- 1South Africa-Switzerland Bilateral Research Chair in Blockchain Technology (SARChI Chair), University of Johannesburg, Auckland Park, South Africa
- 2Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Oduduwa University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria
In contributing to reducing the cost of Renewable Energy solutions, this research explores the potential of Blockchain Technology for cost efficiency based on Transaction Cost Theory. The study employed a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) and Bibliometric Analysis using Rayyan and R-programmed Biblioshiny software to collate data from the Scopus and Web of Science databases. The analysis identified the most globally cited documents, trending topics, keyword co-occurrence, and countries of collaboration. The findings revealed blockchain techniques for Renewable Energy cost optimization, including Blockchain-based Auctioning Systems for Renewable Energy Microgrids, Blockchain Levelised Cost of Energy (BLCOE), Smart Contract-oriented Distributed Energy Systems (DES), and the Internet of Energy (IoE) in Renewable Energy Infrastructure and Demand-Side Management. Moreover, the study highlighted factors influencing the cost of renewable energy solutions, such as feed-in tariffs, institutional policy, unfair competitiveness, investment risk, uncertainty, intermittency, and variability. The research concludes that the responsibility for applying blockchain technology lies with the government and Renewable Energy business organizations. Policy recommendations include integrating blockchain in feed-in tariffs, net metering, power purchase agreements, and carbon pricing. Additionally, the study recommends a Smart Contract-oriented International Auctioneering platform for Renewable Energy components and materials.
Highlights
• Blockchain technology can eliminate and reduce transaction costs of Renewable Energy
• Integrating Blockchain technology with Renewable Energy auctioning platforms will aid cost efficiency
• Smart contract oriented Distributed Energy Systems (DES) will contribute to efficiency and less transaction costs in Renewable Energy systems
• Blockchain Levelized Cost of Energy (BLCOE) will revolutionize the cost build-up of Renewable Energy systems
1 Introduction
Given the environmental hazards and carbon emissions resulting from fossil fuels, there is an evolving consensus on adopting renewable energy as a sustainable energy pathway for the future. This transition also aligns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), the Paris Agreement, and various international commitments and initiatives. According to Sustainable Energy for All (2022) and David L. et al. (2025), Renewable energy is poised to take the central stage in Africa’s energy demand as its capacity is set to increase to 180 GW by 2030 and 1.2 TW by 2050. According to the report and research, renewable energy will significantly cut the global energy mix, like other parts of the world. However, the acceleration of the adoption of renewable energy has a cost perspective. There is a need to clarify and answer the cost dynamics of adopting renewable energy. According to the Research of Verbruggen et al. (2009), the cost and price of renewable energy solutions are a significant challenge in adopting renewable energy. According to the authors, energy goods and services prices greatly impact Renewable energy supplies and subsequent utilization.
The issue of cost perspectives and discussion affecting the adoption of renewable energy against fossil fuels is a recurring issue, given the 1995 report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) titled “The true cost of Renewables: An analytic response to the coal industry’s attack on renewable energy” to the report by the Center for Energy and Economic Development (Swezey and Wan, 1995). The disagreement between these two entities stems from the cost associated with Renewable Energy in terms of technological costs, with Renewable energy in terms of technological costs, subsidies, and incentives from the government. This shows that the cost associated with renewable energy has been a recurring issue for more than 2 decades, which this paper seeks to address. Furthermore, the research of Gioutsos et al. (2018) shows that discussion and research around the cost of renewable energy is the bedrock of renewable energy optimization and hybrid renewable electricity systems, using models such as Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE), Net Present Value (NPV), Loss of Load Probability (LOLP), Loss of Power Supply Probability (LPSP), Loss of Power Probability (LOPP), and Load Coverage Rate (LCR). Rahman et al. (2019) opined that Renewable Energy Costs are generally higher because of their initial capital investments. The authors stated that these costs are sometimes referred to as emission reduction costs or avoidance costs. The authors further gave a comparative cost for electric energy across different sources in United States cents Per Kilowatt-hour: Coal (3.97–5.39); Wind (5.79–34.57), and Solar PV (41.57–61.59), showing the high cost of renewables.
Moreover, the acceleration of Renewable Energy is confronted by decades of investment and profitability expectations in the fossil fuel, which has led to what the Guardian in February 2022 called “Monster Profits” (Milman, 2023). According to the News Platform, five Oil and Gas companies in 2022 made 195 billion USD, the most profitable in their history. The companies include Exxon, Shell, Total, Chevron, and BP. The Guardian observed that the combined profit of 195 billion USD was twenty (20) times greater than the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) budget of 9.6 billion USD. The former US President, Joe Biden in the Milman (2023) called the profit “Outrageous” and the United Nation’s Secretary General, Antonio Guterres, frowning at the Monster Profits, stated that “if you cannot set a credible course for net-zero emissions, with 2025 and 2030 targets covering all your operation, you should not be in business…. Your core product is our core problem … We need renewables revolutions, not a self-destructive fossil fuel resurgence”. These profits indicate that attaining an optimal cost for renewable energy, accessible even to those affected by energy poverty, largely depends on how investments in fossil fuel technologies are managed, as such investments exert a competitive influence on the pricing and overall cost of renewable energy solutions.
Bogdanov et al. (2021) classified these technologies into six: Electricity Generation (Condensing coal power plants, oil-based internal combustion engine open cycle, combined cycle gas turbines, and Gas and oil–based combined heat and power plants); Heating technologies (Fossil fuel boilers); Transport (Light duty vehicles, LDV, 2-3 Wheelers, Medium–duty vehicles, MDV; Heavy duty Vehicles, HDV, Internal combustion engine vehicles, ICE trains, and Liquid fuel ICE propelled vessels); Sector Coupling Technologies (Fuel synthesis technologies, H2-toX synthesis technologies, steam turbines, seawater desalination, pumping technologies, water storage technologies; and direct electrical heaters); and Electricity transmission technologies (high voltage AC and DC Power line, and AC/DC Converters).
According to Synwoldt and Reis (2011), the electricity production cost is made up of investment and operating costs, which is favorable to fossil fuel as against renewable energy, as shown in Figure 1, whereby most of the electricity production costs of renewable energy sources are higher than those of Fossil fuel.
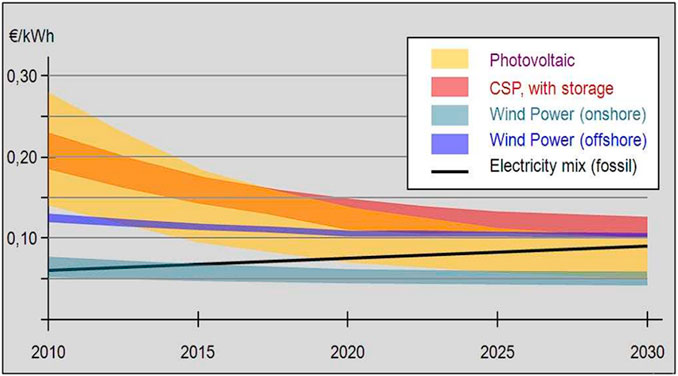
Figure 1. Electricity Production cost trends (Synwoldt and Reis, 2011).
According to the 2023 Global Overview of Renewable Energy, as of 2021, there are 395 billion USD loans and underwritings for fossil fuels against a paltry 53 billion USD for renewable energy, as shown in Figure 2 (REN 21, 2023). Given these large amounts of investment in fossil fuels, the question remains: Who bears the brunt of high investment in Fossil fuels? The huge investment in this fossil fuel greatly affects the cost of renewable energy, given the economic yields of these investments and the possible tax revenue from the investments.
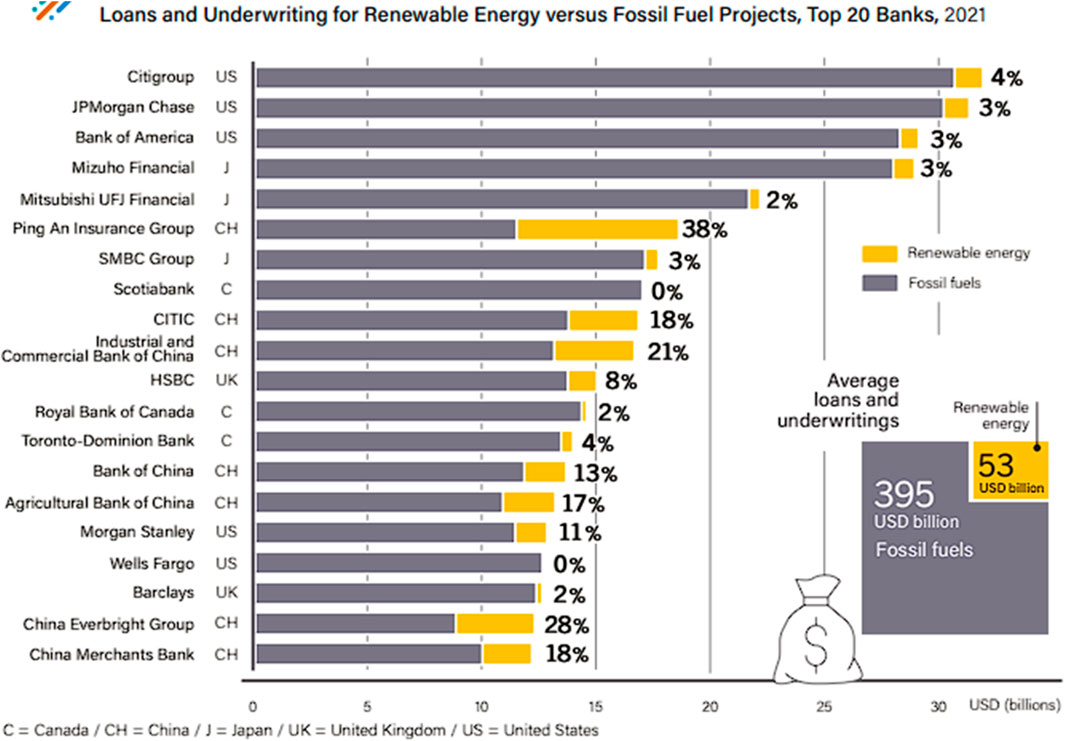
Figure 2. Loans and underwriting comparison for Fossil fuels and renewables (REN 21, 2023).
Moreover, the price increase of renewable energy raw materials and uncertainty affect their cost (Mackenzie, 2022). According to the author, the increasing price for raw materials such as Manganese, Lithium, Nickel, Copper, and Cobalt used for Renewable Energy, is having a huge cost on Renewable Energy solutions, given their high demand. According to the author, the price of Lithium carbonate-oriented battery in China jumped to 41060 USD per tonne in 2022, which is more than five times in 2021, while Cobalt doubled to 70208 USD per tonne and nickel increased by 15% in 2022–20045 USD. The author also noted that copper is now at an all-time high at 510000 per tonne, and given its irreplaceable trait in renewables, its impact on the overall cost is inevitable. Compared to coal, it costs 2–3 times more to produce 1 MW of copper onshore wind or solar than coal. Also, offshore wind requires 5–8 times more copper per 1 MW than coal (Mackenzie, 2022).
Eckstein et al. (2020) opined that Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) of renewable energy is highly sensitive to financing cost, which is influenced by regulatory and policy frameworks. In world bank policy research working paper, Timilsina (2020) calculated the LCOE of various technologies of renewable and non–renewable energy technologies. The LCOE expressed in energy ($/Mwh) included annualized capital cost, fixed operating and maintenance cost, variable operating and maintenance cost, fuel cost, overnight construction cost, capacity recovery factor, capacity availability factor, heat rate, and economic life. The author utilized data from IRENA, Lazard, IEA, EIA, and NREL, encompassing both minimum and maximum values, thereby leading to a median value of LCOE as shown in Figure 3: Solar PV ($51/Mwh), Concentrated Solar ($129/Mwh), Wind Onshore ($52/Mwh), Wind Offshore ($130 Mwh), Gas combined cycle ($67/Mwh), Gas turbine ($94/Mwh), Geothermal ($56/Mwh), and Biomass ($81/Mwh). These findings show that the cheapest technologies are hydro, solar PV, wind onshore, and geothermal. However, considering the billions of people lacking access to energy and epileptic power supply, there is a need to address the uncertainty and perceived high cost of renewable energy solutions. The cheapest LCOE in Timilsina (2020) is hydro at $48/Mwh, and the energy poverty threshold is spending greater than or equal to 10% of household income and of which poverty line by the United Nations is earning less than or equal to $2.15 per day as income (UN, 2024), shows that there is a need for a cost-effective approach in the production, supply chain and utilization of renewable energy solutions.
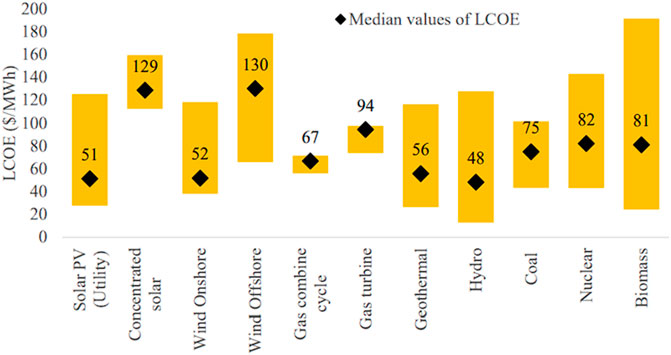
Figure 3. LCOE values for Energy Technologies (Timilsina, 2020).
The environmental importance and benefits of Renewable Energy for humanity are not in contention. However, the question centers on the rate of accelerating the adoption. The research of Swezey and Wan (1995), Verbruggen et al. (2009), Gioutsos et al. (2018), Rahman et al. (2019), and Milman (2023) shows that renewable energy initial capital and installation costs, and previous investments in Fossil fuel energy are the Pendulum in the global energy transition. Hence, Blockchain Technology has become a pivotal counterbalancing pendulum. The research of Zhipping (2024) shows that Blockchain technology aids in reducing transaction fees, streamlining operations, and enhancing transparency along the critical enterprise value chain. This is because Blockchain has the capacity and feature to digitalize and improve the end-to-end value chain, leading to tamper-proof exchange of asset histories, authentication of transactions, enhanced supply chain security and transparency, and smart contracting (Wüst and Gervais, 2018; Janssen et al., 2020). The research of Zhipping (2024) outlined value chain areas and possible cost improvement through Blockchain technology. These are procurement (lower transaction fees and settlement times; sourcing automation; and contract enforcement savings); Manufacturing (improved quality, dynamic capacity balancing, and reduced scraps and delays); inventory management (predictive analytics, centralized oversights, and lower holding and expiry); logistics and Distribution (cold chain integrity, sensor–driving rerouting, and lower disputes and recalls); and Retail and Aftersales (Grey market, reduced counterfeiting and faster warranty claims). Furthermore, the research of Hoffmeister and Stossberger (2018) averred that Blockchain technology could reduce the following transaction costs: Search and information costs, contracting costs, monitoring costs, and enforcement costs.
The research of Wei (2023) posited that challenges occurring within the financial management space can be addressed by blockchain technology. These include asymmetric information between investors and enterprise managers, leading to high transaction costs (including execution, intermediary, decision, negotiation, and information search costs). As stated by the authors, other challenges include costs involving border payments, leading to trust costs and cross–border clearing payments, which can be addressed by Blockchain technology, leading to borderless payments and transactions. The research of Panuparb (2019) confirms the potential blockchain technology using smart contracts in accelerating invoice processing efficiency for transparent and secure transactions within supply chain finance. Furthermore, Wang et al. (2020) opined that Blockchain technology can prevent cost waste in the lifecycle cost management of weapon equipment, which includes the cost of usage, maintenance cost, support cost, development cost, project demonstration cost, and production cost.
The insights from various scholarly research in the preceding paragraphs have confirmed that Blockchain can reduce the cost of renewable energy. The integration of Blockchain technology with renewable energy is an evolving area with a lot of applications. The research of Nassiry (2018) of the Asian Development Bank Institute established the utilization of Blockchain in revamping the energy sector business model towards a decentralized energy system, leading to Peer–to–Peer energy transactions and increasing the efficiency of carbon credits trade. Onete et al. (2023) called the integration of Blockchain technology in Renewable Energy a sustainable technology tool, which is beneficial across different renewable energy sources such as Biomass, geothermal, hydroelectricity, wind, and solar energy in application areas such as Grid transactions, peer–to–peer transactions, sustainability attribution, and energy financing, among others. In addition, Reichmuth et al. (2018) research outlines how blockchain technology is disrupting the renewable energy landscape through the transparency of energy assets, ensuring trust in asset trading, standardization of processes, and tokenization of renewable energy plants, among other uses. This is also confirmed in the Special Report of the Global Blockchain Business Council (2021). The research of Juszczyk and Shahzad (2022) emphasized that blockchain technology in renewable energy has led to energy democratization, energy token incentives for low-carbon energy generation, automated mechanisms for metering and billing, and automation of green energy certificates.
Therefore, given the substantial applications of Blockchain technology in renewable energy and the capacity of blockchain technology in reducing renewable energy costs, there is a dearth of research on utilizing blockchain technology for cost efficiency, thereby reducing the cost of renewable energy solutions. Hence, this paper aims to leverage Blockchain Technology to increase the cost efficiency of renewable energy solutions. In achieving this aim, this paper will address two cogent research questions, which are:
a. What are the Blockchain cost Efficiency techniques for Renewable Energy solutions?
b. What are the influencing factors shaping the cost of renewable energy solutions?
Given the production mechanism, LCOE of renewable energy, and international dimensions, there is a need to understand the various factors influencing the cost of renewable energy solutions and products. This will aid in formulating necessary policy frameworks and identifying areas of applying blockchain technology, thereby reducing the costs of renewable energy, accelerating the adoption of renewable energy penetration, and contributing to the ongoing global energy transition.
2 Transaction cost theory
Transaction cost theory (TCT) focuses on how much work, money, or resources are required for two parties to execute an exchange, using the transaction as the fundamental unit of measurement. The transaction cost theory, proposed by Coase (1937), explains the existence of firms by focusing on the costs associated with transactions via market mechanisms. This idea has become one of the most significant subfields of New International Economics (NIE), a theory that prioritizes process efficiency above resource allocation efficiency and places a greater emphasis on transactions than pricing. Knowledge of the nature of transactions is diversified by transaction cost theory since they are not uniform and involve varying degrees of interdependency, risk, and uncertainty. Williamson’s theory of transaction costs (transaction costs associated with the management, governance, and enforcement of transactions/contracts) focuses on designing ex-post contract governance structures to mitigate specific types of expected ex-post contractual hazards (Chen and Webster, 2012).
Furthermore, transaction costs refer to the expenditures incurred to trade a good or service between two entities, above and beyond the cost of the good or service itself (Fiorini et al., 2018). Understanding costs is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about operations. Bounded rationality, which suggests decision-makers have limited cognitive abilities, can lead to incomplete contracts. This suggests that people base their decisions on assumptions, hopes, and beliefs, rather than logical calculations, highlighting the importance of understanding these costs in business decision-making (Lu et al., 2023). Hence, the objectives of the TCT are to minimize expenses and maximize transaction performance.
Consequently, based on opportunism, linked to bounded rationality, involves businesses acting in their best interests to increase financial returns at the expense of weaker parties. This behavior can involve lying, hiding facts, or dishonest bargaining. Research in transaction cost economics shows that opportunistic behavior is most common in environments with high uncertainty, complexity, and significant asset-specific investments, which is very visible within the Renewable Energy paradigm. This highlights the importance of choosing appropriate governance structures to manage relationships and mitigate risks during transactions (Galvin et al., 2021). Also, businesses often decide to outsource tasks based on transaction costs, which can lead to internalization rather than outsourcing. The decision is influenced by cost-benefit analysis, balancing potential savings against risks of increased opportunism and bounded rationality. Hence, this paper introduces Blockchain Technology as a viable digital technology to navigate the complex decision-making process involved in the cost of transactions that build up the cost of renewable energy solutions.
Vlasov and Okhlopkov (2022) examined the impact of digital technology on business transaction costs, focusing on marketing, contract negotiation, and the role of information technology. The study employed theoretical generalization, synthesis, and logical analytic techniques. They surveyed Russian business owners and directors to assess the use of digital technologies in marketing, vetting potential counterparties, negotiating contract terms, and ensuring counterparties fulfill their commitments. Additionally, the study explored the priorities and challenges businesses face when adopting new technologies. The findings support the theory that companies are increasingly leveraging digital technology to reduce transaction costs. Also, Casati et al. (2024) explored the use of blockchain technology for secure contractual agreements, arguing that it eliminates intermediaries and creates faster, more transparent supply chains. They argue that blockchain eliminates trust through crypto-enforced agreements based on transparency and consensus. The technology enhances monitoring, openness, data immutability, and improved information flow. As a distributed, immutable database, blockchain facilitates more effective and transparent transactions, making it an innovative technology because consensus-based record validation eliminates the need for a reliable middleman.
Hence, based on transaction cost theory and the works of Vlasov and Okhlopkov (2022) as well as Casati et al. (2024), and David et al. (2024), Blockchain technology emerges as a transformative tool for improving the efficiency of renewable energy supply chains. Blockchain significantly reduces transaction costs associated with energy installation, raw material procurement, investment flows, and microgrid operations by decentralizing and automating verification processes. It further enhances governance choices by embedding trust in the system, minimizing the reliance on costly intermediaries, and enabling seamless peer-to-peer transactions. Blockchain technology mitigates opportunistic behavior, environmental ambiguity, and behavioral uncertainty, ensuring all parties operate within a transparent, auditable, and tamper-proof framework. This transparency fosters legitimacy in contractual agreements, investment opportunities, and pricing structures, thereby accelerating renewable energy adoption and strengthening distributed energy markets and microgrid environments. In this way, Blockchain streamlines operational efficiency, reduces cost, and ensures equitable participation in the renewable energy ecosystem.
3 Methodology
This research employed two statistical qualitative mechanisms to answer the research questions. The first qualitative method utilized was the Systematic Literature Review (SLR). According to Lame (2019), the SLR is a systematic mechanism of synthesizing research output in the form of scientific evidence to answer a particular research question so that the output is reproducible and transparent. According to the author, the essence of the SLR is risk reduction of biases and ensuring transparency at every stage of the review process, thereby appraising the quality of the research for objective output. Therefore, in achieving the objectives of the SLR, this research utilized the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) of Page et al., (2021), which entails a step-by-step process of screening research papers used in answering the research questions.
Furthermore, the paper utilized a Bibliometric analysis, which, according to Donthu et al. (2021) and David et al. (2023), a Bibliometric analysis is a quantitative technique that explores the intellectual structure of research findings and the derivation of novel ideas for investigation. In addition, the research employed the scientific mapping of Bibliometric analysis, focusing on Bibliographic coupling and co-word analysis proposed by Donthu et al. (2021).
3.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Given the dynamics of research output on Blockchain Technology and the cost efficiency of renewable energy, inclusion and exclusion criteria were set as shown in Table 1 while generating data from databases.
3.2 Research database
This study utilized the two databases focusing on renewable energy and blockchain technology (Junaidi et al., 2023), with the search query shown in Table 2. Also, the Boolean Operator “AND” choice ensures that all papers include the three major keywords: Blockchain, Renewable Energy, and Cost.
3.3 Software
The analysis of the research documents in achieving the research objectives was done using two software, which are the Rayyan (http://www.rayyan.ai/) for Systematic Literature Review and R-Studio oriented Biblioshiny Analysis (https://www.bibliometrix.org/home/index.php/layout/biblioshiny). According to Valizadeh et al. (2022), the Rayyan is a web based automated screening tool used for Systematic Literature Review, as it helps the reviewers in screening research outputs. This study utilized the Rayyan software in screening research articles and abstracts, leading to exclusion of duplicated documents and research publications outside the inclusion criteria stated in Table 1. Moreover, the Bibliometric analysis was done using the Biblioshiny web application, which is built on R–programming language. According to Burkut (2023), Biblioshiny is a web application that provides an interface for Bibliometrix, which performs the logical and statistical science mapping of publications. Hence, this study follows the bibliometric analysis outlined in Farooq (2021) and David et al. (2023).
3.4 PRISMA
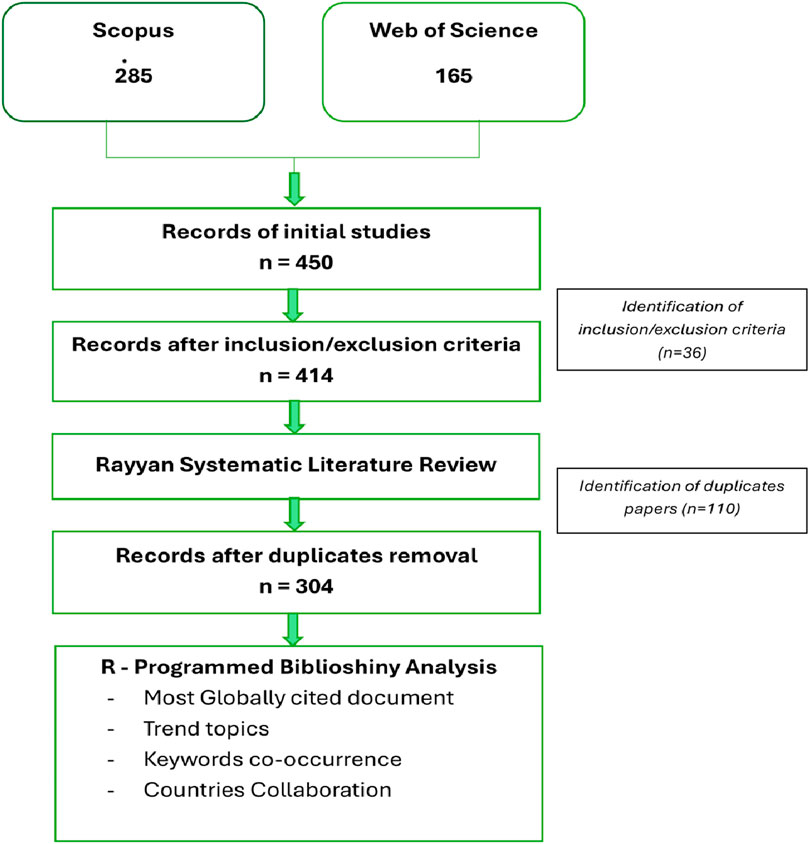
Figure 4 shows the PRISMA output, showing the systematic process of review of research output from the two databases in Table 2.
4 Results and findings
As shown in the PRISMA outline of Figure 4, this study utilized two globally cited and indexed databases: Scopus and Web of Science, given the nature of this study. Hence, the analysis was subjected to the two databases, using the R-Programming language-oriented Biblioshiny for the Bibliometric analysis. The analysis included the Most Globally cited documents, the trending topics, the Keyword co-occurrence, and the Country with collaboration to address the research questions. These various categories of analysis were done to unearth answers to the research questions.
4.1 Most globally cited documents
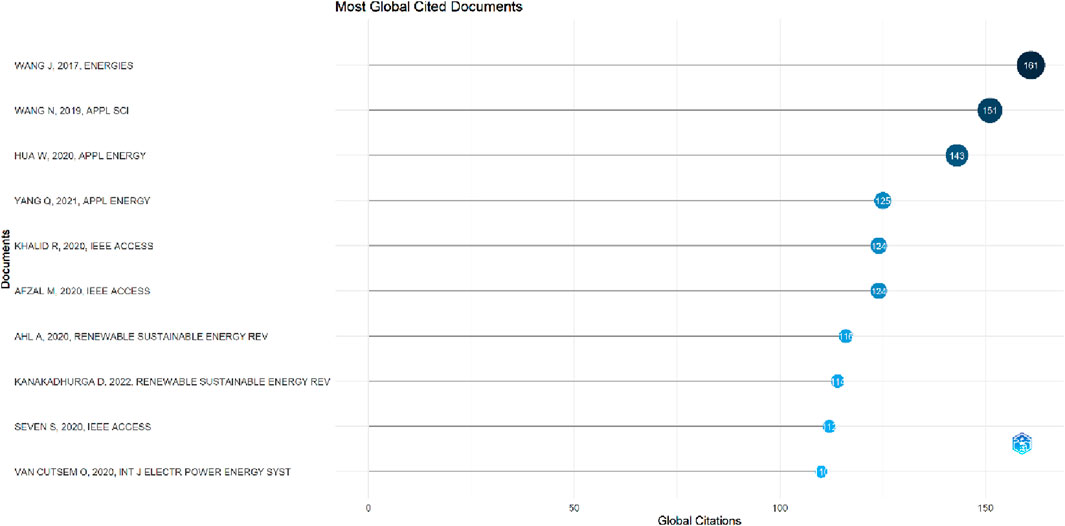
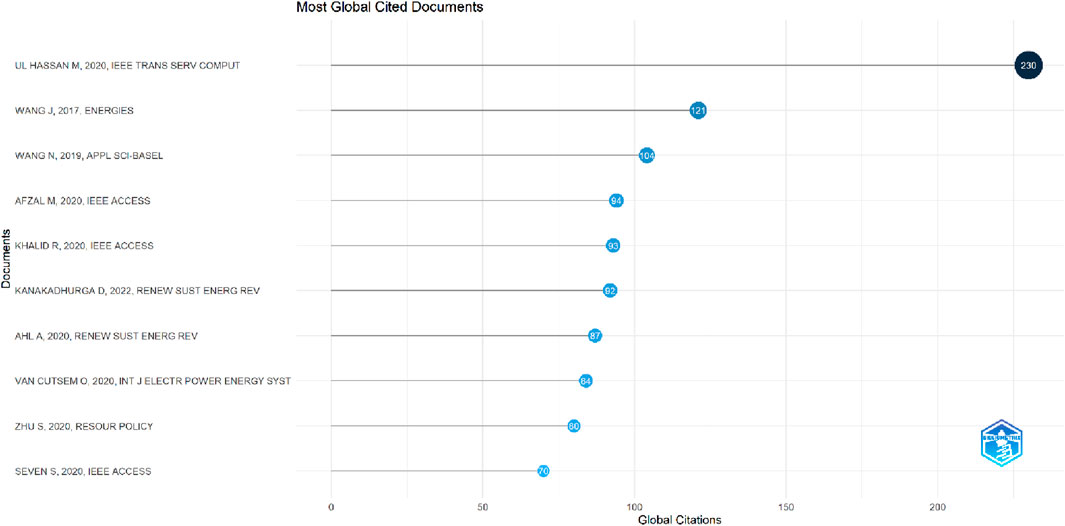
According to Figures 5, 6, the two most globally cited document on optimizing blockchain for renewable energy cost are Hassan et al. (2020) in their paper (DEAL: Differentially private auction for blockchain-based Microgrids Energy Trading) and the research of Wang et al. (2017) in their research paper (A Novel Electricity Transaction Mode of Microgrids Based on Blockchain and Continuous Double Auction).
4.2 Trending topics
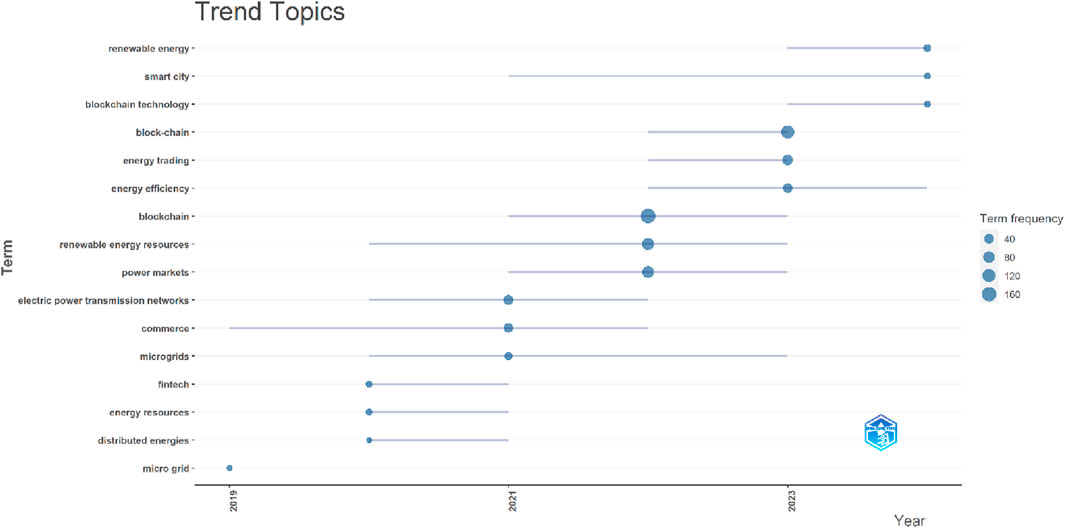
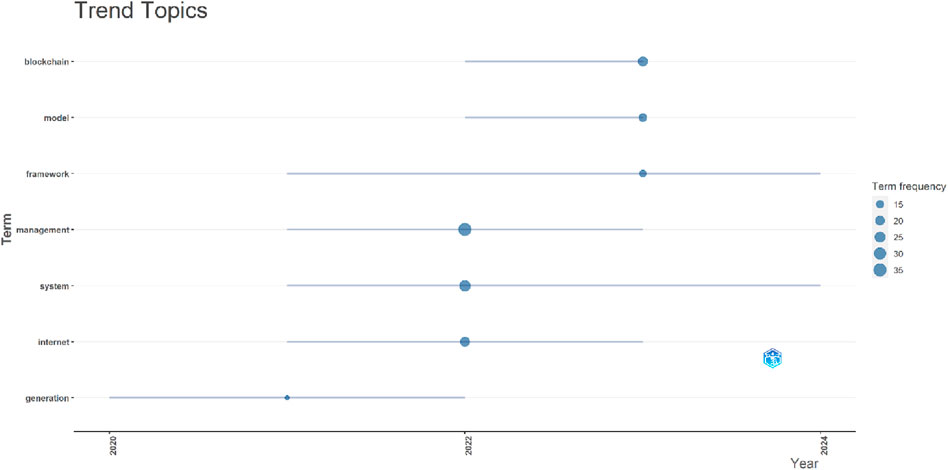
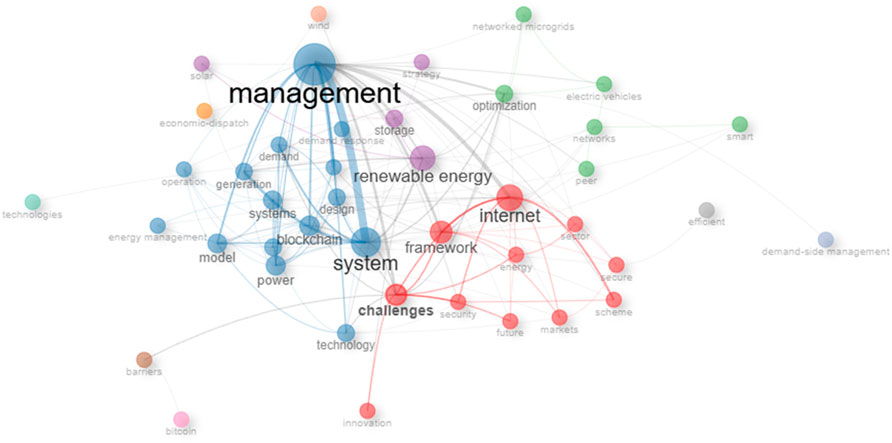
Figure 7 shows that the most trending topics on the subject matter within the Scopus databases include Electric power transmission network, commerce, microgrids, blockchain, renewable energy sources, power markets, block-chain, energy trading, energy efficiency, and renewable energy. Figure 8 of the Web of science databases shows that the most trending topics are generation, management, system, internet, blockchain, model, and framework.
4.3 Keyword co-occurrence
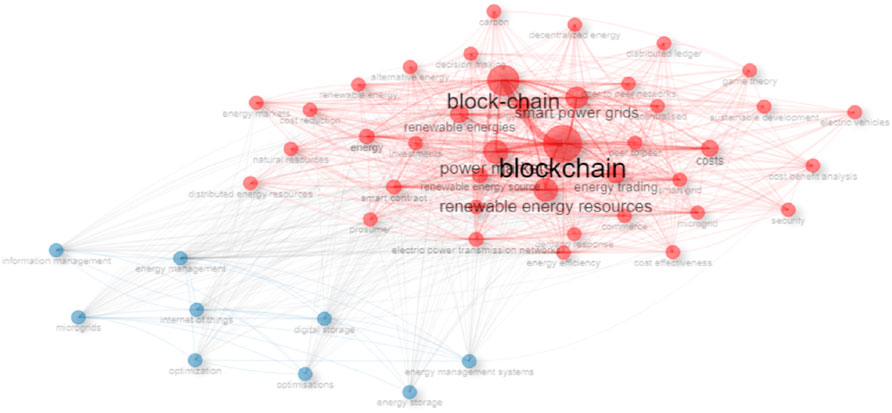
Figure 9 shows that there are two clusters for the intellectual interactions of keywords. The first cluster in red colour includes the following keywords: blockchain, block-chain, renewable energy resources, power markets, smart power grids, renewable energies, costs, energy trading, renewable energy source, electric power transmission networks, energy policy, energy, energy efficiency, smart contract, commerce, smart grid, energy utilization, microgrid, peer to peer, peer to peer networks, decentralized, renewable energy, alternative energy, energy markets, cost reduction, demand response, distributed ledger, decision making, cost effectiveness, investments, carbon, cost benefit analysis, game theory, security, decentralized energy, distributed energy resources, prosumer, sustainable development, electric vehicles, and natural resources. The second cluster in blue color includes the following keywords: energy management, Internet of things, microgrids, digital storage, information management, energy management systems, energy storage, optimisations and optimization.
Furthermore, Figure 10 shows there are four major clusters and other keywords. The first cluster in red color entails Internet, challenges, frameworks, energy, security, scheme, future, markets, sector, secure, and innovation. The second blue cluster encompasses the keywords of management, system, blockchain, technology, model, systems, microgrids, power, demand, design, generation, market, energy management, operation, and demand response. The third cluster in green color includes keywords such as optimization, networks, electric vehicles, peer, smart, and networked microgrids. The fourth cluster includes keywords in orange: renewable energy, storage, strategy, and solar. The remaining keywords are economic dispatch, barriers, bitcoin, efficient, technologies, wind, and demand-side management.
4.4 Country of collaboration
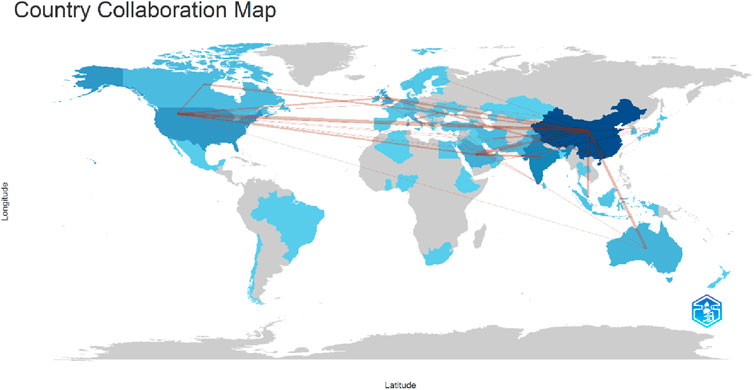
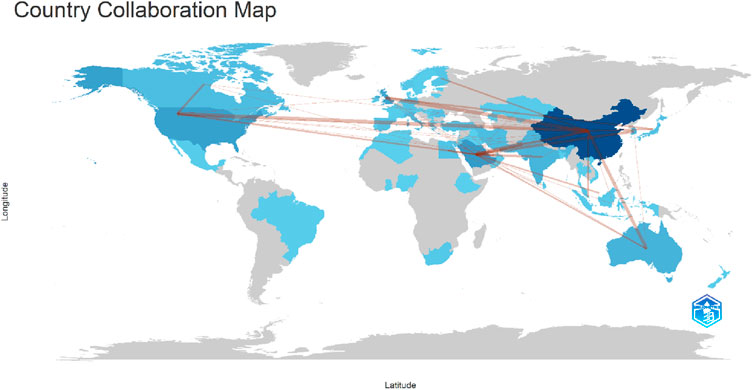
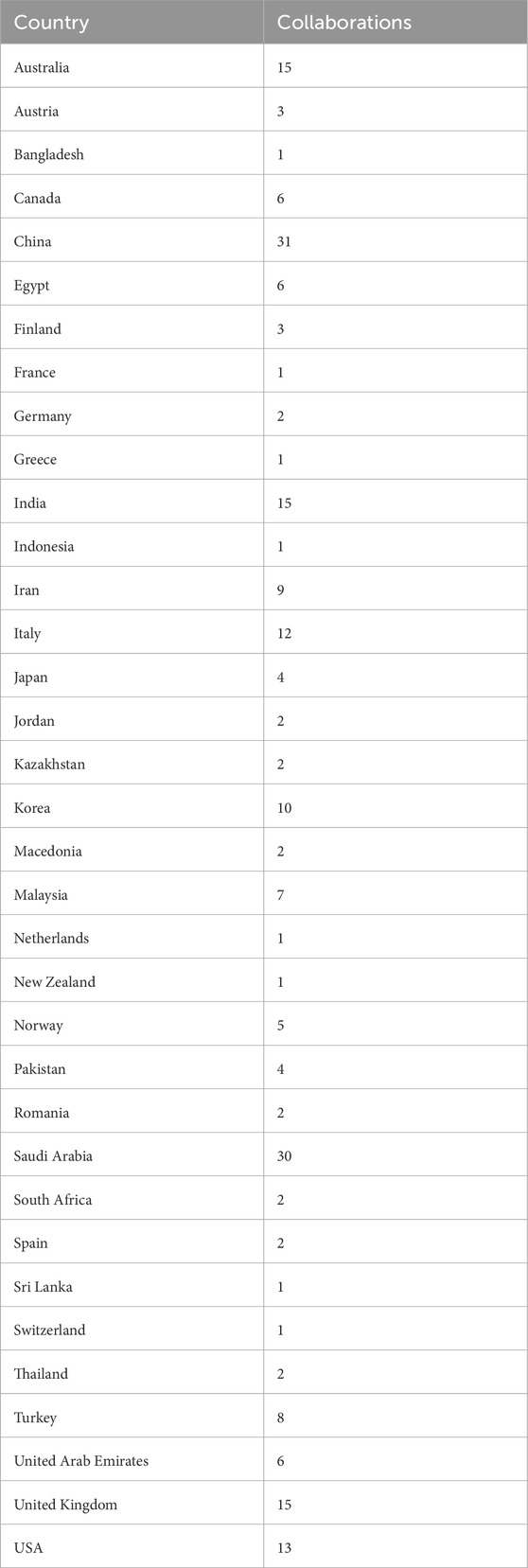
The countries of collaboration illustrate the cooperative relationships among authors from different countries and, in many cases, from diverse institutions. Such collaborations advance research in a particular field and bring multiple perspectives to the same subject, leading to a richer and more nuanced understanding. Also, beyond co-authorship, international collaborations open avenues for knowledge exchange, technology transfer, policy learning and adaptation, and strengthening research scholarship. They also foster academic mobility and global networks, vital for addressing complex challenges that transcend national boundaries. Therefore, when leveraging blockchain technology for cost efficiency, it is essential to recognize how networks can harness the benefits of collaboration to maximize value and impact. Consequently, the countries of collaboration from Figures 11, 12 of Scopus and Web of Science databases are somewhat the same.
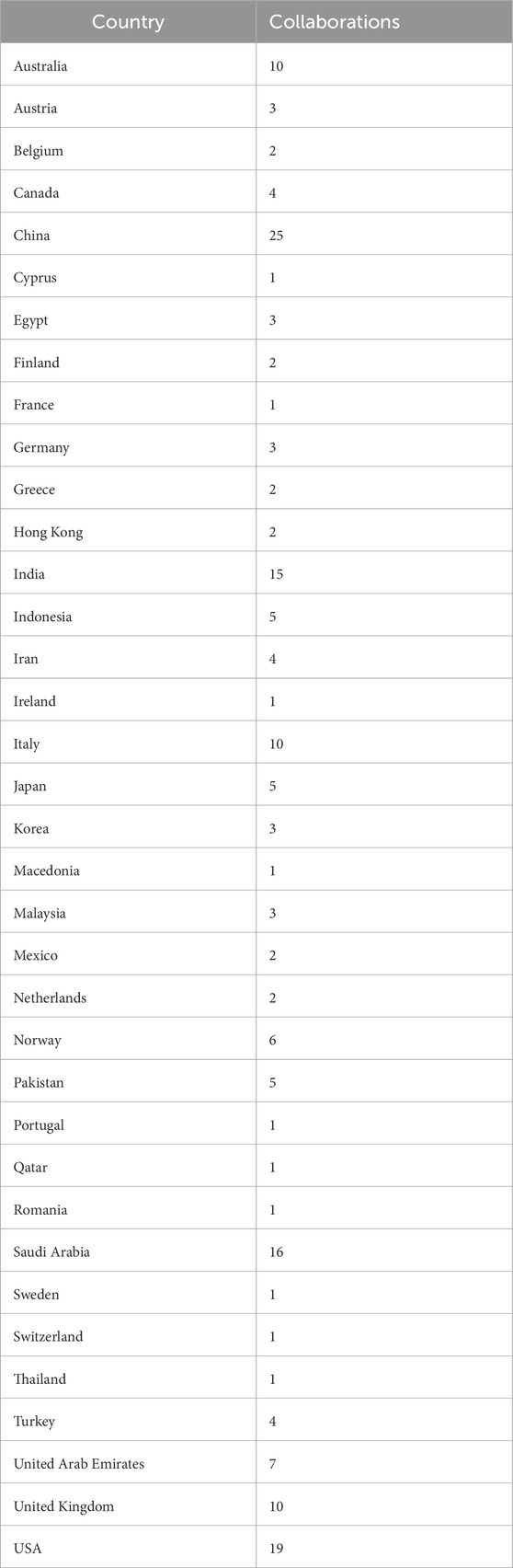
According to the statistics of collaboration, the top countries of collaboration with other countries in the Scopus database are shown in Table 3 and in Figure 11:
In the web of science of collaborations, the following countries of collaborations are shown in Table 4 and their interconnected is depicted in Figure 12.
5 Discussion
5.1 Blockchain cost efficiency techniques for renewable energy solutions
The two most globally cited papers were reviewed to address objective one of this research. Also, the insights from the trending topics were reviewed, which show the application areas of Blockchain technology within the Renewable Energy sector. Moreover, the keyword co-occurrence in different clusters also points to the intellectual interaction of using blockchain for renewable energy cost Efficiency.
The research of Hassan et al. (2020) developed a Differentially Private Auction for Blockchain-based microgrid energy trading, using the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus of consortium blockchain to make the microgrid auction more secure and private. The developed model led to the maximization of revenue to sellers, provision of moderate cost for the auction mechanism, preservation of the bids of individual participants, ensuring fair shares for all participants, and protection of the outcome of auction results from adversaries and inference attacks. Moreover, the research of Wang et al. (2017) integrated the UTXO Blockchain model with the Continuous Double Auction (CDA) mechanism in optimizing the distributed generation (DG) based renewable energy system, leading to an adaptive aggressiveness (AA) strategy in the microgrid electricity market. According to the authors, this proposed initiative ensures a dynamic and seamless microgrid electricity transaction between trading parties, ensures adaptive tracing of market information and quotes in accordance with transaction prices and price fluctuations, and there is a direct settlement of transactions between the DG and the consumers. The two top authors revealed that the integration of Blockchain technology with relevant energy auctioning strategies aids in optimizing renewable energy cost.
Moreover, the trending topics in Figures 7, 8 suggest that the evolving nature of Blockchain technology across all the phases (sources, generation, system, management, electric power transmission network, and energy efficiency) of renewable energy utilization in addressing cost issues, as evidenced in terms such as power markets, commerce, and energy trading. This further depicts the capability of the various features of blockchain technology to revolutionize the transactions and cost perspectives of renewable energy.
Furthermore, there are two clusters in Figure 9. The keywords of the first cluster entail the use of blockchain technology and smart contract within the renewable energy system, facilitating seamless transactions and cost efficiency. The keywords in the second cluster highlight the need digitalizing the entire energy value chain for cost reduction. Also, Figure 10 revealed four (4) clusters. The first cluster encompasses the digitalization of the energy management systems. The second cluster reemphasizes the need to apply blockchain across the different phases of the energy value chain. The third cluster reveals the need to digitalize a networked microgrid. The keywords in the fourth cluster and other keywords highlight the need for demand-side management strategies to optimize renewable energy.
There may be arguments and divergent perspectives that the cost of Renewable Energy is due to the unsaturated nature of the energy market compared to fossil fuel energy sources. However, as explained in Section 1 of this paper, the cost component of renewable energy faces a multidimensional perspective in terms of production cost, level of investment in comparison with fossil fuel, tax revenue from fossil fuel, and the increasing price of raw materials for renewable energy.
However, Figures 5–10 has produced different cost efficiency techniques, as highlighted in the preceding paragraphs of this section. Below are four (4) techniques for cost efficiency of Renewable Energy. The cost efficiency of renewable energy focuses on the usage of Blockchain in reducing the Installation/production cost of renewable energy and the transaction costs of energy supply and demand between energy producers and energy consumers.
5.1.1 Blockchain-based Auctioning system for renewable energy microgrid
Renewable energy microgrid is an optimal distributed energy system (DES) that aids in enhancing demand side management in load management and is an avenue for the interoperability of different energy systems for the benefit of consumers and producers. However, given the intermittent nature and variability of renewable energy sources, the prosumer system, where consumers also act as energy producers, has rapidly evolved as a transformative model in the energy landscape. This shift has empowered end-users to contribute to energy generation and facilitated the rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading systems, irrespective of size, where excess energy can be traded within localized networks or broader grids. The prosumer-driven trading ecosystem introduces opportunities for decentralized energy markets, reducing reliance on traditional monopolistic utility structures and enhancing resilience against power disruptions. As a result, new auctioning mechanisms and market models have emerged to govern how renewable energy is priced, allocated, and exchanged.
However, the research Wang et al. (2017) and Hassan et al. (2020) has shown that the auctioning mechanism is not enough in optimizing revenue for trading partners or securing their transactions; hence, the authors introduced blockchain technology. Therefore, the auctioneering within energy trading platforms should be blockchain-oriented to reduce transaction costs such as documentation and administrative costs, brokerage fees, cleaning and settlement costs in the auctioneering process, bogus staffing costs, hedging costs, security costs, default, and contract breaching costs, data acquisition costs, and various compliance costs. The automated and trustless features of Blockchain technology can eliminate and reduce various transaction costs within the auctioneering systems. According to Laarabi and Chegri (2022), Blockchain technology is an emerging technology that aids cost management. The authors rely on transaction costs economics theory and opine that the blockchain technology features could aid in reducing ex ante transaction costs (information and negotiation costs) and ex post transaction costs (implementation, monitoring, and enforcement costs).
As inferred in Hassan et al. (2020) and established in Bains (2022) of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) Notes for Fintech, Blockchain Consensus mechanisms aid in achieving the efficiency and optimization of the various transaction costs when auctioning for Renewable Energy microgrids. The consensus mechanism includes Proof-of-work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake (PoS), Delegated-Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), Practical and Instanbul Byzantine Fault Tolerance (Pbft/Ibft), Federated Byzantine Fault Tolerance (Fbft), and Proof-of-Elapsed-Time (PoET). These consensus mechanisms collectively function as strategies to guarantee transparency, fairness, and resilience in the renewable energy auctioning process, ensuring that bidding activities are not subject to manipulation or interference. Proof-of-Work (PoW) provides a foundation of trust by validating every auction bid securely, keeping bidding records transparent and tamper-proof. Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Proof-of-Elapsed-Time (PoET) enhance cost efficiency by minimizing energy consumption and optimizing gas utilization, thereby reducing the transaction costs associated with auction processes.
Meanwhile, Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) introduces a democratic dimension, enabling stakeholders within the energy market to elect trusted validators or experts to authenticate transactions, thus reinforcing collective participation and accountability. Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) models, including PBFT, IBFT, and FBFT, focus on ensuring the integrity of auction outcomes by maintaining system reliability even when some blockchain nodes act erroneously or maliciously. However, these mechanisms need not operate in isolation; they can be deployed in hybrid configurations tailored to the specific characteristics of the renewable energy or prosumer system.
Therefore, utilizing Blockchain technology within the energy auctioneering process will reduce costs associated with the demand and supply of Renewable Energy. However, while the auctioneering process of Renewable microgrids usually entails big corporations and urban areas, local energy providers and government entities can embrace the blockchain technology in reducing the transaction costs of energy supply to urban poor areas and rural areas, which will inevitably reduce the cost of utilizing renewable energy, making it competitive with the cost of fossil fuel-based energy.
5.1.2 Blockchain levelised cost of energy (BLCOE)
The levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is one of the most measurable indicators of the cost involved in producing a kilowatt of energy. As mentioned earlier in Section 1, the LCOE considers capital costs, operational costs, end-of-life costs, the time value of money, and other monetary incentives. However, the trending topics in Figures 7, 8 highlight the need to introduce Blockchain to minimize costs throughout renewable energy generation, transmission, distribution, and storage systems. This is confirmed by the research of Samuel et al. (2020), which introduced the Blockchain levelized cost of energy (BLCOE) as a least cost solution mechanism, which reduces energy costs by approximately 95% for batteries and 75% for solar modules at 0.11$/kWh. The various transaction costs that build up to the installation, production, and capital costs in LCOE in renewable energy can be reduced optimally through blockchain technology. For instance, Blockchain Technology can reduce and eliminate the following types of costs: negotiation costs, risk mitigation costs, costs associated with licensing and permitting bureaucracy, and financing costs. This will be achieved through the reduction of intermediaries, streamlining of processes, automation of various cost-oriented costs and fees, reduction in data collection and collation, increased data sharing and information sorting, and improved transparency of transactions.
Moreover, in the traditional levelized energy cost, a blockchain system will optimize the operational cost of Renewable Energy, focusing on administrative, compliance, and staffing costs. Furthermore, in a BLCOE, various renewable energy incentives, subsidies, and initiatives will be implemented with transparency, trustless accountability, standardized prices, and real-time process and cost performance monitoring.
5.1.3 Smart contract oriented distributed energy systems (DES)
The Distributed Energy Systems (DES) focuses on the nature of utilizing renewable energy across different utilities, aspects, and sectors, which are usually based on the Distributed Generation (DG) of microgrids. According to the comprehensive review of Nadeem et al. (2023), the DES is a dynamic system that aids in the ongoing sustainable energy transition in terms of cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency, improvement in energy security, peak load management, and contributes to energy resilience. Hence, the first cluster of the keyword co-occurrences highlights the need to sustain and expand the DES. However, as noted in Nadeem et al. (2023), the DES is a technologically intensive system requiring a lot of procedures, stakeholders, and interoperation with existing grids, which has led to issues of quality of power and grid stability, thereby increasing the cost of installation, transmission, and cost of purchasing power.
Hence, the introduction of the smart contract influences the cost, resilience, and quality dynamics of Distributed Energy Systems (DES), as inferred from the keyword clusters. Smart contracts, by nature of their technological capability, enable automated and enforceable transactions (David L. O. et al., 2025) across the energy ecosystem, which reduces the transactional costs of negotiating, intermediaries, and other operational expenses associated with contracts within the energy ecosystem. Moreover, they can enhance the resilience of DES by facilitating decentralized coordination, ensuring reliable energy distribution based on contractual agreements, and enabling real-time responses to system disturbances, distortions, and failures. In terms of quality, smart contracts can provide verifiable audit trails along the entire energy value chain, thereby promoting trust and accountability among stakeholders. The impact of these capabilities is amplified by the fact that DES spans the whole energy value chain, from generation and storage to distribution and consumption, which makes it suitable for managing the complexity of renewable energy systems, optimizing performance, and fostering sustainable energy practices. This is confirmed by the research of Honari et al. (2023) that smart contracts reduce the cost of operation in the energy market within the DES by eliminating third parties, matching consumers and producers with demand patterns and congruent production and ensuring market access to smaller–scale energy producers. This cost-effectiveness of smart contracts within the DES is also confirmed in the research of Bouachir et al. (2022), Saxena et al. (2019), and Gao et al. (2022).
5.1.4 Internet of energy (IoE) in renewable energy infrastructure and demand side management
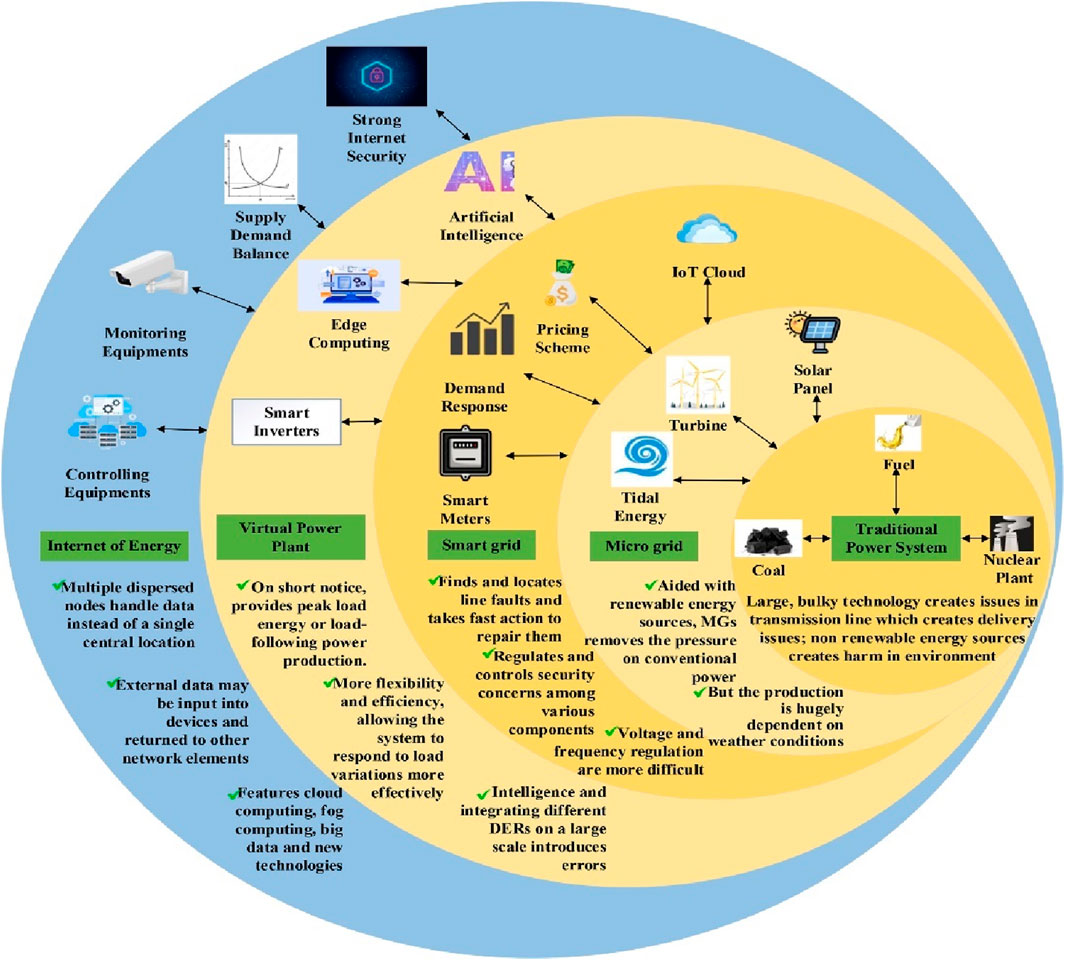
Given the acceleration of the adoption of Renewable Energy systems, the focus of researchers and policymakers has led to the energy sector’s decarbonization, decentralization, and digitalization agenda (David L. O. et al., 2025). Blockchain technology is at the heart of the 3D’s Agenda. However, these agendas have always focused on renewable energy systems with little consideration and concentration on renewable energy infrastructure, which has led to more investments in fossil fuels than in renewable energy. The research of Yusida et al. (2022) positions renewable energy infrastructure as a significant pillar in energy security and the economic welfare of a country. As inferred from the clusters of the Keyword co-occurrences, the digitalization of the Renewable Energy Infrastructure will contribute to reducing the cost of investment. Hence, the Internet of Energy (IoE) aids in simplifying processes, performance evaluation, and real-time monitoring of renewable energy systems, contributing to the cost of utilizing renewable energy infrastructure. The IoE is the summation of the application of technological advancement of the Fourth Industrial Revolution within the energy sector. According to Farhan et al. (2023), the IoE evolution as shown in Figure 13, can reduce the cost of energy supply. Moreover, according to the keyword co-occurrence, there is a need for the interoperation of IoE with Demand Side Management (DSM) for cost efficiency, which according to Bakare et al. (2023), aids in reducing the cost of energy acquisition and the cost of monitoring energy. This is confirmed in the research of Alhasnawi and Jasim (2021), who developed an IoE enabled DSM called the Real-time Electricity Scheduling (RTES), which aids in the cost-effectiveness of smart microgrids. Also, the research of Shahryari and Anvari-Moghaddam (2017) affirmed that through IoE-oriented DSM, the volume of transmitted data will be reduced, which will also aid in the reduction of cost of energy. Consequently, the interoperation of IoE with DSM and Renewable Energy Infrastructure can be achieved through Blockchain technology (Yi et al., 2021).
5.2 Influencing factors shaping the cost of renewable energy solutions
Figures 11, 12 show the research collaboration between countries in applying Blockchain within Renewable Energy for cost efficiency. The figures show that China and the USA are the top countries that collaborate with other countries. The research of Jiang et al., (2022) stated that factors influencing Renewable Energy in the Residential sector of the USA includes percentage of renewable energy consumption, demographics (per capita GDP, population, and education attainment), renewable energy availability (in terms of renewable energy production, and number of utilities), consumers affordability (current retail price, residential monthly bill, household income and median price premium); and Regulatory compliance motivation (in terms of number of government financial incentives and number of government regulatory policies). These factors focus on the cost of renewable energy supply and demand, which can be addressed in the various blockchain-oriented techniques in Section 5.1. Using data between 1980–2011, Lin et al. (2015) analyzed the factors that influence Renewable electricity in China, which include GDP per capita, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), trade openness, share of fossil fuel in energy consumption, and financial development. The factor in China highlights the need to channel the capability of Blockchain in attracting and retaining foreign direct investment within the renewable energy sector, which will contribute to the reduction of the cost of installing renewable energy solutions.
Consequently, Renewable energy solutions have become a critical component in the global transition towards a more sustainable energy future. However, the cost of these technologies is influenced by a multitude of factors that determine their accessibility and scalability, as shown in Sections 1 and 5.1 of this paper. Some identified contributing factors include institutional policy, feed-in tariff, investment risk and uncertainty, and unfair competition amongst energy producers (Mendonca, 2007). Additionally, government policies and subsidies can either incentivize or hinder the growth of renewable energy, thus impacting overall market dynamics (Mohammad et al., 2022).
Given the collaboration dynamics as stated in Section 4, some countries have viable trade-in tariff models, making it easy for the investment in renewable energy to be attractive and profitable. Spain and China are regarded as the leading countries that recorded an appreciable amount of investment in exploring renewable energy solutions due to effective trade-in tariff policies (Ibrahim et al., 2021; Ming et al., 2013). Germany is also considered another country with a viable trade-in tariff strategy for renewable energy investment, which has led to the creation of 214,000 jobs and a reduction in acid rain as a result of greenhouse gas emission (Mendonca, 2007). Conversely, countries like United Kingdom, United States, and Japan currently have a mild trade-in tariff law for renewable energy solutions (Dong-Xiao et al., 2021). Similarly, most African countries are yet to embrace these frameworks, thereby making renewable energy solutions unattractive due to the high cost of implementation, which is evidently revealed in Tables 3, 4 of the countries with different collaborations. The list of countries with their corresponding investment in renewable energy solutions in 2018 is given in Table 5 and Figure 14 (Africa Energy Portal, 2019).
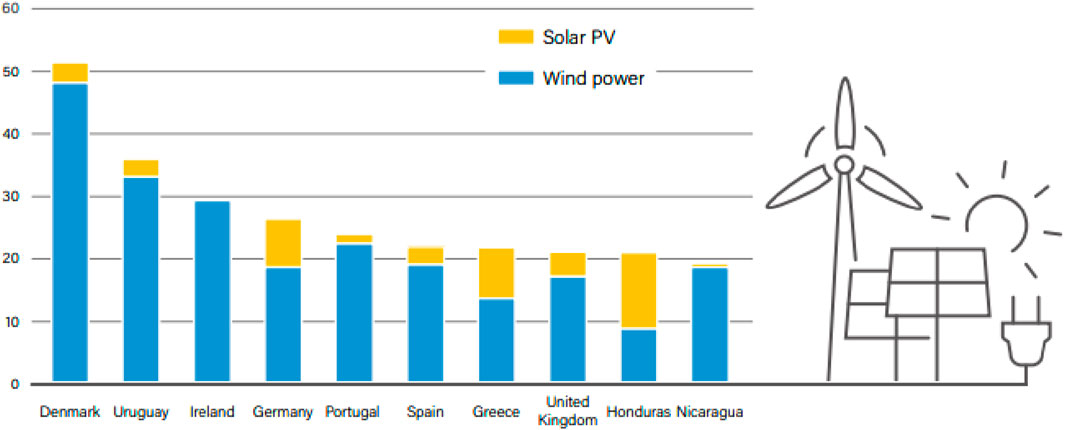
Figure 14. Share of top countries’ electricity generation from RE in 2018 (Africa Energy Portal, 2019).
In summary, factors influencing the cost of renewable energy vary significantly from one region to another, depending on several factors, including government policies, energy market dynamics, technological advancements, and local resource availability. The influencing factors shaping the cost of renewable energy solutions are summarized as follows:
a. Feed-in tariff: The adoption of renewable energy has faced some challenges as a result of subsidies for nuclear and fossil fuels for centralized power generation from the government. This attempt has made the investment in RE unattractive to the energy investors. To address this problem, a pricing policy should be implemented such that power generated from the RE is estimated with a substantial profit margin to attract investment.
b. Institutional policy: The government’s interest in generating large-scale energy for a centralized distribution has led to the introduction of policies supporting fossil fuels. Institutional policies can significantly impact the cost of renewable energy by shaping market incentives and regulatory frameworks. Governments can reduce costs through subsidies, tax incentives, and grants, thereby encouraging investment in renewable technologies. Conversely, restrictive regulations or inconsistent policies can increase costs by creating uncertainty, thus affecting the willingness of businesses and investors to commit to renewable energy projects.
c. Unfair competitiveness: This can drive up the cost of renewable energy by creating an uneven playing field where traditional energy sources receive preferential treatment from the government. Similarly, subsidies and financial support for fossil fuels can distort the market, making it more difficult for renewable energy to compete on price. This can lead to reduced investment in renewable technologies and slow down the transition to a cleaner energy landscape.
d. Investment risk and uncertainty: Factors such as fluctuating government policies, changing market demands, or evolving technologies can create a volatile environment that deters investment. Investment risk can significantly impact the cost of renewable energy by discouraging potential investors from committing resources to long-term projects. This hesitation can lead to increased financing costs and slower development of renewable infrastructure.
e. Intermittency and variability: The intermittency and variability of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind can challenge grid stability and reliability. Integrating renewable energy into the grid may require additional investments in balancing resources, energy storage, or backup generation capacity, which can increase costs and tariffs.
However, to optimize renewable energy and make it attractive to energy investors, the following energy efficiency factors are recommended:
i. Feed-in Tariffs: In this context, feed-in tariffs will be optimized to guarantee renewable energy producers a fixed payment for the electricity they generate over a set period. These tariffs are often set above market rates to incentivize investment in renewable energy projects. Countries such as Germany, Spain (Garcia-Alvarez and Mariz-Perez 2012), and Japan (Ayoub and Yuji, 2012) have implemented programs like this to promote renewable energy deployment.
ii. Net metering system of prosumer: This scheme allows RES owners to offset their electricity bills by selling excess electricity generated back to the grid at a retail rate. This mechanism is prevalent in many parts of the world, including the United States (Herath and Tyner, 2019), Canada (Sow et al., 2019), and parts of Europe (Ines et al., 2020).
iii. Power purchase agreements: This model involves contracts between renewable energy producers and utilities or corporate buyers, specifying the terms of electricity sale over a long-term period. This often includes fixed or variable pricing structures depending on the region and market conditions.
iv. Carbon pricing: The cost of fossil fuel-based electricity generation will increase sharply with the introduction of carbon pricing mechanisms. This could involve schemes such as carbon taxes, emissions trading fees etc., which can indirectly support renewable energy by increasing the cost of fossil fuel-based electricity generation, thereby making it unattractive.
v. AI-Based Energy Pricing: Building on the research of Huang et al. (2024), the predictive power of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly through deep learning models, can be harnessed to analyze and forecast electricity market prices with higher accuracy. Such predictive capabilities enable more informed decision-making and improve operational planning, thereby enhancing the sustainability of smart renewable energy systems. Similarly, the work of Alvarez-Diazcomas et al. (2019) demonstrates how deep learning models within smart grid research have been effectively applied to predict electricity market pricing. Integrating AI-driven price forecasting into renewable energy markets will optimize cost efficiency and support grid stability, energy trading, and long-term sustainability goals (Badrudeen et al., 2024).
6 Conclusion
The research has provided comprehensive insights into utilizing Blockchain technology for cost efficiency of Renewable Energy solutions, initiatives, and projects. Therefore, in conclusion, the study reveals that the responsibility of interoperation of Blockchain technology for cost efficiency of Renewable Energy solutions falls within government entities in terms of Regulations (as highlighted in Section 5.2), Renewable Energy organizations and businesses in terms of operational remodification, and the need for prosumers. It is incumbent upon government entities to provide appropriate regulatory guidelines and operational frameworks for Blockchain technology for renewable energy, which will allow the decentralization of the sector and increase the repurposing of the transaction aspect of the sector, which will inevitably reduce the cost associated with the supply and demand of energy.
Moreover, government blockchain technology-oriented guidelines will serve as a confidence booster for investors in renewable energy, invariably increasing FDI in the sector, thereby reducing the capital cost associated with the renewable energy sector. Furthermore, the role of renewable energy entities and business organizations stems from embracing blockchain technology within their operational framework, thereby eliminating and reducing costs associated with renewable energy transactions. Also, Renewable Energy businesses embracing blockchain aid in enhancing their performance and increasing customer satisfaction (energy consumers). In addition, the cost efficiency of Renewable Energy solutions is inevitable without the need to increase the prosumer market. Many residential areas are not engaged in producing and selling renewable energy, not to mention participating in a blockchain-oriented auctioneering and smart contracts-oriented DES and DSM, which would significantly impact the cost of using renewable energy. Therefore, government and renewable energy businesses should employ educational and awareness strategies to liberalize the prosumer market and increase participation.
Also, given the level of investment in fossil fuel energy sources and government tax revenues from these sources, which a cost-effective renewable energy system may reduce, it is suggested that the blockchain technology system be introduced in phases. The phased approach should consider major areas with populations experiencing high energy poverty and the top regions experiencing the adverse effects of fossil fuels.
7 Policy recommendations
Drawing from the insights and conclusions of this study, two (2) key policy recommendations are proposed to enhance renewable energy cost efficiency through integrating blockchain technology.
7.1 Blockchain applications in existing renewable energy initiatives
Many initiatives are propelling the adoption and acceleration of Renewable Energy solutions. These initiatives highlight the need to embrace renewable energy solutions based on the environmental benefits. However, introducing Blockchain technology will accelerate the adoption of applications in areas such as Feed-in-Tariffs, Net metering, power purchase agreements, and carbon pricing mentioned in Section 5.2. Integrating blockchain technology within these areas will systematically reduce the operational and transaction costs associated with Renewable Energy solutions. It will also improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the DSM and DSM models.
7.2 Smart contract-oriented international auctioneering platforms for renewable energy components and materials
The instability and fluctuation of prices of Renewable Energy solutions are a detriment to the cost optimization and efficiency in many countries, given their high tariffs and levies. However, through a smart contract-oriented international auctioneering platform and systems, middlemen and intermediaries are cut off from the acquisition process, which is responsible for the high capital and installation cost of renewable energy solutions. The platform will ensure bidders and suppliers worldwide bid transparently, fairly, and securely, ensuring the procurement mechanism is devoid of cost encumbrances. This platform will ensure and fix issues relating to high tariffs and levies on the importation of Renewable energy components and materials, thereby liberalizing the Renewable Energy market to increase foreign direct investment and efficiency.
8 Areas for further research
Given the evolving dynamics of blockchain technology in driving energy cost efficiency and system optimization, several avenues for future exploration emerge from this study.
First, there is a pressing need to develop models and frameworks for Blockchain Levelized Cost of Energy (BLCOE), with an appropriate block diagram and application areas. These frameworks could serve as comprehensive tools for assessing and integrating the entire renewable energy value chain, from generation and distribution to storage and consumption, while providing standardized benchmarks for measuring cost efficiency. Establishing BLCOE models would also allow researchers, policymakers, and industry practitioners to compare blockchain-enabled renewable systems with conventional energy solutions on both technical and economic fronts.
Second, considering the concept of gas optimization in blockchain utilization, and the findings of this study confirming blockchain’s potential to enhance cost efficiency, further research is required to design strategies that minimize or optimize gas usage. This would ensure blockchain applications in energy solutions remain technologically viable and economically sustainable. This is because optimized gas consumption would contribute to lowering transaction costs, reducing the environmental footprints of blockchain operations, and improving the overall scalability of blockchain-enabled renewable energy projects.
Author contributions
NN: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LD: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. TB: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Africa Energy Portal (2019). Renewables 2019 global status report. Available online at: https://www.ren21.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/gsr_2019_full_report_en.pdf (Accessed May 24, 2024).
Alhasnawi, B. N., and Jasim, B. H. (2021). A new internet of things enabled trust distributed demand side management system. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 46 (2021), 101272. doi:10.1016/j.seta.2021.101272
Alvarez-Diazcomas, A., López, H., Carrillo-Serrano, R. V., Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J., Vázquez, N., and Herrera-Ruiz, G. (2019). A novel integrated topology to interface electric vehicles and renewable energies with the grid. Energies 12 (21), 4091. doi:10.3390/en12214091
Ansarin, M., Ghiassi-Farrokhfal, Y., Ketter, W., and Collins, J. (2020). The economic consequences of electricity tariff design in a renewable energy era. Appl. Energy 275, 115317. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115317
Ayoub, N., and Yuji, N. (2012). Governmental intervention approaches to promote renewable energies—Special emphasis on Japanese feed-in tariff. Energy Policy 43, 191–201. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2011.12.056
Badrudeen, T. U., Opeyemi David, L., and Nwulu, N. (2024). Management of environmental and economic tradeoffs for the optimization of renewable energy scheme. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 43 (1), 2355645. doi:10.1080/14786451.2024.2355645
Bains, P. (2022). “Blockchain consensus mechanisms: a primer for supervisors,” in Fintech note. Washington, DC, United States: International Monetary Fund IMF. Available online at: https://www.imf.org/-/media/Files/Publications/FTN063/2022/English/FTNEA2022003.ashx.
Bakare, M. S., Abdulkarim, A., Zeeshan, M., and Shuaibu, A. N. (2023). A comprehensive overview on demand side energy management towards smart grids: challenges, solutions, and future direction. Energy Inf. 6, 4. doi:10.1186/s42162-023-00262-7
Bogdanov, D., Ram, M., Aghahosseini, A., Gulagi, A., Oyewo, A. S., Child, M., et al. (2021). Low-cost renewable electricity as the key driver of the global energy transition towards sustainability. Energy 227, 120467. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2021.120467
Bouachir, O., Aloqaily, M., Özkasap, Ö., and Ali, F. (2022). Federated grids: Federated learning and blockchain-assisted P2P energy sharing. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. (6), 424–436. doi:10.1109/TGCN.2022.3140978
Burkut, E. B. (2023). “Scientific literature in the field of architecture (2018-2022) in Türkiye: r bibliometrix biblioshiny application and science mapping,” in Architectural sciences and theory, practice and new Approaches-I. 2023. Editors M. Dal, and L. Karataş (Ankara, Turkey: Iksad Publications), 1, 01–27.
Casati, M., Soregaroli, C., Frizzi, G., and Stranieri, S. (2024). Impacts of blockchain technology in agri-food: exploring the interplay between transactions and firms’ strategic resources. Supply Chain Manag. An Int. J. 29, 51–70. doi:10.1108/SCM-09-2023-0443
Chen, S. C. Y., and Webster, C. (2012). “Institutional economics: new,” in International encyclopedia of housing and home. Editor S. J. Smith (Elsevier), 78–85. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-047163-1.00640-8
David, L., Nwulu, N., Aigbavboa, C., and Adepoju, O. (2023). Towards global water security: the role of cleaner production. Clean Eng. Technol. 17, 100695. doi:10.1016/j.clet.2023.100695
David, L. O., Aigbavboa, C., Nwulu, N., and Adepoju, O. O. (2024). “Application of digital technologies of the fourth industrial revolution (4IR) in water, energy, and food (WEF) nexus,” in Sustainable synergy: a digital framework for the water-energy-food nexus project delivery in developing economies (Cham: Green Energy and Technology. Springer). doi:10.1007/978-3-031-72833-4_9
David, L., Kgomo, M., and Aigbavboa, C. (2025a). Smart contract in construction procurement: insights and recommendations from South Africa. Front. Built Environ. 11, 1620790. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2025.1620790
David, L. O., Nwulu, N. I., Aigbavboa, C. O., Adepoju, A., and Adepoju, O. O. (2025b). Evaluating the use of blockchain technology and identifying critical success factors for the successful implementation of renewable energy projects in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 44 (1), 2449867. doi:10.1080/14786451.2025.2449867
Dong-xiao, Y., Ya-qiang, J., Wang, C., Nie, P.-yan, and Sun, P. (2021). Analysis of renewable energy subsidy in China under uncertainty: feed-in tariff vs. renewable portfolio standard. Energy Strategy Rev. 34 (2021), 100628. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2021.100628
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., and Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 133 (2021), 285–296. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Eckstein, J., Kurdziel, M., Nascimento, L., and Ordonez, J. A. (2020). “Decreasing costs of renewables - Insights on energy sector planning and climate policy from three country case studies,” in Working paper sustainability and innovation. doi:10.24406/isi-n-615628%0A
Farhan, M., Reza, T. N., Badal, F. R., Islam, M. R., Muyeen, S. M., Tasneem, Z., et al. (2023). Towards next generation internet of energy systems: framework and trends. Energy AI, 14. doi:10.1016/j.egyai.2023.100306
Farooq, R. (2021). A review of knowledge management research in the past three decades: a bibliometric analysis. VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 54, 339–378. doi:10.1108/VJIKMS-08-2021-0169
Fiorini, P. de C., Seles, B. M. R. P., Jabbour, C. J. C., Mariano, E. B., and Jabbour, A. B. L. de S. (2018). Management theory and big data literature: from a review to a research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 43, 112–129. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.07.005
Galvin, P., Tywoniak, S., and Sutherland, J. (2021). Collaboration and opportunism in megaproject alliance contracts: the interplay between governance, trust and culture. Trust Gov. Megaprojects 39 (4), 394–405. doi:10.1016/j.ijproman.2021.02.007
Gao, G., Song, C., Bandara, T. G. T. A., Shen, M., Yang, F., Posdorfer, W., et al. (2022). FogChain: a blockchain-based peer-to-peer solar power trading system powered by fog AI. IEEE Internet Things J. 9, 5200–5215. doi:10.1109/JIOT.2021.3109057
Garcia-Alvarez, M., and Mariz-Perez, R. (2012). Analysis of the success of feed-in tariff for renewable energy promotion mechanism in the EU: lessons from Germany and Spain. Procedia-Social Behav. Sci. 65, 52–57. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.11.090
Gioutsos, D. M., Blok, K., Van Velzen, L., and Moorman, S. (2018). Cost-optimal electricity systems with increasing renewable energy penetration for islands across the globe. Appl. Energy 226, 437–449. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.05.108
Global Blockchain Business Council (2021). Blockchain technology for the energy sector. GBBC Spec. Rep. Available online at: https://assets.ctfassets.net/so75yocayyva/1ugPQs2hyyTz73EcYgfZfI/ef0b95ca0948fa6af382ea57ab925948/OSI_-_Blockchain-Technology-for-the-Energy-Sector.pdf.
Hassan, M. U., Rehmani, M. H., and Chen, J. (2020). DEAL: differentially private auction for blockchain-based microgrids energy trading. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 13 (2), 263–275. doi:10.1109/TSC.2019.2947471
Herath, N., and Tyner, W. (2019). Intended and unintended consequences of US renewable energy policies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 115, 109385. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2019.109385
Hoffmeister, J., and Stossberger, B. (2018). The impact of blockchain technology on transaction costs. A procurement perspective. Copenhagen, Denmark: Master Thesis.
Honari, K., Rouhani, S., Falak, N. E., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Liang, H., et al. (2023). Smart contract design in distributed energy systems: a systematic review. Energies 16, 4797. doi:10.3390/en16124797
Huang, C., Zhao, T., Huang, D., Cen, B., Zhou, Q., and Chen, W. (2024). Artificial Intelligence-based power market price prediction in smart renewable energy systems: combining prophet and transformer models. Heliyon 10 (20), e38227. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38227
Ibrahim, I. D., Hamam, Y., Alayli, Y., Jamiru, T., Sadiku, E. R., Kupolati, W. K., et al. (2021). A review on Africa energy supply through renewable energy production: nigeria, Cameroon, Ghana and South Africa as a case study. Energy Strategy Rev. 38, 100740. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2021.100740
Ines, C., Guilherme, P., Esther, M., Swantie, G., Stephen, H., and Lars, H. (2020). Regulatory challenges and opportunities for collective renewable energy prosumers in the EU. Energy Policy 138, 111212–112020. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111212
Janssen, M., Weekrakkody, V., Ismagilova, E., Sivarajah, U., and Irani, Z. (2020). Int. J. Inf. Manag. 50, 302–309. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.08.012
Jiang, R., Wu, P., Song, Y., Wu, C., Wang, P., and Zhong, Y. (2022). Factors influencing the adoption of renewable energy in the U.S. residential sector: an optimal parameters-based geographical detector approach. Renew. Energy 201, 450–461. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.09.084
Junaidi, N., Abdullah, M. P., Alharbi, B., and Shaaban, M. (2023). Blockchain-based management of demand response in electric energy grids: a systematic review. Energy Rep. 9, 5075–5100. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2023.04.020
Juszczyk, O., and Shahzad, K. (2022). Blockchain technology for renewable energy: principles, applications and prospects. Energies 15, 4603. doi:10.3390/en15134603
Laarabi, M., and Chegri, B. (2022). Le rôle de la blockchain dans la réduction des coûts de transaction: une revue de la littérature, des théories et des modèles (Blockchain's role in reducing transaction costs: a review of the literature, theories and models). International Journal of Accounting, Finance, Auditing. Manag. Econ. 3 (2-1), 398–418. doi:10.5281/zenodo.6390362
Lin, B., Omoju, O. E., and Okonkwo, J. U. (2015). Factors influencing renewable electricity consumption in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 55 (22016), 687–696. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.11.003
Lu, J., Bai, J., Zhao, H., and Zhang, X. (2023). The effect of “Offline-to-Online” trust transfer on the utilization of online medical consultation among Chinese rural residents: experimental study. J. Med. Internet Res. 25, e43430. doi:10.2196/43430
MacKenzie, C. (2022). “Digging into the numbers - will the price and supply of raw materials hinder the renewable energy revolution,” in Green giraffe advisory. Available online at: https://green-giraffe.com/publication/blog-post/digging-into-the-numbers-will-the-price-and-supply-of-raw-materials-hinder-the-renewable-energy-revolution/.
Mendonca, M. (2007). Feed-in tariffs: accelerating the deployment of renewable energy. Abingdon, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom: Earthscan Publisher United Kingdom copyright World Future Council.
Milman, O. (2023). Monster profits' for energy giants reveal a self-destructive fossil fuel resurgence. Guard. Available online at: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2023/feb/09/profits-energy-fossil-fuel-resurgence-climate-crisis-shell-exxon-bp-chevron-totalenergies.
Ming, Z., Ximei, L., Na, L., and Song, X. (2013). Overall review of renewable energy tariff policy in China: evolution, implementation, problems and countermeasures. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 25, 260–271. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2013.04.026
Mohammad, A., Ghiassi-Farrokhfal, Y., Ketter, W., and Collins, J. (2022). The economic consequences of electricity tariff design in a renewable energy era. Appl. Energy 275, 115317. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115317
Mollah, M. B., Zhao, J., Niyato, D., Lam, K., Zhang, X., Ghias, A. M. Y. M., et al. (2020). Blockchain for future smart grid: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 8, 18–43. doi:10.1109/jiot.2020.2993601
Nadeem, T. B., Siddiqui, M., Khalid, M., and Asif, M. (2023). Distributed energy systems: a review of classification, technologies, applications and policies. Energy Strategy Rev. 48, 101096. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2023.101096
Nassiry, D. (2018). The role of fintech in unlocking green finance: policy insights for developing countries, 883. Tokyo: Asian Development Bank Institute. Available online at: https://www.adb.org/publications/role-fintech-unlocking-green-finance.
Onete, C. B., Budz, S., Bucur-Teodorescu, I., Chita, S. D., Sava, S., and Bucur, C. (2023). The relationship between renewable energy and blockchain as a sustainable technology tool\uff00\uff00tnshrp between Renewable rnergy andeBlockchainbas a Sustainabls TechnologytTool, The tucharest University of Economic Studies, Bucharest 25, 64, 919–932. doi:10.24818/ea/2023/64/919
Panuparb, P. (2019). Cost-benefit analysis of a blockchain-based supply chain finance solution. Master Thesis: University of Cambridge. Available online at: https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/122254.
Rahman, M. M., Faizal, H. M., Saat, A., and Abdul Wahid, M. (2019). “Higher initial costs for renewable electricity: emission, water, and job creation benefits offset the higher costs,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, March 5-7, 2019 (Bangkok, Thailand).
Reichmuth, T., Schar, F., and Roth, J. (2018). “Blockchain. Disrupting the renewable energy landscape,” in SUSI partners. Sustainable investments. A SUSI partners AG white paper in cooperation with the center for innovative finance. Basel, Switzerland: University of Basel. Available online at: https://edoc.unibas.ch/68782/1/Blockchain_-_Disrupting_the_Renewable_Energy_Landscape_EN.pdf.
REN21 (2023). Renewables 2023. Glob. Status Rep. Available online at: https://www.ren21.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/GSR2023_GlobalOverview_Full_Report_with_endnotes_web.pdf.
Samuel, O., Almogren, A., Javaid, A., Zuair, M., Ullah, I., and Javaid, N. (2020). Leveraging blockchain technology for secure energy trading and least-cost evaluation of decentralized contributions to electrification in Sub-Saharan Africa. Entropy 22 (2), 226. doi:10.3390/e22020226
Saxena, S., Farag, H., Brookson, A., Turesson, H., and Kim, H. (2019). “Design and field implementation of blockchain based renewable energy trading in residential communities,” in Proceedings of the 2019 2nd international conference on smart grid and renewable energy (SGRE), Doha, Qatar, 19–21 November 2019 (IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA), 1–6.
Shahryari, K., and Anvari-Moghaddam, A. (2017). “Demand side management using the internet of energy based on fog and cloud computing,” in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData) (Exeter, UK), 931–936. doi:10.1109/ithings-greencom-cpscom-smartdata.2017.143
Sow, A., Rousse, M. M., and Haillot, D. (2019). Economic analysis of residential solar photovoltaic electricity production in Canada. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 33, 83–94. doi:10.1016/j.seta.2019.03.003
Sustainable Energy for All (2022). “Africa renewable energy manufacturing,” in Opportunity and advancement. Available online at: https://www.seforall.org/system/files/2023-01/%5BFINAL%5D%2020220115_ZOD_SEForAll_AfricanManufacturingReport.pdf.
Swezey, B. G., and Wan, Y. (1995). The true cost of renewables: an analytical response to the coal industry's attack on renewable energy. Colorado, United States: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Available online at: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/legosti/old/20032.pdf.
Synwoldt, C., and Reis, A. (2011). “Cost trends of renewable energy technologies for the power generation,” in Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH. Available online at: https://energypedia.info/images/c/cc/Cost_Trends_of_Renewable_Energy_Technologies_for_the_Power_Generation.pdf.
Timilsina, G. R. (2020). Demystifying the costs of electricity generation technologies. Washington, DC, United States: World Bank Group. Available online at: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/125521593437517815/pdf/Demystifying-the-Costs-of-Electricity-Generation-Technologies.pdf.
United Nations (2024). Goal 1: end poverty in all forms everywhere. Available online at: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/poverty/.
Valizadeh, A., Moassefi, M., Nakhostin-Ansari, A., Hosseini Asl, S. H., Saghab Torbati, M., Aghajani, R., et al. (2022). Abstract screening using the automated tool Rayyan: results of effectiveness in three diagnostic test accuracy systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 22 (1), 160. doi:10.1186/s12874-022-01631-8
Verbruggen, A., Fischedick, M., Moowaw, W., Weir, T., Nadai, A., Nilsson, L. J., et al. (2009). Renewable energy costs, potentials, barriers: conceptual issues. Energy Policy 38 (2010), 850–861. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2009.10.036
Vlasov, M., and Okhlopkov, A. (2022). The impact of digital technologies on transaction costs of firms. Econ. Analysis Theory Pract. 21, 497–521. doi:10.24891/ea.21.3.497
Wang, J., Wang, Q., Zhou, N., and Chi, Y. A. (2017). A novel electricity transaction mode of microgrids based on blockchain and continuous double auction. Energies 10, 1971. doi:10.3390/en10121971
Wang, L., Zhang, Y., and Ren, Y. (2020). “Application of blockchain in life cycle cost management of weapon equipment,” in 2020 2nd International Conference on Applied Machine Learning (ICAML), 361–365. doi:10.1109/ICAML51583.2020.00079
Wei, J. (2023). “Application of blockchain technology in the field of financial management,” in Fmet 2022, aebmr. Editor V. Gaikar 227, 291–298. doi:10.2991/978-94-6463-054-1_33
Wu, J., and Khoi Tran, N. (2018). Application of blockchain technology in sustainable energy systems: an overview. Sustainability 10, 3067. doi:10.3390/su10093067
Wüst, K., and Gervais, A. (2018). “Do you need a blockchain?,” in 2018 Crypto Valley Conference on Blockchain Technology (CVCBT), Zug, Switzerland, 45–54. doi:10.1109/CVCBT.2018.00011
Yi, H., Lin, W., Huang, X., Cai, X., Chi, R., and Nie, Z. (2021). Energy trading IoT system based on blockchain. Swarm Evol. Comput. 64 (2021), 100891. doi:10.1016/j.swevo.2021.100891
Yusida, E., Stevens, T., and Bianchi, E. (2022). Renewable energy infrastructure development and its impact to economic around the world: a case in Italy, Indonesia, and US. Econ. Sustain. Sci., 163–172. doi:10.2478/9788366675711-019
Keywords: auctioneering, blockchain technology, cost, cost efficiency, renewable energy, smart contract
Citation: Nwulu N, David L and Badrudeen TU (2025) Leveraging blockchain technology for cost efficiency of renewable energy. Front. Energy Res. 13:1640117. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2025.1640117
Received: 03 June 2025; Accepted: 06 October 2025;
Published: 20 October 2025.
Edited by:
Solomon Giwa, Olabisi Onabanjo University, NigeriaReviewed by:
Leo Raju, SSN College of Engineering, IndiaVipina Valsan, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, India
Copyright © 2025 Nwulu, David and Badrudeen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Love David, bG92ZW9wZXllbWlkQHVqLmFjLnph
 Nnamdi Nwulu
Nnamdi Nwulu Love David
Love David Tayo Uthman Badrudeen
Tayo Uthman Badrudeen