- Guizhou Power Grid Co. Ltd., Guiyang, China
To address the challenges of delayed response and insufficient regulation accuracy in pumped storage systems under high-penetration renewable energy scenarios, this paper proposes a real-time control method based on an Adaptive Moving Average (AMA) channel strategy. The method treats water head as the core control variable and constructs a dynamic regulation channel that enables real-time trend tracking and boundary identification. When the head state deviates beyond adaptive channel limits, the system triggers output adjustment procedures. Compared to conventional PI and expert-rule-based strategies, the proposed method introduces a self-tuning mechanism and fault-tolerant recovery logic, enhancing state awareness and boundary-driven control responsiveness. The AMA channel framework—adapted from financial technical analysis—offers superior flexibility and trend adaptability, enabling precise regulation under volatile grid conditions. Simulation studies across multiple scenarios, including frequency disturbance response, AGC signal tracking, and head fluctuation interference, demonstrate that the proposed strategy significantly reduces regulation deviation (RMSE: 8.95 vs. 21.42), improves response speed, and maintains economic dispatch performance. Ablation experiments further confirm its robustness under parameter failure conditions. These results validate the method’s engineering applicability and its potential for intelligent control deployment in complex power systems.
1 Introduction
The accelerating transformation of global energy systems has led to a dramatic increase in the penetration of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar (Bukovsky et al., 2023). While these sources offer environmental and economic benefits, their inherent intermittency and unpredictability introduce significant challenges to power system stability, particularly in maintaining grid frequency and ensuring reliable dispatch (Yang, 2020; Xie et al., 2021). As a result, the dynamic adaptability and regulation precision of control resources have become critical to the secure operation of modern power grids. Among available technologies, pumped storage systems stand out as the only large-scale, long-duration, and high-power energy storage solution capable of bidirectional regulation. Their ability to absorb excess renewable generation and provide rapid frequency support positions them as a cornerstone of grid flexibility (Li et al., 2022). However, the full potential of pumped storage systems remains underutilized due to limitations in conventional control strategies.
One of the primary challenges lies in the complex hydraulic behavior of pumped storage units, especially the dynamic variation of water head, which directly affects output capacity and regulation margin (Diniz, 2013). Head conditions are influenced not only by unit-level operations but also by basin hydrology, reservoir levels, and multi-unit coordination (Chen et al., 2023). These nonlinear, time-varying, and regionally coupled dynamics make real-time control particularly difficult. Traditional control methods, such as proportional-integral (PI) controllers and expert rule-based systems, rely on static parameters and fixed boundaries. While simple to implement, they often suffer from delayed response, poor adaptability, and frequent boundary violations under volatile grid conditions. Recent advances in intelligent control—such as fuzzy logic, Model Predictive Control (MPC), and Reinforcement Learning—have improved foresight and optimization capabilities. However, these methods typically require high model fidelity and computational resources, and they still struggle with real-time boundary identification and fault tolerance, especially in systems with strong physical constraints and multi-variable coupling (Shichun et al., 2025; Yang, 2021).
To address these limitations, this paper introduces a novel real-time control strategy for pumped storage systems based on Adaptive Moving Average (AMA) channel modeling. Originally developed for trend analysis in financial markets, AMA channels offer dynamic interval construction and sensitivity to state fluctuations (Li et al., 2012). By transferring this concept to energy system control, we construct a head-state-driven regulation framework that enables real-time trend tracking, boundary identification, and automatic output adjustment. The proposed method treats water head as the core control variable and builds a dynamic regulation channel whose centerline and boundaries adapt to the rate of head change and system perturbation intensity. When the head state deviates beyond the channel limits, the control system triggers output adjustment procedures (Li et al., 2019). A parameter self-tuning module continuously optimizes the strategy based on frequency deviation (Wang et al., 2022), AGC signal variation, and unit ramping capacity, while a strategy recovery mechanism ensures fault tolerance under parameter failure or recognition errors (Yu et al., 2022).
Compared to conventional fixed-boundary approaches, the AMA-based strategy provides superior adaptability and responsiveness. It integrates state-aware regulation, boundary-driven activation, and constraint-aware execution, forming a closed-loop control system suitable for high-volatility grid environments (Luo et al., 2022). The method also embeds physical constraints such as reservoir limits and unit ramp rates into the channel construction, ensuring safe and feasible regulation behavior (Qinghui et al., 2024). To validate its effectiveness, a multi-scenario simulation platform is developed, covering day-ahead economic dispatch, intraday real-time control, AGC frequency response, and head fluctuation interference. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed strategy significantly improves regulation accuracy, shortens response time, enhances head stability, and reduces operational costs. Ablation experiments further confirm its robustness and economic resilience under parameter degradation (Wang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2025).
This research makes three key contributions. First, it establishes a head-state-driven adaptive channel control framework that enables precise and stable regulation of pumped storage systems under complex disturbances (Pei et al., 2022; Sayed, 2008; Wang et al., 2022). Second, it demonstrates the interdisciplinary transfer of AMA channel theory from financial modeling to energy system control, expanding the application boundaries of technical analysis methods. Third, it validates the strategy’s performance advantages and fault tolerance across multiple scenarios, providing a scalable and intelligent control pathway for pumped storage systems in high-renewable grids (Wang et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2020). These findings offer both theoretical insights and practical tools for advancing the reliability and flexibility of future power systems.
2 Theoretical foundations of control strategy
As the complexity of power system operations continues to increase, control strategy research has gradually shifted from traditional linear static models toward nonlinear time-varying systems. In power systems with significantly higher penetration of renewable energy, dynamic characteristics such as frequency fluctuations, load disturbances, and dispatch uncertainties have become typical features of system operation. This has driven control theory toward intelligent development, incorporating real-time state monitoring, adaptive regulation, and predictive response capabilities. As a critical flexibility resource for grid regulation, the control strategy design for pumped-storage hydroelectric systems has consequently evolved into a new phase dominated by dynamic optimization as the primary technical approach.
2.1 Context of control strategy evolution
Traditional pumped storage control methods rely on fixed parameter settings and linear model construction, and are suitable for planning and scheduling under stable operating conditions. However, in the operating environment where the new energy output fluctuates drastically and the grid frequency changes rapidly, this kind of method often suffers from the problems of response lag and insufficient regulation accuracy, which seriously restricts the regulation potential of the pumped storage system and the depth of participation. Therefore, the research on control strategies has gradually developed in the direction of state-awareness, adaptive regulation, and predictive response capability.
In recent years, fuzzy control, model predictive control (MPC), and adaptive control have received extensive attention in pumped storage systems. Among them, adaptive control is increasingly valuable in complex systems because of its parameter self-tuning and state sensitivity. Its core advantage lies in its ability to adjust the control parameters in real time according to the system operation state, thus improving the regulation accuracy and system stability.
2.2 Background and motivation for introducing adaptive channeling theory
The power output of wind power, photovoltaic, and other intermittent power sources is highly fluctuating, with large prediction errors, frequent frequency shifts, and intensified pressure on the response to scheduling commands and the traditional control strategy based on static parameter settings gradually exposes lagging response, insufficient regulation accuracy, and low margin utilisation in actual operation. Especially in the pumped storage system, the head change has a direct impact on the capacity and regulation range of the unit, and its nonlinear and time-varying characteristics make it difficult to adapt the fixed-boundary control strategy to the complex operating environment.
In order to improve the dynamic response capability and regulation accuracy of the system, state-awareness, adaptive regulation, and trend identification mechanisms have been gradually introduced into the control strategy research in recent years. In this context, channel modelling methods have become a potential tool for constructing dynamic control frameworks due to their boundary identification and trend tracking capabilities. Among them, the Adaptive Moving Average Channel (AMA Channel), as a dynamic interval modelling method with the ability of parameter self-tuning and fluctuation sensing, has been widely used to identify the trend strength and signal boundaries in financial technical analysis, and its core idea is to dynamically adjust the channel centreline and upper and lower tracks according to the change rate of state variables and disturbance strength, to achieve more sensitive control framework. The core idea is to dynamically adjust the channel centreline and upper and lower tracks according to the rate of change of state variables and the intensity of perturbation, so as to achieve a more sensitive response and a more robust control.
The introduction of AMA channel theory into the control strategy of the pumped storage system not only realizes dynamic modelling and boundary identification of the head state, but also triggers the regulation process automatically when the state deviates from the safety zone, which improves the system’s responsiveness to frequency perturbation and scheduling commands. Compared with the traditional Bollinger Bands and other fixed-channel methods, the AMA channel has stronger trend adaptability and parameter flexibility, which is suitable for real-time control under high volatility and high uncertainty grid environments.
2.3 Theoretical foundations of adaptive channeling
Adaptive Moving Average Channel (AMA Channel) is originally derived from the trend identification method in the financial field, and its core idea is to dynamically adjust the width of the channel and the position of the centre line to adapt to the volatility of the state variable and the trend strength. In the control system, the idea can be migrated to: according to the rate of change of state variables and the intensity of perturbation, dynamically adjust the control interval and regulation strategy, so as to achieve a more sensitive response and more robust control.
The adaptive channel uses AMA as the middle rail and combines volatility indicators (such as average true volatility, ATR) to construct the upper and lower rails, forming a dynamic price channel.
Upper track: usually
Lower track: usually
The centre line of an AMA channel usually consists of a weighted moving average whose weights are adjusted as the state changes. Let a state variable be an adaptive moving average can be expressed as shown in Equation 1:
Included among these
The upper and lower trajectory lines in this study can be expressed as shown in Equation 2:
Included among these
The model is capable of trend tracking and fluctuation sensing, and is suitable for dynamic modelling of the head state and identification of the regulation boundary in pumped storage systems.
2.4 Control strategy adaptation logic
Embedding the adaptive channel approach into the control strategy of pumped storage systems requires a multi-level adaptation process from theoretical abstraction to engineering realisation. The process involves not only the mapping of state variables and channel construction mechanism, but also the parameter adjustment logic, boundary triggering strategy, system constraints handling, and the integration with the existing scheduling system.
In pumped storage systems, head state
The core advantage of the adaptive channel is that the parameters can be updated in real time as the system state changes. To realise this mechanism, a parameter tuning function needs to be constructed, can be expressed as shown in Equation 3:
Included among these:
In practical engineering applications, pumped storage systems have a variety of operational constraints, such as the upper and lower water level limits, minimum output of the unit, and the rate of climb limit etc. The control strategy needs to embed these constraints in the channel construction to form a “constrained channel”. The control strategy needs to embed these constraints in the channel construction to form a “constrained channel”, can be expressed as shown in Equation 4:
In this way, it ensures that the regulated behaviour does not break through the physical boundaries and guarantees the safety of system operation. The adaptive channel control strategy needs to be designed to interface with existing dispatch systems (e.g., AGC, frequency control centre).
2.5 Pathways for adaptive channeling in pumped storage control
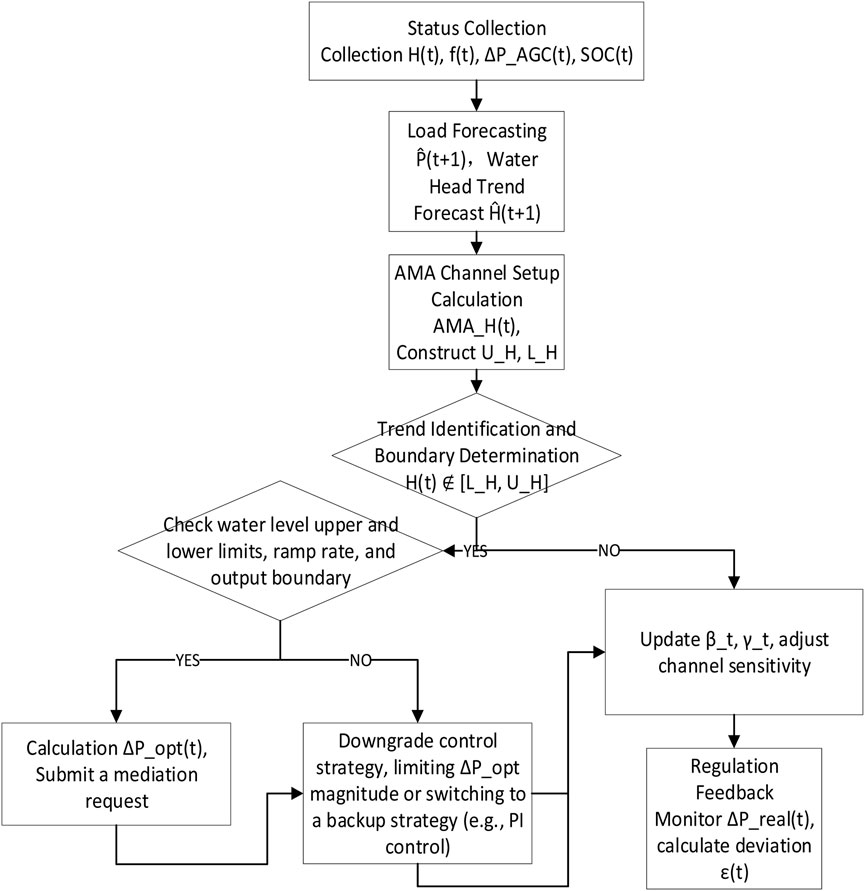
In order to realise the adaptive channel control strategy in a pumped storage system, it is necessary to construct a complete control process with the functions of state sensing, channel construction, boundary identification, regulation response, and parameter update. The whole control process can be divided into five core modules, namely: state acquisition, channel construction, boundary judgement, regulation execution, and parameter update. The control strategy flow chart is shown in the Figure 1.
2.6 Research value of methodological evolution
The control strategy integrates the trend recognition capability of the adaptive channel and the parameter regulation mechanism of the control system, with good dynamic response performance and engineering adaptability. The theoretical basis is derived from the dynamic modelling approach in the financial field, but the systematic reconstruction of state variable mapping, boundary identification, and regulation triggering is achieved in pumped storage systems, which facilitates the transition of control strategy from static scheduling to active regulation.
In addition, the method has good scalability and can be applied to other flexible resources with state fluctuation characteristics, such as energy storage systems, virtual power plants, etc., which provides theoretical support and technical guarantee for the construction of a stable regulation system in a high proportion of new energy grids.
3 Control method construction and design
3.1 Control model construction
Based on the core logic of state-driven regulation, dynamic channel identification, and boundary-triggered response, the proposed control strategy constructs an adaptive head regulation model tailored for pumped storage systems. Rather than a single algorithm, the model comprises five integrated functional modules: state acquisition, AMA channel construction, boundary judgment, regulation execution, and parameter update. These modules form a composite control system that can be embedded into the main control platform, enabling rapid response to frequency disturbances and dispatch commands.
The model uses water head as the core driving variable and integrates state perception, trend tracking, boundary detection, and regulation triggering into a unified framework. Through the AMA channel mechanism, it dynamically identifies head-state trends and activates regulation procedures when deviations from safe operating boundaries are detected. By collecting key operating parameters in real time—such as head level, grid frequency, and AGC signals—the model evaluates whether the system is approaching a regulation threshold. Upon boundary violation, it calculates the optimal output adjustment and updates control parameters based on feedback, forming a closed-loop, self-optimizing structure suitable for high-precision scheduling in volatile grid environments.
In practical operation, the strategy combines event-driven triggers with periodic evaluation, executing its core logic on a 2-s cycle. When either frequency deviation or head state breaches the adaptive channel boundaries, the system immediately initiates the regulation process. The strategy maintains closed-loop interaction with the AGC scheduling system via two-way coupling, ensuring that output adjustments are confirmed and refined in real time. It also embeds physical constraints—such as reservoir level limits, unit ramping capacity, and minimum output thresholds—into the channel construction to guarantee engineering feasibility and operational safety. To ensure robustness under persistent deviation or parameter failure, the model includes a fault-tolerance mechanism and automatic fallback logic. If the regulation error—measured by RMSE or deviation persistence—exceeds predefined thresholds, the system switches to alternate strategies such as PI control or expert rules, maintaining continuous and stable operation in highly volatile grid conditions.
3.2 Algorithm flow design
In the algorithm design of the adaptive channel control strategy, the overall process is state-driven as the core, and a closed-loop control system with the ability of trend identification, boundary judgement, regulation response, and strategy update is constructed. The algorithm constructs a dynamic channel structure by real-time acquisition of key parameters such as head, grid frequency, AGC command, combined with short-term prediction information, and triggers the regulation process when the head state breaks through the boundary. Physical constraints are checked before the regulation is executed to ensure that the output adjustment behaviour is in line with the water level limit and the unit’s climbing capacity; then, the optimal output adjustment amount is calculated according to the system state and submitted to the dispatch application. After the adjustment is completed, the system will evaluate the deviation according to the actual response results and update the control parameters accordingly to improve the adaptability and accuracy of the strategy. If the deviation continues to be abnormal, the algorithm will automatically enter the strategy reconfiguration process, switching to an alternate control model or introducing expert rules, so as to ensure stable operation and continuous optimisation of the system in a highly volatile grid environment.
Key parameters in the control strategy include:
Weighting factor
Included among these
Channel Sensitivity
Among them
In the algorithm design of the adaptive channel control strategy, the overall process is built around the dynamic identification of the head state and regulation response, forming a closed-loop control system with trend sensing, boundary judgement, constraint verification, output execution, and strategy update. The algorithm firstly obtains key parameters such as head, grid frequency and AGC command through the state acquisition and short-term prediction module, and builds an adaptive channel to identify the operating trend and regulation boundary; when the head state breaks through the upper and lower rails of the channel, the system triggers the regulation process, and conducts physical constraints checking to ensure the engineering feasibility of the output behaviour before regulation. Subsequently, the controller calculates the optimal amount of output adjustment according to the current system state and submits the scheduling application, monitors the actual response results, and evaluates the adjustment deviation, dynamically updating the control parameters to improve the adaptability and accuracy of the strategy. If the deviation continues to be abnormal, the algorithm automatically enters the strategy reconfiguration process, switching to an alternate control model or introducing expert rules to ensure the stable operation and continuous optimisation of the pumped storage system in a highly volatile grid environment.
4 Simulation example analysis
In order to verify the dynamic response performance and regulation accuracy of the proposed adaptive channel control strategy in a pumped storage system, this paper constructs a multi-scenario simulation platform and analyzes the examples with actual unit parameters and dispatch data. The simulation covers key aspects such as day-ahead economic dispatch, intraday real-time control, AGC frequency response, and head dynamics, in order to comprehensively assess the adaptability and engineering value of the control strategy in a high proportion of new energy grids.
4.1 Day-ahead vs. intraday scheduling performance analysis
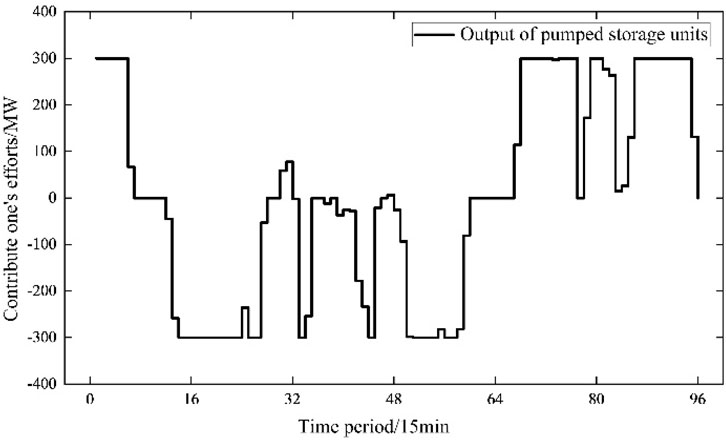
During the day-ahead scheduling phase, the pumped storage system needs to reasonably arrange the charging and discharging strategies according to the load forecast and the new energy output plan to optimise the system operating costs. The results of the day-ahead economic dispatch of pumped storage units are shown in the following figure, which shows the distribution of each unit’s output under the baseline strategy. It can be seen that the system gives priority to the units with large regulation margins to participate in the dispatch during the peak load hours, and arranges the charging and discharging operations during the trough hours to improve the overall energy efficiency. The outcomes of the latest economic dispatching of pumped-storage power units is shown in the Figure 2.
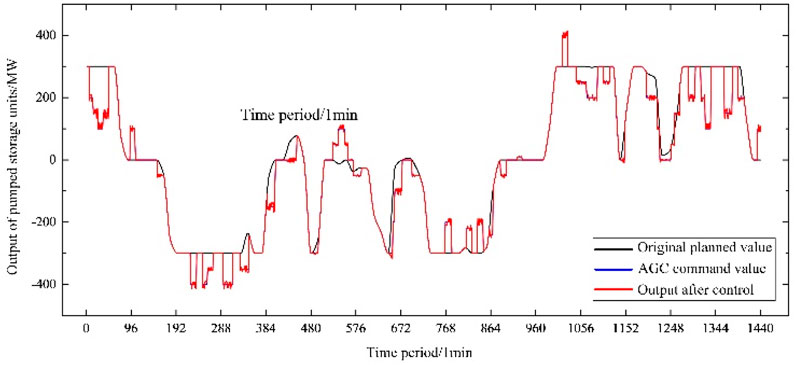
Entering the intraday real-time control stage, the intraday real-time control output curve of the pumped storage unit is shown in Figure 3, which shows the response process of the adaptive channel strategy under frequency perturbation conditions. Compared with the traditional fixed-parameter control, this strategy can quickly identify the head state deviation and trigger the regulation process after the perturbation occurs, and the output curve shows stronger continuity and stability, effectively suppressing the frequency fluctuation.
As shown in Figure 3, the figure presents the active power output characteristics of the pumped storage unit during the intraday real-time regulation process, which is as follows: when the frequency regulation command is not obtained from the central regulator, the unit’s operating state strictly maintains the consistency with the preset plan value; when the system receives the frequency regulation command, it will automatically switch to the automatic power generation control mode to perform the frequency regulation task based on the comprehensive assessment of the unit’s operating parameters and under the premise of ensuring that all conditions meet the requirements. When the system receives the frequency adjustment command, it will automatically switch to automatic power generation control mode to perform the frequency adjustment task based on a comprehensive evaluation of the unit’s operating parameters and on the premise of ensuring that all conditions meet the requirements. It is worth noting that the sampling period of the system is set to 15 min, which means that a complete operating day is divided into 1,440 discrete periods. The empirical study data show that the plan tracking control strategy is adopted in a total of 945 operating periods within the sample period examined, and this operation mode significantly improves the response accuracy of pumped storage units to the grid dispatch commands so that they can strictly follow the power output target value set by the economic dispatch plan in the previous day, and this precise power tracking mechanism not only guarantees the operational reliability of the generation system, but also This precise power tracking mechanism not only ensures the operational reliability of the power generation system, but also fundamentally avoids the risk of scheduling assessment due to the deviation of the actual power output from the planned value.
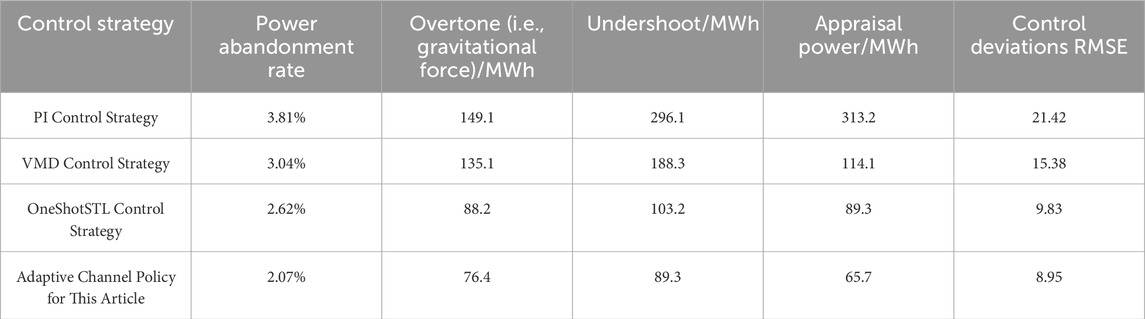
The comparison table of consumption and control effects evaluates the comprehensive benefits of the control strategies at the system level, in which the adaptive channel strategy outperforms the comparison strategy in terms of new energy consumption rate, regulation accuracy, and operation cost, which verifies its advantages in multi-objective scheduling. The comparison table of consumption and control effect is shown in the Table 1.
4.2 Control strategy regulation performance evaluation
To further evaluate the performance of the control strategy in dynamic regulation, this paper introduces an active power prediction model as an auxiliary module, which is used to improve the foresight of channel construction and the accuracy of boundary identification.
The model prediction comparison quantifies the prediction error, and the average deviation is controlled within ±0.6 MW, indicating that the model has good trend tracking capability. The model prediction comparison table is shown in the Table 2.
Through the comparative analysis of multidimensional performance evaluation indexes, the adaptive channel control method proposed in this study is significantly better than the benchmark model in terms of prediction accuracy and stability, and this result verifies the applicability and advancement of the method in the task of ultra-short-term prediction of the active power of energy bases. The excellent performance of the model not only provides a solid technical guarantee for the control strategy designed in this study, but also opens up a new technical path for the improvement of power system regulation efficiency and the efficient use of energy resources.
4.3 Head dynamic response and boundary control analysis
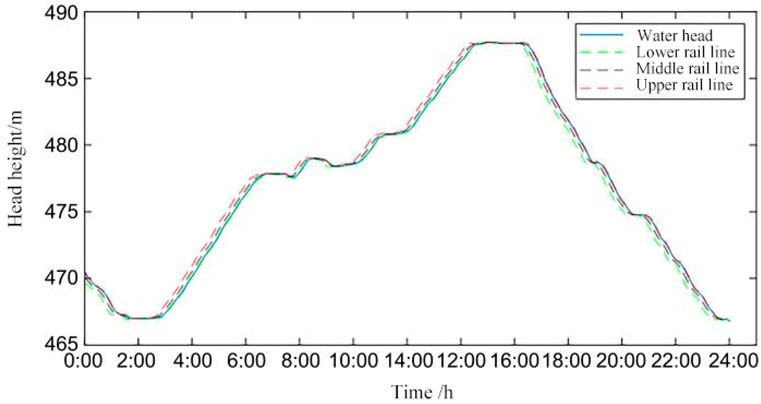
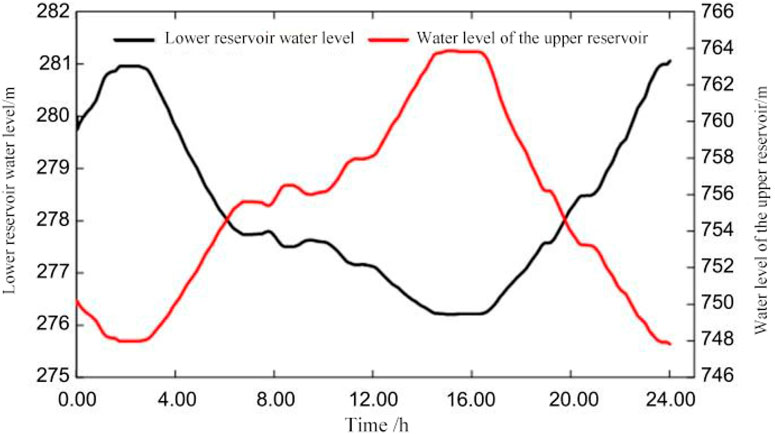
As a key operating variable of the pumped storage system, the dynamic change of the head state directly affects the output capacity and regulation margin of the unit. The head change curves of the pumped storage units and the water level change curves of the upper and lower reservoirs show the head response process of the system under different regulation strategies. It can be observed that under the traditional control strategy, the head fluctuates greatly, and there is the risk of boundary breakthrough and regulation lag; while the adaptive channel strategy can effectively identify the head trend and trigger the regulation in advance, so that the head state always operates within the safety zone. The head curve of a pumped - storage power unit is shown in the Figure 4. Graph depicting the alteration in water levels of the upper and lower reservoirs is shown in the Figure 5.
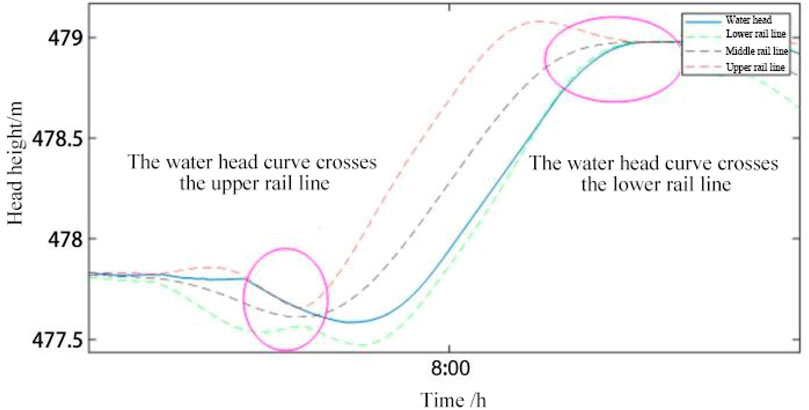
In order to systematically verify the applicability of the head optimisation control method proposed in this study, considering the relatively stable range of head change during the actual operation of the pumped storage power plant, this study focuses on selecting representative head change characteristic time periods to carry out detailed research. As shown in Figure 4, during the 7:00–9:00 time period, with the grid connection of the PV unit, the pumped storage unit frequently receives AGC commands from the dispatch centre to reduce the output, which leads to a continuous fluctuation of the FM target value around the planned output benchmark, and prompts the unit to switch to pumping condition to perform charging operation to meet the system FM demand. During this process, the operating head of the unit showed a continuous upward trend and broke through the upper track threshold for the first time, at which time the optimisation strategy was immediately activated, generating the optimised planned output scheme through real-time calculation and submitting the application for output adjustment for the next time period to the dispatch centre. Around 8:00, the head curve dropped back and returned to the zone. Subsequently, during the 8:00–9:00 period, under the influence of the successive power reduction orders in the previous period, the head indicator broke through the lower track one after another, triggering the second intervention of the optimisation strategy, which completed the update of the scheduling order before the end of the time period by reducing the pumping power and re-calculating the optimised output scheme, and prompted the water head to rise to the normal fluctuation range around 9:00. Since 9:00, the output of each unit in the system has been stabilised, and the pumped storage units have been switched from FM mode to plan tracking mode, effectively avoiding the risk of overcharging and over-discharging triggered by the continuous rise of the water head by initiating the discharge operation at the right time. Local curve of head variation for pumped - storage units 1 is shown in the Figure 6.
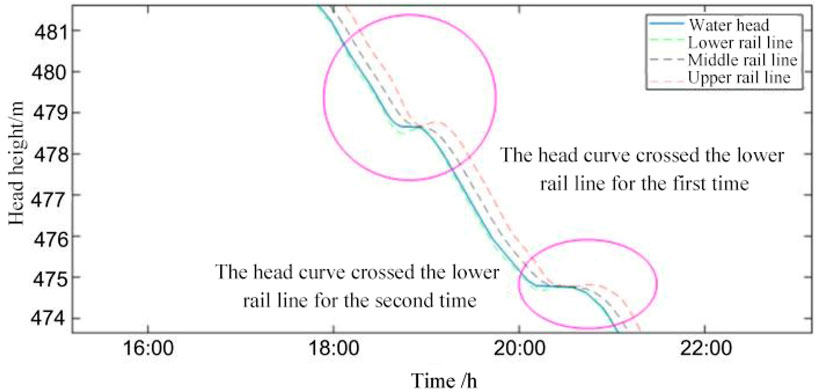
An in-depth study of the daytime operating characteristics of the pumped storage unit shows that, as shown in Figure 5, during the peak load period of the power system from 18:00 to 22:00, the unit frequently receives a number of AGC FM incremental commands from the central regulator, which prompts the unit to switch to the turbine operating condition and perform the discharging operation in order to effectively make up for the power deficit of the power grid. Under this condition, the head curve continued to run near the lower limit, and the first time the head curve broke through the lower limit occurred during the period of 18:00–20:00, at which time the head optimization control strategy was activated, and by applying for adjusting the subsequent planned output to the dispatch centre, the head curve was successfully brought back to the normal operating range; similarly, during the period of 20:00–22:00, the head curve was again affected by the successive incremental instructions, and the unit was again affected by the continuous incremental instructions. Similarly, during the period of 20:00–22:00, the head curve again broke through the lower limit under the influence of the continuous increase in commands. Local curve of head variation for pumped - storage units 2 is shown in the Figure 7.
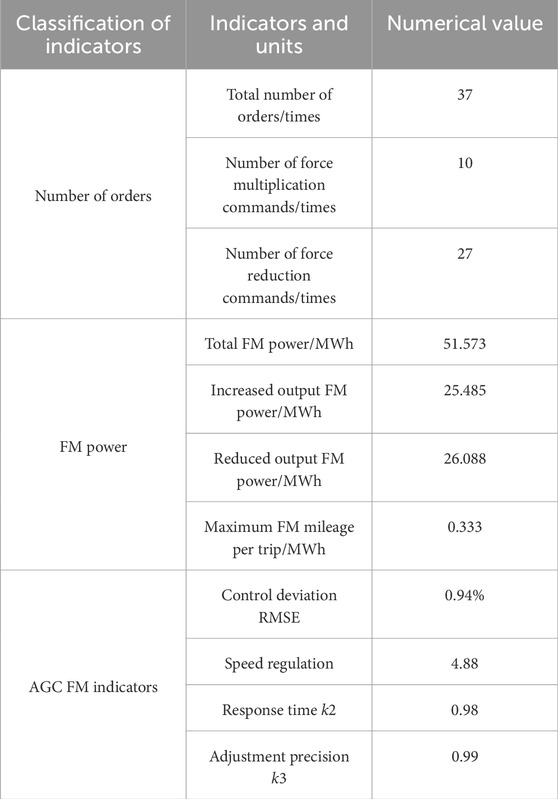
Adaptive channel strategy in the head control has a stronger boundary identification ability and regulation stability, effectively avoiding the water level breakthrough and regulation of overshoot phenomenon, improving the operational safety of the system and regulation accuracy. AGC FM mode of the indicators is shown in the Table 3.
5 Concluding remarks
As the penetration rate of new energy continues to rise, the uncertainty and dynamics of power system operation are increasing, and the traditional scheduling and control methods are facing serious challenges in terms of frequency stability, regulation accuracy, and response speed. This paper focuses on the strategic role of pumped storage system in the high proportion of new energy power grid, and proposes a control strategy integrating adaptive channel theory, taking the head state as the core driving variable, and constructing a regulation framework with the ability of trend identification, boundary judgement and parameter self-tuning, to realise the dynamic sensing and efficient response to the key state of the system.
Through theoretical modelling and algorithm design, this paper constructs a complete control process system and carries out multi-dimensional simulation verification under typical operation scenarios. The results show that the proposed control strategy exhibits significant advantages in frequency perturbation response, AGC command tracking, head boundary control, and economic scheduling, with low regulation deviation, short response time, strong system stability, and good engineering adaptability and deployment value. Especially in the strategy ablation experiment, the adaptive channel method shows strong fault tolerance and recovery mechanisms, which further verify its robustness and practicality in the complex grid environment.
In addition, this paper also explores the interdisciplinary migration path of the financial technology analysis method in energy system control, introduces the AMA channel modelling idea into pumped storage control strategy design, expands the application boundary of channel theory in the engineering field, and provides theoretical support and methodological references for the construction of an intelligent control system with state-awareness and self-adaptive regulation capability.
Future research can further combine deep learning and reinforcement learning methods to improve the self-learning ability of channel parameters and strategy optimisation; at the same time, it can be expanded to multi-unit cooperative control and regional dispatch scenarios to build a more systematic and generalised pumped storage control platform, which will contribute to the construction of a safe, efficient and low-carbon modern power system with stronger technical support.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
FY: Writing – original draft. GW: Writing – review and editing. SA: Writing – review and editing. HS: Writing – review and editing. QZ: Writing – review and editing. JC: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors FY, GW, SA, HS, QZ, and JC were employed by Guizhou Power Grid Co. Ltd.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bukovsky, I., Dohnal, G., and Homma, N. (2023). Comments on “Convergence Analysis of Adaptive Exponential Functional Link Network” [Feb 21 882-891]. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 34 (9), 6677–6678. doi:10.1109/tnnls.2021.3123540
Chen, P., Zhang, X., Guo, X., Li, D., and Gao, X. (2023). Secondary frequency regulation of a hybrid coal-fired generator and BESS power station considering random characteristics of AGC instructions. Power Syst. Prot. Control 51 (12), 168–177. doi:10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.221600
Diniz, P. S. R. (2013). Adaptive filtering: algorithms and practical implementation. 4th ed. Netherlands: Springer Nature.
Li, D.-C., Chang, C. J., Chen, C. C., and Chen, W. C. (2012). Forecasting short-term electricity consumption using the adaptive grey-based approach—an Asian case. Omega (Oxford) 40 (6), 767–773. doi:10.1016/j.omega.2011.07.007
Li, A., and Barber, R. F. (2019). Multiple testing with the structure-adaptive Benjamini–Hochberg algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B, Stat. Methodol. 81 (1), 45–74. doi:10.1111/rssb.12298
Li, B., Wang, J., Liang, S., and Wei, C. (2022). AGC real-time control strategy based on LSTM recurrent neural network. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 42 (03), 128–134. doi:10.16081/j.epae.202111014
Luo, Y., Chang, Y., Zhao, Y., Wang, Q., You, L., and You, L. (2022). Control policy of pumped storage power station based on power grid frequency stability. Smart Power 50 (11), 97–103+118. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2022.11.016
Pei, J., Yao, J., Huang, S., Chen, S., Chen, Z., Chen, Z., et al. (2022). Its adaptive stability control strategy. Zhonggúo Dianji Gongchéng Xúebao 16, 5922. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.211331
Qinghui, L., Jian, Q., Xianggen, Y., Zhichang, L., Yikai, W., Lingjin, Z., et al. (2024). Calculation method of external fault short circuit current of variable speedpumped storage unit based on time-domain dynamic process. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 44 (03), 166–171+179. doi:10.16081/j.epae.202307002
Shichun, L., Jiahong, X., Haobin, L., Chuanzhou, Z., Xinyang, T., and Qiujie, W. (2025). Frequency regulation cooperative control strategy of power grid based on hybrid energy storage of storage battery and variable speed pumped storage. Energy Storage Sci. Technol., 1–14. doi:10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2025.0475
Sun, Q., Zhou, W.-X., and Fan, J. (2020). Adaptive huber regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 115, 254–265. doi:10.1080/01621459.2018.1543124
Wang, J., Liao, Y., Han, W., Ding, J., and Yang, W. (2021). Modeling and active power control characteristics of pumped storage-wind hybrid power system in the context of peak carbon dioxide emission. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 52 (09), 172–181. doi:10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2021.09.018
Wang, Z., Yu, Y., Gao, W., Davari, M., and Deng, C. (2022). Adaptive, optimal, virtual synchronous generator control of three-phase grid-connected inverters under different grid Conditions-An adaptive dynamic programming approach. IEEE Trans. Industrial Inf. 18 (11), 7388–7399. doi:10.1109/tii.2021.3138893
Wang, H., Zhang, X., Sun, Y., Sun, Y., and Sun, Y. (2025). Source-grid-storage coordinated control strategy for improving frequency regulation performance. Renew. Energy Resour. 43 (07), 960–969. doi:10.13941/j.cnki.21-1469/tk.2025.07.017
Xie, H., Wang, C., Liu, P., Liu, H., Xu, G., Li, P., et al. (2021). Application of joint frequency regulation technology of energy storage and thermal power in China Southern power grid. Dianli Xit. Zidonghua/Automation Electr. Power Syst. 45 (04), 172–179. doi:10.7500/AEPS20200206004
Yang, Yu (2020). Research on energy storage capacity allocation considering wind power tracking plan output and auxiliary thermal power AGC frequency modulation. Xinjiang University. doi:10.27429/d.cnki.gxjdu.2020.000116
Yang, Z. (2021). Virtual synchronous generator control of variable SpeedPumped-Storage unit with full-size converter. Beijing Jiaotong University. doi:10.26944/d.cnki.gbfju.2021.001898
Keywords: adaptive moving average channel, real-time control, pumped storage, frequency response, head state
Citation: Yang F, Wang G, An S, Su H, Zhang Q and Chen J (2025) Real-time control method and performance evaluation of pumped storage system based on adaptive moving average channel strategy. Front. Energy Res. 13:1711460. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2025.1711460
Received: 23 September 2025; Accepted: 22 October 2025;
Published: 14 November 2025.
Edited by:
Bo Li, Guangxi University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Yang, Wang, An, Su, Zhang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fu Yang, OTI4OTIwMjYzQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Fu Yang
Fu Yang Guosong Wang
Guosong Wang