- 1Department of Home economy, College of Basic education, The Public Authority for Applied Education and Training (PAAET), Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 2Department of Management, College of Business and Economics, American University of Kuwait, Salmiya, Kuwait
Introduction: Residential energy consumption in Kuwait ranks among the highest globally, largely due to villa-style housing and intensive air conditioning use under extreme climatic conditions. While prior studies have explored factors such as household size, occupancy, and thermostat settings, the combined impact of structural and behavioral determinants remains underexplored. This study addresses this gap by integrating villa ownership types, renovation practices, and energy-efficient technology adoption with constructs from the Theory of Planned Behavior (Attitude, Subjective Norms, and Perceived Behavioral Control).
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted among households across Kuwait. Data were analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) to examine the relationships between structural and behavioral determinants of residential energy consumption. The model incorporated both tangible factors (e.g., villa ownership, renovation behavior) and psychological constructs influencing energy-saving intentions and actions.
Results: The analysis revealed that villa ownership and renovation practices significantly influence household energy demand, serving as key structural drivers. Among behavioral constructs, Perceived Behavioral Control and Attitude had strong positive effects on energy-saving behaviors, whereas Subjective Norms exhibited a weaker influence. The results underscore the interplay between contextual housing characteristics and individual behavioral factors in shaping consumption.
Discussion and Conclusion: Findings highlight that energy consumption patterns in Kuwait are deeply rooted in socio-economic and cultural contexts—particularly villa culture and subsidized energy pricing—which differentiate Kuwait from other regions. The study advances understanding of residential energy behavior by linking physical housing attributes with behavioral constructs. Practical implications are offered for households, policymakers, and private-sector stakeholders, outlining strategies for targeted energy-efficiency interventions and sustainable behavioral change in the Gulf region.
1 Introduction
Energy consumption in residential sectors worldwide plays a pivotal role in shaping national energy policies, particularly in regions characterized by extreme climatic conditions. Residential buildings account for a significant share of global electricity usage, influenced by a combination of socio-economic, environmental, and technological factors. The rapid growth of urbanization, coupled with rising living standards, has led to an increasing demand for energy across the globe. Addressing inefficiencies in residential energy use is essential for achieving sustainability and mitigating the environmental impacts of high energy consumption (Alqatan et al., 2025; Dehwah and Asif, 2019).
In Kuwait, residential energy consumption ranks among the highest globally on a per capita basis, primarily driven by the prevalence of large villa-style homes that significantly contribute to the nation’s electricity usage. These villas account for approximately 58.4% of the total electricity consumption in the residential sector, reflecting the unique architectural and cultural preferences prevalent in the country (Al-Mutairi et al., 2011). The extreme climatic conditions, particularly the prolonged hot summers with temperatures often exceeding 50 °C (Alahmad et al., 2023), necessitate extensive use of air conditioning systems, which are responsible for approximately 72% of the total electrical usage in residential buildings (Alajmi and Phelan, 2020).
Moreover, the socio-economic landscape in Kuwait, characterized by substantial government energy subsidies (Gelan and AlAwadhi, 2022) further exacerbates the high levels of energy consumption. The substantial subsidies provided by the government effectively lower the cost of electricity, leading to higher consumption rates among households (Ma and Zeng, 2022). While high energy consumption has historically been associated with economic growth and development, in Kuwait the concern lies in the sustainability of such patterns. The country’s nearly exclusive reliance on oil and natural gas for power generation, combined with generous subsidies, results in disproportionately high per capita consumption. This dependence exacerbates carbon emissions, places pressure on domestic fuel allocation, and raises long-term concerns about energy security and economic opportunity costs (Alhajeri et al., 2019; AlRukaibi and AlSalem, 2022; Naseeb et al., 2022).
Kuwait’s energy consumption dynamics are intricately tied to both demand-side factors and the prevailing energy supply structure. The nation’s exceptionally high per capita electricity use is primarily driven by the extensive reliance on air conditioning in residential villas, which alone accounts for approximately 72% of residential consumption (Alajmi and Phelan, 2020). According to the Kuwait Energy Outlook (2019), the building sector contributes nearly 90% of total electricity demand, underscoring the urgency of improving household efficiency to mitigate peak loads that frequently exceed 15 GW during the extreme summer months (Saber and Maref, 2019; Sedaghat et al., 2023).
The energy generation framework in Kuwait predominantly relies on fossil fuels, with oil and natural gas constituting nearly the entire energy mix. This reliance poses significant sustainability challenges, as carbon emissions from power generation are compounded by Kuwait’s limited progress in integrating renewable energy sources (Alhajeri et al., 2019; Al-Kenane et al., 2025; Hamed et al., 2020). While current infrastructure can meet peak loads, this dependence on fossil fuels raises concerns regarding resilience and long-term sustainability (Alhajeri et al., 2019). The Kuwaiti government aims to derive 15% of domestic energy needs from renewable sources by 2030, emphasizing the necessity for substantial policy and infrastructural changes to reduce reliance on hydrocarbons (Al-Fadhli et al., 2022).
High per capita energy consumption has implications beyond environmental degradation; there are significant economic opportunity costs associated with current energy utilization patterns. Maintaining domestic fuel consumption at current levels not only conflicts with national sustainability goals but also inhibits the country from pursuing economic pathways linked to renewable energy sectors (Hamwi et al., 2022; Naseeb et al., 2022). By addressing inefficiencies in demand-side energy consumption, Kuwait can alleviate pressures on the electricity grid and contribute towards broader objectives of sustainability, energy security, and emissions reduction.
In summary, Kuwait’s energy consumption profile, characterized by high demand for electricity largely driven by residential practices and a fossil-fuel-dependent supply system, necessitates urgent attention regarding the reduction of household energy intensity. Integrating efficient technologies and policies could substantially relieve the strain on the grid during peak periods and align Kuwait’s energy practices with sustainable development goals. While earlier research (Jaffar et al., 2019) identified key drivers of energy use in villas, including thermostat settings, villa size, and occupancy levels, evolving socio-economic conditions and technological advancements necessitate updated investigations. This study addresses these gaps by incorporating new variables that reflect emerging household and structural dynamics in Kuwait. For example, villa ownership type (government-built versus custom-built) captures differences in construction quality and space utilization that influence cooling loads. Renovation practices are significant because they often involve insulation upgrades, window replacements, and air-conditioning system improvements that directly affect energy efficiency. Likewise, the adoption of energy-efficient technologies, such as double-glass windows or LED lighting, reflects behavioral and financial choices that mediate household energy intensity. Including these variables allows for a more comprehensive understanding of how both structural and behavioral factors shape residential consumption, thereby extending previous research that primarily focused on household size, thermostat settings, and occupancy patterns. To provide a behavioral foundation for examining energy-saving practices, this study draws on an established theoretical model.
Beyond household-level drivers, recent work emphasizes the importance of examining the decoupling between electricity consumption, economic growth, and environmental impacts. For instance, a study done by (Laghari et al., 2023) demonstrated that energy efficiency gains can mitigate environmental degradation while sustaining economic development, highlighting the need to contextualize residential demand within broader sustainability debates. This perspective reinforces the significance of situating Kuwait’s residential energy consumption within both household-level dynamics and national policy frameworks.
1.1 Theoretical framework
This study is grounded in the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), which posits that individual behavior is determined by behavioral intention, itself shaped by three constructs: Attitude toward the behavior (ATT), Subjective Norms (SN), and Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC) (Ajzen, 1991). TPB has been widely applied in studies of energy and environmental behavior to explain why individuals adopt or resist energy-saving practices (Ali et al., 2019; Hossain et al., 2022). In Kuwait’s context, where household energy choices are influenced by cultural norms, perceptions of control (e.g., ability to adopt efficiency measures), and attitudes toward conservation, TPB provides a robust framework. Accordingly, ATT, SN, and PBC were selected as the key behavioral attributes in this study, ensuring theoretical grounding and comparability with international scholarship.
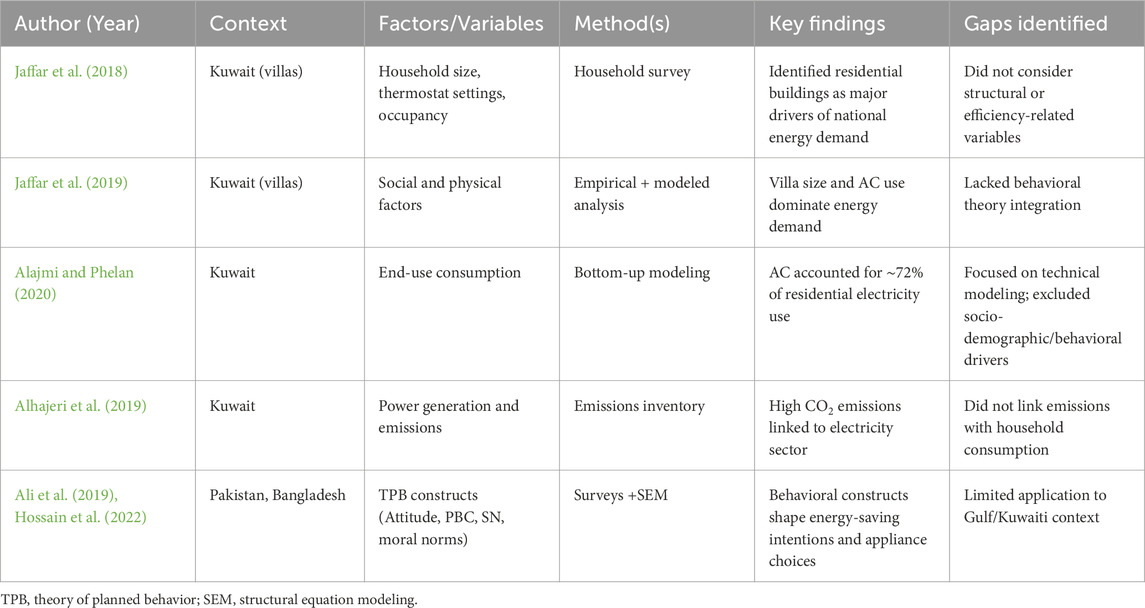
Table 1 provides a summary of relevant studies, highlighting their factors, methods, key findings, and identified gaps. This synthesis makes clear the scope of prior research and the specific gaps that the present study seeks to address.
As shown in Table 1, prior studies in Kuwait have mainly emphasized household size, occupancy, and technical modeling, while international studies have applied behavioral constructs such as Attitude, Perceived Behavioral Control, and Subjective Norms in different contexts. However, no study has yet integrated structural variables with behavioral constructs in the Kuwaiti context. This gap motivates the present research questions. Accordingly, this study is guided by the following research questions:
RQ1: How do socio-demographic and structural household factors—such as villa ownership type, renovation practices, and adoption of energy-efficient technologies—affect residential energy consumption patterns in Kuwait?
RQ2: To what extent do behavioral constructs from the Theory of Planned Behavior (Attitude, Perceived Behavioral Control, and Subjective Norms) influence energy-saving behaviors among Kuwaiti households?
RQ3: How are these structural and behavioral determinants interrelated, and what do these relationships reveal about pathways for improving household energy efficiency?
To address these questions, this study employs descriptive analysis of household and villa characteristics, followed by Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) to evaluate direct, indirect, and mediating effects among behavioral constructs.
By addressing these questions, this study contributes new insights into both structural and behavioral drivers of residential energy consumption in Kuwait.
2 Materials and methods
This study employed a quantitative cross-sectional survey to examine the socio-demographic, structural, and behavioral determinants of energy consumption among households in Kuwaiti villas. The survey instrument was structured into different comprehensive sections, encompassing socio-demographic data, building characteristics, energy usage practices (e.g., air conditioning and lighting), appliance utilization, and payment awareness. This structured approach ensured a holistic understanding of the variables influencing energy use.
2.1 Sample and data collection
Data were collected from 813 households across all six governorates of Kuwait. The sampling strategy employed stratified random sampling to ensure representation across various socio-economic groups and villa types. Interviews were conducted face-to-face by trained enumerators to address potential biases and ensure data reliability. Within each selected household, a single adult respondent was surveyed—preferably the head of household or a member responsible for energy-related decisions such as paying bills or selecting appliances. This approach ensured consistency in the type of information collected and avoided multiple responses from the same household. Respondents were assured anonymity, and the questionnaire was pre-tested for clarity before the full survey rollout.
The structured questionnaire consisted of 52 items divided into four main sections. The first section addressed socio-demographic characteristics, including employment status, education level, family size, and age distribution. The second section covered villa and structural attributes, such as ownership type, construction date, built-up area, number of floors, presence of unused rooms, renovation practices, insulation, and window types. The third section focused on appliances and energy use practices, including air-conditioning systems, lighting, refrigerators, televisions, and other household appliances, along with electricity billing information. Finally, the fourth section measured behavioral constructs derived from the Theory of Planned Behavior (Attitude, Subjective Norms, and Perceived Behavioral Control), using a five-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree, 5 = strongly agree).
2.2 Data analysis
The statistical methodology employed in this study involved a comprehensive approach to evaluating the relationships among the constructs of Attitude (ATT), Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), and Subjective Norms (SN). Descriptive statistics were first calculated to summarize demographic, socioeconomic, and villa-related variables, providing insights into household characteristics and energy usage behaviors. This initial step was crucial for identifying patterns and understanding the sample distribution. Data preparation included screening for missing values, as well as testing for reliability using Cronbach’s Alpha to ensure internal consistency of the constructs.
In the subsequent steps Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) was employed to examine the to examine the hypothesized relationships among the constructs of Attitude (ATT), Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), and Subjective Norms (SN). PLS-SEM was chosen for its suitability in handling complex models with multiple constructs and its ability to assess both the measurement model and the structural model simultaneously. This approach allowed for the evaluation of indicator reliability, internal consistency, convergent validity, and discriminant validity within the measurement model, as well as the estimation of path coefficients and mediation effects in the structural model. In the structural model evaluation, path coefficients, t-statistics, and p-values were calculated using bootstrapping with 5,000 resamples, providing robust estimates for the hypothesized relationships. Bootstrapped estimation of indirect effects is consistent with recent applications in related social-science models (e.g., AlReshaid et al., 2025). All the analysis was carried out using JAMOVI (2.3.28) (The jamovi project, 2024) and SmartPLS 4 software.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic characteristics
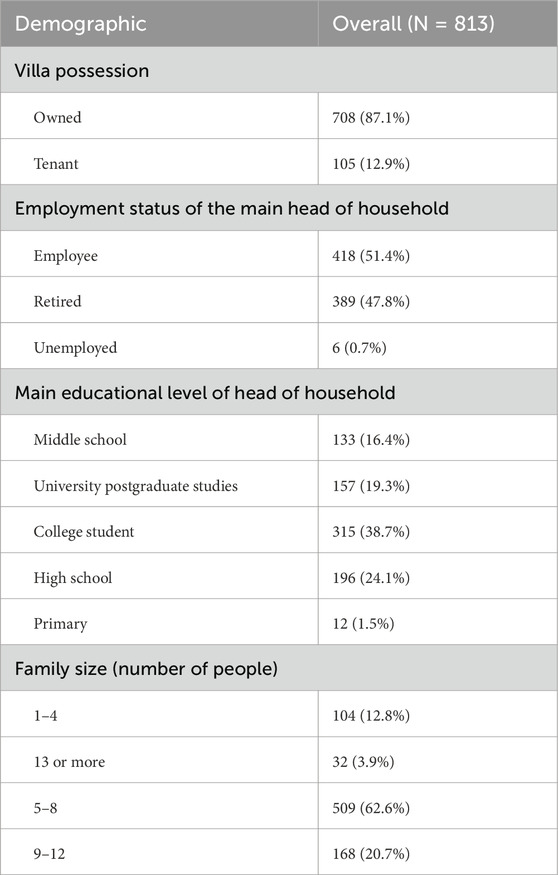
The demographics and socioeconomic characteristics of the surveyed households (N = 813) reveal insightful trends (Table 2). Regarding villa possession, a significant majority of households (87.1%) own their villas, while only 12.9% are tenants. The employment status of the head of the household shows that 51.4% are employed, 47.8% are retired, and a minimal 0.7% are unemployed, indicating a predominantly stable income structure among households. In terms of educational attainment, the most common level of education among household heads is college-level studies, accounting for 38.7% of the sample, followed by high school graduates at 24.1%, and those with postgraduate university studies at 19.3%. A smaller proportion reported middle school education (16.4%), while only 1.5% of household heads had completed primary school education.
Family size distribution highlights that the majority of households consist of 5-8 members (62.6%), followed by households with 9–12 members (20.7%), and smaller families of 1-4 members (12.8%). Larger families of 13 or more members were less frequent, representing only 3.9% of the total sample. These findings collectively provide a detailed overview of the demographic and socioeconomic attributes of the households, emphasizing trends in villa ownership, employment stability, educational attainment, and family size, which are important considerations in analyzing household dynamics in the study context.
Table 3 represents the distribution of household income levels among surveyed households (N = 813). Among the surveyed households (N = 813), the majority (60.1%) reported a monthly income of 1,000–2500 KD, followed by 17.2% earning 2,501–3500 KD. Lower-income households (<1000 KD) accounted for 11.8%, while higher-income households (>3500 KD) made up 10.8%. This distribution highlights a predominance of middle-income families with notable representation from both lower- and higher-income groups.
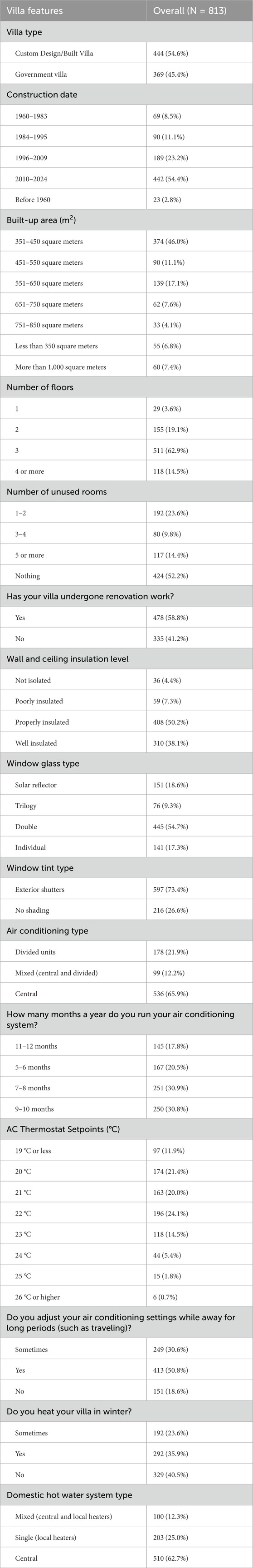
The descriptive analysis of villa characteristics among the surveyed households (N = 813) reveals various trends (Table 4). Custom-designed villas comprise 54.6% of the sample, while government villas account for 45.4%. Most villas were constructed between 2010 and 2024 (54.4%), followed by 1996–2009 (23.2%). The predominant built-up area ranges from 351 to 450 m2 (46.0%), with 17.1% falling within 551–650 m2. Most villas have three floors (62.9%), and over half (52.2%) report no unused rooms. Renovations have been conducted in 58.8% of the villas.
Regarding insulation, 50.2% are properly insulated, and 38.1% are well-insulated. Double-glass windows dominate (54.7%), and most villas utilize exterior shutters for window tinting (73.4%). Central air conditioning is the most common type (65.9%), with 61.7% of households using air conditioning for 7–10 months annually. Thermostat setpoints commonly range between 20 °C and 23 °C, with 24.1% setting it at 22 °C. Adjustments to air conditioning during long absences are made by 50.8% of respondents. Heating usage in winter is less frequent, with 40.5% of households not heating their villas. Finally, domestic hot water systems are predominantly central (62.7%), reflecting widespread integration of centralized heating systems in modern villas.
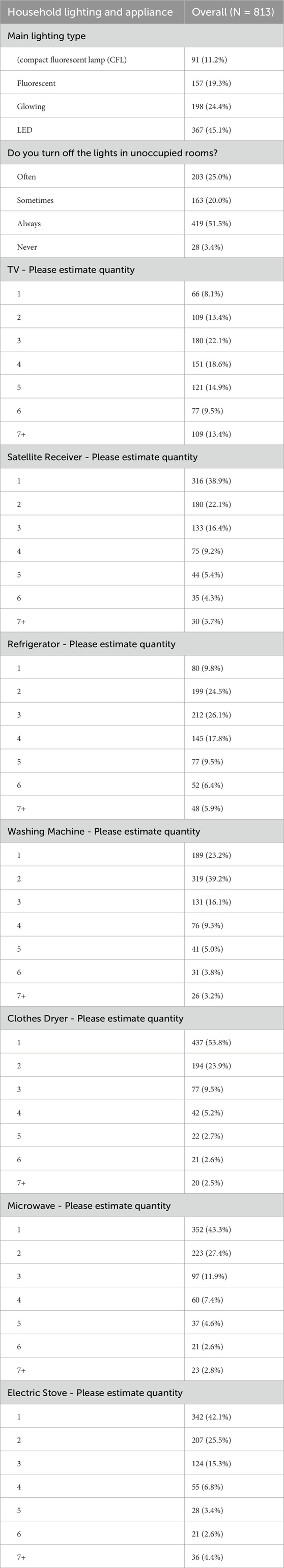
The analysis of household lighting and appliance ownership among the surveyed households (N = 813) reveals significant trends in energy use and device prevalence (Table 5). LED lighting is the most common type, used by 45.1% of households, followed by glowing lights (24.4%) and fluorescent lights (19.3%), with compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) being the least common (11.2%). A majority of respondents (51.5%) reported always turning off lights in unoccupied rooms, with 25.0% doing so often and 20.0% sometimes, while 3.4% never turn off lights.
Television ownership shows diverse patterns, with 22.1% of households having 3 TVs and 13.4% owning seven or more. Satellite receivers are similarly common, with 38.9% of households owning one, and 16.4% possessing three. Refrigerator ownership is widespread, with 26.1% of households owning three units and 24.5% owning two. Washing machines are prevalent, with 39.2% of households having two and 23.2% owning one. Clothes dryers are less commonly owned, with 53.8% of households reporting one and 23.9% owning two.
Microwaves and electric stoves are also widely used, with 43.3% and 42.1% of households, respectively, owning one unit. A smaller percentage of households report multiple units for these appliances, with 27.4% owning two microwaves and 25.5% owning two electric stoves. These findings highlight a strong presence of energy-efficient lighting and the prevalence of multiple household appliances, reflecting varying consumption patterns and energy usage behaviors in the sample.
The analysis of electricity-related behaviors and perceptions among the surveyed households (N = 813) provides insights into energy usage and financial patterns (Table 6). The majority of households (46.2%) reported an estimated annual electricity bill between 501 and 1000 KWD, followed by 33.5% with bills under 500 KWD. A smaller proportion (13.7%) had bills ranging from 1,001 to 1500 KWD, and only 6.6% reported bills exceeding 1500 KWD.
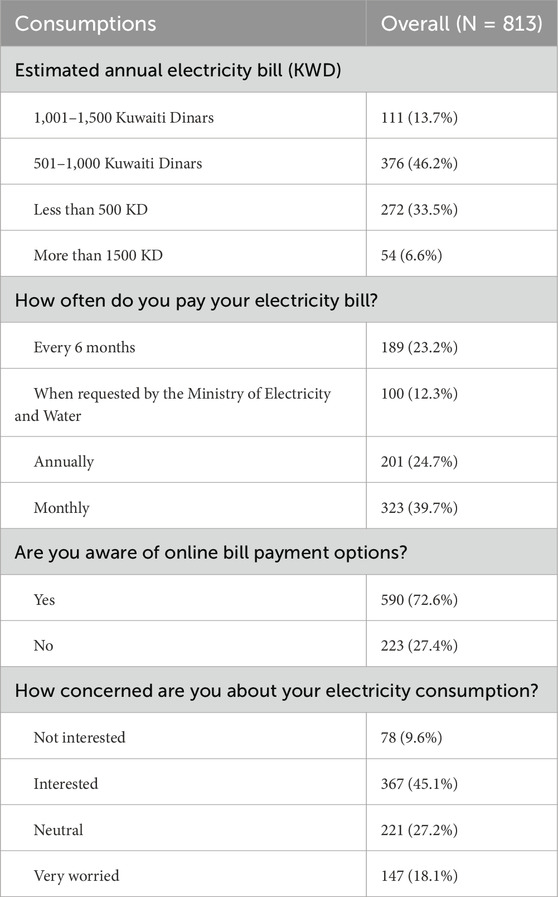
Table 6. Electricity billing practices, payment awareness, and consumption concerns among surveyed households (N = 813).
Payment frequency varies, with 39.7% of respondents paying monthly, 24.7% paying annually, 23.2% every 6 months, and 12.3% paying only when requested by the Ministry of Electricity and Water. Awareness of online bill payment options is high, with 72.6% of households acknowledging this option.
Regarding concerns about electricity consumption, 45.1% of respondents expressed interest, and 18.1% were very worried, while 27.2% remained neutral, and 9.6% were not interested. These findings reflect diverse billing practices and varying levels of awareness and concern about electricity usage, suggesting opportunities for promoting energy-saving behaviors and online payment adoption.
3.2 Reliability analysis
The reliability analysis for the constructs of Attitude (ATT), Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), and Subjective Norms (SN) demonstrates acceptable internal consistency (Table 7). The Cronbach’s α values for each item range between 0.856 and 0.867 when individual items are excluded, indicating that the overall scale is robust. Item-rest correlations for most items are above 0.5, further supporting the reliability of the constructs. Notably, ATT4, PBC3, and PBC4 exhibit the highest item-rest correlations (0.637, 0.644, and 0.645, respectively), suggesting strong alignment with the overall scale. These results validate the reliability of the measurement instrument used in the study.
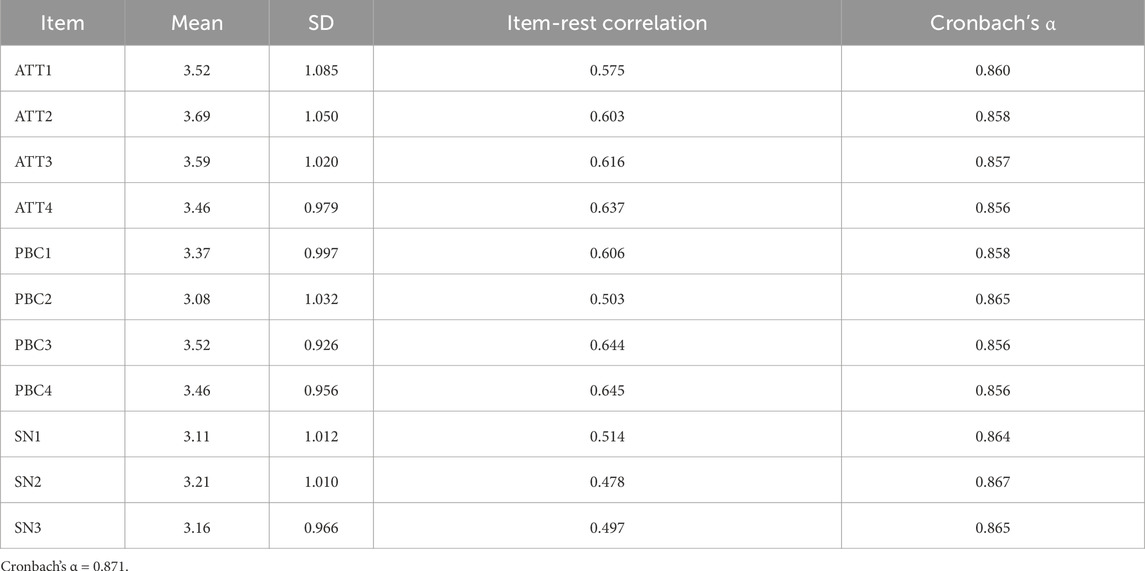
Table 7. Reliability statistics for attitude (ATT), perceived behavioral control (PBC), and subjective norms (SN) constructs.
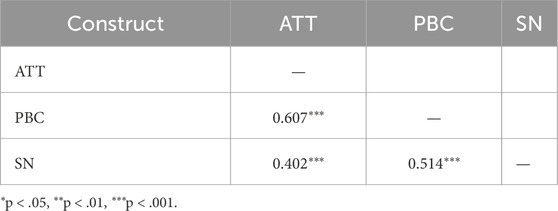
The correlation matrix presents the relationships among the constructs of Attitude (ATT), Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), and Subjective Norms (SN) (Table 8). Significant positive correlations were observed between all constructs at the p < 0.001 level. ATT and PBC exhibited a strong correlation (rp = 0.607), indicating that individuals with favorable attitudes tend to perceive greater control over the behavior. Similarly, ATT and SN demonstrated a moderate correlation (rp = 0.402), suggesting that subjective norms positively influence attitudes. Additionally, PBC and SN showed a moderate correlation (rp = 0.514), highlighting the interconnection between perceived control and the influence of social norms. These findings underscore the theoretical alignment and interdependence of these constructs within the study framework.
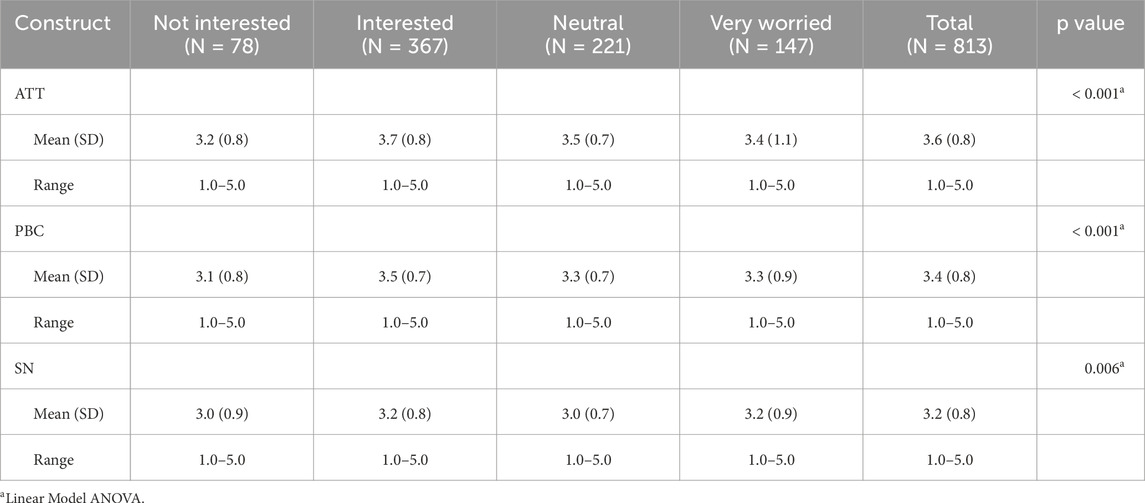
The analysis highlights significant differences in Attitude (ATT), Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), and Subjective Norms (SN) across levels of concern about electricity consumption (Table 9). For ATT (p < 0.001p < 0.001), the “interested” group had the highest mean score (3.7 ± 0.8), while the “not interested” group scored the lowest (3.2 ± 0.8). PBC also varied significantly (p < 0.001p < 0.001), with the “interested” group reporting the highest mean (3.5 ± 0.7) and the “not interested” group the lowest (3.1 ± 0.8). For SN (p = 0.006p = 0.006), the “interested” and “very worried” groups showed the highest means (3.2), while the “not interested” and “neutral” groups scored lower (3.0).
3.3 SEM for the conceptual proposed frame work
The Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) approach utilized in the proposed conceptual framework provides a robust analytical method for simultaneously examining relationships among observed variables, latent constructs, and their indicators. This approach enables the evaluation of hypothesized associations, including direct, indirect (mediating) effects, while also measuring the significance and strength of each pathway, thereby supporting the validation of theoretical models. Figure 1 depicts the basic node diagram with corresponding loadings.
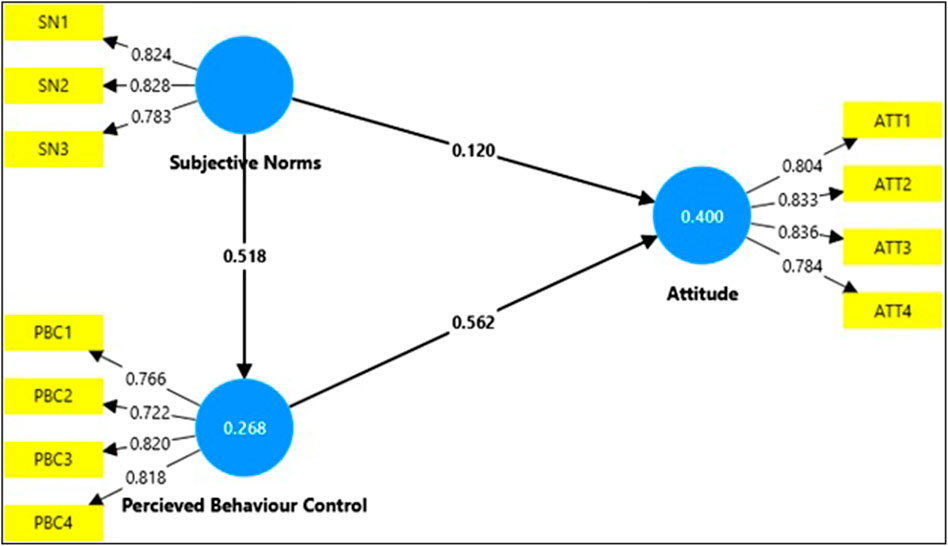
Figure 1. Structural equation model showing relationships among Subjective Norms, Perceived Behavioral Control, and Attitude, with standardized path coefficients and indicator loadings.
3.3.1 Measurement model assessment
In PLS-SEM, assessing the measurement model is a crucial step to ensure the constructs’ reliability and validity prior to evaluating the structural model. This process involves evaluating indicator reliability through outer loadings, internal consistency using Cronbach’s Alpha and Composite Reliability (rho_a and rho_c), and convergent validity via the Average Variance Extracted (AVE). Furthermore, multicollinearity is assessed using the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF), with values below the commonly accepted threshold of 5 indicating low multicollinearity among indicators (Diamantopoulos and Siguaw, 2006). Meeting these criteria ensures that the measurement model is robust, enabling the subsequent structural model evaluation.
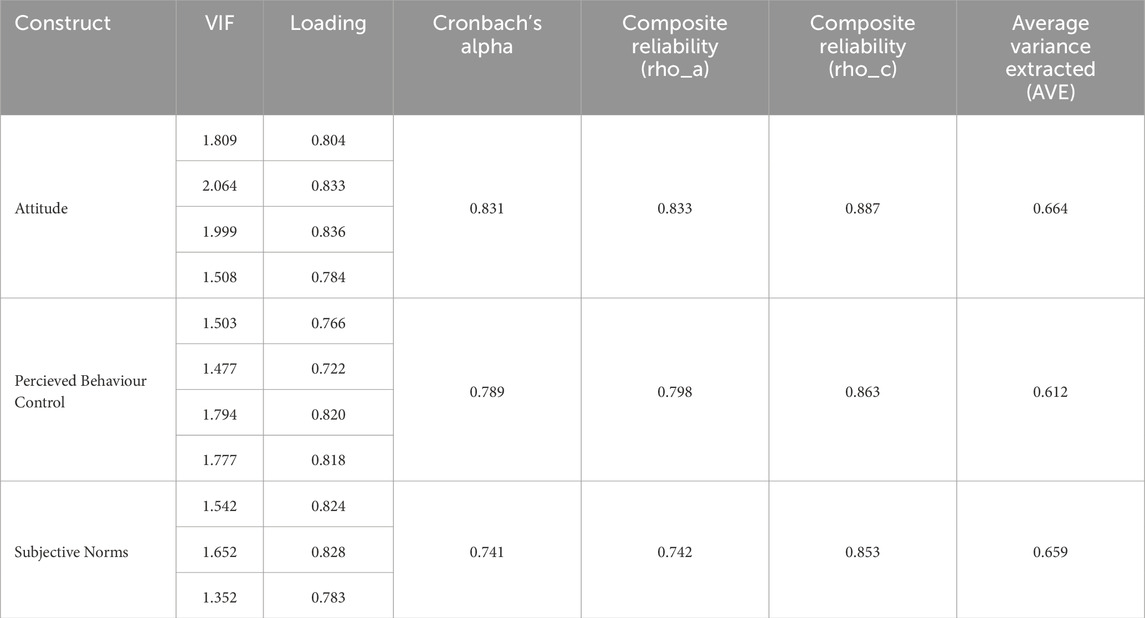
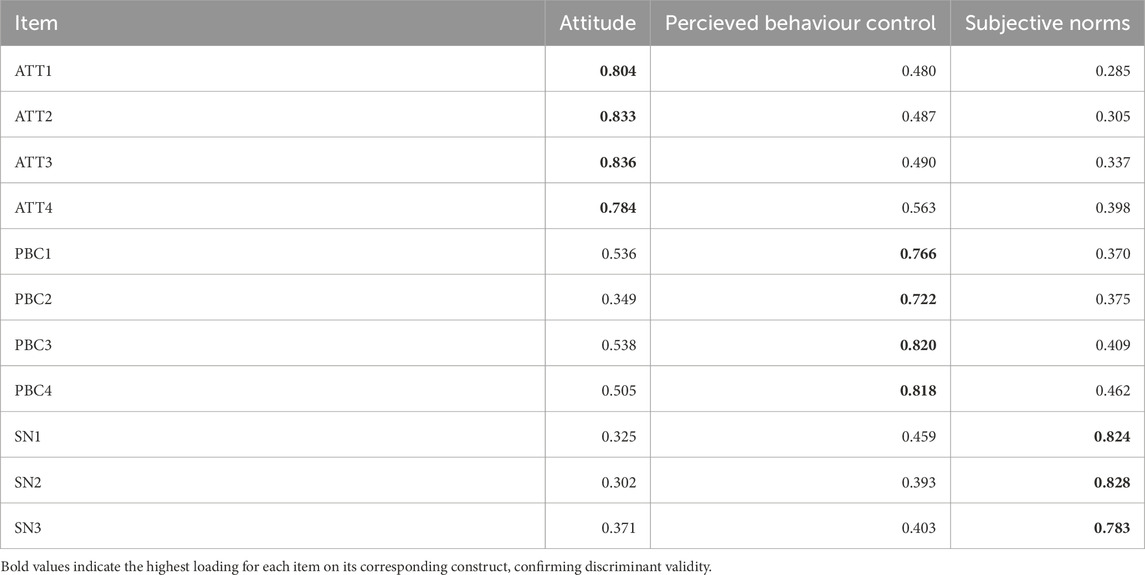
Table 10 provides the results of the measurement model assessment for the constructs Attitude, Perceived Behavioral Control, and Subjective Norms, using multiple statistical metrics. Each construct is measured through several items, with their respective outer loadings exceeding the threshold of 0.70, which indicates strong indicator reliability (J. F. Hair et al., 2012). For example, the outer loadings for Attitude range from 0.784 to 0.836, while those for Perceived Behavioral Control range from 0.722 to 0.820, and Subjective Norms range from 0.783 to 0.828. Additionally, the VIF values for all items are well below 3, confirming the absence of multicollinearity issues.
Internal consistency is supported by Cronbach’s Alpha values of 0.831 for Attitude, 0.789 for Perceived Behavioral Control, and 0.741 for Subjective Norms, indicating satisfactory reliability (Hair et al., 2017; Nunnally and Bernstein, 1994). Composite reliability values from 0.742 to 0.887 across all constructs, further reinforcing their internal consistency and robustness (Hair et al., 2017). The AVE values for the constructs are 0.664, 0.612, and 0.659, respectively, all exceeding the 0.50 threshold recommended by (Fornell and Larcker, 1981), thereby establishing strong convergent validity.
In conclusion, the measurement model demonstrates excellent reliability, validity, and consistency across all constructs, providing a robust foundation for further structural model analysis.
The cross-loading results confirm discriminant validity (Table 11), with each indicator showing the highest loading on its intended construct (Hair et al., 2017). Attitude indicators (ATT1-ATT4) load strongly on their construct (0.784–0.836). Similarly, PBC indicators (PBC1-PBC4) load highest on PBC (0.722–0.820), and SN indicators (SN1-SN3) exhibit the strongest loadings on SN (0.783–0.828). These results ensure the constructs are distinct and measured accurately.
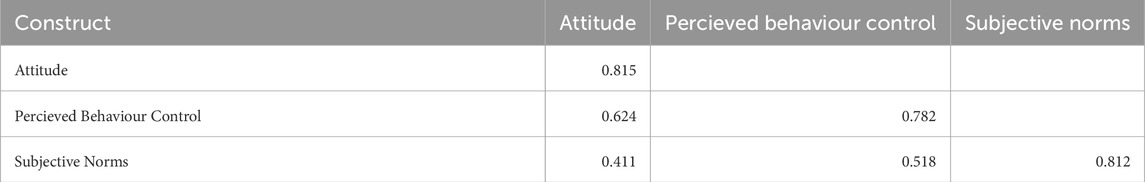
The Fornell-Larcker criterion was employed to assess discriminant validity among the constructs Attitude, Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), and Subjective Norms (SN) (Table 12). The results confirm that the square root of the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) for each construct exceeds its correlations with other constructs, indicating that each construct is distinct and captures unique aspects of the model (Hair et al., 2017). These results provide strong evidence of discriminant validity, ensuring that the constructs are appropriately differentiated within the measurement model.
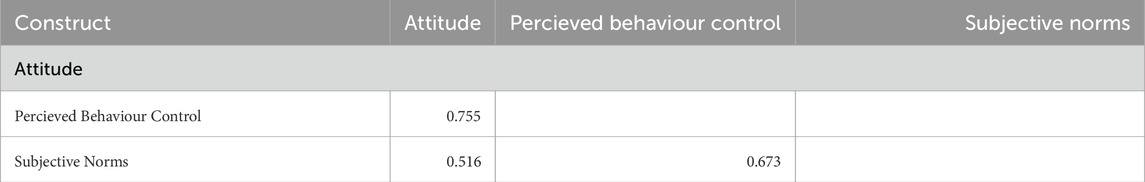
The third criterion for assessing discriminant validity is the Heterotrait-Monotrait (HTMT) ratio (Henseler et al., 2015), which evaluates the degree of similarity between constructs (Table 13). The HTMT values among the constructs Attitude, Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), and Subjective Norms (SN) were all below the recommended threshold of 0.85 (Henseler et al., 2015), confirming acceptable discriminant validity. Specifically, the HTMT value between Attitude and PBC is 0.755, between Attitude and SN is 0.516, and between PBC and SN is 0.673. These results further support that the constructs are sufficiently distinct and appropriately measured, ensuring the robustness of the measurement model.
3.3.2 Structural model assessment
Structural model assessment in SEM evaluates the relationships among constructs by analyzing path coefficients and significance levels. This includes testing direct, and indirect (mediating) effects to determine the strength and direction of hypothesized associations.
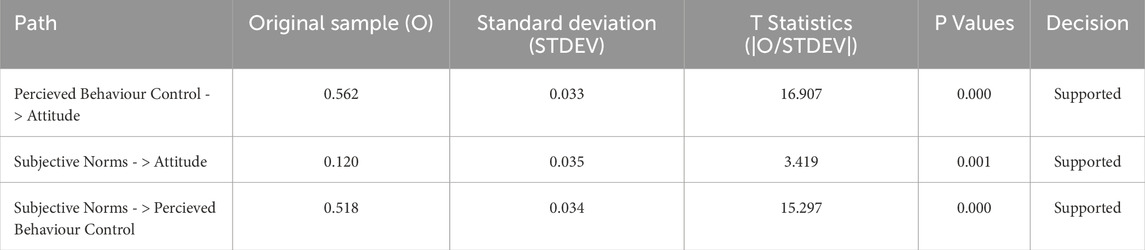
The structural model results confirm the hypothesized relationships among Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), Subjective Norms (SN), and Attitude (Table 14). The relationship between PBC and Attitude is strong and significant (β = 0.562, t = 16.907, p < 0.001), indicating a substantial positive effect. Similarly, SN has a positive and significant influence on Attitude (β = 0.120, t = 3.419, p = 0.001), though the effect is weaker compared to PBC. Furthermore, SN significantly affects PBC (β = 0.518, t = 15.297, p < 0.001), highlighting its strong contribution.
These results demonstrate that PBC and SN are significant predictors of Attitude, with PBC having the strongest direct effect. Additionally, SN influences PBC, further reinforcing the robustness of the structural model.
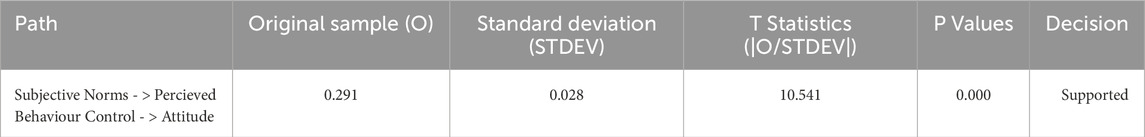
Table 15 presents the results of mediation analysis. It examines whether the mediation effect of Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC) for Subjective Norms (SN) and Attitude (ATT).
The structural model results indicate a significant indirect effect of Subjective Norms (SN) on Attitude through Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC) (β = 0.291, t = 10.541, p < 0.001). This finding supports the hypothesis that PBC mediates the relationship between SN and Attitude, emphasizing the role of PBC as a key pathway through which SN influences Attitude.
4 Discussion
4.1 Behavioral and structural determinants of energy consumption
The study of residential energy consumption in Kuwaiti villas reveals a complex interplay between behavioral and structural factors, particularly highlighting the significant role of air conditioning practices. The extreme climatic conditions in Kuwait necessitate heavy reliance on cooling systems, with thermostat settings commonly reported between 20 °C and 23 °C. This reliance on energy-intensive cooling behaviors is corroborated by research indicating that air conditioning constitutes a major contributor to residential energy consumption, accounting for a substantial portion of peak electricity demand (Peffer et al., 2011; Solanki et al., 2022). The findings suggest that households’ thermostat settings directly influence energy use, as higher settings can lead to increased energy consumption (Belazi et al., 2019; Susanto et al., 2018).
Moreover, structural attributes such as villa insulation levels and window types significantly impact energy efficiency. Proper insulation has been shown to enhance energy performance by reducing the cooling load required to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures (Boait and Alshahrani, 2018). Studies indicate that well-insulated buildings can substantially decrease energy demand, thus mitigating the adverse effects of high cooling needs associated with extreme weather conditions (Peffer et al., 2011; Solanki et al., 2022).
4.2 Demographic influences
Socio-demographic characteristics, such as villa ownership and income levels, are significant predictors of energy consumption in Kuwait. The cultural preference for larger residential spaces, as evidenced by the high prevalence of villa ownership, inherently leads to increased energy demands for cooling and maintenance. This trend is supported by findings from Jaffar et al., who highlighted that residential buildings account for nearly 60% of the national electrical power generated in Kuwait, with villas being a primary contributor to this consumption (Jaffar et al., 2018). The larger footprint of villas necessitates greater energy use, particularly for air conditioning, which is critical in the extreme climate of Kuwait.
Furthermore, the study indicates that higher-income households are more likely to adopt energy-efficient technologies, such as double-glass windows and centralized air conditioning systems. This suggests that affordability plays a crucial role in shaping energy efficiency practices. Research by Pelenur indicates that financial capability significantly influences the adoption of energy-efficient technologies, as households with higher income levels tend to invest more in such improvements (Pelenur, 2018). However, it is important to note that Pelenur’s study found only a small number of strong correlations between distinct energy viewpoints and specific energy efficiency technologies or behaviors, suggesting that being environmentally aware may not directly lead to the adoption of energy-efficient technologies.
4.3 Behavioral constructs and energy-saving attitudes
The analysis utilizing Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) highlights the critical role of behavioral constructs in influencing energy-saving behaviors. Specifically, the strong influence of Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC) on Attitude (ATT) and the mediating role of PBC in the relationship between Subjective Norms (SN) and ATT are consistent with the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) as proposed by Ajzen in 1991 (Ajzen, 1991). This theoretical framework posits that individuals’ intentions to engage in a behavior are shaped by their attitudes, perceived control, and the influence of social norms (Ali et al., 2019).
Supporting this, Jaffar et al. (2018) emphasized the necessity for behavioral interventions aimed at promoting sustainable energy use, indicating that enhancing individuals’ perceived control can significantly impact their energy-saving behaviors (Jaffar et al., 2018). Furthermore (Hossain et al., 2022), found that subjective norms, alongside attitudes and perceived behavioral control, significantly influence consumers’ intentions to purchase energy-efficient appliances, reinforcing the importance of social influences in driving energy-saving practices.
Awareness campaigns designed to enhance perceived control and leverage social norms could effectively foster greater adoption of energy-saving practices. For instance (Suntornsan et al., 2022), demonstrated that behavioral intention mediates the effect of perceived behavioral control on energy-saving behaviors, suggesting that interventions that increase individuals’ confidence in their ability to save energy can lead to more proactive energy-saving actions.
In conclusion, the integration of behavioral constructs within the framework of the Theory of Planned Behavior provides valuable insights into the factors influencing energy-saving behaviors. By focusing on enhancing perceived behavioral control and utilizing social norms, stakeholders can develop effective strategies to promote sustainable energy consumption.
4.4 Critical reflections and contradictions
While several of our findings align with prior international studies, some variations can be better understood through Kuwait’s unique socio-economic and environmental context. For example, the strong influence of villa ownership type and renovation practices on household energy consumption diverges from studies in European and Asian contexts, where building codes and energy-efficiency regulations are stricter (Ali et al., 2019; Hossain et al., 2022). In Kuwait, however, generous energy subsidies reduce the financial incentives for households to adopt efficiency upgrades, which may explain why structural factors such as villa type and renovation choices exert a more pronounced effect.
Another point of contrast lies in the limited predictive strength of Subjective Norms (SN) compared to findings in collectivist societies such as Bangladesh and Pakistan, where social expectations significantly shape household energy-saving practices (Hossain et al., 2022). In Kuwait, despite cultural emphasis on family and community, the combination of economic affluence, subsidized utilities, and limited regulatory enforcement may weaken the role of peer or community pressure in influencing energy behaviors. Instead, Attitude (ATT) and Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC) appear to play stronger roles, reflecting the importance of individual perceptions of cost, comfort, and control over energy choices in the Kuwaiti context.
These findings highlight the importance of situating household energy behavior within the local policy and socio-economic environment. Unlike regions where rising energy prices and strict building codes act as strong behavioral motivators, Kuwait’s heavily subsidized energy system and reliance on large villas create distinct drivers of consumption. Recognizing these contextual differences not only explains the observed variations but also underscores the need for locally tailored policy interventions that go beyond global best practices.
5 Conclusion
This study investigated the structural and behavioral determinants of residential energy consumption in Kuwait, examining villa ownership types, renovation practices, adoption of energy-efficient technologies, and behavioral constructs derived from the Theory of Planned Behavior. The analysis demonstrates that household characteristics and behavioral choices interact with broader contextual factors to shape energy demand. The contribution of this research lies in integrating both structural and behavioral perspectives within a single empirical framework, offering evidence from the Kuwaiti residential sector where high energy intensity remains a pressing concern. By highlighting how household decision-making intersects with socio-economic conditions, the findings enrich theoretical understanding of energy behavior and extend the application of the Theory of Planned Behavior to a new regional context. Beyond its theoretical value, this work provides an empirical foundation for future studies to explore household energy transitions in rentier economies, where affordability often masks the urgency of conservation.
5.1 Implications for households
Households play a central role in reducing energy intensity, as villa ownership type, renovation practices, and energy-saving behaviors directly influence electricity consumption. Residents can contribute to reducing demand by adopting energy-efficient technologies such as double-glass windows, LED lighting, and modern cooling systems, while also maintaining thermostat settings at more sustainable levels, typically between 24 °C and 26 °C during summer months. Periodic renovations that improve insulation, enhance window sealing, and upgrade air-conditioning systems are equally important in mitigating energy waste. Beyond these structural measures, households must also embrace behavioral shifts, particularly by strengthening their perceived control over energy-saving practices, which has been shown to encourage more consistent and proactive energy conservation.
5.2 Implications for government and policymakers
The government, particularly the Ministry of Electricity, Water, and Renewable Energy (MEWRE), has a pivotal role in shaping energy efficiency outcomes through regulatory and policy interventions. Stronger enforcement of building and insulation codes for both new and existing villas is essential, along with the introduction of targeted subsidies or financial incentives to support retrofitting of older properties with advanced insulation and efficient cooling technologies. At the same time, gradual reform of energy subsidies is necessary to discourage wasteful consumption while safeguarding vulnerable households through socially sensitive measures. In addition, the government can strengthen its role by launching public awareness campaigns that not only highlight the environmental benefits of energy-saving practices but also emphasize their economic advantages, thereby encouraging households to take action.
5.3 Implications for the private sector
The private sector, including construction companies and appliance manufacturers, is equally critical to the transition toward sustainable residential energy use. By developing and marketing affordable energy-efficient construction materials and appliances tailored to Kuwait’s climatic conditions, private firms can facilitate the adoption of new technologies across a wider range of households. Collaborations between private companies and government agencies can also generate cost-effective retrofitting packages that make renovations more accessible to middle-income families. Furthermore, expanding after-sales services and providing warranties will help build consumer confidence in long-term investments, ensuring that households are more likely to adopt and sustain energy-efficient technologies.
In summary, addressing Kuwait’s high residential energy demand requires a multi-stakeholder approach. Households must adopt energy-saving practices, the government must create an enabling regulatory and policy environment, and the private sector must provide cost-effective technological solutions. Clear delineation of roles ensures that responsibilities are shared, coordinated, and actionable. By combining structural reforms, behavioral interventions, and policy innovations, Kuwait can reduce household energy intensity, alleviate pressures on its electricity grid, and contribute to broader sustainability and energy security objectives.
6 Limitations
The sample was representative of Kuwaiti households, cultural and climatic factors unique to Kuwait may limit the generalizability of the findings to other regions. In addition, the cross-sectional design restricts the ability to capture temporal dynamics or causal inferences, which future longitudinal or experimental studies could address. For example, time-lagged dyadic designs similar to AlReshaid et al. (2025) can mitigate common-method concerns and strengthen causal inference in relational models. The reliance on self-reported data for energy practices and behaviors may introduce response bias, underscoring the need for complementary objective measurements, such as smart metering data. Moreover, the study focuses exclusively on villa-style homes, leaving scope for investigating energy consumption in other residential types such as apartments. Finally, the analysis did not account for broader macroeconomic or policy shifts (e.g., subsidy reforms or renewable energy integration) that may influence household energy behaviors over time. Addressing these limitations will further enrich the understanding of residential energy consumption dynamics in Kuwait and beyond.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by American University of Kuwait, Kuwait. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AA: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SA-S: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. AA: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This publication was made possible by the support of the AUK Open Access Publishing Fund.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the American University of Kuwait.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The authors acknowledge the use of Generative AI in the preparation of this manuscript. Specifically, Generative AI tools were employed to enhance the clarity and structure of certain sections of the paper.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 50, 179–211. doi:10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-t
Al-Fadhli, F., Alhajeri, N., Aly, A., and Alsulaili, A. (2022). Modeling the impact of reducing sulfur content of liquid fuels consumed by power plants on the air quality of Kuwait using AERMOD. J. Eng. Res. 10 (4A), 44–58. doi:10.36909/jer.17637
Al-Kenane, K., Almoraish, A., Al-Enezi, D., Al-Matrouk, A., AlBuloushi, N., and Alreshaid, F. (2025). The process through which young adults form attitudes towards sustainable products through social media exposure in Kuwait. Sustainability 17 (10), 4442. doi:10.3390/su17104442
Al-Mutairi, H., Dewsbury, J., and Lane-Serff, G. F. (2011). Energy and the implication of residential cooling in hot climates: a case study for developing an effective solution for residential cooling energy demand in Kuwait. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 150, 859–870. doi:10.2495/SDP110711
Alahmad, B., Al-Hemoud, A., Al-Bouwarthan, M., Khraishah, H., Kamel, M., Akrouf, Q., et al. (2023). Extreme heat and work injuries in Kuwait’s hot summers. Occup. Environ. Med. 80 (6), 347–352. doi:10.1136/oemed-2022-108697
Alajmi, T., and Phelan, P. (2020). Modeling and forecasting end-use energy consumption for residential buildings in Kuwait using a bottom-up approach. Energies 13 (8), 1981. doi:10.3390/en13081981
Alhajeri, N. S., Al-Fadhli, F. M., and Aly, A. Z. (2019). Unit-based emissions inventory for electric power systems in Kuwait: current status and future predictions. Sustainability 11 (20), 5758. doi:10.3390/su11205758
Ali, S., Ullah, H., Akbar, M., Akhtar, W., and Zahid, H. (2019). Determinants of consumer intentions to purchase energy-saving household products in Pakistan. Sustainability 11 (5), 1462. doi:10.3390/su11051462
Alqatan, A., Simmou, W., Shehadeh, M., AlReshaid, F., Elmarzouky, M., and Shohaieb, D. (2025). Strategic pathways to corporate sustainability: the roles of transformational leadership, knowledge sharing, and innovation. Sustainability 17 (12), 5547. doi:10.3390/su17125547
AlReshaid, F., Erturk, A., Alkhayyat, R., Abdallah, F., Abidi, O., and De La Roche, M. (2025). Are we on the same wavelength? supervisor–subordinate cognitive style congruence and its association with supervisors’ self-awareness through leader–member exchange. Front. Psychol. 16, 1583837. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1583837
AlRukaibi, D., and AlSalem, A. (2022). A comparative analysis of the carbon dioxide emissions-energy profile in Kuwait: status quo versus 2030. J. Eng. Res. 10 (3B), 12–33. doi:10.36909/jer.14403
Belazi, W., Ouldboukhitine, S.-E., Chateauneuf, A., and Bouchair, A. (2019). Experimental and numerical study to evaluate the effect of thermostat settings on building energetic demands during the heating and transition seasons. Appl. Therm. Eng. 152, 35–51. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.02.020
Boait, P. J., and Alshahrani, J. (2018). Reducing high energy demand associated with air-conditioning needs in Saudi Arabia. Energies (Basel). 12, 87. doi:10.3390/en12010087
Dehwah, A. H., and Asif, M. (2019). Assessment of net energy contribution to buildings by rooftop photovoltaic systems in hot-humid climates. Renew. Energy 131, 1288–1299. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.031
Diamantopoulos, A., and Siguaw, J. A. (2006). Formative Versus reflective indicators in organizational measure development: a comparison and empirical illustration. Br. J. Manag. 17 (4), 263–282. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8551.2006.00500.x
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 18 (1), 39–50. doi:10.1177/002224378101800104
Gelan, A. U., and AlAwadhi, A. S. (2022). “Distributional effects of reduction in energy subsidy: evidence from Kuwait,” in Handbook of research on energy and environmental finance 4.0 (IGI Global), 102–143. Available online at: https://www.igi-global.com/chapter/distributional-effects-of-reduction-in-energy-subsidy/298746.
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., and Mena, J. A. (2012). An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 40 (3), 414–433. doi:10.1007/s11747-011-0261-6
Hair, J., Hollingsworth, C. L., Randolph, A. B., and Chong, A. Y. L. (2017). An updated and expanded assessment of PLS-SEM in information systems research. Industrial Manag. & Data Syst. 117 (3), 442–458. doi:10.1108/imds-04-2016-0130
Hamed, A. A., Sayed, M. E., and Meshari, L. (2020). Assessment of future water, energy, and food nexus by using weap and leap models in the state of Kuwait. J. Environ. Sci. 49 (9), 495–526. doi:10.21608/jes.2020.206395
Hamwi, H., Rushby, T., Mahdy, M., and Bahaj, A. S. (2022). Effects of high ambient temperature on electric vehicle efficiency and range: case study of Kuwait. Energies 15 (9), 3178. doi:10.3390/en15093178
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 43 (1), 115–135. doi:10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Hossain, I., Fekete-Farkas, M., and Nekmahmud, M. (2022). Purchase behavior of energy-efficient appliances contribute to sustainable energy consumption in developing country: moral norms extension of the theory of planned behavior. Energies 15 (13), 4600. doi:10.3390/en15134600
Jaffar, B., Oreszczyn, T., Raslan, R., and Summerfield, A. (2018). Understanding energy demand in Kuwaiti villas: findings from a quantitative household survey. Energy Build. 165, 379–389. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.01.055
Jaffar, B., Oreszczyn, T., and Raslan, R. (2019). Empirical and modelled energy performance in Kuwaiti villas: understanding the social and physical factors that influence energy use. Energy Build. 188, 252–268. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2019.02.011
Laghari, F., Ahmed, F., Li, H. X., and Bojnec, Š. (2023). Decoupling Electr. Consum. Effic. Environ. Degrad. Econ. Growth An Empir. Analysis. Energies 16, 2620. Available online at: https://www.academia.edu/download/105010054/pdf.pdf.
Ma, L., and Zeng, Z. (2022). A survey of the influence of air distribution on indoor environment and building energy efficiency. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2287 (1), 012041. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/2287/1/012041
Naseeb, A., Ramadan, A., and Al-Salem, S. M. (2022). Economic feasibility study of a carbon capture and storage (CCS) integration project in an oil-driven economy: the case of the State of Kuwait. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (11), 6490. doi:10.3390/ijerph19116490
Peffer, T., Pritoni, M., Meier, A., Aragon, C., and Perry, D. (2011). How people use thermostats in homes: a review. Build. Environ. 46 (12), 2529–2541. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2011.06.002
Pelenur, M. (2018). Household energy use: a study investigating viewpoints towards energy efficiency technologies and behaviour. Energy Effic. 11 (7), 1825–1846. doi:10.1007/s12053-018-9624-x
Saber, H. H., and Maref, W. (2019). Energy performance of cool roofs followed by development of practical design tool. Front. Energy Res. 7, 122. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2019.00122
Sedaghat, A., Soleimani, S. M., Al-Khiami, M. I., Sabati, M., Rasul, M., Narayanan, R., et al. (2023). Development of a novel low-energy building: effects of room orientation and wall materials. Key Eng. Mater. 945, 101–108. doi:10.4028/p-26jy0u
Solanki, P. S., Dua, P., and Ashraf, S. A. (2022). Energy saving to diminish the electricity demand by regulating HVAC system. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1055 (1), 012009. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/1055/1/012009
Suntornsan, S., Chudech, S., and Janmaimool, P. (2022). The role of the theory of planned behavior in explaining the energy-saving behaviors of high school students with physical impairments. Behav. Sci. 12 (9), 334. doi:10.3390/bs12090334
Susanto, E., Alhamid, M. I., Nasruddin, N., and Budihardjo, B. (2018). An experimental investigation into the effect of thermostat settings on the energy consumption of household refrigerators. Int. J. Technol. 9 (2), 364–371. doi:10.14716/ijtech.v9i2.1055
The jamovi project (2024). Jamovi. Available online at: https://www.jamovi.org.
Keywords: energy consumption, behavioral determinants, residential energy efficiency, Kuwaitivillas, sustainable practices
Citation: Aljuwaisri AM, Al-Shamali S and Alsaber A (2025) Determinants of residential energy consumption in Kuwaiti homes: a cross-sectional study. Front. Energy Res. 13:1561829. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2025.1561829
Received: 14 March 2025; Accepted: 01 October 2025;
Published: 16 October 2025.
Edited by:
Muyiwa S. Adaramola, Norwegian University of Life Sciences, NorwayReviewed by:
Štefan Bojnec, University of Primorska, SloveniaSalina Daud, Universiti Malaysia Pahang Al-Sultan Abdullah, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Aljuwaisri, Al-Shamali and Alsaber. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ahmad Alsaber, YWxzYWJlckBhY3Mta3cuY29t
 Anfal M. Aljuwaisri1
Anfal M. Aljuwaisri1 Ahmad Alsaber
Ahmad Alsaber