- School of Economics, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China
National innovative industrial clusters serve as pivotal platforms for technological innovation and play a vital role in advancing urban green technological innovation (GTI). This study empirically examines the impact of the pilot innovative industrial cluster policy on urban GTI using panel data from 281 prefecture-level cities in China (2006–2021), employing a difference-in-differences (DID) model that treats the policy as a quasi-natural experiment. The findings reveal that the pilot policy has significantly catalyzed urban GTI, a conclusion that remains robust after a series of robustness tests. Heterogeneity analysis indicates that the promotional effect is more pronounced in eastern and western cities, as well as in cities with high environmental concern and strong intellectual property protection (IPP). Mechanism analysis demonstrates that the policy drives GTI primarily through three channels: enhancing entrepreneurial activity, agglomerating scientific and technological talent, and increasing financial and scientific investment. Furthermore, the policy significantly improves urban energy utilization efficiency, with GTI acting as a critical mediating mechanism. These findings provide valuable empirical evidence and strategic insights for policymakers to refine the cluster policy and foster sustainable urban development towards achieving the dual-carbon goals.
Highlights
1. Innovative industrial clusters and GTI: Our study demonstrates that innovative industrial clusters significantly promote urban green technological innovation (GTI) in China.
2. Mechanisms of impact: The policy enhances GTI through three primary channels: increased entrepreneurial activity, higher density of innovation talent, and stronger financial and technological investment.
3. Heterogeneity analysis: The impact of innovative industrial clusters on GTI varies across cities, with more pronounced effects in eastern and western regions, environmentally focused cities, and cities with high levels of intellectual property protection.
4. Energy efficiency: The policy also improves urban energy use efficiency, with GTI identified as a key mechanism driving this improvement.
5. Policy implications: Our findings provide policy insights for enhancing innovative industrial cluster policies to support sustainable urban development and accelerate the realization of the dual-carbon goals.
1 Introduction
Innovation is a key driver of national economic growth. Innovation-oriented industrial clusters are crucial for implementing China’s innovation-driven development strategy and accelerating high-level technological self-reliance (Zhao et al., 2020). Strengthening these clusters is vital for building a modern industrial system and maintaining innovation at the core of China’s modernization. Currently, China’s economy is in a high-quality development phase, driven by structural transformation and new growth models. However, substantial challenges remain in the low-carbon energy transition and integrated industrial development. On one hand, China faces dual pressures of low “green concentration” and “innovation concentration,” with energy consumption expected to remain rigid in the near term, making the path to ecological civilization long and complex (Zhao, 2023). On the other hand, despite being the world’s largest manufacturing country, China’s transition from a manufacturing giant to a manufacturing powerhouse is hindered by low technological content and a lack of well-known brands.
GTI is a core pathway to address these challenges. By integrating environmental constraints with technological progress, GTI directly supports China’s dual-carbon goals1 and sustainable urbanization (Cui et al., 2024). However, several critical gaps remain in the existing literature. While prior studies have examined the drivers of GTI, including talent, capital, and innovation systems (Xu and Hu, 2024; Zuo and Zhou, 2024), they often fail to consider how internal innovation dynamics interact with external institutional conditions, particularly in the urban context. Moreover, although industrial policies have been examined for their environmental and economic impacts, including their roles in promoting urban development, structural upgrading, and high-quality growth, limited attention has been given to innovative industrial clusters. These clusters serve as a meso-level policy instrument that integrates local innovation resources, supports the diffusion of green technologies, and promotes collaborative innovation. In particular, the causal relationship between such cluster policies and GTI remains underexplored, as does the mediating role of GTI in improving urban energy efficiency. Existing empirical studies predominantly focus on national or sectoral perspectives (Sueyoshi and Goto, 2018), offering limited insights into how localized industrial interventions shape energy performance in rapidly urbanizing economies (Zhao, 2023).
To fill these gaps, this study treats China’s innovative industrial cluster pilot policy as a quasi-natural experiment and employs a difference-in-differences (DID) approach using panel data from 281 prefecture-level cities between 2006 and 2021. The study investigates how such industrial policies promote urban GTI and, in turn, increase energy efficiency. Methodologically, the study provides robust causal identification by applying a DID model that controls for potential endogeneity and captures the dynamic impacts of policy implementation over time. This allows for a credible evaluation of long-term policy effects on urban sustainability outcomes. Theoretically, this study advances understanding by emphasizing the role of innovative industrial clusters as meso-level policy instruments. Rather than focusing on isolated tools like subsidies or industrial parks, the analysis highlights how clusters integrate talent, capital, and technology to create supportive regional innovation ecosystems conducive to green transformation. Substantively, the article contributes by uncovering the mediating role of GTI in linking industrial policy to urban energy performance. Through mechanism analysis, it demonstrates that cluster-based policies improve energy efficiency primarily by increasing entrepreneurship, innovation talent density, and financial investment in science and technology. Overall, this study bridges industrial policy, green innovation, and urban environmental performance, offering both empirical evidence and theoretical insights for promoting sustainable development in rapidly urbanizing economies. It informs policy design aimed at achieving dual goals of industrial upgrading and ecological sustainability.
2 Literature review
2.1 Research on the factors driving green technological innovation
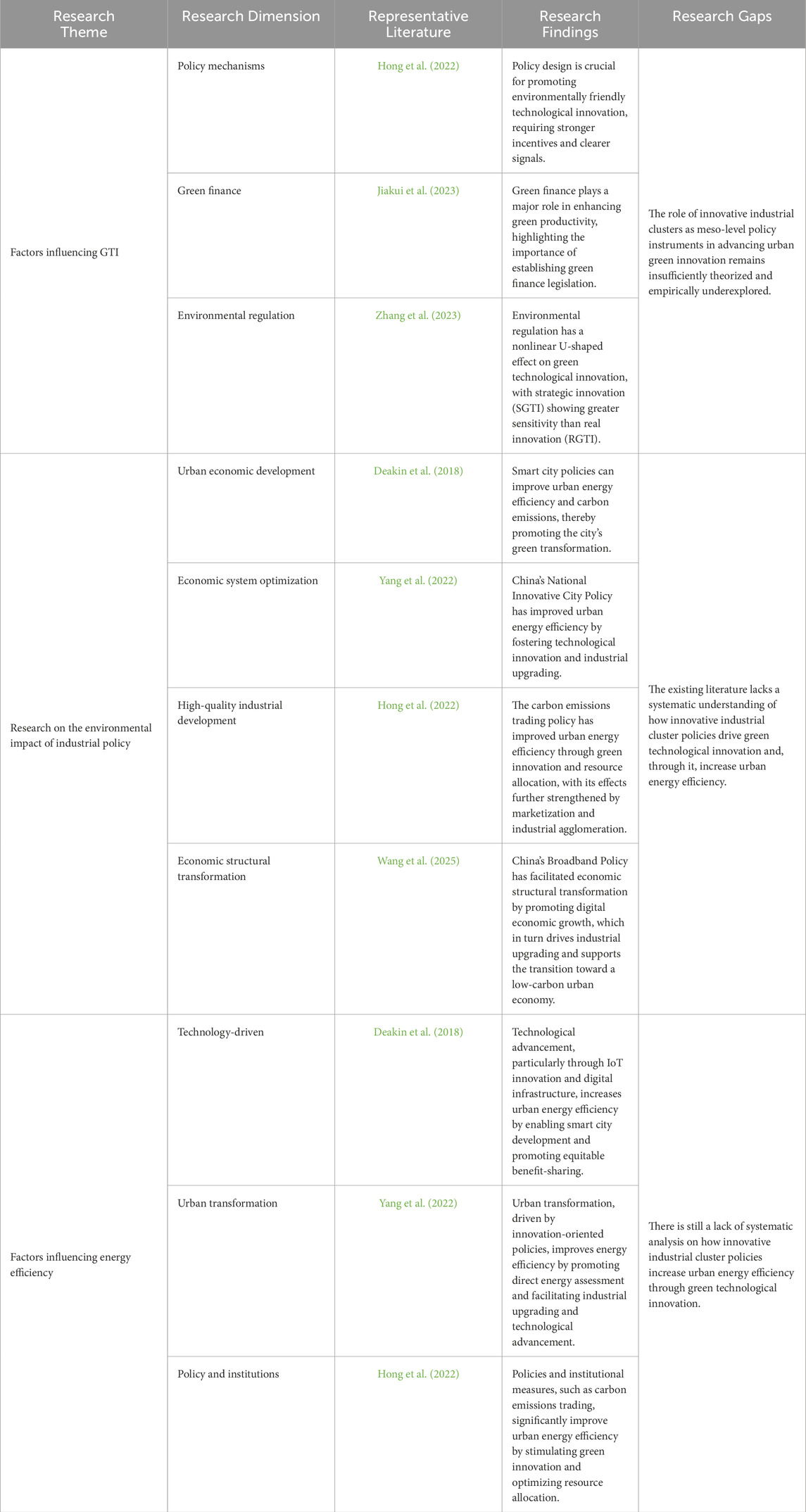
GTI is a critical pathway to achieving sustainable development (Liu M. et al., 2024). Existing studies have extensively explored its driving factors, focusing on policy mechanisms, green finance, and environmental regulation. In terms of policy mechanisms, Norberg-Bohm (1999) emphasized that well-designed policy incentives are essential for promoting environmentally friendly technological innovation, and that clear policy signals and strong incentives can encourage firms to adopt green technologies. Hong et al. (2021) further showed that green credit policies significantly enhance GTI by easing corporate debt financing constraints. Regarding green finance, Jiakui et al. (2023) provided empirical evidence that green finance plays a key role in improving green total-factor productivity and highlighted the need to establish a comprehensive legal framework for green finance. In the field of environmental regulation, Zhang et al. (2023) distinguished between real green technological innovation (RGTI) and strategic green technological innovation (SGTI), finding a U-shaped relationship between environmental regulation and both forms of GTI, with SGTI being more sensitive to regulatory intensity. These studies provide valuable theoretical and empirical insights into the multifaceted drivers of green innovation. However, little attention has been paid to the role of innovative industrial clusters as a meso-level policy instrument for promoting green innovation at the urban level. There is still a lack of systematic analysis on how such clusters facilitate the diffusion of green technologies, enable collaborative innovation, and enhance the allocation of innovation resources.
2.2 Research on the environmental impact of industrial policy
Industrial policy plays an increasingly prominent role in shaping environmental outcomes, particularly as green development becomes a national strategic priority. A growing body of literature has begun to examine the environmental impacts of industrial policy, including its potential to improve urban energy efficiency and promote sustainable industrial transformation. From the perspective of urban economic development, studies such as Deakin et al. (2018) propose smart city frameworks based on the Triple Helix model, highlighting the importance of IoT infrastructure and fair benefit-sharing in driving green transformation beyond conventional goals like energy savings and emissions reduction. In terms of economic system optimization, Yang et al. (2022) evaluated the National Innovative City Policy in China (2005–2017) and found that it improved urban energy efficiency through mechanisms such as innovation promotion and industrial upgrading, thereby enhancing the overall functioning of the urban economic system. Focusing on high-quality industrial development, Hong et al. (2022) employed a DID model to analyze the impact of carbon emissions trading in 276 Chinese cities from 2003 to 2016. Their results suggest that green innovation and improved resource allocation served as key transmission channels for increasing both single-factor and total-factor energy efficiency. Furthermore, they noted that market-oriented reforms and industrial agglomeration significantly amplified the policy effects. From the perspective of economic structural transformation, existing studies suggest that industrial policy can support the shift from resource-intensive to innovation-driven development models; however, the mechanisms linking this transformation to improvements in environmental efficiency remain insufficiently explored. Addressing this gap, Wang et al. (2025) examine how digitalization fosters urban sustainability by analyzing the impact of the digital economy on per capita CO2 emissions across 286 Chinese cities from 2000 to 2023. Their findings show that digital economic growth significantly reduces emissions through increased urban population density and green innovation, with the effects further strengthened by industrial upgrading and partially offset by expanded transportation infrastructure.
Existing research has explored the environmental impacts of industrial policy from multiple perspectives, including urban economic development, system optimization, high-quality industrial growth, and economic structural transformation. While the broader effects of industrial policy are well-documented, the literature has largely overlooked the specific role of innovative industrial cluster policies as a meso-level intervention in this process. In particular, there remains a substantial gap in understanding how such policies causally promote green technological innovation, and how green innovation, in turn, serves as a key transmission mechanism for improving urban energy efficiency.
2.3 Research on the influencing factors of urban energy efficiency
Improving urban energy efficiency is a critical objective for achieving sustainable development and addressing environmental challenges in rapidly urbanizing regions. Enhancing energy efficiency not only reduces resource consumption and carbon emissions but also promotes economic vitality and urban livability. Existing research identifies three main drivers influencing urban energy efficiency improvements: technological progress, urban transformation, and policy frameworks.
From the perspective of technological progress, Deakin et al. (2018) proposed a smart city development theory based on the Triple Helix model, emphasizing the role of regional IoT innovation and digital infrastructure. They highlight that beyond energy savings and emission reductions, equitable benefit-sharing mechanisms are essential for sustainable urban energy transitions. Regarding urban transformation, Yang et al. (2022) analyzed China’s National Innovative City Policy using panel data from 2005 to 2017, finding that the policy improves urban energy efficiency through both direct energy assessment and indirect pathways such as industrial upgrading and innovation. In terms of policy and institutional factors, Hong et al. (2022) applied a difference-in-differences model to evaluate the impact of carbon emissions trading across 276 Chinese cities from 2003 to 2016. Their findings indicate that the carbon trading system significantly increases single-factor and total-factor energy efficiency through stimulating green innovation and optimizing resource allocation, with the effects further amplified by marketization and industrial agglomeration.
However, despite these insights, the role of innovative industrial cluster pilot policies in promoting urban energy efficiency remains underexplored, particularly the key mediating role of green technological innovation. This study aims to fill this gap by deconstructing the mechanism linking industrial cluster policies, green technological innovation, and improvements in energy use efficiency.
In summary, although existing literature provides a solid theoretical foundation for understanding GTI, industrial policy, and urban energy efficiency, substantial research gaps remain. Table 1 summarizes the relevant literature and corresponding research gaps. First, the urban-level impact of industrial policies—particularly those embedded in innovative industrial clusters—has not been systematically explored in the context of GTI. Second, most industrial policy studies focus on economic growth and structural upgrading, with limited attention to their environmental and innovation-oriented outcomes. Third, research on energy efficiency tends to emphasize technological and spatial factors, often overlooking the role of meso-level industrial policy instruments. Notably, few studies have integrated innovative industrial cluster pilot policies, GTI, and energy efficiency within a unified analytical framework. This article aims to bridge these gaps by examining how cluster-based policy interventions influence GTI and, in turn, increase urban energy efficiency. By highlighting the mediating role of GTI and emphasizing the importance of targeted policy support, the study contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of how industrial policy can promote sustainable urban development across economic, social, and environmental dimensions.
3 Policy background and theoretical analysis
3.1 Policy background
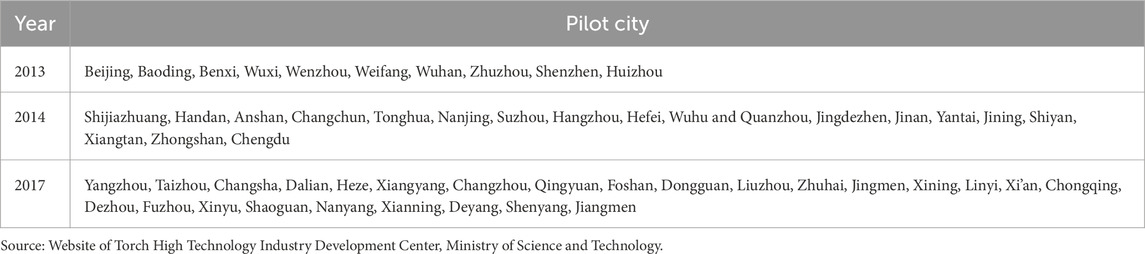
In June 2013, the Ministry of Science and Technology officially released 10 pilot innovative industrial clusters, including the Beijing Zhongguancun mobile Internet industrial cluster, marking that China’s pilot of innovative industrial clusters has entered a new stage. The pilot cities for innovative industrial clusters are listed in Table 2. These innovative industrial clusters were able to obtain financial subsidies and preferential policies from governments that helped to provide technical expertise as well as tax reductions for enterprises in the clusters (Xu and Hu, 2024).
3.2 Theoretical analysis
3.2.1 Direct effect analysis
GTI not only relies on the support of key factors such as human capital, technical resources, and funds but also is profoundly influenced by the regional innovation environment (Wu et al., 2022). Promoting urban GTI is crucial for ensuring energy security and addressing climate change (Du et al., 2019). Originating from Keynesianism in the 1930s, government policy can promote innovation activities both directly and indirectly (Guo et al., 2021). Therefore, implementing the innovative industrial cluster pilot policy helps pilot regions integrate domestic and international resources, foster innovation factor agglomeration, and promote urban development in GTI. On the one hand, innovative industrial clusters have established a science and technology service system that supports the healthy and sustained development of industries. This system integrates research institutions, business incubators, and intellectual property services closely linked to the industrial chain. It has formed standardized mechanisms for cultivation, incubation, and growth, providing strong support for the strategic development of clusters (Liu Y. et al., 2024). Through the agglomeration of innovation resources and elements, enterprises, universities, and research institutions within the cluster can strengthen cooperation and exchange. This collaboration promotes the development of green technology innovation and enhances a city’s GTI capacity (Cheng et al., 2024). On the other hand, a key feature of innovative industrial clusters is the active role of government in organizing, guiding, and regulating cluster development (Wu et al., 2022). This includes a range of policies, measures, and support mechanisms that encourage cooperation among enterprises, research institutions, and service providers along the industrial chain. These efforts reflect not only the government’s involvement but also the operation of a multi-sector coordination mechanism. Government interventions—such as capital support, tax incentives, talent recruitment, and targeted measures—create a favorable policy environment. They provide essential resources that support green technology R&D and innovation, directly promoting urban GTI development.
Based on the above analysis, this article puts forward the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1. The innovative industrial cluster pilot policy has a positive role in promoting urban green technology innovation and promoting urban sustainable development.
3.2.2 Mechanism analysis
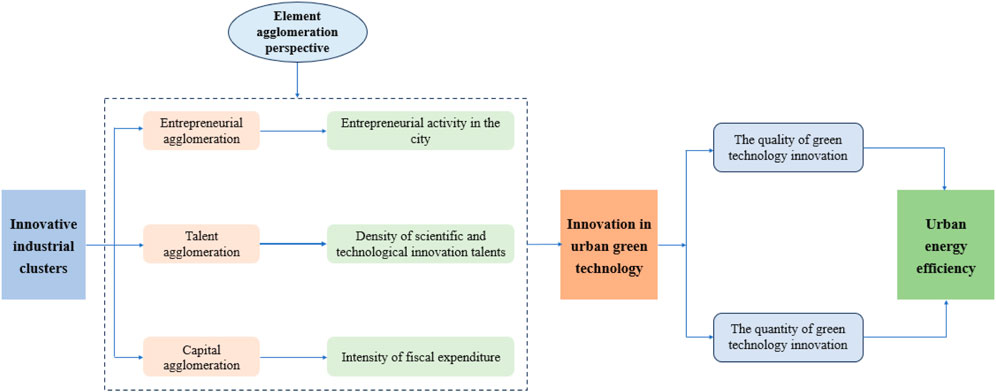
From the perspective of innovation elements, human capital, technology, and capital are essential resources for green innovation (Molden and Clausen, 2021). A higher level of innovation factor agglomeration is more conducive to promoting green R&D and improving the green innovation system. This article examines how the pilot policy for innovative industrial clusters promotes urban GTI and supports sustainable development through three key channels: urban entrepreneurial activity, the density of sci-tech innovation talent, and capital investment in science and technology.
3.2.2.1 Urban entrepreneurial activity
Entrepreneurial activity is a key indicator of a region’s entrepreneurial vitality and is widely recognized in entrepreneurship research (Cullen et al., 2014). Schumpeter (1934) described entrepreneurship as a process of “creative destruction,” where entrepreneurs innovate by combining resources in new ways. Innovation is thus a core feature of entrepreneurship. However, entrepreneurs often face resource constraints and limited capabilities. According to the knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship, innovative industrial clusters can serve as important sources of entrepreneurial opportunities (Acs et al., 2013). Incumbent firms typically retain innovations aligned with their strategies, while other knowledge is released into the public domain through spillovers. These spillovers provide high-potential opportunities for entrepreneurs to explore green innovation (Agarwal et al., 2004; Audretsch and Keilbach, 2007).
Moreover, the implementation of innovative industrial cluster pilot policies can reduce barriers to entrepreneurship through supportive measures, including funding, tax incentives, and infrastructure. These policies also help integrate key entrepreneurial resources, such as incubators, venture capital, and mentoring networks, providing an enabling environment for green startups (Sun et al., 2025). For example, the creative industry cluster in the Yangtze River Delta, with strong manufacturing agglomeration, has spurred the growth of green-oriented ventures. Under the dual-carbon goal, rising demand for eco-friendly products has driven these startups to focus on green technology R&D and market deployment. This market-driven dynamic forms a virtuous cycle of green innovation, contributing to urban GTI and sustainable development.
Overall, creative industry clusters play an important role in promoting entrepreneurial activity by continuously stimulating entrepreneurs’ innovation and enthusiasm through knowledge spillovers, policy support, and resource integration.
3.2.2.2 The density of scientific and technological innovation talent
Talent is the strategic core resource for innovation and development (Rosokhata et al., 2020). In order to carry out scientific research continuously, innovative industrial clusters need more sci-tech talent to form scientific research teams. On the one hand, local governments generally attract talent through talent introduction policies and talent incentive mechanisms to build a talent team. The inflow of science and technology talent can provide a strong supplement for local innovation factors, thus optimizing the structure of local innovation factors (Audretsch and Feldman, 1996). For example, the Foshan High-tech Zone has promoted industrial structure to optimize and upgrade by attracting high-end talent, among which introducing high-tech industrialization and entrepreneurship teams is a key link. The local government has actively built a “talent dividend” to achieve a positive interaction between talent and industry. Talent drives industrial development, and that industry attracts more talent (Porter, 1998). On the other hand, scientific and technological talent is an important factor to measure the knowledge absorption capacity of a region (Zucker et al., 1994). In the high-tech industry, they play an irreplaceable role in identifying, acquiring, transforming, and innovatively applying technology and knowledge. Enterprises, universities, and research institutions within innovative industrial clusters form close innovation networks, offering diverse opportunities for exchange and collaboration. These networks help stimulate the innovation spirit and creativity of scientific and technological talent (Etzkowitz and Leydesdorff, 2000; Faggian and McCann, 2009).
In conclusion, implementing the pilot policy effectively promotes the convergence of sci-tech talent. Regions with abundant talent resources are more likely to drive innovation and support the sustained growth of technology- and knowledge-intensive industries. This, in turn, facilitates the upgrading of innovative industrial clusters and enhances their overall competitiveness. Moreover, the talent pool provides essential support for cities to achieve GTI. Through knowledge and technology spillovers, innovative talent helps upgrade technical equipment, phase out outdated production capacity, and improve both enterprise productivity and technological strength.
3.2.2.3 Intensity of financial investment in science and technology
The Ministry of Science and Technology provides both policy guidance and financial support to facilitate the identification and cultivation of pilot clusters through the Management Measures for Innovative Industrial Cluster Pilots framework. This policy framework promotes the rapid circulation and optimized allocation of key economic resources such as talent, technology, and capital, thereby laying a solid foundation for regional innovation development (Xu and Hu, 2024). To enhance regional innovation capacity, the government increases fiscal expenditure on science and technology by actively mobilizing social capital and coordinating public–private resources. For example, in Suzhou Industrial Park, government-backed guidance funds have successfully attracted private venture capital, boosting early-stage investment in green and high-tech startups. Local governments further reinforce this effort by improving the design of venture capital and angel investment mechanisms, encouraging capital inflows into innovative enterprises. These measures not only reduce financing constraints for startups but also stimulate the commercialization of green technologies, supporting the broader goal of sustainable urban innovation.
In particular, under the guidance of the pilot policy, the structure of government investment in science and technology is becoming more targeted and efficient. Fiscal resources are now strategically allocated according to regional industrial priorities and evolving innovation trends, with an increasing focus on green R&D. Priority is given to key areas that align with sustainable development goals, including renewable energy, green manufacturing, and low-carbon technologies. For example, in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, local governments have established dedicated green innovation funds to support enterprises engaging in photovoltaic, hydrogen energy, and smart grid technologies. These targeted investments not only accelerate the commercialization of green technologies but also help reduce regional carbon emissions and industrial energy intensity. Furthermore, by strengthening project management, adopting performance-based fund allocation, and promoting third-party evaluation mechanisms, the government improves the effectiveness of sci-tech funding. These efforts ensure that public investment delivers both economic returns—such as industrial upgrading—and environmental benefits, including cleaner production and improved urban sustainability (Bozeman and Corley, 2004; Zhang et al., 2023).
Implementing the pilot policy encourages governments to increase policy support and scientific research funding, strengthen linkages among innovation actors, and promote collaborative networks and technology transfer. These measures help high-pollution and high-consumption enterprises upgrade and transform, thereby fostering urban green transformation and sustainable development.
Hypothesis 2. The pilot innovative industrial cluster policy contributes to urban GTI and urban sustainable development through promoting urban entrepreneurial activity, increasing sci-tech innovation talent density, and strengthening financial investment intensity in sci-tech.
The study’s theoretical framework is illustrated in Figure 1.
4 Research design
4.1 Model setting
4.1.1 Benchmark regression model
With the help of the DID model, this article aims to control the time and individual differences of the research objects before and after the implementation of the innovative industrial cluster pilot policy (Li et al., 2021) Therefore, in this study, the cities implementing the innovative industrial clusters pilot policy are set as the treatment group, and the other cities are set as the control group. Equation 1 presents the benchmark regression model
Among them,
4.1.2 Role mechanism test
This article will further investigate the specific mechanism of action, mainly from the perspective of innovation agglomeration, talent agglomeration, and capital agglomeration, the three paths of action for an empirical test. Equation 2 illustrates the mechanism analysis model.
Media represent the mechanism variables, including urban entrepreneurial activity, sci-tech innovation talent density, and financial investment intensity in sci-tech.
4.2 Variable selection
4.2.1 Explained variables
In this article, the number of green patent applications is used as a measure of urban GTI. Referring to the method described by Li et al. (2023), this research uses the number of green invention patent applications to measure the substantive GTI, namely, the quality of GTI (gti1). The quantity of green utility model patent applications serves as an indicator of the quantity of strategic GTI (gti2). Substantive green technology innovation promotes technological progress, which belongs to high-level technological innovation and focuses on quality (Liang et al., 2025). Strategic green innovation refers to utility model patents, which have relatively lower technical content and usually do not lead to substantial technological advancements (Liu M. et al., 2024).
4.2.2 Explanatory variables
The innovative industrial clusters pilot policy is regarded as a dummy variable (
4.2.3 Mechanism variables
Based on previous theoretical analysis, the innovative industrial clusters pilot policy may have a mechanism impact on urban GTI. Among them, urban entrepreneurial activity(Eship) refers to the research practice of Zhang et al. (2024), using the number of new enterprises per 100 people as the measurement index of entrepreneurial activity. The density of scientific and technological innovation talent (Techhum) refers to the research practice of Tao et al. (2022) and Khin and Ho (2019), using the density of scientific and technological innovation talent, using the proportion of information transmission, software, and information technology in the total number of employees of the city (%) to measure the talent resources of scientific and technological innovation. The intensity of financial investment in science and technology (Fintech) is measured by the proportion of science and technology expenditure in local fiscal expenditure (%) by referring to the research practice of Zhang et al. (2025).
4.2.4 Control variables
Referring to existing literature and the specific questions of this study (Liu Y. et al., 2024; Xu and Hu, 2024), this article selects the following control variables: 1. Financial development (Fin), which is represented by the ratio of financial industry added value to GDP. 2. The level of opening to the outside world (Open) is represented by the ratio of total import and export volume to GDP. 3. The level of urban industrialization (Industry) is measured by the ratio of industrial added value to GDP (%). 4. Economic development level (LnPgdp) is denoted by the logarithm of per capita gdp.
4.3 Data sources
In view of the accessibility and completeness of data, the final sample selects 281 prefecture-level cities from 2006 to 2021, including 55 innovative industrial cluster pilot cities. The data sources are as follows: first, pilot data are from the Torch Center of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China. The second is the green patent data from the State Intellectual Property Office of China. Third, city-level data of other characteristic indicators are taken from the National Bureau of Statistics of China and statistical yearbooks over the years. The missing data are imputed using the mean value method. Cities with a large amount of missing data, such as Laiwu, Chaohu, Tongren, and Lhasa, were deleted.
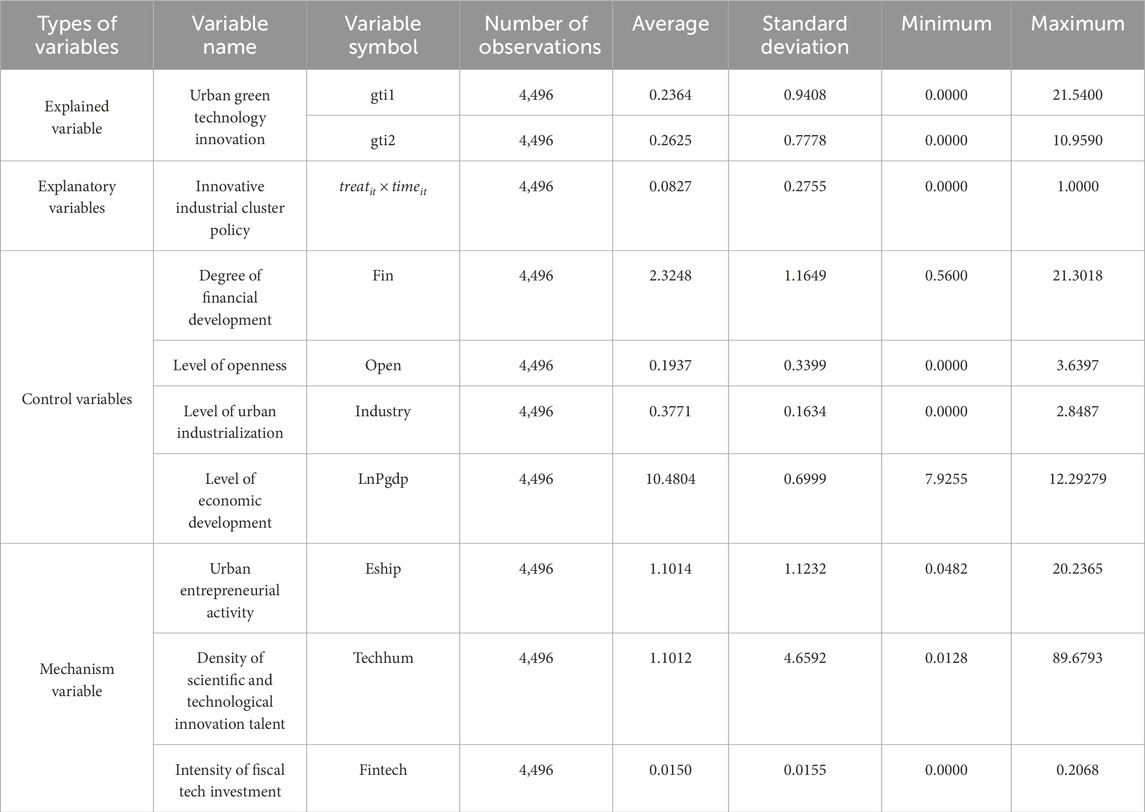
4.4 Descriptive statistics
Table 3 presents the descriptive statistics of the main variables in this study. The values of urban green technology innovation exhibit a wide range between the minimum and maximum, indicating an uneven development of green technology innovation activities across Chinese cities. The average value of the innovative industrial cluster policy is 0.0827, meaning that 8.27% of the samples in this study belong to the treatment group, which suggests that China's industrial cluster policy is still in an emerging stage of development.
5 Empirical results and analyses
5.1 Benchmark regression
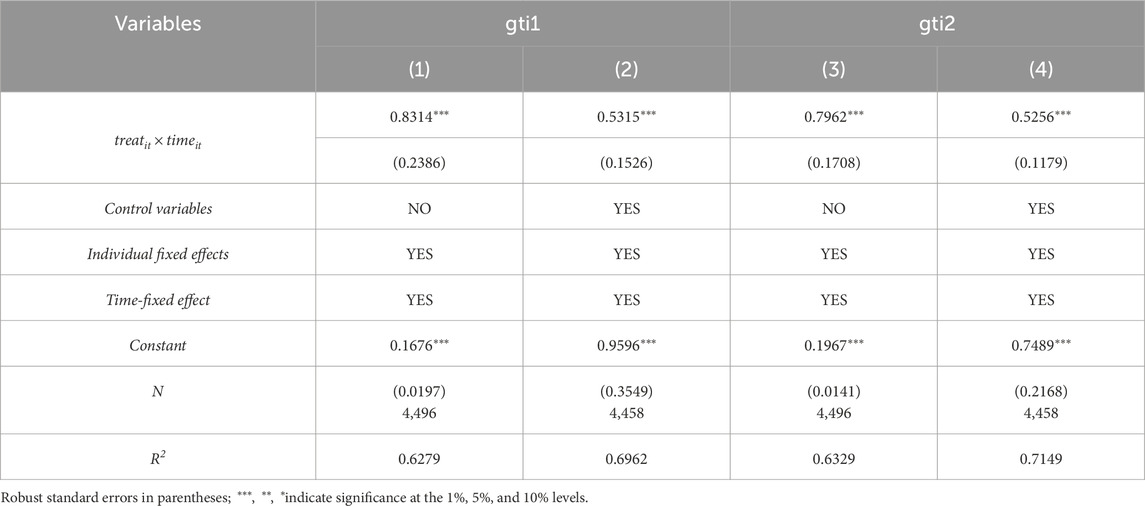
Table 4 presents the baseline regression outcomes, where the explanatory variable’s coefficient,
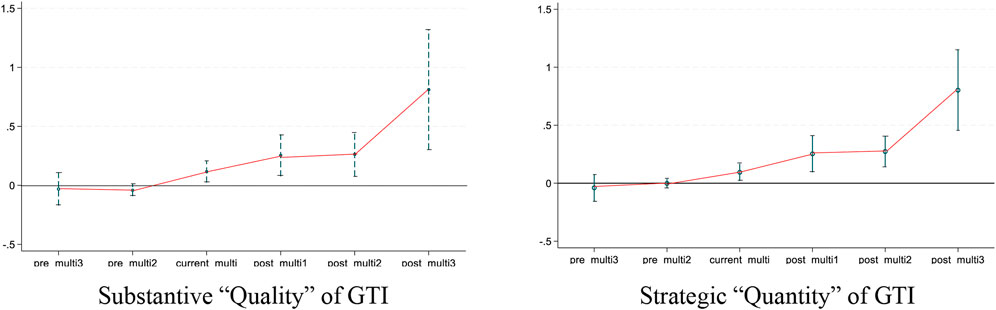
5.2 Parallel trend and dynamic effect test
This study uses the event analysis method to test whether the hypothesis of parallel trend is met before implementing the policy. That the experimental group and the control group meet the parallel trend hypothesis is an important prerequisite for applying the DID model; otherwise, the difference after implementing the policy may be caused by other differences. In this study, there should be no substantial difference in green technology innovation between the two groups of cities before the policy implementation, indicating that the experimental group and control group meet the parallel trend hypothesis. To further examine dynamic effects, this study selects the year before policy implementation as the base period. The study uses the interaction term between dummy variables of 3 years before and after policy implementation and the treatment variable
5.3 Robustness test
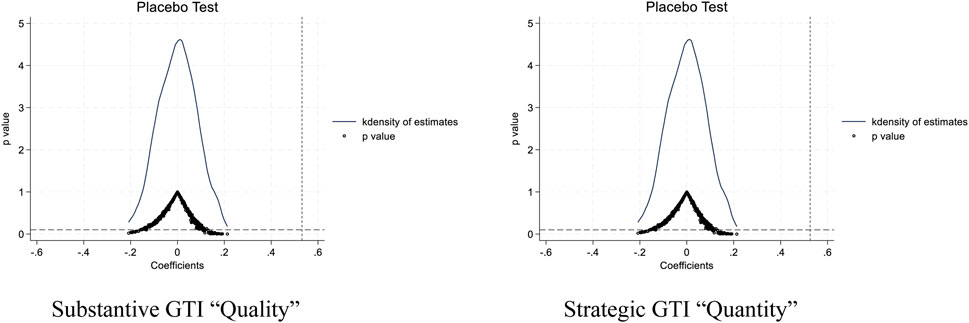
5.3.1 Placebo test
Aiming to eliminate other unobserved factors’ potential influence, this article adopts the method of independent repeated test, and randomly selects the cities implementing the pilot policy in the sample with the same number of treatment groups as in the benchmark regression as the pseudo-experimental group. Then, in the light of Formula 1, the pseudo-experimental group was regressed repeatedly 500 times, and the pseudo-experimental group variables’ estimated coefficient and P value distribution were obtained, as presented in Figure 3. The results indicate that the estimated coefficients for both the quality and quantity of urban GTI are concentrated around 0, following a normal distribution. This excludes potential interference from unobservable factors in the regression results.
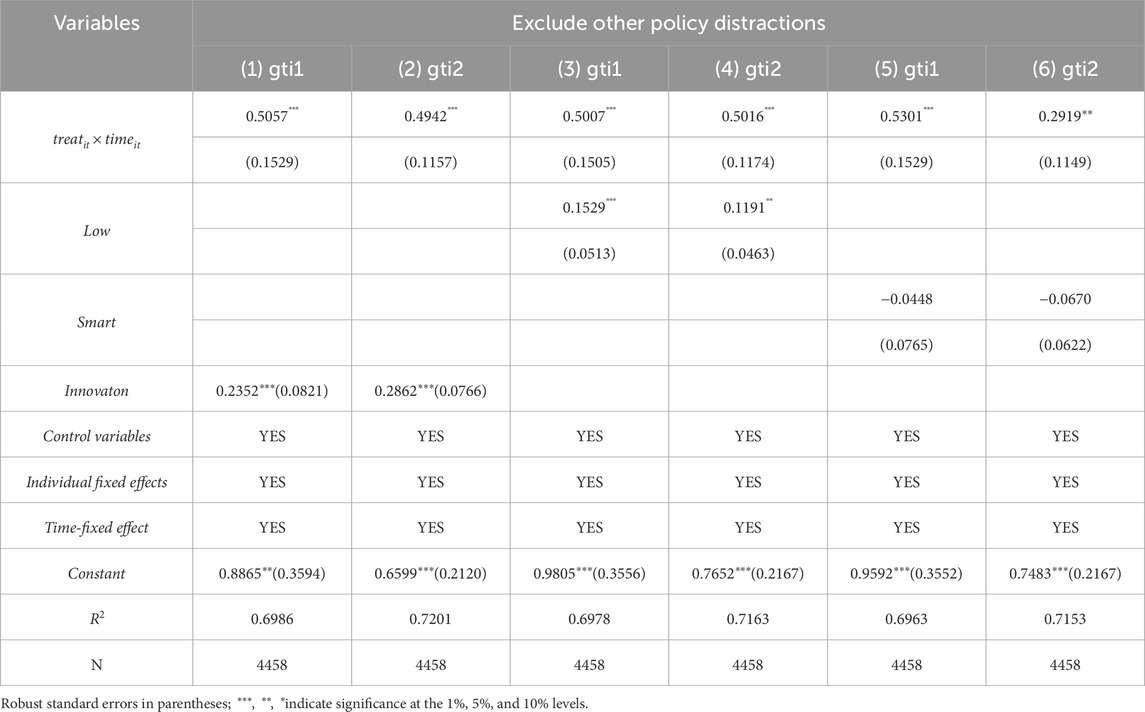
5.3.2 Exclusion of other policy disturbances
To avoid interference caused by the superposition effect of other policies on urban GTI during the pilot policy implementation, this article introduces dummy variables for the low-carbon city pilot policy (Low), the smart city pilot policy (Smart), and the innovation-driven policy (Innovation) into the benchmark regression model, respectively. The regression results in columns (1)–(6) of Table 5 demonstrate that the estimated coefficient remains positive and significant at the 1% level, indicating robust policy effects.
5.3.3 Replace explained variables
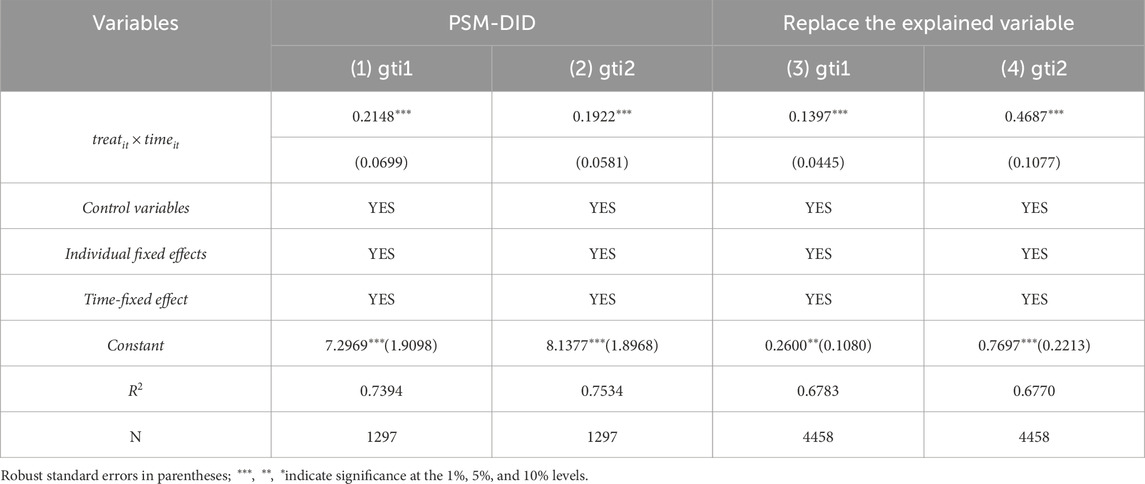
In the robustness test, the article uses the number of green invention patent authorizations to represent GTI’s quality substantively, and the number of green utility patent authorizations to represent its quantity. A subsequent regression analysis was performed, with the results presented in columns (3) and (4) of Table 6. The estimated coefficient remains robustly positive at the 1% significance level, closely mirroring benchmark regression outcomes.
5.3.4 Propensity score matching (PSM-DID)
Local pilot policies serve as a unique model of policy innovation and governance in China. In the sample of 281 cities in this study, the treatment group and the control group meet the common trend assumption, but obviously, selecting pilot policies for innovative industrial clusters is not a completely random process, potentially introducing sample selection bias. To further verify benchmark regression results’ robustness, this article further introduces the propensity score matching-difference-in-differences (PSM-DID) method based on the benchmark regression for robustness test. Specifically, the Logit model and 1:1 nearest neighbor matching within 0.01 calipers are used to select financial development degree, urban industrialization level, industrial structure optimization, population density, and so on as matching variables. The propensity matching score is obtained through Logit regression estimation, and the city with the most similar score to the treatment group is used as the control group. The regression results after propensity score matching (PSM) processing are detailed in columns (1) and (2) of Table 6, consistent with the benchmark regression results, further verifying the robustness of the conclusions.
5.4 Heterogeneity analysis
5.4.1 Heterogeneity of urban location
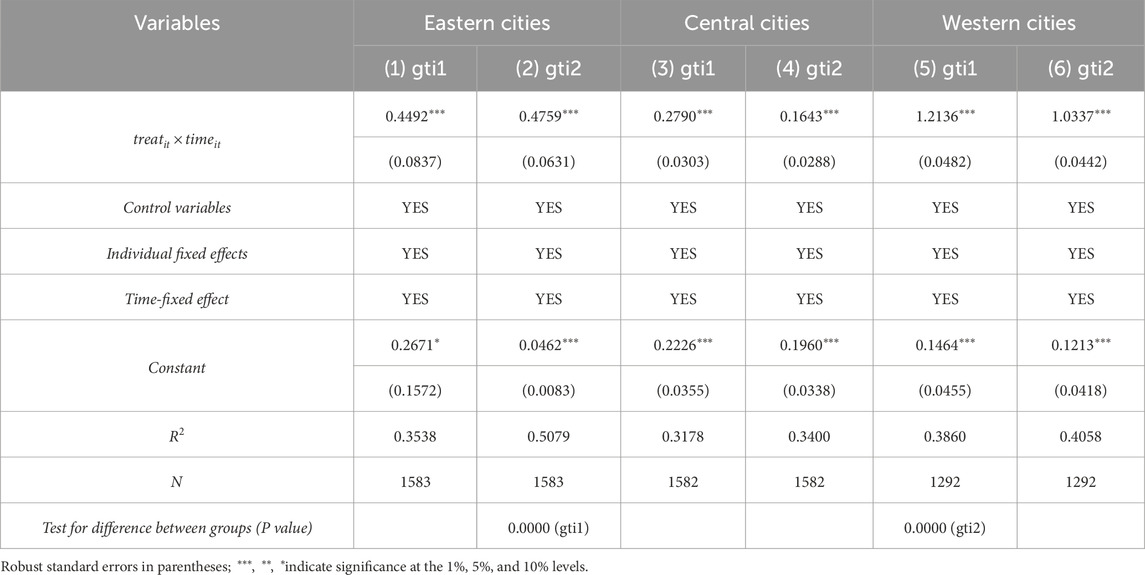
There are substantial regional differences in the development of innovative industrial clusters and urban GTI. Columns (1)–(6) of Table 7 report regression results by region, dividing the sample into eastern, central, and western areas. The estimated coefficients for the pilot policy’s impact on GTI are significantly positive across all three regions, suggesting the policy has nationwide benefits. However, the effect size varies, and Chow test results confirm statistically significant differences between groups.
The pilot policy demonstrates a more pronounced effect in the eastern and western regions. In the western region, this may be attributed to stronger policy preferences and targeted support mechanisms. To compensate for structural disadvantages such as inadequate infrastructure and weak innovation ecosystems, the central government has directed substantial resources—financial subsidies, tax incentives, talent attraction policies, and preferential access to national science and technology projects—to the western provinces. These incentives enhance the region’s capacity to absorb and utilize innovation resources, thereby accelerating the formation and upgrading of green innovation clusters.
In contrast, the eastern region benefits from its mature market economy, advanced industrial base, and well-established innovation systems. The presence of leading enterprises, high-level universities, and abundant venture capital contributes to both the quality and scale of GTI. Local governments in the east also tend to have more fiscal autonomy and stronger administrative capacity to implement the pilot policy effectively.
However, the central region lags. Its relatively weak economic foundation, limited access to innovation resources, and lower policy intensity hinder the development of green innovation. Compared with the western region, which receives more direct national policy support, the central region lacks sufficient targeted interventions. As a result, both the input and output levels of GTI in the central region remain modest.
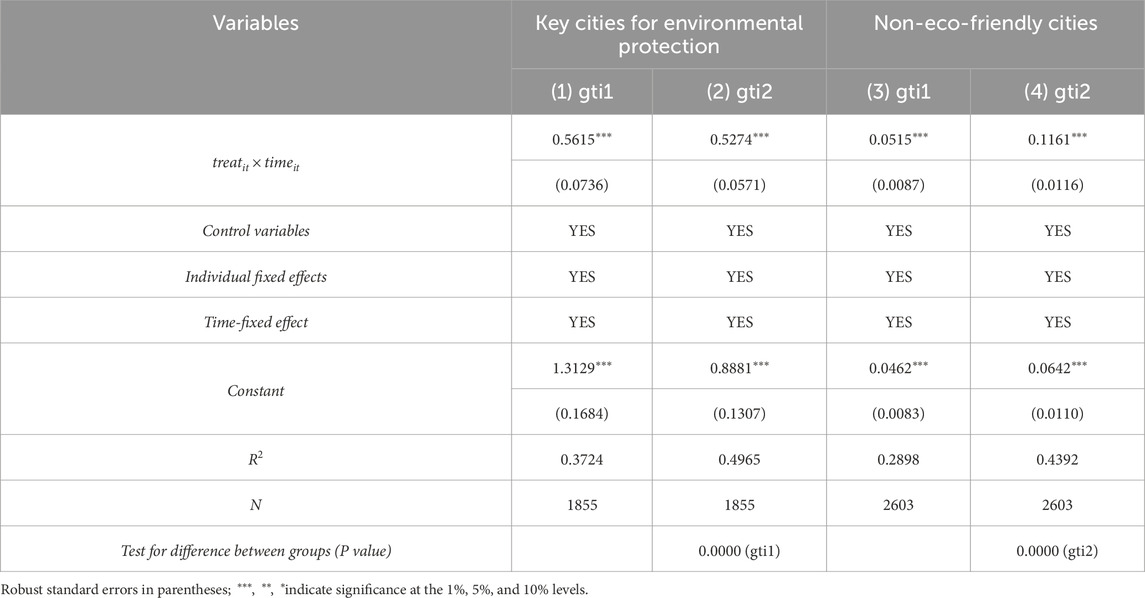
5.4.2 Heterogeneity of government attention to environmental protection
Urban environmental concern exhibits heterogeneity, reflecting substantial differences among cities in how they address ecological issues and pursue sustainable development. Based on China’s “11th Five-Year Plan for Environmental Protection,” cities are categorized into key environmental protection cities and non-key cities for regression analysis. As shown in Table 8, Columns (1)–(4), the estimated coefficients demonstrate that the innovative industrial cluster pilot policy exerts a significantly stronger positive effect on GTI in key environmental protection cities. The Chow test further confirms the statistical significance of the difference between these two groups. This disparity is largely because key cities—especially those in ecologically sensitive or heavily industrialized regions—are subject to stricter environmental regulations, more frequent audits, and higher emission standards. For instance, in the western region, cities such as Lanzhou and Xi’an have implemented local regulations aligned with national ecological red lines, intensifying environmental governance pressure and creating strong demand for green technologies.
Moreover, key cities often receive prioritized support from central and local governments, including preferential access to fiscal transfers, project approvals, and green infrastructure investment. The pilot policies for innovative industrial clusters in these cities are more tightly aligned with sustainability goals, promoting renewable energy, low-carbon industrial technologies, and pollution control. Chongqing Liangjiang New Area, for example, has integrated the cluster pilot with its smart low-carbon urban development strategy, actively developing hydrogen energy, green data centers, and circular economy parks. These bundled policy instruments—ranging from green finance and carbon market pilots to incubator programs—create a favorable environment for GTI. In contrast, non-key cities often face weaker regulatory pressure and receive less focused support, leading to lower levels of innovation input and output. Without robust institutional incentives and dedicated resources, their ability to translate pilot policy into green innovation outcomes remains limited.
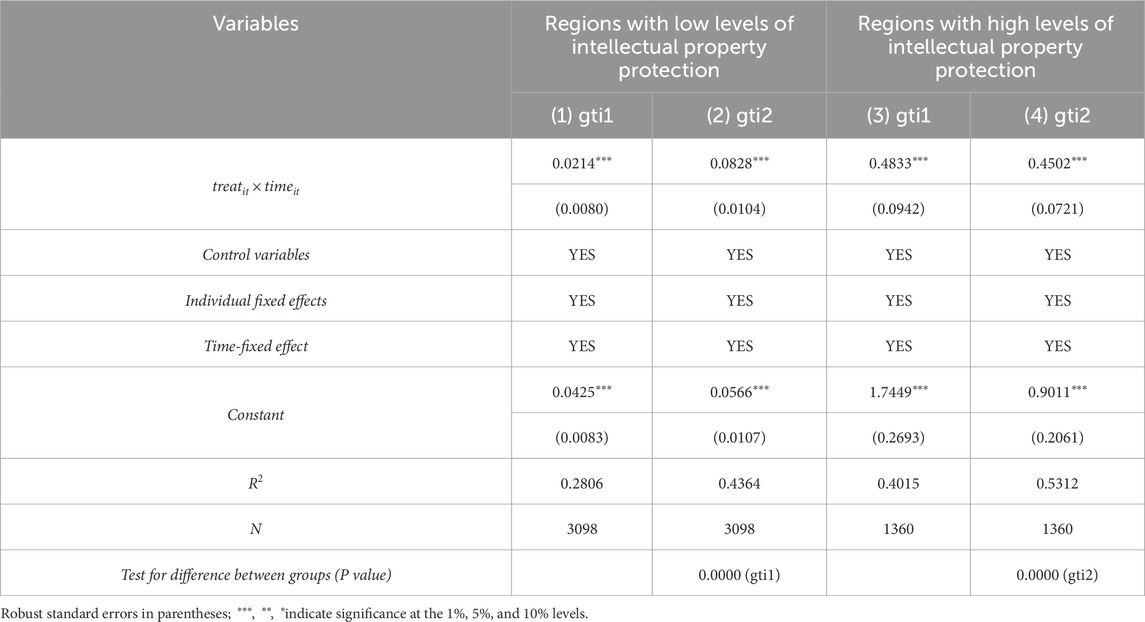
5.4.3 Heterogeneity of IPP level
The article refers to the IPP measurement method described by Shen and Huang (2019) and uses urban GDP for descaling. Meanwhile, to compare intellectual property protection intensity at the city level, the explicit comparative advantage index (RCA) was used as a reference.
Among them,
Based on the degree of intellectual property rights (IPR) protection, cities are categorized into high-protection and low-protection groups using the sample mean as the threshold. Regression analyses are then conducted separately for the two groups, with the results presented in Table 9, Columns (1) to (4). All estimated coefficients are positive and statistically significant, indicating that the pilot policy for innovative industrial clusters has a favorable effect on GTI across both groups. The Chow test confirms that the differences between the high and low IPR protection groups are statistically significant, suggesting that the policy’s impact on improving the quality and quantity of GTI is more pronounced in regions with stronger IPR protection.
This result can be attributed to several factors. First, in regions with robust IPR protection, innovators’ rights are more effectively safeguarded, which significantly reduces the risk of intellectual property infringement. This legal assurance encourages greater investment in innovation activities, as firms and researchers are more confident that they can reap the rewards of their efforts. In such environments, innovators are more likely to commercialize their technologies through patent licensing and technology transfer, promoting a virtuous cycle of innovation and diffusion that accelerates GTI. Second, regions with high IPR protection typically possess well-developed intellectual property service infrastructures, including patent agencies, legal advisory services, and technology asset valuation systems. These services not only help reduce the transaction costs of innovation but also facilitate the rapid transformation of R&D outputs into marketable green technologies, thereby strengthening the link between innovation and sustainable development.
6 Mechanism test
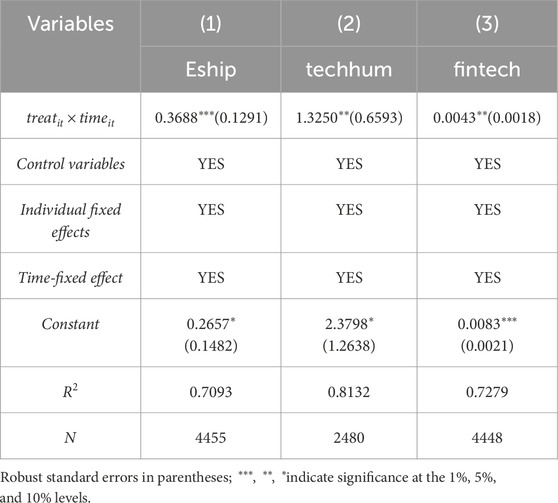
Column (1) of Table 10 reports that pilot policies significantly boost urban entrepreneurial activity, with an estimated coefficient of 0.3688, significant at 1% level, indicating that these pilot policies have significantly promoted urban entrepreneurial activity. Results reveal that the pilot policy provides entrepreneurs with broader development space and opportunities by optimizing the entrepreneurial environment and promoting the integration of resources. Meanwhile, the policy also guides entrepreneurs to attach more importance to the green and sustainable development mode, injecting new vitality into the city’s sustainable growth.
Column (2) of Table 10 reports that the pilot policy significantly increases sci-tech innovation talent density, with an estimated coefficient of 1.3250, significant at 5%, indicating that the pilot policy effectively increases sci-tech innovation talent. Implementing the policy can better promote sci-tech talent agglomeration, driving the continuous upgrading of innovative industrial clusters and enhancing their overall competitiveness. Additionally, the policy also provides a solid talent support and technology foundation for urban green innovation, fostering ongoing advancements in green technology and promoting the city’s sustainable development.
Column (3) of Table 10 demonstrates that the pilot policy significantly increases fiscal investment in sci-tech, with an estimated coefficient of 0.0043, significant at 1%. This indicates that the policy encourages stronger government support and increased financial investment in research, fostering collaboration among innovation entities. It catalyzes enterprises to embark on pioneering technological innovation in critical domains like energy conservation, emission reduction, clean energy, and eco-friendly materials, thereby improving R&D efficiency and green technology commercialization rates. Consequently, Hypothesis 2 is unequivocally substantiated.
7 Further analysis
7.1 Analysis of the impact of innovative industrial cluster pilot policy on energy efficiency
Drawing on the research of Tang et al. (2023), this article uses an undirected super efficiency SBM model that includes unexpected outputs and uses Dearun Tools software to calculate the green total-factor energy efficiency under the assumption of constant returns to scale to represent the energy utilization efficiency (eff) of each city. In the selection of variables, labor, capital, and energy are used as input factors. Each city’s GDP is regarded as the expected output, while industrial sulfur dioxide, soot, and wastewater emissions are considered as unexpected output. Control variables include the level of financial development, high-level urban industrialization level, and industrial structure (ais) with the added value of the third industry and measured by the ratio of the added value of the second industry (Zhang et al., 2019), population density (lndensity), with urban population and urban administrative area of the measured values of the ratio of the land area (Baur et al., 2014).
Table 11 presents the empirical test results of how the pilot policy for innovative industrial clusters impacts urban energy efficiency. To address potential endogeneity issues, we used a mixed OLS model, a panel two-way fixed effect model, and a multi-dimensional panel fixed effect model for regression analysis. Results are shown in columns (1), (2), and (3) of Table 11, with an estimated coefficient of 0.0366, significant at 1%. This indicates that the pilot policy positively promotes urban energy efficiency, with robust results confirmed by tests such as the parallel trend test and the placebo test. The pilot policy for innovative industrial clusters likely boosts urban energy efficiency by guiding the development of high-tech and strategic emerging industries, which tend to have higher energy efficiency and lower energy consumption. This contributes to optimizing the city’s industrial structure. Additionally, innovative industrial cluster pilot policy encourages enterprises to increase R&D investment, fostering technological innovation that increases energy use efficiency and drives continuous advancements in energy technology, thereby strongly supporting overall improvements in urban energy efficiency.
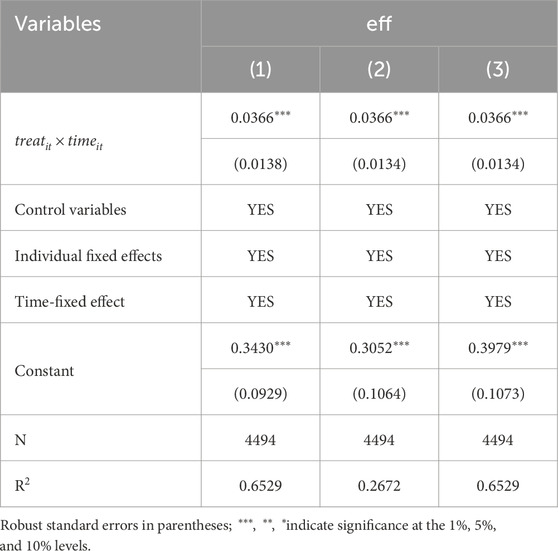
Table 11. Empirical test of the energy utilization efficiency of the innovative industrial cluster pilot.
7.2 Mechanism analysis of urban green technology innovation
The article selects empirical GTI and strategic GTI as mechanism variables to analyze more deeply how innovative industrial cluster pilot policies impact urban energy utilization efficiency. The mechanism analysis results are shown in Table 12. The coefficients of
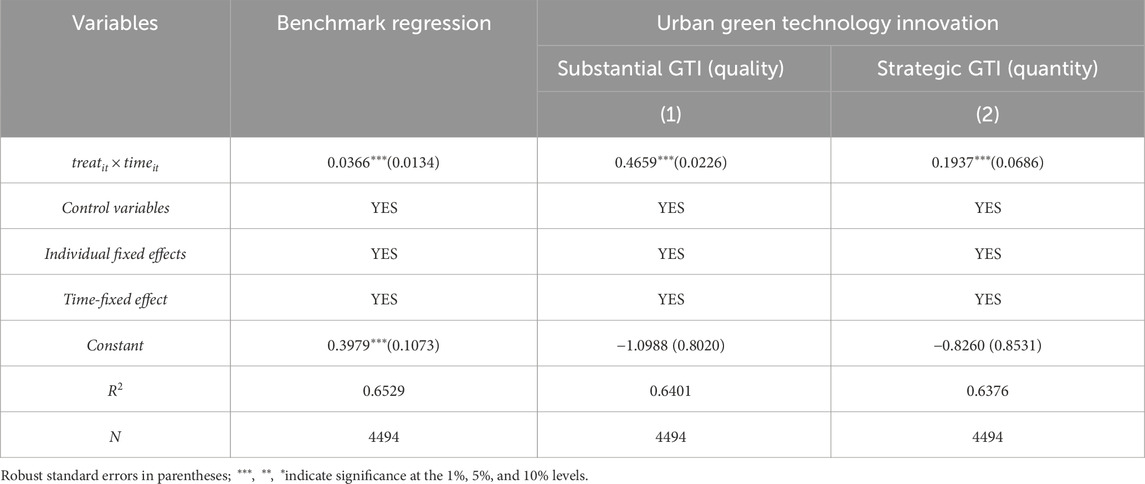
Table 12. Mechanism test of the energy utilization efficiency of the innovative industrial cluster pilot.
Therefore, the quality and quantity of urban green technology innovation are crucial for improving urban energy utilization efficiency under the pilot policies for innovative industrial clusters. By strengthening research and application, fostering industrial agglomeration and synergistic effects, and under policy guidance and support measures, cities can continuously improve energy efficiency and promote sustainable development.
8 Discussion
8.1 Theoretical and empirical implications
The empirical findings of this study provide strong evidence for the pivotal role of China’s innovative industrial cluster pilot policy in promoting urban GTI and increasing energy efficiency. Robustness checks confirm that targeted industrial policies can function as effective meso-level instruments. They not only stimulate innovation but also translate technological advances into measurable environmental outcomes. This extends prior research on the importance of policy design and institutional support in fostering green innovation ecosystems (Norberg-Bohm, 1999; Jiakui et al., 2023). The results underscore the multiple pathways through which innovation can mediate environmental performance.
Placing these findings in an international context highlights their broader relevance. China’s cluster policy shows parallels with South Korea’s heavy and chemical industry strategy, demonstrating how coordinated institutional frameworks and innovation-driven upgrading can generate competitive advantages and structural economic transformation (Lane, 2025). Similarly, evidence from the European Union and OECD countries indicates that integrated policies—combining market mechanisms, institutional robustness, and strong intellectual property regimes—are critical for advancing energy efficiency and green growth (Deakin et al., 2018; Hong et al., 2022). Together, these comparisons reinforce the view that supportive institutional environments are essential to maximize the impact of industrial innovation policies.
Experiences from other developing countries provide important comparative insights into the role of institutional design and policy frameworks in shaping green industrial transformation. In Ethiopia, weak institutional capacity and limited implementation often undermine the effectiveness of green industrial policies, contrasting with China’s stronger institutional coordination (Shen et al., 2023). India illustrates a different pathway, where state-organized financing with minimal fiscal expenditure has enabled a rapid scale-up of solar deployment. This model differs from China’s more fiscally expansive, state-driven investment approach, which has more effectively fostered technological upgrading and industrial clustering (Larsen, 2025). Brazil, India, and South Africa, as second movers in electromobility, benefit from lower technological risks but face fiercer global competition, unlike China’s early and state-driven experimentation that shaped EV development under high uncertainty (Lema et al., 2024). Brazil’s policy orientation toward biofuels and emerging green hydrogen pathways also reflects a distinct strategy, but fragmented governance and limited emissions reduction stand in sharp contrast to China’s large-scale industrial cluster strategy, which more successfully integrates innovation with environmental outcomes (Dos Santos Martins et al., 2024). Taken together, these comparisons highlight that while local institutional quality, financial capacity, and industrial legacies condition policy effectiveness, the fundamental mechanisms linking industrial policy, innovation, and environmental sustainability remain broadly applicable. Accordingly, China’s experience not only deepens theoretical understanding of meso-level policy design but also offers transferable lessons for both developed and developing countries seeking to advance sustainable industrial transformation.
8.2 Policy implications
Several policy recommendations can be drawn based on the empirical findings to maximize the effectiveness of China’s innovative industrial cluster pilot policy in promoting GTI and energy efficiency. First, targeted fiscal and institutional support is essential to promote GTI, especially in ecologically fragile or industrially transforming regions. Measures such as dedicated R&D funds, tax incentives, preferential green financing, and institutional innovations like R&D centers and technology incubators can accelerate green technology commercialization. This approach offers a transferable lesson for other developing and emerging economies facing similar resource constraints.
Second, robust intellectual property (IP) protection enhances the effectiveness of innovation policies. Strengthening legal frameworks, establishing IP courts or mediation centers, expanding legal aid, and supporting subject matter experts (SMEs) through training and integrated IP service platforms can help ensure that technological advances translate into market outcomes. Globally, regions with weak innovation systems can apply these insights to improve green innovation performance.
Finally, aligning industrial cluster strategies with local comparative advantages and fostering collaborative innovation ecosystems can maximize policy impact. Strategic planning, supply chain coordination, and technology matchmaking, together with public–private partnerships and university–enterprise–research collaboration, create synergies that enhance both GTI and sustainability. These principles offer actionable guidance for policymakers in developed and developing countries seeking to leverage industrial clusters for sustainable urban development.
9 Conclusion
9.1 Research conclusion
This study provides both theoretical and empirical insights into the role of China’s innovative industrial cluster pilot policy in advancing urban GTI and energy efficiency. The results indicate, first, that the policy exerts a sustained positive effect on urban GTI, which remains consistent after a range of robustness checks, including parallel trend assessments and endogeneity treatments. Second, the heterogeneity analysis suggests that the policy effect is more evident in the eastern and western regions, in cities with stronger environmental protection orientations, and in those with more developed intellectual property protection. Third, the mechanism analysis identifies three key channels through which the policy promotes GTI: enhancing entrepreneurial activity, increasing the concentration of science and technology talent, and expanding financial investment in innovation. Finally, further evidence shows that the policy contributes to improvements in urban energy efficiency, with GTI serving as a mediating mechanism.
Overall, these findings contribute to a better understanding of how meso-level industrial policies may link innovation and environmental outcomes. While the conclusions are derived from the Chinese context, the evidence may hold broader relevance for other emerging economies seeking to design industrial policies that integrate technological upgrading with sustainable development.
9.2 Research limitations
Several limitations of this study merit careful consideration. First, data availability constrains the analysis, limiting the examination of micro-level firm behaviors, sectoral heterogeneity, and dynamic innovation processes. This may obscure important within-industry variations in how industrial policies affect GTI and energy efficiency. Second, although China’s innovative industrial cluster pilot policy provides a valuable quasi-natural experiment, the transferability of the findings to other institutional contexts remains uncertain. Differences in governance capacity, industrial structures, and policy implementation mechanisms may influence both the magnitude and direction of policy effects. Third, the study relies primarily on prefecture-level data, which may overlook intra-urban heterogeneity, such as variations across districts, industrial parks, or firm networks. These limitations highlight the need for future research that integrates multi-scalar data, cross-national comparisons, and firm-level evidence to better understand how industrial policies foster sustainable innovation.
9.3 Future research directions
Future research could extend this study in several concrete ways. First, cross-national comparative analyses could evaluate the effectiveness of innovative industrial cluster policies across countries with varying institutional capacities, governance structures, and levels of economic development. Such studies could employ comparable city- or region-level panel data to ensure consistency. Second, firm- or establishment-level research could leverage microdata to examine how policy interventions affect innovation behaviors, R&D investment, and technology adoption. This approach would provide a more detailed understanding of the causal mechanisms linking policy to GTI and energy performance. Third, sector-specific studies could focus on high-impact industries, such as clean energy, advanced manufacturing, or green transportation. These studies could investigate how policy design interacts with industry characteristics, resource endowments, and technological trajectories, offering practical insights for designing targeted interventions that enhance both innovation and environmental outcomes.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
PZ: Conceptualization, Writing – eview and editing, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Methodology. XN: Writing – original draft, Software, Methodology, Visualization, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1The dual-carbon goals specifically refer to China’s strategic targets of achieving carbon peak before 2030 and carbon neutrality before 2060, which were proposed in September 2020. The term “carbon peak” means that the emissions of carbon dioxide will reach a maximum at a certain point in time and then gradually decline. Carbon neutrality, on the other hand, refers to offsetting all emitted carbon dioxide through means such as afforestation, energy conservation and emission reduction, and carbon capture technologies, thereby achieving net-zero emissions.
References
Acs, Z. J., Audretsch, D. B., and Lehmann, E. E. (2013). The knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship. Small Bus. Econ. 41 (4), 757–774.
Agarwal, R., Echambadi, R., Franco, A. M., and Sarkar, M. B. (2004). Knowledge transfer through inheritance: spin-Out generation, development, and survival. Acad. Manag. J. 47 (4), 501–522. doi:10.2307/20159599
Audretsch, D. B., and Feldman, M. P. (1996). R&D spillovers and the geography of innovation and production. Am. Econ. Rev. 86 (3), 630–640.
Audretsch, D. B., and Keilbach, M. (2007). The theory of knowledge spillover entrepreneurship. J. Manag. Stud. 44 (7), 1242–1254. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6486.2007.00722.x
Baur, A. H., Thess, M., Kleinschmit, B., and Creutzig, F. (2014). Urban climate change mitigation in Europe: looking at and beyond the role of population density. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 140 (1), 04013003. doi:10.1061/(asce)up.1943-5444.0000165
Bozeman, B., and Corley, E. (2004). Scientists’collaboration strategies: implications for scientific and technical human capital. Res. policy 33 (4), 599–616. doi:10.1016/j.respol.2004.01.008
Cheng, X., Gao, J., Liu, Y., Yu, Z., He, Y., and Yu, W. (2024). Thriving through innovation: boosting green tech performance in China's new energy sector. Renew. Energy 237, 121553. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2024.121553
Cui, Z., Wang, Q., Wang, X., and Yang, J. (2024). Green technology innovations and corporate customer concentration—The perspectives of financing constraints and social responsibility. Sustainability 16 (20), 9109. doi:10.3390/su16209109
Cullen, J. B., Johnson, J. L., and Parboteeah, K. P. (2014). National rates of opportunity entrepreneurship activity: insights from institutional anomie theory. Entrepreneursh. Theory Pract. 38 (4), 775–806. doi:10.1111/etap.12018
Deakin, M., and Reid, A. (2018). Smart cities: under-Gridding the sustainability of city-districts as energy efficient-low carbon zones. J. Clean. Prod. 173, 39–48. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.054
Dos Santos Martins, P. H., Serrano, A. L. M., Rodrigues, G. A. P., Vergara, G. F., Saiki, G. M., Borges, R. V., et al. (2024). Brazil’s new green hydrogen industry: an assessment of its macroeconomic viability through an input–output approach. Economies 12 (12), 333–20. doi:10.3390/economies12120333
Du, K., and Li, J. (2019). Towards a green world: how do green technology innovations affect total-factor carbon productivity. Energy Policy 131, 240–250. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2019.04.033
Du, K., Li, P., and Yan, Z. (2019). Do green technology innovations contribute to carbon dioxide emission reduction? Empirical evidence from patent data. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 146, 297–303. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2019.06.010
Etzkowitz, H., and Leydesdorff, L. (2000). The dynamics of innovation: from national Systems and “Mode 2” to a Triple Helix of university–industry–government relations. Res. policy 29 (2), 109–123. doi:10.1016/s0048-7333(99)00055-4
Faggian, A., and McCann, P. (2009). Human capital, graduate migration and innovation in British regions. Camb. J. Econ. 33 (2), 317–333. doi:10.1093/cje/ben042
Guo, Y., Xia, X., Zhang, S., and Zhang, D. (2021). Environmental regulation, government R&D funding and green technology innovation: evidence from China provincial data. Sustainability 10 (4), 940.
Hong, M., Li, Z., and Drakeford, B. (2021). Do the green credit guidelines affect corporate green technology innovation? Empirical research from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. public health 18 (4), 1682. doi:10.3390/ijerph18041682
Hong, Q., Cui, L., and Hong, P. (2022). The impact of carbon emissions trading on energy efficiency: evidence from quasi-experiment in China's carbon emissions trading pilot. Energy Econ. 110, 106025. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106025
Jiakui, C., Abbas, J., Najam, H., Liu, J., and Abbas, J. (2023). Green technological innovation, green finance, and financial development and their role in green total factor productivity: empirical insights from China. J. Clean. Prod. 382, 135131. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135131
Khin, S., and Ho, T. C. (2019). Digital technology, digital capability and organizational performance: a mediating role of digital innovation. Int. J. Innovation Sci. 11 (2), 177–195. doi:10.1108/ijis-08-2018-0083
Lane, N. (2025). Manufacturing revolutions: industrial policy and industrialization in South Korea. Q. J. Econ. 140, 1683–1741. doi:10.1093/qje/qjaf025
Larsen, M. (2025). Green industrial policy under financial constraints: insights from India’s state-led decarbonization. World Dev. 195, 107153. doi:10.1016/j.worlddev.2025.107153
Lema, R., Wuttke, T., and Konda, P. (2024). The electric vehicle sector in Brazil, India, and South Africa: are there green windows of opportunity? Industrial Corp. Change 33 (6), 1430–1459. doi:10.1093/icc/dtae014
Li, Y., Zhang, J., Yang, X., Wang, W., Wu, H., Ran, Q., et al. (2021). The impact of innovative city construction on ecological efficiency: a quasi-natural experiment from China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 28, 1724–1735. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2021.09.012
Li, X., Guo, F., Xu, Q., Wang, S., and Huang, H. (2023). Strategic or substantive innovation? The effect of government environmental punishment on enterprise green technology innovation. Sustain. Dev. 31 (5), 3365–3386. doi:10.1002/sd.2590
Liang, Z., Shen, Y., Yang, K., and Kuang, J. (2025). The impact of high-tech enterprise certification on green innovation: evidence from listed companies in China. Sustainability 17 (1), 147. doi:10.3390/su17010147
Liu M, M., Li, S., Li, Y., Shi, J., and Bai, J. (2024). Evaluating the synergistic effects of digital economy and government governance on urban low-carbon transition. Sustain. Cities Soc. 105, 105337. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105337
Liu Y, Y., Deng, W., Wen, H., and Li, S. (2024). Promoting green technology innovation through policy synergy: evidence from the dual pilot policy of low-carbon city and innovative city. Econ. Analysis Policy 84, 957–977. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2024.10.005
Molden, L. H., and Clausen, T. H. (2021). Playing 3D chess, or how firms can thrive under complexity: the mediating role of innovation capabilities in the use of innovation input. J. Bus. Res. 125, 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.11.049
Norberg-Bohm, V. (1999). Stimulating ‘green’ technological innovation: an analysis of alternative policy mechanisms. Policy Sci. 32 (1), 13–38. doi:10.1023/a:1004384913598
Porter, M. E. (1998). Clusters and the new economics of competition. (Boston: Harvard Business Review). 76 (6), 77–90.
Rosokhata, A. S., Saher, L. Y., Stoyanets, N., and Butrym, O. (2020). Impact of highly qualified personnels migration on economic and innovative development (doctoral dissertation).
Shen, G. B., and Huang, Y. J. (2019). The impact of intellectual property protection at the city level on the introduction of foreign investment by Chinese enterprises. Finance Trade Econ. 40 (12), 143–157.
Shen, W., Ayele, S., and Worako, T. K. (2023). The political economy of green industrial policy in Africa: unpacking the coordination challenges in Ethiopia. Energy Policy 179, 113633. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2023.113633
Sueyoshi, T., and Goto, M. (2018). Environmental assessment on energy and sustainability by data envelopment analysis. John Wiley and Sons.
Sun, R., He, D. Y., and Yan, J. J. (2025). Dynamic analysis of green technology innovation in products and processes under supply chain competition scenarios—A study based on stochastic differential game model. J. Environ. Manag. 373, 123545. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.123545
Tang, X., Zhang, Q., Li, C., Zhang, H., and Xu, H. (2023). The effects and driving factors of low-carbon transition of international oil companies: evidence from a Super-SBM model. Energies 17 (1), 157. doi:10.3390/en17010157
Tao, Z., Zhang, Z., and Shangkun, L. (2022). Digital economy, entrepreneurship, and high-quality economic development: empirical evidence from urban China. Front. Econ. China 17 (3), 393.
Wang, T., Li, R., Zhang, Q., and Sun, S. (2025). Digitalization and urban carbon emissions: unraveling the mechanisms of agglomeration economics. J. Environ. Manag. 387, 125855. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.125855
Wu, G., Xu, Q., Niu, X., and Tao, L. (2022). How does government policy improve green technology innovation: an empirical study in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 9, 799794. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2021.799794
Wurlod, J. D., and Noailly, J. (2018). The impact of green innovation on energy intensity: an empirical analysis for 14 industrial sectors in OECD countries. Energy Econ. 71, 47–61. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2017.12.012
Xu, J., and Hu, W. (2024). How do external resources influence a firm's green innovation? A study based on absorptive capacity. Econ. Model. 133, 106660. doi:10.1016/j.econmod.2024.106660
Yang, J., Xiong, G., and Shi, D. (2022). Innovation and sustainable: can innovative city improve energy efficiency? Sustain. Cities Soc. 80, 103761. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2022.103761
Zhang, R., Sun, B., and Liu, M. (2019). Do external technology sourcing and industrial agglomeration successfully facilitate an increase in the innovation performance of high-tech industries in China? IEEE Access 7, 15414–15423. doi:10.1109/access.2019.2895782
Zhang, M., Yan, T., Gao, W., Xie, W., and Yu, Z. (2023). How does environmental regulation affect real green technology innovation and strategic green technology innovation? Sci. Total Environ. 872, 162221. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162221
Zhang, C., Liu, D., Du, L., He, J., and Wang, H. (2024). Can informatization improve urban entrepreneurial activity? Evidence from China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 11 (1), 1667–12. doi:10.1057/s41599-024-04161-4
Zhang, H., Zhang, K., Yan, T., and Cao, X. (2025). The impact of digital infrastructure on regional green innovation efficiency through industrial agglomeration and diversification. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 12 (1), 220–15. doi:10.1057/s41599-025-04512-9
Zhao, Y. (2023). Realistic challenges and optimization path of global ecological civilization construction. Environ. Resour. Ecol. J. 7 (5), 69.
Zhao, R., Cao, Y. U., Zheng, X., and Wang, H. (2020). The innovation economy calls for proactive growth of intellectual property by various innovation carriers–A China case. Glob. Transitions Proc. 1 (1), 23–31. doi:10.1016/j.gltp.2020.04.001
Zucker, L. G., Darby, M. R., and Brewer, M. B. (1994). Intellectual capital and the birth of US biotechnology enterprises.
Keywords: innovative industrial clusters, green technology innovation, urban entrepreneurial activity, double-difference modeling, sustainable urban development, energy utilization efficiency
Citation: Zhou P and Ning X (2025) Green innovation effects and energy efficiency enhancement of China’s innovative industrial cluster pilot policies: evidence from 281 cities. Front. Energy Res. 13:1610157. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2025.1610157
Received: 11 April 2025; Accepted: 09 September 2025;
Published: 13 October 2025.
Edited by:
Maria Johansson, Linköping University, SwedenReviewed by:
A. S. M. Monjurul Hasan, University of Technology Sydney, AustraliaTaiyeb Hasan Sakib, BRAC University, Bangladesh
Copyright © 2025 Zhou and Ning. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pinglu Zhou, emhvdXBsQGx6dS5lZHUuY24=
 Pinglu Zhou
Pinglu Zhou Xiaoya Ning
Xiaoya Ning