- 1Department of Infectious Disease, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
- 2Department of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Purpose: This study investigated the clinical features, risk factors, and recurrence of immune-mediated liver injury (IMLI) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
Methods: A retrospective cohort of 274 NSCLC patients receiving ICIs was analyzed. Baseline inflammatory markers, including white blood cell count (WBC), albumin levels, and prognostic nutritional index (PNI), were assessed for their association with IMLI. Risk factors were identified using logistic regression, and recurrence outcomes were analyzed.
Results: IMLI incidence was 35.4%, with 15.5% of cases classified as grade 3-4. WBC ≤11.0×109/L (P<0.001) and albumin ≥35 g/L (P<0.001) were independent predictors of IMLI. Among patients with IMLI, 28.9% experienced recurrence, with 17.9% classified as grade 3-4. Recurrence risk was not significantly higher than the initial onset (P=0.21).
Conclusion: Low baseline inflammatory status predicts IMLI in NSCLC patients undergoing ICI therapy. Monitoring baseline inflammatory markers can guide risk stratification, and re-challenging ICIs in selected patients appears feasible without significantly increasing recurrence risk.
Background
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), offering improved survival outcomes by enhancing T-cell mediated anti-tumor immunity (1). However, ICIs can also induce immune-related adverse events (irAEs) (2, 3), including immune-mediated liver injury (IMLI) (4–7). IMLI is a potentially serious side effect that complicates the clinical management of NSCLC patients undergoing ICI therapy (2, 8). The incidence of IMLI in NSCLC patients has been reported to vary widely, ranging from 15% to 50%, with a significant proportion of cases being severe (grade 3-4) (2, 9–12). While the pathophysiology of IMLI is still under investigation, the inflammatory status of patients prior to ICI therapy may play a role in the development of these adverse events (13, 14).
Previous studies have demonstrated the potential for inflammatory biomarkers, such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and absolute eosinophil count (AEC), to predict the occurrence of various irAEs (10, 15, 16). However, the relationship between baseline inflammatory status and IMLI occurrence in NSCLC patients remains unclear. Furthermore, the impact of recurrence on the management of IMLI has not been extensively studied. This study seeks to address these gaps by evaluating the clinical features, risk factors, and recurrence of IMLI in NSCLC patients treated with ICIs, and to explore the predictive value of pre-treatment inflammatory status for IMLI.
Methods
Study design and population
This was a retrospective cohort study conducted at the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University from November 2019 to November 2021. A total of 274 NSCLC patients who received treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) at our institution were included in the analysis. All patients had histologically or cytologically confirmed NSCLC and were treated with ICIs either alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
Data collection
Clinical and laboratory data were collected from electronic medical records. Baseline inflammatory markers, including white blood cell count (WBC), albumin level, and prognostic nutritional index (PNI), were recorded. Liver function tests, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and total bilirubin, were monitored during ICI therapy to assess the occurrence of immune-mediated liver injury.
Outcome Measures
The primary outcome was the occurrence of IMLI, which was defined according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. Patients who developed liver injury during ICI treatment were classified into different grades based on the severity of liver damage. The secondary outcome was the recurrence of IMLI, defined as the reappearance of liver injury after resolution of the initial episode. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were also calculated.
Statistical analysis
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to identify potential risk factors for IMLI development. Variables with a P-value <0.05 in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate model. Univariate analysis of survival and calculation of hazard ratios was performed using Cox’s proportional hazards model. Multivariate analysis of survival was carried out using a backward conditional approach: variables with a p-value > 0.10 were removed in a stepwise fashion to leave only those with an independent significant relationship with survival. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to plot survival curves. Log-rank testing and Mantel–Byar time-dependent analysis were applied to assess statistically significant differences in survival. Odds ratios and Student’s t-test were used to assess associations between variables.All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version [26.0 version], SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL), and a P-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient Characteristics
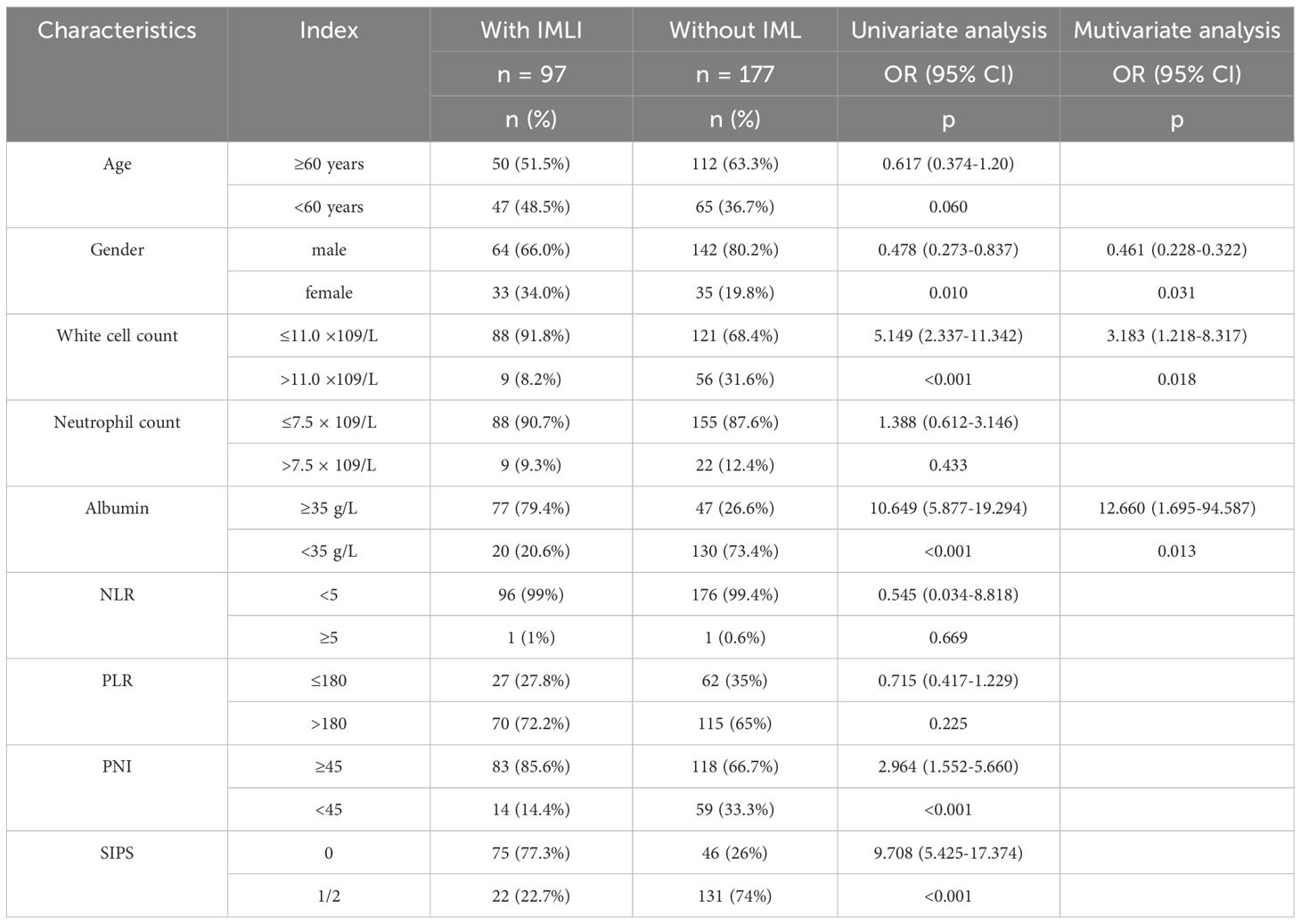
A total of 274 NSCLC patients were included in the study, with a median age of 61 ± 11 years (range:26–86 years). Among these patients, 206 (75%) were male, and 68 were female. The majority of patients were diagnosed with stage IV NSCLC (72%). 92% of patients received PD-1 inhibitor therapy, while the remaining patients received PD-L1 inhibitor or CTLA-4 inhibitor therapy (Table 1). Patients receiving combined targeted therapy (anti-angiogenic drugs, EGFR inhibitors) had a higher incidence of liver dysfunction, although the difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.056).
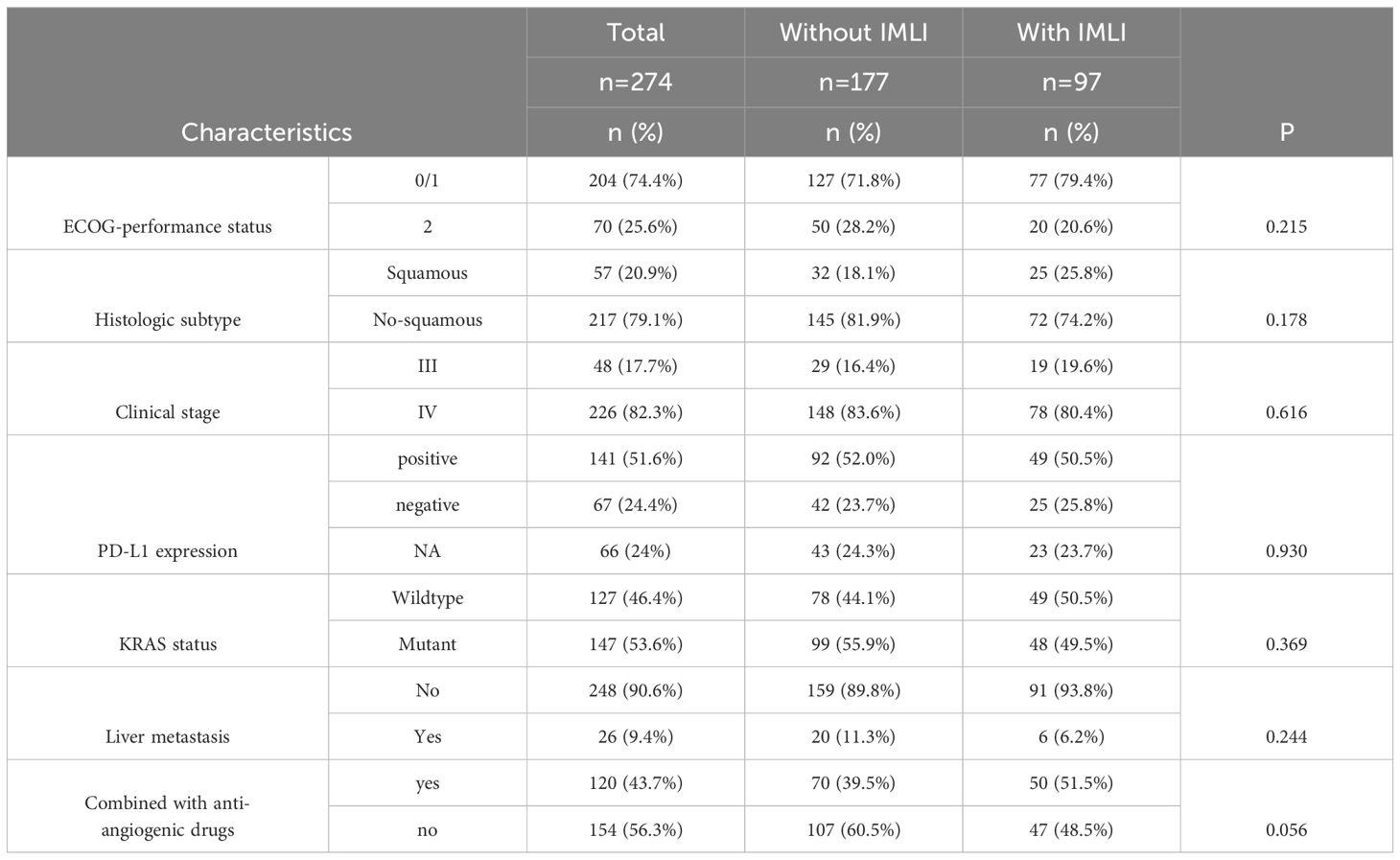
Table 1. Patient characteristics and the relationship between routine clinicopathological variables and incidence of immune-related adverse events in patients with NSCLC treated with ICIs.
Risk factors for IMLI development
The incidence of IMLI was 35.4% (97/274), with 15.5% (15/97) classified as grade 3–4 liver injury. The median time to onset of IMLI was 85 ± 82 days (range: 15–720 days).
Patients with IMLI exhibited varying degrees of immune-related damage to other organs, including hyperthyroidism (7.1%), proteinuria (12.7%), elevated creatinine (23.8%), elevated cardiac enzymes (7.1%), and skin toxicity (0.8%). The prevalence of fatty liver in IMLI patients was 20%. Methylprednisolone treatment was administered to 47 patients (48.5%).
Univariate analysis identified several baseline inflammatory markers significantly associated with IMLI occurrence. White blood cell count ≤11.0×109/L (P<0.001), albumin ≥35 g/L (P<0.001), and PNI ≥45 (P<0.05) were found to be significant predictors of IMLI development. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that WBC ≤11.0×109/L (P<0.001) and albumin ≥35 g/L (P<0.001) were independent risk factors for the development of IMLI (Table 2).
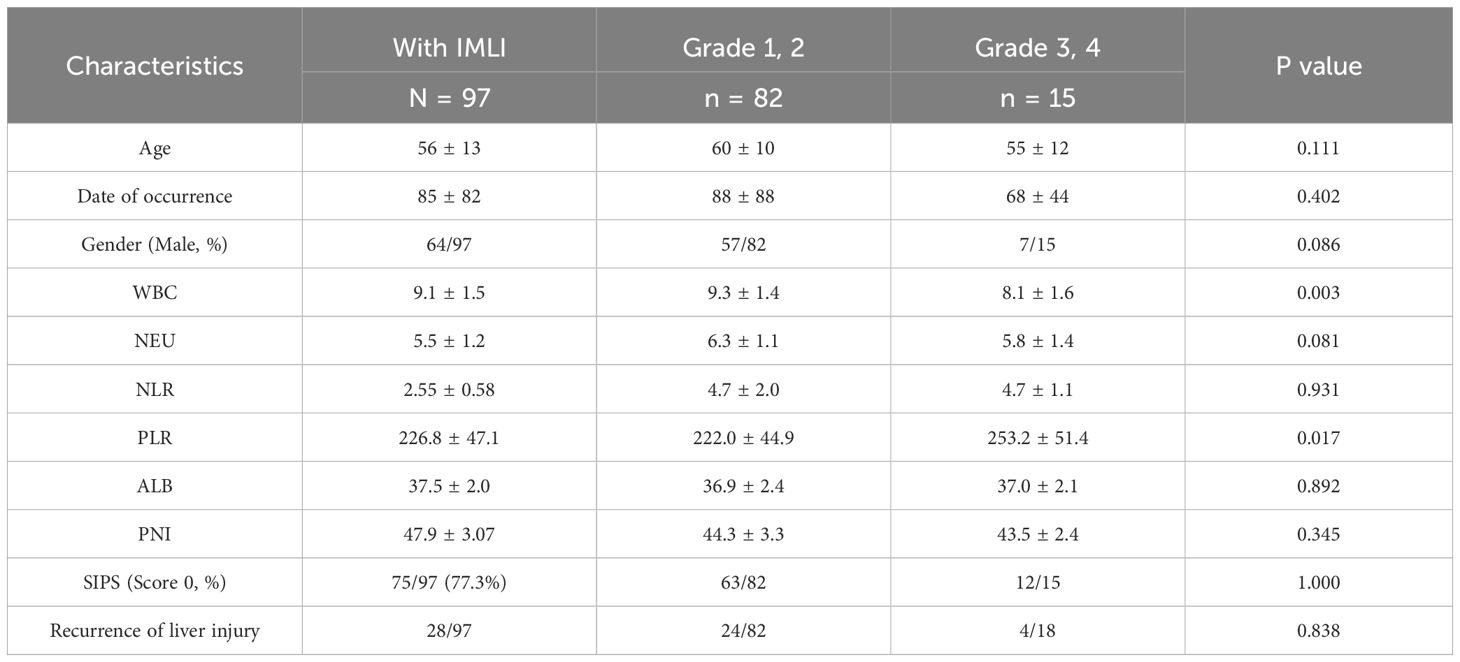
Incidence of IMLI
The overall incidence of IMLI in this cohort was 35.4% (n=97). Among these, 84.5%(82/97) had grade 1–2 IMLI, and 15.5%(15/97) experienced grade 3–4 IMLI. Comparison between patients with grade 1–2 and grade 3–4 liver injury revealed no significant differences in sex, age, time to liver injury onset, or recurrence of liver dysfunction. However, among inflammation-related biomarkers, white blood cell (WBC) count (P = 0.003) and PLR (P = 0.017) were significantly higher in the grade 3–4 liver injury group. In contrast, neutrophil count, NLR, PNI, and SIPS (score 0) showed no significant differences between the two groups (Table 3).
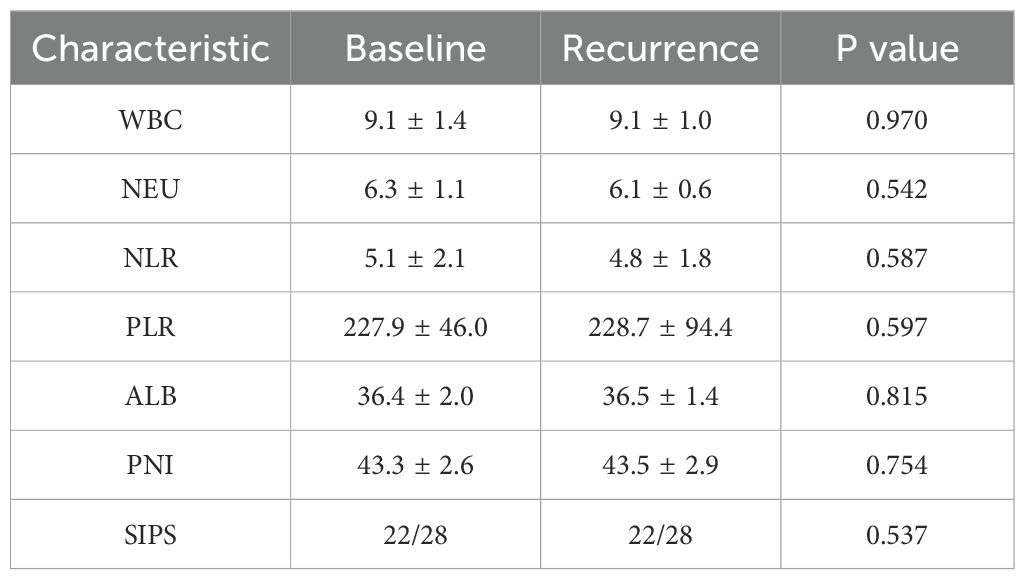
Recurrence of IMLI
Among the 97 patients with IMLI, 28.9% (n=28) experienced a recurrence of liver injury, with 17.9% (n=5) of these recurrences classified as grade 3-4. The recurrence rate of IMLI was not significantly higher than the initial onset of liver injury (P=0.21). The inflammatory status at the time of recurrence was similar to that at the time of initial injury (Table 4), indicating that the immune state had returned to baseline following treatment resolution.
Survival analysis
The median follow-up time was 15.1 months. Patients with irAEs had a significantly longer median PFS (16.1 months vs. 5.7 months, P<0.001) and OS (23.6 months vs. 10.1 months, P<0.001) compared to those without irAEs. However, there were no significant differences in PFS and OS between patients with mild and severe AEs (P=0.560 and P=0.539, respectively) (Figure 1).
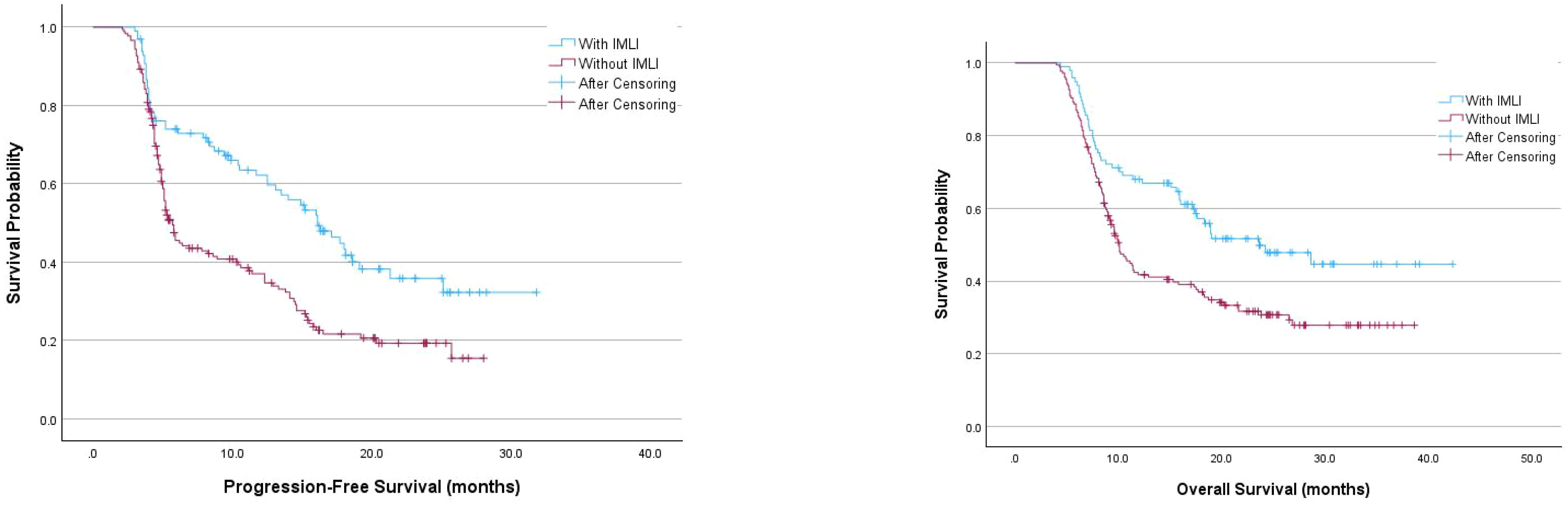
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier survival curves examining the relationship between the occurrence of immune-related IMLI and progression-free survival or overall survival in patients.
Discussion
This study analyzed a cohort of 274 NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) to investigate the clinical characteristics, risk factors, and recurrence patterns of immune-mediated liver injury (IMLI). The overall incidence of IMLI was 35.4%, with 15.5% of cases classified as grade 3–4 liver injury. Our findings highlight the significant role of baseline inflammatory status in predicting IMLI occurrence, as patients who developed IMLI exhibited a markedly lower inflammatory status prior to treatment compared to those without IMLI. Specifically, univariate analysis identified several baseline markers, including white blood cell count (WBC ≤11.0×109/L), albumin levels (≥35 g/L), and the prognostic nutritional index (PNI ≥45), as significantly associated with IMLI. Multivariate analysis further confirmed that lower WBC (P = 0.018) and higher albumin levels (P = 0.013) were independent predictors of IMLI. These findings underscore the importance of baseline systemic inflammation as a key determinant of IMLI risk during ICI therapy.
Beyond traditional inflammatory markers, we also evaluated systemic inflammation-related biomarkers, including the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and systemic inflammation prognostic score (SIPS). While NLR and SIPS did not differ significantly between patients with and without IMLI, PLR was significantly elevated in patients with severe (grade 3–4) liver injury compared to those with mild to moderate (grade 1–2) liver injury (P = 0.017). Additionally, WBC count was significantly higher in severe cases (P = 0.003). These findings suggest that while a lower baseline inflammatory status predisposes patients to IMLI, more severe cases may be characterized by an exaggerated immune response once liver injury is initiated. This observation aligns with previous reports suggesting that excessive immune activation contributes to severe immune-related adverse events (irAEs) (17).
The mechanistic basis for this association likely involves the interplay between baseline immune surveillance and the heightened immune activation induced by ICIs (18). By inhibiting the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways, ICIs enhance T-cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity but can also lead to immune dysregulation, resulting in irAEs such as IMLI (5, 6, 17). Patients with lower baseline inflammatory markers, including reduced WBC, albumin, and PNI, may have weaker baseline immune surveillance, making them more susceptible to dysregulated immune responses following ICI initiation. This hypothesis aligns with prior studies linking inflammatory biomarkers such as NLR and PLR to irAE development (19–21). Our findings extend this evidence by highlighting the predictive value of these markers specifically in IMLI. Furthermore, the association between elevated PLR and severe IMLI suggests that immune hyperactivation may be more pronounced in cases of severe liver injury. In this study, the inflammatory markers selected were white blood cells, neutrophils, and albumin. While previous research in NSCLC has identified lower baseline levels of NLR, PLR, CRP, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, and CXCL19 as associated with irAEs (2), some inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and IL-6, were not routinely measured in this cohort, potentially introducing selection bias. Future studies should incorporate a broader range of inflammatory markers to provide more comprehensive insights.
Another key finding of our study is the recurrence pattern of IMLI. Among the 97 patients who developed IMLI, 28.9% experienced recurrence, with 17.9% of these cases classified as grade 3–4. Patients who experienced recurrence were slightly younger than those who did not (mean age: 59.3 vs. 58.9 years, P = 0.047), though the difference was marginal. Notably, among patients who initially presented with grade 3–4 liver injury, 26.7% experienced recurrence, and 75% of these cases progressed to severe (grade 3–4) liver injury upon recurrence. These findings indicate that while the overall recurrence risk is moderate, patients with a history of severe IMLI may be at a higher risk of developing severe recurrence. However, inflammatory markers during recurrence were comparable to those observed during initial IMLI onset, suggesting that immune recovery after initial treatment was sufficient to restore the baseline state. Additionally, the recurrence rate was not significantly higher than the initial onset rate (P = 0.21), implying that ICI re-treatment does not substantially increase the likelihood of recurrence. These observations align with previous studies demonstrating that recurrent irAEs, while not uncommon, are often manageable and do not necessarily compromise treatment efficacy (8, 22). For instance, studies in melanoma patients have reported a low likelihood of irAE recurrence following ICI re-challenge, with minimal impact on treatment response or survival outcomes (23, 24).
From a clinical perspective, our findings have important implications for the management of IMLI and ICI re-challenge strategies. While irAEs remain a challenge in immunotherapy, our data suggest that ICI re-treatment may be feasible in selected patients with prior IMLI. This is particularly relevant for patients with recurrent IMLI, who demonstrated similar immune tolerance and recurrence risk upon re-exposure to ICIs. Moreover, the observed median time to IMLI onset (~85 days) underscores the need for close monitoring during the first three months of therapy (4, 10), particularly in high-risk patients with low baseline inflammatory status. Early identification and prompt management of IMLI during this period could help mitigate disease severity and optimize treatment outcomes. Given that nearly half (48.5%) of IMLI patients in our cohort required corticosteroid therapy (e.g., methylprednisolone), early intervention may also reduce the need for prolonged immunosuppressive treatment, thereby minimizing treatment delays and optimizing the therapeutic window of ICIs.
Current guidelines from ASCO (25), ESMO (26), and Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) (27) diagnosis and treatment guidelines for colorectal cancer 2018 (English version) generally recommend permanent ICI discontinuation in patients experiencing grade 3–4 irAEs. However, emerging evidence suggests that ICI re-challenge may be a viable option in carefully selected cases. Our study contributes to this growing body of literature by demonstrating that IMLI recurrence does not significantly increase following ICI re-treatment. Nonetheless, clinicians should weigh the risks and benefits on a case-by-case basis, considering factors such as the patient’s response to initial ICI therapy, baseline inflammatory status, and the severity of prior irAEs. The apparent immune recovery observed in recurrent IMLI cases suggests a potential window for safe ICI re-challenge in appropriately monitored patients. Notably, among inflammation-related biomarkers, neither NLR nor SIPS was associated with IMLI recurrence, indicating that these markers may be more relevant for predicting initial onset rather than recurrence risk.
Finally, the IMLI incidence reported in this study (35.4%) aligns with prior estimates ranging from 15% to 50%. The variability in reported incidence rates likely reflects differences in study populations, treatment regimens, and diagnostic criteria. For instance, our cohort had a high proportion of patients receiving PD-1 inhibitors, which may have influenced the observed IMLI incidence. Notably, the incidence of grade 3–4 IMLI in our study (15.5%) was higher than some prior reports, potentially due to variations in treatment combinations, such as the inclusion of ipilimumab in dual-therapy regimens. Additionally, the relatively high prevalence of fatty liver (20%) in our cohort may have contributed to an increased susceptibility to liver injury, as underlying hepatic conditions have been implicated as potential risk factors for ICI-related hepatotoxicity.
This study provides novel insights into the risk factors, recurrence patterns, and clinical management of IMLI in NSCLC patients undergoing ICI therapy. Low baseline inflammatory status, as indicated by markers such as WBC, albumin, and PNI, is a significant predictor of IMLI, highlighting the potential for these markers to be used in risk stratification and early intervention (9, 19). Additionally, IMLI recurrence does not appear to be significantly increased with ICI re-treatment, suggesting that ICI re-challenge may be feasible in selected patients. However, patients who initially present with severe IMLI should be closely monitored, as they may be at a higher risk of severe recurrence. Future research should focus on prospective validation of these findings and further exploration of the underlying immunopathology of IMLI. By integrating predictive biomarkers with individualized treatment strategies, clinicians can optimize ICI therapy while minimizing the risk of adverse events, ultimately improving outcomes for patients with NSCLC.
This study, as a retrospective analysis, has several methodological limitations. Firstly, the data collection for inflammatory markers was incomplete, resulting in a limited number of inflammatory parameters being included in the analysis. Secondly, for patients who experienced poor efficacy following IMLI, the absence of data prevented us from comparing PFS and OS between the retreatment and non-retreatment groups. Moreover, the study did not systematically analyze the potential impact of combined chemotherapy regimens on liver dysfunction. Lastly, the evaluation of ICI adverse reactions was incomplete; data on toxicity in organs other than the liver were notably absent, which may have introduced statistical bias. Future studies should aim to conduct prospective, multicenter clinical trials that focus on: 1) the mechanisms underlying the recurrence of ICI-related adverse reactions; and 2) improving long-term survival outcomes (PFS and OS) through standardized monitoring and management of adverse reactions.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
LY: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. CL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. YL: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. XL: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. YH: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. BW: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. JS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The “Dengfeng Hospital” project, jointly funded by the Guangzhou Science and Technology Bureau’s 2023 Basic Research Plan and the municipal schools (2023A03J0340).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Jiang Y, Li R, Li X, and Zhang N. Risk factors of immune-mediated hepatotoxicity induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Oncol. (2024) 31:7129–43. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31110525
2. Hu X, Wang L, Shang B, Wang J, Sun J, Liang B, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated toxicity in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: An updated understanding of risk factors. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1094414. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1094414
3. Postow MA, Sidlow R, and Hellmann MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:158–68. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1703481
4. Miah A, Tinoco G, Zhao S, Wei L, Johns A, Patel S, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced hepatitis injury: risk factors, outcomes, and impact on survival. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:2235–42. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04340-3
5. Gudd C, Sheth R, Thursz MR, Triantafyllou E, and Possamai LA. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. (2023) 43:402–17. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1776761
6. Remash D, Prince DS, Mckenzie C, Strasser SI, Kao S, and Liu K. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related hepatotoxicity: A review. World J Gastroenterol. (2021) 27:5376–91. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i32.5376
7. Savino A, Rossi A, Fagiuoli S, Invernizzi P, Gerussi A, and Vigano M. Hepatotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy: diagnosis, management, and future perspectives. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 17(1):76. doi: 10.3390/cancers17010076
8. Parlati L, Sakka M, Retbi A, Bouam S, Hassani L, Meritet JF, et al. Burden of grade 3 or 4 liver injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. JHEP Rep Vol. (2023) 5:100880. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100880
9. Moey M, Tomdio AN, Mccallen JD, Vaughan LM, O'brien K, Naqash AR, et al. Characterization of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related cardiotoxicity in lung cancer patients from a rural setting. JACC CardioOncol. (2020) 2:491–502. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2020.07.005
10. Raynes G, Stares M, Low S, Haron D, Sarwar H, Abhi D, et al. Immune-related adverse events, biomarkers of systemic inflammation, and survival outcomes in patients receiving pembrolizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancers. (2023) 15:5502. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235502
11. Xu M, Xu L, Hao Y, Shao K, and Song Z. Clinical characteristics and prognostic implications of immune-related hepatitis in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a retrospective study. J Thorac Dis. (2024) 16:1900–10. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1684
12. Vaddepally R, Doddamani R, Sodavarapu S, Madam NR, Katkar R, Kutadi AP, et al. Review of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)-their incidence, management, multiorgan irAEs, and rechallenge. Biomedicines. (2022) 10(4):790. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040790
13. Kerepesi C, Abushukair HM, Ricciuti B, Nassar AH, Adib E, Alessi JV, et al. Association of baseline tumor-specific neoantigens and CD8(+) T-cell infiltration with immune-related adverse events secondary to immune checkpoint inhibitors. JCO Precis Oncol. (2024) 8:e2300439. doi: 10.1200/PO.23.00439
14. Sun J, Schiffman J, Raghunath A, Ng TD, Chen H, and Sharma P. Concurrent decrease in IL-10 with development of immune-related adverse events in a patient treated with anti-CTLA-4 therapy. Cancer Immun. (2008) 8:9.
15. Chu X, Zhao J, Zhou J, Zhou F, Jiang T, Jiang S, et al. Association of baseline peripheral-blood eosinophil count with immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis and clinical outcomes in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Lung Cancer. (2020) 11:150:76–82. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.08.015
16. Hirasawa Y, Kubota Y, Mura E, Suzuki R, Tsurui T, Iriguchi N, et al. Maximum efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors occurs in esophageal cancer patients with a low neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and good performance status prior to treatment. Anticancer Res. (2024) 44:3397–407. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17160
17. Shojaie L, Ali M, Iorga A, and Dara L. Mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitor-mediated liver injury. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2021) 11:3727–39. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.10.003
18. Godel P, Shimabukuro-Vornhagen A, and Von Bergwelt-Baildon M. Understanding cytokine release syndrome. Intensive Care Med. (2018) 44:371–3. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4943-5
19. Lin X, Deng H, Yang Y, Wu J, Qiu G, Li S, et al. Peripheral blood biomarkers for early diagnosis, severity, and prognosis of checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis in patients with lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:698832. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.698832
20. Egami S, Kawazoe H, Hashimoto H, Uozumi R, Arami T, Sakiyama N, et al. Peripheral blood biomarkers predict immune-related adverse events in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with pembrolizumab: a multicenter retrospective study. J Cancer. (2021) 12:2105–12. doi: 10.7150/jca.53242
21. Pavan A, Calvetti L, Dal Maso A, Attili I, Del BP, Pasello G, et al. Peripheral blood markers identify risk of immune-related toxicity in advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Oncologist. (2019) 24:1128–36. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0563
22. Santini FC, Rizvi H, Plodkowski AJ, Ni A, Lacouture ME, Gambarin-Gelwan M, et al. Safety and efficacy of re-treating with immunotherapy after immune-related adverse events in patients with NSCLC. Cancer Immunol Res. (2018) 6:1093–9. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0755
23. Haanen J, Ernstoff M, Wang Y, Menzies A, Puzanov I, Grivas P, et al. Rechallenge patients with immune checkpoint inhibitors following severe immune-related adverse events: review of the literature and suggested prophylactic strategy. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8(1):e000604. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000604
24. Riveiro-Barciela M, Barreira-Diaz A, Callejo-Perez A, Munoz-Couselo E, Diaz-Mejia N, Diaz-Gonzalez A, et al. Retreatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors after a severe immune-related hepatitis: results from a prospective multicenter study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 21:732–40. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.03.050
25. Schneider BJ, Naidoo J, Santomasso BD, Lacchetti C, Adkins S, Anadkat M, et al. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: ASCO guideline update. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:4073–126. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01440
26. Haanen J, Carbonnel F, Robert C, Kerr KM, Peters S, Larkin J, et al. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:iv119–42. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx225
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitors, immune-mediated liver injury, immune-related adverse events, clinical features, inflammatory biomarkers
Citation: Yang L, Zhuo C, Li C, Liu Y, Liu X, Huang Y, Wu B and Su J (2025) Clinical features and risk factors of immune-mediated liver injury in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 15:1575376. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1575376
Received: 12 February 2025; Accepted: 28 July 2025;
Published: 13 August 2025.
Edited by:
Elisabetta Razzuoli, Liguria and Valle d’Aosta (IZSPLVA), ItalyReviewed by:
Guochun Zhang, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, ChinaAna-Maria Singeap, Grigore T. Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Zhuo, Li, Liu, Liu, Huang, Wu and Su. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chao Zhuo, Y2hhb19zaGVlcEAyNjMubmV0
 Ling Yang
Ling Yang Chao Zhuo
Chao Zhuo Chonghuan Li2
Chonghuan Li2 Jiawei Su
Jiawei Su