- Rubber Technology Centre, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India
The effect of aramid short fibers on the cure characteristics, processing behaviour, as well as the physical and mechanical properties of ethylene-propylene-diene terpolymer rubber (EPDM) is investigated. The EPDM rubber is reinforced with hybrid fillers like aramid fibers, silica, and carbon black while undergoing peroxide vulcanization. Masterbatches are prepared using an internal mixer while keeping different fiber percentages such as 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15 and 20 phr. Then, the impact of these different fiber percentages on the viscoelastic, mechanical and dynamic properties of the base rubber of the V-belt is studied; the results indicate that viscosity, maximum–minimum torque, and cure rate were increased by adding fiber, the fiber content has a great influence on the mechanical properties as well. At 6 phr fiber loading, the tensile strength decreased slightly to 18.76 MPa, elongation at break reached 413.4%, tear strength improved to 76.2 kgf/cm, and abrasion loss dropped to 61.1 mm3—demonstrating an excellent equilibrium of strength, flexibility, and wear resistance. The introduction of fibers decreased resilience and flexibility (which led to poorer results in flex testing for high-concentration fiber-reinforced composites). Heat build-up and compression set were increased with fiber concentration for the composites. From the De-Mattia Fatigue Study, it is clear that 6 phr of fiber concentration shows the best fatigue life, in which the crack initiates after 367 kilocycles, which is the highest among all, and full rupture of the specimen occurs at 545 kilocycles. The crack growth resistance test indicated that the 6 phr fiber-filled sample possessed very little crack extension: only 4 mm after 10,000 cycles and 13 mm after 25,000 cycles. This shows that the specimen with 6 phr is most resistant to fracture development. This research allows for the development of rubber composites with precisely controlled mechanical properties for demanding engineering uses. In addition, it provides a valuable benchmark for future investigations of alternative fiber reinforcement, especially natural ones. A better understanding of the fundamental principles of tension, tear, and wear in such compounds can lead to the design of more sustainable materials due to their extended lifespan.
Introduction
Short fibers have been commonly used to enhance the strength of rubbers, plastics, and flexible polymers for many years. In contrast to conventional reinforcing agents such as carbon black or silica, these short fibers provide an exceptional synergy in the polymer composites. Even at low loadings of these short fibers, they improve material stiffness and help the polymer matrix in shape retention and thermal resistance. Moreover, unlike materials developed with long, continuous fibers, these short-fiber composites may be produced with conventional techniques such as calendering, molding, and extrusion, offering a great advantage (Zhang H. et al., 2023; Soltani et al., 2014; Wazzan, 2004). It is important to recognize that the alignment of these fibers within the material can influence its strength and other properties variably based on the testing direction (Longitudinal or transverse). In recent years, additive manufacturing has turned out to be a promising technique to fabricate fiber-reinforced polymer composites with precise control over fiber alignment and architecture. A thorough review described different FDM (fused deposition modeling) mechanisms used to make continuous-fiber reinforced composites (Karimi et al., 2024). It suggested the possibility of tailoring mechanical performance through process control. Furthermore, employed the Taguchi optimization method to develop highly stretchable 3D-printed elastomers with superior mechanical integrity (Bayati et al., 2025). While the present study does not utilize additive manufacturing techniques, these findings highlight the relevance of fiber orientation, dispersion, and process-structure-property relationships, core concepts that underpin our approach using conventional compounding and calendering.
Short fiber-reinforced elastomers, particularly those augmented with aramid, are utilized in various applications, including tires, transmission belts, hoses, and seals, due to their ease of processing and low cost, as well as to modify the mechanical and tribological properties of rubber composites (Botan et al., 2017; Kashani, 2009). The improved dynamic mechanical behavior, reduced heat build-up, and enhanced wear properties of these composites all contribute to their extensive use across many different fields. Recently, there has been an increasing focus on enhancing short fiber-matrix interactions with optimum loading to get improved load-bearing capacity and fatigue resistance in rubber-based systems (Hintze et al., 2014; Botros et al., 2000). The growing complexity of operational situations, including elevated speeds and temperatures in automotive and industrial contexts, has required the development of elastomers with customized properties for high performance. Short fibers serve a dual function by offering mechanical reinforcement and altering energy dissipation mechanisms in the elastomer during cyclic deformation. When effectively dispersed and aligned, these fibers can markedly affect crack initiation thresholds and inhibit propagation, thus prolonging the lifespan of rubber components (Zhang Y. et al., 2023; Zhong et al., 2019).
The investigation of fiber-reinforced elastomer composites regarding their tribological and dynamic mechanical behavior has been performed by many researchers in the past, adding several fiber types, including carbon fiber, cellulose fiber, polyamide fiber, and short-cut aramid fiber (López-Manchado et al., 2002; Dominic et al., 2020). For instance, Hintze et al. (2014) studied curing, mechanical behavior, heat build-up, and Crack Growth Resistance under cyclic loading in EPDM and NR rubber composites using Twaron and Technora aramid fibers and reported improved fatigue crack growth resistance under cyclic loading. Shirazi et al. and Sathi et al. discussed the challenges with dispersion and interfacial adhesion, emphasizing the role of surface treatments and compatibilizers in achieving effective fiber reinforcement in elastomeric composites (Shirazi et al., 2013; Gopi et al., 2019). This indicates that our untreated aramid short fibers may reach a critical performance threshold depending on the loading and alignment of fibers in the matrix. Sheik Mohammed et al. (2016) have also reported about enhancing the interfacial interaction that includes the use of dry bonding systems like resorcinol/hexamethylenetetramine/silica (HRH) maintains good composite mechanical properties, including tensile strength, hardness, and modulus at 100% elongation, and compression set by enhancing aramid fiber/NBR adhesion. Seong et al. (2020) examined the reinforcing properties of aramid fiber and the influence of carbon black on the mechanical properties of ethylene-acrylic rubber as a function of filler loading, revealing that the reinforcement of acrylic rubber with a combination of 10 phr aramid and 20 phr carbon black shows a synergistic effect. Yang et al. (2020) demonstrated that a minimal quantity of aramid fiber (merely 6 phr) within the rubber matrix could significantly improve the mechanical properties, fatigue life, and cut-resistance performance of the short fiber reinforced carbon black-EPDM composites. Botros et al. and Zhang et al. examined fiber orientation effects on crack propagation and fatigue resistance, demonstrating the importance of processing-induced fiber alignment, similar to our calendering strategy (Zhang H. et al., 2023; Botros et al., 2000). Previous research has identified several limiting factors for the extensive application of short aramid fibers in a rubber matrix. These include the maintenance of a high aspect ratio in the fibers (minimizing breakages during processing), control of fiber orientation to effectively reinforce the engineered component, the development of a robust interface through physicochemical bonding, achievement of a high degree of dispersion, and optimal formulation of the rubber compound to support processing and enhance stress transfer while preserving as much flexibility as possible to maintain dynamic properties (Gopi et al., 2019; Arl et al., 2023; Shibulal and Naskar, 2011). The fatigue, abrasion wear, compression set, and mechanical performance of elastomers reinforced with short-cut aramid fiber, carbon black, and silica are investigated in this work. The novelty of this research is that it combines short aramid fibers with hybrid fillers (carbon black and silica) in EPDM matrices in a systematic way. The objective is to make a practical application in the base rubber of V-belts. The study finds a unique ideal fiber concentration (6 phr) that strikes the best balance between mechanical strength, resistance to wear and tear, fatigue life, and thermal behaviour. This study is different from earlier ones since it provides a comprehensive correlation among processing behaviour (Mooney viscosity, cure characteristics), filler loading, and long-term performance parameters (heat build-up, Ross flex fatigue), offering a practical guideline for industrial-scale elastomer design. This work intends to help develop next-generation fiber-reinforced elastomeric composites with optimal multifunctional performance by systematically changing the filler content and assessing how filler distribution, orientation, and interaction affect the resultant properties.
Experimental
Materials and methods
This study used EPDM as the primary rubber material. The EPDM rubber utilized was Vistalon 706, characterized as a medium Mooney viscosity of 42 MU [ML (1+4) @125°C] and consisting of 65% ethylene content cured by a peroxide curing system (Luperox F40). This EPDM rubber is available in compact bale form and is manufactured by ExxonMobil. Three different types (N330, VN3 silica, and m-Aramid fiber) of hybrid reinforcing fillers were used in the rubber product. The Conex m-Aramid short-cut fiber is composed of finely chopped strands cut with a length of 1 mm and a density of 1.38 g/cm3. Chemicals such as Zinc oxide, zinc stearate, coagent (Asada R20 S), curative (Luperox F40), antioxidant (Ethanox 4703), antiozonants (TDQ), process oil (Struckpar 2280 paraffinic oil), etc., were obtained as commodity products from different manufacturing companies according to their grade name as represented in the given formulation below.
Mixing of the blends
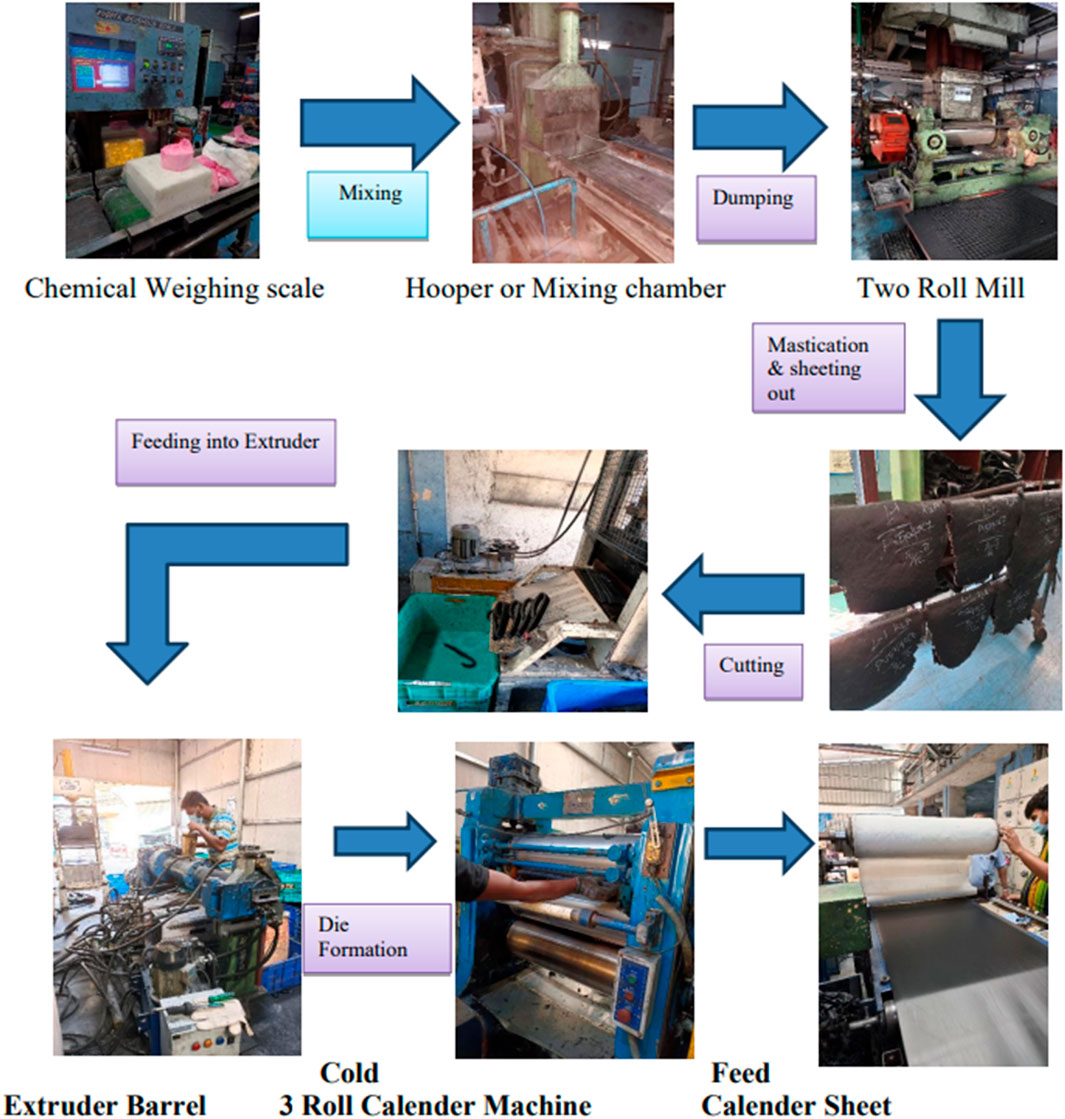
Compounding was done in K2A Intermixer (Alfred Herbert India Limited), following the sequence given in Figure 1 for all Master batches represented in Table 1. The total mixing time was 6 min, and the rotor speed was 1,000 rpm. At first, rubber and chemicals were charged into the closed mixing chamber. After that, carbon black, silica, and aramid fibers were added, followed by the addition of processing oil. The compound was then dumped and sheeted using a two-roll mill at 165°C. The masterbatches were then rolled into sheets on a two-roll mill and kept for cooling. For the final stage, Masterbatches are mixed with Peroxide curing agents, and accelerators and antioxidants are added. Total mixing time at intermixer for final stage is 2–3 min at 700 rpm, and finally dumped at 2-roll mill at 120°C. After that, masterbatches were again rolled into sheets on the 2-roll mill and were stored at room temperature for at least 24 h before their properties were determined.
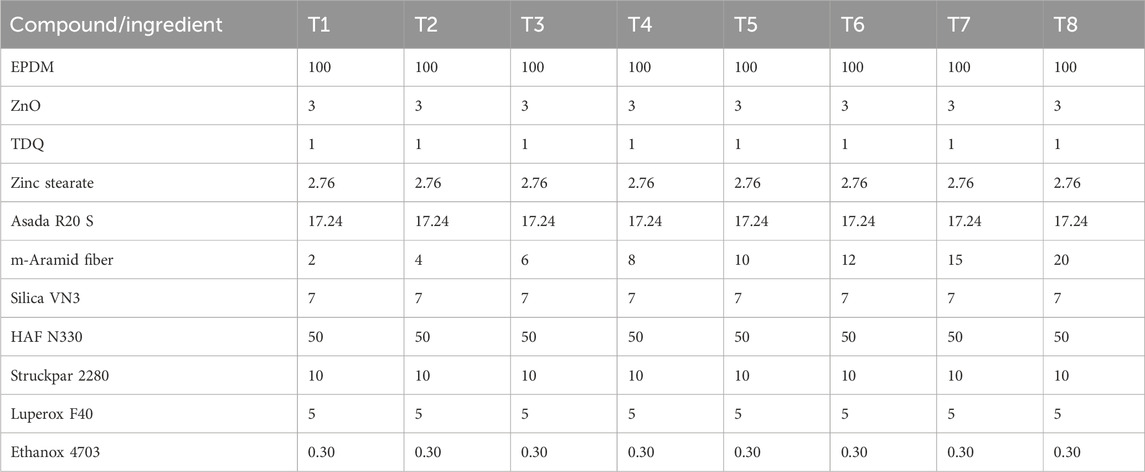
Table 1. Formulations of rubber composites (*weight express in phr–parts per hundred grams of rubber).
Processing of rubber samples
At this stage of the process, following the mixing of rubber samples, the EPDM remains uncured, indicating that it can be molded or shaped with the use of heat, and it possesses a sticky texture. The calendering process involves handling rubber by pressing the heat-softened material into the middle of three counter-rotating rollers. The rollers compress the sheet as it traverses through them. The gap between the cylinders governs the thickness of the resultant product, referred to as the nip region, which is kept at 0.5 mm in this process for all Masterbatches. The calendering process is intended to align 60%–80% of the chopped fibers along the longitudinal direction of each sheet. The calendared sheets were then molded under certain conditions using a compression molding machine (Santosh Industries, India) at 165°C for 30 min at 1,000 psi pressure, adhering to uniform conditions for all samples, and subsequently tested according to the relevant ASTM standards. Zhong et al. (2019) used internal mixers and compression molding to manufacture their aramid composites, but they did not use calendering to align the fibers like we did to mimic industrial-scale sheet processing as shown in Figure 2. By adapting established methodologies to our specific needs, especially DeMattia (ASTM D813) and Ross Flex testing (ASTM D1052) for fatigue testing, we can fully evaluate both isotropic and anisotropic mechanical response. This is something that is not commonly talked about in the literature for these kinds of systems.
Testing and characterization techniques
Rheometric study
The rheometric study was performed on the Ektrontek EKT2005 Rheometer at 180°C for 6 min, and Mooney viscosity was tested at 125°C for 5 min in the MV2000 Mooney Viscometer by Alpha Technologies. The compounded rubber sample (weight of 25–30 g) was kept in the cavity of the Mooney viscometer. It was allowed to preheat for 1 min, and for the remaining 4 min, it was allowed to shear. The Mooney value is denoted as ML (1+4) @ 125°C (López Manchado and Arroyo, 2002).
Curing
The mixed sheets were molded at their respective conditions in a compression molding machine (Santosh Industries, India) at 165°C for 30 min at 1,000 psi pressure (For all samples, the same conditions were followed) and tested as per the respective ASTM standards.
Tensile and tear strength
To characterize the mechanical behavior of the sample materials, including tensile strength, elongation at break, and modulus of elasticity, standardized testing methodologies were employed. Molded sheets with a controlled thickness of 2.5 ± 0.5 mm were fabricated. From these sheets, dumbbell-shaped specimens were prepared in accordance with the ASTM D-412 standard for tensile property assessment. Similarly, samples for tear strength evaluation were cut following the guidelines outlined in ASTM D-624. All mechanical tests were conducted using an Instron 3366 Universal Testing Machine. Physical properties testing was done before and after aging, and the aging condition was 125°C for 70 h in a hot air oven.
Hardness
Sample hardness was quantified using a Shore-A durometer (Wallace Cogenix Hardness Tester), adhering to the testing protocol specified in ASTM D 2240-15. Reported hardness values represent the average of three independent measurements.
Compression set
The compression set of the EPDM rubber samples was determined according to the ISO 815-1972 standard. Testing was conducted for a period of 72 h at a temperature of 125°C, with a constant compression of 25%.
Abrasion resistance
Abrasion resistance index (ARI) was measured in the rotary drum abrader (ASTM D5963), and ASTM Compound B was taken as a reference sample to calculate ARI and volume loss of samples.
Heat build-up
Heat Build-up of the samples is studied as per ASTM D-623. This is done by using the Goodrich Flexometer, clamping the sample inside the chamber, and monitoring the increase in the temperature of the sample when it is operated under a constant 30 Hz frequency, 2 KPa stress, and stroke of 1,800 cycles/min conditions.
Demattia fatigue
Resistance to flex cracking was evaluated using the DeMattia test, following the procedures outlined in ASTM D813. Specifically, Molded DeMattia specimens were subjected to repeated flexing and deflexing cycles using a DeMattia Flexometer. The length of crack propagation with the number of cycles completed was monitored and recorded at 30-min intervals. Reported values represent the average of measurements obtained from three independent samples (Muthukannan et al., 2024).
Ross flex test
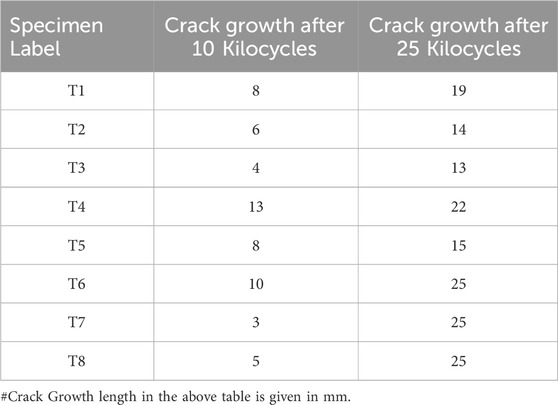
The described methodology aims to assess the ability of a polymer to withstand the development and propagation of cuts or cracks under conditions of cyclic flexing. In this study, the chamber temperature of 70°C was maintained for the testing, and then the crack length was recorded at predetermined cycles of 10 k and 25 k. The standard specimen dimensions are 152 mm in length, 25 mm in width, and 6.4 mm in thickness, as specified by ASTM D1052. A notch approximately 2.5 mm deep is typically introduced on one side of the sample to initiate cracking and evaluate its resistance to crack growth under repeated flexing.
Results and discussion
Mooney viscosity and cure characteristics
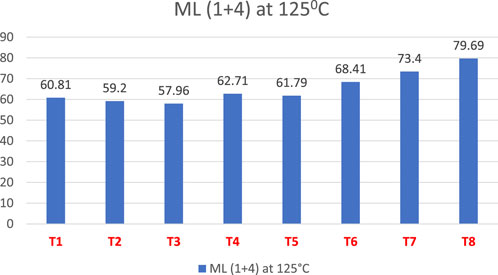
The Mooney analysis of the samples is presented in Figure 3. In the rubber matrix, fibers serve as stiff fillers. They limit the mobility of polymer chains as their concentration rises, leading to greater resistance to deformation under shear. This directly results in higher Mooney viscosity values. The torque value changes with the concentration of aramid fibers, which ranges from 2 to 20 phr. The T8 compound has the highest torque value among all due to the increased concentration of aramid fibers.
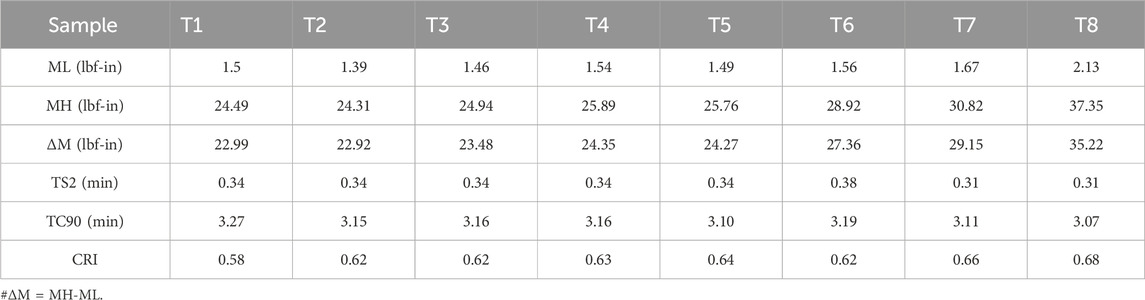
From Table 2, as fiber concentration increases, the cure rate index (CRI) increases, but TS2 and TC90 decrease due to better heat transfer through the fiber–matrix interfaces and improved curative distribution, moreover, aramid fibers may absorb or anchor curatives at the interface, leading to localized early cure and reducing cure time. ΔM, which is the difference between maximum and minimum torque (MH-ML), also increases because of fiber-induced stiffening and interfacial effects that raise crosslink density (Sreeja and Kutty, 2003).
Mechanical properties
Tensile strength
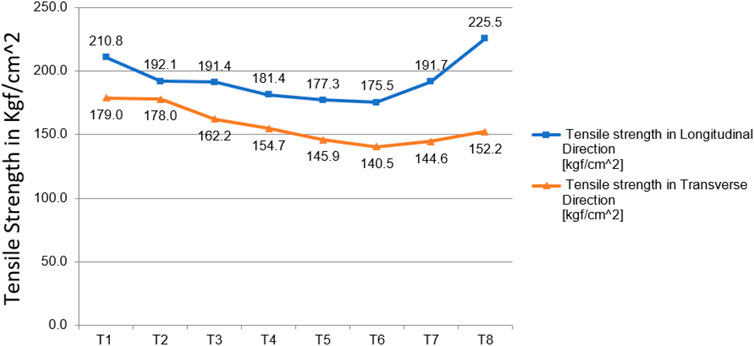
Aramid short fibers were incorporated into EPDM rubber formulations at varying concentrations up to 20 phr, as indicated in Table 1. The tensile strength was assessed and illustrated in Figure 4. A significant reduction in tensile strength for the gum compound occurs up to 12 phr of fiber loading. The tensile strength in both longitudinal and transverse directions drops up to 12 phr fiber loading and subsequently increases gradually in the case of T7 and T8 composites. At 12 phr, the reinforcing effect is inadequate to offset the dilution effect caused by the fibers, resulting in a loss in tensile strength. The limited quantity of fibers prevents uniform stress transfer throughout the matrix, causing localized stress at the fiber-matrix interface and resulting in inefficient reinforcement. It is essential to understand the intrinsic restrictions related to the short fiber length. Short fibers possess a limited aspect ratio (length-to-diameter ratio), which limits their capacity to effectively withstand load and transfer stress across extended distances within the matrix. The reinforcing efficiency at lower fiber loadings is reduced. Increased fiber concentrations result in a greater number of fibers obstructing the fracture front, leading to a more uniform distribution of stress; hence, tensile strength rises with fiber concentration beyond 12 phr. The tensile strength in the transverse direction decreases with fiber content up to 12 phr, the same as in the longitudinal direction of the rubber matrices, after which it remains relatively stable. This results from the weakening of the rubber matrix, which results from transversely oriented fibers. The comparatively stable tensile strength in the transverse direction beyond 12 phr indicates the limited ability of the short fibers to successfully bridge cracks, as we anticipated that over 60% of the short fibers would be oriented in the longitudinal direction following the milling and calendering processes (Pittayavinai et al., 2017; Correia et al., 2017).
Elongation at break and load @50%, 100%, 200%, 300% elongation of compounds
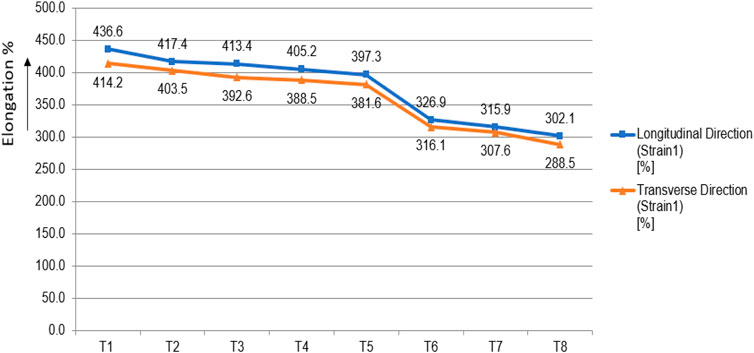
As depicted in Figure 5, the elongation at break exhibits an inverse relationship with fiber concentration (Soltani et al., 2014; Ling et al., 2020). Initially, a significant reduction in elongation is observed between fiber loadings of T5 and T6. Beyond this point, the elongation at break plateaus remains relatively stable in both measured directions across fiber concentrations ranging from 12 to 20 phr. This behavior suggests effective fiber alignment within the rubber matrix in the mill direction. Consequently, the incorporation of aramid short fibers enhances the stress-strain response of the rubber vulcanizates at lower strain levels. The observation that elongation plateaus after a specific threshold signifies that the fiber network has attained saturation; beyond this concentration, additional fibers increasingly contribute less to limiting the material’s extensibility. This action indicates strong adhesion between the aramid short fibers and the rubber matrix. Robust adherence would enable the fibers to efficiently limit the rubber’s deformation, leading to the noted high stress at low strain. If adhesion were inadequate, the fibers would easily come out of the matrix, giving increased elongation (Shirazi et al., 2013).
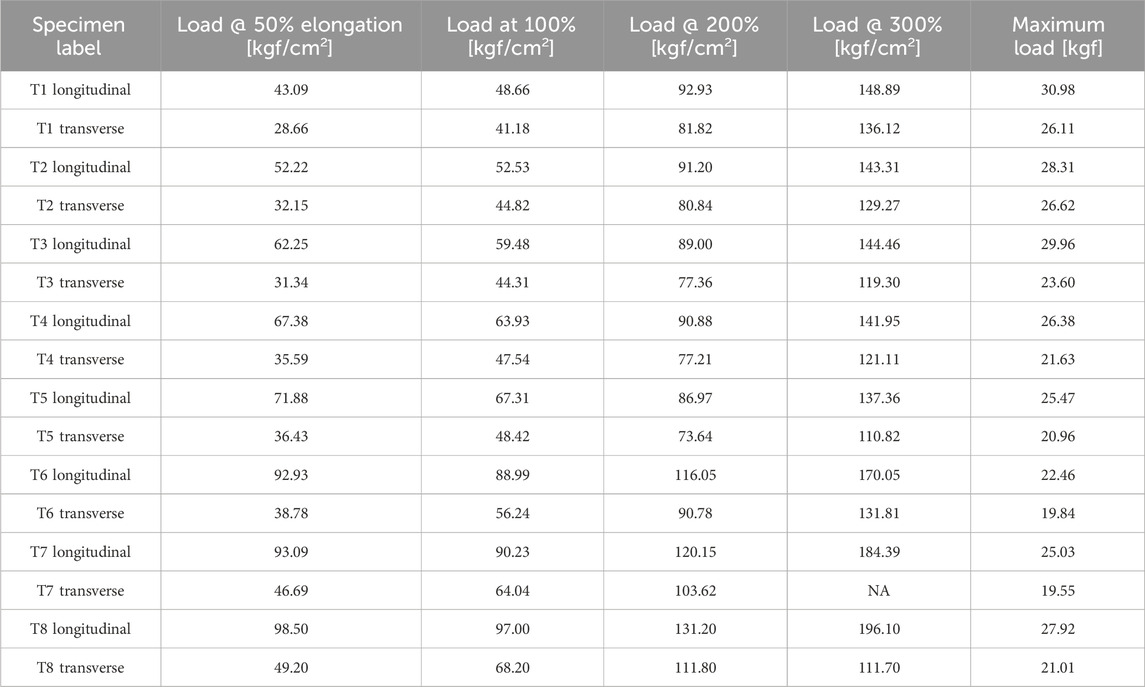
From Table 3, it is clear that load increases with an increase in elongation %. In General, higher durometer materials show higher load on elongation. This supports the conclusion that the fibers, when adequately bonded to the rubber, create a stiffer and stronger material.
Tear strength
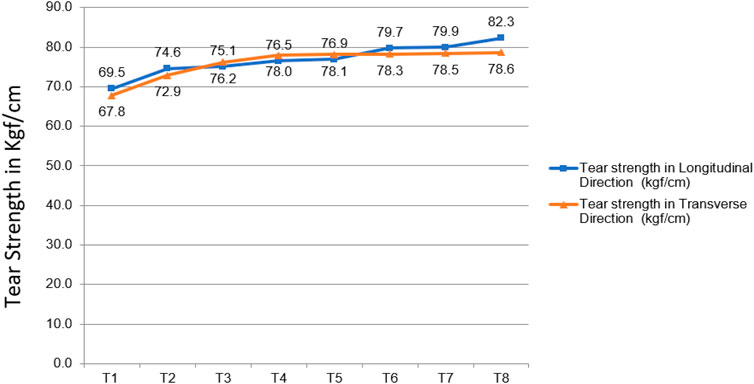
Figure 6 depicts the correlation between tear strength and the fiber content within the composite materials. Generally, an increase in fiber content corresponded to an increase in tear strength, observed in both the longitudinal and transverse directions (Kumar and Thomas, 1995). This enhancement is likely due to the increased physical impedance to crack propagation provided by the higher fiber concentration. Furthermore, at a given fiber loading, tear strength was consistently higher in the longitudinal direction compared to the transverse direction. This anisotropic behavior in tear resistance is attributable to the alignment and orientation of the reinforcing fibers. When tested in the transverse direction, the fibers tend to align parallel to the advancing crack front, offering reduced resistance to tear propagation. The crack can more easily propagate along the fiber-matrix interface when the fibers are parallel to it. This leads to reduced tear values compared to the longitudinal direction, where the fibers are oriented perpendicularly to the crack path, requiring more energy to break or pull them out of the matrix. The variation in tear strength highlights the necessity of considering fiber orientation in the development of composite materials for applications where tear resistance is a crucial performance parameter.
Aging study (mechanical properties of the compounds before and after aging)
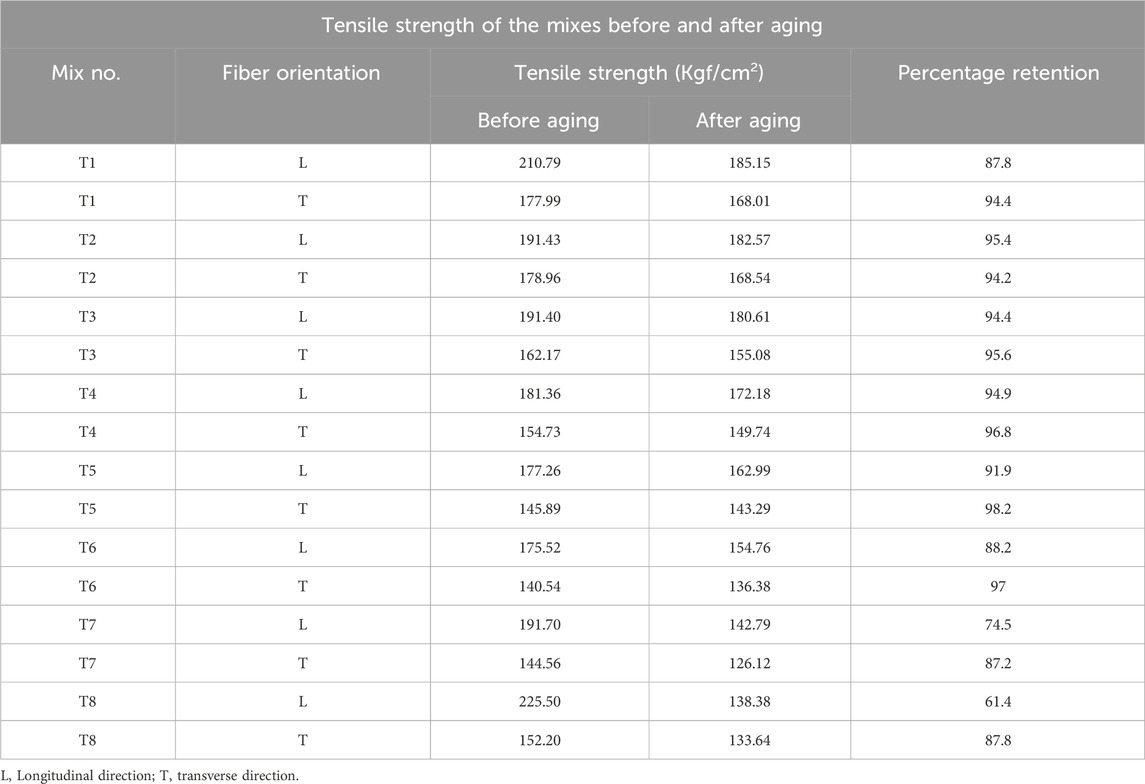
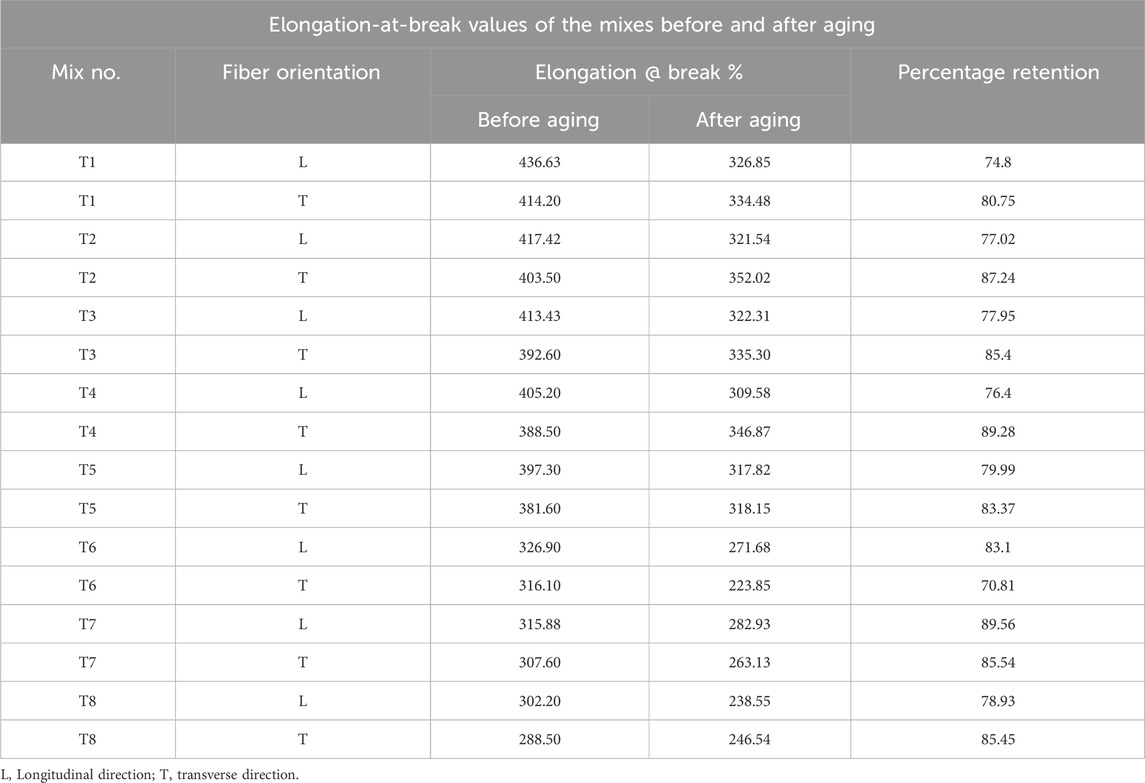
Table 4 presents the retention of tensile properties of the composites before and after aging. The tensile strength retention percentages of all compounds are greater in the transverse direction than in the longitudinal direction. Retention is notably inadequate for T7 and T8, particularly in the longitudinal direction. This indicates that the aging process adversely affects longitudinal tensile strength more than transverse tensile strength. A plausible reason for the variation could originate in the orientation of the aramid fibers and their interaction with the EPDM matrix under aging circumstances. Prolonged exposure to 125°C can accelerate differential thermal expansion between the aramid fibers and the EPDM matrix, resulting in increased stress concentrations at the fiber-matrix interface in the longitudinal direction. This may lead to micro-cracking or debonding at the interface, weakening the material’s tensile strength along the fiber direction. Moreover, the elevated temperature may promote oxidative degradation of the EPDM matrix preferentially in the longitudinal direction due to greater exposure along the fiber length, thereby reducing the load transfer efficiency between the fibers and the matrix. Meanwhile, elongation at break also exhibits poor retention in the longitudinal direction, as illustrated in Table 5. The decrease in elongation at break values upon aging indicates that the material becomes increasingly brittle, especially along the longitudinal axis, likely due to the aforementioned reasons associated with fiber-matrix interface degradation. This behavior is essential to evaluate for applications where the composite has to withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures, as in power transmission belts, which highlights the necessity for deeper investigation into aging mechanisms and potential strategies to enhance the long-term durability of these composites under such thermal aging conditions. Additionally, investigating the efficiency of specific stabilizing techniques, such as adding antioxidants or changing the fiber surface treatment, could be quite crucial in raising the aging resistance of these composites.
Hardness study
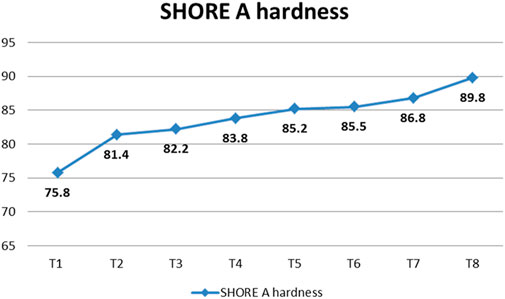
As the concentration of short aramid fibers in EPDM rubber composites increases, the Shore A hardness correspondingly increases. The rigid, high-modulus fibers reduce the flexibility of the rubber matrix, resulting in a material that is less responsive to surface indentation. The higher fiber loading improves the composite’s resistance to deformation under localized pressure, yielding a stiffer surface and enhanced hardness measurements. Moreover, better stress transfer between the rubber and the fibers leads to the noted increase in surface hardness. Based on the data shown in Figure 7, it can be concluded that T1 has the lowest shore A hardness value of 75.8, whereas T8 has the maximum hardness value of 89.8.
Compression test
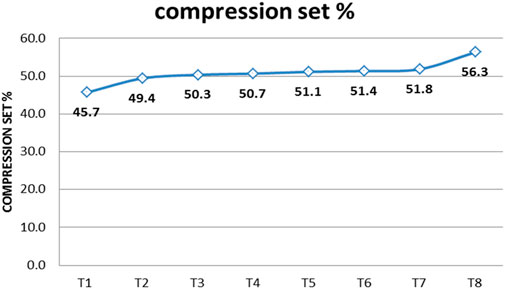
The compression set of EPDM rubber formulations was evaluated according to ISO 815-1972, employing a 72-h test duration at a temperature of 125°C and 25% compression. Compression set is a critical performance parameter, particularly for V-belt applications where resistance to permanent deformation under sustained load is essential. The results, presented in Figure 8, demonstrate a clear correlation between fiber content within the rubber matrix and compression set. Specifically, an increase in fiber loading leads to a corresponding increase in the observed compression set percentage, indicating a reduced ability of the material to recover its original dimensions after sustained compressive stress over time. The increase in compression set with increased fiber loading results from the stiff nature of the fibers, which restricts the elastic deformation and recovery of the EPDM matrix. As fiber concentration increases, the mobility of polymer chains diminishes, resulting in greater permanent deformation during prolonged compression. This leads to a high compression set value, indicating reduced resilience, which may affect the long-term ability to maintain its shape and contact pressure in V-belt applications. T8 is showing the highest compression set % value of 56.3 among all rubber composites due to having the highest short aramid fibers.
Abrasion resistance
Abrasion resistance refers to the ability of polymeric materials to withstand surface wear caused by mechanical action. This test becomes very important for products that are in continuous friction with another surface, like the base of the power transmission belt, which is in continuous contact with the pulley, and the tire tread, which is in continuous contact with the road. The higher value of ARI indicates better abrasion resistance, while the lower value of ARI indicates poorer abrasion resistance. Abrasion resistance registers an improvement with an increase in fiber content (Corrêa et al., 1998). These are calculated with standard given formulas.
Where constant values according to ASTM D5963 are: Normal abrasiveness-200.0, Standard Rubber Mass Loss-215.0.
To calculate the abrasion resistance index (ARI)
Density of standard Rubber-1.353.
The abrasion resistance was performed using a DIN abrader. The abrasion sheet used was corundum (aluminum oxide). The diameter of the cylinder is 150 mm, and the length is 500 mm, rotating at a speed of 40 rpm. The diameter and thickness of the test specimen were 16 mm and 6 mm, respectively. The density of the samples was measured. The test run was performed, and the results were taken as the average of three test runs. The weight of the specimen before and after the test was measured.
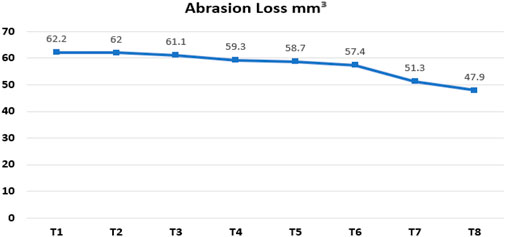
From Figure 9, it is clear that by adding a high concentration of Fibers into the elastomer, the abrasion loss (mm3) gets reduced to a certain level, which means higher fiber concentration leads to better abrasion resistance properties.
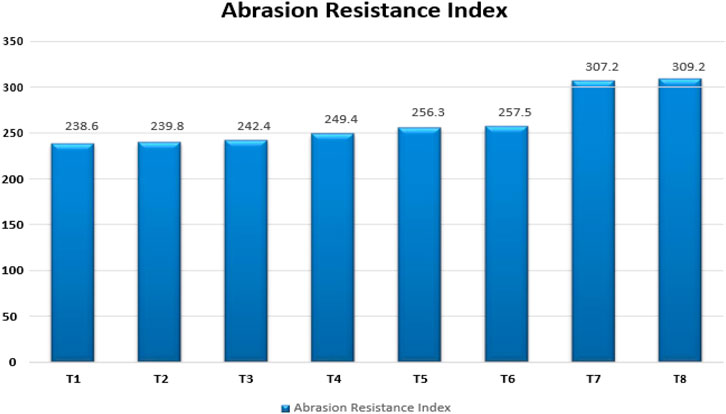
Similarly, the Abrasion Resistance index value is High for T8 and low for T1 as shown in Figure 10, which also determines the same. It is necessary for the base rubber of a power transmission belt to have a higher abrasion resistance index. So, depending upon the application, we can select the particular fiber concentration compound. But in case of higher fiber concentration, many factors play a vital role, like High Mooney viscosity, Hardness, and brittle nature, leading to fast rupture of base rubber on flexing, which is not suitable for power transmission belts.
DeMattia fatigue test
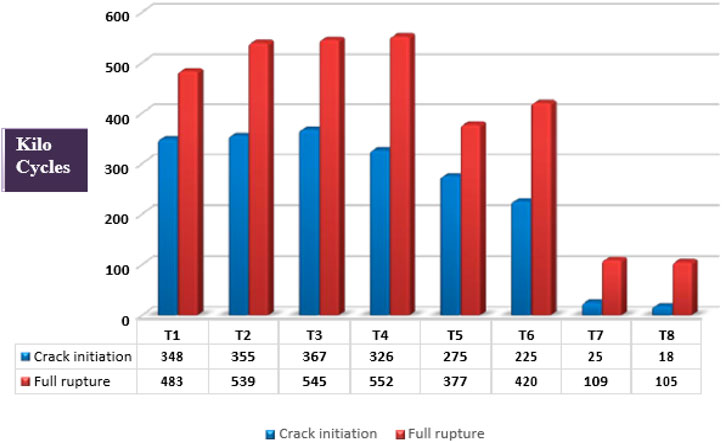
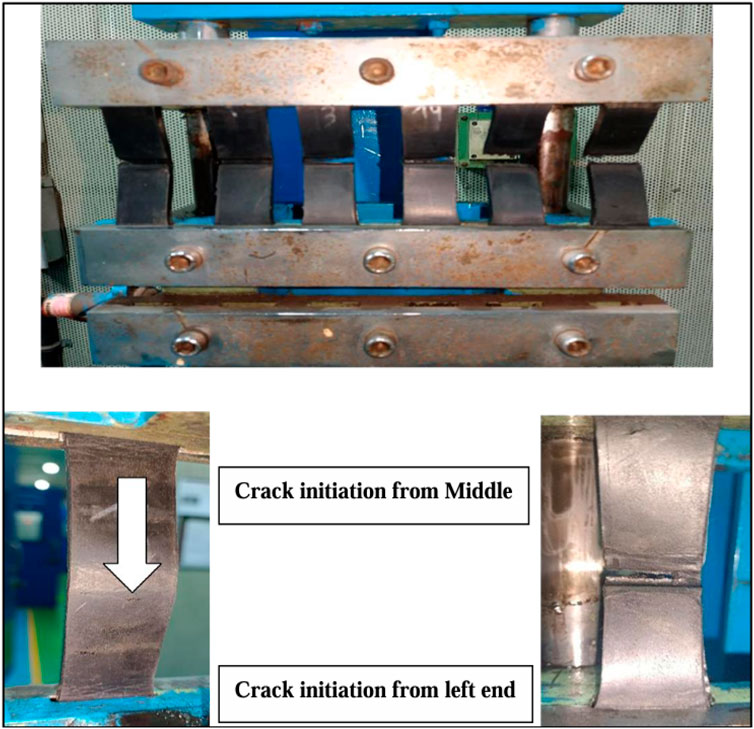
From the DeMattia Fatigue Study, it can be clearly seen from Figure 11 that T7 and T8 with 15 phr and 20 phr fiber concentration, respectively, exhibit significantly reduced fatigue life as recorded at approximately 109 kilocycles and 105 kilocycles, the main cause of this low fatigue life is the composites increasing brittleness at higher fiber loadings, which reduces elastic deformation and promotes early fracture initiation. Particularly, the T8 specimen shown in Figure 12 shows behavior typical of brittle failure, in which stress concentration becomes more dominant than energy dissipation, by showing crack initiation from the center of the test strip. In contrast, T5 and T6 composites with 10 phr and 12 phr aramid fiber exhibit a significant increase in fatigue life; it reaches 377 kilocycles and 420 kilocycles, respectively. This implies that a modest fiber loading level offers enough reinforcement to inhibit the spread of cracks and preserves matrix flexibility to absorb cyclic stress, hence improving the fatigue performance. Furthermore, we can see that fatigue life is improved in the case of T4, and it has been achieved up to 552 Kilocycles, which is the highest among all. Notably, in the case of T3 Compound with 6 phr of fiber concentration, showing the best Fatigue Life, in which the crack initiated after 367 Kilocycles, which is the highest among all, and full rupture of the specimen occurred at 545 kilocycles (Li and Xin, 2018).
Overall, the data clearly show that aramid fibers facilitate mechanical reinforcement, but excessive loading causes brittleness, which could cause quick fracture failure. Maximizing fatigue life in fiber-reinforced elastomer composites depends thus upon optimizing fiber content. The numerical values in Figure 12 are in Kilo Cycles units.
Heat build-up study
During dynamic applications, excessive heat generation in rubber products promotes further curing, hence increasing hardness and brittleness. Dynamic stress-strain cycles, therefore, easily cause premature fractures in engineered or consumer products. It directly impacts the service life, durability, and performance under dynamic conditions, especially in applications like tires, V-belts, and seals, where continuous flexing occurs. The use of short aramid fibers in rubber composites usually causes an increase in heat buildup, resulting from increased internal friction and limited mobility of polymer chains. With an increase in fiber content, the interactions at the fiber–matrix interface become more prominent, resulting in greater energy dissipation under cyclic loading. Although aramid fibers provide mechanical reinforcement, their low thermal conductivity and rigidity could block heat dissipation, leading to localized temperature increases. The cumulative effect results in increased heat buildup in the composite as the percentage of short aramid fibers rises.
From Table 6, it is clear from T1 to T8 that the temperature of rubber composites increases as the fiber content increases after predetermined cycles, which clearly indicates that the high fiber content in the elastomeric composite leads to the generation of higher heat.
Ross flex testing results at elevated temperature
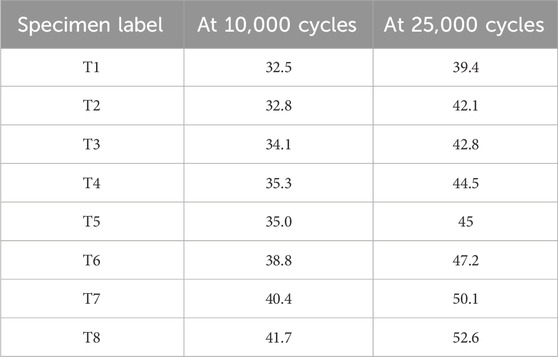
Traditional V-belts, typically fabricated from natural or common synthetic rubber formulations, are generally limited to operating temperatures below 90°C. Furthermore, at even lower temperatures around 60°C, accelerated degradation of the rubber material becomes a concern. Maintaining equivalent drive durability and performance under elevated temperature conditions necessitates making it larger and stronger than usual to withstand the increased thermal stress and prevent premature failure. It is estimated that a 10°C increase in operating temperature above 60°C reduces V-belt lifespan by approximately 50%. Consequently, achieving equivalent service life at a working temperature of 90°C would necessitate utilizing 8 times more belts, a solution that is both economically impractical and mechanically inefficient. In contrast, EPDM belts offer superior thermal stability, maintaining consistent performance across a temperature range of −40°C–110°C and are capable of operating at temperatures exceeding 130°C. This makes EPDM an ideal candidate for high-temperature belt applications where long-term durability is essential. So, in this study, to simulate realistic service conditions and assess the crack growth behavior under dynamic flexing, the Ross Flex testing was conducted at a chamber temperature of 70°C. As shown in Figure 13. Then, the Crack length was recorded at predetermined cycles of 10 k and 25 k, which are given in Table 7, given below. It is very clear that T3 shows the best results among all tested specimens. After 10 kilocycles, the crack length was around 4 mm, and after 25 kilocycles, it was just 13 mm, while in the case of T6, T7, and T8, all specimens were fully ruptured after 25 Kilocycles. But the initial crack length after 10 kilocycles in T7 and T8 was very low, 3 mm and 5 mm, respectively. This clearly shows that a higher content of aramid fibers in the compound resists the crack growth, but up to a certain limit. If the content is very high, like 15 and 20 phr, then other factors like high viscosity, high hardness, and brittle nature weaken the compound and cause rapid rupture of the compound on flexing and deflexing.
In the case of T2 and T1, crack growth values were slightly increased in comparison to T3 due to the lower content of aramid fibers. This clearly shows that aramid fibers play a vital role in crack growth resistance. So, from the data analysis, it is clear that the aramid fiber content of 6 phr gave better results in crack growth resistance.
Conclusion
This work investigated, for V-belt applications, the mechanical and dynamic properties of vulcanized EPDM rubber reinforced with hybrid fillers like carbon black (N330), silica, and aramid fibers. The physical performance of the EPDM matrix was greatly affected by the aramid fiber content. The composite with 6 phr aramid fiber showed the finest balance of mechanical properties among all analyzed formulations.
• It possessed high tensile strength, ideal elongation at break, and low abrasion loss, thereby indicating enhanced wear resistance. On the other hand, the 100% modulus was found to be maximum at 20 phr fiber content, showing more stiffness.
• Tear strength increased with fiber content in both directions. This was particularly evident in the crack growth resistance test, where the 6 phr fiber-filled sample showed minimal crack extension, only 4 mm after 10,000 cycles and 13 mm after 25,000 cycles, highlighting the best resistance to fracture growth.
• Higher fiber concentrations were seen to provide a high compression set%, a necessary characteristic for dynamic sealing in V-belts, which suggests lower elastic recovery that may negatively affect V-belt performance, and excessive fiber loading (15–20 phr) also led to increased brittleness, Compression set, hardness, and heat build-up.
• From the DeMattia Fatigue Study, the 6hr fiber-filled compound demonstrated exceptional fatigue resistance, with crack initiation delayed until 367 kilocycles and full rupture occurring at 545 kilocycles, the highest fatigue life recorded among all specimens.
• These findings imply that a fiber loading of about 6 phr provides the best balance between mechanical strength, fatigue life, thermal stability, and dynamic performance, thereby making it quite suitable for demanding V-belt applications.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
PG: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Data curation. SC: Writing – review and editing, Resources. ND: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
I want to acknowledge the Ministry of Human Resource and Development (MHRD), Government of India, for funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Arl, A., Bayram, A., Karahan, M., and Arslan, O. (2023). Comparative evaluation of mechanical properties of short aramid fiber on thermoplastic polymers. Mater. Science- Pol. 41 (1), 161–176. doi:10.2478/msp-2023-0012
Bayati, A., Ahmadi, M., Rahmatabadi, D., Khodaei, M., Xiang, H., Baniassadi, M., et al. (2025). 3D printed elastomers with superior stretchability and mechanical integrity by parametric optimization of extrusion process using Taguchi Method. Mater Res. Express 12 (1), 015301. doi:10.1088/2053-1591/ada1a6
Botan, M., Musteata, A. E., Ionescu, T. F., Georgescu, C., and Deleanu, L. (2017). Adding aramid fibers to improve tribological characteristics of two polymers. Tribol. Industry. 39 (3), 283–293. doi:10.24874/ti.2017.39.03.02
Botros, S. H., Younan, A. F., and Essa, M. M. (2000). Effect of fiber reinforcement on thermal stability and swelling behavior of CR/NBR blends. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 39 (2), 393–414. doi:10.1081/ppt-100100037
Corrêa, R. A., Nunes, R. C. R., and Franco Filho, W. Z. (1998). Short fiber reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer composites. Polym. Compos 19 (2), 152–155. doi:10.1002/pc.10086
Correia, C. A., De Oliveira, L. M., and Valera, T. S. (2017). The influence of bleached jute fiber filler on the properties of vulcanized natural rubber. Mater. Res. 472–478. doi:10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2017-0126
Dominic, M. C. D., Joseph, R., Begum, P. M. S., Joseph, M., Padmanabhan, D., Morris, L. A., et al. (2020). Cellulose nanofibers isolated from the Cuscuta Reflexa plant as a green reinforcement of natural rubber. Polym. (Basel) 12 (4), 814. doi:10.3390/polym12040814
Gopi, S. S., Kim, H., Seong, Y., Kang, G., and Nah, C. (2019). Enhancing the dispersion and adhesion of short aramid fibers in bromo-isobutylene-isoprene rubber using maleated polybutadiene resin via co-vulcanization with 4, 4’ bis(maleimido)diphenylmethane. Polym. Compos 40 (8), 2993–3004. doi:10.1002/pc.25141
Hintze, C., Stoček, R., Horst, T., Jurk, R., Wiessner, S., and Heinrich, G. (2014). Dynamic behavior of short aramid fiber-filled elastomer composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 54 (12), 2958–2964. doi:10.1002/pen.23854
Karimi, A., Rahmatabadi, D., and Baghani, M. (2024). Various FDM mechanisms used in the fabrication of continuous-fiber reinforced composites: a review. Polymers 16, 831. doi:10.3390/polym16060831
Kashani, M. R. (2009). Aramid-short-fiber reinforced Rubber as a tire tread composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 113 (2), 1355–1363. doi:10.1002/app.30026
Kumar, R. P., and Thomas, S. (1995). Tear and processing behaviour of short sisal fibre reinforced styrene butadiene rubber composites. Polym. Int. 38 (2), 173–182. doi:10.1002/pi.1995.210380210
Li, W., and Xin, Z. (2018). Flexural fatigue life prediction of a tooth V-belt made of fiber reinforced rubber. Int. J. Fatigue 111, 269–277. doi:10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.02.025
Ling, X., Hu, Y. L., Lai, W. W., and Wang, Y. (2020). “Formulation of EPDM heat-resistant V-ribbed belt,” in IOP conference series: materials science and engineering (Institute of Physics Publishing).
López Manchado, M. A., and Arroyo, M. (2002). Short fibers as reinforcement of rubber compounds. Polym. Compos 23 (4), 666–673. doi:10.1002/pc.10466
López-Manchado, M. A., Biagitti, J., and Kenny, J. M. (2002). Comparative study of the effects of different fibers on the processing and properties of ternary composites based on PP-EPDM blends. Polym. Compos 23 (5), 779–789. doi:10.1002/pc.10476
Muthukannan, P., Neethirajan, J., and Naskar, K. (2024). Nylon 66 short fiber reinforcement in EPDM power transmission belting: a path to enhanced mechanical performance. Polym. Eng. Sci. 64 (6), 2612–2626. doi:10.1002/pen.26714
Pittayavinai, P., Thanawan, S., and Amornsakchai, T. (2017). Comparative study of natural rubber and acrylonitrile rubber reinforced with aligned short aramid fiber. Polym. Test. 64, 109–116. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.09.033
Seong, Y., Sathi, S. G., Park, J., Park, I. S., and Nah, C. (2020). Role of carbon black for enhancing the mechanical properties of short aramid fiber reinforced ethylene-acrylic rubber. Fibers Polym. 21 (1), 127–137. doi:10.1007/s12221-020-9346-5
Sheik Mohammed, H., Elangovan, K., and Subrahmanian, V. (2016). Studies on aramid short fibers reinforced acrylonitrile butadiene rubber composites. Available online at: www.ijacskros.com.
Shibulal, G. S., and Naskar, K. (2011). RFL coated aramid short fiber reinforced thermoplastic elastomer: mechanical, rheological and morphological characteristics. J. Polym. Res. 18 (6), 2295–2306. doi:10.1007/s10965-011-9643-1
Shirazi, M., De Rooij, M. B., Talma, A. G., and Noordermeer, J. W. M. (2013). Adhesion of RFL-coated aramid fibres to elastomers: the role of elastomer-latex compatibility. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 27 (17), 1886–1898. doi:10.1080/01694243.2013.764145
Soltani, S., Naderi, G., and Mohseniyan, S. (2014). Mechanical, morphological and rheological properties of short nylon fiber reinforced acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber composites. Fibers Polym. 15 (11), 2360–2369. doi:10.1007/s12221-014-2360-8
Sreeja, T. D., and Kutty, S. K. N. (2003). Cure characteristics and mechanical properties of short nylon fiber reinforced natural rubber - reclaimed rubber blends. Polym. - Plastics Technol. Eng. 42 (2), 239–252. doi:10.1081/ppt-120017926
Wazzan, A. A. (2004). Physico-mechanical properties of EPDM/nylon-6 short fiber composites. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomaterials 53 (1), 59–67. doi:10.1080/00914030490263487
Yang, B., Li, P., Luo, Z., Zhong, J., and Yin, L. (2020). Influence of thermal oxidation and maleinized liquid polybutadiene on dynamic and static performance of short aramid fiber-reinforced carbon black-ethylene propylene diene monomer composites. Polym. Compos 41 (5), 2036–2045. doi:10.1002/pc.25518
Zhang, H., Luo, Z., Zhong, J., Wang, X., and Xu, Y. (2023a). Effect of long aramid fiber on the properties of styrene-butadiene rubber composites based on extrusion. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater Struct. 46 (2), 527–539. doi:10.1111/ffe.13882
Zhang, Y., Ma, X., Yang, M., Lan, D., Li, X., Gao, Z., et al. (2023b). Ablation resistance of ethylene propylene diene monomer insulation materials reinforced with liquid hyperbranched polycarbosilane coated aramid fibers. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 217. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2023.110510
Keywords: ethylene propylene-diene terpolymer (EPDM), fibre-matrix interaction, viscoelastic properties, aramid fibre, hybrid composite, reinforced rubber
Citation: Gupta P, Chattopadhyay S and Das NC (2025) Short fiber reinforced elastomeric composites with enhanced mechanical and tribological properties for potential application in V-belts. Front. Mech. Eng. 11:1629780. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2025.1629780
Received: 16 May 2025; Accepted: 18 June 2025;
Published: 08 July 2025.
Edited by:
Mohit Goswami, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, IsraelReviewed by:
Davood Rahmatabadi, University of Tehran, IranSumesh Keerthiveettil Ramakrishnan, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czechia
Copyright © 2025 Gupta, Chattopadhyay and Das. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Narayan Chandra Das, bmNkYXNAcnRjLmlpdGtncC5hYy5pbg==
 Piyush Gupta
Piyush Gupta Santanu Chattopadhyay
Santanu Chattopadhyay Narayan Chandra Das
Narayan Chandra Das