- 1Department of Tuberculosis, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Pathology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Hematology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China
Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma(ENKTCL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma(DLBCL) are specific subtypes of non-Hodgkin lymphoma(NHL), which lack specific features and are difficult to diagnose. The clinical features of lymphoma and tuberculosis are similar, which are easy to be misdiagnosed and lead to delayed treatment. This report describes two cases, one that of a 34-year-old man who was diagnosed with epididymal tuberculosis because of fever, progressive epididymal enlargement, positive T-cell Spot Test(T-SPOT), and epididymal magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) suggesting possible epididymal tuberculosis. He was treated with anti-tuberculosis therapy for 1 month, but the patient’s epididymis continued to grow. Needle biopsy pathology and immunochemical examination showed an epididymal NK/T cell lymphoma, which gradually shrank after chemotherapy. Meanwhile, a 77-year-old female patient was reported who was diagnosed with adrenal tuberculosis because of fever, night sweats, abdominal pain, positive QuantiFERON-TB Gold(QFT) test, and adrenal tuberculosis detected by positron emission tomography/computed tomography(PET/CT). She received anti-tuberculosis treatment for 2 weeks, but her symptoms were not improved. Biopsy pathology and immunochemical examination showed adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, which deteriorated rapidly after chemotherapy and she finally died. In this report, epididymal NK/T cell lymphoma and adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma are rare, and the disease develops rapidly. The diagnosis depends on pathological morphology and immunohistochemistry. Early detection, diagnosis, and treatment are crucial for the prognosis of patients.
1 Introduction
Lymphoma is a group of diseases with malignant proliferation of lymphocytes, which are mainly divided into non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (1). Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTCL) is a subtype of NHL. It often involves the human nasal cavity but can also be rarely seen in the human lung, adrenal gland, testis, and other body parts (2). Primary testicular lymphoma accounts for 1%-2% of NHL, 80% of which are diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Testicular NK/T cell lymphoma is rare, and epididymal NK/T cell lymphoma is even rarer (3). DLBCL is a common subtype of NHL, with an incidence of about 25-40% (4). Patients usually present with progressively enlarged lymph nodes or extranodal space-occupying lesions. About 60% of patients have primary tumors in lymph nodes and 40% in extranodal organs. About 25% of DLBCL are found to involve the adrenal glands on autopsy, but primary adrenal lymphomas are rare, accounting for only 1% (5). Tuberculosis (TB) is a specific infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which can occur in all body systems, most commonly in the lungs (6). Extrapulmonary tuberculosis(EPTB) accounts for only 15% (7), and epididymal and adrenal tuberculosis belong to EPTB. The clinical features of lymphoma and TB are similar, such as fever, night sweats, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. When combined with tuberculosis infection, pathological biopsy is not easy to obtain; lymphoma is easily misdiagnosed as TB, leading to delayed treatment and affecting the prognosis of patients (8). This report discusses the clinical presentation and diagnosis of epididymal NK/T-cell lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adrenal gland, as well as a review of the literature on the misdiagnosis of lymphoma and tuberculosis to minimize leakage and misdiagnosis to assist in proper clinical treatment, and to improve patient survival.
2 Case presentation
2.1 Case 1
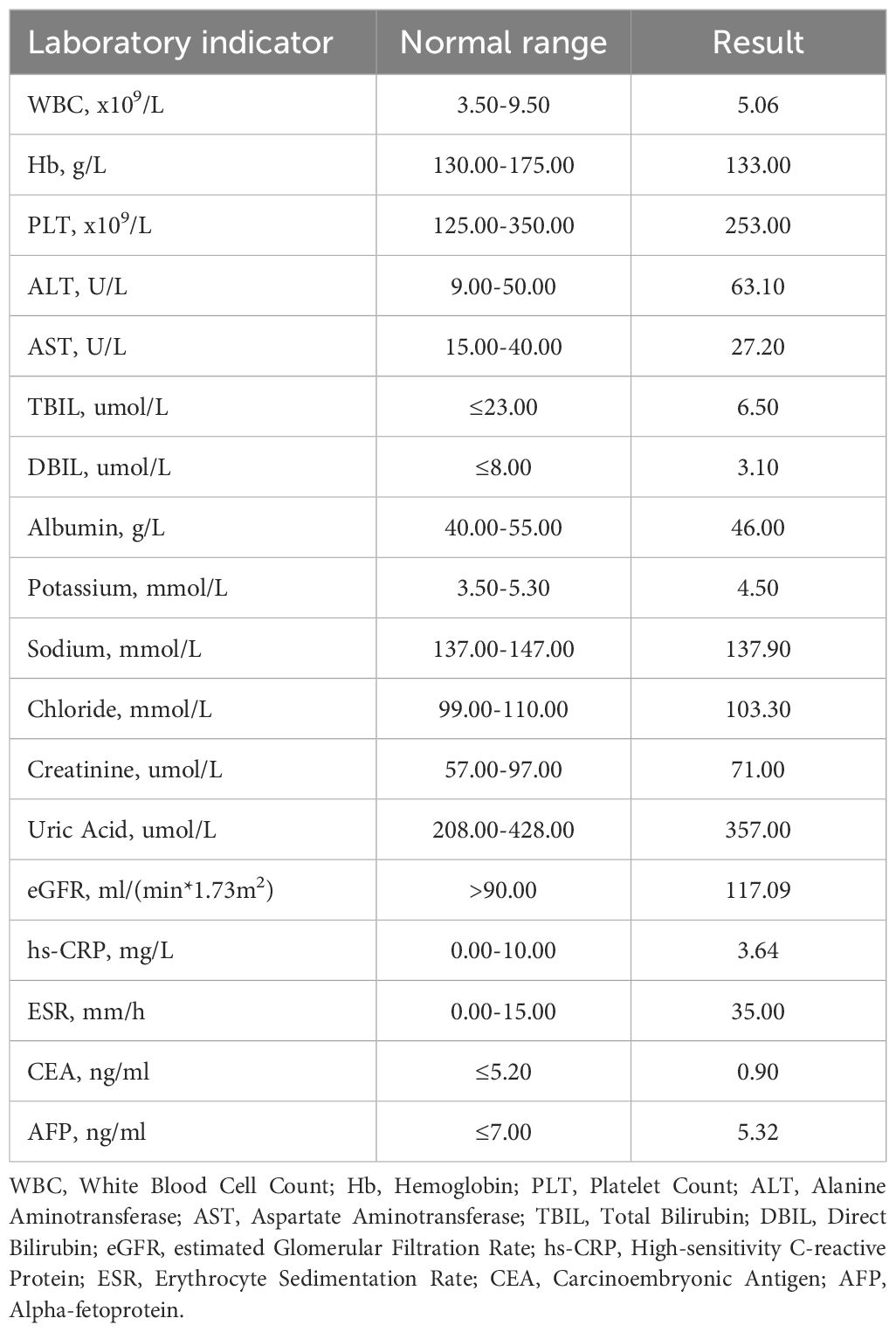
A 34-year-old male patient was admitted to another hospital for fever and gradual enlargement of epididymis in August. The patient’s T-cell Spot Test(T-SPOT) and Purified Protein Derivative(PPD) tests were positive. Ultrasonography of the testis and epididymis showed irregular enlargement of the right and epididymis; a hypoechoic area in the right testis was 41×28mm, and the tail of the right epididymis was 28×27mm (Figure 1A). Magnetic Resonance Imaging(MRI) of the testis and epididymis showed soft tissue shadows in both testes, which showed equal hypointensity on T1WI equal hypointensity and uneven signal intensity on fat-suppression T2, and slightly higher signal intensity on DWI (Figure 1B). The possibility of epididymal tuberculosis was considered in other hospitals. The patient was treated with anti-tuberculosis therapy, and the epididymis continued to enlarge after 1 month of treatment. He subsequently visited our hospital; the laboratory test results are shown in Table 1. The pathology of the right epididymis puncture biopsy suggested atypical hyperplasia of T lymphocytes. The immunohistochemistry findings demonstrate positivity for CD3, CD20, Ki-67 (80%), CK, CD68, CD8, CD4, CD5, CD79a, CD56, GranB, TIA-1, BCL-2, and BCL-6, while WT-1 and CD10 are negative. Molecular pathology confirms positivity for EBER (Figure 2). Combined with immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization results, ependymal NK/T-cell lymphoma diagnosis was made. The patient received chemotherapy and radiotherapy for 3 months, and the epididymis gradually shrunk.
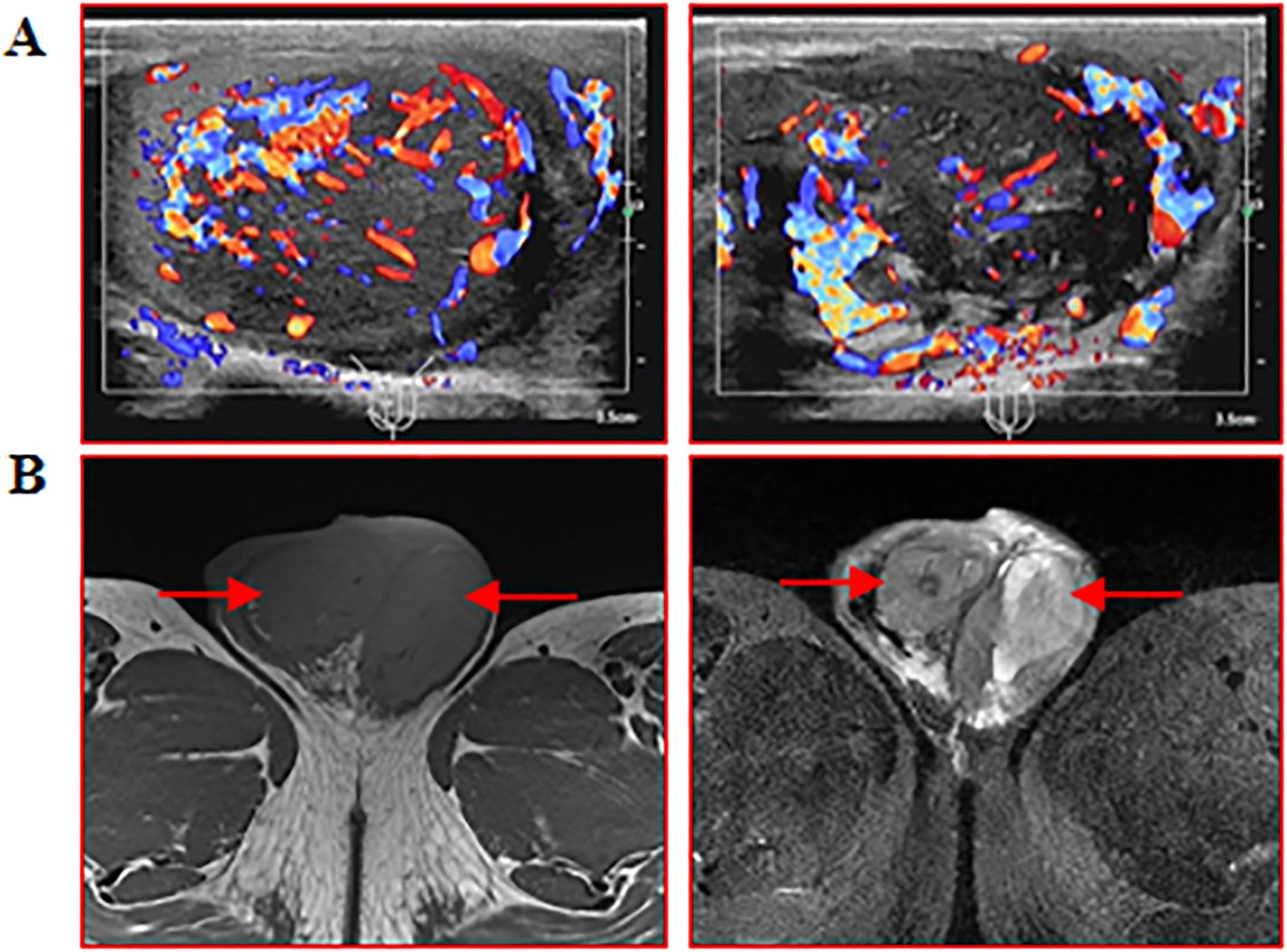
Figure 1. Ultrasonography and MRI of the testis and epididymis were performed. (A) Testis and epididymis B ultrasound: scale bar, 3.5 cm; (B) MRI of testis and epididymis: red arrows indicate enlarged testis and epididymis.
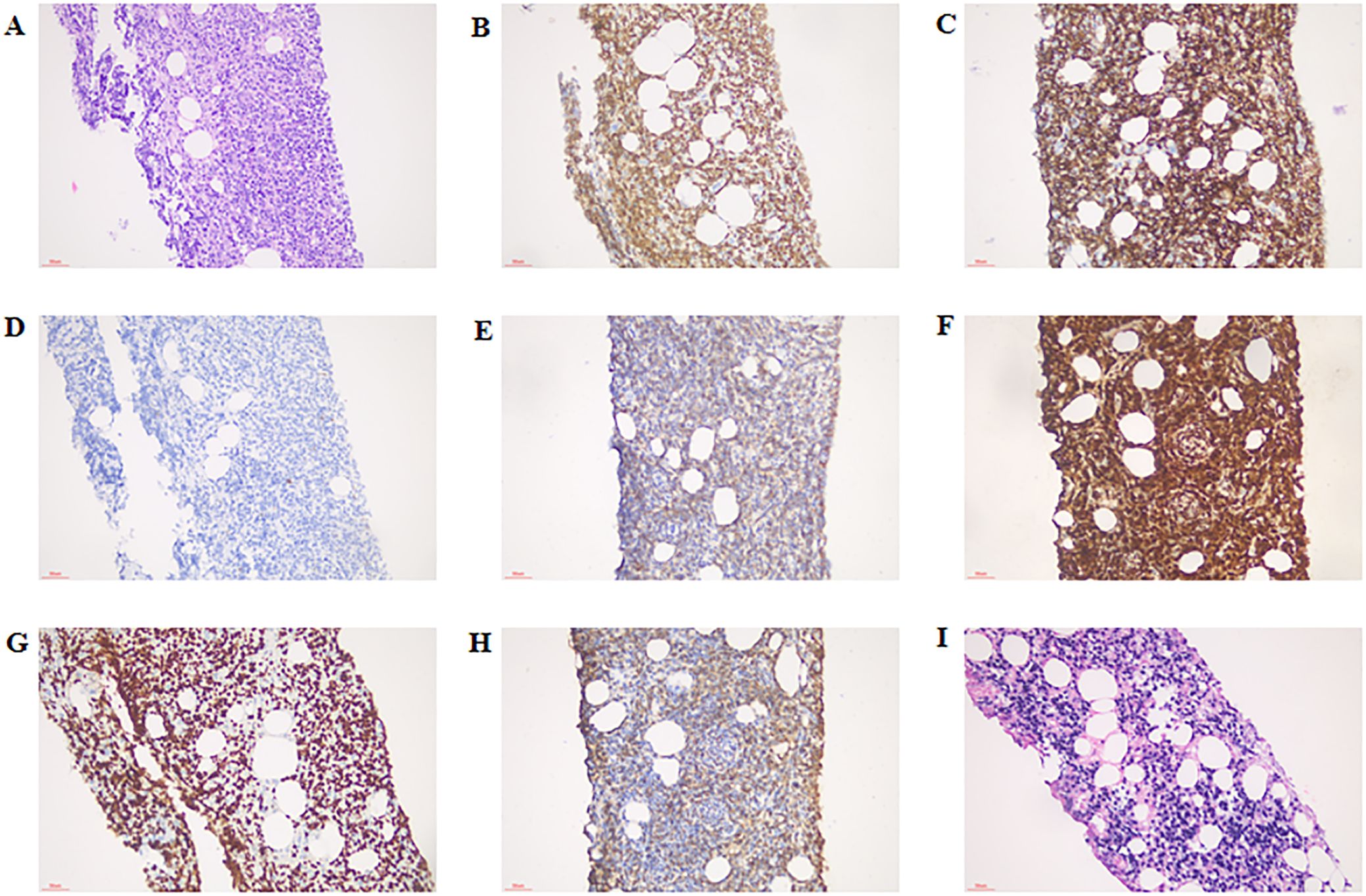
Figure 2. Immunostaining for cytokines in the right epididymis. (A) HE staining, × 200 magnification; (B) CD3 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (C) CD8 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (D) CD20 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (E) CD56 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (F) GranB positive staining ×200 magnification; (G) Ki-67 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (H) TIA-1 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (I) EBER (molecular diagnostics) positive staining, ×200 magnification. HE, hematoxylin-eosin.
2.2 Case 2
A 77-year-old female patient was admitted to another hospital due to afternoon fever, night sweats, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, dizziness, fatigue, listlessness, insomnia, and weight loss for 20 days. The patient’s QuantiFERON-TB Gold(QFT) test was positive. Adrenal MRI revealed that the left and right sizes were approximately 73×73×51mm and 79×87×63mm, respectively. T1WI showed a slow signal, T2W, fat-suppression T2W showed an isointense and slightly hyperintense mixed signal, and an enhanced scan showed no noticeable enhancement (Figure 3A). Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) showed a soft tissue density mass of 67×47mm and 83×52mm in the left and right adrenal regions, respectively, with a flocculent blur surrounding it, and increased FDG metabolism with a max value of 32.6 to 33.6 (Figure 3B). The patient was treated with anti-tuberculosis therapy. There was no significant improvement in symptoms after 2 weeks of treatment. He subsequently visited our hospital; the laboratory test results are shown in Table 2. A right adrenal gland puncture biopsy suggested antacid staining (-) and PAS staining (-). The immunohistochemistry results show positivity for CD20, CD79a, Ki-67 (90%), Bcl-2, Bcl-6, MUM-1, C-myc, CD15, P53, CD22, and CD19, while CD3, CD5, CD10, ALK, CD30, HHV8, CD38, CyclinD1, and EMA are negative (Figure 4). In situ hybridization: EBER(-).FISH: The BCL6 isolation probe was negative, with a total number of 100 cells, of which 1% were isolated cells; the BCL-2 isolation probe was negative, with a total number of 100 cells, of which 2% were isolated cells; and MYC isolation probe was positive, with a total number of 105 cells, of which 71.43% were isolated cells. Combined with morphology, immunohistochemistry, and fluorescence in situ hybridization, the diagnosis of adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, the non-GCB type, was made. The patient was treated with chemotherapy but unfortunately died due to rapid deterioration 81 days after the initial symptoms.

Figure 3. MRI and PET/CT of the adrenal glands. (A) Cross-sectional and coronal MRI images of the adrenal gland; (B) Coronal PET/CT images of the adrenal gland. The red arrow indicates the enlarged adrenal gland.
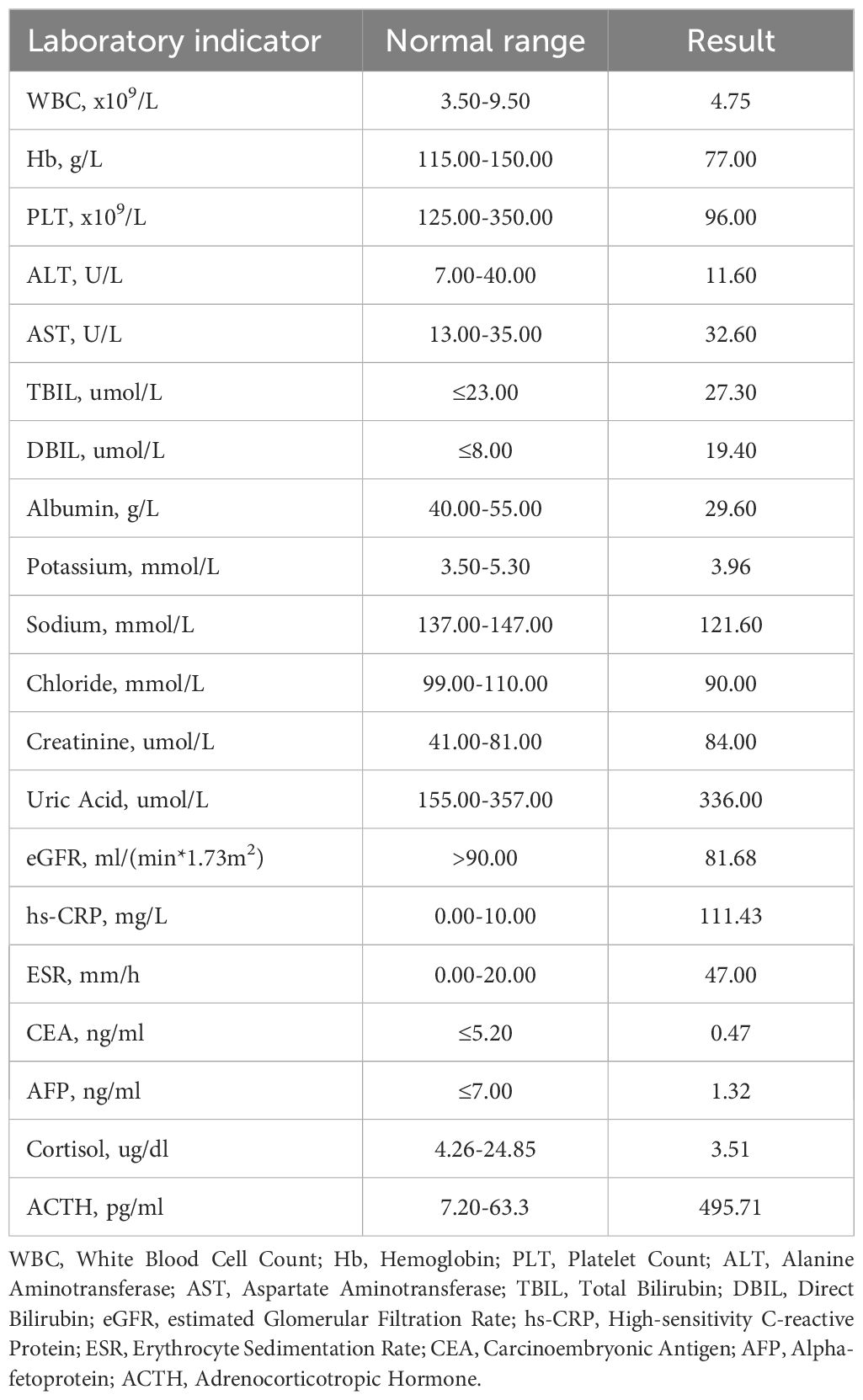
Table 2. Laboratory results of adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients' findings on admission.
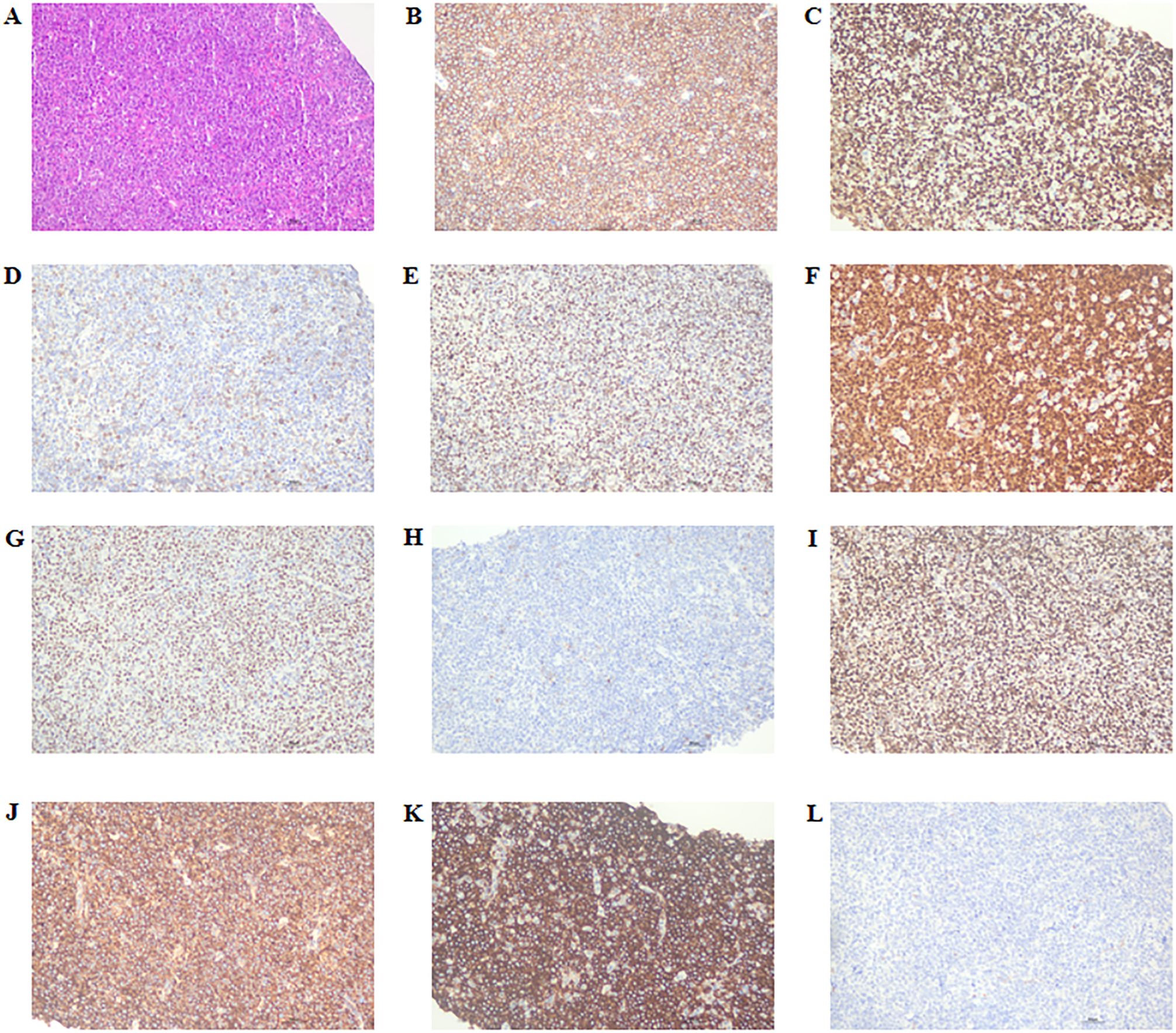
Figure 4. Immunostaining in the right adrenal gland for cytokines. (A) HE staining, × 200 magnification; (B) CD20 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (C) Ki-67 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (D) Bcl-2 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (E) Bcl-6 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (F) MUM-1 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (G) C-myc positive staining, ×200 magnification; (H) CD15 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (I) P53 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (J) CD22 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (K) CD19 positive staining, ×200 magnification; (L) CD10 negative staining, ×200 magnification. HE, hematoxylin-eosin.
3 Discussion
ENKTCL can be divided into nasal type (involving the nasal cavity and upper respiratory tract), non-nasal type (involving the skin, gastrointestinal tract, testes, and other organs), and disseminated type (involving multiple organs) (9). The incidence of ENKTCL varies significantly among different ethnic groups, and the disease mainly occurs in Asia (especially Japan, China, and Korea) and Central and South America. It is rarer in other regions (10). The pathogenesis of ENKTCL is mainly related to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, related gene abnormalities, abnormal activation of signaling pathways, and changes in the tumor microenvironment. The clinical manifestations of ENKTCL are atypical, and it is not easy to diagnose and treat early. About 30%-40% of patients will be accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever, night sweats, and weight loss (11). The pathological features of ENKTCL are coagulation necrosis centered on blood vessels, mixed infiltration of various inflammatory cells, and panischemic necrosis of normal tissues. The EBV detection rate of ENKTCL is as high as 90%, which is this pathological type’s most important clinical feature (12). The pathology-specific immunophenotypes of ENKTCL showed CD56(+), CD3ϵ(+), TIA-1(+), Granzyme B(+), perforin(+), Ki-67(+), and EBER hybridisation(+) (13, 14). ENKTCL is highly invasive and vascular destructive, highly aggressive, and has a poor prognosis. The 5-year overall survival rate of nasal-type patients is about 54%, while the 5-year overall survival rate of non-nasal-type patients is only 34% (15). Epididymal NK/T cell lymphoma is sporadic among non-nasal type extranodal NK/T cell lymphomas, with only one documented case involving the epididymis reported to date. DU W et al. described a case in which a cytological examination of a right scrotal mass puncture performed at another institution initially suggested right epididymal tuberculosis. The PPD test was negative. To achieve a definitive diagnosis, a right epididymectomy was performed, and postoperative pathological assessment identified the condition as right epididymal non-Hodgkin lymphoma, specifically NK/T-cell lymphoma (16). Epididymal tuberculosis usually has an insidious onset and a long course of disease and often manifests as a unilateral painless mass with or without urinary tract irritation symptoms. Epididymal tuberculosis is difficult to differentiate from epididymal lymphoma only by clinical manifestations and physical examination. Clinically, epididymal tuberculosis should be suspected when there is a history of tuberculosis infection, the T-SPOT test or QFT test result is positive, epididymal CT examination shows epididymal enlargement, ring lesions, and nodular enhancement, and general antibiotic treatment is poor. However, an epididymal tumor should be suspected if the mass rapidly grows, with ill-defined borders, firm texture on palpation, and irregular surface characteristics. However, the final diagnosis was based on pathological examination (17). In general, due to the lack of specific clinical manifestations, imaging examination, and complex pathology, epididymal NK/T cell lymphoma easily leads to misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis, which should be paid enough attention in the diagnosis and treatment. Accurate pathological examination is the main basis for diagnosis. Early detection and diagnosis are of great significance for improving the survival of patients.
Primary Adrenal lymphoma (PAL) is usually bilateral than unilateral patients, accounting for 75% of the total incidence of PAL. The male-to-female ratio is 2∶1, and the elderly are more commonly affected (18). The etiology of PAL is still unclear, and its occurrence may be related to hematopoietic system abnormalities, immune system disorders, viral infections, and gene mutations. PAL lacks specific symptoms and signs and often manifests as abdominal pain, abdominal distension, lower back discomfort, unexplained fever, poor appetite and fatigue, and weight loss (19). DLBCL is the most common subtype of PAL, accounting for about 75% of all PAL cases. Histologically, the adrenal tissue is replaced by diffuse large lymphocytes. Based on the expression of related proteins detected by IHC, Hans classification system divided DLBCL into the following Germinal Center B-cell-like(GCB) type: CD10(+) or CD10(-), BCL6 (+)/MUM-1(-), and non-Germinal Center B-cell like(non-GCB) type: CD10(-), BCL6 (+), MUM-1 (+) or CD10(-), BCL6 (+) (20), non-GCB type DLBCL is often considered to be associated with poor prognosis (21). Adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (non-GCB type) is a relatively rare lymphoma, and its clinical manifestations are similar to adrenal tuberculosis. Jiang LM et al. reported a case involving a patient with a history of tuberculosis exposure and a positive T-SPOT test. Adrenal CT revealed bilateral adrenal gland enlargement, while adrenal biopsy pathology suggested granulomatous inflammation. The patient was clinically diagnosed with adrenal tuberculosis; however, no improvement was observed following anti-tuberculosis therapy. Subsequent lymphoma-related immunohistochemical analysis of the original specimen confirmed a diagnosis of adrenal peripheral T-cell lymphoma with granulomatous features (22). Adrenal tuberculosis is usually transmitted to the adrenal gland by Mycobacterium tuberculosis through the blood. Up to 12% of patients with adrenal tuberculosis have an asymptomatic infection, and clinical signs associated with primary adrenal insufficiency become evident only when more than 90% of the adrenal glands have been destroyed. Common symptoms included fatigue, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, hyponatremia, and hyperkalemia. In the early stage of adrenal destruction by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, mass-like enlargement may occur, which should be differentiated from adrenal lymphoma. When the patient has evidence of tuberculosis infection, the T-SPOT test or QFT test results are positive, and the bilateral adrenal CT scan shows signs of nodular enlargement, thickening, and calcification, adrenal tuberculosis should be suspected, but the final diagnosis is based on pathological examination. Adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is a kind of malignant tumor with rapid progress and poor prognosis. Due to the atypical clinical manifestations and imaging examination, the incidence is low, which can easily be missed or misdiagnosed. Therefore, for patients with symptoms such as abdominal pain, unexplained fever, and weight loss, when unilateral or bilateral adrenal masses are found, this disease should be considered, and needle biopsy or surgery should be performed in time to confirm the diagnosis.
We reviewed PubMed and Web of Science papers using “lymphoma” AND “tuberculosis.” Only Case Reports were included. Based on the search results, Table 3 chronologically summarizes cases of misdiagnosis between lymphoma and tuberculosis reported in the English literature. Seventeen cases were identified, with disease sites including the prostate, central nervous system, lungs, lymph nodes, larynx, abdomen, stomach, and vertebrae (23–39). Among these, nine patients with lymphoma were initially misdiagnosed with tuberculosis. Four of these patients succumbed to the disease after receiving only anti-tuberculosis therapy, having been clinically diagnosed with tuberculosis based on medical history, physical examination, and auxiliary tests. Their conditions deteriorated following diagnostic anti-tuberculosis treatment and final histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses confirmed lymphoma. The remaining five lymphoma patients showed clinical improvement following appropriate management, including chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, or surgical intervention upon definitive lymphoma diagnosis. Conversely, eight cases of tuberculosis were initially misdiagnosed as lymphoma, but correct diagnosis and subsequent anti-tuberculosis treatment resulted in significant clinical improvement. Min Bai et al. described a patient whose initial biopsy pathology suggested prostate lymphoma. Following R-CHOP chemotherapy, the patient’s condition worsened; however, a repeat biopsy identified prostate tuberculosis, and recovery was achieved after appropriate anti-tuberculosis therapy (23). Mário Henrique Magalhães Barros et al. and Hideki Asakawa et al. reported cases in which biopsy pathology initially indicated cervical lymph node and gastric tuberculosis. However, these patients failed to respond to anti-tuberculosis treatment and repeat biopsies later confirmed cervical lymph node and gastric lymphoma, respectively (32, 38). These findings highlight the potential for diagnostic confusion between lymphoma and tuberculosis, emphasizing the need for early biopsy, histopathological analysis, and immunohistochemistry to establish a definitive diagnosis. In cases where a patient’s condition fails to improve with initial treatment, repeat or multiple biopsies should be considered to rule out an alternative pathology and ensure timely and appropriate therapeutic intervention.
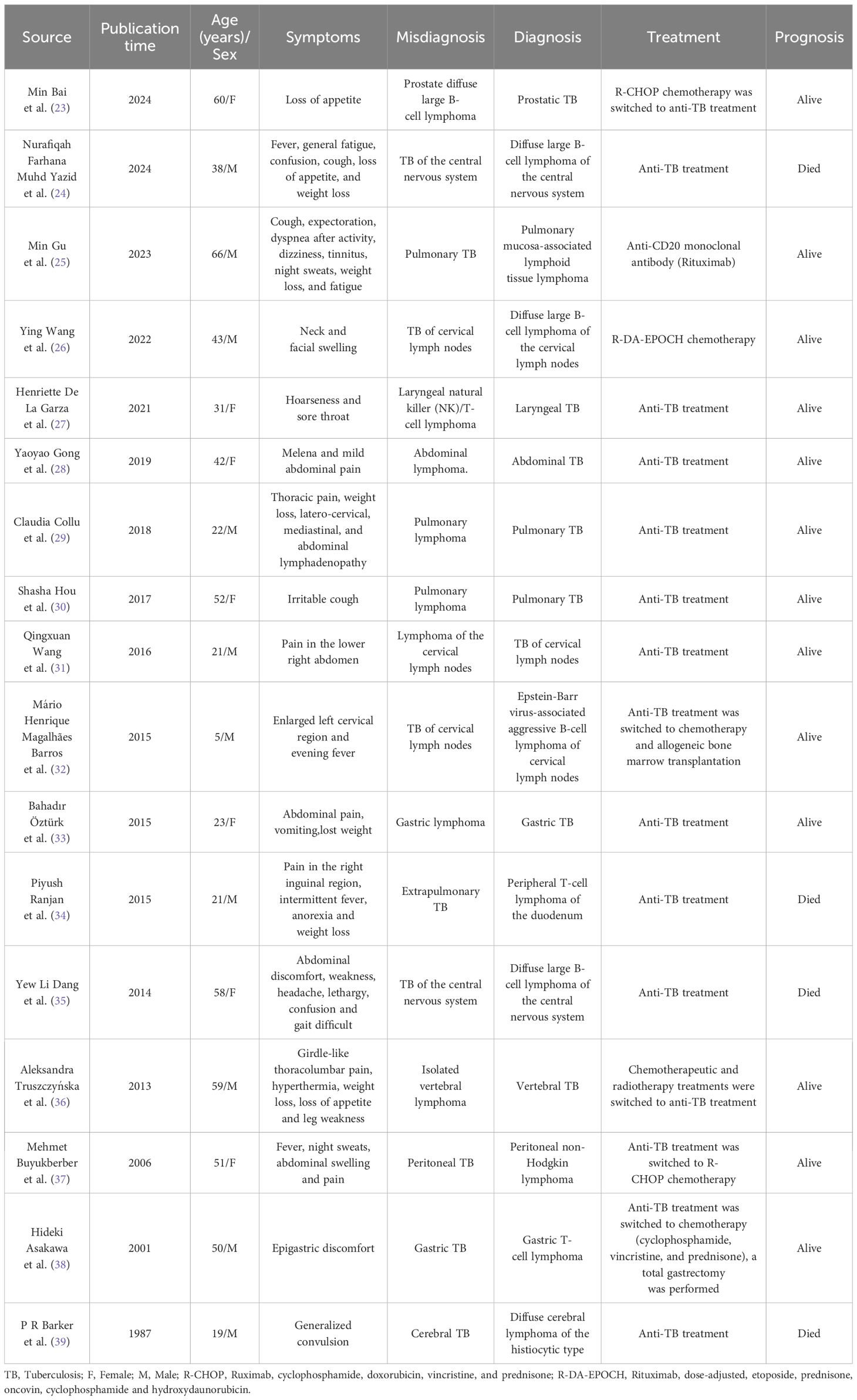
Table 3. Cases of misdiagnosis between lymphoma and tuberculosis have been reported in the English literature.
In this report, epididymal NK/T cell lymphoma and adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma are specific subtypes of rare and challenging lymphomas. Both lymphoma and TB can involve multiple systems and organs, and their early clinical manifestations are not specific. However, the pathological diagnosis of lymphoma is affected by many factors, such as the location, staining, quality, duration of disease, and the experience of pathologists. When the pathology is inconsistent with the clinical diagnosis, multiple biopsies at different sites are more helpful to confirm the diagnosis. At the same time, in areas with a high incidence of TB, a positive TB immunological test is more common, and imaging examination may confuse lymphoma with TB. Therefore, in diagnosing adrenal lymphoma or tuberculosis, clinicians can not only make a diagnosis by biochemical and imaging examination results but also need to comprehensively analyze the patient’s symptoms, clinical signs, bacteriology, histopathology, and treatment efficacy.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study complied with ethical guidelines, and the protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (approval number: 2024-S021-01). All procedures adhered to ethical standards outlined by the Declaration of Helsinki and local regulations. The patients provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
DY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XHL: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Methodology. YXY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ZTF: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HRL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QLZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LX: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Intramural Project of the Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (Grant No. KY-GW-2024-25).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Khoury JD, Solary E, Abla O, Akkari Y, Alaggio R, Apperley JF, et al. The 5th edition of the world health organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: myeloid and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms. Leukemia. (2022) 36:1703–19. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01613-1
2. Jiménez-Pérez JC and Yoon MK. Natural killer T-cell lymphoma of the orbit: an evidence-based approach. Semin Ophthalmol. (2017) 32:116–24. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2016.1228405
3. Nejjari H, Ait Zine I, Ammouri W, Bernousssi Z, and Kabbaj H. Primary testicular extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type associated with epstein-barr virus infection: A moroccan case report. Cureus. (2024) 16:e63361. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63361
4. Miranda-Filho A, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Marcos-Gragera R, Steliarova-Foucher E, and Bray F. Global patterns and trends in the incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Causes Control. (2019) 30:489–99. doi: 10.1007/s10552-019-01155-5
5. Laurent C, Casasnovas O, Martin L, Chauchet A, Ghesquieres H, Aussedat G, et al. Adrenal lymphoma: presentation, management and prognosis. QJM. (2017) 110:103–9. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcw174
6. Chakaya J, Khan M, Ntoumi F, Aklillu E, Fatima R, Mwaba P, et al. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020 - Reflections on the Global TB burden, treatment and prevention efforts. Int J Infect Dis. (2021) 113 Suppl 1:S7–S12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.107
7. Rodriguez-Takeuchi SY, Renjifo ME, and Medina FJ. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis: pathophysiology and imaging findings. Radiographics. (2019) 39:2023–37. doi: 10.1148/rg.2019190109
8. Sun J, Li G, Zhang N, Li S, and Chen R. Analysis of lymphoma presenting with pulmonary symptoms: report of 79 cases. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. (2014) 37(8):597–600. Chinese.
9. Tse E, Zhao WL, Xiong J, and Kwong YL. How we treat NK/T-cell lymphomas. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:74. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01293-5
10. Reneau JC, ShIndiapina P, Braunstein Z, Youssef Y, Ruiz M, Farid S, et al. Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphomas: current approaches and future directions. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:2699. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102699
11. Lim SH, Hong JY, Lim ST, Hong H, Arnoud J, Zhao W, et al. Beyond first-line non-anthracycline-based chemotherapy for extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: clinical outcome and current perspectives on salvage therapy for patients after first relapse and progression of disease. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:2199–205. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx316
12. Bi XW, Wang H, Zhang WW, Wang JH, Liu WJ, Xia ZJ, et al. PD-L1 is upregulated by EBV-driven LMP1 through NF-κB pathway and correlates with poor prognosis in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol. (2016) 9:109. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0341-7
13. Asano N, Kato S, and Nakamura S. Epstein-Barr virus-associated natural killer/T-cell lymphomas. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. (2013) 26:15–21. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2013.04.002
14. Asano N, Suzuki R, Kagami Y, Ishida F, Kitamura K, Fukutani H, et al. Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of cytotoxic molecule expression in nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. Am J Surg Pathol. (2005) 29:1284–93. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000173238.17331.6b
15. Fox CP, Civallero M, Ko YH, Manni M, Skrypets T, Pileri S, et al. Survival outcomes of patients with extranodal natural-killer T-cell lymphoma: a prospective cohort study from the international T-cell Project. Lancet Haematol. (2020) 7:e284–94. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30283-2
16. Du W, Yang JY, Huang M, Li JC, and Song F. A case report of epididymal testicular NK/T-cell lymphoma. J Pract Oncology. (2012) 27:664–5. doi: 10.13267/j.cnki.syzlzz.2012.06.011
17. Tessler FN, Tublin ME, and Rifkin MD. Ultrasound assessment of testicular and paratesticular masses. J Clin Ultrasound. (1996) 24:423–36. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0096(199610)24:8<423::AID-JCU3>3.0.CO;2-M
18. Li S, Wang Z, Wu Z, Zhuang H, and Xu Y. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of primary adrenal diffuse large B cell lymphoma in a large contemporary cohort: a SEER-based analysis. Ann Hematol. (2019) 98:2111–9. doi: 10.1007/s00277-019-03740-9
19. Wang Y, Ren Y, Ma L, Li J, Zhu Y, Zhao L, et al. Clinical features of 50 patients with primary adrenal lymphoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2020) 11:595. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00595
20. Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. (2004) 103:275–82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1545
21. Lu TX, Miao Y, Wu JZ, Gong QX, Liang JH, Wang Z, et al. The distinct clinical features and prognosis of the CD10+MUM1+ and CD10−Bcl6−MUM1− diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:20465. doi: 10.1038/srep20465
22. Jiang LM, Peng JX, He YF, Hu ZW, Wang LJ, and Li XL. Report of one case with primary adrenal lymphoma misdiagnosed as adrenal tuberculosis [chinese. Chin J Endocrinol Metab. (2015) 31:541–1. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2015.06.017
23. Bai M, Yu Q, Yuan L, Zhao Y, Zheng M, Su L, et al. Prostate tuberculosis mimicking Malignancy on 18F-FDG PET/CT in a patient with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A case report. Med (Baltimore). (2024) 103:e38296. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038296
24. Muhd Yazid NF, Che Ros MIA, and Setia SA. A rare case of primary CNS lymphoma in an HIV-positive patient mimicking CNS tuberculosis. Cureus. (2024) 16:e62426. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62426
25. Gu M, Ji D, Lu Y, Ping G, and Yan C. Rare primary pulmonary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma misdiagnosed with tuberculosis: A case report. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e36125. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036125
26. Wang Y, Chen M, Ni C, Tong J, Chen P, Zhang Y, et al. Case report: primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma invasion of extranodal thyroid tissue mimicking tuberculosis and confounded by similar ultrasonic appearance. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:879295. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.879295
27. De La Garza H, Flores R, and Grosu HB. A case of laryngeal tuberculosis mimicking lymphoma. Cureus. (2021) 13:e13744. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13744
28. Gong Y, Li S, Rong R, Chen X, and Jiang L. Isolated gastric varices secondary to abdominal tuberculosis mimicking lymphoma: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. (2019) 19:78. doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-0998-9
29. Collu C, Fois A, Crivelli P, Tidore G, Fozza C, Sotgiu G, et al. A case-report of a pulmonary tuberculosis with lymphadenopathy mimicking a lymphoma. Int J Infect Dis. (2018) 70:38–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.02.011
30. Hou S, Shen J, and Tan J. Case report: multiple systemic disseminated tuberculosis mimicking lymphoma on 18F-FDG PET/CT. Med (Baltimore). (2017) 96:e7248. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007248
31. Wang Q, Chen E, Cai Y, Zhang X, Li Q, and Zhang X. A case report: systemic lymph node tuberculosis mimicking lymphoma on 18F-FDG PET/CT. Med (Baltimore). (2016) 95:e2912. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002912
32. Barros MH, Leite E, Chabay P, Morais V, Stefanoff G, and Hassan R. Diagnosing lymphoma in a setting with a high burden of infection: a pediatric case of Epstein-Barr virus-associated aggressive B-cell lymphoma with t(8;14) (q23;q32) and extensive necrosis mimicking tuberculosis. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. (2015) 48:108–11. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0153-2014
33. Öztürk B, Nural MS, Ecemiş Ö, and Danacı M. Imaging findings of an isolated gastric tuberculosis case mimicking lymphoma and infiltrative gastric cancer. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2015) 26:65–6. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2015.5992
34. Ranjan P, Dutta S, Kakkar A, Goyal A, Vikram NK, Sharma MC, et al. T-cell lymphoma masquerading as extrapulmonary tuberculosis: case report and review of literature. J Family Med Prim Care. (2015) 4:280–3. doi: 10.4103/2249-4863.154677
35. Dang YL, Hor JY, Chia YK, Lim TT, and Eow GB. Suprasellar lymphoma masquerading as tuberculosis of the central nervous system. Acta Neurol Belg. (2014) 114:239–41. doi: 10.1007/s13760-013-0217-3
36. Truszczyńska A, Nowak-Misiak M, Rąpała K, and Walczak P. Tuberculosis of the spine masquerading as a spine lymphoma. A case report and discussion of diagnostic and therapeutic traps. Neurol Neurochir Pol. (2013) 47:189–93. doi: 10.5114/ninp.2013.33823
37. Buyukberber M, Sevinc A, Cagliyan CE, Gulsen MT, Sari I, and Camci C. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma with high adenosine deaminase levels mimicking peritoneal tuberculosis: an unusual presentation. Leuk Lymphoma. (2006) 47:565–8. doi: 10.1080/10428190500395472
38. Asakawa H, Tsuji M, Tokumine Y, Kashihara T, Okuno M, Takenaka R, et al. Gastric T-cell lymphoma presenting with epithelioid granulomas mimicking tuberculosis in regional lymph nodes. J Gastroenterol. (2001) 36:190–4. doi: 10.1007/s005350170128
Keywords: epididymal lymphoma, adrenal lymphoma, epididymal tuberculosis, adrenal tuberculosis, misdiagnosis
Citation: Ye D, Liu X, Yang Y, Yang Y, Fei Z, Liu H, Zhan Q and Xia L (2025) Case Report: Epididymal NK/T-cell lymphoma and adrenal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma are misdiagnosed as tuberculosis: two case reports and literature review. Front. Oncol. 15:1529049. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1529049
Received: 26 November 2024; Accepted: 13 May 2025;
Published: 03 June 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandra Cuomo, University of Naples Federico II, ItalyReviewed by:
Arnab Kundu, R G Kar Medical College and Hospital, IndiaHasan Haydar, University of Hama, Syria
Copyright © 2025 Ye, Liu, Yang, Yang, Fei, Liu, Zhan and Xia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lu Xia, eGlhbHVAc2hhcGhjLm9yZw==
 Dan Ye
Dan Ye Xuhui Liu1
Xuhui Liu1