- 1Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Pabna University of Science and Technology, Pabna, Bangladesh
- 2Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Rajshahi University of Engineering and Technology, Rajshahi, Bangladesh
- 3Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering, Feni University, Feni, Bangladesh
- 4School of Information and Communication Technology, Griffith University, Brisbane, QLD, Australia
- 5Center for Advanced Analytics (CAA), COE for Artificial Intelligence, Faculty of Engineering & Technology (FET), Multimedia University, Melaka, Malaysia
Rural communities in Bangladesh face persistent energy access challenges due to geographic isolation and inadequate infrastructure. This study investigates the design and optimization of off-grid hybrid renewable energy systems for five distinct rural locations, utilizing solar photovoltaic (PV), wind turbines (WT), and four types of battery energy storage systems (BESS): ZnBr Flow, Li-Ion NMC, Lead-Acid, and LiFePO4. Using HOMER Pro (version 3.14.2), simulations were performed based on real hourly load profiles and resource data (solar irradiance, wind speed, and temperature) from NASA. Each system configuration was assessed for economic feasibility, renewable energy penetration, and environmental impact. Results show that the PV-WT-ZnBr Flow battery configuration outperformed others at all sites, achieving the lowest Net Present Cost (NPC) of $171,720, Cost of Energy (COE) of $0.0688/kWh, and 100% Renewable Fraction (RF) with zero carbon emissions. ZnBr Flow batteries demonstrated high efficiency, long lifespan (30 years), and low maintenance requirements. Sensitivity analysis revealed the influence of resource variability, load profiles, and component costs. This study confirms that ZnBr-based hybrid microgrids offer a viable, cost-effective, and scalable solution for sustainable rural electrification in Bangladesh and other remote or underdeveloped regions worldwide.
1 Introduction
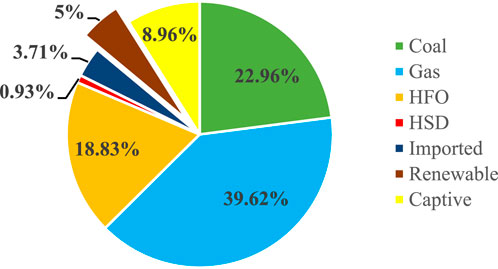
Bangladesh has in fact been experiencing constant economic growth, which has resulted in rising electricity demand (Sieed et al., 2020). The local sector currently dominates consumption, but since saturation levels of access are reached, the industry and services sectors will also be a big contributor to electricity consumption levels for the subsequent decades (Debnath and Mourshed, 2022). Up to 2023, Bangladesh’s national electrification level is significantly over 96%, although it hides vast disparities between urban and rural spheres (Haq et al., 2024). The majority of rural and off-grid locations, particularly the hill tracts, coastal belts, riverine islands (chars), and forest-edged villages, remain without stable or inaccessible grid electricity due to geographical inaccessibility as well as under-developed infrastructure (Zomers, 2014; Kumar et al., 2021). Renewable energy systems have become an economic solution to mitigate electricity shortages, particularly in isolated rural areas (Yu and Geoffron, 2020). Nevertheless, most aid-financed photovoltaic (PV) systems in off-grid areas are plagued by neglect because of insufficient funding for maintenance (Pandyaswargo et al., 2022; Adenle, 2020). Bangladesh is at a critical point of crisis in the matter of its energy resources due to the rapid urbanization of the country and growing energy demands (Bagdadee et al., 2025). Furthermore, the dense population and low-lying delta nature of the country make it challenging to meet its needs in an environmentally friendly manner that is compatible with the problem of global warming (Islam et al., 2021). The rapid expansion of the renewable energy sources is crucial in order to achieve the net-zero carbon goals, with the role of renewables being anticipated at 60% of the electricity generated by 2030 and 90% by 2050 (Akash et al., 2024; Bouckaert et al., 2021). The Figure 1 is for Bangladesh’s energy composition in 2025 with an installed capacity of 31,261 MW. Gas remains the dominant component at 39.62%, then coal (22.96%) and HFO (18.83%). The significant fact is that renewable energy contributes only 1,562.84 MW, only 5% of the installed capacity (Electricity Generation Mix, 2025). This low percentage is a sign of Bangladesh’s infancy in harnessing sustainable energy. While its tremendous prospect in solar and wind power, the country is still reliant on fossil fuels. However, the contribution of renewable energy to the national grid reflects greater investment and policy focus (Avwioroko, 2023; Deng and Guo, 2017). Progress in this area must be enhanced in the pursuit of energy security, climate resilience, and carbon emissions mitigation. Strategic growth of renewables would significantly transform Bangladesh’s energy future (Joarder et al., 2024; Hussain et al., 2024).
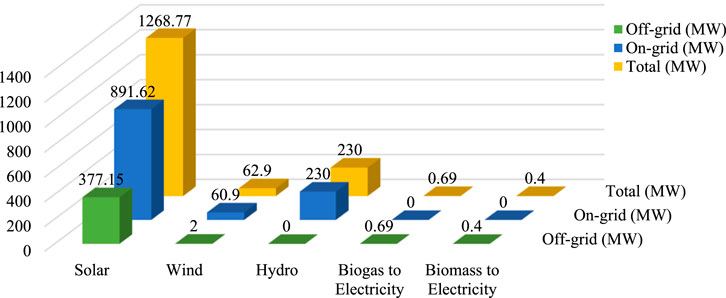
Bangladesh has experienced a steady increase in electricity demand over the last decade, with electricity generation more than doubling and access to electricity rising from 47% in 2009 to 94% in 2019, primarily driven by the household sector (Sieed et al., 2020; Taheruzzaman and Janik, 2016; Hasan and Mohammad, 2019). Around 16% of the global population lacks access to electricity, significantly impacting productivity and sustainable development (Mohn, 2020). In Bangladesh, where 64.96% live in rural areas, many experience substandard electricity quality, hindering economic growth and exacerbating climate vulnerability (Fyza and Sarkar, 2020). Fossil fuel reservoirs are depleting daily, and the world will run out of fossil fuels in the coming years, highlighting the urgency of addressing the fossil fuel crisis alongside rising costs and scarcity (Hosseini, 2022; Wood, 2020). In a bid to provide security in terms of energy, nations are moving primarily onto RE energy sources to meet their power demands (Zafar et al., 2018). As of December 2021, global RE generation capacity was 3146 GW, according to REN21 (Abdullah-Al-Mahbub and Islam, 2023). The Figure 2 indicates Bangladesh’s capacity for renewable in 2025 to be 1,562.76 MW. Solar energy leads the way with 1,268.77 MW, of which 377.15 MW is off-grid and 891.62 MW is on-grid, reflecting extensive use across the nation. Wind power adds 62.9 MW, while hydropower adds 230 MW, all being on-grid. Biogas and biomass electricity are minimal at 0.69 MW and 0.4 MW, respectively (RE Generation Mix, 2025). Dominance of solar highlights its strategic importance, whereas restricted progress of other sources suggests untapped possibility (Abdullah-Al-Mahbub et al., 2022). Diversification of clean technologies is essential to design a more diversified, sustainable, and resilient energy future of Bangladesh (Safi et al., 2023).
Approximately 76% of the population in Bangladesh resides in rural areas, where access to electricity has significantly improved under the Rural Electrification Program—expanding from just 250 villages in 1971 to 39,684 villages—contributing to improved living standards and reduced poverty rates (BARKAT, 2005). Power outages, particularly those lasting longer than 8 h, are increasing, most notably during the hot summer months of June, July, and August, showing the vulnerability of the electrical system to climate-change-fueled weather events (Pahwa, 2016; Singh, 2024). As it increases in numbers and increasing energy needs, the conventional energy system that relies heavily on non-renewable resources is increasingly found wanting (Piyal et al., 2023; Ali et al., 2024). The availability of RES like solar and wind relies mainly on seasonal fluctuations in solar irradiance and wind speeds. One solution to the problem is to import HRES, which are developed to blend multiple sources of energy to minimize the effect of these fluctuations (Jaiswal et al., 2022; Ali et al., 2025a). Integrating RE sources with accessible battery capacity is vital to address the problem of stochastic power generation and over-reliance on the national grid. Solar and wind are abundant in quantity and cause no environmental cost (Ayua and Emetere, 2024; Baidya et al., 2025). A hybrid RES-based power system is the optimal option for rural electrification where extension of the utility grid is not possible (Krishan and Suhag, 2019).
The integration of various battery technologies to hybrid renewable energy systems has become the high-profile area globally aimed at optimization of access to energy at the regional scale. A number of studies have made use of the HOMER Pro program in order to estimate the techno-economic feasibility of various battery configurations to match geography, climate, and load conditions. Kumar et al. (2024) investigated the viability of an HRES for rural electrification in India’s Billerahalli village. A hybrid system was created combining solar PV, wind, hydrogen storage, electrolyzers, and batteries. The most cost-saving combination was identified and presented in the study as wind turbines, hydrogen storage, and electrolyzers with a lowest NPC of $5.21 million and LCOE of $0.25/kWh. This configuration provided a 99.8% proportion of renewable energy, reduced carbon emissions, and was extremely cost-effective and thus the best answer for rural electrification that is sustainable. Solanki et al. (2024) compared lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries in HOMER Pro for hybrid off-grid systems. Lithium-ion showed better performance with reduced net present cost ($191,000), cost of energy ($0.415/kWh), and increased renewable fraction (∼81%). The study shows the effectiveness and greater lifespan of lithium-ion, which is economically and environmentally sound. However, it only considered two types of batteries and did not perform sensitivity analysis on load fluctuation and fuel prices, thus limiting its broader application. Ciez and Whitacre (2016) analysis techno-economically analyzed hybrid PV/diesel/battery systems with three batteries. It was concluded that the low-cost and high-energy lithium-ion batteries were able to compete with the non-renewable options. The lead-acid batteries are preferable at lower discount rates, and lithium ion batteries are capable of lower power costs at higher discount rates. Shezan et al. (2016) assessed the performance of an off-grid wind-diesel-battery-PV hybrid power system, based on HOMER software, for a remote area. The results showed that, compared to conventional power systems, NPC and CO2 emissions of the optimized system can be reduced by about 29.65% and 16 tons, respectively. Dhundhara et al. (2018) examined the technical and economic viability of different configurations of wind/PV/diesel/biodiesel power systems with two types of batteries. The results showed that the lithium-ion battery was more feasible, both technically and economically, than lead-acid battery, which was expected to play a prominent role in various applications of future power systems. Paudel et al. (2011) optimized PV/wind hybrid systems with lead-acid batteries for telecommunication services in Nepal’s remote locations. GFM-800 battery design achieved higher reliability (99.99%) and low total system cost. The paper offers realistic design and operating data for off-grid power solutions in remote sites. However, the research focused on lead-acid technology and a particular location, thus preventing applicability to other battery technologies and sites. Shezan et al. (2021) optimized a hybrid microgrid for Penang Island resort using renewable energy and battery storage. The system had an NPC of $21.66 million and a renewable penetration of 27.8%. Although the battery type was not detailed, results were reported to demonstrate improved energy efficiency and utilization of excess energy to loads. The lack of battery details makes impossible the identification of storage performance, critical to replication to other microgrids.
Akram and Abdul-Kader (2024) evaluated second-life lithium-ion batteries (SLBs) for energy storage in renewable systems. SLBs offered a cost-effective and sustainable solution by repurposing spent EV batteries, facilitating increased integration of renewable energy. HOMER Pro simulations show attractive economic benefits, yet uncertainty over battery degradation and regulation constraints limit the deployment. The study underscores the significance of standardized testing and regulatory frameworks to make SLBs more commercially viable and reliable. Sarker et al. (2024) studied second-life lithium-ion batteries in residential PV systems. HOMER Pro simulations revealed that SLBs effectively store excess solar power, save money, and achieve maximum renewable fraction. However, performance inconsistencies relying on diversified battery aging and non-standardized certification procedures were observed. The study suggests SLBs as a clean, viable option for residential PV energy storage but calls for quality control improvement for large-scale adoption. Kebede et al. (2021) modeled seven lithium-ion chemistries against flooded lead-acid batteries in HOMER Pro. LiFePO4 batteries had 10%–25% less cost of energy than lead-acid due to improved cycle life and energy density. The analysis confirms the technical and financial advantage of lithium-ion for off-grid systems. Limitations include a homogeneous temperature assumption and omission of end-of-life recycling expenditures, which affect real-world sustainability analysis. AbdElrazek et al. (2025) optimized a solar-wind hybrid power plant with battery storage for a Saudi Arabian EV charging station. EV demand was adequately addressed by HOMER Pro optimization through cost-renewable balance. The unspecified battery type reduces the overall transparency of storage performance and cost-effectiveness, and assumptions being geography-specific can limit broader application. However, the study demonstrates the feasibility of hybrid renewables to complement EV infrastructure. Kwon et al. (2024) combined battery and hydrogen energy storage in a hybrid configuration using deep reinforcement learning for optimal control. Analysis with HOMER Pro revealed a 13.2% increase in the fraction of renewables, a decrease in CO2 emissions by 78.69%, and cost savings of 23.5%. The hybrid system applies batteries to short-term and hydrogen for seasonal storage. The advanced control scheme and high resource needs may, however, hinder real-world implementation in developing nations. Arsad et al. (2022) compared hydrogen storage and battery technology in solar-wind hybrid systems. Hydrogen was preferable for long- to seasonal-term storage, while batteries were better suited for short-term utilization. Despite cost benefits in bulk storage for hydrogen, high initial investment and infrastructural challenges are still playing the role of a limiting factor. The study presents good guidance to select energy storage technology based on storage time but encounters economic and technical hurdles to hydrogen technology.
Although a number of studies have examined hybrid renewable energy systems in Bangladesh, most of them have taken into account single locations, generalized assumptions, or a single type or a few battery storage technologies. These studies often fail to account for extensive geographic, socio-economic, and load demand diversity prevailing in the rural locations of the country. In addition, comparative analyses of different kinds of batteries (i.e., Lead-Acid, Lithium-Ion, and Nickel-based batteries) in different rural settings using simulation tools like HOMER Pro have been few. Without such a comparison, it is not evident which battery configuration offers the best techno-economic and environmental performance in region-specific contexts. The lack of in-depth assessments undermines the ability of policymakers and practitioners to make location-specific and informed decisions for rural electrification. This study bridges this gap by optimizing and comparing different battery storage options in some rural areas of Bangladesh with HOMER Pro, with the expectation of finding the cheapest and most sustainable hybrid system configurations.
1.1 Objectives of the study
The major objective of this research is to evaluate and optimize the performance of different battery storage technologies in hybrid off-grid renewable energy systems in different rural locations of Bangladesh according to HOMER Pro simulation software. The study focuses on techno-economic performance analysis of different battery types, viz., Lead-Acid, Lithium-Ion, and others, under different regional conditions like load demand and variability of renewable energy sources. It also aims to identify the most cost-effective and efficient battery configuration for every region by assessing key performance measures such as NPC, COE, and RF. In addition, the study examines the feasibility of one battery solution fitting multiple rural sites. Through these objectives, the study seeks to provide evidence-based policy suggestions to guide informed sustainable rural electrification policies and investments that are responsive to the unique energy needs and constraints of different regions in Bangladesh. To bridge the gap of rural Bangladesh battery technology studies, this study has tried to optimize and contrast different battery storage alternatives using HOMER Pro. With a focus on cost, performance, and integration with renewables across regions, this study will identify regionally appropriate battery setups for regionally compliant sustainable rural electrification solutions.
1.2 Contributions of the study
This paper makes the following key contributions:
• It presents a comparative techno-economic analysis of four battery technologies across five geographically diverse rural locations in Bangladesh using HOMER Pro.
• It incorporates real hourly load and meteorological data to ensure accurate simulation, enhancing the realism and replicability of the results.
• It identifies ZnBr Flow batteries as a regionally robust and scalable solution for off-grid electrification.
• It provides actionable insights for energy planners and policymakers by linking technical results with rural energy access and sustainability goals.
1.3 Organization of the paper
Section 2 outlines the methodology, including simulation tools, resource assessment, and modeling assumptions. Section 3 presents the simulation results and a detailed techno-economic and environmental performance comparison. Section 4 provides the conclusion, highlighting key findings and future research directions.
2 Methods and materials
To study the operational behavior of the renewable energy scenarios holistically, a systematic analytical framework was employed in this research. It consisted of the selection of study area, load profile study, renewable resource data collection, microgrid design, techno-economic modeling and optimization, and environmental impact analysis, culminating in the overall research conclusion.
2.1 HOMER Pro software
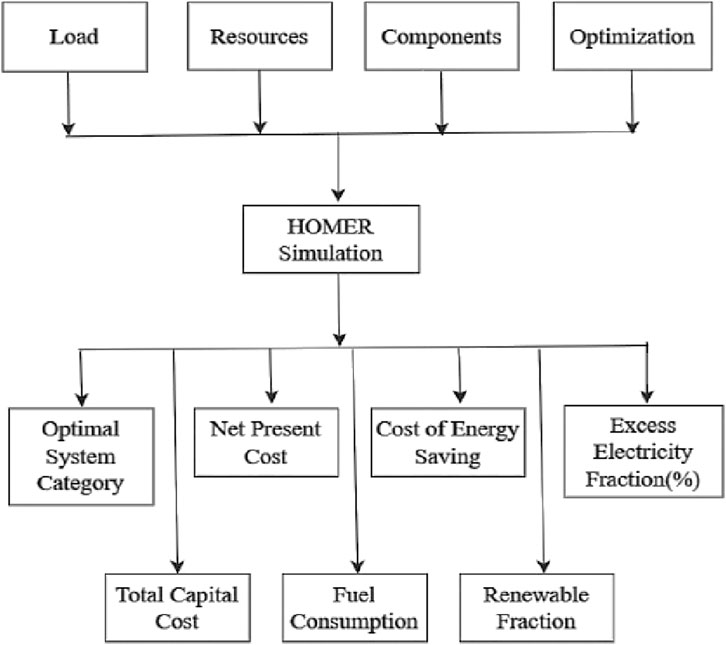
HOMER Pro is hybrid renewable energy system simulation and optimization software, version 3.14.2 to be precise. Drawing on a user base established through decades of working with distributed power systems, it is among the most popular pieces of software available on the market for the optimization, design, and analysis of microgrids and renewable energy systems worldwide (Mahmud et al., 2022). The National Renewable Energy Laboratory developed a simulation package in the form of HOMER to assist the respective stakeholders in selecting the most appropriate energy mix for renewable microgrids (HOMER, 2024). HOMER models, analyzes technical feasibility, and optimizes architectures of complex hybrid power systems. HOMER models, analyzes technical feasibility, and designs complex hybrid power systems. It predicts life-cycle cost, performance, and distributed generation for remote sites, which makes microgrid design problems simpler (Homer Energy, 2024). HOMER Pro simulates a wide range of renewable and non-renewable energy systems and features advanced applications like battery backup and hydrogen systems (Douiri, 2019). Its calculation module optimizes the system configuration based on technical and economic criteria like NPC and COE. HOMER Pro is a sophisticated simulation tool with consideration like resource availability, load demand, and operational constraints; It simulates system configurations to determine the most economic and optimal solution for the hybrid renewable energy system (Hossain et al., 2019). Figure 3 shows HOMER Pro architecture which allows the customer to select the optimal hybrid renewable energy system considering budget and technological benefits (Sultana et al., 2021; Razmjoo et al., 2019). The system simulates through the input parameters: load, resources, components, and optimization criteria. HOMER Pro is a comprehensive financial and environmental analysis tool that calculates payback periods, capital expenditures, and operating expenses, providing information on a project’s financial viability and evaluating carbon emissions.
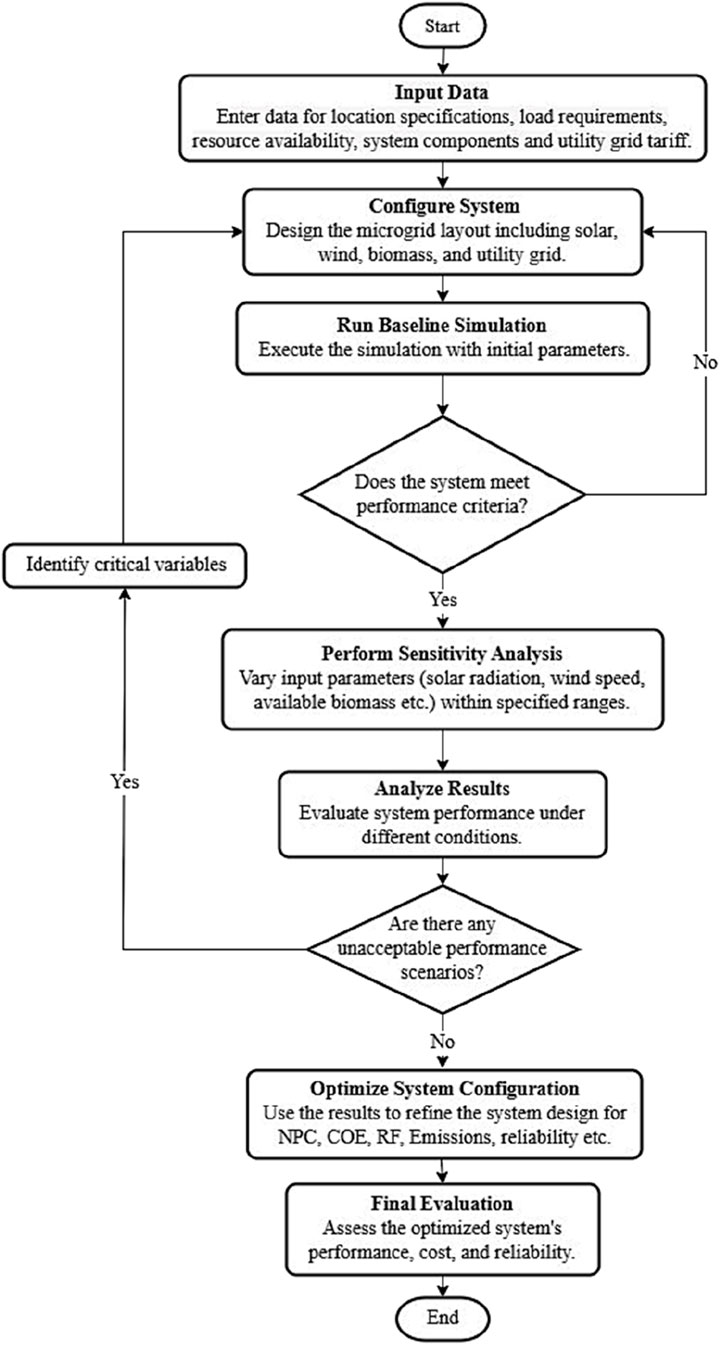
The work flow in HOMER Pro is shown in Figure 4 design data set and system configuration input, first performance testing with base-line simulation (Ali et al., 2024). System performance with variations sensitivity analysis, identification of critical variables, least cost, maximum reliability, and minimum emissions optimization, along with feasibility.
HOMER Pro minimizes battery storage too, trading energy reliability for expense, and models life-cycle expenses and environmental effects in a manner that microgrids are economical, sustainable, and future-proof for energy requirements (Alyahya et al., 2025; Zou et al., 2024; Imanloozadeh et al., 2024).
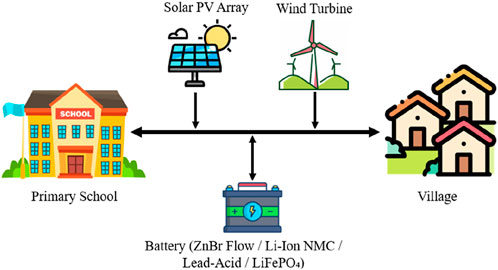
Figure 5 presents a schematic of a hybrid renewable energy system (HRES) tailored for an isolated village, integrating PV panels, WT, and various BESS such as Lead-Acid, LiFePO4, Li-Ion NMC, and ZnBr flow batteries. This configuration ensures a reliable electricity supply to critical loads like schools and households. Combining multiple renewable sources with diverse storage technologies enhances system efficiency, stability, and sustainability in off-grid settings (Ali et al., 2025b; Ahmed et al., 2023). Such hybrid systems have been shown to be effective in meeting the energy demands of remote areas in Bangladesh.
2.2 Selection of study area
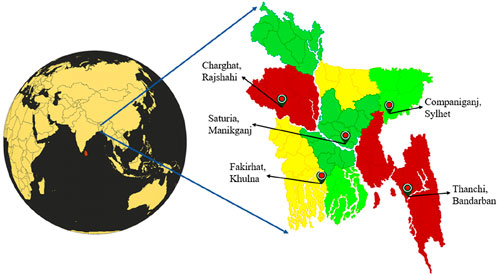
This study investigates five geographically and socio-economically distinct rural locations of Bangladesh: Charghat, Rajshahi (24°22.5′N, 88°36.0′E); Saturia, Manikganj (23°50.5′N, 90°0.3′E); Fakirhat, Khulna (22°45.3′N, 89°31.4′E); Thanchi, Bandarban (22°10.8′N, 92°13.7′E); and Companiganj, Sylhet (24°49.1′N, 91°54.9′E). These locations have been selected with the perspective of variability of geography, climate, and access to energy so that a comparative assessment of battery storage technologies for hybrid off-grid systems can be undertaken. All of these regions are plagued by unstable or poor grid connectivity, which takes a toll on agriculture, domestic business, educational institutions, and medical services. Despite numerous renewable energy prospects in these locations (solar and hydro to biomass) the optimum energy solutions have not been put into practice yet. The aim of this study is to examine and recommend sustainable battery-based hybrid systems with HOMER Pro tailored to each location’s specific energy needs and resources. Figure 6 shows the global location of Bangladesh and indicates the selected five rural study sites, graphically indicating their spatial positions and the need for localized, authentic energy infrastructure to facilitate sustainable rural development.
2.3 Load profile analysis
Figure 7 presents the average load profiles of a rural Bangladeshi village and its school, derived from actual consumption data utilized for microgrid simulation in HOMER Pro. The village contains roughly 2,500 residents living within 850 houses. This demographic and energy consumption profile was adopted as a representative rural load profile and applied uniformly across all five study locations for consistency in comparative analysis. While local variations in population exist, this standardization allows for controlled optimization focused on the impact of renewable resource availability and battery technology differences. Refined household energy use includes 1,200 units of 60-W ceiling fans, 2,200 units of 15-W LED lamps, and 50 units of 100-W TVs. This equates to an average per day energy consumption of 502.00 kWh and a peak load of 107.79 kW. Subfigure (a) shows the hour-by-hour fluctuation of village load, with the evening peak. Subfigure (b) shows monthly variations, where persistent evening peaks are seen all year round. The five-day-a-week primary school from 9:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. utilizes 16 ceiling fans at 60 W each and 35 LED bulbs at 15 W each, operating on average at 8.35 kWh/day with peak load of 1.21 kW. Subfigure (c) and subfigure (d) show the daily and monthly load of the school respectively, with the school hours marked as peak usage time. This specific load pattern was required to maximize hybrid microgrid system design tailored to local demand structures.
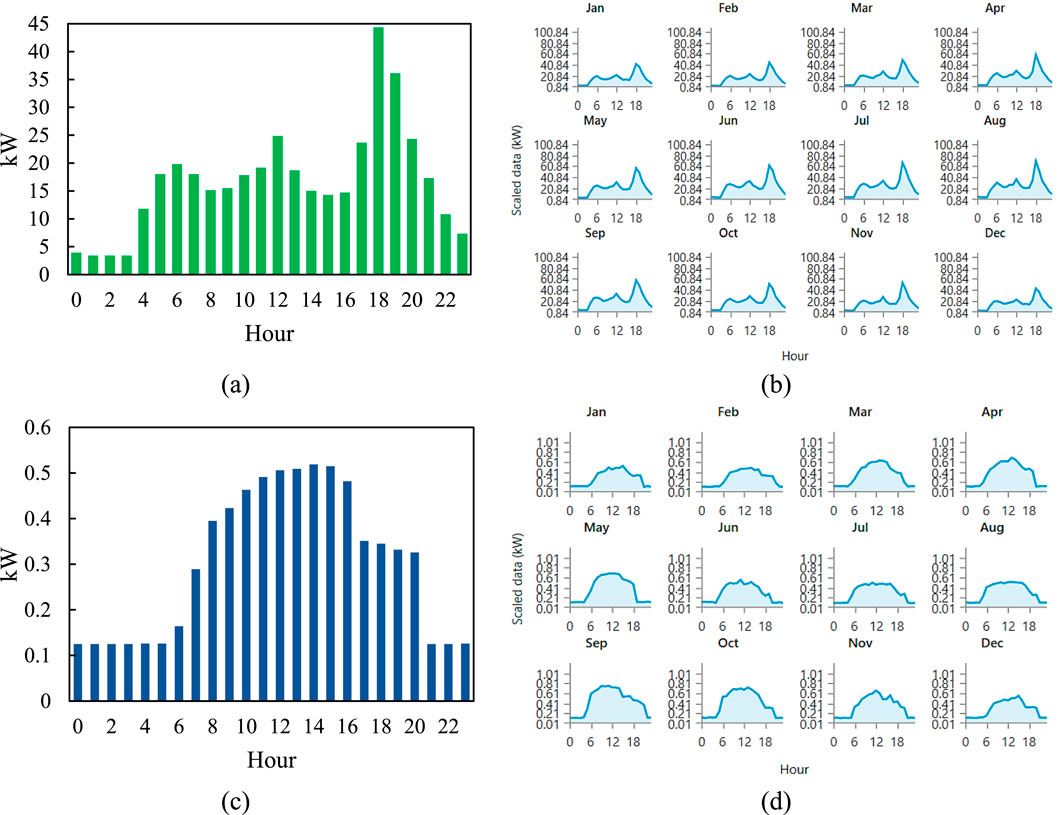
Figure 7. Hourly and monthly load variation profiles: (a) hourly residential load, (b) monthly residential load, (c) hourly educational load, and (d) monthly educational load in the study area.
2.4 Data collection of renewable resources
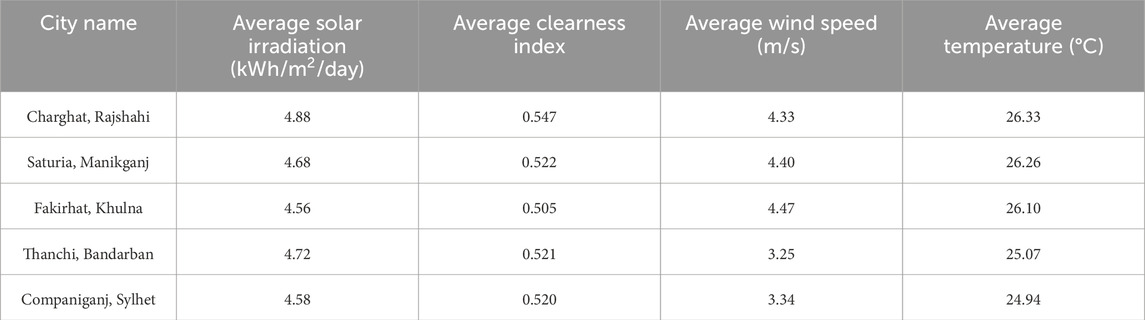
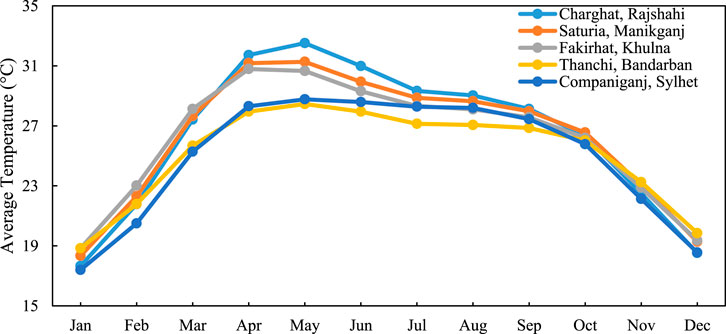
To carry out the HOMER simulation, it is necessary to obtain information on renewable energy resources such as solar radiation, the clearness index, temperature, and wind speed at specific location (Jakhrani et al., 2012). The NASA/Power database to obtain solar irradiation data for the selected locations in Bangladesh, comparing it with ground-based measurements over a 34-year period from 1984 to 2017 for validation purposes (Jed et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2008). Table 1 illustrates the key meteorological parameters—mean solar irradiation, clearness index, wind speed, and temperature—used for simulating the renewable energy systems of five rural areas of Bangladesh. Charghat, Rajshahi has the highest solar irradiation (4.88 kWh/m2/day) and clearness index (0.547), i.e., high solar resource potential. Facirhat, Khulna has the highest mean wind speed (4.47 m/s), having potential for wind energy generation. Thanchi, Bandarban and Companiganj, Sylhet have comparatively lower wind speeds, i.e., higher solar resource dependence. These environmental factors affect hybrid system optimization with HOMER Pro and are the reasons for region-specific energy system planning.
2.4.1 Solar irradiance and clearness index
Solar irradiance is a major indicator for energy generation in PV systems, as higher solar radiation enhances potential output (Taha and Babiker, 2019). The clearness index, indicating atmospheric transparency, influences the sunlight reaching panels, thereby affecting their efficiency and overall performance (Louis and Tertsea, 2023). The Figure 8 illustrates monthly variation in daily solar radiation and clearness index for five rural sites. Maximum solar radiation is found in April at Charghat (6.33 kWh/m2/day), followed by Saturia (5.90) and minimum at Fakirhat in September (3.83). Clearness index is maximum in January at Thanchi (0.648) and maximum at Charghat in December (0.652). During the monsoon period (June–August), both radiation and clearness index are reduced to a great extent, with minimum clearness index being 0.353 found at Fakirhat in July. However, radiation levels are not significantly different at Thanchi and Companiganj during this period. These zonal and seasonal variations show the impact of cloud cover and atmospheric transparency on solar power potential. Charghat and Thanchi offer relatively uniform solar performance throughout the year, whereas Fakirhat varies, indicating a need for hybrid configurations. This evaluation is added to system design from local resource profiles in efficient energy planning in HOMER Pro.
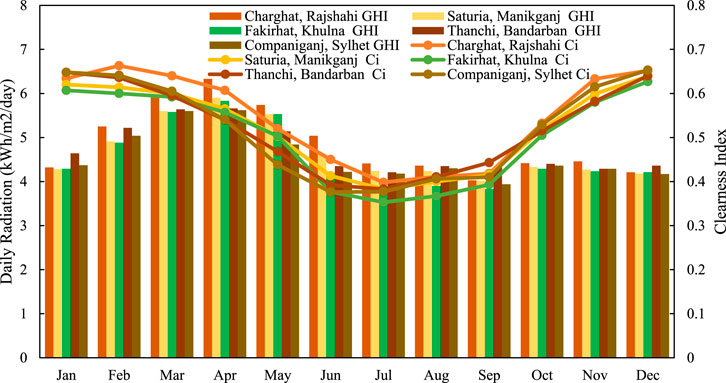
Figure 8. Monthly trends of daily solar irradiation and clearness index for selected off-grid locations in Bangladesh.
2.4.2 Wind speed
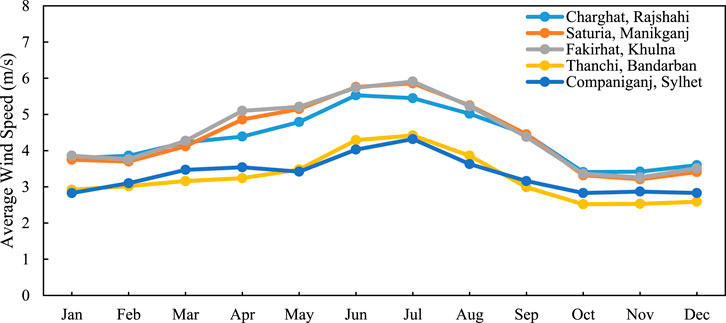
Wind speed directly affects the output of WT; higher wind speeds lead to increased electricity generation, while lower speeds result in reduced output (El-Ahmar et al., 2017; Qi et al., 2024). The Figure 9 shows the average monthly wind speed in five Bangladesh rural areas. Wind speed is highest between May and July with Fakirhat, Khulna registering the highest of 5.91 m/s in July, followed by Saturia, Manikganj (5.86 m/s) and Charghat, Rajshahi (5.45 m/s). This increased wind speed during summer and monsoon months indicates that there are good prospects for power production by utilizing wind power. In contrast, the minimum speed is recorded from February to October with Thanchi, Bandarban always yielding the minimum values, for instance, 2.52 m/s in October and 2.53 m/s in November. Companiganj, Sylhet also witnesses low wind speed during these months (e.g., 2.83 m/s in December and January). Seasonal differences are crucial for optimal hybrid system design in HOMER Pro where wind resources complement solar conditions.
2.4.3 Temperature
The Figure 10 indicates the average monthly fluctuation in five rural districts of Bangladesh. May is the warmest month with Charghat being the highest at 32.52 °C, Saturia second (31.27 °C), and Fakirhat third (30.66 °C), while Thanchi and Companiganj are slightly cooler at 28.46 °C and 28.77 °C respectively. January is the lowest month with Charghat on 17.66 °C and Companiganj lower at 17.4 °C. A steep increase in temperature from February to April is observed, with Charghat increasing from 21.78 °C to 31.72 °C, and Fakirhat from 23.02 °C to 30.79 °C. In monsoon months (June–August), the temperature becomes uniform between 27 °C and 30 °C, Thanchi being always the coolest. Overall, the graph depicts significant seasonality, with increased inshore temperatures and relatively intermediate conditions offshore in the hilly and northeast areas, validating the assessment of temperature-sensitive renewable energy system performance. As temperatures increase, the efficiency of solar panels decreases due to heightened electrical resistance, resulting in lower output voltage and power production (Klugmann-Radziemska, 2023; Eze et al., 2024).
2.5 System modeling
This section lays out the methodology used by HOMER in simulating the key components of an isolated renewable energy system. These are the PV array, WT system, and different types of BESS in multiple regions. HOMER simulates system performance using component-specific technical and economic inputs. The PV and WT models take into account local solar radiation and wind speed, respectively, and the BESS model tracks state of charge, charge/discharge efficiency, and lifecycle. Each component’s behavior is simulated for varying load and resource conditions to optimize the system design. The subsequent subsections provide detailed mathematical models and operational assumptions of each component for accurate performance and cost analysis of the hybrid renewable energy system.
2.5.1 Solar PV model
PV cells work by transforming sun energy into electrical power using semiconductor devices, with silicon-based material being utilized as the primary material in the cells (Redouane et al., 2025). The actual PV power output can be formulated in terms of rated capacity, derating factors, solar radiation, and temperature effects, as formulated in Equation 1 (Kumar et al., 2025; Qasim et al., 2025). In addition, the cell temperature in Equation 1 can be calculated based on ambient conditions, as in Equation 2 (Barakat et al., 2022; Eteiba et al., 2018). Cell temperature significantly affects efficiency; higher temperatures generally reduce power output (Nguyen et al., 2024; Hossein Jahangir et al., 2022).
where,
2.5.2 WT model
HOMER employs a robust platform for modeling wind power production by integrating environmental, physical, and technical factors in order to achieve accurate power output prediction. The procedure begins with the inputting of wind resource data, typically time series at hourly or sub-hourly resolution. A significant initial step is scaling reference wind speed data to the WT hub height, for which two advanced methods are offered by HOMER: the power law method, widely used for general applications and expressed in Equation 3 (Barakat et al., 2024; Güven and Mahmoud Samy, 2022), and the logarithmic law method, preferred for complex terrains where higher precision is required and planned in Equation 4 (Serat et al., 2024). Actual conditions usually vary because of air density variations, which HOMER adjusts for through a density adjustment calculation, described in Equations 5, 6 (El-Maaroufi et al., 2024; Bilal et al., 2025). Besides, HOMER simulates system losses by a multiplicative sequence of efficiency factors, as described in Equation 7.
2.5.3 BESS model
HOMER simulates the BESS by utilizing the Kinetic Battery Model (KiBaM) which models the battery system as two separate energy tanks: available energy tank and bound energy tank. The two-tank system is a better representation of the complex electrochemical reactions occurring in the battery while in use. Based on this concept, the energy stored in the battery bank is the integral of available and bound energy devised in Equation 8. Therefore, the power level that can be discharged by the battery is constrained by Equation 9 (Ali et al., 2025b). Similarly, the power level that can be discharged by the battery is constrained by Equation 10. After calculating the actual charge or discharge power, HOMER computes the resulting available and bound energy at the end of the time step by the subsequent Equations 11, 12, respectively (Homer Energy, 2025).
Three various limits are computed by HOMER in order to get the maximum charging power of a storage bank, with the minimum value being the ultimate limit after applying charging efficiency, as in Equation 13. The first limit is based on the kinetic battery model, which calculates maximum absorbable power based on available energy, as in Equation 10. The second limit is based on the maximum charge rate, as scheduled in Equation 14. The third limit considers the maximum charging current, as in Equation 15. In contrast, HOMER considers discharging losses after energy exits the two-tank system. Therefore, the maximum discharge power of the storage bank is determined using Equation 16 (ALAhmad et al., 2025). For reliable operation of the BESS, its SOC should always be maintained above a specified minimum value, as given by Equation 17 (Fatih Guven et al., 2024). Additionally, the initial energy capacity of the BESS can be determined using Equation 18 (Ba-swaimi et al., 2024a; Ba-swaimi et al., 2024b; Abed et al., 2025).
2.5.4 Converter model
The installation of the power conversion equipment in HOMER’s model framework becomes extremely important while planning IHRES systems with both AC and DC components (Mokhtara et al., 2021). This conversion stage provides the capability for AC-DC or DC-AC transformation of electricity to ensure optimized power flow regulation for IHRES. Because there is bound to be some loss of energy, the power input and output to the converter are connected through its rate of conversion efficiency, less than 100%, as illustrated in Equation 19 (Güve et al., 2022; Ba-swaimi et al., 2025).
2.6 Economic modelling
Economic modelling in HOMER plays a crucial role in the evaluation of the financial viability and cost-effectiveness of different configurations of energy generation systems. With the assessment of the cost and benefit effects of different system configurations, economic modelling assists stakeholders in making informed investment choices on clean and sustainable energy options (Ezekwem et al., 2024).
The HOMER Pro simulations were conducted using a project lifetime of 25 years, a nominal discount rate of 15%, and an annual inflation rate of 9%. These values reflect regional economic conditions and investment expectations in rural energy projects in Bangladesh. Using Equation 22, HOMER internally converts these inputs into a real discount rate for cost optimization. All financial outputs such as NPC, COE, and IRR are expressed in real USD. This clarification ensures transparency and enables replication by future researchers using similar assumptions.
2.6.1 NPC
NPC is a financial tool to measure the cost-effectiveness of a project or investment in its lifespan. It accounts for the present value of money by discounting future cash flows to their present amount. NPC is the total cost of a project, such as initial investment, operational costs, and any future revenue or savings, in present value terms. The total NPC can be determined by applying the Formula 20 given below (Aziz et al., 2020):
where
where N is the number of years and i is calculated employing (Twaha et al., 2012):
where,
2.6.2 LCOE
LCOE is found by dividing the total costs of the project (capital expenditures, operating expenditures, and fuel expenditures) by the total electricity generated during the project’s life. It is the average cost per unit of electricity produced and can be employed to equate various energy sources or technologies. It can be employed to identify the cost competitiveness and economic viability of alternative generation of energy. The formula of LCOE is presented in Equation 23 (Ezekwem et al., 2023):
where,
2.6.3 IRR
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR): Another significant parameter to employ in assessing the financial viability of a system is the IRR. The IRR is the expected return on investment as a percentage. To calculate the IRR, the NPC will need to be reduced to zero at a given discount rate. The IRR can be calculated using Equation 24 (Jawad et al., 2023).
The parameters being considered are in line with the values contained in the NPC formula. The higher the IRR, the higher is the return after subtracting the costs of production (Ashraful Islam et al., 2024).
2.6.4 RF
RF is a measurement of the proportion of energy generated from renewable sources over the total energy generated within the system. It is dimensionless and calculated by Equation 25 (Nallolla et al., 2022):
where,
2.7 Techno-economic specifications
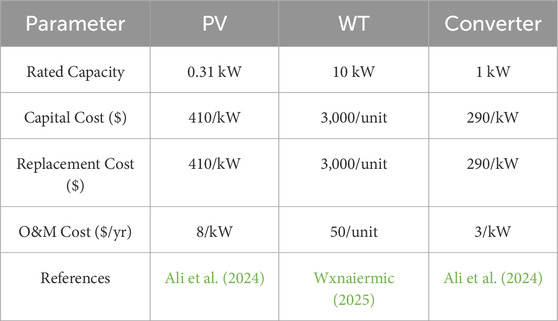
The techno-economic variables give the rated capacities, capital and replacement costs, and annual O&M costs of the major system components, including the PV system, WT, and power converter which is shown in Table 2. Generic 10 kW horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWTs) was used in the microgrids that offer an inexpensive, scalable, and low-maintenance solution that is more powerful and efficient than vertical-axis turbines, but delivers reliable decentralized energy production (Zahariea et al., 2018; Winslow, 2017). The variables are needed to determine system performance, estimate life cycle cost, and conduct financial analysis for ensuring the viability and sustainability of the hybrid renewable energy system.
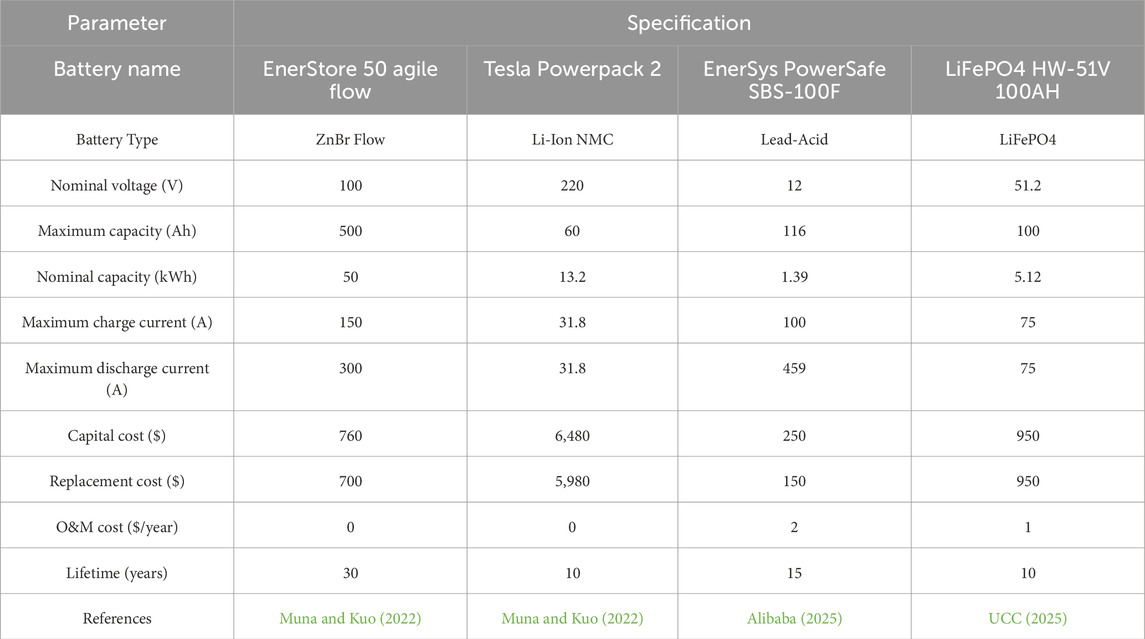
Table 3 presents an overview of the specifications of four battery technologies being considered for energy storage use in the hybrid renewable energy system. The EnerStore 50 Agile Flow battery is a zinc-bromine flow battery with a nominal voltage of 100 V and high energy capacity of 50 kWh. It boasts a long lifespan of 30 years and high charge/discharge currents, making it suitable for large-scale storage. The Tesla Powerpack 2 is a lithium-ion NMC battery with a nominal capacity of 13.2 kWh and voltage of 220 V. It is a high-efficiency grid-scale storage battery with a lifespan of 10 years. The EnerSys PowerSafe SBS-100F is a lead-acid battery with a lower capacity of 1.39 kWh but with high discharge current and modest cost, which makes it more appropriate for backup applications. Lastly, LiFePO4 HW-51V 100AH battery provides 5.12 kWh capacity with excellent thermal stability and a 10-year lifespan, making it suitable for home and medium-scale application.
3 Result and discussion
This section gives techno-economic and environmental outcomes achieved through simulations that were carried out using HOMER Pro software. In this research, hybrid renewable power systems have been studied for Bangladesh’s five upazila cities based on residential and community load patterns. Four different battery technologies were incorporated and compared to select the optimal system configuration for each site. Key performance indicators like COE, NPC, PV capacity, contribution of wind power, battery storage, bi-directional converter capacity, produced excess electricity, and RE levels of penetration were investigated. Analysis reveals that optimal configurations vary immensely from site to site because resource availability and loads change. It was selected with systems based on their cost value and environmental compatibility as a combination of trade-off among renewable penetration and system costs. Among the battery types, the storage technology choice impacted NPC and RE use significantly. In addition, the research identifies the surplus energy potential and the function of grid integration. Generally, the results validate location-based hybrid system configurations to enable sustainability and affordability in decentralized power systems.
3.1 Optimized hybrid system assessment
The best design is the most cost-effective and sustainable hybrid energy system for each upazila, as identified by HOMER Pro simulations. Every system includes solar PV, wind turbines, a bi-directional converter, and one of four battery technologies. The designs were tailored to fit local demand profiles while minimizing NPC and COE, maximizing RE penetration, and energy excess and storage capacity under different geographic conditions.
The Figure 11 shows an evident trend for the performance of hybrid renewable energy systems with varying battery technologies. At all the sites, the hybrid of photovoltaic and wind turbine with ZnBr battery (PV-WT-ZnBr) consistently yields the minimum NPC and COE. For instance, in Fakirhat, this combination generates an NPC of $178,691 and COE of $0.0716/kWh, approximately 90% lower in NPC than the most expensive combination, WT-Li Ion NMC. In Saturia, the PV-WT-ZnBr combination is $172,960.8 for NPC and $0.0693/kWh for COE, a cost reduction of 91% over the most expensive one. Thanchi provides a shorter cost spread, but PV-WT-ZnBr is still different with an NPC of $212,645.5 and COE of $0.0852/kWh, approximately 76% less than the PV-Li Ion NMC system. In Charghat, the most efficient system remains PV-WT-ZnBr with an NPC of $171,720.1 and COE of $0.0688/kWh-about 91% less than WT-LiFePO4. PV-WT-ZnBr posts the least in Companiganj with NPC of $218,276.4 and COE of $0.0874/kWh, and thus the NPC reduces by 77% as compared to PV-Li Ion NMC. All the above results verify that PV-WT-ZnBr is the economically most attractive source of power generation in the decentralized sector and therefore the optimum option for rural electrification at all the five research locations.
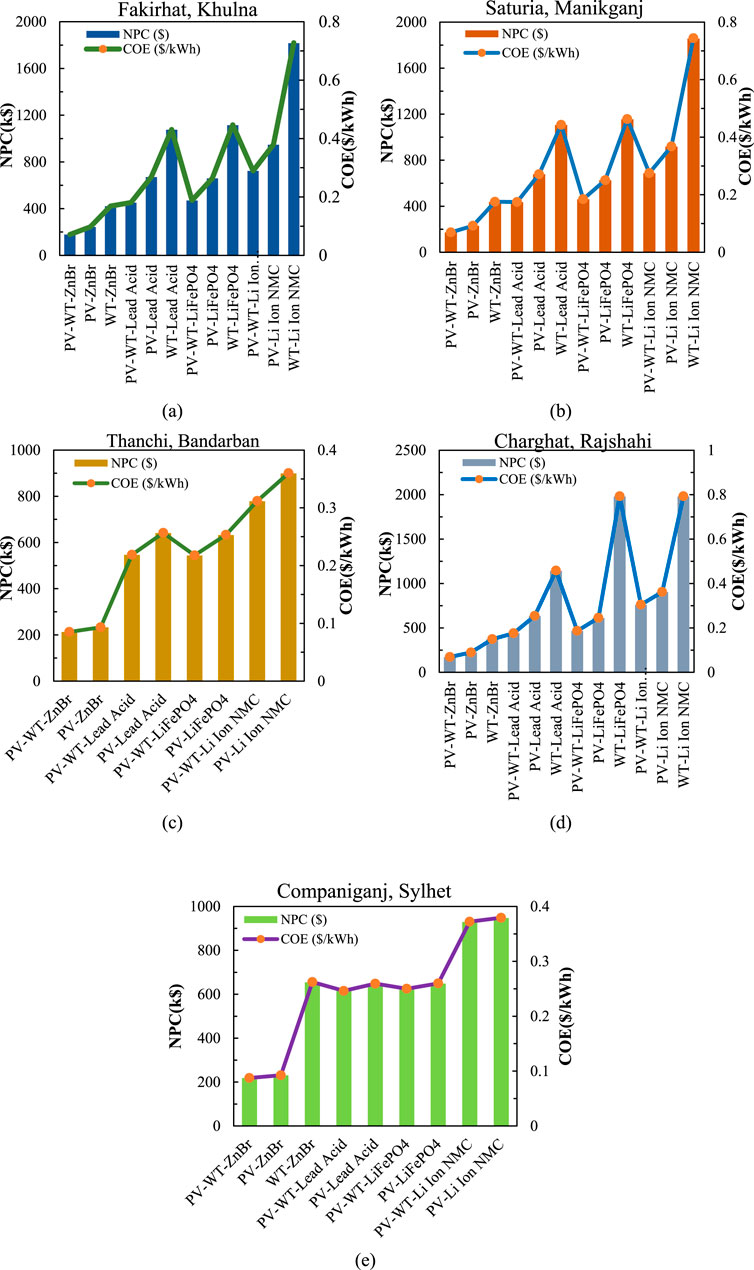
Figure 11. Comparison of Net Present Cost and Cost of Energy for various battery-supported hybrid systems in: (a) Fakirhat, Khulna; (b) Saturia, Manikganj; (c) Thanchi, Bandarban; (d) Charghat, Rajshahi; and (e) Companiganj, Sylhet.
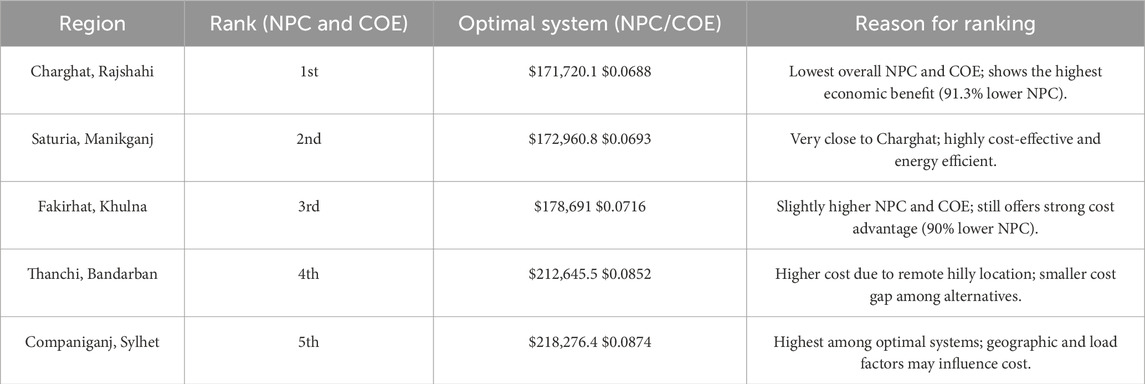
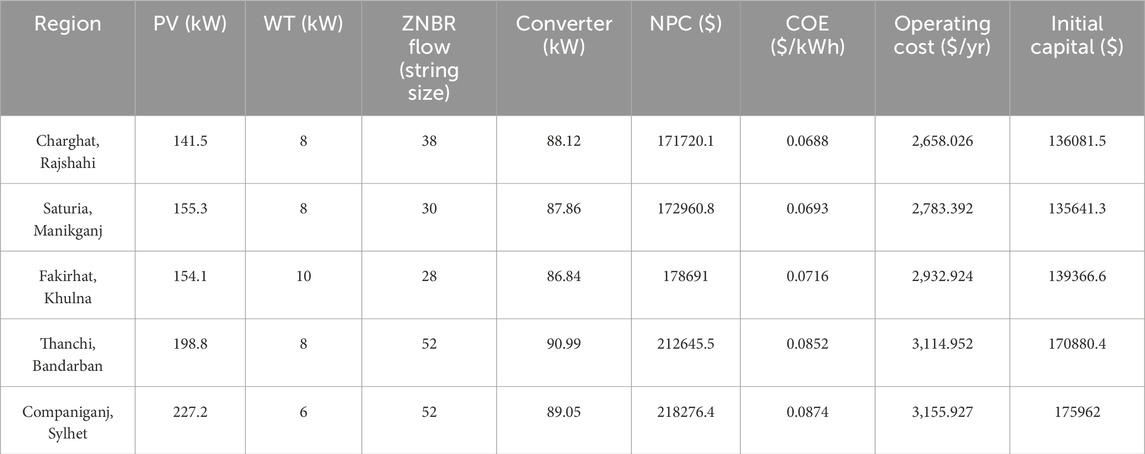
The Table 4 provides a relative comparison of five sites in Bangladesh (Charghat, Saturia, Fakirhat, Thanchi, and Companiganj) based on the NPC and COE of the most appropriate hybrid energy system, PV-WT-ZnBr. Charghat ranks the best with the lowest NPC and COE, followed closely by Saturia and Fakirhat. Thanchi and Companiganj rank lower due to higher costs, which are likely dictated by geographical and logistical factors. Despite regional disparity, PV-WT-ZnBr is the most cost-effective system throughout. This table highlights regional variations in system performance and enables targeted energy planning for rural electrification in Bangladesh.
3.2 Optimized system architecture
The Table 5 presents an overview of the optimized system design by region for the most cost-effective hybrid configuration: PV-WT-ZnBr. Some of the key system components like the size of PV, WT capacity, ZnBr battery size, and ratings of the converters are provided. Economic metrics such as NPC, COE, operating cost per year, and the initial capital requirement are also provided. Among all locations, Charghat (Rajshahi) has the lowest NPC ($171,720.1) and COE ($0.0688/kWh), followed by Saturia and Fakirhat. Thanchi and Companiganj are relatively costly, mainly due to larger component sizes and remote site conditions. This design shows how resource availability, load demand, and site constraints influence optimized hybrid energy solutions for different rural locations.
It is important to note that all five optimized PV–WT–ZnBr hybrid systems achieved a Renewable Fraction (RF) of 100%, indicating complete reliance on renewable energy sources and no dependency on fossil fuels or the grid.
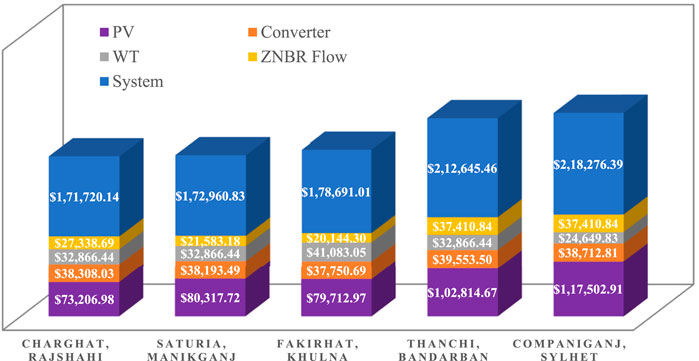
The Figure 12 shows the cost breakdown of the optimized PV-WT-ZnBr hybrid systems in five rural sites of Bangladesh. A stacked bar representing the combined NPC for each site represents the individual cost contribution of PV, WT, converter, and ZnBr flow battery components. Charghat, Rajshahi has the lowest total NPC of $171,720.14, where PV ($73,206.98), converter ($38,308.03), WT ($32,866.44), and ZnBr battery ($27,338.69) costs are minimum. Saturia, Manikganj has an NPC of $172,960.83, where PV cost is slightly higher ($80,317.72) but battery cost is minimum ($21,583.18). Fakirhat, Khulna has a total of $178,691.01, where ZnBr battery cost is minimum ($20,144.30) but WT cost is maximum ($41,083.05). Thanchi, Bandarban and Companiganj, Sylhet are exposed to the highest NPCs of $212,645.46 and $218,276.39, respectively, due to increased PV ($102,814.67 and $117,502.91) and battery costs ($37,410.84 per unit). The study highlights differences in regional component pricing despite using the same hybrid configuration.
The Figure 13 represents comparative annualized cost elements—Capital, Replacement, O&M, Salvage, and Total Cost—across five different locations in Bangladesh: Charghat (Rajshahi), Saturia (Manikganj), Fakirhat (Khulna), Thanchi (Bandarban), and Companiganj (Sylhet). The annualized total cost is lowest in Charghat ($12,807.36) and highest in Companiganj ($16,279.65), primarily attributable to higher capital and O&M cost in the latter. The highest proportion of total costs in all the sites is capital expenses, for which Companiganj reports the largest amount at $13,123.72. Operating and maintenance expenses also rise successively from Charghat to Companiganj, which may indicate greater degrees of operation or logistical challenges. Negative salvage values in every one of the sites indicate loss through depreciation, for which the largest depreciation value of −$667.40 is reported in Fakirhat. The bar graph effectively brings out such variations, especially in capital and O&M items. These results highlight the significant position of infrastructural and geographical factors in the determination of the economic feasibility of renewable energy installation.
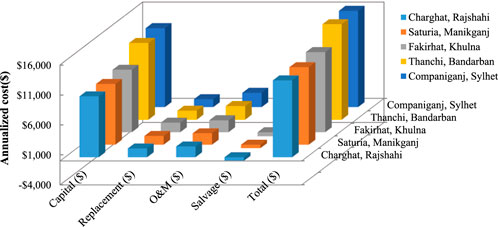
Figure 13. Annualized cost breakdown of PV-WT-ZnBr hybrid systems across selected bangladeshi locations.
The Figure 14 shows comparative power generation and surplus electricity of PV-WT-ZnBr hybrid systems for five locations in Bangladesh. Parameters used are percentage contribution of PV generation, WT generation, and surplus electricity generated. Companiganj, Sylhet possesses the highest PV generation with 92.6%, which is a highly solar-dependent system, followed closely by Thanchi and Saturia. On the other hand, Khulna’s Fakirhat has the maximum WT generation of 36.1%, suggesting favorable wind conditions in the region. Surplus electricity, as a measure of unused or surplus energy, is maximum in Companiganj (31.3%) and Fakirhat (30.7%), possibly due to lesser demand relative to system capacity or restricted storage utilization. Thanchi has the minimum combined PV and WT contribution, suggesting a more balanced or restricted energy generation pattern. The 3D bar chart best displays such variations, pointing to regional dependence on solar or wind resources. Such outcomes dictate optimal hybrid system configurations specific to local renewable resource availability.
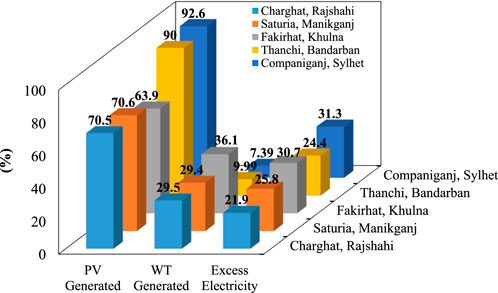
Figure 14. Surplus trends and location-based generation profiles in hybrid PV-WT-ZnBr energy systems.
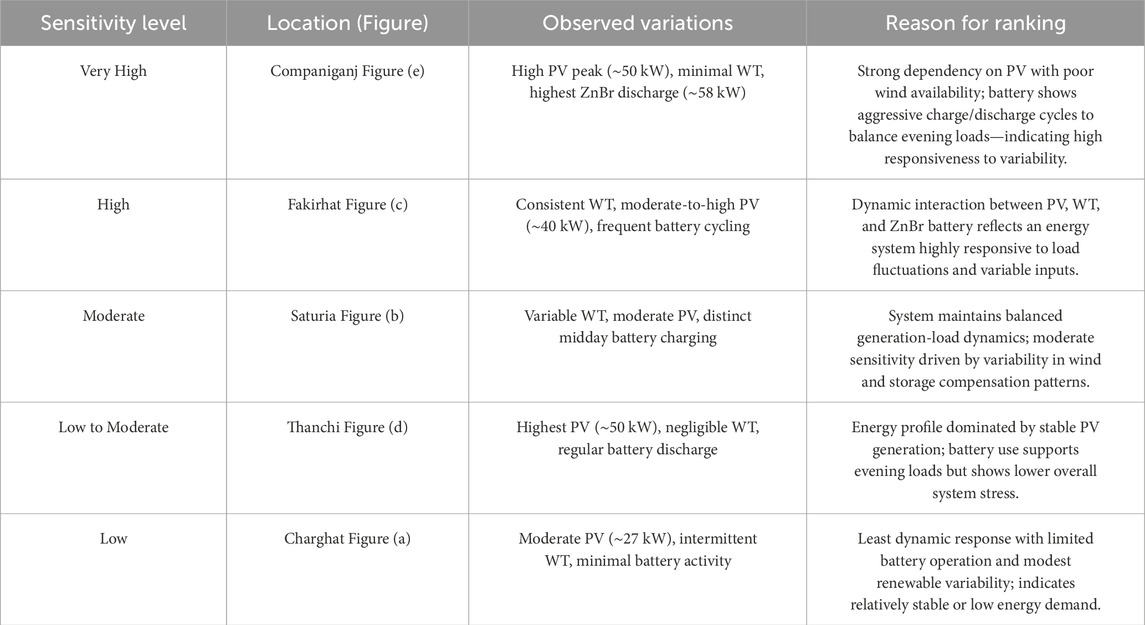
In Figure 15, five locations in Bangladesh are represented- Bangladesh’s west, southwest, south, and southeast regions, namely, west Charghat (a), Saturia (b), Fakirhat (c), Thanchi (d) and Companiganj (e) on 1 August-while the PV and WT outputs, ZnBr battery charge/discharge and total electrical load served are on focus. Within this context, each dataset plots the hours of fluctuation in an interesting interference between renewable resources and local storage systems. Figure a (Charghat, Rajshahi) has a moderate PV peaking around noon (∼27 kW), with wind generation coming and going throughout the day. ZnBr battery discharging occurs mainly at early morning and evening hours, indicating peak load support outside of solar generation hours. Load served tracks fairly well with generation, helped by discharge from battery at key times. Figure b (Saturia, Manikgonj) has higher variability in wind power and a bit stronger PV generation than Charghat. ZnBr charging occurs during midday while discharging peaks during early morning and evening, which shows that energy shifting is efficient to support high-demand periods. Energy management appears optimized with very little unserved load. Figure c (Fakirhat, Khulna) has consistent wind contributions and high PV generation (∼40 kW peak). Battery activity (both charge and discharge) is frequent, suggesting a dynamic storage strategy balancing intermittent renewables with demand. Discharge events are longer and more sustained than in previous cases. Figure d (Thanchi, Bandarban) shows the strongest PV output (∼50 kW), likely due to favorable solar irradiance. Wind input is minimal, and ZnBr discharge activity is quite balanced, showing high reliance on PV and battery synergy to satisfy the demand, especially with no considerable wind generation. Figure e (Companiganj, Sylhet) has the highest ZnBr discharge values (∼58 kW), even with minimal wind energy. PV generation shows considerable peaks, and batteries are aggressively charged midday and discharged in the evening. This prioritizes a storage approach for favorable solar but unfavorable wind conditions. In general, site-to-site variability in resource availability demands site-specific energy strategies. PV generation dominates in most areas, and battery storage is crucial for load balancing where the wind output is less.
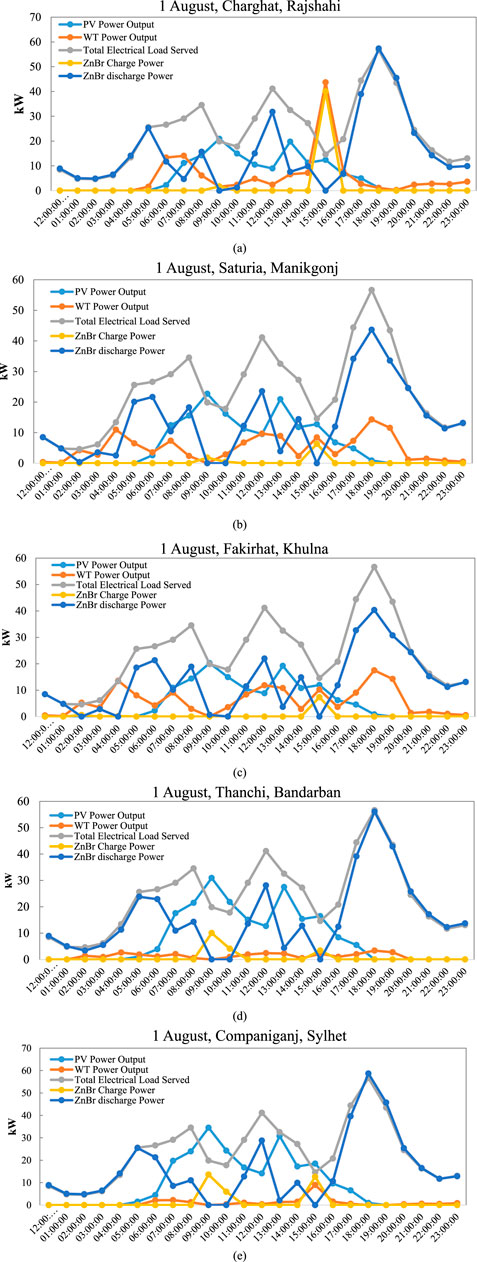
Figure 15. Comparative analysis of hourly renewable energy generation, storage utilization, and load served on 1 August across five locations in Bangladesh (a) charghat, (b) saturia, (c) fakirhat, (d) thanchi, and (e) companiganj.
This sequence underlines the extent to which different resource profiles (solar and wind) and storage dynamics impact each system’s responsiveness to input variability and load dynamics which is shown in Table 6. The more responsive areas (Companiganj and Fakirhat) are subjected to greater variation in energy flow and require intervention more frequently by battery systems. Charghat and Thanchi, respectively, experience more consistent or less reactive patterns that signal either decreased demand or more regular energy provision.
3.3 Community-level implications of optimized systems
The results of this study have several direct implications for rural communities. Firstly, the optimized PV-WT-ZnBr configurations offer a cost of energy as low as $0.0688/kWh, which is significantly cheaper than diesel-based systems or informal local generators. This can reduce household energy expenses by up to 50%, especially in areas reliant on expensive and unreliable fuel-based systems.
Secondly, these hybrid systems ensure 100% renewable fraction and zero carbon emissions, improving energy security by eliminating dependency on imported fuels and the vulnerable national grid. With systems designed using real load profiles and local resources, communities benefit from resilient, decentralized electricity access capable of powering schools, health centers, and small businesses even during grid outages or climatic disruptions.
Lastly, the ZnBr battery’s long lifespan and low maintenance improve system sustainability and reduce the financial burden of frequent battery replacement. These outcomes support sustainable rural development, education continuity, and better healthcare delivery.
The prime aim of this paper is to design and compare hybrid off-grid renewable energy systems for rural electrification in Bangladesh by comparing the different battery energy storage technologies. Comparing different system configurations with combinations of solar PV, wind turbines, and four different battery types—ZnBr Flow, Li-Ion NMC, Lead-Acid, and LiFePO4—using HOMER Pro in five geographically remote locations, the study is conducted. The novelty of this work is its comprehensive, location-specific analysis based on real load profiles and local resource inputs, which most previous studies lacked. Moreover, the paper compares various commercially available battery technologies for the first time under identical system conditions and concludes that the ZnBr Flow battery is the most cost-effective and environmentally benign. The work incorporates techno-economic modeling supplemented with environmental and scalability considerations and presents a practicable and flexible model for rural electrification. This multi-battery, multi-location approach provides a replicable framework for policymakers and engineers tasked with eliminating energy poverty in off-grid communities throughout the world.
The significant contributions of this paper are an exhaustive comparative study of four battery energy storage technologies in hybrid PV-WT systems in five rural localities of Bangladesh with the help of HOMER Pro. It provides region-specific optimization based on real load and resource information, which confirms the superior techno-economic and environmental efficiency of ZnBr Flow batteries. The paper provides a reproducible and scalable method for designing affordable, 100% renewable off-grid systems. With the inclusion of battery selection, system design, and sensitivity analysis, the paper has valuable lessons for rural electrification planning in developing countries with similar geographical and energy access limitations.
4 Conclusion
Data-driven simulation was utilized to assess the effects of different battery storage technologies on the cost-effectiveness and performance of hybrid renewable microgrids in rural Bangladesh. By modeling five locations, it is found that installations mixing PV and wind power with ZnBr Flow batteries consistently perform better. Amongst the three battery-integrated configurations, PV-WT-ZnBr recorded the lowest NPC of $171,720 and a COE of $0.0688/kWh, along with operating cost of $2,658.03 and capital cost of $136,082. It also achieved a 100% RF, or the full utilization of renewable energy resources. ZnBr Flow batteries offered promising advantages in the form of a 30-year lifespan, rapid charge/discharge capability, and minimal maintenance requirements, which rendered them extremely promising for stand-alone off-grid remote operation applications. These observations emphasize the importance of selecting battery technologies based on technical as well as economic factors in decentralized energy planning. While the outcomes provide a viable sustainable electrification model, there is one major limitation in that system performance and resource information were solely derived through simulation. This introduces uncertainty for real-world outcomes under varying environmental and use conditions. For greater practical applicability, pilot microgrids are suggested to be implemented in similar rural settings by future studies. These applications would validate simulation results, provide insight into real-world operational behavior, and enable the integration of socio-economic determinants, ultimately making the model more scalable and resilient.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
MA: Methodology, Supervision, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Software, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Validation, Resources, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Project administration. DB: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Resources, Formal Analysis, Software, Investigation, Data curation, Project administration, Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Validation. MS: Methodology, Supervision, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Validation, Resources, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. AA: Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Investigation, Conceptualization, Software, Methodology, Resources, Project administration, Formal Analysis, Validation. MH: Data curation, Validation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization, Investigation, Visualization, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Pabna University of Science and Technology, Pabna-6600, Bangladesh, for providing access to the Renewable Energy Laboratory and other facilities that supported the successful completion of this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
AbdElrazek, A. S., Soliman, M., and Khalid, M. (2025). Evaluating the techno-economic viability of a solar PV-wind turbine hybrid system with battery storage for an electric vehicle charging station in khobar, Saudi arabia. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2502.05654 (Accessed: May 29, 2025).
Abdullah-Al-Mahbub, M., and Islam, A. R. M. T. (2023). Current status of running renewable energy in Bangladesh and future prospect: a global comparison. Heliyon 9 (3), e14308. doi:10.1016/J.HELIYON.2023.E14308
Abdullah-Al-Mahbub, M., Islam, A. R. M. T., Almohamad, H., Al Dughairi, A. A., Al-Mutiry, M., and Abdo, H. G. (2022). Different forms of solar energy progress: the fast-growing Eco-friendly energy source in Bangladesh for a sustainable future. Energies 15 (18), 6790. doi:10.3390/EN15186790
Abed, M., Reddy B, A., Jyothsna, T. R., and Mohammed, N. (2025). Optimal sizing and performance assessment of stand-alone PV systems using optimum hybrid sizing strategy. Results Eng. 25, 103793. doi:10.1016/J.RINENG.2024.103793
Acakpovi, A., Adjei, P., Nwulu, N., and Asabere, N. Y. (2020). Optimal hybrid renewable energy system: a comparative study of wind/hydrogen/fuel-cell and wind/battery storage. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020 (1), 1–15. doi:10.1155/2020/1756503
Adenle, A. A. (2020). Assessment of solar energy technologies in Africa-opportunities and challenges in meeting the 2030 agenda and sustainable development goals. Energy Policy 137, 111180. doi:10.1016/J.ENPOL.2019.111180
Ahmed, P., Rahman, M. F., Haque, A. K. M. M., Mohammed, M. K. A., Toki, G. F. I., Ali, M. H., et al. (2023). Feasibility and techno-economic evaluation of hybrid photovoltaic system: a rural healthcare center in Bangladesh. Sustain. 15 (2), 1362. doi:10.3390/SU15021362
Akash, F. A., Shovon, S. M., Rahman, W., Rahman, M. A., Chakraborty, P., and Monir, M. U. (2024). Greening the grid: a comprehensive review of renewable energy in Bangladesh. Heliyon 10 (5), e27477. doi:10.1016/J.HELIYON.2024.E27477
Akram, M. N., and Abdul-Kader, W. (2024). Repurposing second-life EV batteries to advance sustainable development: a comprehensive review. Batter. 2024 10 (12), 452. doi:10.3390/BATTERIES10120452
Alahmad, A. K., Verayiah, R., Shareef, H., Ramasamy, A., and Ba-swaimi, S. (2025). Optimizing renewable energy and green technologies in distribution systems through stochastic planning of distributed energy resources. Energy Convers. Manag. X 25, 100834. doi:10.1016/J.ECMX.2024.100834
Ali, M. F., Hossain, M. A., Julhash, M. M., Ashikuzzaman, M., Alam, M. S., and Sheikh, M. R. I. (2024). A techno-economic analysis of a hybrid microgrid system in a residential area of Bangladesh: optimizing renewable energy. Sustainability 16 (18), 8051. doi:10.3390/SU16188051
Ali, M. F., Halim, M. A., Julhash, M. M., and Ashikuzzaman, M. (2025a). Economic and environmental benefits of grid-connected PV-biomass systems in a Bangladeshi university: a HOMER Pro approach. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2025 (1), 5053853. doi:10.1155/ETEP/5053853
Ali, M. F., Sheikh, M. R. I., Akter, R., Islam, K. M. N., and Ferdous, A. H. M. I. (2025b). Grid-connected hybrid microgrids with PV/wind/battery: sustainable energy solutions for rural education in Bangladesh. Results Eng. 25, 103774. doi:10.1016/J.RINENG.2024.103774
Alibaba (2025). Powersafe high voltage energy storage battery Sbs-100f 12v100ah Uninterruptible power supply - Buy energy storage battery Pack energy storage battery high power energy storage battery backup product on Alibaba. com. Available online at: https://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/PowerSafe-High-Voltage-Energy-Storage-Battery_1601403088551.html (Accessed May 31, 2025).
Alyahya, S., Colleges, O., Zaky, A. A., Yousif, B., and Dawoud, S. M. (2025). Optimal planning and Decision-making for hybrid microgrids: integrating diverse renewable sources with battery systems. doi:10.21203/RS.3.RS-5790784/V1
Arsad, A. Z., Hannan, M., Al-Shetwi, A. Q., Mansur, M., Muttaqi, K., Dong, Z., et al. (2022). Hydrogen energy storage integrated hybrid renewable energy systems: a review analysis for future research directions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 47 (39), 17285–17312. doi:10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2022.03.208
Ashraful Islam, M., Naushad Ali, M., Mollick, T., Islam, A., Benitez, I. B., Sidi Habib, S., et al. (2024). Assessing the feasibility and quality performance of a renewable Energy-Based hybrid microgrid for electrification of remote communities. Energy Convers. Manag. X 23, 100674. doi:10.1016/J.ECMX.2024.100674
Avwioroko, A. (2023). The potential, barriers. and strategies to upscale renewable energy adoption in developing countries: Nigeria as a case study. Eng. Sci. Tecnol. J. 4 (2), 46–55. doi:10.51594/ESTJ.V4I2.1288
Ayua, T. J., and Emetere, M. E. (2024). Technical and economic simulation of a hybrid renewable energy power system design for industrial application. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 28739–21. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-77946-x
Aziz, A. S., Tajuddin, M. F. N., Adzman, M. R., Mohammed, M. F., and Ramli, M. A. M. (2020). Feasibility analysis of grid-connected and islanded operation of a solar PV microgrid system: a case study of Iraq. Energy 191, 116591. doi:10.1016/J.ENERGY.2019.116591
Ba-swaimi, S., Verayiah, R., Ramachandaramurthy, V. K., and Alahmad, A. K. (2024a). Long-term optimal planning of distributed generations and battery energy storage systems towards high integration of green energy considering uncertainty and demand response program. J. Energy Storage 100, 113562. doi:10.1016/J.EST.2024.113562
Ba-swaimi, S., Verayiah, R., Ramachandaramurthy, V. K., Alahmad, A. K., and Padmanaban, S. (2024b). Two-stage strategic optimal planning of distributed generators and energy storage systems considering demand response program and network reconfiguration. Energy Convers. Manag. X 24, 100766. doi:10.1016/J.ECMX.2024.100766
Ba-swaimi, S., Verayiah, R., Ramachandaramurthy, V. K., Alahmad, A. K., and Padmanaban, S. (2025). Optimal configuration and sizing of integrated hybrid renewable energy systems for sustainable power supply in healthcare Buildings. Results Eng. 26, 104800. doi:10.1016/J.RINENG.2025.104800
Bagdadee, A. H., and Zhang, L. (2025). Investigate the implementation of smart grid-integrated renewable distributed generation for sustainable energy development in Bangladesh. Energy Rep. 13, 2433–2453. doi:10.1016/J.EGYR.2025.01.083
Baidya, H., Rahman Zisan, M. T., Alif, A. Z., Ahmed, A., Hasan, M., and Chowdhury, N. U. R. (2025). Techno-Economic Comparative analysis of hybrid renewable energy systems optimization considering Off-Grid remote area electrification in Bangladesh. Energy Convers. Manag. X 26, 101004. doi:10.1016/J.ECMX.2025.101004
Barakat, S., Emam, A., and Samy, M. M. (2022). Investigating grid-connected green power systems’ energy storage solutions in the event of frequent blackouts. Energy Rep. 8, 5177–5191. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2022.03.201
Barakat, S., Osman, A. I., Tag-Eldin, E., Telba, A. A., Abdel Mageed, H. M., and Samy, M. M. (2024). Achieving green mobility: multi-objective optimization for sustainable electric vehicle charging. Energy Strateg. Rev. 53, 101351. doi:10.1016/J.ESR.2024.101351
Barkat, A. (2005). Bangladesh rural electrification program: a success story of poverty reduction through electricity. arXiv, 331–370. doi:10.1142/9789812701787_0037
Bilal, M., Bokoro, P. N., and Sharma, G. (2025). Hybrid optimization for sustainable design and sizing of standalone microgrids integrating renewable energy, diesel generators, and battery storage with environmental considerations. Results Eng. 25, 103764. doi:10.1016/J.RINENG.2024.103764
Bouckaert, S., Pales, A. F., McGlade, C., Remme, U., Wanner, B., Varro, L., et al. (2021). Net zero by 2050: a Roadmap for the global energy sector. Available online at: https://trid.trb.org/View/1856381.
Ciez, R. E., and Whitacre, J. F. (2016). Comparative techno-economic analysis of hybrid micro-grid systems utilizing different battery types. Energy Convers. Manag. 112, 435–444. doi:10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2016.01.014
Debnath, K. B., and Mourshed, M. (2022). Why is Bangladesh’s electricity generation heading towards a GHG emissions-intensive future? Carbon Manag. 13 (1), 216–237. doi:10.1080/17583004.2022.2068454
Deng, Y., and Guo, W. (2017). A review of investment, financing and policies support Mechanisms for renewable energy development. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 502, 981–995. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-1837-4_82
Dhundhara, S., Verma, Y. P., and Williams, A. (2018). Techno-economic analysis of the lithium-ion and lead-acid battery in microgrid systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 177, 122–142. doi:10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2018.09.030
Douiri, M. R. (2019). A predictive model for solar photovoltaic power based on Computational intelligence Technique. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44 (8), 6923–6940. doi:10.1007/s13369-019-03725-w
Ezekwem, C., Muthusamy, S., and Ezekwem, P. C. (2024). Optimal selection and design of grid-connected hybrid renewable energy system in three selected communities of Rivers State. Sci. Afr. 25, e02305. doi:10.1016/J.SCIAF.2024.E02305
El-Ahmar, M. H., El-Sayed, A. H. M., and Hemeida, A. M. (2017). Evaluation of factors affecting wind turbine output power. 2017 19th Int. Middle-East Power Syst. Conf. MEPCON 2017 - Proc., 1471–1476. doi:10.1109/MEPCON.2017.8301377
El-Maaroufi, A., Daoudi, M., and Ahl Laamara, R. (2024). Techno-economic analysis of a PV/WT/biomass off-grid hybrid power system for rural electrification in northern Morocco using HOMER. Renew. Energy 231, 120904. doi:10.1016/J.RENENE.2024.120904
Electricity Generation Mix (2025). National database of renewable energy. Available online at: https://www.renewableenergy.gov.bd/index.php?id=7 (Accessed May 29, 2025).
Eteiba, M. B., Barakat, S., Samy, M. M., and Wahba, W. I. (2018). Optimization of an off-grid PV/Biomass hybrid system with different battery technologies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 40, 713–727. doi:10.1016/J.SCS.2018.01.012
Eze, V. H. U., Richard, K., Ukagwu, K. J., and Okafor, W. (2024). Factors influencing the efficiency of solar energy systems. J. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. 6 (3), 119–131. doi:10.36079/LAMINTANG.JETAS-0603.748
Ezekwem, C., and Muthusamy, S. (2023). Feasibility study of integrating the renewable energy system for increased electricity access: a case study of Choba community in Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 21, e01781. doi:10.1016/J.SCIAF.2023.E01781
Fatih Guven, A., Abdelaziz, A. Y., Mahmoud Samy, M., and Barakat, S. (2024). Optimizing energy Dynamics: a comprehensive analysis of hybrid energy storage systems integrating battery banks and supercapacitors. Energy Convers. Manag. 312, 118560. doi:10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2024.118560
Fyza, N., and Sarkar, M. A. R. (2020). Renewable energy for rural development in Bangladesh. J. Inst. Eng. 15 (3), 122–132. doi:10.3126/JIE.V15I3.32159
Güven, A. F., Yörükeren, N., and Samy, M. M. (2022). Design optimization of a stand-alone green energy system of university campus based on Jaya-Harmony Search and Ant Colony Optimization algorithms approaches. Energy 253, 124089. doi:10.1016/J.ENERGY.2022.124089
Güven, A. F., and Mahmoud Samy, M. (2022). Performance analysis of autonomous green energy system based on multi and hybrid metaheuristic optimization approaches. Energy Convers. Manag. 269, 116058. doi:10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2022.116058
Haq, I., Khan, M., Chakma, S., Hossain, M. I., Sarkar, S., Rejvi, M. R. A., et al. (2024). Determinants of household adoption of clean energy with its rural–urban disparities in Bangladesh. Dent. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 2356. doi:10.1038/S41598-024-52798-7
Hasan, M. K., and Mohammad, N. (2019). An Outlook over electrical energy generation and mixing policies of Bangladesh to achieve sustainable energy Targets -Vision 2041. 2nd Int. Conf. Electr. Comput. Commun. Eng. ECCE 2019, 1–5. doi:10.1109/ECACE.2019.8679446
HOMER (2024). Hybrid renewable and distributed generation system design software. Available online at: https://homerenergy.com/ (Accessed December 01, 2024).
Homer Energy (2024). Solving problems with HOMER. Available online at: https://homerenergy.com/products/pro/docs/3.15/solving_problems_with_homer.html (Accessed December 01, 2024).
Homer Energy (2025). HOMER Pro user manual. Available online at: https://homerenergy.com/products/pro/docs/ (Accessed May 31, 2025).
Hossain, M. A., Pota, H. R., Squartini, S., Zaman, F., and Muttaqi, K. M. (2019). Energy management of community microgrids considering degradation cost of battery. J. Energy Storage 22, 257–269. doi:10.1016/J.EST.2018.12.021
Hossein Jahangir, M., Bazdar, E., and Kargarzadeh, A. (2022). Techno-economic and environmental assessment of low carbon hybrid renewable electric systems for urban energy planning: Tehran-Iran. City Environ. Interact. 16, 100085. doi:10.1016/J.CACINT.2022.100085
Hosseini, S. E. (2022). Fossil fuel crisis and global warming. Fundam. Low. Emiss. Flameless Combust. Its Appl., 1–11. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-85244-9.00001-0
Hussain, M. N., Zaman, M. R., Halim, M. A., Ali, M. S., and Khan, M. Y. A. (2024). A comprehensive review of renewable and sustainable energy sources with solar photovoltaic electricity Advancement in Bangladesh. Control Syst. Optim. Lett. 2 (1), 1–7. doi:10.59247/CSOL.V2I1.59
Imanloozadeh, A., Nazififard, M., and Hashemi-Dezaki, H. (2024). Optimal technoeconomic reliability-oriented design of islanded multicarrier microgrids with electrical and hydrogen energy storage systems considering emission concerns. Energy Sci. Eng. 12 (6), 2702–2745. doi:10.1002/ESE3.1774
Islam, M. S., Al-Amin, A. Q., and Sarkar, M. S. K. (2021). Energy crisis in Bangladesh: challenges, progress, and prospects for alternative energy resources. Util. Policy 71, 101221. doi:10.1016/J.JUP.2021.101221
Jaiswal, K. K., Chowdhury, C. R., Yadav, D., Verma, R., Dutta, S., Jaiswal, K. S., et al. (2022). Renewable and sustainable clean energy development and impact on social, economic, and environmental health. Energy Nexus 7 (Sep), 100118. doi:10.1016/J.NEXUS.2022.100118
Jakhrani, A. Q., Othman, A. K., Rigit, A. R. H., and Samo, S. R. (2012). Assessment of solar and wind energy resources at five typical locations in Sarawak. J. Energy Environ. 4 (1). Available online at: https://journal.uniten.edu.my/index.php/jee/article/view/120 (Accessed: May 30, 2025).
Jawad, A., Hasan, M. S., Faruqui, M. F. I., and Al Masood, N. (2023). Small-scale floating photovoltaic systems in university campus: a pathway to achieving SDG 7 goals in Bangladesh. Energy Convers. Manag. 297, 117722. doi:10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2023.117722
Jed, M., Ihaddadene, N., El Hacen Jed, M., Ihaddadene, R., and El Bah, M. (2022). Validation of the accuracy of NASA solar irradiation data for four african regions. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 17 (1), 29–39. doi:10.18280/IJSDP.170103
Joarder, M. S. A., Raihan, A., Salehi, M., Walasek, R., and Zimon, G. (2024). Analysis of the current development of renewable energy technologies in Bangladesh. Wseas Trans. Environ. Dev. 20, 883–894. doi:10.37394/232015.2024.20.82
Kebede, A. A., Coosemans, T., Messagie, M., Jemal, T., Behabtu, H. A., Van Mierlo, J., et al. (2021). Techno-economic analysis of lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries in stationary energy storage application. J. Energy Storage 40, 102748. doi:10.1016/J.EST.2021.102748
Klugmann-Radziemska, E. (2023). The influence of elevated temperature on the efficiency of photovoltaic modules. arXiv. doi:10.20944/PREPRINTS202311.0807.V1
Krishan, O., and Suhag, S. (2019). Techno-economic analysis of a hybrid renewable energy system for an energy poor rural community. J. Energy Storage 23, 305–319. doi:10.1016/J.EST.2019.04.002
Kumar, A., Deng, Y., He, X., Kumar, P., and Bansal, R. C. (2021). A rural microgrid based on hydrokinetic energy system for rough Topographies. IEEE Int. Symp. Ind. Electron., 1–6. doi:10.1109/ISIE45552.2021.9576377
Kumar, P. H., Gopi, R. R., Rajarajan, R., Vaishali, N. B., Vasavi, K., and Kumar P, S. (2024). Prefeasibility techno-economic analysis of hybrid renewable energy system. e-Prime - Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 7, 100443. doi:10.1016/J.PRIME.2024.100443
Kumar, P. H., Alluraiah, N. C., Gopi, P., Bajaj, M., P, S. K., Kalyan, C. N. S., et al. (2025). Techno-economic optimization and sensitivity analysis of off-grid hybrid renewable energy systems: a case study for sustainable energy solutions in rural India. Results Eng. 25, 103674. doi:10.1016/J.RINENG.2024.103674
Kwon, K., Lee, H. B., Kim, N., Park, S., and Joshua, S. R. (2024). Integrated battery and hydrogen energy storage for enhanced grid power savings and green hydrogen utilization. Appl. Sci. 14 (17), 7631. doi:10.3390/APP14177631
Louis, T. A., and Tertsea, I. (2023). Environmental factors and the performance of PV panels: an Experimental investigation. Afr. J. Environ. Nat. Sci. Res. 6 (3), 231–247. doi:10.52589/AJENSR-GA3SMDHP
Mahmud, D. M., Ahmed, S. M. M., Hasan, S., and Zeyad, M. (2022). Grid-connected microgrid: design and feasibility analysis for a local community in Bangladesh. Clean. Energy 6 (3), 447–459. doi:10.1093/CE/ZKAC022
Mohn, K. (2020). The gravity of status quo: a review of IEA’s World Energy Outlook. Econ. Energy Environ. Policy 9 (1). doi:10.5547/2160-5890.8.2.KMOH
Mokhtara, C., Negrou, B., Settou, N., Settou, B., and Samy, M. M. (2021). Design optimization of off-grid Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems considering the effects of building energy performance and climate change: case study of Algeria. Energy 219, 119605. doi:10.1016/J.ENERGY.2020.119605
Muna, Y. B., and Kuo, C. C. (2022). Feasibility and techno-economic analysis of electric vehicle charging of PV/Wind/Diesel/Battery hybrid energy system with different battery technology. Energies 15 (12), 4364. doi:10.3390/en15124364
Nallolla, C. A., and Vijayapriya, P. (2022). Optimal design of a hybrid off-grid renewable energy system using techno-economic and sensitivity analysis for a rural remote location. Sustain 14 (22), 15393. doi:10.3390/SU142215393
Nguyen, V. G., Sharma, P., Bora, B. J., Bui, T. M. T., Efremov, C., Tran, M. H., et al. (2024). Techno-economic analysis of a hybrid energy system for electrification using an off-grid solar/biogas/battery system employing HOMER: a case study in Vietnam. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 191, 1353–1367. doi:10.1016/J.PSEP.2024.09.046
Pahwa, A. (2016). Partnerships to facilitate electricity access for the remote rural communities of sub-Sahara Africa. IEEE PES PowerAfrica Conf. PowerAfrica, 83–87. doi:10.1109/POWERAFRICA.2016.7556576
Pandyaswargo, A. H., Wibowo, A. D., and Onoda, H. (2022). Reusing solar panels to improve access to information and communication in an off-grid village: a financial feasibility assessment. Energy Rep. 8, 857–865. doi:10.1016/J.EGYR.2022.05.141
Paudel, S., Shrestha, J. N., Neto, F. J., Ferreira, J. A. F., and Adhikari, M. (2011). “Optimization of hybrid PV/wind power system for remote telecom station,” in 2011 International Conference on Power and Energy Systems, Chennai, India (Chennai, India: IEEE). 1–6. Available online at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6156618
Piyal, A. P., Ahmed, S., Rahman, K. F., and Mohsin, A. S. M. (2023). Energy demand Forecasting using Machine learning perspective Bangladesh. 2023 IEEE IAS Glob. Conf. Renew. Energy Hydrog. Technol. GlobConHT 2023, 1–5. doi:10.1109/GLOBCONHT56829.2023.10087679
Qasim, M. A., Yaqoob, S. J., Bajaj, M., Blazek, V., and Obed, A. A. (2025). Techno-economic optimization of hybrid power systems for sustainable energy in remote communities of Iraq. Results Eng. 25, 104283. doi:10.1016/J.RINENG.2025.104283
Qi, H., Meng, W., Qin, Y., Zhuo, Y., Hu, J., Rao, Z., et al. (2024). The impact of climate change-Induced wind speed decline on wind farm output. 2024 IEEE 2nd Int. Conf. Power Sci. Technol. ICPST 2024, 1453–1458. doi:10.1109/ICPST61417.2024.10602381
Razmjoo, A., Shirmohammadi, R., Davarpanah, A., Pourfayaz, F., and Aslani, A. (2019). Stand-alone hybrid energy systems for remote area power generation. Energy Rep. 5, 231–241. doi:10.1016/J.EGYR.2019.01.010
RE Generation Mix (2025). National database of renewable energy. Available online at: https://www.renewableenergy.gov.bd/index.php?id=4 (Accessed May 29, 2025).
Redouane, A., Saou, R., Belkhier, Y., and Oukaour, A. (2025). Integration of a novel Vernier-DSPM generator in a grid connected hybrid renewable energy system with battery storage. Results Eng. 25, 103814. doi:10.1016/J.RINENG.2024.103814
Safi, M., Chowdhury, S., and Shahabuddin, G. M. (2023). Resources diversification in Bangladesh’s electricity generation: a study on the role of renewable energy sources. J. Eng. Res. Rep. 25 (3), 26–35. doi:10.9734/JERR/2023/V25I3889
Sarker, M. T., Haram, M. H. S. M., Shern, S. J., Ramasamy, G., and Al Farid, F. (2024). Second-life electric vehicle batteries for home photovoltaic systems: transforming energy storage and sustainability. Energies 17 (10), 2345. doi:10.3390/EN17102345
Serat, Z., Danishmal, M., and Mohammad Mohammadi, F. (2024). Optimizing hybrid PV/Wind and grid systems for sustainable energy solutions at the university campus: economic, environmental, and sensitivity analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. X 24, 100691. doi:10.1016/J.ECMX.2024.100691
Shezan, S. A., Julai, S., Kibria, M., Ullah, K., Saidur, R., Chong, W., et al. (2016). Performance analysis of an off-grid wind-PV (photovoltaic)-diesel-battery hybrid energy system feasible for remote areas. J. Clean. Prod. 125, 121–132. doi:10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2016.03.014
Shezan, S. K. A., Ali, S. S., and Rahman, Z. (2021). Design and implementation of an islanded hybrid microgrid system for a large resort center for Penang Island with the proper application of excess energy. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 40 (4), e13584. doi:10.1002/EP.13584
Sieed, J., Komiyama, R., and Fujii, Y. (2020). Long-term projection of hourly electricity demand with sectoral decomposition for developing Economies: Bangladesh case study. J. Jpn. Soc. Energy Resour. 41 (4), 136–142. doi:10.24778/JJSER.41.4_136
Singh, R. (2024). Analyzing Spatiotemporal trends and Anomalies in power outage data across the United States. Proc. - 2024 IEEE Int. Conf. Big Data, BigData 2024, 7417–7421. doi:10.1109/BIGDATA62323.2024.10825495
Solanki, A., Singh, P., Pandit, M., Sawle, Y., Alotaibi, M. A., Malik, H., et al. (2024). Techno-economic-environmental assessment of stand-alone hybrid renewable energy system for different batteries using HOMER-Pro. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 9 (4), 779–800. doi:10.33889/IJMEMS.2024.9.4.040
Sultana, M., Rahman, M., Das, N., and Ur Rashid, M. M. (2021). Feasibility and techno-economic analysis of an off-grid hybrid energy system: a char area in Bangladesh. 2021 Int. Conf. Sci. Contemp. Technol. ICSCT 2021. doi:10.1109/ICSCT53883.2021.9642703
Taha, A. B., and Babiker, S. F. (2019). Irradiance variation effect on the electrical performance of a grid connected PV system. Proc. Int. Conf. Comput. Control. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, ICCCEEE 2019, 1–4. doi:10.1109/ICCCEEE46830.2019.9071427
Taheruzzaman, M., and Janik, P. (2016). Electric energy access in Bangladesh. Trans. Environ. Electr. Eng. 1 (2), 6–17. doi:10.22149/TEEE.V1I2.13
Twaha, S., Idris, M. H., Anwari, M., and Khairuddin, A. (2012). Applying grid-connected photovoltaic system as alternative source of electricity to supplement hydro power instead of using diesel in Uganda. Energy 37 (1), 185–194. doi:10.1016/J.ENERGY.2011.11.051
UCC (2025). LiFePO4 HW-51V100AH-UA lithium ion Phosphate battery price in BD. Available online at: https://www.ucc.com.bd/lifepo4-hw-51v100ah-ua-lithium-ion-phosphate-battery (Accessed May 31, 2025).
Winslow, A. R. (2017). Urban wind generation: comparing horizontal and vertical Axis wind turbines at Clark university in worcester, Massachusetts. Sustain. Soc. Justice. Available online at: https://commons.clarku.edu/idce_masters_papers/127 (Accessed May 31, 2025).
Wood, G. (2020). Fossil fuels in a carbon-constrained world. Palgrave Handb. Manag. Foss. Fuels Energy Transitions, 3–23. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-28076-5_1
Wxnaiermic (2025). Horizontal Axis wind turbine 10kw 220V/380V - wind generator 10kw and wind turbine 10kw. Available online at: https://wxnaiermic.en.made-in-china.com/product/uytJoEKlCvhB/China-Horizontal-Axis-Wind-Turbine-10kw-220V-380V.html (Accessed May 31, 2025).
Yu, H. J. J., and Geoffron, P. (2020). Solar PV market and policies. Photovolt. Sol. Energy Convers. Technol. Appl. Environ. Impacts, 413–437. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-819610-6.00013-2
Zafar, U., Ur Rashid, T., Khosa, A. A., Khalil, M. S., and Rahid, M. (2018). An overview of implemented renewable energy policy of Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 82, 654–665. doi:10.1016/J.RSER.2017.09.034
Zahariea, D., Husaru, C. M., and Husaru, D. E. (2018). Small-scale 10 kW wind turbine on-grid connected for power supply of two different consumers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 444 (8), 082007. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/444/8/082007
Zhang, T., Stackhouse, P. W., Chandler, W. S., Hoell, J. M., Westberg, D., and Whitlock, C. H. (2008). A global perspective on renewable energy resources: nasa’s prediction of worldwide energy resources (power) project. ISES Sol. World Congr. 4, 2636–2640. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-75997-3_532
Zomers, A. (2014). Remote access: context, challenges, and obstacles in rural electrification. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 12 (4), 26–34. doi:10.1109/MPE.2014.2315916
Keywords: hybrid renewable energy system (HRES), battery energy storage system (BESS), techno-economic optimization, off-grid electrification, ZnBr flow battery
Citation: Ali MF, Biswas D, Sheikh MRI, Al Mamun A and Hossen MJ (2025) Techno-economic optimization of battery storage technologies for off-grid hybrid microgrids in multiple rural locations of Bangladesh. Front. Energy Res. 13:1654615. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2025.1654615
Received: 26 June 2025; Accepted: 11 August 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Xiao-Yu Wu, University of Waterloo, CanadaReviewed by:
Teerasak Somsak, Ragamagala University of Technology Lann, ThailandPeddakapu Kurukuri, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Ali, Biswas, Sheikh, Al Mamun and Hossen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Md. Feroz Ali, ZmVyb3owNzEwMjFAZ21haWwuY29t; Md. Jakir Hossen, amFraXIuaG9zc2VuQG1tdS5lZHUubXk=
 Md. Feroz Ali
Md. Feroz Ali Diganto Biswas
Diganto Biswas Md. Rafiqul Islam Sheikh2
Md. Rafiqul Islam Sheikh2