interaction in robotics, as well as improve creativity and collaboration in engineering design. In robotics, LLMs face challenges like the unpredictability of outputs and the need for multimodal integration of language and vision for complex tasks, while in engineering design, generative LLMs can automate tasks and inspire innovation but raise concerns about data privacy, the reliability of generated designs, and the need for human oversight to ensure quality and accuracy.
Research implications
Continuous improvement in data handling and processing algorithms is essential to maximize the utility of LLMs in knowledge discovery. There's a growing need to address the limitations (Liang and Xiao, 2024; Hu et al., 2024) in current LLMs regarding their ability to generate verifiable and accurate outputs (Marques et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Chiarello et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024; Rahman et al., 2024; Alsaqer et al., 2024), crucial for fields that heavily rely on precision. The integration of LLMs into engineering design and discovery opens a variety of research pathways, notably in model improvement and optimization for creative problem-solving. Researchers are challenged to develop LLMs that can better understand the nuanced requirements of engineering problems and generate solutions that align with both technical specifications and aesthetic considerations (Subramani and Suresh, 2020). The study emphasizes the need for further exploration into model accuracy (Marques et al., 2024; Hu et al., 2024), particularly how well LLM-generated designs meet industry standards and regulations. Additionally, it raises questions about the potential for LLMs to facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations, as these models could bridge knowledge gaps across different fields of engineering. Research is also needed to ensure these models' outputs are interpretable, reliable, and not overly reliant on training data that may embed biases or outdated practices. Research into the transparency of AI processes and the reproducibility of results generated by LLMs is necessary to bolster their credibility and utility in scientific research.
Furthermore, the use of LLMs in robotics necessitates new research into model robustness, particularly in unpredictable environments where robots may face obstacles or dynamic conditions. It also calls for advancements in model training to allow LLMs to interpret multimodal data effectively (Donaj and Kačič, 2017), such as combining visual and textual information for comprehensive task planning. This study points to the potential for LLMs to support real-time decision-making, raising questions about their response times, reliability, and safety in critical tasks (Arnautov and Akimov, 2024; Becerra et al., 2024). Furthermore, research is needed to address ethical considerations, especially in autonomous applications where robots make decisions that could impact human safety (Patil and Gudivada, 2024). Ultimately, this area of study is likely to inspire interdisciplinary collaborations to optimize LLMs for robotics, integrating insights from AI, mechanical engineering, and human-computer interaction (Zhang Q. et al., 2024).
Practical implications
Integration of LLMs into the research and development processes can lead to more efficient research cycles and reduce time-to-market for new technologies. Specifically, prototyping faster cycles allowing engineers to explore multiple design options without the usual constraints of time and resources. By automating parts of the ideation process, engineering teams can shift their focus to refining and implementing the most promising designs. LLMs are promising for automating code patch generation, reducing the time developers spend identifying and fixing bugs. This is particularly useful in software maintenance, as shown in Rahman et al. (2024). However, when the generated patches fall below the required quality threshold, manual intervention remains essential to refining them. As well as implementing LLMs in design processes requires companies to establish rigorous validation methods to verify the accuracy and safety of AI-generated solutions before deployment (Kim et al., 2024). Additionally, as these models become more prevalent, the role of the engineer may shift toward overseeing and fine-tuning AI outputs rather than originating designs, prompting a reevaluation of skill sets within the engineering workforce. These shifts could result in more efficient design workflows, though they also necessitate training engineers to effectively interact with AI-driven design tools.
Furthermore, Wang et al. (2024) state the integration of LLMs into robotics could enhance productivity by enabling robots to perform complex tasks autonomously and with higher precision (Lina and Aksyonov, 2024). Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics could benefit from robots equipped with LLMs that understand natural language commands and adapt to varied tasks with minimal reprogramming. However, implementing such systems requires substantial investment in infrastructure, as well as regular testing to ensure LLMs perform reliably in real-world scenarios. Additionally, the adoption of LLMs in robotics may lead to increased demand for specialists who can train, monitor, and troubleshoot these AI-enhanced systems. As these robots become more sophisticated, companies may also need to establish guidelines for ethical uses (Marques et al., 2024).
Engineers and researchers must stay updated with AI developments to leverage these tools effectively, which may include specialized training and changes to curriculum in academic settings. Organizations must ensure robust data governance frameworks to manage the data used by LLMs, ensuring both ethical use and compliance with data protection regulations (Chiarello et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024), and that autonomy provided by LLMs aligns with safety and regulatory standards.
Theme 3. Enhancing engineering education
Eleven articles were categorized under this theme address the usage of technology and innovative methods to improve learning experience, effectiveness, and accessibility of engineering education. This theme explores applications like AI-powered tutoring systems, automated generation of learning content (Liu and Yang, 2024; Al-Kaswan et al., 2024; Ho et al., 2022; MacNeil et al., 2022) or intelligent grading systems (Macedo et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Hu et al., 2024; Marques et al., 2024; Filippi and Motyl, 2024; Sahoo et al., 2024; Nikolic et al., 2023). This theme focuses on how LLMs are transforming engineering education by assisting in content creation, tutoring, and automating administrative tasks. This includes AI-based interactive tools that support students, helping them learn complex concepts faster. AI-driven tutoring systems are being used to provide personalized learning experiences so that engineering students can adapt to the educational content based on individual learning paces and styles. Automated content generation tools are helping educators create customized learning materials, including simulations and interactive modules that enhance understanding of complex engineering concepts. Intelligent grading systems are being developed to assist educators in assessing student performances more efficiently, allowing them to focus more on teaching and less on administrative tasks. Table 10 lists the sampled articles categorized under this theme.
Exemplar studies
Filippi and Motyl (2024) present a systematic review of how LLMs are being used to enhance engineering education, with practical examples demonstrating their value in providing real-time support to students. It highlights how LLMs are being used as virtual tutors, offering students instant feedback on technical questions and guiding them through problem-solving processes in engineering. For educators, the study examines the potential for LLMs to reduce administrative burdens, like grading, through automated assessment of technical assignments. The review also explores how LLMs can generate customized study materials, tailored to meet the learning needs of individual students, thus creating a more personalized educational experience. This systematic analysis provides educators and institutions with a roadmap for integrating LLMs into their curricula to improve learning outcomes.
Another exemplar Liu and Yang (2024) illustrates the application of LLMs within a system modeling and simulation course, showcasing how AI can enhance students' grasp of complex engineering principles. It details how LLMs support students by providing instant feedback on simulation models, assisting them in identifying and resolving errors in real time. The study notes that these AI tools allow students to learn at their own pace, as they can receive guidance on demand, thus minimizing frustration and boosting confidence. Furthermore, the study examines the role of LLMs in generating individualized practice problems and simulations, enabling students to apply theoretical knowledge in a hands-on, interactive way. This case study highlights the potential of LLMs to create a more supportive and adaptive learning environment in technically demanding courses.
Research implications
Research is needed to explore the balance between automated and traditional teaching methods to optimize educational outcomes. There is a significant potential for further research into adaptive learning algorithms that can be better catered to the diverse learning needs/preferences of students. Studies focusing on the long-term impacts of AI integration in engineering education are necessary to understand how these technologies affect learning outcomes and career readiness. Several key areas for future research were highlighted in Filippi and Motyl (2024). Notably the need to examine the impact of LLM-based tutoring on students' retention of knowledge and depth of comprehension over extended periods. It also presents an opportunity to optimize LLMs' accuracy and responsiveness in addressing complex engineering inquiries. There is a call for further exploration of LLMs' adaptability across various engineering disciplines to ensure these AI tools can meet specific and varied curricular demands. Additionally, there is increasing interest in understanding how LLMs can effectively balance automated assistance with human oversight, particularly for tasks that require detailed problem-solving and nuanced feedback. Finally, this study points to the importance of investigating potential biases in AI-generated content, as such biases could shape students' learning experiences and perceptions in unintended ways. Liu and Yang (2024) points to the need for further research into how real-time feedback from LLMs influences student comprehension and engagement in engineering courses. Researchers could investigate the long-term benefits of AI-assisted learning, such as whether students retain more knowledge and perform better in practical applications. Another research direction is examining the adaptability of LLMs across different engineering fields and evaluating their ability to provide context-specific feedback. This case study also prompts researchers to explore the role of educators in an AI-supported classroom, as their roles may evolve from direct instruction to facilitating AI-assisted learning. Additionally, it encourages studies on ethical considerations, such as ensuring students understand the limitations of AI support and avoid over-reliance on automated assistance.
Practical implications
In practice, the adoption of LLMs in engineering education has the potential to make learning more interactive and accessible. Educators could utilize LLMs to provide students with personalized learning experiences, allowing them to focus on creative and critical-thinking skills. For institutions, integrating LLMs requires investment in technology infrastructure and training for educators to use these tools effectively in classrooms. The increased reliance on AI-based assessments and feedback could shift educators' roles toward facilitating learning and managing technology rather than performing manual grading and administrative tasks. There presents a need for curriculum updates to include AI literacy as a core component of engineering education, preparing students for a future where AI tools are integral to the engineering profession.
Additionally, the use of LLMs in system modeling courses offers students a more hands-on learning experience, where they can test models and receive feedback in a controlled environment. This real-time support can reduce student dropout rates in challenging courses, as LLMs help them overcome learning barriers by offering instant, practical assistance. However, it is essential to establish a balance and adaptability and openness from users for where AI tools enhance, rather than replace, traditional teaching, ensuring students still develop independent problem-solving skills. Institutions may also need to consider the ethical implications, such as the risk of students becoming too reliant on AI, potentially diminishing their critical thinking skills, and preventing disparities in educational outcomes.
Theme 4. Ethical considerations and challenges using LLMs
Ethical considerations and challenges within the context of engineering with LLMs pertain to the responsibility of using AI systems in safe, fair, and transparent ways (Cui et al., 2018; D'Angelo et al., 2018; Solaiman et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2022). The ethical challenges are especially pronounced in engineering applications where AI decisions could impact human lives, resources, and broader societal norms (Kim et al., 2024; Sahoo et al., 2024; Hu et al., 2024). We categorized 21 articles that focus on understanding and mitigating risks associated with AI-driven automation, such as biases, data privacy issues, accountability, and the reliability of AI-generated outputs. This theme encompasses issues like AI model bias, data transparency, intellectual property rights, and ethical data handling, particularly in the context of LLMs used in fields such as robotics, infrastructure, and software engineering (Becerra et al., 2024; Ananthajothi et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Cohen and Gokaslan, 2020; Ozkaya, 2023). It also includes considerations around explainability, where decisions or outputs from LLMs should be traceable and understandable. Table 11 lists the sampled articles categorized under this theme.
Exemplar studies
Studies on the ethical implications of AI in engineering, such as the use of AI in public surveillance systems and its impact on privacy, have heavily emphasized the need for explicitness. Patil and Gudivada (2024) broadly review trends and challenges, focusing on ethical considerations such as bias, transparency, and the implications of AI in practical applications. The research additionally provides an overview of the key ethical challenges associated with LLMs, including issues of bias, transparency, and model accountability in engineering applications. It discusses how LLMs, trained on vast datasets, can inadvertently reproduce biases present in those datasets, which pose risks when these models are used in critical engineering domains. The study emphasizes the need for model explainability, particularly in fields like civil and aerospace engineering, where transparent and traceable decisions are essential. Furthermore, the article explores the challenges of intellectual property, noting that AI-generated outputs may reuse or inadvertently disclose proprietary or sensitive information. By systematically reviewing these concerns, the study highlights the urgency of integrating ethical safeguards within AI and LLM applications in engineering.
Hu et al. (2024) and Wang et al. (2023) examine the ethical considerations of using pre-trained LLMs in reliability engineering, a field where AI decisions can have critical implications for public safety. It points out that while LLMs can improve efficiency and predictive accuracy in reliability assessments, they may also introduce risks due to errors in AI-generated recommendations. The article reviews cases where AI outputs were found to be inaccurate or misleading, underscoring the need for rigorous validation and human oversight. Furthermore, the study discusses the potential misuse of AI in reliability engineering if not implemented responsibly, including scenarios where AI might overlook or misinterpret safety-critical parameters. Overall, the article provides a cautionary perspective on the reliance on pre-trained LLMs in safety-sensitive fields.
Research implications
There is an urgent need to develop frameworks that guide the ethical use of AI and other technologies in engineering solutions, focusing on issues like bias, privacy, and accountability. The ethical issues outlined in these studies (e.g., Patil and Gudivada, 2024; Hu et al., 2024; Nikolic et al., 2023) emphasize a need for research into improving bias detection and mitigation methods within LLMs, especially when applied to engineering. Researchers are encouraged to investigate how training datasets influence model outputs and develop guidelines for ethically sourcing data in ways that minimize bias (Zheng et al., 2023). The study also raises questions about model transparency and the need for tools that can explain LLM decision processes to engineers and stakeholders. Additionally, intellectual property issues in AI outputs prompt research into defining clear guidelines around the ownership and accountability of AI-generated content. Overall, the study suggests a multi-disciplinary approach to engineering ethics, involving collaboration between AI researchers, engineers, and ethicists.
Further research was called for into ethical AI training, particularly dataset integrity and ensuring that LLM outputs align with safety protocols. Hu et al. (2024) points to the need for continued research into ensuring the reliability of AI models in fields where safety is paramount. Researchers are encouraged to develop robust validation frameworks that assess the accuracy and reliability of LLM outputs in reliability engineering, emphasizing safety and accountability. The study also suggests exploring collaborative models where LLMs complement, rather than replace, human expertise, especially in decision-making for critical engineering applications. Additionally, it prompts investigation into adaptive AI models that can learn from real-world feedback, helping to improve model accuracy over time.
Along with Hu et al. (2024), Sahoo et al. (2024) and Patil and Gudivada (2024) focus on the ethics of prompt engineering, transparency in model outputs, and the need for clear communication in LLM applications; while also providing an overview of challenges, including ethical issues such as biases in LLM outputs, interpretability, and the responsible use of these models in engineering.
Practice implications
Practitioners must be aware of the ethical implications of their work and strive to adhere to ethical guidelines while developing and implementing engineering solutions using LLMs. This often means staying informed about emerging regulations and societal expectations. Several articles (Wang et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024; Ananthajothi et al., 2024; and Hu et al., 2024) have highlighted the importance of incorporating ethical oversight in the deployment of LLMs, particularly for engineering firms integrating AI into high-stakes applications. Engineering companies may need to establish internal review committees to evaluate the ethical impacts of LLM usage in their projects. Additionally, it underscores the importance of regular audits of LLM outputs to detect and correct any biases, ensuring that AI-driven solutions align with organizational values and regulatory standards. The findings also imply that firms should implement transparency measures, allowing stakeholders to understand the AI decision-making process. Lastly, addressing intellectual property concerns may require the development of internal guidelines for safe data handling and AI output monitoring to prevent inadvertent disclosures.
From a practical standpoint, Hu et al. (2024) spotlights the need for strict regulatory oversight when deploying LLMs in reliability engineering, particularly in industries where safety is a top priority. Companies may need to implement a combination of automated and human reviews for all AI-generated recommendations, ensuring that engineers assess high-risk outputs before implementation. Training protocols may also need updating to prepare engineers for using AI tools responsibly, equipping them with the knowledge to identify and address potential issues with AI outputs. The study suggests that organizations should adopt transparency protocols, making it clear to stakeholders when LLMs are involved in decision-making processes. Additionally, organizations may find it beneficial to develop ethical guidelines that restrict LLM usage in scenarios where there is a high risk of safety-critical misinterpretations.
Theme 5. Integration with real-world engineering practices
Under this theme, we classified 15 studies. Articles focus on applying LLMs in practical engineering settings to enhance workflows, improve design and production efficiency, and support decision-making. This theme is centered on bridging the gap between AI-powered models and traditional engineering practices by implementing LLMs in diverse industries like manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive. The objective is to make LLMs a seamless part of engineering processes, enabling them to assist in complex tasks, optimize production, and enhance quality control (Becerra et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024; Strobelt et al., 2022). It also examines how LLMs can be effectively incorporated into existing engineering practices (Hou et al., 2023; Reynolds and McDonell, 2021) to support real-world tasks. Applications range from decision support in project management to quality assurance in manufacturing and production optimization in industries like automotive and aerospace. Table 12 lists the sampled articles categorized under this theme.
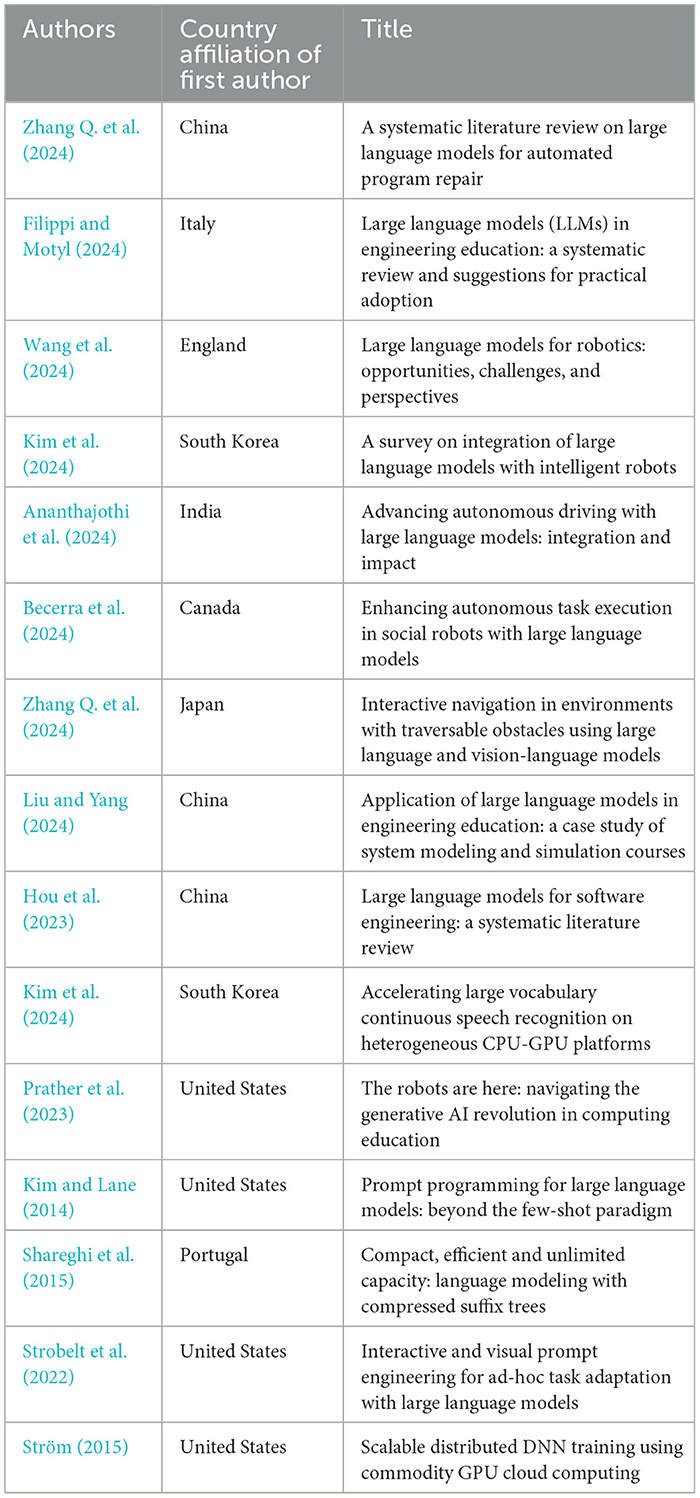
Table 12. Classification of reviewed studies for theme 5: integration with real-world engineering practices.
Exemplar studies
Kim et al. (2024) explores the integration of LLMs with robotics in real-world engineering applications, particularly in fields that require adaptability and real-time decision-making. It outlines examples where LLMs are used to enhance robotic capabilities, allowing robots to interpret complex instructions and adapt to changes in their environments. Specifically, the study discusses applications in manufacturing where LLM-enhanced robots can adjust to new tasks, inspect components, and even handle delicate assembly processes autonomously. Additionally, the article examines how LLMs enable robots to learn from data and human feedback, making them more versatile and reliable in industrial settings. By highlighting successful integrations of LLMs and robotics, the study provides a roadmap for industries aiming to implement AI-driven automation.
Ananthajothi et al. (2024) explores the incorporation of sophisticated LLMs into HighwayEnv for autonomous driving (AD), aiming to replicate intricate human-like driving behaviors, overcoming the limitations inherent in traditional AD systems. HighwayEnv refers to a simulation environment designed for AD research and development; specifically, an open-source Python-based environment that is widely used within the reinforcement learning (RL) and machine learning communities to test and train autonomous driving algorithms in a controlled, customizable setting. Renowned for their sophisticated learning capabilities and natural language processing, LLMs provide innovative solutions to the rigidity and predictability challenges faced by conventional AD frameworks, particularly in adapting to unexpected driving conditions. This research highlights the LLMs' proficiency in interpreting complex driving environments through analysis of sensor data, traffic signals, and other critical road indicators, mirroring human perception and decision-making processes. By leveraging past driving experiences, LLMs enhance their predictive accuracy and adaptability, which are crucial for dynamic decision-making in AD systems. Through detailed examples, the study demonstrates how integrating LLMs into autonomous systems enhances their ability to operate safely and efficiently in real-world conditions.
Research implications
Studies were done to highlight the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in AI, robotics, and engineering fields to improve LLM integration. Kim et al. (2024) suggests multiple avenues for research, particularly into improving the adaptability and learning capabilities of LLM-enhanced robots. Researchers are encouraged to explore methods for refining the decision-making accuracy of LLMs in real-time applications (Becerra et al., 2024; Ananthajothi et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024), especially when robots operate in unpredictable environments. The study also points to the need for developing standards and guidelines that ensure safety and ethical considerations are met when deploying LLM-enhanced robotics in sensitive environments (Kim et al., 2024; Ananthajothi et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024; Prather et al., 2023). Additionally, research could investigate how LLMs interact with different types of robotic hardware and sensors, optimizing their performance in diverse operational conditions (Zhang Q. et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024; Becerra et al., 2024).
The application of LLMs in autonomous driving opens research opportunities for refining model accuracy in high-speed decision-making scenarios (Kim et al., 2024), such as traffic congestion and inclement weather. Researchers are prompted to explore how LLMs can handle real-world driving data, developing adaptive models that can learn from new driving patterns or rare incidents. Ananthajothi et al. (2024) points to the importance of advancing Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication protocols, optimizing LLMs to support real-time data sharing and coordinated actions between vehicles. There's an additional need for research into the ethical and regulatory aspects of LLMs in autonomous driving, ensuring that AI decisions align with safety regulations and societal expectations. Multi-disciplinary research that encompasses AI, engineering, legal, and social sciences to tackle the challenges of AI deployments in public roadways were encouraged.
Wang et al. (2024) highlights profound implications for the future of robotics. By integrating LLMs into robotic systems, the researchers underscore their potential to bridge the gap between human-like reasoning and machine automation. The ability of LLMs to interpret and generate natural language enables more intuitive human-robot interaction, facilitating tasks such as collaborative assembly, autonomous navigation, and adaptive learning. Additionally, the study discusses how LLMs can be leveraged to enhance robot decision-making capabilities by processing contextual information and providing real-time adaptive responses to dynamic environments. However, the research also acknowledges critical challenges, such as the need for robust safety measures, reducing biases inherent in LLMs, and addressing computational constraints, signaling areas where further research and interdisciplinary collaboration are essential to realize their full transformative potential.
Practice implications
The integration of LLMs with robotics and autonomous systems holds considerable potential to boost productivity, flexibility, safety, and operational efficiency, particularly in sectors reliant on repetitive or labor-intensive tasks. Realizing these benefits will require extensive testing, rigorous validation, and dedicated training for engineers and technicians tasked with managing and optimizing these AI-powered systems (Kim et al., 2024; Filippi and Motyl, 2024; Wang et al., 2024; Ström, 2015). Additionally, industries will need to revise operational protocols to ensure AI-driven robots and autonomous systems meet stringent safety and quality standards, especially within high-stakes environments such as aerospace, healthcare, and automotive (Ananthajothi et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). Establishing a robust data infrastructure is also crucial to enable LLMs to continuously adapt to dynamic real-world conditions (Sahoo et al., 2024; Zhang Q. et al., 2024). Regular performance audits are essential for ensuring these systems operate as intended, quickly adjust to situational changes, and comply with regulatory standards. Companies must also proactively engage with regulatory bodies to develop AI safety frameworks and create clear public communication strategies to build trust and transparency around the role of AI in critical decision-making processes (Wang et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024).
Discussions and conclusions
LLMs are profoundly impacting engineering by revolutionizing how complex tasks are automated, decisions are made, and solutions are generated. Their ability to process vast amounts of data and generate human-like responses has been transformative in fields such as robotics, program repair, and system optimization. For instance, LLMs enhance efficiency in debugging code, optimizing designs, and interpreting sensor data in real-time, enabling autonomous operations. They streamline workflows, reduce errors, and cut development times, making them valuable tools for modern engineering. However, their full potential is intricately tied to addressing ethical, reliability, and interdisciplinary challenges, particularly in high-stakes environments.
While the five themes in the findings section are distinct, several papers reviewed in this systematic literature review highlight intersections across these themes. For example, Wang et al. (2024) explored the integration of LLMs in robotics, showcasing their role in automating complex tasks while simultaneously addressing ethical challenges, such as bias and decision-making transparency in real-time applications. Similarly, Zhang Q. et al. (2024) examined the use of LLMs in program repair, demonstrating their ability to enhance system optimization while also raising questions about accountability and the quality of automated outputs in safety-critical environments. Another study by Ananthajothi et al. (2024) investigated the application of LLMs in autonomous driving, focusing on their potential to improve decision-making in unpredictable conditions, but also emphasizing the need for robust evaluation frameworks to ensure reliability and safety.
Further examination of these intersections generates additional observations and implications for research and practice. For example, a potential research question could be: how can LLMs be optimized to enhance both task automation and ethical accountability in high-stakes engineering fields such as aerospace and healthcare? Studies could also explore how multimodal integration of language and sensor data affects the reliability and safety of LLM-enhanced autonomous systems. Additionally, future research could investigate strategies to mitigate bias in LLM outputs while preserving their adaptability and performance in dynamic operational contexts.
The integration of LLMs across various engineering fields highlights both their transformative potential and the challenges they bring. Their application in robotics and autonomous systems has advanced task planning and decision-making, yet studies like Kim et al. (2024) underscore the need for robust safety measures and adaptable algorithms to manage unpredictable environments. Similarly, in the realm of program repair, Zhang Q. et al. (2024) demonstrates that LLMs can automate debugging and optimize code repair processes but also points to the risk of introducing errors if outputs are not thoroughly validated. Ethical concerns, particularly regarding transparency and accountability, were consistently emphasized across high-stakes fields such as aerospace and healthcare. Research, such as that by Patil and Gudivada (2024), stresses the urgency of developing frameworks to address biases in LLM-generated solutions and ensure their alignment with safety and ethical standards. These findings suggest that while LLMs have the potential to revolutionize engineering practices, their deployment requires a careful balance of innovation, ethical oversight, and interdisciplinary collaboration to ensure their reliability and responsible use. Our analysis also highlights opportunities for interdisciplinary collaboration and regulatory engagement to address the challenges of deploying LLMs in critical engineering applications. Developing standards and ethical guidelines, conducting large-scale validation studies (Shareghi et al., 2015), and ensuring public trust through transparency are essential steps for responsible adoption.
The findings of this review reveal four emerging patterns in the application of LLMs to engineering education. First, there is increasing interest across diverse engineering disciplines—such as mechanical, electrical, and computer science—in leveraging LLMs for tasks like AI-assisted tutoring, instant feedback, and curriculum customization (Filippi and Motyl, 2024). Second, ethical and regulatory concerns are gaining prominence, particularly in courses that train students for safety-critical roles. For example, Hu et al. (2024) emphasized the importance of educating future engineers about bias, data provenance, and the limitations of LLM-generated outputs in reliability engineering. Third, the use of LLMs in classrooms has demonstrated clear potential to enhance productivity and foster innovation. Liu and Yang (2024) found that students using LLMs for simulation modeling completed assignments faster and explored creative problem-solving strategies that traditional instruction methods did not facilitate. Lastly, these benefits underscore a pressing need for interdisciplinary collaboration—combining expertise from engineering, AI development, and education research—to ensure the reliability, validity, and scalability of LLM integration in educational settings (Alsaqer et al., 2024). These examples demonstrate that while LLMs offer transformative opportunities, their successful adoption requires careful consideration of pedagogical, ethical, and technical dimensions. These examples were drawn directly from the reviewed literature and have been incorporated to strengthen the educational framing of the study's findings.
In addition to these insights, it is important to contrast how different LLM architectures perform across contexts. General-purpose models such as GPT-4 demonstrate strong versatility in natural language reasoning and adaptability, which makes them particularly suitable for educational applications such as tutoring, automated grading, and generating formative feedback. However, their broad training base also increases the risk of inaccuracies or inappropriate outputs when applied to technical tasks without domain-specific fine-tuning (Panchbhai and Pankanti, 2021). In contrast, domain-specialized models such as CodeBERT or Codex are optimized for structured tasks like program repair, code generation, and translation, where they often outperform GPT-4 in terms of precision and efficiency. This distinction highlights a trade-off between breadth and depth: GPT-4 offers adaptability across disciplines, while CodeBERT provides task-specific accuracy but limited generalizability.
These architectural differences also manifest in the educational vs. industrial contexts examined in this review. In education, the primary benefits of LLMs include personalized support, efficiency in grading, and expanded access to interactive learning resources. The challenges, however, revolve around risks of plagiarism, over-reliance by students, and ethical concerns in maintaining academic integrity. In industry, LLMs are leveraged for productivity gains, rapid prototyping, and decision-support in domains such as autonomous driving and robotics. Yet, challenges in this setting emphasize transparency, validation in safety-critical applications, and the need for workforce re-skilling. Taken together, these contrasts underscore the importance of aligning model choice with context: general-purpose LLMs excel at flexibility in learning environments, while specialized models achieve higher reliability in technical engineering workflows. Future research should prioritize comparative evaluations of different LLM architectures across educational and industrial applications to guide responsible adoption.
Practical implications and real-world applications
Beyond theoretical and methodological contributions, the findings of this review carry important practical implications for multiple stakeholders. In curriculum development, LLMs can support the creation of adaptive learning environments by automating formative feedback, generating personalized practice problems, and assisting instructors in content delivery and assessment. These applications highlight opportunities to embed AI literacy and ethical training into engineering programs, preparing students for an AI-integrated workforce. In industrial contexts, LLMs are already being deployed in tasks such as program repair, robotics task planning, and autonomous driving simulations. Their adoption can accelerate prototyping, enhance quality control, and streamline decision-support systems. However, these benefits require parallel workforce training and organizational strategies to ensure safe and effective integration. From a policy and regulatory perspective, the increasing role of LLMs in safety-critical domains underscores the need for guidelines around transparency, accountability, and ethical deployment. Regulatory frameworks should encourage standards for model validation, auditing of outputs, and responsible integration to ensure reliability while protecting public trust.
By extending insights to these real-world applications, this study strengthens its relevance for educators, practitioners, and policymakers, bridging the gap between academic research and actionable strategies for implementation.
Influence of sample size and scope on generalizability
A notable variation among the reviewed studies lies in the range of sample sizes and the institutional scope of their data collection. Some studies were limited to a single course or cohort of students, often with sample sizes under 100 participants (e.g., Liu and Yang, 2024; Marques et al., 2024), while others aggregated data across multiple courses or institutions, reaching sample sizes of up to 2,000 (e.g., Alsaqer et al., 2024). These differences have direct implications for the generalizability of findings. Smaller-scale studies typically provide rich, context-specific insights into LLM applications but may lack the statistical power or diversity needed to draw broad conclusions. In contrast, larger studies offer more representative data, increasing confidence in the applicability of results to wider educational settings, though they may sacrifice depth in individual learning experiences. These variations also influence how confidently we can infer causal relationships or make cross-disciplinary comparisons. For instance, findings from a simulation-based mechanical engineering course may not seamlessly transfer to project-based learning in civil engineering. Consequently, readers should interpret findings with an awareness of the contextual limitations introduced by sample size and study design. Future research would benefit from combining in-depth case studies with larger, cross-institutional datasets to strike a balance between depth and breadth in understanding LLMs in engineering education.
Limitations and risks in educational contexts
While the integration of LLMs into engineering education offers significant opportunities for enhancing teaching and learning, it also presents several critical challenges that warrant attention. One major concern is bias in AI-generated responses, which can misrepresent technical content or perpetuate inaccuracies when LLMs are trained on incomplete or skewed datasets (Hu et al., 2024). Such biases can influence students' understanding of engineering principles and lead to unintended learning outcomes. Another concern is overreliance on LLMs by students, particularly when used for solving assignments or debugging code. Studies (e.g., Filippi and Motyl, 2024) caution that while LLMs offer convenience, they may also discourage independent problem-solving and critical thinking if not used in a guided environment. There is a need for educators to design scaffolding that helps students understand when and how to appropriately use AI tools. Data privacy is also a pressing issue. When students interact with LLMs using personal or institutional accounts, their data—ranging from homework content to behavioral patterns—may be stored or analyzed by third-party platforms. Patil and Gudivada (2024) emphasize the importance of transparency in how these tools handle data, suggesting the need for clear institutional policies that protect user privacy and define the ethical boundaries of AI use in classrooms. Lastly, the contextual limitations of LLMs must be recognized. These models often struggle with domain-specific queries or nuanced educational content, particularly in advanced engineering courses. Without domain adaptation or expert oversight, LLMs may generate plausible but technically incorrect outputs, potentially misleading learners. Collectively, these risks highlight the importance of responsible AI integration in education—ensuring that LLMs support rather than substitute for core pedagogical goals.
In conclusion, this systematic review synthesizes findings from 23 recent publications on LLM applications in engineering, categorized into five themes: automation of complex tasks, knowledge generation and discovery, enhancing engineering education, ethical considerations, and real-world integration. While these themes provide a structured understanding of the current landscape, the identified intersections underscore the need for comprehensive, collaborative approaches to maximize the benefits of LLMs while addressing their inherent challenges.
Author contributions
SN: Data curation, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Writing – original draft. JK: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Formal analysis, Validation, Methodology, Data curation, Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Financial support was provided by the University of Oklahoma Libraries' Open Access Fund.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. During the preparation of this work, the author(s) used ChatGPT 4o to improve the language and readability. After using this tool/service, the author(s) reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al-Kaswan, A., Izadi, M., and Van Deursen, A. (2024). “Traces of memorisation in large language models for code,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 46th International Conference on Software Engineering, (New York, NY: IEEE; ACM), 1–12. doi: 10.1145/3597503.3639133
Alsaqer, S., Alajmi, S., Ahmad, I., and Alfailakawi, M. (2024). The potential of LLMS in hardware design. J. Eng. Res. doi: 10.1016/j.jer.2024.08.001
Ananthajothi, K., Sudarshan, G. S., and Saran, J. U. (2024). “Advancing autonomous driving with large language models: integration and impact,” in 2024 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI) (IEEE: Chennai, India), 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ACCAI61061.2024.10601908
Arnautov, K. V., and Akimov, D. A. (2024). “Application of large language models for optimization of electric power system states,” in 2024 Conference of Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (ElCon) (IEEE: Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation), 314–317. doi: 10.1109/ElCon61730.2024.10468377
Austin, J., Odena, A., Nye, M., Bosma, M., Michalewski, H., Dohan, D., et al. (2021). Program synthesis with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.07732. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2108.07732
Becerra, L. R., Colmenares, J. R., and Manrique, R. (2024). “Enhancing autonomous task execution in social robots with large language models,” in 2024 10th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA) (IEEE: Athens, Greece), 40–44. doi: 10.1109/ICARA60736.2024.10552978
Biadsy, F., Hall, K., Moreno, P., and Roark, B. (2014). “Backoff inspired features for maximum entropy language models”, in INTERSPEECH, 26452649.
Brown, T., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J. D., Dhariwal, P., et al. (2020). Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 1877–1901.
Buck, C., Heafield, K., and Van Ooyen, B. (2014). “N-gram counts and language models from the common crawl,” in Proceedings of the Language Resources and Evaluation Conference 2014 [Paris: European Language Resources Association (ELRA)], 3579–3584.
Buonamici, F., Carfagni, M., Furferi, R., Volpe, Y., and Governi, L. (2020). Generative design: an explorative study. Comput.-Aided Des. Appl. 18, 144–155. doi: 10.14733/cadaps.2021.144-155
Chen, M., Tworek, J., Jun, H., Yuan, Q., Pinto, H. P. D. O., Kaplan, J., et al. (2021). Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03374. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2107.03374
Chiarello, F., Barandoni, S., Majda Škec, M., and Fantoni, G. (2024). Generative large language models in engineering design: opportunities and challenges. Proc. Des. Soc. 4, 1959–1968. doi: 10.1017/pds.2024.198
Cohen, V., and Gokaslan, A. (2020). Opengpt-2: open language models and implications of generated text. XRDS 27, 26–30. doi: 10.1145/3416063
Cui, S., Zhang, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, W., Liu, T., Wang, S., et al. (2018). FFT: towards harmlessness evaluation and analysis for LLMs with factuality, fairness, toxicity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.18580. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.18580
D'Angelo, A., Stilo, G., and di Marco, A. (2018). A novel relevance score for unsupervised retrieval with large language models," in Proceedings of ACM. Available online at: https://kdd2024.kdd.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/paper_11.pdf
Donaj, G., and Kačič, Z. (2017). Context-dependent factored language models. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music Process. 2017, 1–16. doi: 10.1186/s13636-017-0104-6
Fan, A., Gokkaya, B., Harman, M., Lyubarskiy, M., Sengupta, S., Yoo, S., et al. (2023). ““Large language models for software engineering: Survey and open problems,” in 2023 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Software Engineering: Future of Software Engineering (ICSE-FoSE) (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 31–53. doi: 10.1109/ICSE-FoSE59343.2023.00008
Filippi, S. (2023). Measuring the impact of ChatGPT on fostering concept generation in innovative product design. Electronics 12:3535. doi: 10.3390/electronics12163535
Filippi, S., and Motyl, B. (2024). Large language models (LLMs) in engineering education: a systematic review and suggestions for practical adoption. Information 15:345. doi: 10.3390/info15060345
Ho, N., Schmid, L., and Yun, S. Y. (2022). Large language models are reasoning teachers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.10071. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2212.10071
Hou, X., Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, K., Li, L., et al. (2023). Large language models for software engineering: a systematic literature review. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 33. doi: 10.1145/3695988
Hu, Y., Goktas, Y., Yellamati, D. D., and De Tassigny, C. (2024). “The use and misuse of pre-trained generative large language models in reliability engineering,” in 2024 Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium (RAMS) (IEEE: Albuquerque, NM, USA), 1–7. doi: 10.1109/RAMS51492.2024.10457630
Kim, J., and Lane, I. (2014). “Accelerating large vocabulary continuous speech recognition on heterogeneous cpu-gpu platforms,” in 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (IEEE: Florence, Italy), 3291–3295. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6854209
Kim, Y., Kim, D., Choi, J., Park, J., Oh, N., and Park, D. (2024). A survey on integration of large language models with intelligent robots. Intel. Serv. Robotics 17, 1091–1107. doi: 10.1007/s11370-024-00550-5
Kodali, R. K., Upreti, Y. P., and Boppana, L. (2024). “A quantization approach for the reduced size of large language models,” in 2024 16th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST) (IEEE: Krabi, Thailand), 144–148. doi: 10.1109/KST61284.2024.10499664
Liang, W., and Xiao, G. (2024). “An exploratory evaluation of large language models using empirical software engineering tasks,” in Proceedings of the 15th Asia-Pacific Symposium on Internetware, 31–40. doi: 10.1145/3671016.3674821
Lina, S., and Aksyonov, K. A. (2024). “Error correction for speech recognition systems using large language model reasoning capabilities,” in 2024 IEEE 25th International Conference of Young Professionals in Electron Devices and Materials (EDM) (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 2300–2303. doi: 10.1109/EDM61683.2024.10615066
Liu, C., and Yang, S. (2024). Application of large language models in engineering education: a case study of system modeling and simulation courses. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Educ. doi: 10.1177/03064190241272728
Macedo, M., Tian, Y., Cogo, F., and Adams, B. (2024). “Exploring the impact of the output format on the evaluation of large language models for code translation,” in Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/ACM First International Conference on AI Foundation Models and Software Engineering (IEEE; ACM), 57–68. doi: 10.1145/3650105.3652301
MacNeil, S., Tran, A., Leinonen, J., Denny, P., Kim, J., Hellas, A., et al. (2022). Automatically generating cs learning materials with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.05113. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2212.05113
Marques, N., Silva, R. R., and Bernardino, J. (2024). Using ChatGPT in software requirements engineering: a comprehensive review. Future Internet 16:180. doi: 10.3390/fi16060180
Nikolic, S., Daniel, S., Haque, R., Belkina, M., Hassan, G. M., Grundy, S., et al. (2023). ChatGPT versus engineering education assessment: a multidisciplinary and multi-institutional benchmarking and analysis of this generative artificial intelligence tool to investigate assessment integrity. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 48, 559–614. doi: 10.1080/03043797.2023.2213169
Osborne, M., Lall, A., and Van Durme, B. (2014). “Exponential reservoir sampling for streaming language models,” in Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers) [Stroudsburg, PA: Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL)], 687–692. doi: 10.3115/v1/P14-2112
Ozkaya, I. (2023). Application of large language models to software engineering tasks: Opportunities, risks, and implications. IEEE Softw. 40, 4–8. doi: 10.1109/MS.2023.3248401
Panchbhai, A., and Pankanti, S. (2021). “Exploring large language models in a limited resource scenario,” in 2021 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science and Engineering (Confluence) (IEEE: Noida, India), 147–152. doi: 10.1109/Confluence51648.2021.9377081
Patil, R., and Gudivada, V. (2024). A review of current trends, techniques, and challenges in large language models (LLMs). Appl. Sci. 14:2074. doi: 10.3390/app14052074
Prather, J., Denny, P., Leinonen, J., Becker, B. A., Albluwi, I., Craig, M., et al. (2023). “The robots are here: navigating the generative AI revolution in computing education,” in Proceedings of the 2023 Working Group Reports on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education [New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery (ACM)], 108–159. doi: 10.1145/3623762.3633499
Rahman, M. T., Singh, R., and Sultan, M. Y. (2024). ‘Automating patch set generation from code reviews using large language models,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 3rd International Conference on AI Engineering-Software Engineering for AI (IEEE; ACM), 273–274. doi: 10.1145/3644815.3644981
Reynolds, L., and McDonell, K. (2021). “Prompt programming for large language models: Beyond the few-shot paradigm,” in Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing System (New York, NY: ACM; SIGCHI), 1–7. doi: 10.1145/3411763.3451760
Sahoo, P., Singh, A.K., Saha, S., Jain, V., Mondal, S.S., and Chadha, A. (2024). A systematic survey of prompt engineering in large language models: techniques and applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.07927. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2402.07927
Shareghi, E., Petri, M., Haffari, G., and Cohn, T. (2015). “Compact, efficient and unlimited capacity: language modeling with compressed suffix trees,” in Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (Lisbon, Portugal: Association for Computational Linguistics), 2409–2418. doi: 10.18653/v1/D15-1288
Solaiman, I., Brundage, M., Clark, J., Askell, A., Herbert-Voss, A., Wu, J., et al. (2019). Release strategies and the social impacts of language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.09203. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1908.09203
Strobelt, H., Webson, A., Sanh, V., Hoover, B., Beyer, J., Pfister, H., et al. (2022). Interactive and visual prompt engineering for ad-hoc task adaptation with large language models. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 29, 1146–1156. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2022.3209479
Ström, N. (2015). Scalable Distributed DNN Training Using Commodity GPU Cloud computing. International Speech Communication Association (ISCA). doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2015-354
Subramani, N., and Suresh, N. (2020). Discovering useful sentence representations from large pretrained language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.09049. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2008.09049
Wang, H., Li, J., Wu, H., Hovy, E., and Sun, Y. (2023). Pre-trained language models and their applications. Engineering 25, 51–65. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2022.04.024
Wang, J., Wu, Z., Li, Y., Jiang, H., Shu, P., Shi, E., et al. (2024). Large language models for robotics: opportunities, challenges, and perspectives. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.04334. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2401.04334
Zhang, Q., Fang, C., Xie, Y., Ma, Y., Sun, W., Yang, Y., et al. (2024). A systematic literature review on large language models for automated program repair. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.01466. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2405.01466
Zhang, Z., Lin, A., Wong, C. W., Chu, X., Dou, Q., and Au, K. S. (2024). “Interactive navigation in environments with traversable obstacles using large language and vision-language models,” in 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (Ithaca, NY: IEEE), 7867–7873. doi: 10.1109/ICRA57147.2024.10610751
Zheng, Z., Ning, K., Zhong, Q., Chen, J., Wang, Y., Chen, W., et al. (2023). Towards an understanding of large language models in software engineering tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.11396. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2308.11396
Zhou, Y., Muresanu, A. I., Han, Z., Paster, K., Pitis, S., Chan, H., et al. (2022). Large language models are human-level prompt engineers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.01910. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2211.01910
APPENDIX A
Keywords: engineering applications, ethical AI deployment, large language models, systematic literature review, engineering
Citation: Nguyen SS and Kittur J (2025) Review of current and potential uses of large language models in engineering. Front. Educ. 10:1649650. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1649650
Received: 18 June 2025; Accepted: 15 September 2025;
Published: 08 October 2025.
Edited by:
Pedro Elkind Velmovitsky, University Health Network (UHN), CanadaReviewed by:
Omar Ramzy, Heliopolis University, EgyptRudresh Dwivedi, Netaji Subhas University of Technology, India
Giuliano Lorenzoni, University of Waterloo, Canada
Copyright © 2025 Nguyen and Kittur. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Javeed Kittur, amtpdHR1ckBvdS5lZHU=
 San S. Nguyen
San S. Nguyen Javeed Kittur
Javeed Kittur