- 1Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine, Beibei Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Beibei, Chongqing, China
- 2Department of Gynecology, Beibei Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Beibei, Chongqing, China
- 3Department of Urology, Beibei Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Beibei, Chongqing, China
- 4Department of Obstetrics, Beibei Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Beibei, Chongqing, China
- 5Department of Nursing, Beibei Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Beibei, Chongqing, China
Objective: To study the impact of life education board game teaching on the humanistic care ability and sense of life meaning of nursing interns.
Methods: A self-controlled study design was employed. The nursing education management team at the hospital collaboratively developed a life education board game, which is grounded in the Iceberg Theory, Social Learning Theory, Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, and Positive Psychology as its theoretical frameworks, integrating four teaching objectives into the game. The study involved 90 nursing interns from a tertiary hospital in China. The life education board game teaching activity was implemented in the first department where the interns were assigned. Assessments were conducted using the Care Ability Scale and the Life Meaning Scale at three time points: before the activity, immediately after the activity, and 5 weeks post-activity.
Results: Following the teaching activity, nursing interns demonstrated significantly higher scores in the patience dimension (t = 3.102, P = 0.003) and the total care ability score (t = 3.174, P = 0.002) compared to pre-activity scores. At the 5-week follow-up, significant improvements were still observed in the cognition dimension (t = 4.072, P = 0.000), the patience dimension (t = 3.546, P = 0.001), and the total care ability score (t = 4.159, P = 0.000) compared to baseline. However, no significant differences were found in the cognition and courage dimensions of care ability immediately before and after the activity. The courage dimension also remained statistically unchanged 5 weeks post-activity. Regarding life meaning, except for the freedom of will dimension, no significant differences were observed in the scores of other dimensions or the total life meaning score either immediately after the activity or at the 5-week follow-up.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the feasibility of board games in improving humanistic care competence, though long-term impacts on life meaning require further exploration. Future research may consider extending the observation period to more comprehensively assess the impact of life education board game teaching on the sense of life meaning.
1 Introduction
With the advancement of society, the transformation of medical models, and the increasing awareness of public health, there is a growing expectation for the quality of medical nursing services. Humanistic care plays an important role in improving nursing quality. Humanistic care in nursing is a positive consciousness, willingness, or responsibility to take care of people, manifested in attitudes and values reflected in specific actions (Karlsson and Pennbrant, 2020). Without care, there is no nursing; the core of nursing lies in humanistic care (Jian et al., 2022). Human-centered care prioritizes patients' wellbeing, emphasizing compassionate healthcare practices. Nurses should honor each individual's dignity, show compassion toward every patient, recognize their unique needs, address reasonable requests, and safeguard personal privacy throughout treatment.
China's “Healthy China 2030 blueprint” explicitly mandates strengthening patient-centered compassionate care in healthcare delivery while fostering trust-based physician-patient relationships. Complementing this vision, the National Health Commission's 2023 Action Plan for Enhanced Nursing Services (2023–2025) outlines concrete measures to: 1) Elevate clinical nursing quality through proximity-based care models. 2) Cultivate nurses' proactive service mindset and compassion competency. 3) Deliver holistic patient support encompassing: precision clinical care and psychological accompaniment as well as dignity-preserving humanistic engagement.
Previous studies indicate that the humanistic care abilities of clinical nursing interns in China remain relatively underdeveloped (Lina et al., 2022). While educational institutions offer courses on humanistic care, these often emphasize theoretical knowledge and caregiving techniques, providing limited opportunities for students to engage in hands-on experiences or perceive the essence of humanistic care through social practice.
Existing studies on humanistic care education focus on theoretical training, but lack experiential methods like gamification to bridge the gap between knowledge and practice. As the reserve force of the nursing industry and the backbone of nursing career, the humanistic care ability of nursing interns directly affects the future level and quality of nursing services.
Gamification has emerged as an innovative pedagogical strategy in medical education, demonstrating efficacy in fostering student engagement, collaborative learning, peer instruction, and constructive competition while cultivating intrinsic motivation and lifelong learning competencies. Recent empirical studies across diverse educational contexts—including secondary education (Murillo, 2021; Kurokawa et al., 2023; Lin et al., 2021), undergraduate medical training (Surapaneni, 2024), and clinical mentorship programs (Cooley et al., 2023)—have validated the adaptability of board game-based instructional designs to enhance knowledge retention, pedagogical outcomes, and educational quality for both learners and educators.
Building upon these research foundations, our institution's Nursing Education Department has pioneered a novel curricular intervention integrating life-themed board games into clinical nursing education. This innovation specifically targets the development of humanistic care competencies and value-of-life literacy among nursing interns. The games simulate complex patient care scenarios requiring ethical decision-making, empathy cultivation, and interdisciplinary communication, thereby aligning with Bloom's affective domain learning objectives. Preliminary implementation data indicate measurable improvements in trainees' care ability scores (via the Care Ability Scale).
2 Methods
2.1 Research design
This study adopts a self-controlled design, which is a type of quasi-experimental research.
2.2 Setting and participants
A tertiary hospital in western China, serving as a regional medical center.
Sample Selection: Using cluster sampling, a total of 90 nursing interns who commenced their clinical rotations in July 2024 across 10 clinical departments of the hospital were recruited for the study. The study was conducted over an 11-week period, comprising: (a) a 5-week phase for research design and pedagogical preparation, followed by (b) a 6-week implementation and evaluation stage. The tabletop game-based instructional intervention was delivered in Week 6, with its efficacy assessed in Week 11. All participants were fully informed about the study and provided written consent to participate. The cohort comprised 18 male and 72 female interns, with 19 holding Highest level of education and 71 possessing Bachelor's degree.
2.3 Intervention measures
2.3.1 Teaching preparation
The hospital nursing education management team conducted collaborative curriculum development to define teaching objectives, design the content of the life education board game activity, and establish implementation methods and evaluation criteria. Based on the teaching content, the teaching environment was set up, and necessary materials were prepared.
2.3.2 Introduction to game cards
The main deck consists of 54 value cards, all featuring positive attributes. The auxiliary deck includes 26 opportunity cards (members who draw these cards must complete corresponding directive tasks, primarily for gameplay purposes) and 13 trait cards (neutral or challenging traits).
2.3.3 Teaching demonstration and quality control
A life education board game teaching activity group was formed, comprising nursing education leaders from 10 clinical departments. The head of the hospital nursing education management team was responsible for demonstrating the teaching, training team members, and supervising teaching quality and progress. All team members were uniformly trained to ensure consistent implementation of the life education board game teaching content.
2.3.4 Standardized Implementation of Teaching Activities
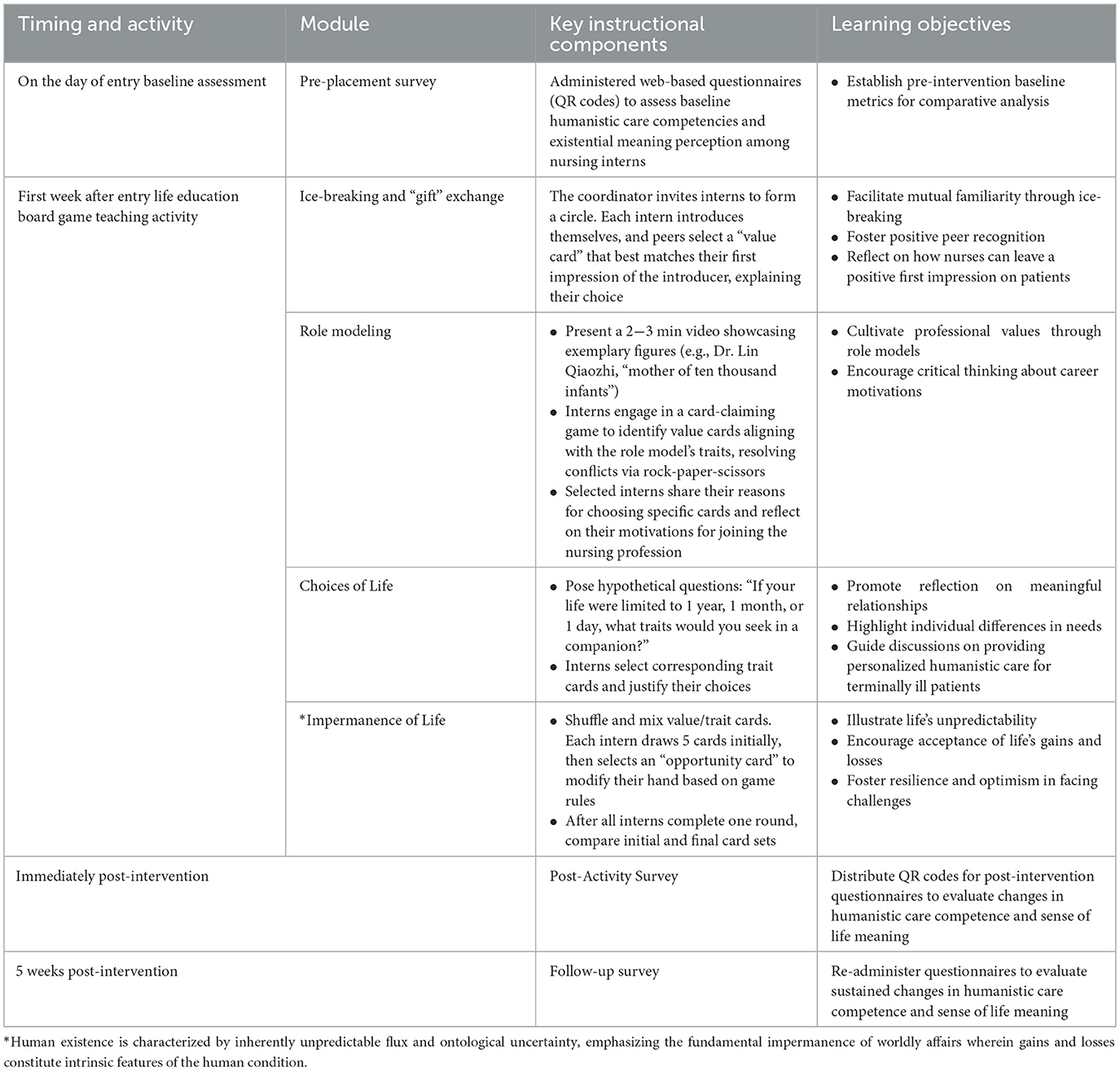
During the first week of the nursing interns‘ rotation, the life education board game activity was conducted in the demonstration room of their respective departments. The department's nursing education leader served as the activity organizer, facilitating the session, distributing cards, and guiding interns in discussions. Six to 10 nursing interns participated in the activity, while the head of the hospital nursing education management team supervised the entire process and collected feedback through interviews. Web-based surveys assessing the interns' humanistic care abilities and sense of life meaning were administered immediately before and after the activity, followed by group interviews to gather feedback from both interns and department nursing education leaders. A third web-based survey was conducted during the sixth week of the internship, just before the interns completed their rotation in the department.
The implementation of the life education board game teaching activity is shown in Figure 1 and Table 1.
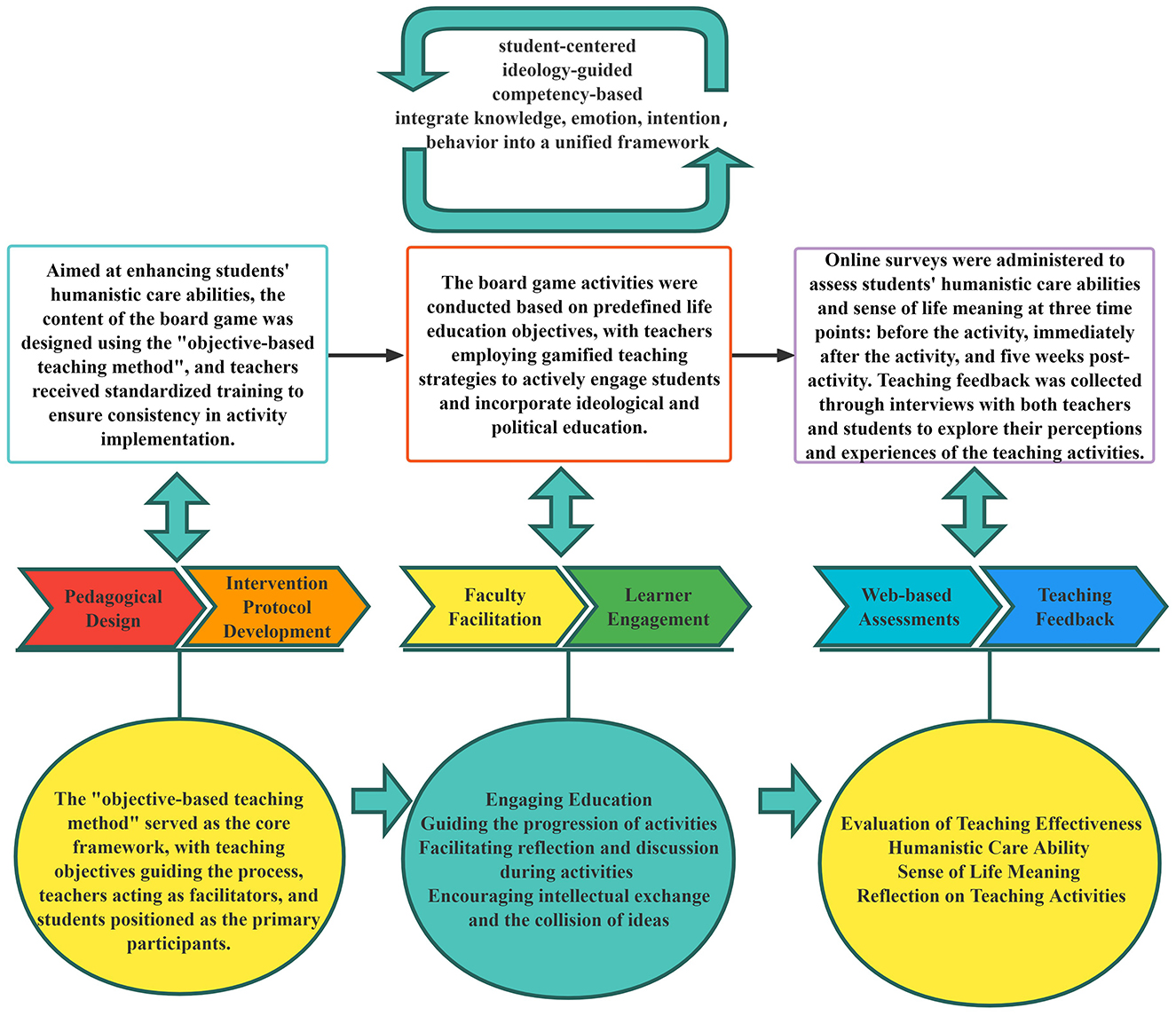
Figure 1. Illustrates the implementation process of the life education board game teaching activity.
2.4 Results measurement and instruments
Care Ability Evaluation Scale: The Chinese version of the Care Ability Evaluation Scale translated and revised by Juan Xu et al., was used to evaluate nursing interns' caring competence before and after the educational intervention (Xu et al., 2009). This scale comprises three dimensions: cognition (14 items), courage (13 items), and patience (10 items), totaling 37 items. A 7–point Likert scale was employed for scoring, where “strongly agree” corresponds to 7 points and “strongly disagree” to 1 point. The total score ranges from 37 to 259, with higher scores indicating stronger humanistic caring competence. The scale demonstrates good psychometric properties, with a Cronbach's α coefficient of 0.84 and content validity of 0.78.
Sense of Life Meaning Scale: The College Students' Sense of Life Meaning Scale developed by Jinlong Liang et al., was used to evaluate the changes in the sense of life meaning of nursing interns before and after the educational intervention. This instrument consists of three dimensions: volitional freedom (4 items), will to meaning (4 items), and meaning in life (5 items), comprising 13 items in total. A 5–point Likert scale was employed for scoring, ranging from 1 (“strongly disagree”) to 5 (“strongly agree”). The scale exhibits excellent reliability, with an overall Cronbach's α coefficient of 0.894 (Liang et al., 2018).
2.5 Data analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 24.0 software. Continuous data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and intergroup comparisons were conducted using paired t-tests.
3 Results
3.1 The life education board game intervention significantly enhanced nursing interns' humanistic care competence, whereas the single-session implementation demonstrated no statistically measurable impact on sense of life meaning outcomes
The results demonstrated statistically significant post-intervention improvements in the patience dimension (t = 3.102, p = 0.003) and total humanistic care competence scores (t = 3.174, p = 0.002) among nursing interns compared to pre-intervention measurements. However, no statistically significant differences were observed in the cognition and courage dimensions of humanistic care competence, nor in any subdomains or total scores of sense of life meaning following the instructional sessions, as shown in Table 2.
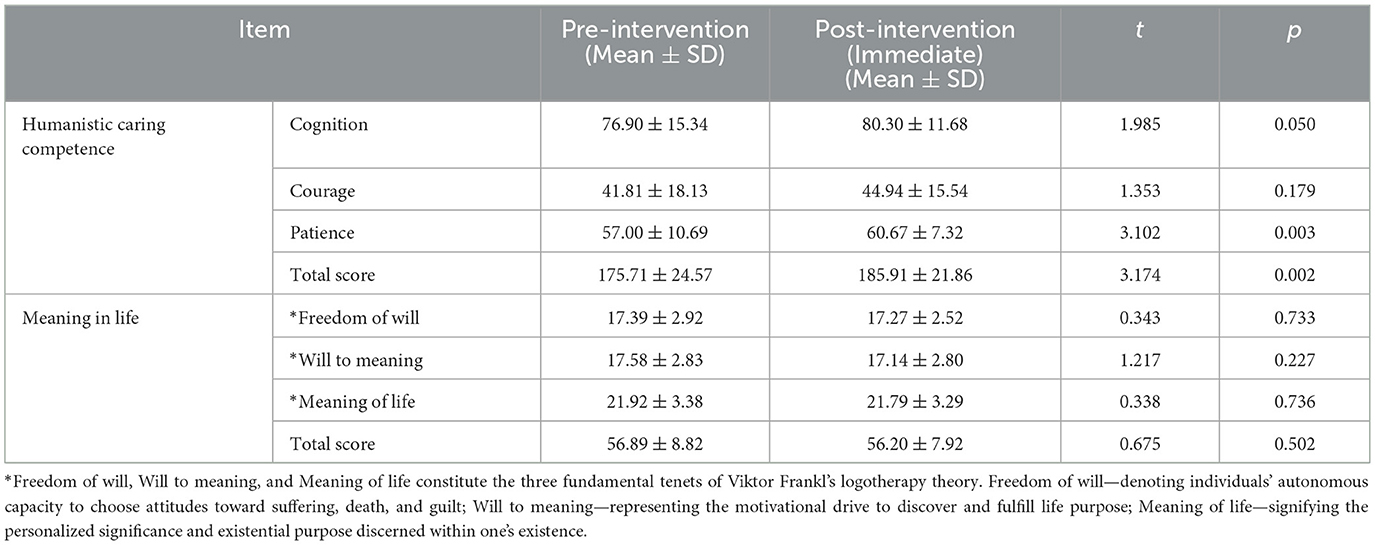
Table 2. Comparison of humanistic caring competence and meaning in life scores among nursing interns before and after the educational intervention.
3.2 Clinical nursing practice activities can enhance nursing interns' cognition in humanistic care
The longitudinal evaluation demonstrated sustained statistically significant improvements in nursing interns' humanistic caring competence 5 weeks after the teaching activity, with marked enhancements observed in the cognition (t = 4.072, p < 0.001), patience (t = 3.546, p = 0.001), and total score (t = 4.159, p < 0.001) compared to pre—intervention measurements, as shown in Table 3. Furthermore, significant differences in the cognition dimension of humanistic caring competence were observed between immediate post-intervention and 5 weeks later, as shown in Table 4.
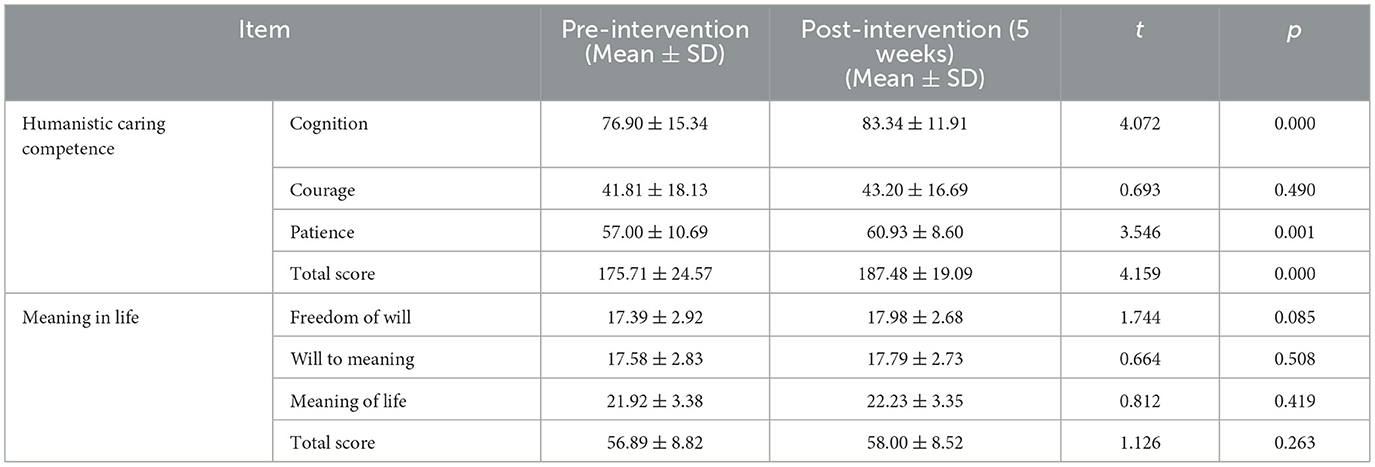
Table 3. Comparison of humanistic caring competence and meaning in life scores in nursing interns before and 5 weeks after the educational intervention.
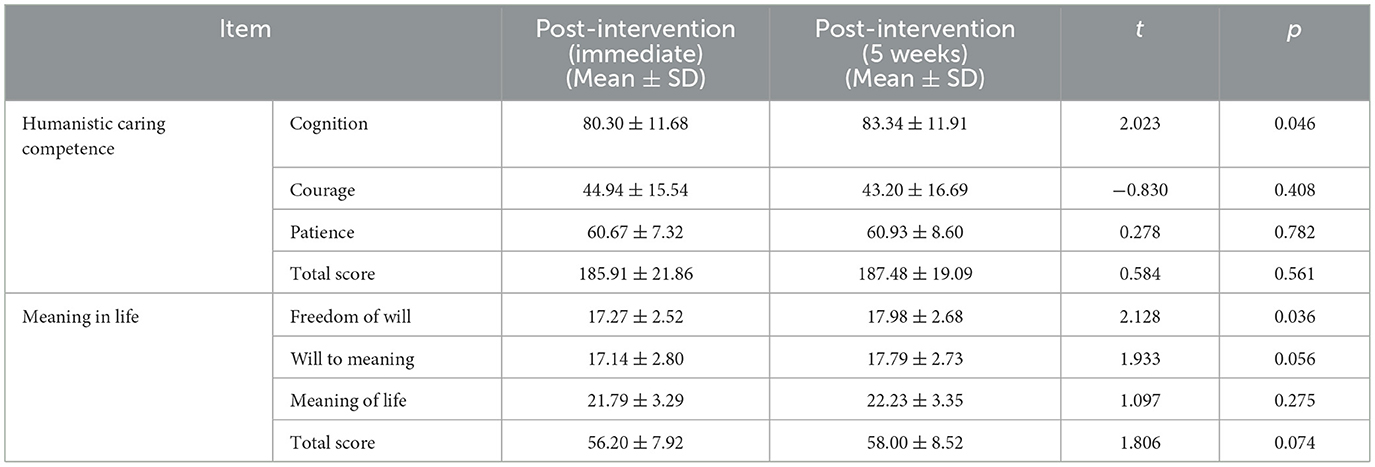
Table 4. Comparison of humanistic caring competence and meaning in life scores in nursing interns immediately after and 5 weeks after the educational intervention.
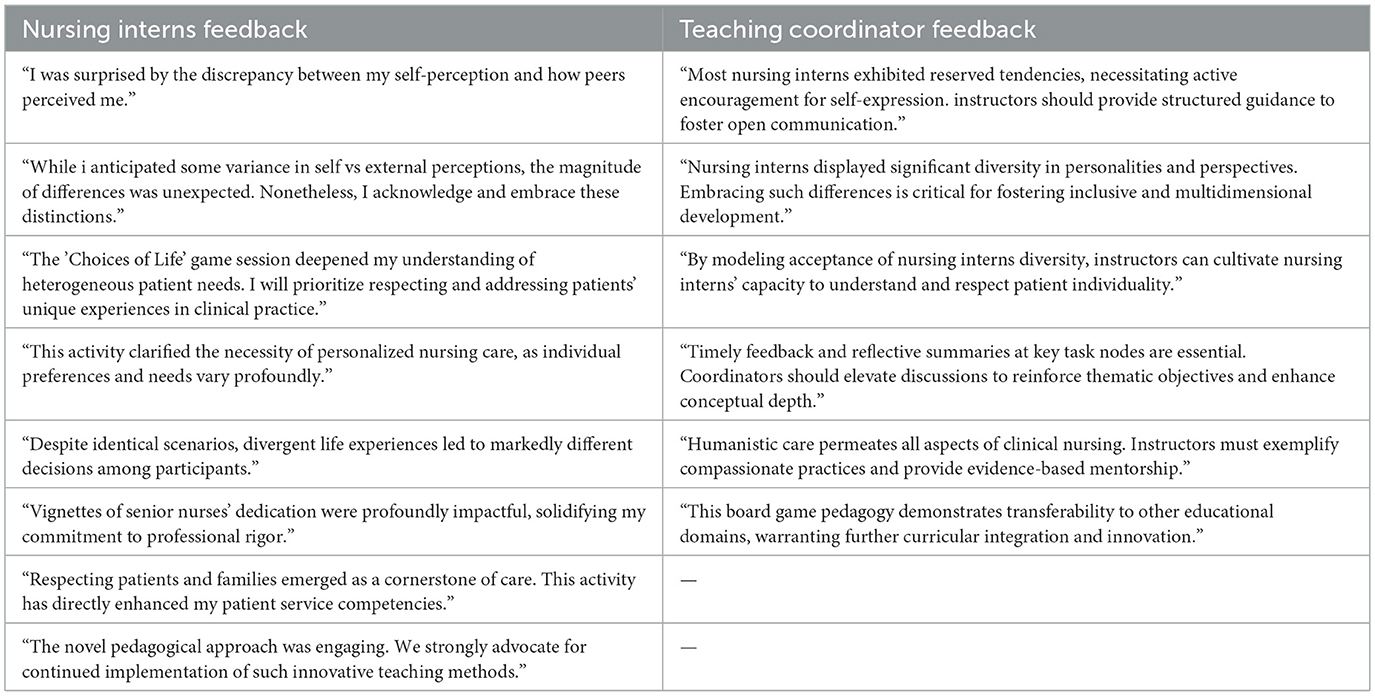
Feedback from nursing interns and teaching leaders on life education board game teaching activity is shown in Table 5.
4 Discussion
4.1 Urgent need to enhance humanistic caring competence in nursing interns
Nursing embodies a “patient-centered” philosophy, with humanistic care representing an essential quality for healthcare professionals (Taghinezhad et al., 2022). Studies indicate that integrating humanistic care into clinical practice improves patient outcomes by fostering physical and mental wellbeing, enhancing medical experiences, increasing satisfaction, and strengthening nurse-patient relationships (Wang et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024; Chai et al., 2024). Policy directives, including “The National Nursing Career Development Plan (2021–2025)” and Notice on Implementing the Thematic Initiative to Enhance Healthcare Service Experience and Promote Patient-Centered Care (National Health Commission, 2023) explicitly mandate healthcare institutions to prioritize humanistic nursing education. As future clinical practitioners, nursing interns must not only master technical expertise but also cultivate profound humanistic competencies.
Pre-intervention assessments revealed that nursing interns' total humanistic caring competence scores (175.71 ± 24.57) and subscale scores for courage (41.81 ± 18.13) and patience (57.00 ± 10.69) fell below established Chinese norms [total: 191.04 ± 19.49; courage: 59.31 ± 10.43; patience: 58.51 ± 6.17), aligning with findings by Jian et al. (2022). This discrepancy may stem from curricular imbalances favoring technical skills over experiential humanistic training during pre-clinical education. Post-intervention results demonstrated persistent deficits in total competence and courage scores relative to norms, though improvements emerged in cognition and patience dimensions over time. These outcomes suggest that humanistic competence develops incrementally through sustained clinical exposure. Limited intervention duration (single session) and interns' early-stage clinical inexperience likely constrained immediate gains. Thus, iterative pedagogical innovations integrating theory with practice are critical to fostering holistic competence.
4.2 Theoretical foundations of life education board game pedagogy
Tabletop gaming—encompassing board games, card games, and strategy simulations—offers immersive, interactive learning environments that enhance engagement, simplify complex concepts, and motivate learners (Chiao and Niu, 2024). Its efficacy in medical education is well-documented (Surapaneni, 2024; Twist and Ragsdale, 2022; Raskurazhev et al., 2021).
Sigmund Freud's Iceberg Theory posits that human consciousness resembles an iceberg: the visible tip represents conscious awareness, while the submerged majority comprises latent psychological constructs such as unconscious desires and emotions (Tang et al., 2024). Icebreaking activities redirect participants' focus to the present moment, mitigating subconscious influences and facilitating open expression. In this study, nursing interns—new to clinical settings and unfamiliar with peers—engaged in a “gift exchange” icebreaker during the first session. This activity dissolved interpersonal barriers, fostered trust, promoted team cohesion, and prompted reflection on strategies for establishing positive first impressions and nurse-patient relationships.
Bandura's (2015) emphasizes observational learning through role modeling, particularly the influence of high-status or charismatic figures on observers' behaviors, attitudes, and values (Price and Archbold, 1995). During the second session, interns analyzed videos depicting exemplary nurses' achievements, internalizing professional knowledge, behaviors, and attitudes. Subsequent value-card discussions guided interns to articulate their career motivations and align with ethical worldviews, reinforcing the formation of professional identity.
Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs (Maslow, 1943) categorizes human needs into ascending tiers: physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. These needs dynamically interact rather than existing in isolation. In the third session, interns navigated simulated scenarios involving terminally ill patients, identifying unmet needs and predicting unexpressed demands. This exercise cultivated skills in delivering personalized, humanistic care tailored to patients' evolving requirements.
Martin Seligman and Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi's Positive Psychology framework (Wang et al., 2023) asserts that individuals possess inherent potential for growth and wellbeing when appropriately guided. Integrating this theory, the final session introduced “Opportunity Cards,” symbolizing life's unpredictable challenges and choices. By completing randomized card-based tasks, interns experienced diverse life scenarios, fostering resilience, adaptability, and acceptance of life's uncertainties. This process emphasized proactive opportunity-seeking and courageous confrontation of challenges, nurturing a balanced mindset toward personal and professional development (Byrd and Abrams, 2022; Fält-Weckman et al., 2024).
4.3 Efficacy of board game pedagogy in enhancing humanistic caring competence
Post-intervention analyses revealed statistically significant improvements in total caring competence scores (P < 0.050) and the patience subscale (P = 0.003) compared to pre-intervention assessments. This findings were preliminary evidence of feasibility and initial effect. Utilizing card-based mechanics and immersive scenarios, this pedagogy enhanced engagement, interpersonal communication, and empathy—critical competencies for humanistic care. Unlike traditional lecture-based methods, the gamified approach increased learner motivation and initiative. Exposure to exemplary nursing professionals' achievement videos during the pedagogical intervention enhanced interns' understanding of the nursing profession's intrinsic value and societal significance. This exposure facilitated the cultivation of aligned professional values and proactive attitudinal orientations, thereby fostering the development of humanistic caring competence. Furthermore, the structured card-based activities—requiring active articulation of perspectives and empathetic engagement with peers' viewpoints—strengthened interns' empathic capacity. Such reflective practices promoted emotional resonance with patient experiences, enabling interns to recognize and address heterogeneous patient needs through deliberate care expression and sustained service patience. Exposure to role-model narratives and reflective discussions strengthened professional values and patient-centered attitudes, aligning with evidence that professional demeanor and empathic capacity significantly influence caring competence (Teng et al., 2024; Yu et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2022).
4.4 Limitations and recommendations for refinement
In this study, the pre-post design used to investigate self-control did not incorporate randomization and failed to account for potential threats to internal validity, as well as external factors that may influence the outcomes (e.g., clinical experience, maturation effects). For instance, clinical practice, curricular training, and personal experiences of nursing interns during the study period could confound the results. Additionally, natural enhancement of humanistic care competence through routine clinical exposure might be erroneously attributed to the Life Education Board Game Pedagogy intervention. Meanwhile, the implementation of this study within a non-controlled educational setting introduces the potential presence of confounding variables. We recommend future studies employ randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to confirm causality.
This study implemented a single-session Life Education Board Game Pedagogy intervention. Although significant improvements were observed in patient-centered attitudes and overall care competence, the intervention demonstrated statistically insignificant effects on cognitive dimensions, moral courage, and sense of life meaning. This suggests the intervention may not effectively enhance overall life meaning, or the chosen scales may not capture subtle changes. These constructs typically develop through longitudinal reflection and clinical immersion, necessitating extended intervention periods. Qualitative feedback from both interns and educators highlighted the activity's novelty and practical utility while emphasizing the need for iterative implementation cycles.
The 5-week follow-up period was relatively short for assessing long-term behavioral changes. Furthermore, the limited frequency of the intervention restricted our ability to evaluate the sustainability of its effects. Post-intervention measurements likely captured transient adaptations rather than enduring transformations. Consequently, the full magnitude of the intervention's impact on nursing interns' humanistic care competence and existential meaning perception remains undetermined.
Future studies should aim to: (1) increase the frequency of the intervention: (2) extend the follow-up period to assess long-term retention (e.g., 3–6 months): (3) diversify modes of delivery, such as through blended learning approaches: (4) include a control group (e.g., traditional instruction vs board game-based intervention) to better isolate intervention effects: (5) evaluate the intervention across diverse contexts (e.g., different countries and levels of healthcare facilities) to improve generalizability; and (6) strengthen clinical integration to enable comprehensive outcome assessment and longitudinal monitoring of sustained effectiveness.
5 Conclusion
This study offers promising preliminary evidence that board games may contribute to the development of humanistic care competencies among nursing interns. By integrating life education concepts into a gamified pedagogical structure, the intervention combines experiential and theoretical learning, facilitating both knowledge acquisition and intrinsic motivation. This approach not only enhanced classroom dynamism but also promoted learner autonomy, supporting the achievement of key educational outcomes.
The presented game-based strategy represents a timely and innovative method for life education, capitalizing on interactive learning. The educational tool demonstrates high intrinsic engagement and aligns effectively with student-centered pedagogy. Its application in authentic teaching environments provides practical value for educators interested in adopting alternative instructional approaches.
Nonetheless, the absence of significant effects on life meaning outcomes, coupled with methodological constraints—such as the lack of a control group and short follow-up duration—indicates a need for more robust investigation. These findings support the implementation of larger, rigorously designed trials to further establish the efficacy of board game-mediated life education within nursing training.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the minor(s)' legal guardian/next of kin for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
QL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YY: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YLL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. H-QY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Chongqing Municipal Education Commission's 14th Five-Year Key Discipline Support Project [grant numbers 20240309].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Byrd, D., and Abrams, Z. (2022). Applying positive psychology to the L2 classroom: acknowledging and fostering emotions in L2 writing. Front. Psychol. 13:925130. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.925130
Chai, X. Y., Bao, X. Y., Dai, Y., Dai, X. X., Zhang, Y., and Yang, Y. L. (2024). Experience of humanistic nursing in hemodialysis nursing for patients with diabetic kidney disease. World J. Diabetes 15, 186–195. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.186
Cooley, J. H., Larson, S., and Cheung, M. (2023). A preceptor development program using an interactive board game. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 15, 769–773. doi: 10.1016/j.cptl.2023.07.004
Fält-Weckman, S., Fagerlund, Å., Londen, M., and Lagerström, M. (2024). Using evidence-based applied positive psychology to promote student wellbeing. Front. Psychol. 15:1415519. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1415519
Jian, S., Ya, M., Qian, Z., Meihua, Y., Cao, X., and Dela Rosa, R. D. (2022). Research progress on humanistic care ability and influencing factors of intern nursing students. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 26, 8637–8643. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202212_30534
Karlsson, M., and Pennbrant, S. (2020). Ideas of caring in nursing practice. Nurs. Philos. 21:e12325. doi: 10.1111/nup.12325
Kurokawa, H., Igei, K., Kitsuki, A., Kurita, K., Managi, S., Nakamuro, M., et al. (2023). Improvement impact of nudges incorporated in environmental education on students' environmental knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors. J. Environ. Manag. 325:116612. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116612
Liang, J., Cui, X., Wu, H., and Peng, X. (2018). Development and reliability and validity analysis of the meaning of life scale for college students. China Health Serv. Manag. 35, 303–307.
Lin, H. C. K., Lin, Y. H., Wang, T. H., Su, L. K., and Huang, Y. M. (2021). Effects of incorporating augmented reality into a board game for high school students' learning motivation and acceptance in health education. Sustainability 13:3333. doi: 10.3390/su13063333
Lina, M., Qin, G., and Yang, L. (2022). Mediating effects of emotional intelligence on the relationship between empathy and humanistic care ability in nursing students: a cross-sectional descriptive study. Medicine 101:e31673. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031673
Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychol. Rev. 50, 370–396. doi: 10.1037/h0054346
Murillo, I. (2021). Revising while playing: development and evaluation of the newly created microbial pursuit game as a pedagogical tool in higher education. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 368:fnab101. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnab101
National Health Commission (2023). Notice on Implementing the Thematic Initiative to Enhance Healthcare Service Experience and Promote Patient-Centered Care. Available online at: https://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/c100068/202305/e2379d47ca3244c7b733fbcfb5f0675a.shtml
Price, V., and Archbold, J. (1995). Development and application of social learning theory. Br. J. Nurs. 4, 1263–1268. (Mark Allen Publishing). doi: 10.12968/bjon.1995.4.21.1263
Raskurazhev, A., Kuznetsova, P., Khizhnikova, A. E., Klochkov, A., Bakulin, I., Annushkin, V., et al. (2021). Neuropoly: an educational board game to facilitate neurology learning. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 15:688210. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2021.688210
Surapaneni, K. M. (2024). “CARBGAME” (CARd and Board GAmes in Medical Education) as an innovative gamification tool for learning clinical enzymology in biochemistry for first year medical students. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 52, 666–675. doi: 10.1002/bmb.21857
Taghinezhad, F., Mohammadi, E., Khademi, M., and Kazemnejad, A. (2022). Humanistic care in nursing: concept analysis using rodgers' evolutionary approach. Iran. J. Nurs. Midwifery Res. 27, 83–91. doi: 10.4103/ijnmr.ijnmr_156_21
Tang, J., Ren, J., Wang, H., Shi, M., Jia, X., and Zhang, L. (2024). Real experience of caregivers of patients with HIV/AIDS from the perspective of iceberg theory: a qualitative research. BMJ Open 14:e079474. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-079474
Teng, X. J., Yan, M. M., Yan-Qun, X. U., Yuan-Zheng, L. I., Tao, X. B., Zou, W. Z., et al. (2024). Humanistic care ability and its influencing factors among Chinese surgical nurses. Nurs. Open 11:e70021. doi: 10.1002/nop2.70021
Twist, K. E., and Ragsdale, J. W. (2022). Candy gland: a diabetes board game for medical students. MedEdPORTAL 18:11294. doi: 10.15766/mep_2374-8265.11294
Wang, F., Guo, J., and Yang, G. (2023). Study on positive psychology from 1999 to 2021: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Psychol. 14:1101157. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1101157
Wang, L., Dai, N., Xiang, M., and Zhao, J. (2024). Clinical effect of a prospective nursing model combined with humanistic care in patients with acute stroke. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 30, 351–355.
Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Xie, Q., Zhou, H., and Cheng, L. (2022). Humanistic caring ability of midwifery students in China and its associated factors: a multi-centre cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ. Today 111:105276. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105276
Xu, J., Liu, Y., and Luo, J. (2009). Investigation on the current situation and influencing factors of nursing staff's caring ability. Nurs. Res. 23, 3306–3308.
Yu, Y., Wan, X., Sun, C., Ji, Y., Zhao, X., Cai, Y., et al. (2025). Medical narrative ability and humanistic care ability of Chinese clinical nurses: the mediating role of empathy ability. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 31:e14046. doi: 10.1111/jep.14046
Keywords: life board game, teaching design, nursing interns, care ability, sense of life meaning
Citation: Li Q, Yang Y, Long Y-L, Yao H-Q and Chen Z-y (2025) Enhancing humanistic care competence in nursing interns: a life education board game pedagogy. Front. Educ. 10:1667906. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1667906
Received: 17 July 2025; Accepted: 15 September 2025;
Published: 02 October 2025.
Edited by:
Ali Mansoor Al-Ameri, University of Kerbala, IraqReviewed by:
Omaima Zubair, University of Mosul, IraqHazim Almashhadani, University of Kerbala, Iraq
Copyright © 2025 Li, Yang, Long, Yao and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhuo-yuanyuan Chen, Y2h6aHl5MTIzQDE2My5jb20=
 Qiong Li
Qiong Li Ying Yang2
Ying Yang2 Hua-Qin Yao
Hua-Qin Yao Zhuo-yuanyuan Chen
Zhuo-yuanyuan Chen