Abstract
Background:
Indocyanine green (ICG) imaging-guided lymphadenectomy has been introduced in gastric cancer (GC) surgery and its clinical value remains controversial. The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of ICG fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy in radical gastrectomy for GC.
Methods:
Studies comparing lymphadenectomy in radical gastrectomy between use and non-use of ICG fluorescence imaging up to July 2022 were systematically searched from PubMed, Web of Science, Embase and Cochrane Library. A pooled analysis was performed for the available data regarding the baseline features, the number of retrieved lymph nodes (LNs), the number of metastatic LNs and surgical outcomes as well as oncological outcomes. RevMan 5.3 software was used to perform the statistical analysis. Quality evaluation and publication bias were also conducted.
Results:
17 studies with a total of 2274 patients (1186 in the ICG group and 1088 in the control group) undergoing radical gastrectomy and lymphadenectomy were included. In the pooled analysis, the baseline features were basically comparable. However, the number of retrieved LNs in the ICG group was significantly more than that in the control group (MD = 7.41, 95% CI = 5.44 to 9.37, P < 0.00001). No significant difference was found between the ICG and control groups in terms of metastatic LNs (MD = -0.05, 95% CI = -0.25 to 0.16, P = 0.65). In addition, the use of ICG could reduce intraoperative blood loss (MD = -17.96, 95% CI = -27.89 to -8.04, P = 0.0004) without increasing operative time (P = 0.14) and overall complications (P = 0.10). In terms of oncological outcomes, the use of ICG could reduce the overall recurrence rate (OR = 0.50; 95% CI 0.28-0.89; P = 0.02) but could not increase the 2-year overall survival rate (OR = 1.25; 95% CI 0.72-2.18; P = 0.43).
Conclusions:
ICG imaging-guided lymphadenectomy is valuable for complete LNs dissection in radical gastrectomy for GC. However, more high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm this benefit.
Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide with more than one million new cases and 760,000 deaths in 2020 (1). At present, radical gastrectomy combined with D2 lymphadenectomy is still the most effective treatment for GC (2, 3). The status of lymph nodes (LNs) is a stronger prognostic factor for the survival of GC patients and sufficient lymphadenectomy can improve the prognosis of GC patients (4–6). Howerer, lymphadenectomy for GC is usually performed without the aid of visual instruments and complete lymphadenectomy is sometimes difficult, especially for inexperienced gastrointestinal surgeons, which always results in LNs residue and in turn leads to tumor recurrence as well as the death of these patient. Therefore, the application of intraoperative navigation technology to assist systematic and complete lymphadenectomy is essential for radical gastrectomy.
Indocyanine green (ICG), a lymphatic tracer with minimal adverse effects, can bind intensely with serum proteins in vivo and emits fluorescence on exposure to near-infrared rays of wavelength 760-780 nm (7, 8). In recent years, ICG fluorescence imaging for LNs tracing has attracted surgeons’ attention and ICG imaging-guided lymphadenectomy has been introduced in GC surgery (9–11). Until now, several studies have reported that ICG imaging-guided lymphadenectomy was applied to GC surgery and showed promising results in increasing the number of retrieved LNs, without increasing operative time and overall complications (12–14). However, whether ICG imaging-guided lymphadenectomy is indeed beneficial for LNs dissection remains unclear. Therefore, further research is needed to validate the efficacy of ICG imaging-guided lymphadenectomy in radical gastrectomy for GC.
The aim of this meta-analysis is to evaluate the efficacy of ICG imaging-guided lymphadenectomy in radical gastrectomy for GC based on the current published studies.
Methods
This meta-analysis was carried out in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) statement.
Search strategy
Studies comparing lymphadenectomy in radical gastrectomy between use and non-use of ICG fluorescence imaging up to July 2022 were systematically searched from PubMed, Web of Science, Embase and Cochrane Library. The keywords used for the search were “gastric cancer”, “lymphadenectomy” and “ICG”. Thus, the following search string was used across the above databases: [“gastric cancer” OR “gastric carcinoma” OR “gastric tumor” OR “stomach cancer” OR “stomach carcinoma” OR “stomach tumor”] AND [“lymphadenectomy” OR “lymph node excision” OR “lymph node dissection”] AND [“indocyanine green” OR “ICG”]. Articles from previously published reviews were also checked for potential articles. The search was conducted independently by two authors (BD and AZ). The search was last performed on July 3, 2022.
Study selection and data extraction
The included studies met the following criteria: (1) GC patients with laparoscopic or robotic surgery; (2) lymphadenectomy performed in accordance with the guidelines for the treatment of GC; (3) comparative studies about lymphadenectomy in radical gastrectomy between use and non-use of ICG fluorescence imaging; (4) studies with reported outcome including the number of retrieved LNs in the ICG and control groups; (5) original research published in English. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) studies published as reviews, comments, letters, case reports, animal studies and meeting abstracts; (2) studies without the outcome about the number of retrieved LNs; (3) unavailability of effective data for meta-analysis.
Two reviewers (BD and AZ) carried out the screening and extraction process independently. First, studies were screened by titles and abstract. Then, the potential studies were checked for full text. For the eligible articles, the following information from each article was recorded: first author, publication year, country, study interval, study design, study object, sample size, extent of lymphadenectomy, ICG dosage and imaging system. Furthermore, the following clinicopathological parameters were extracted from these studies: sex, age, body mass index (BMI), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score, tumor size, pathological stage, histologic type, method of gastrectomy, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, the number of retrieved LNs, the number of metastatic LNs, operation time, intraoperative blood loss, overall complications, overall recurrence rate and 2-year overall survival (OS) rate. Results were checked by a third author (ZL).
Risk of bias assessment
Qualities of the selected studies were assessed according to the Cochrane Handbook. Biases including selection, performance, detection, attrition, reporting and others were evaluated and the outcomes were summarized in the form of a bias graph.
Statistical analysis
The odds ratio (OR) and mean difference (MD) with their 95% confidence interval (CI) were used as the effect size for dichotomous and continuous variables, respectively. For studies that only reported median and range, data were converted into mean and standard deviation (SD) following the method reported by Hozo SP et al. (15). Heterogeneity among studies was assessed by χ2 and I2 statistics. fixed-effects models and random-effects models were used in cases of nonsignificant (I2 ≤ 50%) and significant (I2 > 50%) heterogeneity, respectively. For the assessment of publication bias, a funnel plot was conducted. A P value < 0.05 was considered significant. All of the statistical analyses were performed by RevMan 5.3 software (Cochrane, London, UK).
Results
Characteristics of studies
A total of 612 studies were identified, and 17 studies including 15 retrospective studies and 2 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were ultimately included in this meta-analysis (13, 14, 16–30). The details of the selection procedures are shown to be in line with the PRISMA flowchart (Figure 1). General information from those included studies is summarized in Table 1. The total number of GC patients included was 2274 (1186 in the ICG group and 1088 in the control group). These studies were from five countries (i.e., China, Italy, Korea, Spain and Japan) and were published from 2017 to 2022. The sample size ranged from 20 to 514 patients. Laparoscopic or robotic radical total or distal gastrectomy combined with D1+ or D2 lymphectomy were performed in these studies. Nevertheless, the dosage of ICG and imaging systems considered differed in these studies. According to the Cochrane Handbook, the 17 studies were at slight or moderate risk of bias. The items evaluated for each study are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1
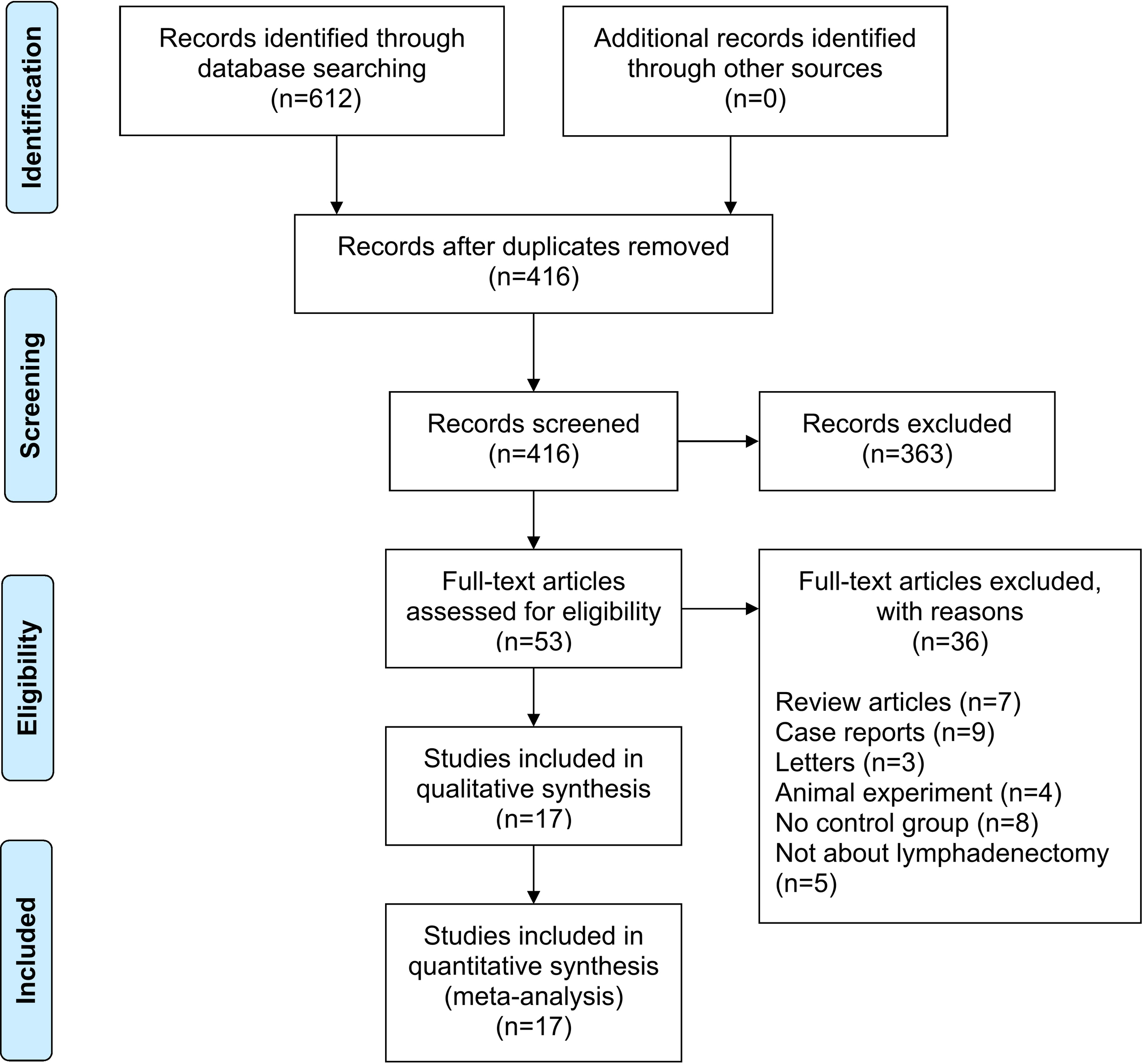
PRISMA flowchart of literature search and selection process. PRISMA preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis.
Table 1
| Reference | Country | Study interval | Study object | Study design | Sample size (ICG: Control) | Method of gastrectomy | Extent of lymphadenectomy | ICG dosage | ICG injection method | ICG injection time | ICG imaging system | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen QY (13) | China | 2018-2019 | pT1-4aN0-3M0 | S;RCT | 129: 129 | laparoscopic TG and DG | D2 | 2.5 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 1 day before surgery | Stryker | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| Cianchi F (14) | Italy | 2014-2018 | pT1-3N0-3M0 | S;R | 37: 37 | laparoscopic TG and DG | D2 | 2.5 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 1 day before surgery | Firefly | 1, 2, 3, 5 |
| Huang ZN (16) | China | 2010-2020 | cT1-4N0-3M0 | M;R;PSM | 94: 94 | laparoscopic TG and DG | D2 | 4.5 mg | subserosal injection | intraoperative | Stryker | 1, 4, 5 |
| Kwon IG (17) | Korea | 2012-2014 | pT1-2N0-1M0 | S;R;PSM | 40: 40 | robotic TG and DG | D1+ or D2 | 3 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 1 day before surgery | NA | 1, 3, 4, 5 |
| Lan YT (18) | China | 2011-2016 | pT1-4N0-3M0 | S;R | 14: 65 | robotic TG and DG | D1+ or D2 | 6 mg | subserosal injection | intraoperative | NA | 1, 3, 4, 5 |
| Lee S (19) | Korea | 2013-2018 | pT1-4aN0-3M0 | S;R | 74: 94 | laparoscopic or robotic TG | D2 + No. 10 | 1.5-3.0 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 1 day before surgery | Firefly and Pinpoint | 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 |
| Liu M (20) | China | 2017-2019 | pT1-4N0-3M0 | S;R | 61: 75 | laparoscopic DG | D2 | 1.25 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 20 to 30 hours before surgery | Stryker | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| Lu X (21) | China | 2015-2019 | pT1-4N0-3M0 | S;R;PSM | 28: 28 | laparoscopic TG, DG and PG | D2 | 2.5 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | intraoperative | Pinpoint | 1, 3, 4, 5, 6 |
| Maruri I (22) | Spain | 2018-2019 | cT1-4N0-3M0 | S;R | 17: 17 | laparoscopic TG and DG | D1+ or D2 | 3 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 18 to 24 hours before surgery | NA | 1, 2, 6 |
| Park SH (23) | Korea | 2017-2018 | pT1-4N0-3M0 | S;R;PSM | 20: 60 | laparoscopic DG | D1+ or D2 | 0.5 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | intraoperative | Pinpoint | 1, 3, 4, 5 |
| Puccetti F (24) | Italy | 2015-2021 | pT1-3N0-3M0 | S;R | 38: 64 | laparoscopic TG | D2 | 0.25 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 12 to 24 hours before surgery | NA | 1, 2, 3 |
| Romanzi A (25) | Italy | 2018-2019 | pT1-4bN0-3M0 | S;R | 10: 10 | robotic DG | D2 | 3 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 18 hours before surgery | Firefly | 1, 3 |
| Tian Y (26) | China | 2019-2020 | NA | S;R | 27: 32 | robotic DG | D2 | 5 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 1 day before surgery | NA | 1, 3, 4, 5 |
| Ushimaru Y (27) | Japan | 2015-2017 | pT1-4N0-3M0 | S;R;PSM | 84: 84 | laparoscopic TG and DG | D1+ or D2 | 0.1 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 1 day before surgery | STORZ | 1, 3, 4, 5 |
| Wei M (28) | China | 2018-2019 | pT1-4aN0-3M0 | S;R | 107: 88 | laparoscopic TG and DG | D2 | 2.5 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 12 to 24 hours before surgery | Stryker | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 |
| Yoon BW (29) | Korea | 2010-2020 | pT1-4aN0-3M0 | S;R;PSM | 21: 42 | laparoscopic DG | D2 | 0.4 mg | endoscopic submucosal injection | 1 day before surgery | NA | 1, 2, 3 |
| Zhong Q (30) | China | 2018-2020 | pT1-4aN0-3M0 | M;RCT | 385: 129 | laparoscopic TG and DG | D2 | 4.5 mg | subserosal injection | intraoperative | Stryker | 1, 2 |
Characteristics of studies.
ICG, indocyanine green; S single centre; M, multicentre; R, retrospective study; PSM, propensity score matching; RCT, randomized controlled trial; NA, not available, 1= number of retrieved lymph nodes, 2= number of metastatic lymph nodes, 3=operative time, 4=intraoperative blood loss, 5=overall complications, 6=overall recurrence rate, 7 = 2-year overall survival.
Figure 2
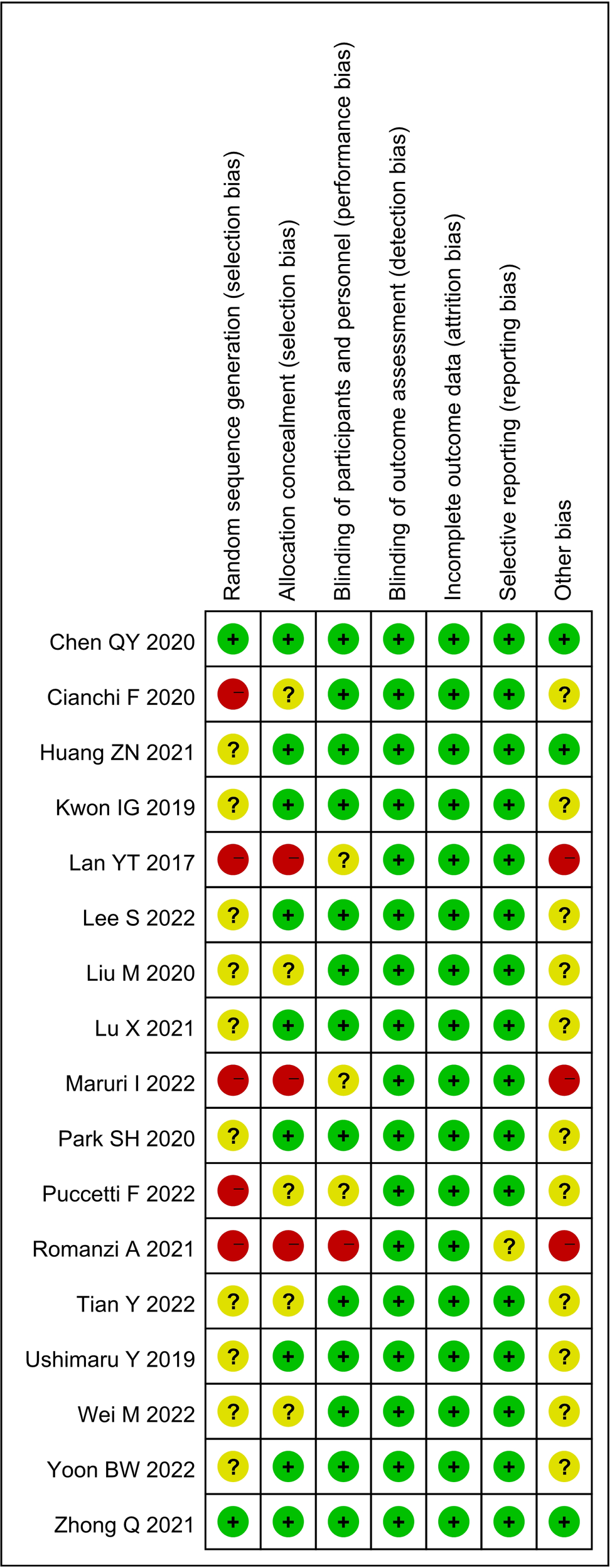
Risk of bias summary for the included studies.
Patient- and tumor-related baseline characteristics
For the patient- and tumor-related variables, sex (male and female), age (mean ± SD), BMI (mean ± SD), ASA score (ASA 1/2 and ASA 3/4), tumor size (mean ± SD), pathological stage (stage 1/2 and stage 3/4), histologic type (differentiated and other types), method of gastrectomy (total gastrectomy and distal gastrectomy) and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (with and without) were analyzed. Except for age (P = 0.0004) and the method of gastrectomy (P < 0.00001), other variables were all comparable between the ICG and control groups (P > 0.05) analysed by the fixed-effects models (I2 ≤ 50%) and random-effects models (I2 > 50%). The baseline parameters between the two groups were basically statistically insignificant, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3
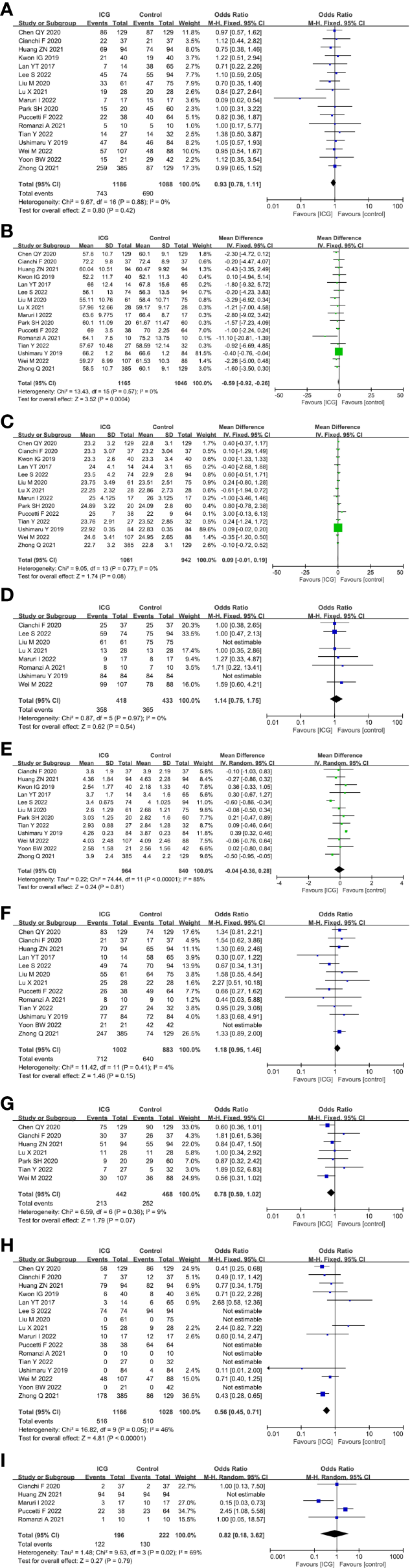
Forest plots showing the assessment of baseline features including (A) sex, (B) age, (C) body mass index, (D) American Society of Anaesthesiologists score, (E) tumor size, (F) pathological stage, (G) histologic type, (H) method of gastrectomy, (I) neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. ICG, indocyanine green.
Efficacy of lymphadenectomy
The primary outcome of this study was to assess the efficacy of lymphadenectomy by using ICG fluorescence imaging. Ultimately, 17 studies (2274 patients) (13, 14, 16–30) reporting this outcome were included in our meta-analysis. The pooled analysis revealed that the number of retrieved LNs in the ICG group was significantly more than that in the control group (MD = 7.41, 95% CI = 5.44 to 9.37, P < 0.00001) (Figure 4A), but there is no significant difference in terms of metastatic LNs between the ICG and control groups (MD = -0.05, 95% CI = -0.25 to 0.16, P = 0.65) (Figure 4B).
Figure 4
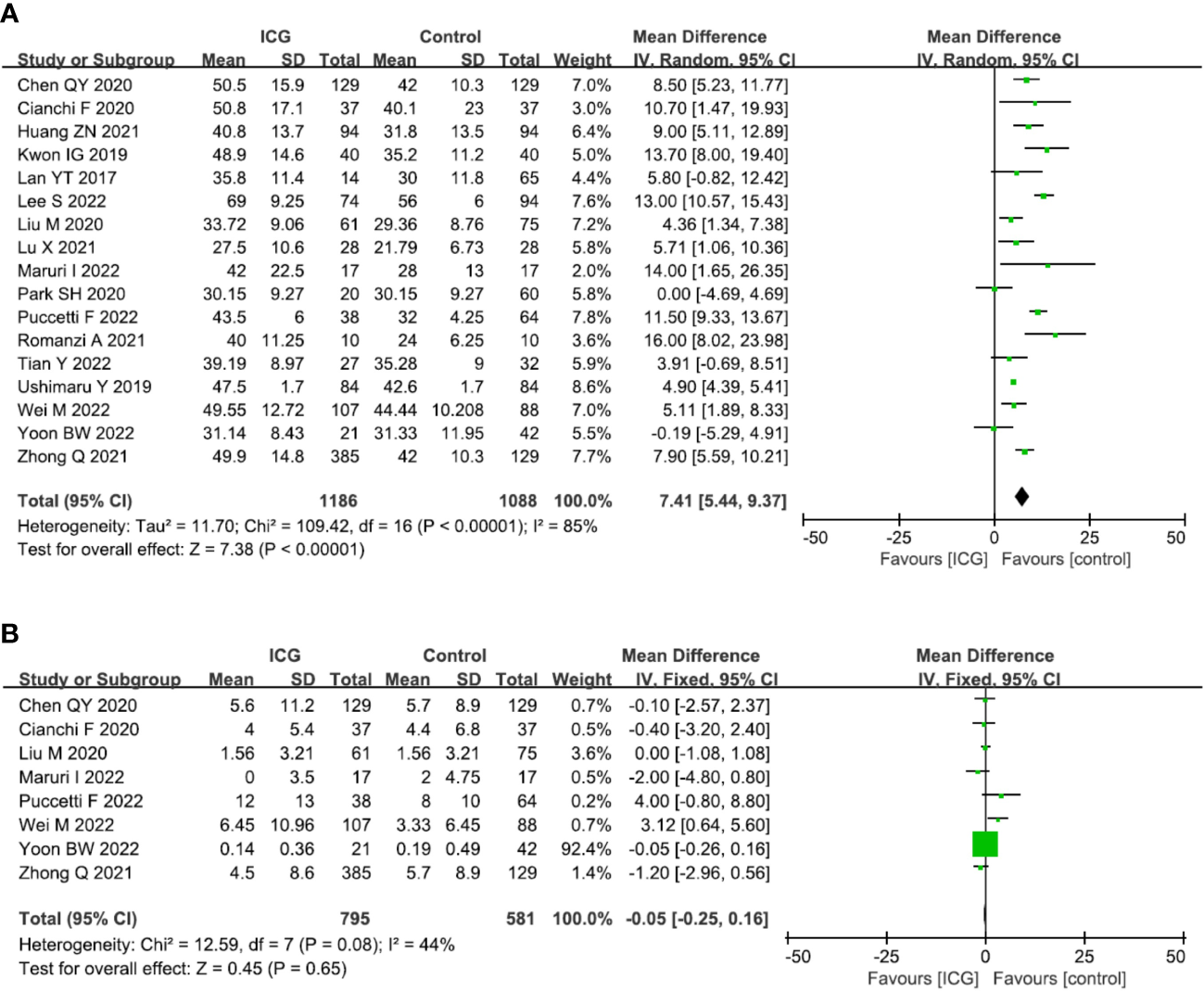
Forest plots showing the assessment of lymphadenectomy including (A) the number of retrieved lymph nodes, (B) the number of metastatic lymph nodes. ICG, indocyanine green.
Surgical outcomes
14 studies (13, 14, 17–21, 23–29) reported the operation time and the pooled analysis showed no difference between the ICG and control groups (MD = −9.38, 95% CI = −21.70 to 2.93, P = 0.14) (Figure 5A). However, 11 studies (13, 16–21, 23, 26–28) reported the intraoperative blood loss and showed that the use of ICG could reduce intraoperative blood loss (MD = -17.96, 95% CI = -27.89 to -8.04, P = 0.0004) (Figure 5B). 12 studies (13, 14, 16–21, 23, 26–28) reported the overall complications and there was a trend that the use of ICG was related to less overall complications with no statistic difference (OR = 0.78, 95% CI = 0.57 to 1.05, P = 0.10) (Figure 5C).
Figure 5
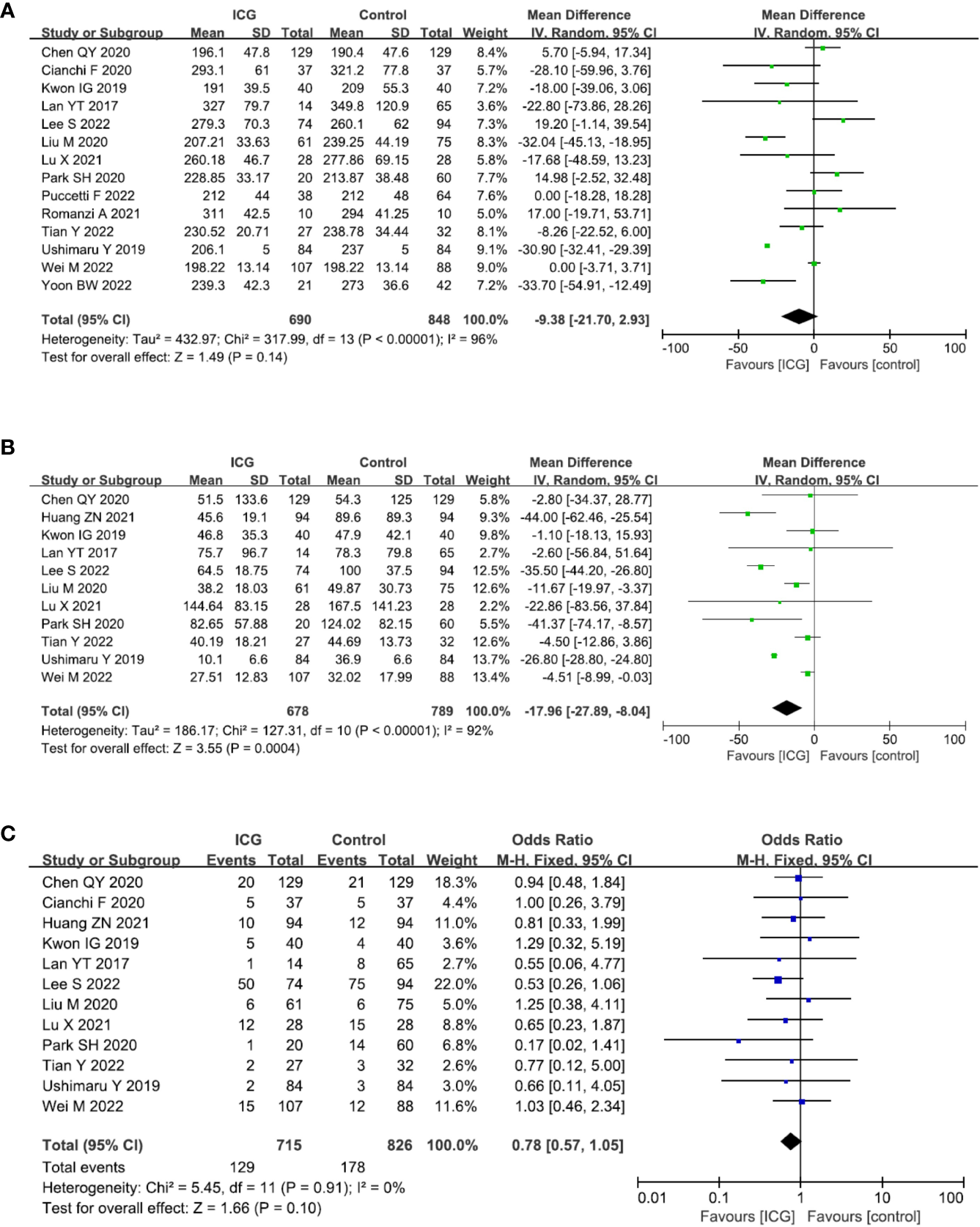
Forest plots showing the assessment of surgical outcomes including (A) operative time, (B) intraoperative blood loss, (C) overall complication. ICG, indocyanine green.
Oncological outcomes
In terms of oncological outcomes, four studies (19, 21, 22, 28) reported the overall recurrence rate and the pooled analysis showed that the use of ICG could reduce the overall recurrence rate (OR = 0.50; 95% CI 0.28-0.89; P = 0.02) (Figure 6A). However, in terms of postoperative overall survival, two studies (19, 28) reported the 2-year overall survival rate but there was no difference between the ICG and control groups (OR = 1.25; 95% CI 0.72-2.18; P = 0.43) (Figure 6B).
Figure 6
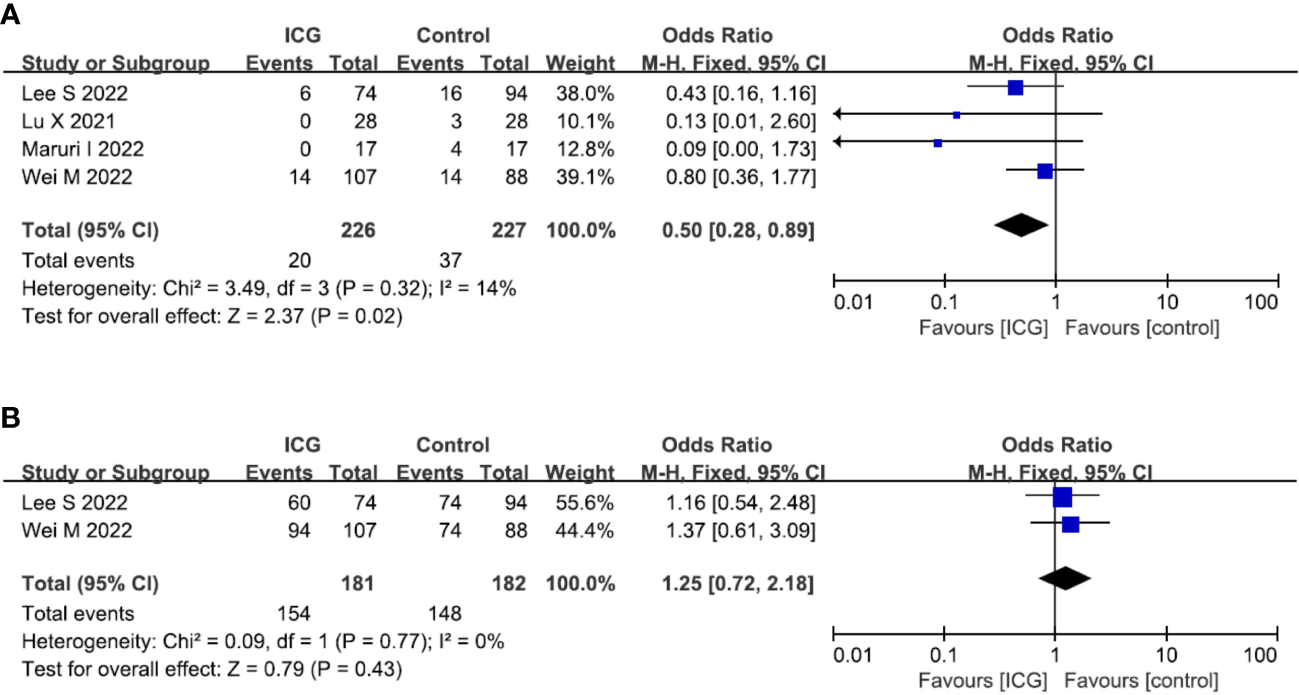
Forest plots showing the assessment of oncological outcomes including (A) overall recurrence rate, (B) 2-year OS rate. ICG, indocyanine green; OS, overall survival.
Publication bias
The funnel plot was used to assess potential publication bias in the meta-analysis of the correlation between the use of ICG fluorescence imaging and the number of retrieved LNs. As shown in Figure 7, the funnel plot was symmetrical, which showed a low risk of publication bias in this study.
Figure 7
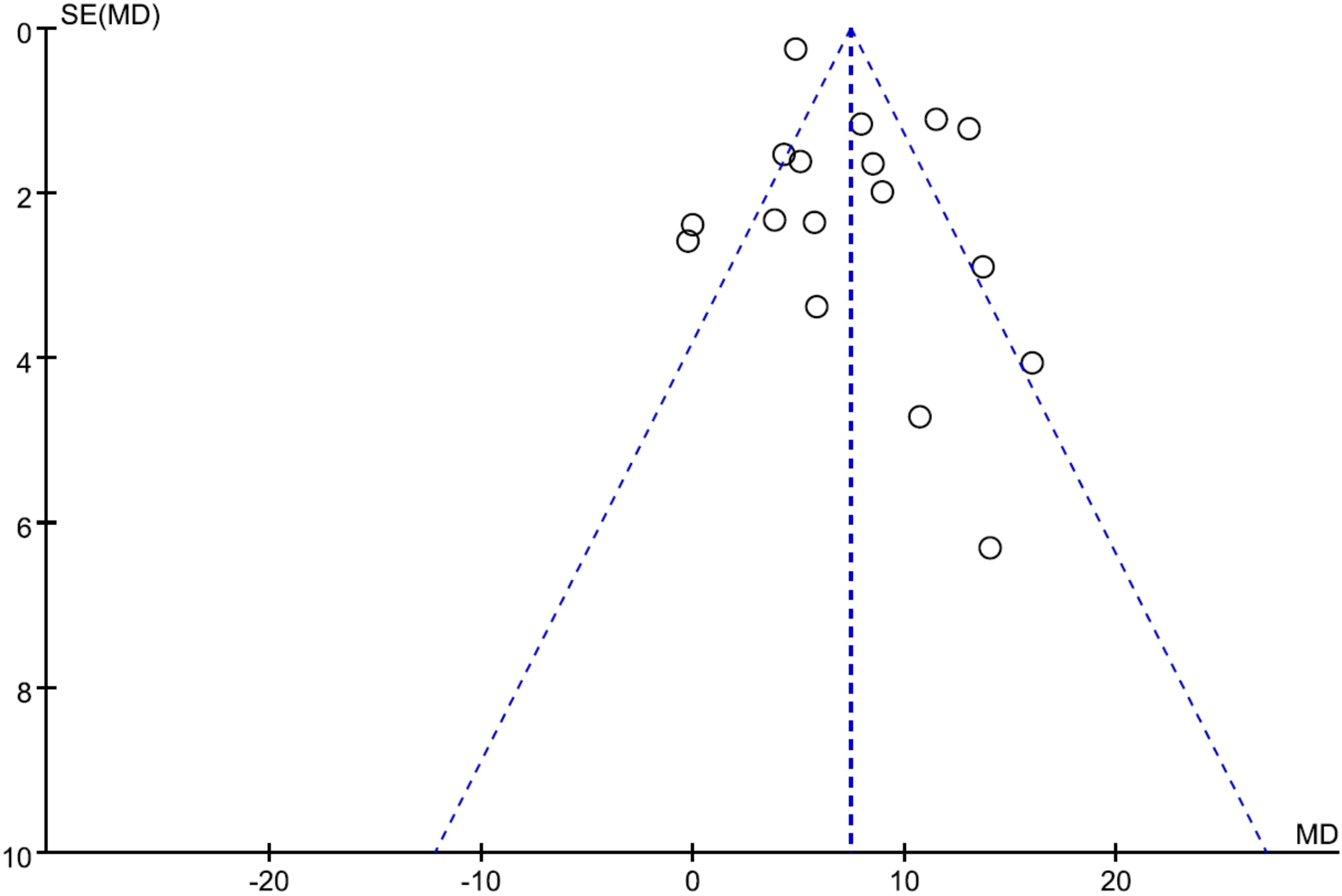
Funnel plots of publication bias for the number of retrieved lymph nodes.
Discussion
GC is one of the most common malignant tumors of digestive tract and radical surgery is the mainstay of treatment, which involves performing gastric resection with negative margins and adequate systemic LNs dissection. The status of LNs is a stronger prognostic factor for the survival of GC patients and radical lymphadenectomy can significantly improve the long-term survival (31, 32). In addition, whether or not the resected LNs have metastasis, complete perigastric lymphadenectomy is important for the accurate staging of tumors and the decision of subsequent treatment (33–35). So the retrieval of more LNs in radical gastrectomy has become the special requirement for gastrointestinal surgeons.
Currently, minimally invasive surgery, including laparoscopic and robotic methods, has been widely used in the treatment of GC, especially for early GC (36, 37). However, the oncological efficacy of minimally invasive techniques for the treatment of advanced GC is still controversial because of the concern about not being able to perform an accurate D2 lymphadenectomy and the oncological safety (38, 39). At present, lymphadenectomy in radical gastrectomy is often performed depending on the surgeon’s experience and without the aid of visual instruments. However, due to the complex lymphatic drainage and abundant LNs around the stomach, it is often difficult for surgeons, especially for those younger and inexperienced surgeons, to perform an accurate and effective D2 lymphadenectomy without increasing surgical complications.
In recent years, ICG fluorescence imaging for LNs tracing has attracted surgeons’ attention and ICG imaging-guided lymphadenectomy has been introduced in GC surgery. Chen QY et al. (13) performed a RCT and indicated that ICG can noticeably improve the number of retrieved LNs without increased complications in GC patients undergoing D2 lymphadenectomy and they recommend ICG fluorescence imaging should be performed for routine lymphatic mapping during laparoscopic gastrectomy, especially total gastrectomy. Kwon et al. (17) also reported that ICG-guided lymphadenectomy is effective in retrieving more LNs than conventional surgery and had a similar incidence of postoperative complications to conventional surgery. Lee S et al. (19) point out ICG fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy is an effective tool for complete LNs dissection at the splenic hilum and it may help select patients who do not need splenic hilar LNs dissection during a total gastrectomy. However, Lan et al. (18) reported that the number of retrieved LNs in the ICG group was not improved compared with the non-ICG group. According to the pooled analysis in our study, the number of retrieved LNs in the ICG group was significantly more than that in the control group (P < 0.00001) and the use of ICG could reduce intraoperative blood loss (P = 0.0004) without increasing operative time (P = 0.14) and overall complications (P = 0.10). Theoretically, total gastrectomy could obtain more LNs than distal gastrectomy. In our combined analysis, the proportion of total gastrectomy in the ICG group is lower than that in the control group (44.3% vs. 49.6%), but more LNs were obtained, which further indicated that ICG fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy could increased the number of retrieved LNs. Also, Yoon BW et al. (29) reported that the use of ICG could secure the oncologically safe of proximal resection margin in totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy, with the advantage of reducing the operation time and has the benefit of locating the tumor. These results suggest that the ICG fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy is valuable in terms of LNs dissection and short-term outcomes. Nevertheless, the present meta-analysis demonstrated that there was no significant difference in metastatic LNs between the ICG and control groups. The reasons for this outcome may be explained as follows: (1) The metastatic LNs can be removed completely by standard D2 lymphectomy without the use of ICG imaging-guided lymphadenectomy, and (2) Some researchers removed all the fluorescent LNs, even these LNs were outside the extent of D2 lymphectomy (13).
Reducing postoperative tumor recurrence and prolonging patients’ survival time are the ultimate goals of standardized and systematic lymphectomy (40–42). Lees et al. (19) reported that ICG fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy could reduce the tumor recurrence rate after surgery, with the recurrence rate 8.1% and 17.0% in the ICG and control groups, respectively. And another two studies also got the similar results (21, 22). However, Wei M et al. (28) pointed out that the tumor recurrence rates were similar between the two groups after surgery, with the recurrence rate 13.1% and 15.9% in the ICG and control groups, respectively. According to the pooled analysis, ICG fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy could reduce the overall recurrence rate (P = 0.02). However, the 2-year OS rates were comparable between the ICG and control groups (P = 0.43). Nevertheless, this result does not indicate that ICG fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy cannot improve the prognosis of GC patients, because there were only two studies reported survival results, and the follow-up period was shorter, without 5-year survival rate. So more studies with longer follow-up are necessary and expected.
Our study has some limitations. Firstly, there were only two RCTs in the included studies, which may increase the risk of selective bias. Therefore, more high-quality RCTs are expected to provide more credible evidence on this issue. Secondly, due to the limitations of data acquisition and language understanding, only English studies were included in this meta-analysis, which may also increase the risk of selective bias. Thirdly, the uses of ICG, including the dosage, injection method, injection time and ICG imaging system, were all different in these studies, which probably led to heterogeneity in the outcomes.
Conclusions
Despite the limitations of the included studies, this meta-analysis indicates that ICG fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy could increase the number of retrieved LNs, reduce intraoperative blood loss and the overall recurrence rate without increasing operative time and overall complications. It is very valuable for complete LNs dissection in radical gastrectomy for GC. Nevertheless, more high-quality prospective studies and RCTs are necessary to confirm this conclusion.
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific Research Project of Southwest Medical University (No.2020ZRQNB026).
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZL made substantial contributions to conception and design for this work. BD, AZ, and ZL collected all the data. BD and ZL were the major contributors in writing the manuscript. YZ, WY, and LL performed critical revision for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1
Sung H Ferlay J Siegel RL Laversanne M Soerjomataram I Jemal A et al . Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association . Japanese Gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018 (5th edition). Gastric Cancer (2021) 24:1–21. doi: 10.1007/s10120-020-01042-y
3
Li Z Song M Zhou Y Jiang H Xu L Hu Z et al . Efficacy of omentum-preserving gastrectomy for patients with gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol (2021) 11:710814. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.710814
4
Li ZL Zhao LY Zhang WH Liu K Pang HY Chen XL et al . Clinical significance of lower perigastric lymph nodes dissection in siewert type II/III adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction: A retrospective propensity score matched study. Langenbecks Arch Surg (2022) 407:985–98. doi: 10.1007/s00423-021-02380-w
5
Ko CS Jheong JH Jeong SA Kim BS Yook JH Yoo MW et al . Comparison of standard d2 and limited lymph node dissection in elderly patients with advanced gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol (2022) 29:5076–82. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-11480-w
6
Li Z Jiang H Chen J Jiang Y Liu Y Xu L . Comparison of efficacy between transabdominal and transthoracic surgical approaches for siewert type II adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol (2022) 12:813242. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.813242
7
Reinhart MB Huntington CR Blair LJ Heniford BT Augenstein VA . Indocyanine green: Historical context, current applications, and future considerations. Surg Innov (2016) 23:166–75. doi: 10.1177/1553350615604053
8
Li Z Zhou Y Tian G Liu Y Jiang Y Li X et al . Meta-analysis on the efficacy of indocyanine green fluorescence angiography for reduction of anastomotic leakage after rectal cancer surgery. Am Surg (2021) 87:1910–9. doi: 10.1177/0003134820982848
9
Park JH Berlth F Wang C Wang S Choi JH Park SH et al . Mapping of the perigastric lymphatic network using indocyanine green fluorescence imaging and tissue marking dye in clinically advanced gastric cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol (2022) 48:411–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2021.08.029
10
Osterkamp J Strandby RB Nerup N Svendsen M Svendsen LB Achiam MP . Time to maximum indocyanine green fluorescence of gastric sentinel lymph nodes and feasibility of combined indocyanine green/sodium fluorescein gastric lymphography. Langenbecks Arch Surg (2021) 406:2717–24. doi: 10.1007/s00423-021-02265-y
11
Jung MK Cho M Roh CK Seo WJ Choi S Son T et al . Assessment of diagnostic value of fluorescent lymphography-guided lymphadenectomy for gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. (2021) 24:515–25. doi: 10.1007/s10120-020-01121-0
12
Ekman M Girnyi S Marano L Roviello F Chand M Diana M et al . Near-infrared fluorescence image-guided surgery in esophageal and gastric cancer operations. Surg Innov (2022) 29(4):540–9. doi: 10.1177/15533506211073417
13
Chen QY Xie JW Zhong Q Wang JB Lin JX Lu J et al . Safety and efficacy of indocyanine green tracer-guided lymph node dissection during laparoscopic radical gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg (2020) 155:300–11. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.6033
14
Cianchi F Indennitate G Paoli B Ortolani M Lami G Manetti N et al . The clinical value of fluorescent lymphography with indocyanine green during robotic surgery for gastric cancer: A matched cohort study. J Gastrointest Surg (2020) 24:2197–203. doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04382-y
15
Hozo SP Djulbegovic B Hozo I . Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol (2005) 5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
16
Huang ZN Su-Yan Qiu WW Liu CH Chen QY Zheng CH et al . Assessment of indocyanine green tracer-guided lymphadenectomy in laparoscopic gastrectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced gastric cancer: Results from a multicenter analysis based on propensity matching. Gastric Cancer. (2021) 24:1355–64. doi: 10.1007/s10120-021-01211-7
17
Kwon IG Son T Kim HI Hyung WJ . Fluorescent lymphography-guided lymphadenectomy during robotic radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer. JAMA Surg (2019) 154:150–8. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.4267
18
Lan YT Huang KH Chen PH Liu CA Lo SS Wu CW et al . A pilot study of lymph node mapping with indocyanine green in robotic gastrectomy for gastric cancer. SAGE Open Med (2017) 5:2104799444. doi: 10.1177/2050312117727444
19
Lee S Song JH Choi S Cho M Kim YM Kim HI et al . Fluorescent lymphography during minimally invasive total gastrectomy for gastric cancer: An effective technique for splenic hilar lymph node dissection. Surg Endosc. (2022) 36:2914–24. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08584-x
20
Liu M Xing J Xu K Yuan P Cui M Zhang C et al . Application of near-infrared fluorescence imaging with indocyanine green in totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy. J Gastric Cancer. (2020) 20:290–9. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2020.20.e25
21
Lu X Liu S Xia X Sun F Liu Z Wang J et al . The short-term and long-term outcomes of indocyanine green tracer-guided laparoscopic radical gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer. World J Surg Oncol (2021) 19:271. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02385-1
22
Maruri I Pardellas MH Cano-Valderrama O Jove P Lopez-Otero M Otero I et al . Retrospective cohort study of laparoscopic ICG-guided lymphadenectomy in gastric cancer from a Western country center. Surg Endosc. (2022). doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09258-y
23
Park SH Berlth F Choi JH Park JH Suh YS Kong SH et al . Near-infrared fluorescence-guided surgery using indocyanine green facilitates secure infrapyloric lymph node dissection during laparoscopic distal gastrectomy. Surg Today (2020) 50:1187–96. doi: 10.1007/s00595-020-01993-w
24
Puccetti F Cinelli L Genova L Battaglia S Barbieri LA Treppiedi E et al . Applicative limitations of indocyanine green fluorescence assistance to laparoscopic lymph node dissection in total gastrectomy for cancer. Ann Surg Oncol (2022) 29(9):5875–82. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-11940-3
25
Romanzi A Mancini R Ioni L Picconi T Pernazza G . ICG-NIR-guided lymph node dissection during robotic subtotal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. a single-centre experience. Int J Med Robot. (2021) 17:e2213. doi: 10.1002/rcs.2213
26
Tian Y Lin Y Guo H Hu Y Li Y Fan L et al . Safety and efficacy of carbon nanoparticle suspension injection and indocyanine green tracer-guided lymph node dissection during robotic distal gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. (2022) 36:3209–16. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08630-8
27
Ushimaru Y Omori T Fujiwara Y Yanagimoto Y Sugimura K Yamamoto K et al . The feasibility and safety of preoperative fluorescence marking with indocyanine green (ICG) in laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Surg (2019) 23:468–76. doi: 10.1007/s11605-018-3900-0
28
Wei M Liang Y Wang L Li Z Chen Y Yan Z et al . Clinical application of indocyanine green fluorescence technology in laparoscopic radical gastrectomy. Front Oncol (2022) 12:847341. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.847341
29
Yoon BW Lee WY . The oncologic safety and accuracy of indocyanine green fluorescent dye marking in securing the proximal resection margin during totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A retrospective comparative study. World J Surg Oncol (2022) 20:26. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02494-5
30
Zhong Q Chen QY Huang XB Lin GT Liu ZY Chen JY et al . Clinical implications of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging-guided laparoscopic lymphadenectomy for patients with gastric cancer: A cohort study from two randomized, controlled trials using individual patient data. Int J Surg (2021) 94:106120. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.106120
31
Dai W Zhai ET Chen J Chen Z Zhao R Chen C et al . Extensive dissection at no. 12 station during d2 lymphadenectomy improves survival for advanced lower-third gastric cancer: A retrospective study from a single center in southern china. Front Oncol (2021) 11:760963. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.760963
32
Liang Y Cui J Cai Y Liu L Zhou J Li Q et al . "D2 plus" lymphadenectomy is associated with improved survival in distal gastric cancer with clinical serosa invasion: A propensity score analysis. Sci Rep (2019) 9:19186. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55535-7
33
Zhang YX Yang K . Significance of nodal dissection and nodal positivity in gastric cancer. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol (2020) 5:17. doi: 10.21037/tgh.2019.09.13
34
Zhang N Bai H Deng J Wang W Sun Z Wang Z et al . Impact of examined lymph node count on staging and long-term survival of patients with node-negative stage III gastric cancer: A retrospective study using a Chinese multi-institutional registry with surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) data validation. Ann Transl Med (2020) 8:1075. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-1358a
35
Komatsu S Ichikawa D Nishimura M Kosuga T Okamoto K Konishi H et al . Evaluation of prognostic value and stage migration effect using positive lymph node ratio in gastric cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol (2017) 43:203–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.08.002
36
Omori T Yamamoto K Hara H Shinno N Yamamoto M Fujita K et al . Comparison of robotic gastrectomy and laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A propensity score-matched analysis. Surg Endosc. (2022) 36:6223–34. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09125-w
37
Lou S Yin X Wang Y Zhang Y Xue Y . Laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg (2022) 102:106678. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2022.106678
38
Rosa F Alfieri S . Laparoscopic gastrectomy for locally advanced gastric cancer. JAMA Surg (2022) 157:545–6. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.7582
39
Otsuka R Hayashi H Uesato M Hayano K Murakami K Kano M et al . Comparison of estimated treatment effects between randomized controlled trials, case-matched, and cohort studies on laparoscopic versus open distal gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg (2022) 407:1381–97. doi: 10.1007/s00423-022-02454-3
40
Kano K Yamada T Yamamoto K Komori K Watanabe H Hara K et al . Association between lymph node ratio and survival in patients with pathological stage II/III gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol (2020) 27:4235–47. doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-08616-1
41
Wang JW Chen CY . Prognostic value of total retrieved lymph nodes on the survival of patients with advanced gastric cancer. J Chin Med Assoc (2020) 83:691–2. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000368
42
Mao M Zhang A He Y Zhang L Liu W Song Y et al . Development and validation of a novel nomogram to predict overall survival in gastric cancer with lymph node metastasis. Int J Biol Sci (2020) 16:1230–7. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.39161
Summary
Keywords
gastric cancer, lymphadenectomy, indocyanine green, fluorescence imaging, minimally invasive surgery
Citation
Dong B, Zhang A, Zhang Y, Ye W, Liao L and Li Z (2022) Efficacy of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging-guided lymphadenectomy in radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 12:998159. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.998159
Received
19 July 2022
Accepted
26 September 2022
Published
18 October 2022
Volume
12 - 2022
Edited by
Beatrice Aramini, University of Bologna, Italy
Reviewed by
Maher Hendi, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, China; Lorenzo Cinelli, San Raffaele Hospital (IRCCS), Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2022 Dong, Zhang, Zhang, Ye, Liao and Li.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zonglin Li, lizonglin85@163.com
This article was submitted to Surgical Oncology, a section of the journal Frontiers in Oncology
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.