- 1Department of Mathematics Education, Faculty of Education, Bursa Uludağ University, Bursa, Türkiye
- 2Department of Mathematics Education, Faculty of Education, Kocaeli University, Kocaeli, Türkiye
In recent years, the rapid development of artificial intelligence technologies has been transforming the nature of engineering education and reshaping the skill sets expected from students. In this context, techno-mathematical literacy (TmL) stands out as a critical competence that enables engineering candidates to use both technology and mathematical thinking in an integrated manner. This study was conducted to examine the effect of artificial intelligence applications performed by engineering candidates on the development of their techno-mathematical literacy and to determine their self-efficacy levels regarding these applications. The study was designed with a quasi-experimental single group pre-test-post-test model from quantitative research approaches. The study group consists of 156 students, selected by simple random sampling method, studying in different programs at the engineering faculty of a state university. The data were collected with the Techno-Mathematical Literacy Scale (TMLS) and the Artificial Intelligence Self-Efficacy Scale (AILS). The data obtained from the pre-test and post-test applications were analysed with descriptive statistics, paired sample t-test, independent sample t-test, and ANOVA through SPSS 27 software. Also, the effect size was calculated. At the end of the six-week implementation process, it was found that artificial intelligence applications significantly increased the techno-mathematical literacy levels and artificial intelligence self-efficacy perceptions of engineering candidates. In addition, there was no significant difference in techno-mathematical literacy level and perception of artificial intelligence self-efficacy in terms of gender, but significant differences were found according to the department variable.
1 Introduction
The global digital transformation is reshaping the traditional definitions of knowledge and skills in engineering education. Today’s engineers are expected not only to have theoretical knowledge but also to be able to use technology effectively, integrate mathematical thinking with digital tools, and generate innovative solutions to complex problems. In this context, the focus of engineering education is increasingly shifting towards interdisciplinary skills, data-driven decision-making processes and artificial intelligence-supported learning experiences. In order for students to be successful in their future professional roles, it has become a critical requirement that they both blend technology with their mathematical literacy and adapt to rapidly developing artificial intelligence applications. Recent studies also emphasise that incorporating digital tools into engineering education enriches learning and fosters student engagement (Su et al., 2025), and that AI-supported approaches require rethinking instructional strategies to prepare students for future professional demands (Honig et al., 2025).
Techno-mathematical literacy (TmL) is defined as a set of competencies that involves the integration of mathematical thinking processes with digital technologies, technical tools, and engineering applications (Hoyles et al., 2010). This approach shows that the knowledge and skills expected from engineering graduates are not only limited to theoretical mathematics, but also include digital tools, data analytics, technical communication, and applied problem solving. TmL has also been closely linked with AI-related competencies, as recent frameworks suggest that techno-mathematical and AI literacy should be developed in parallel to equip students with holistic problem-solving capacities (Annapureddy et al., 2024; Barnard College, 2024).
In literature, studies examining which TmL components engineering professionals most need in their professional life provide important findings. For example, van der Wal et al. (2017) identified data literacy, software-based problem solving, error intuition, number sense, technical creativity, and technical drawing as the prominent TmL components in the daily practices of engineers. These skills represent the points where mathematics meets technology, especially in the design and analysis phases of engineering projects. Moreover, Chen et al. (2025) proposed a generative AI competence framework for engineering curricula, highlighting that future engineers must master both TmL skills and AI competencies in a structured manner.
Research conducted in an educational context shows that the development of TmL in engineering students supports not only mathematics achievement but also professional self-efficacy and problem-solving skills. van der Wal et al. (2019) emphasised that open data analysis, technical reporting, and software-based modelling activities make significant contributions to the development of TmL in engineering students. Similarly, Bakker et al. (2011) states that engineering students gain deeper understanding of mathematical concepts in technology-supported environments while working with real-life problems. Walter (2024) further argued that AI literacy, prompt engineering, and critical thinking are indispensable for creating inclusive and future-ready learning environments, complementing TmL-oriented pedagogies.
Some recent empirical studies also reinforce the importance of TmL in the context of engineering education. For example, as revealed by Kent et al. (2007) that TmL skills of engineering students in their professional learning processes are directly related to labour market expectations. There are also design studies that reveal educational strategies implemented by engineering students that contribute to the acquisition of TmL components. In van der Wal et al. (2019), an innovative mathematics course for engineering students, is designed to successfully communicate inquiry-based teaching approaches that support TmL learning. The comprehensive review in Pepin et al. (2021) shows that innovative practices in mathematics teaching (e.g., the use of digital resources) may be central to the future of engineering education. Furthermore, recent studies in countries such as Germany and the Netherlands show that the ability of engineering students to use mathematical representations on digital platforms, interpret numerical data, and translate them into engineering decisions is becoming increasingly critical (Weigand et al., 2024). In this context, TmL can be defined not only as an auxiliary skill, but also as a basic competence directly required in the practice of the engineering profession. Therefore, integrating TmL into the curriculum in engineering education has become a strategic imperative in terms of preparing students for the professional world. At the same time, Schleiss and Johri (2024) stressed that AI integration in engineering education should be designed according to role-based competencies (e.g., user, implementer, developer), which resonates with the idea of tailoring TmL instruction to disciplinary needs.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is seen as a fundamental tool that transforms students’ professional skills, problem solving capacities and learning experiences in the context of engineering education. AI self-efficacy, awareness, and literacy dimensions stand out as critical variables in the processes of engineering students’ adaptation to technology (Woo et al., 2024; Fan et al., 2025; Siddharth et al., 2025). Woo et al. (2024) showed that a short-term intervention focused on “prompt engineering” increased AI self-efficacy and knowledge levels in a study conducted with engineering students. Fan et al. (2025) reported that the use of generative AI by engineering students in China improved learning efficiency and creativity, but its effect on academic achievement was limited. In the context of AI literacy, the “AI Literacy” course developed by Siddharth et al. (2025) increased not only the technical skills of the students but also their awareness of the social and sustainability dimensions of AI. These recent interventions, together with emerging frameworks (Barnard College, 2024; Annapureddy et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2025), confirm that AI literacy should be considered alongside TmL as a foundational competence in engineering education.
Engineering education is a field, rapidly shaped by technological developments and digital transformation, which necessitates the development of students’ capacity to integrate mathematical and technological skills. In this context, techno-mathematical literacy (TmL) stands out as a critical skill that expresses the ability of prospective engineers to analyse data, think algorithmically, use technology effectively and associate mathematics with engineering problems. Although existing studies reveal that techno-mathematical literacy supports engineering students’ professional competencies and transforms the learning experiences of artificial intelligence applications, studies that address these two areas together are quite limited. In particular, empirical findings examining the interaction between AI self-efficacy and TmL skills are needed. At this point, determining educational strategies that will support engineering students in adapting to digital transformation, will both contribute to academic literature and have important practical implications. This study aims to fill this gap by examining the effects of artificial intelligence applications on students’ TmL skills and AI self-efficacy in the context of engineering education. For this purpose, the study focuses on the following research questions:
RQ1: How do artificial intelligence applications affect prospective engineers’ techno-mathematical literacy levels and AI self-efficacy perceptions?
RQ2: Do the changes in engineering candidates’ techno-mathematical literacy levels and artificial intelligence self- efficacy perceptions differ significantly according to gender and department variables?
2 Research method
This study was conducted in a single-group, quasi-experimental pretest-post-test design, one of the quantitative research methods. This design allows the examination of the effect of the experimental procedure by comparing the pre- and post-application measurements of the participants (Gravetter and Forzano, 2018). The main reason why this design was preferred in the study is that it can directly reveal the effect of artificial intelligence applications on students’ techno-mathematical literacy and self-efficacy in using artificial intelligence. In addition, the difficulty of forming a comparative control group due to the diversity of students selected from different departments made the use of this design appropriate. Although this design provides a strong framework for determining the effects of the intervention, it has limitations in terms of external validity due to the absence of a control group.
2.1 Participants
The research group consists of 156 engineering students studying different programmes in the engineering faculty of a state university. The participants, who were selected by the simple random sampling method, consisted of 28% female (n = 44) and 72% male (n = 112) students. The students are studying in the departments of Computer Engineering (30%, n = 47), Electrical and Electronics Engineering (25%, n = 39), Mechanical Engineering (28%, n = 44) and Civil Engineering (17%, n = 26). This distribution increases the representativeness of the study by reflecting the gender and departmental differences seen in engineering faculties in Turkey. However, as all participants were drawn from a single university, the representativeness of the findings is limited, and caution should be exercised when generalizing the results to broader populations. The students’ level of experience in technology and artificial intelligence varies, and this diversity provides an important advantage in terms of the objectives of the research. To provide further clarity, the sampling frame consisted of undergraduate students enrolled in compulsory courses across these four departments. Recruitment was conducted through in-class announcements, and students who volunteered were included in the pool. Initially, 168 students were eligible to participate, of whom 160 provided consent. After excluding incomplete responses, data from 156 students were retained for the final analysis (168 eligible → 160 consented → 156 completed). Participation was entirely voluntary; students were given detailed information about the purpose and process of the research; and their informed consent was obtained. In addition, the necessary permissions were obtained from the relevant Ethics Committee of the university for the conduct of the study.
2.2 Data collection tools
Artificial Intelligence Self-Efficacy Scale (AISES) developed by Wang and Chuang (2023) was used to determine the participants’ self-efficacy perceptions about artificial intelligence. The scale consists of a total of 22 items and is graded on a 5-point Likert scale. The Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient of the scale has been reported as above 0.90 and has been found valid in different samples. In this study, the scale was adapted into Turkish and sufficient reliability values were obtained as a result of preliminary tests. In this study, Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient was found to be 0.81. The adaptation process was carried out through translation and back-translation by bilingual experts, followed by expert panel review for content validity. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) indicated good fit indices (CFI = 0.95, TLI = 0.94, RMSEA = 0.052, SRMR = 0.047), with item loadings ranging between 0.62 and 0.83 (p < 0.001). Reliability analysis also included McDonald’s ω (0.88), confirming the internal consistency of the scale.
The Techno-mathematical Literacy Scale (TMLS), developed by Demir and Tortop (2025), was used to measure the TML skills of the participants. The scale consists of a total of 12 items and is graded on a 5-point Likert scale. The scale includes items reflecting the basic dimensions of TmL such as basic mathematical competence, technology-supported mathematics learning, data literacy and numerical reasoning, digital mathematical communication, and collaboration. The content validity of the scale was ensured by expert opinions, and its construct validity was tested by exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the scale was reported as 0.85. In this study, the Cronbach alpha reliability coefficient of the scale was found to be 0.78, CFA results confirmed the construct validity with satisfactory fit indices (CFI = 0.96, TLI = 0.95, RMSEA = 0.049, SRMR = 0.045), and item loadings ranged from 0.58 to 0.81 (p < 0.001). Internal consistency was confirmed with Cronbach’s α = 0.91 and McDonald’s ω = 0.90.
2.3 Process and data analysis
The research was conducted over a six-week implementation process. A total of 156 students participated in weekly sessions lasting approximately three hours.
Week 1: An orientation session was held to inform participants about the purpose, functioning, and ethical principles of the study. The AI tools to be used were introduced, including ChatGPT (v4.0) and Google Gemini (1.5). Students were provided with the Artificial Intelligence Applications User Guide, which contained sample prompts and task guidelines.
Week 2: Students practiced with structured prompts focusing on data analysis and algorithmic thinking. Example prompts included: “Generate a step-by-step solution for an optimization problem in civil engineering” and “Explain the mathematical model behind heat transfer in everyday language”.
Weeks 3–5: Students worked in groups of 4–5 members, completing discipline-specific problem-solving tasks. Each week was dedicated to a different TmL dimension:
Week 3: Data literacy and numerical reasoning (e.g., using AI to analyze and interpret datasets related to energy consumption).
Week 4: Digital mathematical communication (e.g., generating graphs, symbolic outputs, and step-by-step explanations of differential equations with AI tools).
Week 5: Technology-supported problem solving (e.g., creating algorithmic approaches for scheduling or structural analysis).
Week 6: Student groups presented their solutions and reflected on the use of AI in supporting mathematical modeling and problem solving.
Throughout the intervention, the instructor acted as a facilitator, providing guidance on appropriate AI use, monitoring group work, and giving formative feedback. The “Artificial Intelligence Applications User Guide” and sample prompts used during the intervention are provided as Supplementary Material to support replication and transparency.
Pre-test and post-test applications were conducted to measure changes in AI self-efficacy and TmL levels. The data obtained from these measures were analyzed using SPSS 27 software. Descriptive statistics (arithmetic mean, standard deviation, frequency, and percentage), paired sample t-tests, independent sample t-tests, and one-way ANOVA were applied. Statistical assumptions were checked prior to analyses: the normality of the distributions (Shapiro–Wilk) and the homogeneity of variances (Levene) were both satisfied. For multiple comparisons, Tukey’s HSD test was employed. The significance level was accepted as 0.01, and effect sizes were interpreted using eta-square (η2) coefficients. Effect sizes were reported together with 95% confidence intervals, and paired Cohen’s d was calculated for pre–post comparisons. Subgroup sample sizes are provided on the tables.
3 Results
In this section, the findings related to the problems posed in the research questions (RQ1 and RQ2) are presented, and the analyses of the TmL and AI self-efficacy levels of the prospective engineers are reported in detail.
When Table 1 is analysed, a significant difference was found between the pre-test (X̄ = 39.48) and post-test (X̄ = 42.61) scores of TmL levels of engineering candidates (t = −3.764, p < 0.001). The effect size was η2 = 0.084, 95% CI [0.02, 0.15], corresponding to a moderate effect. The paired Cohen’s d was 0.48, indicating a medium effect. Similarly, a significant difference was found between the pre-test (X̄ = 84.92, SD = 7.72) and post-test scores (X̄ = 92.62, SD = 6.16) of AI self-efficacy (t = −3.197, p = 0.001). The effect size was η2 = 0.062, 95% CI [0.01, 0.12], corresponding to a small-to-medium effect. The paired Cohen’s d was 0.41, supporting the magnitude of this improvement. According to the results, an increase was observed in the TmL skills and AI self-efficacy of prospective engineers following the artificial intelligence applications.
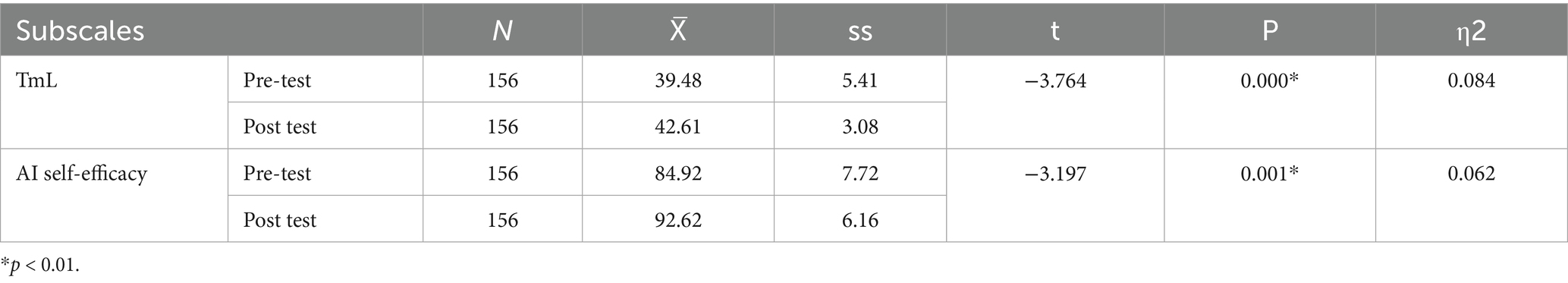
Table 1. Paired T-test analysis of TmL and AI self-efficacy levels of engineer candidates pre-test-post-test results.
When the results of Table 2 are analysed, it is seen that the mean pre-test TmL scores of male engineer candidates are higher than those of female candidates according to the gender variable. However, this difference is not statistically significant (t = −1.181, p > 0.01). Similarly, when the post-test scores were analysed, it was determined that the mean of males was higher than females, but the difference was not significant (t = −1.491, p > 0.01). These findings show that TmL scores do not differ depending on gender; in other words, gender is not a determining variable.
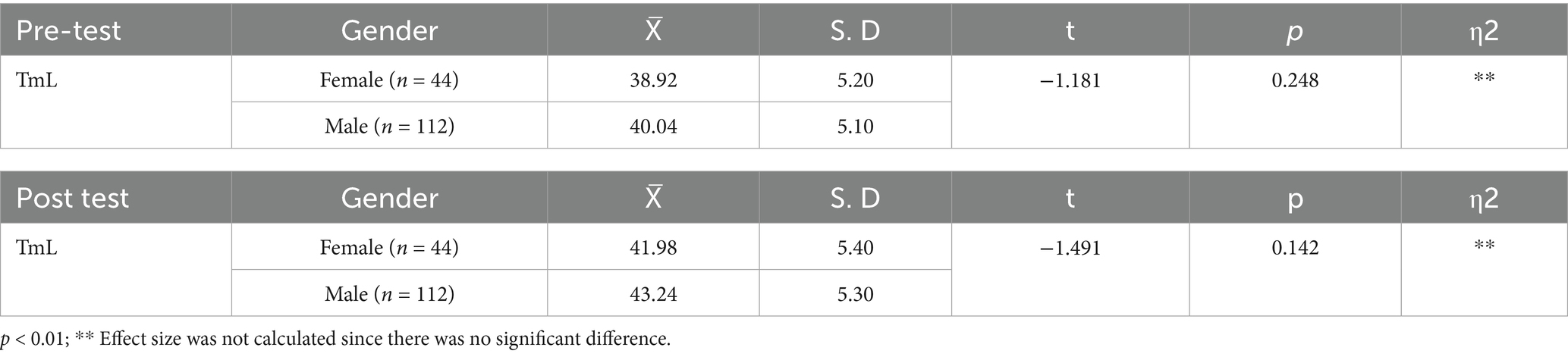
Table 2. Independent samples t-test analysis of TmL pre-test-post-test scores of prospective engineers regarding gender variable.
When the results of Table 3 are analyzed, it is seen that there is no statistically significant difference in the AI self-efficacy levels of engineer candidates after the pre-test depending on gender (t = −1.121, p = 0.264). Although the averages of male students are higher than those of female students, this difference is not significant. There is no statistically significant difference in the AI self-efficacy levels of engineer candidates after the post-test based on gender (t = −0.832, p = 0.412). The averages of female students are almost at the same level as male students.
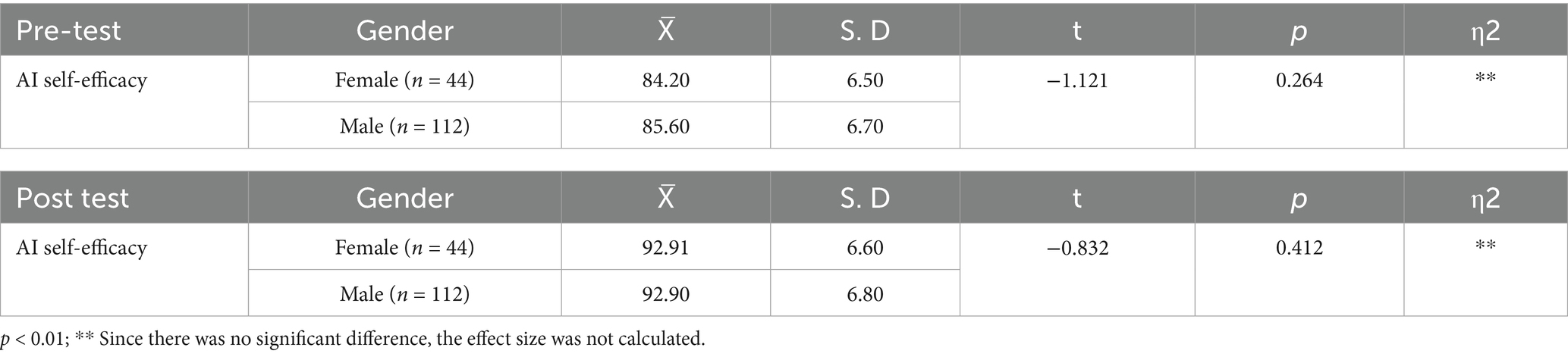
Table 3. Independent samples t-test analysis of engineer candidates’ AI self-efficacy pre-test-post-test scores regarding gender variable.
When Table 4 is analysed, it is seen that the pre-test TmL levels of engineering candidates differ significantly according to the departments (F = 9.162, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.28, 95% CI [0.15, 0.40]). While computer engineering students scored higher than the other departments, the mean scores of electrical-electronics engineering students were higher than those of mechanical and civil engineering students. Similarly, significant differences depending on the department variable continued in the post-test results (F = 11.31, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.18, 95% CI [0.09, 0.27]). Computer and electrical-electronics engineering students reached higher TmL levels compared to mechanical and civil engineering students. These effect sizes indicate a large effect at pre-test and a medium effect at post-test, supporting the robustness of departmental differences.
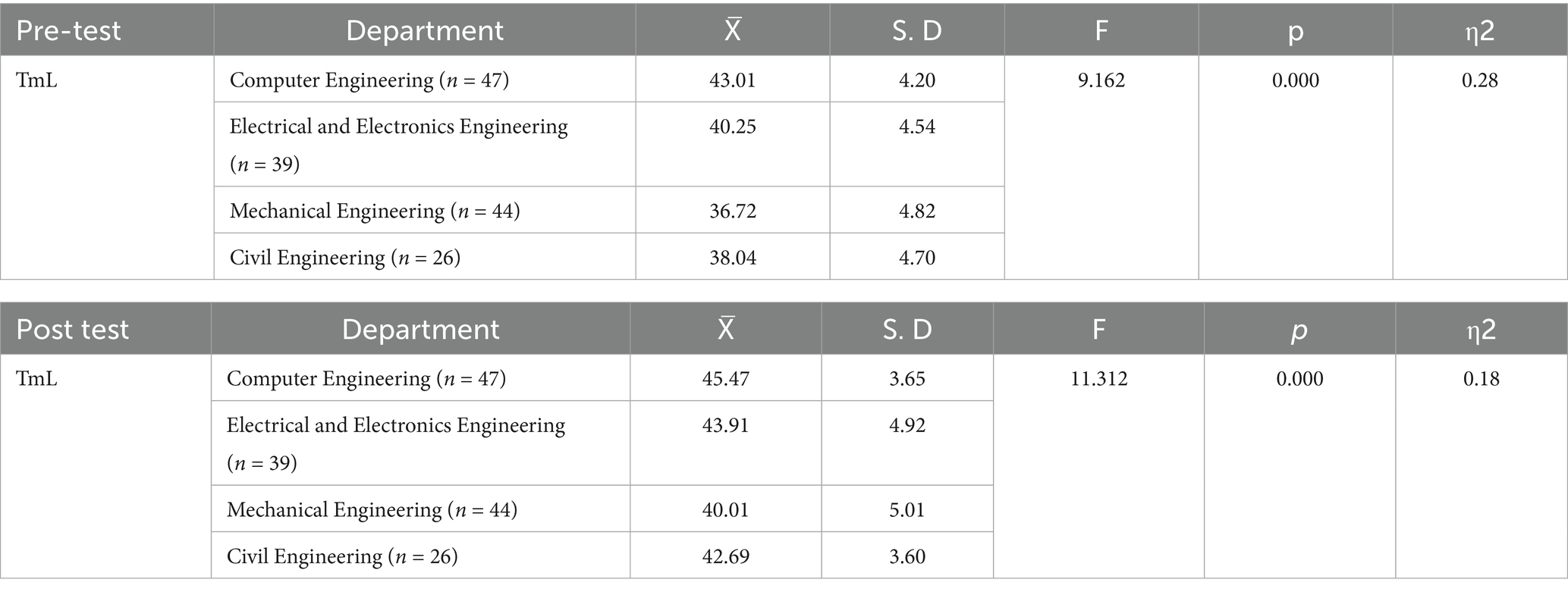
Table 4. ANOVA analysis of pre-test and post-test TmL scores of prospective engineers by department variable.
When the results of Table 5 are analysed, it is seen that there is a significant difference between the pre-test AI self-efficacy levels of the engineer candidates depending on the department they study (F = 7.974, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.17, 95% CI [0.07, 0.26]). According to Tukey’s test results, the mean AI self-efficacy scores of computer engineering students were significantly higher than those of mechanical and civil engineering students. In addition, the mean scores of electrical-electronics engineering students were higher than those of mechanical and civil engineering students. In the post-test findings, significant differences depending on the department variable are observed (F = 7.321, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.16, 95% CI [0.06, 0.25]). In conclusion, when TmL and AI self-efficacy levels were analysed, significant differences were observed among the departments of the engineering candidates. Similar to the effect on TmL levels, the application was associated with increases in AI self-efficacy levels in all departments, and it was determined that students in computer and technology-oriented departments were in a more advantageous position. These effect sizes indicate a medium effect in both pre- and post-test comparisons, supporting the robustness of departmental differences while also showing that discipline-specific advantages persist.
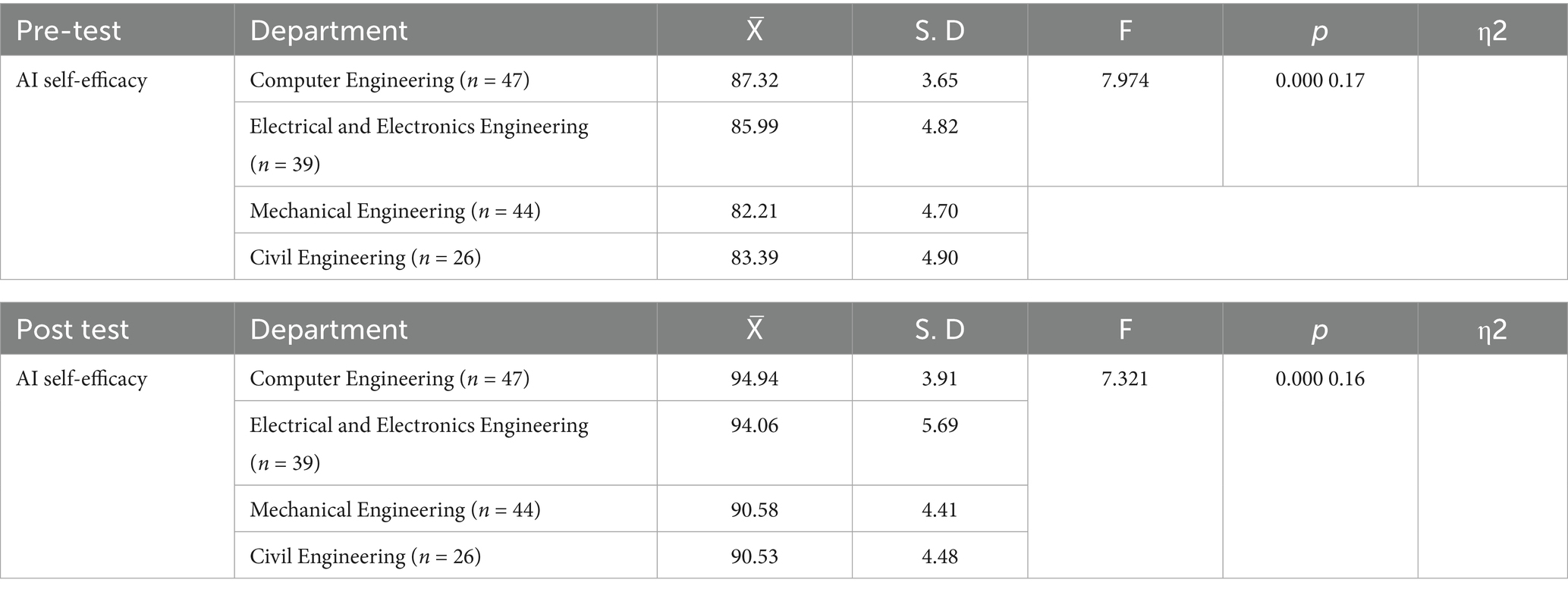
Table 5. ANOVA analysis of prospective engineers’ AI self-efficacy pre-test and post-test scores regarding the department variable.
4 Discussion
This study suggests that artificial intelligence (AI) applications may support improvements in both TmL and AI self-efficacy levels of engineering students. The findings indicate that AI-supported learning environments can strengthen not only technological skills but also the capacity to integrate mathematical thinking into the engineering context. This result is in line with previous research (Hoyles et al., 2010; van der Wal et al., 2017; van der Wal et al., 2019), which revealed that TmL is a critical competence in engineering education. Moreover, the findings in the area of AI self-efficacy are in line with the results reported by Woo et al. (2024), Fan et al. (2025), and Siddharth et al. (2025). In addition, Su et al. (2025) demonstrated that incorporating digital tools into engineering curricula improves student engagement and enriches teaching processes, which supports our evidence that AI-based applications provide both cognitive and motivational benefits. Honig et al. (2025) similarly underlined that integrating generative AI tools in engineering pedagogy requires rethinking instructional design, reinforcing the transformative potential of AI-supported environments.
In the interdepartmental difference analysis, computer engineering and electrical and electronics engineering students showed higher levels of TmL and AI self-efficacy than other departments, suggesting that the student population of technology-oriented disciplines is more familiar with digital tools and representation skills. The studies defining the AI literacy framework emphasise that such skills may be more developed especially in disciplines that require technical/digital infrastructure (Long and Magerko, 2020). This interpretation is also supported by Hibbert et al. (2024), who proposed a four-stage AI literacy framework (understanding, using, evaluating, and creating AI) that explains how learners in technical fields can more rapidly progress through literacy stages. In addition, the GenAI Competence Framework for Engineering Curriculum Enhancement (Chen et al., 2025) provides structured tiers of generative AI competencies and concrete strategies to embed them across engineering programmes, complementing our findings about discipline-based differences.
In the analysis based on the gender variable, no significant difference was observed. This finding is in line with the study by Asio and Sardina (2025) which shows that gender is not a determining factor in AI literacy and AI self-efficacy gains. This suggests that AI-supported teaching approaches have an inclusive nature and are effective independent of demographic characteristics. Walter (2024) also emphasised the role of AI literacy, prompt engineering, and critical thinking as essential components of inclusive AI-supported learning environments, which is consistent with our evidence that demographic variables do not restrict these gains. Annapureddy et al. (2024) likewise identified twelve generative AI literacy competencies that highlight the multifaceted nature of AI-supported learning, aligning with our interpretation that TmL and AI self-efficacy should be addressed together.
These findings suggest that AI applications in engineering education may provide not only short-term gains but also hold long-term transformation potential. The study contributes to the literature by indicating that TmL and AI self-efficacy can develop together. In particular, the fact that students in technology-oriented disciplines reached higher levels indicates that AI-supported teaching strategies could be adapted according to disciplinary needs. This conclusion is consistent with Schleiss and Johri (2024), who argued that AI integration in engineering education should be adapted to role-based competencies (e.g., user, implementer, developer), highlighting the need for discipline-specific teaching designs. In addition, the fact that there is no gender difference suggests that such applications offer an inclusive learning environment and indicates that AI can be considered an egalitarian learning tool in engineering education. By combining techno-mathematical literacy with AI self-efficacy, this study extends existing AI literacy and competence frameworks by highlighting how cognitive confidence in AI use and domain-specific mathematical competencies can mutually reinforce each other in engineering education.
4.1 Theoretical implications
This study extends existing models by explicitly combining techno-mathematical literacy (TmL) with AI self-efficacy, two constructs that have usually been treated separately. While discussions of AI literacy often emphasise skills such as using, evaluating, and creating with AI, they rarely address the mathematical reasoning competencies that are essential in engineering. By linking TmL with AI self-efficacy, this study shows that confidence in applying AI tools and competence in mathematically informed reasoning are mutually reinforcing. This integration contributes to theory by offering a more comprehensive model for understanding how AI literacy can be operationalised in engineering contexts.
4.2 Practical contributions
From a curricular perspective, the findings suggest that engineering programmes should explicitly include learning activities that target both TmL and AI self-efficacy. Examples may include project-based modules where students use AI applications for data analysis, mathematical modelling, and digital communication of findings. Such integration would strengthen not only students’ ability to engage with AI confidently but also their capacity to apply mathematical reasoning within engineering practice. Embedding these competencies into curricula can therefore help produce engineers who are both mathematically literate and AI literate, ready to respond to the technological and problem-solving challenges of the 21st century.
4.3 Limitations and future directions
Since the research was conducted in a single university, the generalizability of the findings is limited. Although the sample size is sufficient, the distribution among departments is unbalanced and this may affect comparisons. The absence of a control group makes it unclear whether the observed improvements are solely due to AI practices or to environmental factors. Self-report scales were used for TmL and AI self-efficacy measures, which carry the risk of social favorability bias or over-reporting. Triangulation with performance-based measures or qualitative data is recommended for future studies.
In this study, a single-group pretest–posttest design was employed. While this design allows for the observation of changes before and after the intervention, the absence of a control group limits internal validity. Potential alternative explanations, such as maturation, repeated testing effects, instructor influence, or Hawthorne effects, may have contributed to the observed differences. Therefore, the findings should not be interpreted as direct causal effects of AI applications but rather as trends observed following the intervention. Future studies incorporating control or comparison groups, as well as longitudinal designs, are recommended to strengthen causal inferences.
This study examined the short-term effects of AI-supported interventions, but the extent to which gains could be sustained in the long term was not assessed. Furthermore, the intervention was designed for a specific group of AI-based interventions, different AI tools or broader instructional designs may yield different results. In the study, TmL and AI self-efficacy were considered as the primary variables; however, other important constructs such as computational thinking, digital problem solving, and collaborative skills were excluded.
In future studies, the effects and retention of AI practices can be examined more reliably by using experimental and control group and longitudinal designs. Studies in different universities and cultural contexts will increase the generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, the inclusion of variables such as mathematical reasoning, cognitive flexibility, and academic resilience may provide a deeper understanding of the impact of AI on learning processes. Research comparing various AI tools and pedagogical strategies will reveal which applications are more effective in specific disciplines.
5 Conclusion
This study showed that significant increases were observed in engineering students’ TmL and AI self-efficacy levels following artificial intelligence applications. The findings revealed that the application was effective in all departments, but students studying in computer and technology-oriented fields were in a more advantageous position. In addition, no significant difference was found depending on the gender variable, indicating that AI-supported learning environments are inclusive. These applications, which were associated with concurrent improvements in TmL and AI self-efficacy levels, contributed to observed enhancements in students’ basic mathematical competence, technology-supported mathematics learning, data literacy, and digital mathematical communication skills needed in the digital transformation era.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethics approval was obtained from the Social and Human Sciences Ethics Committee of Kocaeli University (approval no: E-94094268-200-717270). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
RB: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2025.1695351/full#supplementary-material
References
Annapureddy, R., Fornaroli, A., and Gatica-Perez, D. (2024). Generative AI literacy: twelve defining competencies. arXiv. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.12107
Asio, J. M. R., and Sardina, D. P. (2025). Gender differences on the impact of AI self-efficacy on AI anxiety through AI self-competency: a moderated mediation analysis. J. Pedagog. Res. 9, 55–71. doi: 10.33902/JPR.202533231
Bakker, A., Kent, P., and Noss, R. (2011). Techno-mathematical literacies in the workplace: Improving workplace activity through technology and mathematics. Dordrecht: Springer.
Barnard College. (2024). A framework for AI literacy. Educ. Rev. Available online at: https://er.educause.edu/articles/2024/6/a-framework-for-ai-literacy
Chen, Y., Liu, X., and Zhang, H. (2025). A GenAI competence framework for engineering curriculum enhancement in higher education. Int. J. Technol. Educ. Dev., 9, 55–70. Available online at: https://open-publishing.org/journals/index.php/ited/article/view/1455
Demir, B., and Tortop, H. S. (2025). Techno-mathematical literacy self-efficacy development of the scale. J. Math. Educ. Teach. Practice. (in press).
Fan, L., Deng, K., and Liu, F. (2025). Educational impacts of generative artificial intelligence on learning and performance of engineering students in China. Sci. Rep. 15:26521. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06930-w
Gravetter, F. J., and Forzano, L. A. (2018). Research methods for behavioral sciences. 6th Edn. Boston: Cengage Learning.
Hibbert, M., Altman, E., and Shippen, T. (2024). A framework for AI literacy. Educ. Rev. Available online at: https://er.educause.edu/articles/2024/6/a-framework-for-ai-literacy
Honig, C. D., Rios, S., and Desu, A. (2025). Generative AI in engineering education: understanding acceptance and use of new GPT teaching tools within a UTAUT framework. Australas. J. Eng. Educ. 30, 145–159. doi: 10.1080/22054952.2025.2467500
Hoyles, C., Noss, R., Kent, P., and Bakker, A. (2010). Improving mathematics at work: The need for techno-mathematical literacies. London: Routledge.
Kent, P., Noss, R., Guile, D., Hoyles, C., and Bakker, A. (2007). Characterising the use of mathematical knowledge in boundary-crossing situations at work. Mind Cult. Act. 14, 64–82. doi: 10.1080/10749030701307747
Long, D., and Magerko, B. (2020). What is AI literacy? Competencies and design considerations. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ‘20) (pp. 1–16). New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery.
Pepin, B., Biehler, R., and Gueudet, G. (2021). Mathematics in engineering education: a review of the recent literature with a view towards innovative practices. Int. J. Res. Undergrad. Math. Educ. 7, 163–188. doi: 10.1007/s40753-021-00139-8
Schleiss, C., and Johri, A. (2024). A roles-based competency framework for integrating artificial intelligence (AI) in engineering courses. arXiv. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.12796
Siddharth, S., Prince, B., Harsh, A., and Ramachandran, S. (2025). The world of AI: a novel approach to AI literacy for first-year engineering students. In A. I. Cristea, E. Walker, Y. Lu, O. C. Santos, and S. Isotani (Eds.), Artificial intelligence in education. Posters and late breaking results, workshops and tutorials, industry and innovation tracks, practitioners, doctoral consortium, blue sky, and WideAIED (Communications in Computer and Information Science, 2591, pp. 250–257). Cham: Springer.
Su, M., Ma, L., Zhang, D., Yunusa-Kaltungo, A., and Cheung, C. (2025). Exploring benefits and concerns of incorporating digital tools into engineering education. Eur. J. Educ. Pedagog. 6, 45–51. doi: 10.24018/ejedu.2025.6.1.909
van der Wal, N. J., Bakker, A., and Drijvers, P. (2017). Which techno-mathematical literacies are essential for future engineers? Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 15, 87–104. doi: 10.1007/s10763-017-9810-x
van der Wal, N. J., Bakker, A., and Drijvers, P. (2019). Teaching strategies to foster techno-mathematical literacies in an innovative mathematics course for future engineers. ZDM 51, 885–897. doi: 10.1007/s11858-019-01095-z
Walter, N. (2024). Embracing the future of artificial intelligence in the classroom: the relevance of AI literacy, prompt engineering, and critical thinking. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 21:48. doi: 10.1186/s41239-024-00448-3
Wang, W., and Chuang, C. (2023). Developing the artificial intelligence self-efficacy scale for pre-service teachers. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 61, 23–46. doi: 10.1007/s10639-023-12015-w
Weigand, H.-G., Trgalová, J., and Tabach, R. (2024). Mathematics teaching, learning, and assessment in the digital age. ZDM–Mathematics Education 56, 525–541. doi: 10.1007/s11858-024-01612-9
Keywords: artificial intelligence applications, techno-mathematical literacy, self-efficacy, engineering education, 21st century skills
Citation: Beyazhancer R and Demir B (2025) Enhancing techno-mathematical literacy and AI self-efficacy in engineering education through artificial intelligence applications. Front. Educ. 10:1695351. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1695351
Edited by:
Heidi Kloos, University of Cincinnati, United StatesReviewed by:
Jem Cloyd Tanucan, Colonial Beach Public Schools, United StatesEdiric Gadia, Gordon College, Philippines
Copyright © 2025 Beyazhancer and Demir. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rumeysa Beyazhancer, cnVtZXlzYWJleWF6aGFuY2VyQHVsdWRhZy5lZHUudHI=
 Rumeysa Beyazhancer
Rumeysa Beyazhancer Baris Demir
Baris Demir