- 1Whitaker Cardiovascular Institute, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA
- 2Cardiovascular Research Center, GeneSys Research Institute, Boston, MA, USA
- 3Yale Cardiovascular Research Center, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA
- 4Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, NC, USA
- 5Radiation Oncology, School of Medicine, University of California Davis, Sacramento, CA, USA
- 6Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, USA
- 7Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA
A corrigendum on
In the paper titled “Ionizing Particle Radiation as a Modulator of Endogenous Bone Marrow Cell Reprogramming: Implications for Hematological Cancers,” there was secretarial error made at our end in “Figure 1,” which should be corrected. At some point of the submission in Figure 1, A and B were disarranged in the slide. No other correction is needed as the text and figure legends are correct.
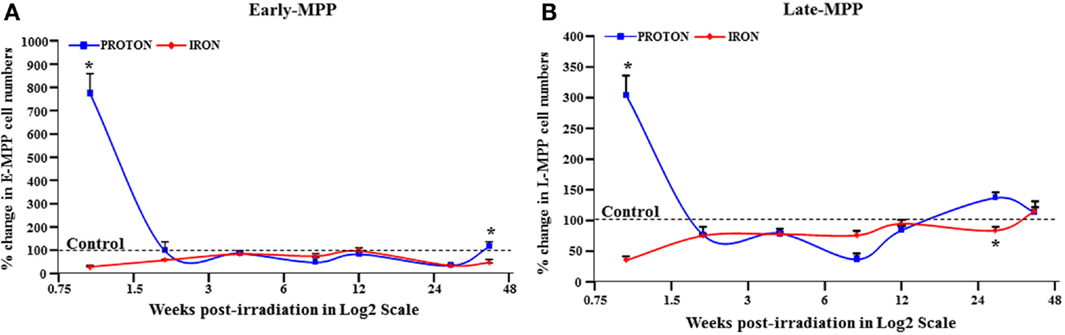
Figure 1. E-MPP and L-MPP cell numbers are downregulated by 56Fe- and 1H-IR but recover to control levels by 40 weeks post-IR. Effect of full-body single dose of proton (1H) at 0.5 Gy, 1 GeV and iron (56Fe) at 0.15 Gy, 1 GeV/nucleon of ionizing radiation (IR) on survival of multipotent progenitor cell populations was examined. The survival of (A) E-MPPs and (B) L-MPPs in the BM after particle IR in C57BL/6NT mice were determined at 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 28, and 40 weeks post-IR. Total BM-derived mononuclear cells were triple-stained with FITC-labeled RAM34 antibody (that consists of CD34, c-kit, and Sca1 antibodies), PE-Cy7-AC133, and PE-hematopoietic lineage cocktail (CD3e, Ly-6G/Ly-6C, CD11b, CD45R/B220, TER-119), then sorted by FASC for (A) E-MPPs (CD34+/c-kit+/Sca-1+/AC133+/Lin−) and (B) L-MPPs (CD34+/c-kit+/Sca-1+/AC133−/Lin−). Percentage changes in cell numbers were calculated relative to control sham irradiated mice, which was set to 100% for each time point. Solid lines represent mean ± SEM (n = 6/group) for 1H-IR (solid blue lines) and 56Fe-IR (solid red lines). “*” represents statistically significant differences compared to control with p < 0.05.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Keywords: progenitors, endogenous reprogramming, hematological cancer, radiation, HSC
Citation: Muralidharan S, Sasi SP, Zuriaga MA, Hirschi KK, Porada CD, Coleman MA, Walsh KX, Yan X and Goukassian DA (2015) Corrigendum: Ionizing Particle Radiation as a Modulator of Endogenous Bone Marrow Cell Reprogramming: Implications for Hematological Cancers. Front. Oncol. 5:255. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00255
Received: 29 October 2015; Accepted: 05 November 2015;
Published: 25 November 2015
Edited and Reviewed by: Marco Durante, GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Germany
Copyright: © 2015 Muralidharan, Sasi, Zuriaga, Hirschi, Porada, Coleman, Walsh, Yan and Goukassian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: David A. Goukassian, ZGF2aWQuZ291a2Fzc2lhbkB0dWZ0cy5lZHU=, ZGdvdWthc3NAYnUuZWR1
 Sujatha Muralidharan1
Sujatha Muralidharan1 David A. Goukassian
David A. Goukassian