- 1Department of Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, China
- 2Department of Pathology, Basic Medical College, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
- 3Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) constitute a class of small non-coding RNAs that play a pivotal role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. The dysregulation of miRNAs has been widely implicated in the pathogenesis of diverse human cancers. Among these, miR-205 has attracted considerable attention owing to its aberrant expression patterns in multiple cancer types, where it regulates tumor initiation and progression via diverse molecular mechanisms. Apoptosis, a fundamental biological process essential for cellular homeostasis, represents a tightly regulated form of programmed cell death that significantly influences cancer development under both physiological and pathological conditions. In malignant cells, miR-205 exhibits a dual regulatory role by modulating apoptosis-related signaling pathways and their downstream target genes, thereby displaying both oncogenic and tumor-suppressive functions. This comprehensive review systematically explores recent advances in understanding the functional role of miR-205 in apoptosis regulation across a spectrum of human malignancies and highlights its potential therapeutic implications for future cancer therapies.
1 Introduction
The global burden of cancer continues to escalate, with both incidence and mortality rates demonstrating a persistent upward trajectory, underscoring the profound and growing impact of neoplastic diseases on public health systems worldwide (1), A pivotal determinant underlying this concerning phenomenon is the ability of malignant cells to evade programmed cell death through diverse molecular mechanisms, thereby facilitating tumor progression and therapeutic resistance (2). Apoptosis, a genetically programmed form of cell death, constitutes a critical biological mechanism that suppresses the proliferation of damaged or aberrant cells. The evasion of this regulatory process by malignant cells represents a fundamental hallmark of cancer, contributing to tumor progression and conferring resistance to therapeutic interventions. Within this context, there is increasing recognition that therapeutic strategies targeting the induction of programmed cell death through precise modulation of apoptotic pathways may constitute a promising and potentially transformative approach in oncology. However, despite this therapeutic potential, the current understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying apoptotic regulation in neoplastic cells remains fragmentary and incomplete, necessitating further comprehensive investigation (3). The ultimate objectives are to enhance overall survival rates and improve the quality of life for cancer patients. Extensive research efforts have been devoted to elucidating the regulatory relationships between microRNAs (miRNAs) and apoptotic pathways in neoplastic cells. miRNAs represent a class of small, evolutionarily conserved non-coding RNA molecules, typically comprising 18 to 24 nucleotides in length. These regulatory molecules exert their biological functions through sequence-specific interactions with the 3’-untranslated regions (3’-UTRs) of target messenger RNAs (mRNAs), thereby modulating post-transcriptional gene expression (4, 5). A significant proportion of miRNAs are fundamentally implicated in both genetic and epigenetic alterations that influence cancer-associated gene networks. Dysregulation of miRNA expression profiles can lead to developmental perturbations and has been demonstrated to play a pivotal role in oncogenic transformation and tumorigenic processes (6). MicroRNAs exert their regulatory influence on oncogene function across multiple pivotal stages of tumorigenesis, encompassing tumor initiation, progression, and metastatic dissemination, through precise targeting and modulation of cancer-associated genes (7). In this comprehensive review, we systematically examine the functional roles and molecular mechanisms through which miR-205 regulates apoptotic processes in malignant cells across diverse cancer types (8). Furthermore, we critically evaluate its clinical significance and potential therapeutic value in tumor regulation, while establishing a theoretical framework to facilitate its translation into clinical applications for cancer prevention and treatment strategies.
2 Overview of miR-205
miR-205 was initially characterized through comparative genomic analyses of murine and Fugu rubripes sequences. Subsequent investigations have further identified its conserved expression patterns in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and human genomes, demonstrating its evolutionary significance across vertebrate species (9–11). miR-205 is genomically located at chromosome 1 (1q32.2) in humans. This microRNA is characterized by a highly conserved core sequence (5’-UCCUUUCAUUCCACCGGAGUCUG-3’) that is essential for its functional activity and specific molecular interactions with target mRNAs (12).
2.1 Physiological function of miR-205
miR-205 has been demonstrated to play a critical role in numerous essential physiological processes (Figure 1). Specifically, it regulates skin stem cell differentiation, is indispensable for epithelial cell homeostasis, inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and modulates cellular proliferation and differentiation processes. Wang et al. demonstrated that in miR-205 knockout skin stem cells, the expression levels of negative regulators of the PI3K-AKT pathway, including Frk, Inpp4b, Inppl1, and Phlda3, were significantly upregulated. This led to the inhibition of PI3K signaling and a marked downregulation of phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) levels, resulting in the premature termination of skin stem cell differentiation (13). Furthermore, miR-205 has been shown to facilitate cutaneous wound healing through the promotion of keratinocyte migration, thereby enhancing the re-epithelialization process (14). Yu et al. further demonstrated that elevated expression of miR-205 results in the downregulation of lipid phosphatase SHIP2, consequently activating the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in keratinocytes. This pathway activation is essential for inhibiting apoptotic processes and plays a critical role in promoting efficient wound healing (15). Basal cells are recognized as progenitor cells responsible for epithelial cell generation. miR-205 exhibits high expression levels in prostate basal cells, where it mediates the deposition of laminin-332 and its cognate receptor integrin-β4 within the basement membrane. This molecular mechanism is crucial for maintaining prostate basal cell homeostasis and preserving the structural integrity and physiological function of the prostate gland (16). The investigation conducted by Teta et al. has revealed that miR-205 exhibits prominent expression in epidermal keratinocytes while being conspicuously absent in follicular cells, demonstrating its tissue-specific expression pattern in epithelial compartments (17). E-cadherin, a critical transmembrane protein essential for maintaining intercellular adhesion in epithelial tissues, is negatively regulated by the transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Emerging evidence demonstrates that miR-205 directly targets and downregulates ZEB1 and ZEB2, thereby upregulating E-cadherin expression and effectively inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in epithelial cells. These findings underscore the pivotal role of miR-205 in modulating E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and maintaining epithelial phenotype integrity (18, 19). Furthermore, miR-205 has been demonstrated to play a significant regulatory role in embryonic developmental processes. Elevated expression levels of miR-205 have been shown to induce the upregulation of multiple members of the calmodulin family (including Cdh4, Cdh5, Cdh6, and Cdh11) as well as various genes associated with cell adhesion. This upregulation subsequently activates the β-catenin/Tcf-Lef signaling pathway, which is critically involved in extraembryonic endoderm formation and spermatogenic processes (20). In addition, miR-205 has been identified as a regulator of multiple key molecular targets that are essential for modulating cellular proliferation, differentiation, and migratory processes (21).
2.2 miR-205’s dual role in cancer
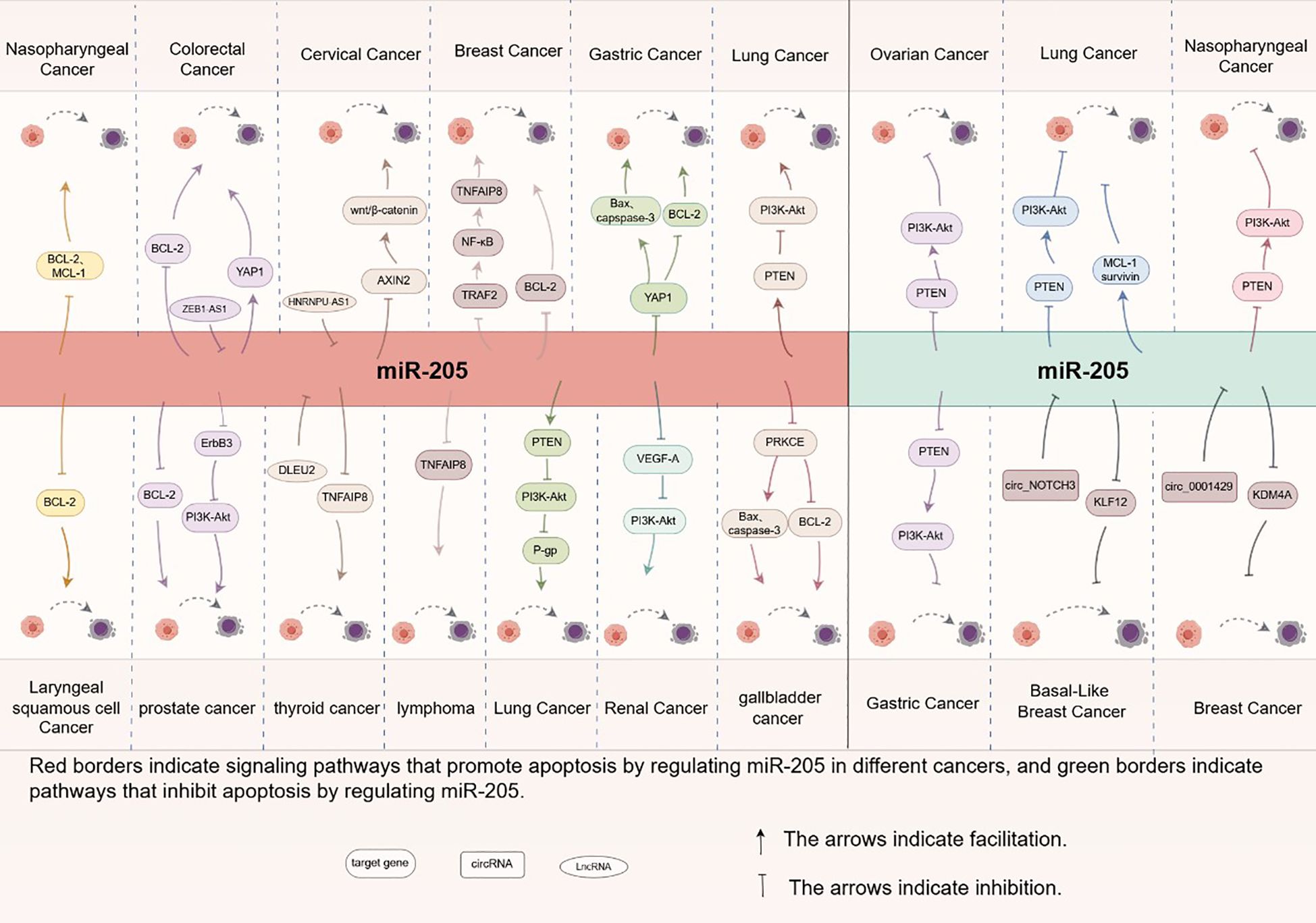
Bioinformatics analysis utilizing the TCGA database has revealed significant differential expression patterns of miR-205 across various cancer types compared to adjacent normal tissues (see Figure 2). miR-205 is significantly upregulated in multiple malignancies, including non-small cell lung cancer, bladder carcinoma, esophageal adenocarcinoma, ovarian carcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, endometrioid adenocarcinoma, and head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, where it functions as an oncogenic driver promoting tumorigenic processes. In contrast, miR-205 expression is markedly downregulated in other cancer types, such as breast carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, prostate adenocarcinoma, and cutaneous melanoma, where it appears to exert tumor-suppressive functions (8, 12). Even in the same cancer, the role of miR-205 may vary depending on the subtype. For example, in triple-negative breast cancer, miR-205 usually plays a tumor suppressor role, whereas in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, its role may be more complex (22). In the molecular context, the role of miR-205 is highly dependent on the expression patterns of its target genes and regulated signaling pathways in different cancers. For example, in breast cancer, miR-205 inhibits EMT by specifically targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2, thereby exerting tumor suppressor effects (18); Whereas, in cervical cancer cells, up-regulation of miR-205 can significantly target and inhibit CHN1 expression levels, thereby promoting tumor cell proliferation (23). In addition, miR-205 may also regulate tumors by modulating the tumor microenvironment. For example, miR-205 was significantly induced by hypoxia in cervical and lung cancer cells, while significant suppression of ASPP2 was observed. It was confirmed by further studies that the hypoxia-induced ASPP2 inhibition was mainly attributed to miR-205 elevated (24). miR-205 may also influence tumor progression by regulating immune cell functions (immune microenvironment) such as T cells and macrophages. For example, Fan et al. found in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients undergoing radiotherapy that radiotherapy upregulated the expression level of miR-205, which promotes autophagy in lung cancer cells, maintains the survival of memory T-cells, and promotes the self-renewal of B1 cells, which facilitates the death of tumor cells and enhances the patient’s anti-tumor immunity (25). In addition, miR-205 expression may also be tightly influenced by epigenetic regulation. miR-205 expression is regulated by DNA methylation and histone modifications. For example, miR-205 is often simultaneously silenced and acquires DNA hypermethylation in muscle-invasive bladder tumors and low-differentiated bladder cell lines, regulating bladder cancer cell proliferation and differentiation (26). Similarly, Kim ES et al. showed that ionizing radiation (IR) enhances the hypermethylation of miR-205-5p CpG islands through activation of Src in lung or breast cancers, leading to a decrease in miR-205-5p expression, which in turn stimulates Bcl-w, mediated proliferation and metastasis of human lung or breast cancer cells (27).

Figure 2. miR-205 expression in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) pan-cancer (http://bioinfo.jialab-ucr.org/CancerMIRNome/).
In summary, the dual role of miR-205 may depend specifically on various factors such as cancer type, molecular background and tumor microenvironment. In-depth exploration of whether miR-205 acts as an angel or a devil in different cancers is of great significance for the future research of miR-205.
3 miR-205 regulates the mechanism of apoptosis in tumor cells
Apoptosis represents a highly regulated and genetically programmed cellular process that mediates controlled cell death under both physiological homeostasis and pathological conditions (28). It is a key mechanism for maintaining normal cellular homeostasis by removing senescent and diseased cells, thereby supporting overall organismal health and normal cellular functions (29, 30). When cells become cancerous, they acquire the ability to evade apoptosis, which promotes their uncontrolled development. This ability to evade apoptosis has now become a recognized “hallmark of cancer” (2).
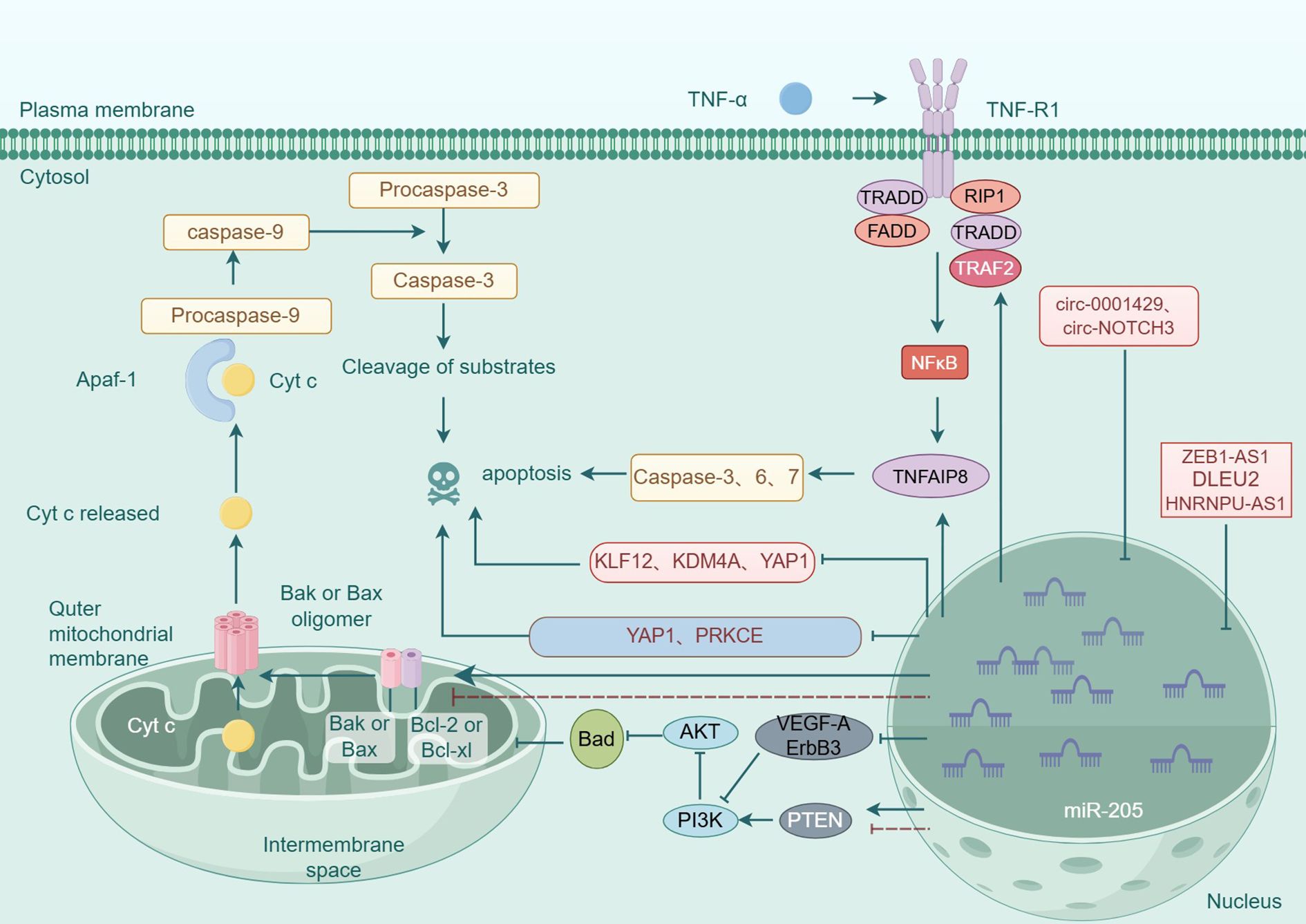
Apoptosis is predominantly mediated through two well-characterized molecular pathways: the intrinsic pathway and the extrinsic pathway. The intrinsic pathway, alternatively referred to as the mitochondrial-mediated pathway, is initiated by intracellular stimuli including but not limited to growth factor deprivation, genotoxic stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress (31). The critical event in the intrinsic apoptotic pathway is mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Extensive research has established that BCL-2 family proteins, comprising both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic members, play a crucial regulatory role in tumor progression through their modulation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. This regulatory mechanism is mediated primarily through the controlled release of cytochrome c and subsequent activation of caspase cascades (32). In contrast, the extrinsic apoptotic pathway is initiated through specific ligand-receptor interactions, where death ligands bind to their cognate transmembrane death receptors, triggering downstream apoptotic signaling cascades (33). Dysregulation of death receptor-mediated signaling in the extrinsic apoptotic pathway contributes to tumorigenesis by promoting malignant cell survival and proliferation (34). Both apoptotic pathways converge on the activation of caspase cascades, which execute the biochemical and morphological changes characteristic of programmed cell death (35). Based on these findings, it is hypothesized that the regulation of apoptotic processes may hold significant potential for the development of novel therapeutic strategies in cancer treatment. Analysis of the molecular mechanisms by which miR-205 regulates tumors reveals that it can inhibit cancer progression by controlling the apoptotic processes in tumor cells.
3.1 Regulation of endogenous apoptotic pathways by miR-205
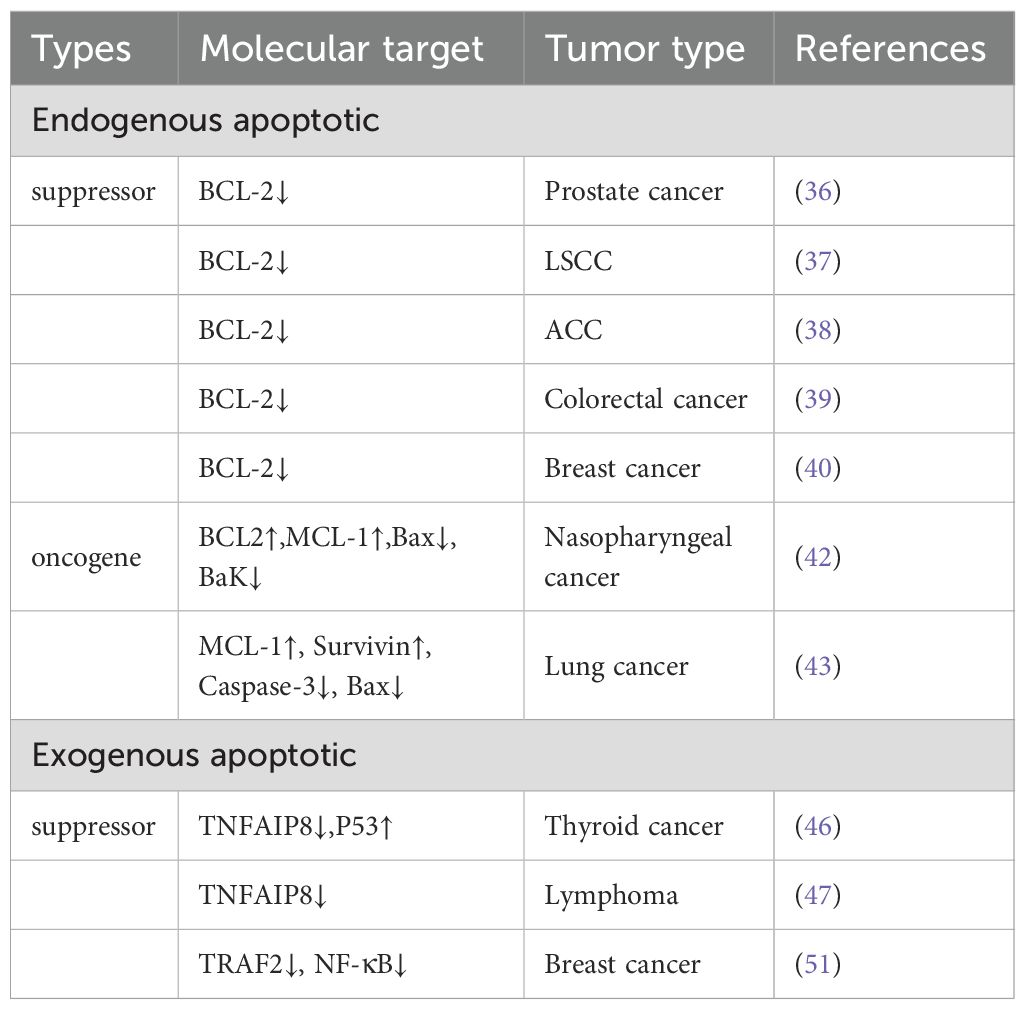
Accumulating evidence from numerous studies has demonstrated that miR-205 can directly modulate BCL-2 expression, thereby regulating apoptotic processes in multiple cancer types. Specifically, in prostate cancer cells, laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), and adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) SW-13 cells, miR-205 upregulation has been shown to significantly reduce both BCL-2 mRNA and protein expression levels. This downregulation subsequently enhances apoptotic activity and inhibits cancer cell proliferation and metastatic potential (36–38). Furthermore, deoxyelephantopin (DET), a bioactive sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Elephantopus scaber (Asteraceae), has been extensively characterized for its potent anti-inflammatory and anti-neoplastic properties. This phytochemical compound has emerged as a promising therapeutic candidate for the treatment of various pathological conditions, particularly due to its demonstrated capacity to inhibit proliferation across multiple cancer cell lines. Notably, a seminal study conducted by Ji et al. revealed that DET induces miR-205 upregulation, which subsequently targets and downregulates BCL-2 expression in colorectal carcinoma cells. This molecular mechanism promotes apoptotic cell death, suggesting DET’s potential as a novel therapeutic agent for clinical oncology applications (39). Qiu et al. demonstrated in their investigation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells that miR-205 overexpression significantly enhances cleaved Caspase-3 expression while concurrently reducing the BCL-2/Bax ratio, thereby inducing apoptotic cell death in malignant cells (40).
Notably, Myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL-1), a pro-survival member of the BCL-2 protein family, serves as a critical anti-apoptotic regulator in cellular homeostasis (41). In nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, transfection with miR-205-5p mimics significantly upregulated the protein expression of both BCL-2 and MCL-1, while concurrently downregulating the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bak. Apoptotic activity is significantly suppressed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells (42). ZAROGOULIDIS P et al. demonstrated that miR-205 overexpression in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines A549 and H1975 significantly inhibits Caspase-3 activation and Bax expression, while concurrently upregulating MCL-1 and Survivin protein levels, ultimately resulting in the suppression of apoptotic pathways in malignant pulmonary cells (43).
In summary, miR-205 directly targets and modulates the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein BCL-2 in multiple cancer types, thereby regulating intrinsic apoptotic pathways (in Table 1).
3.2 Regulation of exogenous apoptotic pathways by miR-205
In tumor cells, miR-205 primarily modulates extrinsic apoptosis through the TNFR1/TNF receptor signaling pathway. TNF-α, a transmembrane protein, activates the NF-κB pathway upon binding to its receptor TNF-R1, thereby inducing the expression of TIPE family proteins, including TNFAIP8 and TIPE2 (44). Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 8 (TNFAIP8) functions as an anti-apoptotic regulator in malignant cell (45). Yang et al. demonstrated that miR-205 overexpression in thyroid carcinoma cells specifically downregulates TNFAIP8 expression while upregulating the pro-apoptotic protein p53, ultimately promoting apoptotic cell death in thyroid cancer cells (46). Similarly, Li et al. demonstrated that miR-205 upregulation in lymphoma cells specifically targets and downregulates TNFAIP8 expression, consequently inducing apoptotic cell death in conjunctival mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma (47). The TNF-R1 receptor itself possesses a death domain that, under certain conditions, can activate caspase cascades and induce apoptosis (48). Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-2 (TRAF2), which normally acts in concert with other members of the TRAF protein family, is involved in inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and stimulating the TNFR response to various mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascades (49). TRAF2 is established as a critical regulatory component in the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway (50). In breast carcinoma cells, miR-205 upregulation specifically targets TRAF2, leading to significant downregulation of both TRAF2 mRNA and protein expression levels. This suppression of TRAF2 subsequently inhibits NF-κB signaling pathway activation, ultimately resulting in the attenuation of apoptotic processes (51).
3.3 Regulation of other apoptotic factors
3.3.1 PTEN/PI3K-Akt pathway
miR-205 has been demonstrated to regulate the expression of multiple oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, including but not limited to ZEB1, PTEN, ErbB3, and VEGF-A, through target gene modulation (21), which regulates the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, thereby mediating the occurrence of cellular apoptosis. In cancer, the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is often found to be over-activated. This over-activation results in increased cell proliferation, a reduction in apoptosis, and a greater propensity for tumor formation and metastasis (52).
ErbB3, a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family, functions as a potent oncogenic driver when overexpressed or genetically altered, activating downstream tumorigenic signaling cascades (53). Li and colleagues demonstrated that miR-205 upregulation in prostate carcinoma cell lines specifically targets and suppresses ErbB3 expression, consequently attenuating PI3K-Akt signaling pathway activity. This molecular inhibition results in significant downregulation of BCL-2 expression, concomitant upregulation of Bax and cleaved caspase-3/caspase-9 levels, and ultimately enhances apoptotic cell death in malignant prostate cells (54). VEGF-A, a critical regulator of angiogenesis, plays a pivotal role in promoting tumor-associated vascularization and interacts with PI3K to activate Akt signaling, consequently suppressing apoptotic processes in malignant cells (55, 56). In renal carcinoma cells, miR-205 overexpression results in the significant downregulation of both VEGF-A and PTEN expression. This molecular suppression inhibits PI3K-Akt signaling pathway activation and subsequently induces apoptotic cell death (57, 58). P-glycoprotein (P-gp) represents a membrane-associated drug efflux transporter that is critically involved in mediating multidrug resistance (MDR) phenotypes in cancer cells (59). Li et al. demonstrated that miR-205 overexpression in doxorubicin-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells significantly upregulated the expression of its target gene PTEN. This molecular alteration inhibited PI3K-AKT signaling pathway activity, leading to subsequent downregulation of P-gp expression. Consequently, these molecular changes restored chemosensitivity to doxorubicin and induced apoptotic cell death in the previously resistant malignant cells (60).
In lung, ovarian, gastric, and nasopharyngeal carcinomas, miR-205 functions as an oncogenic regulator. Comprehensive statistical analyses demonstrate that in lung cancer (LC) tissues, miR-205 expression is significantly upregulated, while PTEN expression is concurrently downregulated. miR-205-mediated suppression of PTEN results in the marked upregulation of PI3K and phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) expression levels, ultimately leading to the attenuation of apoptotic processes in malignant pulmonary cells (61). miR-205 overexpression in ovarian or gastric carcinoma cells specifically targets and downregulates PTEN expression, leading to the subsequent upregulation of phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) levels and ultimately resulting in the suppression of apoptotic cell death (62, 63). Mao et al. demonstrated that transfection with miR-205 mimics in nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2 cells significantly upregulated AKT expression while concurrently downregulating PTEN levels, ultimately resulting in the attenuation of apoptotic processes in malignant nasopharyngeal cells (64). Xin et al. identified that the long non-coding RNA LA16c-313D11.11 directly interacts with and suppresses miR-205 activity in endometrial carcinoma, consequently upregulating its target gene PTEN. This molecular interaction indirectly inhibits PI3K-AKT signaling pathway activation and promotes apoptotic cell death in malignant endometrial cells (65).
3.3.2 Other genes
miR-205 has been demonstrated to directly modulate tumor cell apoptosis through the regulation of specific target genes, as comprehensively summarized in Table 2. A particularly significant target is protein kinase C epsilon (PRKCE), a member of the protein kinase C (PKC) family, which has been strongly correlated with unfavorable clinical outcomes in gallbladder carcinoma (GBC) (66). Recent studies have established that PRKCE functions as an anti-apoptotic regulator, inhibiting programmed cell death in malignant cells and consequently promoting tumor progression (67). Zhang et al. have elucidated that the overexpression of miR-205 specifically targets and downregulates PRKCE and BCL-2 expression, while simultaneously upregulating pro-apoptotic markers Bax and cleaved caspase-3. This molecular mechanism significantly enhances the induction of apoptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cells (68). Furthermore, in the context of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), miR-205 targets the PTK7 gene. Overexpression of miR-205 results in decreased levels of PTK7 at both the protein and mRNA levels, significantly increasing the apoptosis rate of ALL cells (69). YAP1 is usually considered as a carcinogen in tumors, which can promote the development of many cancers, including gastric cancer (70). Xian et al. have demonstrated that miR-205 overexpression specifically targets and downregulates YAP1 expression in gastric cancer cell lines SGC-7901 and HGC-27. This regulatory mechanism leads to a significant alteration in the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, characterized by decreased BCL-2 levels and concomitant upregulation of both caspase-3 and BAX, ultimately promoting programmed cell death in gastric carcinoma cells (71). Studies have shown that circRNAs can be used as a microRNA sponge to chelate microRNA, thus affecting the expression of target mRNA and dynamically regulating the process of mRNA translation (72). Xu et al. demonstrated that hsa_circ_0001429 downregulates miR-205 expression in breast carcinoma through molecular sequestration, consequently upregulating its target gene KDM4A and ultimately suppressing apoptotic processes in malignant breast cells (73). Similarly, circ_NOTCH3 interacts with miR-205 and targets KLF12, leading to the downregulation of KLF12 expression in basal-like breast cancer cells. This molecular interaction promotes tumor progression and suppresses apoptotic processes (74).
CHN1, a GTPase-activating protein, has been identified as a potential target of miR-205 through bioinformatics analysis. Liu et al. demonstrated that CHN1 mRNA expression is significantly elevated in cervical carcinoma tissues compared to adjacent non-neoplastic tissues. Downregulation of miR-205 directly targets and upregulates CHN1 expression, consequently suppressing apoptotic processes in cervical cancer cells (23). Niu et al. further demonstrated that miR-205 is regulated by the long non-coding RNA HNRNPU-AS1 in cervical cancer. They observed that elevated HNRNPU-AS1 levels inhibit miR-205 expression, leading to the upregulation of its target gene AXIN2 and subsequent activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This signaling cascade is known to promote apoptotic cell death and suppress cervical cancer progression (75). Similarly, in colorectal carcinoma, miR-205 exhibits oncogenic properties. Jin et al. demonstrated that the long non-coding RNA ZEB1-AS1 directly targets and downregulates miR-205 in colon cancer cells. This molecular interaction results in the upregulation of YAP1 expression and a subsequent increase in apoptotic cell death in malignant colorectal cells (76).
In summary, miR-205 plays a critical role in regulating cellular apoptosis through the modulation of multiple genes and signaling pathways (see Figure 3), exhibiting both oncogenic and tumor-suppressive functions depending on the cellular context (see Figure 4). Recent studies have identified novel apoptosis-related signaling pathways, including those mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress. However, research specifically investigating miR-205’s role in apoptotic regulation remains in its early stages and requires further experimental validation. These findings highlight the necessity for more comprehensive studies to elucidate the precise molecular mechanisms and functional impacts of miR-205.These molecular insights highlight miR-205’s therapeutic potential, as discussed below.
4 The value in cancer treatment
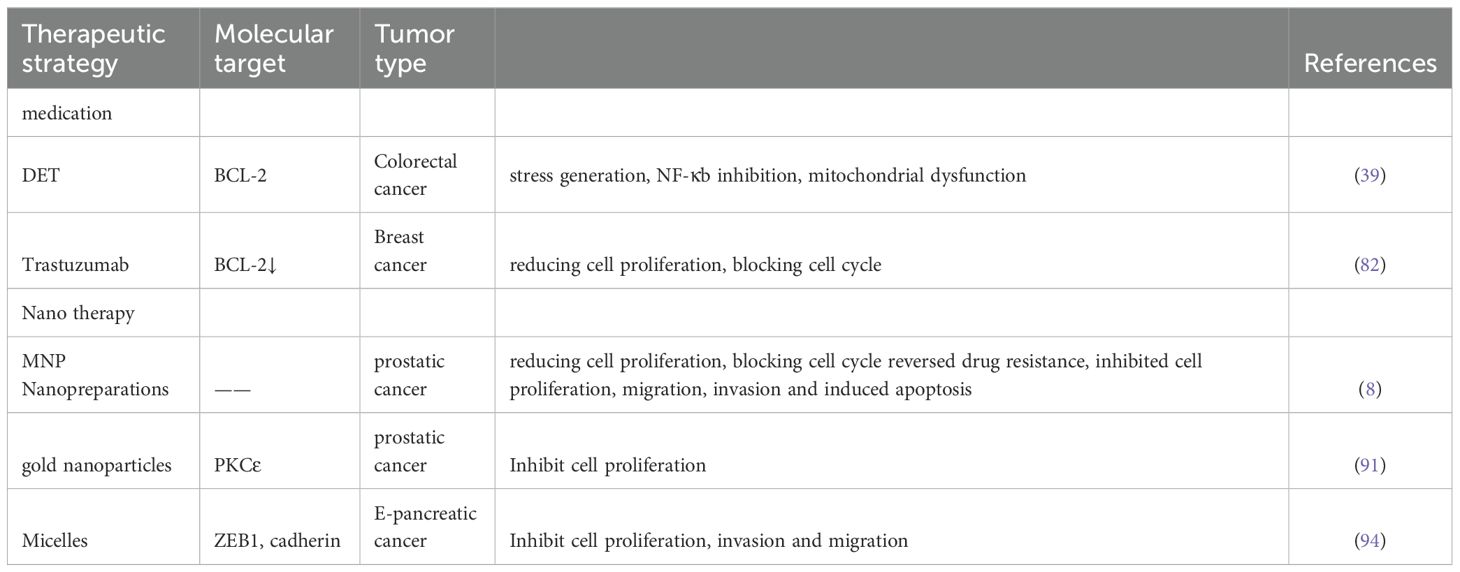
Current therapeutic strategies for cancer, including radiotherapy and chemotherapy, primarily exert their anti-tumor effects by inducing DNA damage to trigger tumor cell death. However, malignant cells with impaired apoptotic pathways frequently develop resistance to these conventional treatments (77). Therefore, exploring novel therapeutic strategies to induce tumor cell apoptosis represents a critical approach for modulating specific molecular pathways and advancing cancer treatment (in Table 3).
4.1 Additive effects with drugs
Pharmacological treatment remains a cornerstone of cancer therapy, as numerous traditional medicinal compounds have demonstrated the capacity to inhibit tumor migration and invasion while inducing apoptosis, thereby suppressing cancer progression. To date, various bioactive compounds derived from traditional medicines have shown significant efficacy in clinical applications. DET, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from the Compositae plant Elephantopus scaber L., promotes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells through mechanisms involving oxidative stress generation, NF-κB inhibition, and mitochondrial dysfunction (78, 79). Ji et al. demonstrated that DET upregulates miR-205 expression in colon cancer cells, thereby promoting apoptotic cell death. Mechanistically, DET enhances miR-205 expression in malignant colon cells and significantly increases chemosensitivity through the miR-205/BCL-2 signaling axis, resulting in potent antitumor effects (39). Trastuzumab is a chemotherapeutic agent currently widely used for the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer (80). In clinical trials, Whittle JR et al. confirmed the downregulated expression of miR-205 in a patient-derived xenograft model obtained from trastuzumab-resistant tumors (81). In order to utilize miR-205 as a therapeutic tool in the treatment of breast cancer, Piovan C et al. observed that higher miR-205 expression was significantly associated with a better prognosis by analyzing 52 patients with HER2+ BC who were clinically treated with adjuvant trastuzumab. In addition, their study demonstrated that restoring miR-205 to reverse trastuzumab resistance could further improve the therapeutic efficacy of trastuzumab by reducing cell proliferation and blocking cell cycle progression (82).
4.2 Role in drug resistance of cancer cells
Many studies have shown that aberrant expression of miRNAs may be associated with resistance to anticancer drugs. Resistance mechanisms are often associated with changes in related proteins such as PTEN, PDCD4, P-gp and MDR1. In turn, changes in proteins may be directly related to mutations, aberrant expression or translocation of miRNA coding genes, which may affect the expression of related miRNAs, leading to alterations in the function of the target mRNAs, thereby affecting the expression of the target proteins, and thus silencing the target genes fundamentally (83). The 3 ‘ UTR of mRNAs contains binding sites for important translational regulatory elements, including miRNAs, cytoplasmic polyadenylation elements (CPEs), proteins and protein complexes. Deletions in the 3’ UTR of the target mRNA also lead to deletion of the miRNA binding site, which results in loss of miRNA function. to et al. demonstrated that in drug-resistant S1MI80 cells, there was an approximately 1500-bp deletion in the 3 ‘ UTR of the downstream target gene of ABCG2 mRNA of hsa- miR-519c, and thus the miRNA was unable to bind to the ABCG2 mRNA binding, resulting in ABCG2 overexpression in drug-resistant tumor cells (84). In addition, drug transport is an important part of drug disposition. p-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) are closely related to multidrug resistance. Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) is a molecular determinant of the pharmacokinetic properties of many human drugs. pan et al. found that miR-328 negatively regulated BCRP expression, and inhibition of miR-328 led to an increase in BCRP protein levels in MCF/MX100 cells, which enhanced drug efflux, decreased cellular drug concentration, and ultimately led to the drug resistance phenotype (85). Currently, most studies on miRNAs related to cellular drug resistance have focused on apoptosis and drug transporters. Once one of the molecules involved in apoptosis is altered, a drug resistance phenotype may emerge. miRNA down- or up-regulation affects the expression of drug transporters, drug targets, or apoptosis- and cell cycle-related components, and thus affects cellular drug resistance (86). For example, Bhatnagar N et al. found that up-regulation of miR-205 and miR-31 down-regulated the downstream target gene Bcl-w and promoted apoptosis levels, restoring the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to chemotherapy (87).
Therefore, miRNAs are expected to serve as biomarkers of chemotherapy resistance.
4.3 miR-205-based nanotherapies
There are two main types of miRNA delivery vectors, viral and non-viral delivery systems. Viral vectors are commonly used for efficient transfer of various genes, oligonucleotides, siRNAs and miRNAs into various target cells or tissues/organs. Several viral vectors such as adenoviral, retroviral and lentiviral vectors have been used for preclinical and clinical evaluation. All of these vectors are very effective in achieving higher delivery efficiencies, however, their poor loading capacity, high toxicity levels and immunogenicity induction limit their clinical translation (88, 89). Therefore, the development of non-viral vectors has received much attention due to the successful and stable delivery of miRNAs.
Nanotechnology-based delivery is a potential method for safely delivering miRNAs and overcoming these associated barriers. Nanotherapies were initially designed primarily to deliver anticancer drugs. However, it has since been discovered that nanoparticles can also successfully deliver nucleic acid molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins/antibodies (90). Chauhan N et al. established a preparation technique/methodology for the successful generation of MNP nanopreparations. It was also demonstrated that the prepared MNP nano-formulations containing miR-205 were safe for use in cellular systems. In two prostate cancer cell lines, C4–2 and PC-3, this preparation achieved excellent cellular internalization by endocytosis, escaping endosomal and lysosomal degradation. In addition, they combined this novel MNP miR-205 formulation with docetaxel. It was found that upregulation of miR-205 successfully reversed drug resistance and sensitized prostate cancer cells to docetaxel treatment. It also significantly inhibited prostate cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion and induced apoptosis (8). Another miR-205 nano-formulation based on gold nanoparticles delivers miR-205 to prostate cancer cells. This reduces protein kinase C Epsilon (PKCϵ) levels and inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation (91). A cationic copolymer formulation (micelles) prepared by Mittal et al. This micellar formulation has higher stability to miR-205 with particle sizes ranging from 62 nm to 122 nm. It was used to deliver miR-205 and gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer to sensitize drug-resistant cells to drug treatment and inhibit cancer cell proliferation. Meanwhile, the expression level of E-cadherin was up-regulated and that of ZEB1 was down-regulated, inhibiting pancreatic cancer cell invasion and migration. In addition, as miR-205 reversed the drug resistance of these cells, in vivo results showed that the tumor growth and weight were significantly reduced after treatment with the gemcitabine-miR-205 complex formulation (92).
In summary, nano-formulation-based delivery of miR-205 is expected to improve the targeted efficacy of cancer therapy.
5 The role of other regulated cell death mechanisms
In addition to apoptosis, cell death can occur through various other mechanisms, including autophagy, necroptosis, necrosis, and ferroptosis.
Autophagy, a regulated form of programmed cell death, constitutes a cellular adaptive mechanism that relies on lysosomal degradation to respond to adverse environmental stimuli (93). Under normal physiological conditions, autophagy can degrade aging organelles and unwanted protein, and recover its products for energy sources and raw materials for anabolism (94). However, dysregulated or excessive autophagy can induce a distinct form of programmed cell death, known as autophagic cell death (95, 96). Recent studies have shown that miR-205 can directly modulate the expression of specific tumor suppressor genes and autophagy-related factors, thereby regulating autophagic processes in cancer cells (97, 98).
Zhuo et al. discovered that miR-205 is significantly upregulated in endometrial carcinoma (PR) cells, where it suppresses PTEN expression, leading to the activation of the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. This molecular cascade subsequently enhances the conversion of autophagy marker LC3-I to LC3-II and upregulates Beclin1 protein levels, ultimately promoting autophagic cell death in malignant cells (99). Furthermore, TP53INP1 directly interacts with key autophagy-related molecules, including LC3 and Atg8 family proteins, thereby facilitating autophagic processes (100). Wang et al. demonstrated that miR-205 upregulation directly targets and suppresses TP53INP1 expression, thereby inhibiting radiation-induced autophagic processes in prostate carcinoma cells (98).
It is crucial to recognize that the interplay between autophagy and apoptosis is highly complex. Indeed, these two cellular processes share common regulatory stimuli and signaling pathways, while exhibiting a degree of mutual inhibition under specific conditions (101).
Beclin1, a critical component in autophagosome formation, serves as a direct substrate for caspase-8. The interaction between Beclin1 and caspase-8 has been observed across multiple cell types and plays a regulatory role in both apoptotic and autophagic processes. For instance, studies have demonstrated that caspase-8-mediated downregulation of Beclin1 expression suppresses autophagic activity during herpes simplex virus infection (102). Furthermore, AKT plays a pivotal role in the cross-regulation of apoptotic and autophagic pathways. Diao et al. demonstrated that AKT phosphorylation not only enhances autophagic activity but also downregulates the expression of key apoptosis-related factors, including Bax and caspases (103).
These findings highlight the complex interplay between miR-205, apoptotic pathways, and autophagic processes, establishing a robust foundation aimed at elucidating their molecular interactions.
Furthermore, in recent years, the concept of “PANoptosis” has emerged as a significant research focus. PANoptosis represents a dynamic form of programmed cell death that integrates molecular features of pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (104). PANoptosis plays a critical role in the pathogenesis and progression of diverse diseases, including infectious diseases, malignancies, neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory conditions (105). Studies have demonstrated that pyroptosis not only suppresses tumor cell proliferation but also establishes a tumor-promoting microenvironment, ultimately facilitating cancer progression (106). Both apoptosis and necroptosis are recognized as essential anti-cancer mechanisms (107). As a higher-order version of these three death pathways, PANoptosis likely plays a crucial role in therapeutic strategies for disease management. Zhang et al. found that upregulating miR-18a expression in MC3T3-E1 cells significantly suppressed the protein levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1-α) and NLRP3, thereby promoting PANoptosis of osteoblasts in response to TNF-α induction (108). Furthermore, Wang et al. analyzed kidney clear cell carcinoma (ccRCC) samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and three Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. They identified seven upregulated miRNAs (hsa-miR-155-5p, hsa-miR-15a-5p, hsa-miR-16-5p, hsa-miR-181a-5p, hsa-miR-21-5p, hsa-miR-210-3p, and hsa-miR-223-3p) and two downregulated miRNAs (hsa-miR-141-3p and hsa-miR-200a-5p), which were significantly associated with PANoptosis-related prognostic features. These findings demonstrate that miRNAs are associated with PANoptosis in tumor cells and may represent a novel therapeutic strategy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) (109). Currently, investigations into the relationship between miRNAs and PANoptosis remain in the preliminary stages. Although the potential link between miR-205 and PANoptosis in tumor cells has not yet been elucidated, it represents a promising area for future research, potentially leading to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment.
6 Conclusions
miRNAs have significantly advanced our understanding of diverse biological processes in organisms. miRNAs play pivotal roles in nearly all biological pathways and are intricately linked to tumor development and progression. Consequently, miRNAs have emerged as promising biomarkers and are being actively developed as novel tools for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic intervention. Recent studies have demonstrated that miR-205 regulates the cell cycle, promotes cellular differentiation, induces apoptosis, and modulates tumorigenesis and cancer progression. miR-205 has been identified as a critical biomarker in oncology, underscoring its clinical significance. Additionally, miR-205 serves as a direct target for certain pharmacological agents, offering potential therapeutic benefits. It can also be used as a direct target for certain drugs to treat diseases. Some studies have proved that miR-205 can be used in combination with some chemotherapeutic drugs to play a role in the treatment of cancer. It can also correct the resistance of many drug-resistant cells to drugs, which is of great significance for the clinical treatment of various cancers. Existing evidence indicates that miR-205 exhibits diverse roles across different cancer types, either promoting or inhibiting apoptosis depending on the specific cancer type and cellular context. The complex regulatory functions of miR-205 and its multifaceted biological effects necessitate further investigation. These findings highlight the potential of targeting miR-205 expression as a promising strategy for cancer therapy.
Apoptosis is a fundamental regulatory mechanism essential for maintaining organismal homeostasis and preventing aberrant cell proliferation. Dysregulation of apoptotic pathways contributes to the pathogenesis of various diseases, including cancer. Extensive research has revealed that miR-205 modulates apoptosis-related signaling pathways and targets key genes to either promote or inhibit apoptosis, thereby influencing cancer progression. The ability of miR-205 to induce apoptosis in malignant cells has significant implications for advancing medical and healthcare practices, making it a rational and increasingly utilized therapeutic target. miR-205 has the potential to enhance the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents; however, comprehensive clinical trials are required to validate its therapeutic potential.
The regulation of apoptosis through miRNA-mediated mechanisms represents a critical approach in cancer treatment. Although significant research has been conducted on the role of miRNAs in apoptosis regulation across various cancers, several unresolved issues remain. For instance: (1) How can drugs that induce apoptosis via miRNA modulation be optimally selected for clinical application? (2) Do these therapeutic agents alter intracellular miRNA levels upon administration, and could they potentially induce adverse effects or secondary diseases? Despite these challenges, miRNA-mediated apoptosis induction holds considerable promise as a future strategy for cancer therapy.
miR-205 plays crucial roles in cancer progression and apoptosis regulation, yet its clinical translation faces significant challenges. First, miR-205 displays distinct functional duality across cancer types: while acting as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer, it exhibits oncogenic properties in specific lung cancer subtypes. This context-dependent functionality underscores the importance of tumor microenvironment in determining miR-205’s actions, highlighting the need for comprehensive characterization of its tissue-specific regulatory networks to develop precise therapeutic strategies.
The major obstacle in miR-205-based therapy involves delivery system optimization. Two critical issues must be addressed: (1) achieving tumor-specific delivery of miR-205 modulators (mimics or inhibitors), and (2) improving their in vivo stability. Future research directions should include: (1) Systematic identification of novel miR-205 targets in emerging cell death pathways (e.g., pyroptosis, cuproptosis) using organoid-AI integration platforms. (2) Comprehensive mapping of miR-205 regulatory networks through single-cell sequencing and CRISPR screening. (3) Development of advanced delivery platforms (e.g., exotic-based or nanomaterial systems) to enhance tumor targeting.
Currently, miR-205 research stands at the critical juncture between basic science and clinical implementation. Interdisciplinary integration of molecular biology, bioinformatics, materials science, and clinical research will be essential to overcome current limitations, ultimately transforming miR-205 into a viable precision oncology tool while advancing our fundamental understanding of cell death regulation.
Author contributions
DC: Writing – original draft. HD: Writing – review & editing. YS: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Inner Mongolia Science and Technology Research Project (2024MS08069); Science and Technology Program of the Joint Fund of Scientific Research for the Public Hospitals of Inner Mongolia Academy of Medical Sciences (2024GLLH0323); the Key Technologies Research and development program of Inner Mongolia (2021GG0170); the general Program of Inner Mongolia Medical University (YKD2021MS006); the 14th Five-Year Plan of Science and Technology Innovation in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (2022YFSH0078); Key project of Inner Mongolia Medical University (YKD2021ZD007); Zhiyuan Talent Program of Inner Mongolia Medical University (ZY0202020 and ZY20242107t); Doctoral Start-up Foundation Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University (YKD2024BSQD026); Undergraduate Teaching Reform Research and Practice Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University in 2024 (NYJXGGSJ20244046); Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (2022MS08004); The Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of the Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University (2022NYFYBS004); The research project of Inner Mongolia Medical University Affiliated Hospital (2023NYFYPY010).
Acknowledgments
Figure support was provided by Figdraw.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Hanahan D and Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. (2000) 100:57–70. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81683-9
3. Lopez J and Tait SW. Mitochondrial apoptosis: killing cancer using the enemy within. Br J cancer. (2015) 112:957–62. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.85
4. Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, and Ghaffari SH. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:5451–65. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27486
5. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. (2004) 116:281–97. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5
6. Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2004) 101:2999–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307323101
7. Feliciano A, Castellvi J, Artero-Castro A, Leal JA, Romagosa C, Hernández-Losa J, et al. miR-125b acts as a tumor suppressor in breast tumorigenesis via its novel direct targets ENPEP, CK2-α, CCNJ, and MEGF9. PloS One. (2013) 8:e76247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076247
8. Chauhan N, Dhasmana A, Jaggi M, Chauhan SC, and Yallapu MM. miR-205: A potential biomedicine for cancer therapy. Cells. (2020) 9(9):1957. doi: 10.3390/cells9091957
9. Lim LP, Glasner ME, Yekta S, Burge CB, and Bartel DP. Vertebrate microRNA genes. Sci (New York NY). (2003) 299:1540. doi: 10.1126/science.1080372
10. Wienholds E, Kloosterman WP, Miska E, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Berezikov E, de Bruijn E, et al. MicroRNA expression in zebrafish embryonic development. Sci (New York NY). (2005) 309:310–1. doi: 10.1126/science.1114519
11. Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell. (2007) 129:1401–14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.040
12. Xiao Y, Humphries B, Yang C, and Wang Z. MiR-205 dysregulations in breast cancer: the complexity and opportunities. Noncoding RNA. (2019) 5(4):53. doi: 10.3390/ncrna5040053
13. Wang D, Zhang Z, O’Loughlin E, Wang L, Fan X, Lai EC, et al. MicroRNA-205 controls neonatal expansion of skin stem cells by modulating the PI(3)K pathway. Nat Cell Biol. (2013) 15:1153–63. doi: 10.1038/ncb2827
14. Yu J, Peng H, Ruan Q, Fatima A, Getsios S, and Lavker RM. MicroRNA-205 promotes keratinocyte migration via the lipid phosphatase SHIP2. FASEB journal: Off Publ Fed Am Societies Exp Biol. (2010) 24:3950–9. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-157404
15. Yu J, Ryan DG, Getsios S, Oliveira-Fernandes M, Fatima A, and Lavker RM. MicroRNA-184 antagonizes microRNA-205 to maintain SHIP2 levels in epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2008) 105:19300–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803992105
16. Gandellini P, Profumo V, Casamichele A, Fenderico N, Borrelli S, Petrovich G, et al. miR-205 regulates basement membrane deposition in human prostate: implications for cancer development. Cell Death differentiation. (2012) 19:1750–60. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.56
17. Teta M, Choi YS, Okegbe T, Wong G, Tam OH, Chong MM, et al. Inducible deletion of epidermal Dicer and Drosha reveals multiple functions for miRNAs in postnatal skin. Dev (Cambridge England). (2012) 139:1405–16. doi: 10.1242/dev.070920
18. Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. (2008) 10:593–601. doi: 10.1038/ncb1722
19. Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, Inoue N, Machida H, Nakayama T, et al. MiRNA-205 modulates cellular invasion and migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Trans Med. (2011) 9:30. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-30
20. Li C, Finkelstein D, and Sherr CJ. Arf tumor suppressor and miR-205 regulate cell adhesion and formation of extraembryonic endoderm from pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2013) 110:E1112–21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302184110
21. Vosgha H, Salajegheh A, Smith RA, and Lam AK. The important roles of miR-205 in normal physiology, cancers and as a potential therapeutic target. Curr Cancer Drug targets. (2014) 14:621–37. doi: 10.2174/156800961407140926105634
22. Iorio MV, Casalini P, Piovan C, Di Leva G, Merlo A, Triulzi T, et al. microRNA-205 regulates HER3 in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. (2009) 69:2195–200. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2920
23. Liu J, Li Y, Chen X, Xu X, Zhao H, Wang S, et al. Upregulation of miR-205 induces CHN1 expression, which is associated with the aggressive behaviour of cervical cancer cells and correlated with lymph node metastasis. BMC cancer. (2020) 20:1029. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07478-w
24. Wang X, Yu M, Zhao K, He M, Ge W, Sun Y, et al. Upregulation of MiR-205 under hypoxia promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting ASPP2. Cell Death disease. (2016) 7:e2517. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.412
25. Fan L, Li B, Li Z, and Sun L. Identification of autophagy related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA-subtypes network with radiotherapy responses and tumor immune microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Genet. (2021) 12:730003. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.730003
26. Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjøt L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, et al. Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200 family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J cancer. (2011) 128:1327–34. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25461
27. Kim ES, Choi JY, Hwang SJ, and Bae IH. Hypermethylation of miR-205-5p by IR Governs Aggressiveness and Metastasis via Regulating Bcl-w and Src. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2019) 14:450–64. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.12.013
28. Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Sci (New York NY). (1995) 267:1456–62. doi: 10.1126/science.7878464
29. Das S, Shukla N, Singh SS, Kushwaha S, and Shrivastava R. Mechanism of interaction between autophagy and apoptosis in cancer. Apoptosis: an Int J programmed Cell Death. (2021) 26:512–33. doi: 10.1007/s10495-021-01687-9
30. Rudin CM and Thompson CB. Apoptosis and disease: regulation and clinical relevance of programmed cell death. Annu Rev Med. (1997) 48:267–81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.48.1.267
31. Tait SW and Green DR. Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2010) 11:621–32. doi: 10.1038/nrm2952
32. Cao K and Tait SWG. Apoptosis and cancer: force awakens, phantom menace, or both? Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. (2018) 337:135–52. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.12.003
33. Castillo Ferrer C, Berthenet K, and Ichim G. Apoptosis - Fueling the oncogenic fire. FEBS J. (2021) 288:4445–63. doi: 10.1111/febs.15624
34. Sciarrillo R, Wojtuszkiewicz A, Assaraf YG, Jansen G, Kaspers GJL, Giovannetti E, et al. The role of alternative splicing in cancer: From oncogenesis to drug resistance. Drug resistance updates: Rev commentaries antimicrobial Anticancer chemotherapy. (2020) 53:100728. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100728
35. Fuchs Y and Steller H. Live to die another way: modes of programmed cell death and the signals emanating from dying cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2015) 16:329–44. doi: 10.1038/nrm3999
36. Zhang X, Pan Y, Fu H, and Zhang J. microRNA-205 and microRNA-338-3p reduces cell apoptosis in prostate carcinoma tissue and LNCaP prostate carcinoma cells by directly targeting the B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) gene. Med Sci monitor: Int Med J Exp Clin Res. (2019) 25:1122–32. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912148
37. Tian L, Zhang J, Ge J, Xiao H, Lu J, Fu S, et al. MicroRNA-205 suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol (Northwood London England). (2014) 31:785. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0785-3
38. Wu Y, Wang W, Hu W, Xu W, Xiao G, Nie Q, et al. MicroRNA-205 suppresses the growth of adrenocortical carcinoma SW-13 cells via targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Rep. (2015) 34:3104–10. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4295
39. Ji H, Zhang K, Pan G, Li C, Li C, Hu X, et al. Deoxyelephantopin Induces Apoptosis and Enhances Chemosensitivity of Colon Cancer via miR-205/Bcl2 Axis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(9):5051. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095051
40. Qiu C, Huang F, Zhang Q, Chen W, and Zhang H. miR-205-3p promotes proliferation and reduces apoptosis of breast cancer MCF-7 cells and is associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer patients. J Clin Lab analysis. (2019) 33:e22966. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22966
41. Weng JR, Bai LY, Chiu SJ, Chiu CF, Lin WY, Hu JL, et al. Divaricoside exerts antitumor effects, in part, by modulating mcl-1 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2019) 17:151–9. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.01.004
42. Shi Z, Zhang P, Lu X, Zhu C, Chen C, Zhao S, et al. Down-regulation of miR-205-5p enhances pro-apoptotic effect of 3-bromopyruvate on human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2Z cells. Nan fang yi ke da xue xue bao = J South Med University. (2019) 39:1166–72. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.10.06
43. Zarogoulidis P, Petanidis S, Kioseoglou E, Domvri K, Anestakis D, and Zarogoulidis K. MiR-205 and miR-218 expression is associated with carboplatin chemoresistance and regulation of apoptosis via Mcl-1 and Survivin in lung cancer cells. Cell signalling. (2015) 27:1576–88. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.04.009
44. Niture S, Dong X, Arthur E, Chimeh U, Niture SS, Zheng W, et al. Oncogenic role of tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 8 (TNFAIP8). Cells. (2018) 8(1):9. doi: 10.3390/cells8010009
45. Garcia JA, Ferreira HL, Vieira FV, Gameiro R, Andrade AL, Eugênio FR, et al. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced protein 8 (TNFAIP8) expression associated with cell survival and death in cancer cell lines infected with canine distemper virus. Veterinary Comp Oncol. (2017) 15:336–44. doi: 10.1111/vco.12168
46. Yang J, Huang Y, Dong B, and Dai Y. Long noncoding RNA DLEU2 drives the Malignant behaviors of thyroid cancer through mediating the miR-205-5p/TNFAIP8 axis. Endocrine connections. (2021) 10:471–83. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0046
47. Li YZ, Mou P, Shen Y, Gao LD, Chen XX, and Wei RL. Effect of miR-184 and miR-205 on the tumorigenesis of conjunctival mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma through regulating RasL10B and TNFAIP8. Int J ophthalmology. (2022) 15:1–8. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2022.01.01
48. Medler J and Wajant H. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 (TNFR2): an overview of an emerging drug target. Expert Opin Ther targets. (2019) 23:295–307. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1586886
49. Siegmund D, Wagner J, and Wajant H. TNF receptor associated factor 2 (TRAF2) signaling in cancer. Cancers. (2022) 14(16):4055. doi: 10.3390/cancers14164055
50. Carpentier I, Declercq W, Malinin NL, Wallach D, Fiers W, and Beyaert R. TRAF2 plays a dual role in NF-kappaB-dependent gene activation by mediating the TNF-induced activation of p38 MAPK and IkappaB kinase pathways. FEBS letters. (1998) 425:195–8. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00226-9
51. Tanic M, Zajac M, Gómez-López G, Benítez J, and Martínez-Delgado B. Integration of BRCA1-mediated miRNA and mRNA profiles reveals microRNA regulation of TRAF2 and NFκB pathway. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2012) 134:41–51. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1905-4
52. Zhang HP, Jiang RY, Zhu JY, Sun KN, Huang Y, Zhou HH, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway: an important driver and therapeutic target in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Tokyo Japan). (2024) 31(4):539–51. doi: 10.1007/s12282-024-01567-5
53. Jung BK, Kim YJ, Hong J, Chang HG, Yoon AR, and Yun CO. ErbB3-targeting oncolytic adenovirus causes potent tumor suppression by induction of apoptosis in cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(13):7127. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137127
54. Li J, Cao X, Chu T, Lin K, Chen L, Lv J, et al. The circHMGCS1-miR-205-5p-ErBB3 axis mediated the Sanggenon C-induced anti-proliferation effects on human prostate cancer. Pharmacol Res. (2023) 187:106584. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106584
55. Kang Y, Li H, Liu Y, and Li Z. Regulation of VEGF-A expression and VEGF-A-targeted therapy in Malignant tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2024) 150:221. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05714-5
56. Ruan GX and Kazlauskas A. Axl is essential for VEGF-A-dependent activation of PI3K/Akt. EMBO J. (2012) 31:1692–703. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.21
57. Huang J, Wang X, Wen G, and Ren Y. miRNA−205−5p functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating VEGFA and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in renal carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. (2019) 42:1677–88. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7307
58. Wang H, Chen B, Duan B, Zheng J, and Wu X. miR−205 suppresses cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis via regulation of the PTEN/AKT pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 14:3343–9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5589
59. Nanayakkara AK, Follit CA, Chen G, Williams NS, Vogel PD, and Wise JG. Targeted inhibitors of P-glycoprotein increase chemotherapeutic-induced mortality of multidrug resistant tumor cells. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:967. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19325-x
60. Li M, Li ZH, Song J, Li X, Zhai P, Mu X, et al. miR-205 reverses MDR-1 mediated doxorubicin resistance via PTEN in human liver cancer hepG2 cells. Cell J. (2022) 24:112–9. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.7231
61. Zhu H, Xu Y, Li M, and Chen Z. Inhibition sequence of miR-205 hinders the cell proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells by regulating PETN-mediated PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Mol Biotechnol. (2021) 63:587–94. doi: 10.1007/s12033-021-00321-y
62. Shi X, Xiao L, Mao X, He J, Ding Y, Huang J, et al. miR-205-5p mediated downregulation of PTEN contributes to cisplatin resistance in C13K human ovarian cancer cells. Front Genet. (2018) 9:555. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00555
63. Yao L, Shi W, and Gu J. Micro-RNA 205-5p is involved in the progression of gastric cancer and targets phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) in SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cells. Med Sci monitor: Int Med J Exp Clin Res. (2019) 25:6367–77. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915970
64. Mao Y, Wu S, Zhao R, and Deng Q. MiR-205 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by activation of AKT signalling. J Int Med Res. (2016) 44:231–40. doi: 10.1177/0300060515576556
65. Xin W, Zhao S, Han X, Zhao P, Yu H, Gao X, et al. lncRNA LA16c−313D11.11 modulates the development of endometrial cancer by binding to and inhibiting microRNA−205−5p function and indirectly increasing PTEN activity. Int J Oncol. (2020) 57:355–63. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5046
66. Pichini S, Busardò FP, Ceccanti M, Tarani L, and Pacifici R. Unreliable estimation of prevalence of fetal alcohol syndrome. Lancet Global Health. (2017) 5:e574. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30173-0
67. Kumar S, Ingle H, Mishra S, Mahla RS, Kumar A, Kawai T, et al. IPS-1 differentially induces TRAIL, BCL2, BIRC3 and PRKCE in type I interferons-dependent and -independent anticancer activity. Cell Death disease. (2015) 6:e1758. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.122
68. Zhang GF, Wu JC, Wang HY, Jiang WD, and Qiu L. Overexpression of microRNA-205-5p exerts suppressive effects on stem cell drug resistance in gallbladder cancer by down-regulating PRKCE. Bioscience Rep. (2020) 40(9):BSR20194509. doi: 10.1042/BSR20194509
69. Song Y, Guo NH, and Zheng JF. LncRNA-MALAT1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells via miR-205-PTK7 pathway. Pathol Int. (2020) 70:724–32. doi: 10.1111/pin.12993
70. Kapoor A, Yao W, Ying H, Hua S, Liewen A, Wang Q, et al. Yap1 activation enables bypass of oncogenic Kras addiction in pancreatic cancer. Cell. (2014) 158:185–97. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.003
71. Xian XS, Wang YT, and Jiang XM. Propofol inhibits proliferation and invasion of stomach cancer cells by regulating miR-205/YAP1 axis. Cancer Manage Res. (2020) 12:10771–9. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S270344
72. Thamjamrassri P and Ariyachet C. Circular RNAs in cell cycle regulation of cancers. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(11):6094. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116094
73. Xu Y, Qian C, Liu C, Fu Y, Zhu K, Niu Z, et al. Investigation of the Mechanism of hsa_circ_000–1429 Adsorbed miR-205 to Regulate KDM4A and Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis. Contrast media Mol imaging. (2022) 2022:4657952. doi: 10.1155/2022/4657952
74. Guan B, Li Q, Zhang HZ, and Yang HS. circ_NOTCH3 functions as a protooncogene competing with miR-205-5p, modulating KLF12 expression and promoting the development and progression of basal-like breast carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:602694. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.602694
75. Niu Z, Wang F, Lv S, Lv Y, Liu M, Fu L, et al. HNRNPU-AS1 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis via the microRNA 205-5p/AXIN2 axis and wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cervical cancer. Mol Cell Biol. (2021) 41:e0011521. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00115-21
76. Jin Z and Chen B. LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis. Open Med (Warsaw Poland). (2020) 15:175–84. doi: 10.1515/med-2020-0026
77. Matos AJ and Santos AA. Advances in the understanding of the clinically relevant genetic pathways and molecular aspects of canine mammary tumours: part 1. Proliferation, apoptosis and DNA repair. Veterinary J (London England: 1997). (2015) 205:136–43. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.02.004
78. Lee KH, Cowherd CM, and Wolo MT. Antitumor agents. XV: Deoxyelephantopin, an antitumor principle from Elephantopus carolinianus Willd. J Pharm Sci. (1975) 64:1572–3. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600640938
79. Mehmood T, Maryam A, Zhang H, Li Y, Khan M, and Ma T. Deoxyelephantopin induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells via oxidative stress, NF-κB inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction. BioFactors (Oxford England). (2017) 43:63–72. doi: 10.1002/biof.1324
80. Arteaga CL, Sliwkowski MX, Osborne CK, Perez EA, Puglisi F, and Gianni L. Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: current status and future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2011) 9:16–32. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.177
81. Whittle JR, Lewis MT, Lindeman GJ, and Visvader JE. Patient-derived xenograft models of breast cancer and their predictive power. Breast Cancer research: BCR. (2015) 17:17. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0523-1
82. Cataldo A, Piovan C, Plantamura I, D’Ippolito E, Camelliti S, Casalini P, et al. MiR-205 as predictive biomarker and adjuvant therapeutic tool in combination with trastuzumab. Oncotarget. (2018) 9:27920–8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24723
83. Allen KE and Weiss GJ. Resistance may not be futile: microRNA biomarkers for chemoresistance and potential therapeutics. Mol Cancer Ther. (2010) 9:3126–36. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0397
84. To KK, Zhan Z, Litman T, and Bates SE. Regulation of ABCG2 expression at the 3’ untranslated region of its mRNA through modulation of transcript stability and protein translation by a putative microRNA in the S1 colon cancer cell line. Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 28:5147–61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00331-08
85. Pan YZ, Morris ME, and Yu AM. MicroRNA-328 negatively regulates the expression of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in human cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. (2009) 75:1374–9. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.054163
86. Wu X and Xiao H. miRNAs modulate the drug response of tumor cells. Sci China Ser C Life Sci. (2009) 52:797–801. doi: 10.1007/s11427-009-0114-4
87. Bhatnagar N, Li X, Padi SK, Zhang Q, Tang MS, and Guo B. Downregulation of miR-205 and miR-31 confers resistance to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death disease. (2010) 1:e105. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2010.85
88. Zhang Y, Wang Z, and Gemeinhart RA. Progress in microRNA delivery. J Controlled release: Off J Controlled Release Society. (2013) 172:962–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.09.015
89. Yang N. An overview of viral and nonviral delivery systems for microRNA. Int J Pharm Invest. (2015) 5:179–81. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.167646
90. Shu Y, Pi F, Sharma A, Rajabi M, Haque F, Shu D, et al. Stable RNA nanoparticles as potential new generation drugs for cancer therapy. Advanced Drug delivery Rev. (2014) 66:74–89. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.11.006
91. Hao L, Patel PC, Alhasan AH, Giljohann DA, and Mirkin CA. Nucleic acid-gold nanoparticle conjugates as mimics of microRNA. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse Germany). (2011) 7:3158–62. doi: 10.1002/smll.201101018
92. Mittal A, Chitkara D, Behrman SW, and Mahato RI. Efficacy of gemcitabine conjugated and miRNA-205 complexed micelles for treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer. Biomaterials. (2014) 35:7077–87. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.053
93. Yang Z and Klionsky DJ. Eaten alive: a history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. (2010) 12:814–22. doi: 10.1038/ncb0910-814
94. Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, and Klionsky DJ. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature. (2008) 451:1069–75. doi: 10.1038/nature06639
95. Zhang SW, Feng JN, Cao Y, Meng LP, and Wang SL. Autophagy prevents autophagic cell death in Tetrahymena in response to oxidative stress. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. (2015) 36(3):167–73.
96. Kroemer G and Levine B. Autophagic cell death: the story of a misnomer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 9:1004–10. doi: 10.1038/nrm2529
97. Wu L, Quan W, Yue G, Luo Q, Peng D, Pan Y, et al. Identification of a novel six autophagy-related genes signature for the prognostic and a miRNA-related autophagy predictor for anti-PD-1 therapy responses in prostate cancer. BMC cancer. (2021) 21:15. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07725-0
98. Wang W, Liu J, and Wu Q. MiR-205 suppresses autophagy and enhances radiosensitivity of prostate cancer cells by targeting TP53INP1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2016) 20(1):92–100.
99. Zhuo Z and Yu H. miR-205 inhibits cell growth by targeting AKT-mTOR signaling in progesterone-resistant endometrial cancer Ishikawa cells. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:28042–51. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15886
100. Seillier M, Peuget S, Gayet O, Gauthier C, N’Guessan P, Monte M, et al. TP53INP1, a tumor suppressor, interacts with LC3 and ATG8-family proteins through the LC3-interacting region (LIR) and promotes autophagy-dependent cell death. Cell Death differentiation. (2012) 19:1525–35. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.30
101. Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT, and Tang D. The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death differentiation. (2011) 18:571–80. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.191
102. Marino-Merlo F, Klett A, Papaianni E, Drago SFA, Macchi B, Rincón MG, et al. Caspase-8 is required for HSV-1-induced apoptosis and promotes effective viral particle release via autophagy inhibition. Cell Death differentiation. (2023) 30:885–96. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01084-y
103. Diao W, Guo Q, Zhu C, Song Y, Feng H, Cao Y, et al. USP18 promotes cell proliferation and suppressed apoptosis in cervical cancer cells via activating AKT signaling pathway. BMC cancer. (2020) 20:741. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07241-1
104. Samir P, Malireddi RKS, and Kanneganti TD. The PANoptosome: A deadly protein complex driving pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis). Front Cell infection Microbiol. (2020) 10:238. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00238
105. Rajesh Y and Kanneganti TD. Innate immune cell death in neuroinflammation and alzheimer’s disease. Cells. (2022) 11(12):1885. doi: 10.3390/cells11121885
106. Yu P, Zhang X, Liu N, Tang L, Peng C, and Chen X. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal transduction targeted Ther. (2021) 6:128. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00507-5
107. Zhu P, Ke ZR, Chen JX, Li SJ, Ma TL, and Fan XL. Advances in mechanism and regulation of PANoptosis: Prospects in disease treatment. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1120034. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1120034
108. Zhang W, Xia CL, Qu YD, Li JX, Liu JB, Ou SJ, et al. MicroRNA-18a regulates the Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PANoptosis) of osteoblasts induced by tumor necrosis factor-α via hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Int immunopharmacology. (2024) 128:111453. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111453
109. Wang Y, Zhou J, Zhang N, Zhu Y, Zhong Y, Wang Z, et al. A Novel Defined PANoptosis-Related miRNA Signature for Predicting the Prognosis and Immune Characteristics in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A miRNA Signature for the Prognosis of ccRCC. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(11):9392. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119392
Keywords: apoptosis, cancer, microRNA, miR-205, programmed cell death
Citation: Chai D, Du H and Shi Y (2025) The progress of miR-205 regulating apoptosis in cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1532659. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1532659
Received: 22 November 2024; Accepted: 25 August 2025;
Published: 10 September 2025.
Edited by:
Anca Maria Cimpean, Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaReviewed by:
Mercedes Bermúdez, Autonomous University of Chihuahua, MexicoNeeraj Chauhan, The University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, United States
Copyright © 2025 Chai, Du and Shi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yingxu Shi, c2hpeWluZ3h1QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
 Dandan Chai
Dandan Chai Hua Du
Hua Du Yingxu Shi
Yingxu Shi