- 1Faculty of Life Science and Technology & The Affiliated Anning First People’s Hospital, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China
- 2Department of Radiology, Faculty of Life Science and Technology & The Affiliated Anning First People's Hospital, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common malignant tumor among women worldwide, posing a substantial threat to their health and overall quality of life. Consequently, for early-stage BC, timely screening, accurate diagnosis, and the development of personalized treatment strategies are crucial for enhancing patient survival rates. Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS) addresses the limitations of traditional handheld ultrasound (HHUS), such as operator dependency and inter-observer variability, by providing a more comprehensive and standardized approach to BC detection and diagnosis. Radiomics, an emerging field, focuses on extracting high-dimensional quantitative features from medical imaging data and utilizing them to construct predictive models for disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment evaluation. In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with radiomics has significantly enhanced the process of analyzing and extracting meaningful features from large and complex radiomic datasets through the application of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) algorithms. Recently, AI-based ABUS radiomics has demonstrated significant potential in the diagnosis and therapeutic evaluation of BC. However, despite the notable performance and application potential of ML and DL models based on ABUS, the inherent variability in the analyzed data highlights the need for further evaluation of these models to ensure their reliability in clinical applications.
1 Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most frequent cancers among women worldwide. According to the latest data from the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), approximately 2.3 million new cases of female BC and close to 670,000 related deaths will occur globally in 2022 (1), if it is identified at the early stage, the survival rate is significantly improved.
Automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) is an advanced ultrasound imaging technology approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2012 (2). Compared with conventional ultrasound, ABUS has several advantages, including operator independence, whole-breast coverage and stable image quality. Additionally, ABUS can reconstruct coronal plane (CP) images, which is not achievable with conventional ultrasound. CP imaging is particularly valuable for the diagnosis of breast lesions as it provides crucial anatomical and symptomatic information (3). Comprehensive analysis of tumors using large volumes of image data from ABUS remains a challenge for sonographers. Additionally, the interpretation of ultrasound images may depend on the clinical experience of sonographers, which can affect the diagnostic accuracy and efficacy of ABUS (4).
Radiomics is a field that analyzes a vast number of medical images to extract numerous features reflecting disease characteristics, and explores the associations between the features and patients’ prognoses for precision medicine (5). Specifically, this technology employs various image processing algorithms to enhance image quality and utilizes diverse techniques and methods for high-throughput data analysis to extract quantitative features—such as shape, texture, and filtering characteristics—from regions of interest (ROIs). Traditional radiomics often uses software to extract and screen those features that can most effectively capture the intra-tumor and inter-tumor heterogeneity. Then, it uses statistical analysis methods such as multivariate logistic regression (LR) analysis to construct the model (6).
Significant advances in the field of Artificial intelligence (AI), it holds promise in increasing the diagnostic value of ultrasound imaging for histological analysis based on machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) (7, 8). Radiomics can enhance the utility of existing data for clinicians by integrating advanced mathematical analysis from AI (9). The integration of radiomics with imaging tool like Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and mammography (MG) shows promise for early BC screening (10, 11). In breast ultrasonography, the large volume of data, easy accessibility of images, and diverse image types have led to the increasing involvement of AI-based radiomics in the diagnostic process. Currently, multimodal ultrasound radiomics is one of the most active areas of investigation (12–14). ABUS, an emerging breast imaging technology, offers high-quality image presentation, allowing for the extraction of more precise ultrasound features with strong diagnostic potential.
We searched on PubMed and Web of Science for publications from 2020 up to September 2024. The search keywords included “Automated Breast Ultrasound”, “Breast Cancer”, “Deep Learning”, “Machine Learning” and “Artificial Intelligence”. A total of 46 relevant papers were included. This review outlines the fundamental concepts of ABUS, radiomics, and AI, aiming to summarize the current status and research progress of ABUS radiomics based on traditional ML and DL algorithms in the applications of assisting BC detection, diagnosis, classification, and prognosis evaluation.
2 Methods
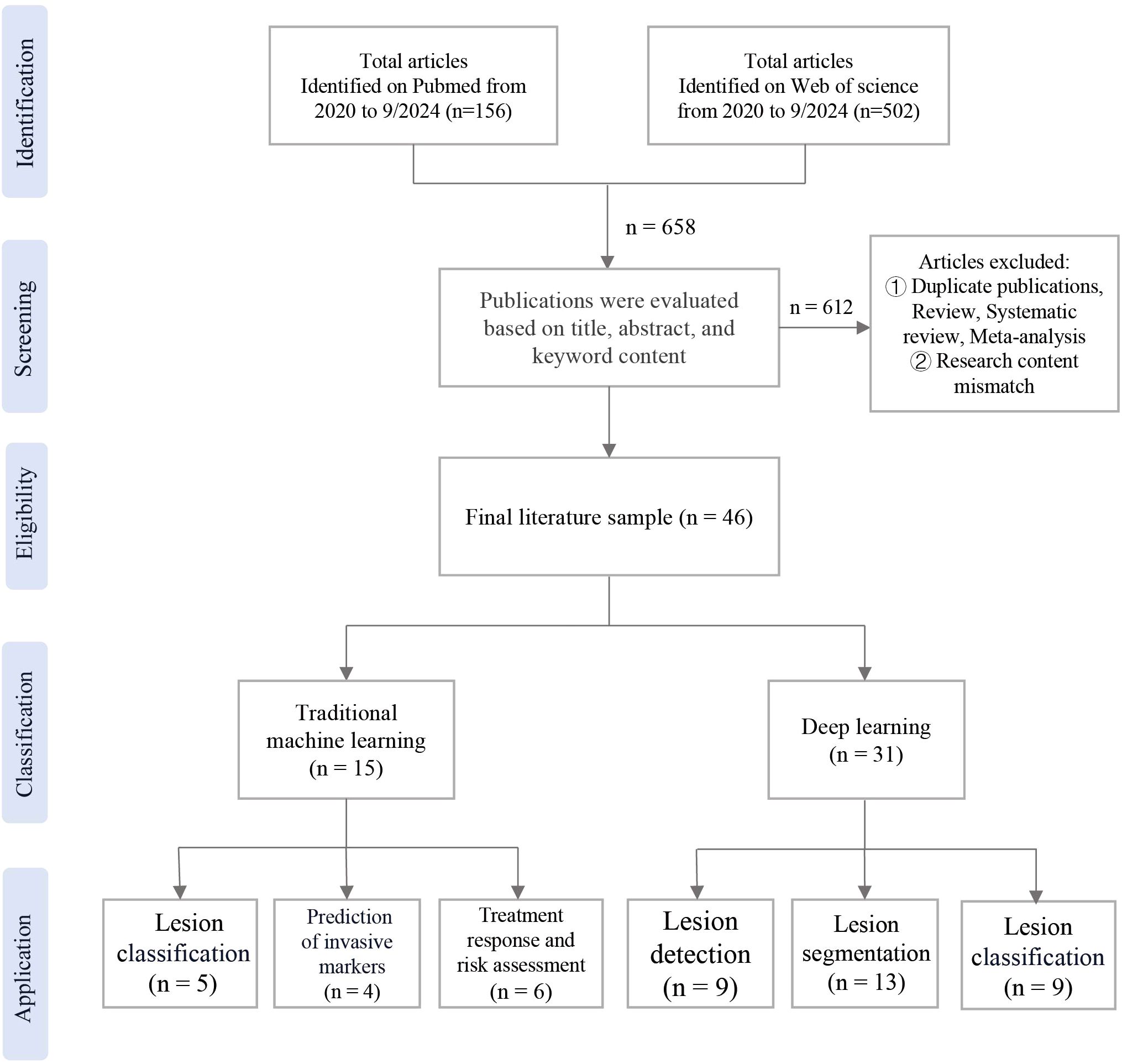
The publications were searched in the databases of PubMed and Web of Science. The search was limited to studies published between 2020 and September 2024. Exclusion criteria were applied, which were not associated with radiomics. Additionally, studies consisting solely of review, systematic review, meta-analysis were excluded. Following the removal of duplicate studies, A total of 46 relevant papers were included, the workflow of the study was shown in Figure 1.
3 Introduction to ABUS and radiomics
3.1 Overview and workflow of ABUS
Studies have shown that women with extremely dense breast tissue have a 4.7 times higher risk of breast cancer compared to those with lower breast density (15). Since the 1980s, researchers have proposed the development of ABUS technology in response to the limitations of MG in screening dense breasts (16, 17). Currently, ABUS has been evaluated as a complementary tool to MG, providing the ability to scan the entire breast without operator variability while maintaining the benefits of handheld ultrasound (HHUS), including superior tissue penetration and lesion characterization (18).
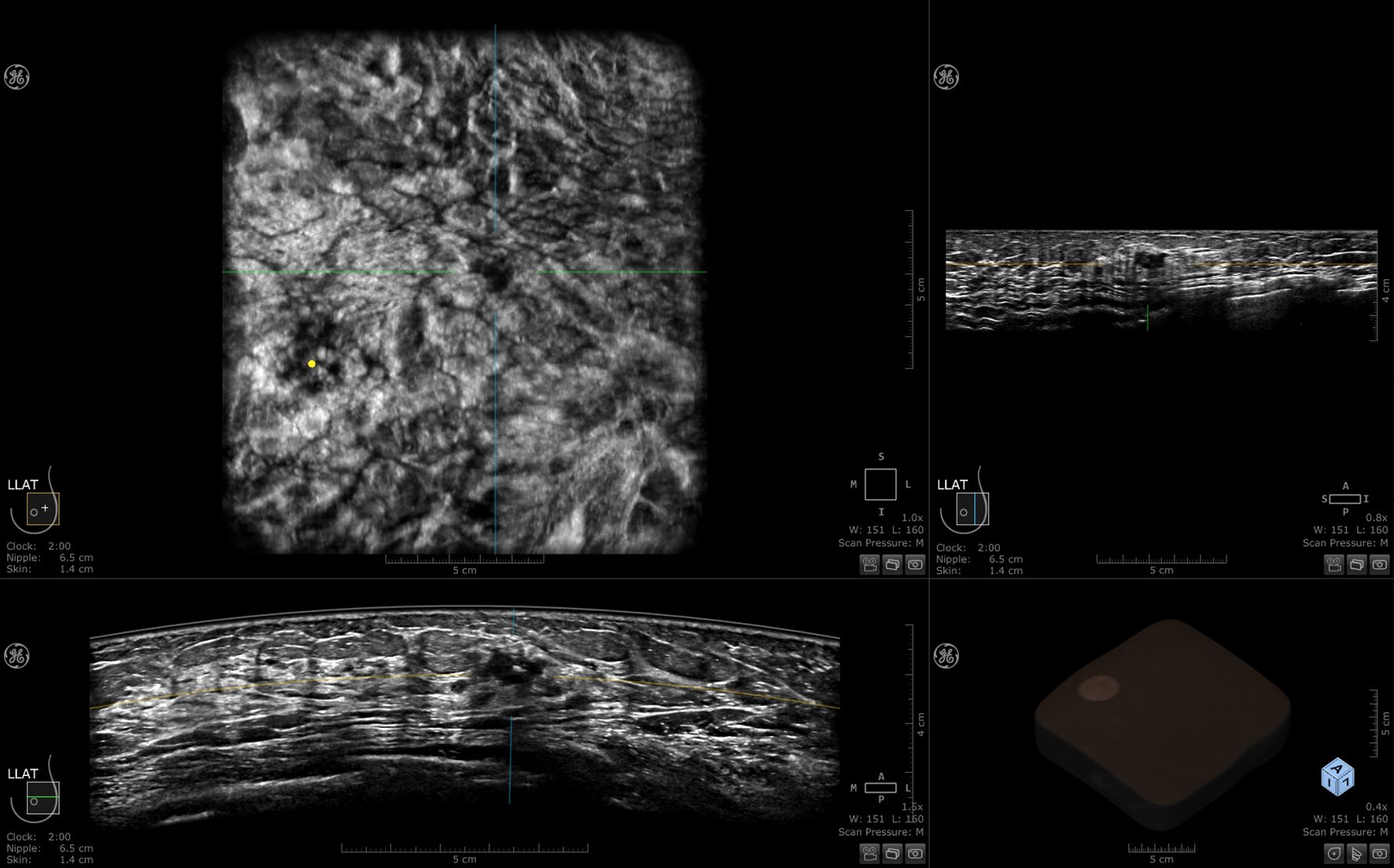
ABUS is a computer-based ultrasound screening system designed to evaluate the entire breast tissue using an automated probe. This system ensures symmetry and bilaterality in screening results. Each breast is imaged in three different views: axial, sagittal, and coronal. Volumetric data is stored and transferred to a workstation after the scan. This eliminates the need for sonographers to perform image acquisition and interpretation simultaneously during breast screening using ABUS. ABUS helps standardize breast ultrasound and overcome limitations of ultrasound, including reduced operator dependency and shorter examination times (3). Currently available ABUS systems include both prone and supine scanning modes (19), the most commonly used in clinical practice are mainly supine, including the Invenia ABUS system from GE and ACUSON S2000 automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) from Siemens (3, 20). In this article, the 3D Automated Breast Ultrasound technology is uniformly referred to as ABUS. The basic structure of both ABUS systems includes a main unit (ultrasound diagnostic device), high-frequency and large-sized sensors, a curved transducer, and an image data processing system. A set of ABUS images generated by Invenia ABUS is displayed in Figure 2.
3.2 Radiomics
Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) has greatly enhanced disease detection and diagnosis by extracting tumor characteristics through advanced computational analysis, particularly in breast and lung cancer screening. Recently, radiomics has emerged as an important extension of CAD (21), which involves extracting numerous quantitative features from medical images using automated or semi-automated high-throughput software tailored to a specific imaging modality. This process identifies relevant features that reflect both macroscopic (e.g., tumor shape and texture) and microscopic information (e.g., pathology and genetics), enabling predictive models for clinical functions such as screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and efficacy assessment (22, 23).
Currently, ultrasound-based radiomics employs two distinct approaches for feature extraction: semi-automatic methods requiring manual segmentation with subsequent traditional ML analysis (24), and fully automated DL methods capable of performing end-to-end tasks including image segmentation, lesion detection, and classification. These DL techniques can be further categorized into supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised learning paradigms (25, 26).
The current workflow of radiomics is divided into five main steps: ①Image acquisition. In clinical practice for BC, commonly used imaging modalities include ultrasound, MG, and MRI. Medical images must be acquired in strict compliance with operational standards (27). ②Pre-processing and tumor segmentation. Image pre-processing typically involves noise removal and resolution enhancement. Because of the lack of standardized methods for segmentation and feature extraction, image segmentation primarily focuses on delineating the ROIs (28). Common image segmentation techniques include manual, semi-automatic, and automatic segmentation (29). ③Feature Extraction, which includes statistical texture features, morphological features, and filtering features. DL extracts more abstract features directly from raw data (27). ④Feature selection to reduce overfitting by using methods like filtering methods (23), wrapper methods, and embedding methods (30). ⑤Modeling to predict disease prognosis and biological behavior through feature analysis, followed by training ML or DL models, the models were evaluated through cross-validation and external validation sets (23, 27, 31). The ABUS radiomics workflow integrating both traditional ML and DL approaches is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3. The radiomics workflow for ABUS imaging integrates two distinct methodologies. Traditional machine learning relies on manual processes including image acquisition, feature extraction and selection, followed by model construction to complete tasks. Deep learning primarily employs convolutional neural networks (CNN) composed of three core components: convolutional layers for local feature extraction, pooling layers for dimensionality reduction, and fully connected layers that map extracted features to output layers for final task execution. SVM, Support Vector Machine; LASSO, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator; RF, Random Forest; ROC, Receiver Operating Characteristic.
4 Introduction and applications of traditional machine learning for ABUS radiomics
4.1 Introduction of traditional machine learning for ABUS radiomics
ML is a critical branch of AI that leverages datasets to train models and generates predictions by synthesizing information from all data samples. These predictions can then be used to assist in clinical decision-making. As of November 2022, the FDA has approved 521 ML algorithms for clinical use, of which 392 can be applied to radiomics (32). To enable clinical applications, common ML methods can be categorized into the following types, including reinforcement learning, unsupervised learning, and supervised learning (33). ML algorithms used in traditional radiomics are typically supervised. Supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data, allowing the model to learn the mapping between inputs and outputs with instances of the expected outputs labeled by a human which is referred to as the “ground truth” (34).
In ABUS radiomics, traditional ML algorithms are mainly applied to texture analysis, screening, and extraction of quantitative features from radiomics images to create predictive models and decision-support tools. The steps of ultrasound radiomics based on traditional ML algorithms are mainly divided into image segmentation, feature extraction, feature screening, and model build. The image segmentation part is mainly performed in a semi-automatic form, with one or more physicians with years of imaging experience performing ROIs regions through platforms such as 3D Slicer, ITKSNAP, MaZda, SEG3D2, and Deepwise. The manual delineation of ROIs is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process (35–39). The Python-based pyradiomics package is a widely used tool for feature extraction in radiomics studies. It provides a convenient and comprehensive open-source platform that can efficiently process and extract numerous radiomic features (40, 41). For feature selection, statistical tests such as the t-test, chi-square test, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression, and Gradient Boosted Decision Trees (GBDT) are commonly employed to reduce the feature dimensionality and enhance the model’s generalization ability.
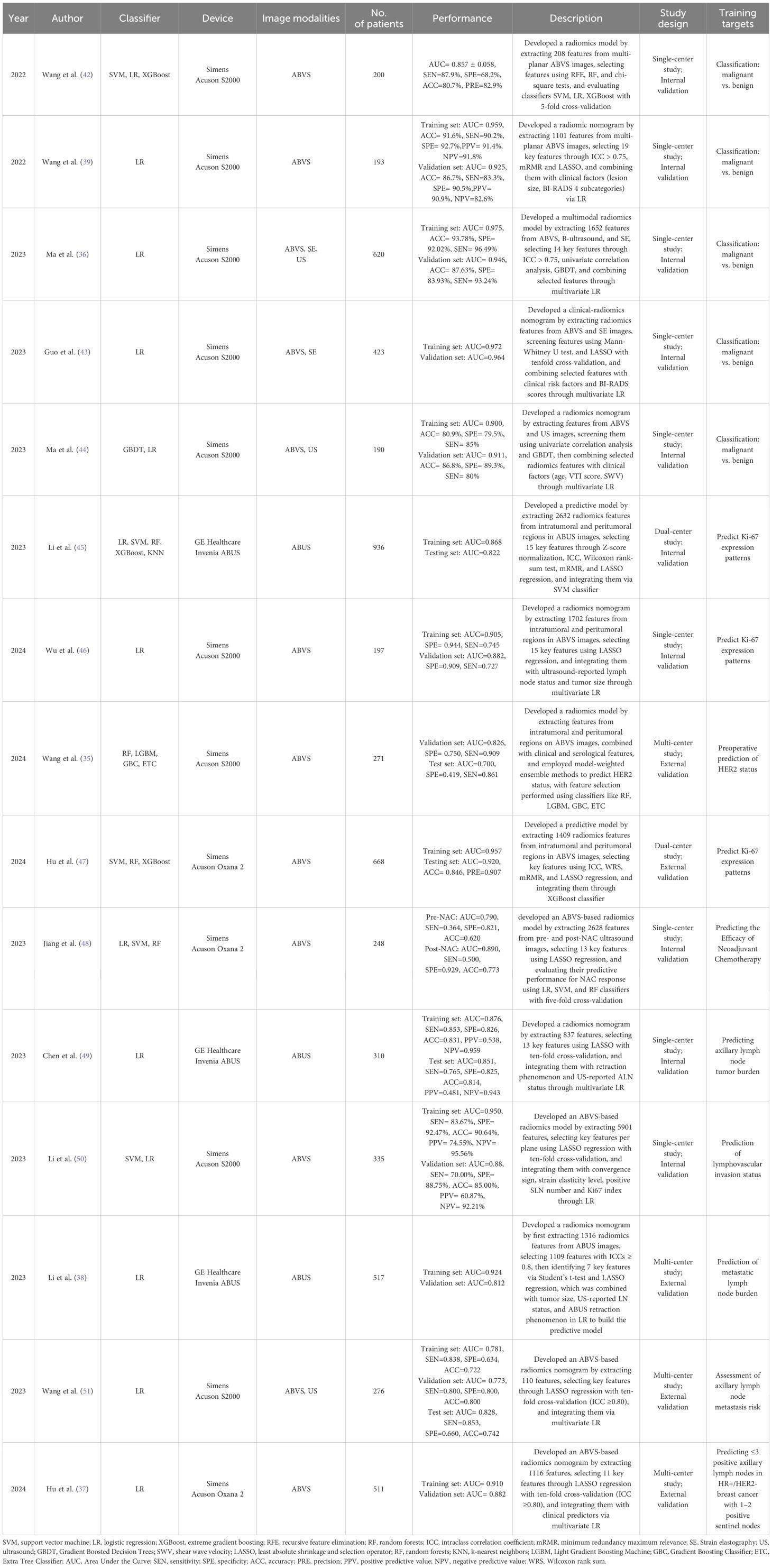
Although traditional radiomics methods require manual feature extraction, many clinicians prefer these approaches for constructing models and implementing clinical functions. This is because of their advantages in terms of model interpretability and flexibility in clinical applications. These methods have been effectively used to differentiate between benign and malignant tumors, predict axillary lymph node metastasis, assess the efficacy of neoadjuvant therapies, and predict preoperative Ki-67 expression levels. Table 1 summarizes the performance of traditional ML methods applied to ABUS radiomics.
4.2 Applications of traditional machine learning for ABUS radiomics
4.2.1 Lesion classification
Accurate screening of benign and malignant breast lesions enables timely intervention in patients with malignant tumors, significantly improving survival rates and preventing unnecessary treatments for those with benign lesions. Currently, the accurate and consistent identification of certain lesions through visual inspection remains challenging. Several studies have explored the diagnostic potential of traditional ML techniques applied to ABUS radiomics to distinguish between benign and malignant breast lesions. ABUS, as a 3D ultrasound modality, provides a three-plane view, with image segmentation typically performed using axial plane (AP) and CP. Images obtained from these two planes are generally easier to analyze and interpret. This aligns better with the reading preferences of radiologists and the requirements of clinical examination.
Wang et al. manually segmented the largest lesions in AP and CP views using ITK-SNAP and developed a classification model with Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR), and Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost). The SVM model achieved the best performance, with an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.857 ± 0.058 and sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), accuracy (ACC), and precision (PRE) values of 87.9%, 68.2%, 80.7%, and 82.9%, respectively. The study found that features from the AP provided superior classification performance compared to the CP, and leveraging data from both planes enabled the construction of a model with more comprehensive performance (42).
Ma et al. developed an ABVS model using CP features and a multimodal model combining ABVS, B-ultrasound, and strain elastography (SE). The multimodal model demonstrated superior performance compared to other models, achieving an AUC of 0.946 on the validation set, significantly enhancing the model’s diagnostic efficacy. Several studies have demonstrated that multimodal models exhibit superior performance compared to unimodal imaging models (36, 43). Multimodal models involving ABUS data are typically based on combinations of ABUS with HHUS, SE, contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEU), or digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) (43, 44, 52). Since ABUS provides three-dimensional views, multiplanar features can significantly improve classification performance. Compared to HHUS, ABUS’s CP texture features demonstrate superior performance in distinguishing benign and malignant lesions. However, reconstructed coronal images have relatively lower resolution, which may lead to the omission of critical features such as microcalcifications. Additionally, most current studies focus on features extracted from the largest cross-sectional area of tumors, leaving the three-dimensional volumetric information underutilized. Future research should explore dynamic imaging characteristics of benign and malignant lesions to further enhance diagnostic accuracy.
4.2.2 Prediction of invasive markers
BC is a highly heterogeneous disease, with multiple potential therapeutic molecular targets that play crucial roles in cell metastasis, invasion, apoptosis, and cell cycle regulation. Ki-67 is a crucial biomarker for assessing BC; its expression level reflects the tumor’s proliferative activity (53, 54). Accurate Ki-67 assessment provides valuable information for BC management (45–47).
Wu et al. developed an ABVS-based radiomics model for Ki-67 prediction by analyzing ROIs in CP across different Ki-67 expression levels. They reconstructed peritumoral ROIs using a dilation algorithm, selected features through LASSO regression, and constructed the predictive model via LR. The model demonstrated robust performance with AUC values of 0.905 in the training set and 0.882 in the validation set. Utilizing readily accessible input data, this approach shows significant clinical value (46).
The expression of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is closely linked to the prognosis of BC, with HER2-positive cases accounting for about 14% of all female BC cases (55). These patients demonstrate greater heterogeneity, and lower survival rates. HER2 expression indicates clinical aggressiveness and aids physicians in treatment decisions (56, 57). Since trastuzumab received approval for HER2-positive metastatic BC in 1998, several tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting HER2 have been approved for clinical use (58). Due to its critical role, HER2 has become an essential diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker for BC (59).
Wang et al. developed four optimal models using weighted and feature combination methods to predict HER2 status in BC using ABVS-based radiomics features. The weighted combination model achieved an AUC of 0.700, SEN of 86.1%, and SPE of 41.9% in test set (35). Due to the lack of a strict standard for ROIs division, outlining accuracy can impact model performance. To minimize operator bias in semi-automatic segmentation, multiple sonographers are employed for ROIs delineation. Optimized weighted combination models that include ABVS-based intra tumoral and peritumoral radiomics features along with clinical data show promise for noninvasive preoperative prediction of HER2 status in BC.
However, current ABUS primarily provides morphological and echogenic features while lacking functional information (e.g., hemodynamics), which may limit its predictive capability for certain biomarkers. Therefore, multimodal integration becomes particularly crucial for improving the accuracy of predicting tumor marker expression levels.
4.2.3 Treatment response and risk assessment
Neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) is a common treatment for early-stage BC that reduces tumor size, enhances surgical removal success, and increases the likelihood of breast-conserving surgery (60, 61). It can also eliminate axillary lymph node metastases (ALND) detectable during sentinel lymph nodes (LNs) biopsy post-treatment. Currently, effectiveness assessments mainly rely on post-treatment evaluations, which may delay timely treatment adjustments.
Jiang et al. collected ABVS images from patients within one week before the start of NAC and one week after the second NAC cycle to identify image features associated with NAT efficacy. The results showed that the prediction performance of features extracted after the second treatment cycle was significantly superior to that of pretreatment features (AUC 0.89 vs. 0.79). This suggests that postoperative assessment differs from pre-treatment evaluation, likely due to changes in the tumor microenvironment following treatment (48).
ALND, including the number and distribution of positive LNs, is a key factor in determining the pathological stage of BC (62). Therefore, an accurate assessment of ALND involvement is essential for developing appropriate treatment plans. ALND can be diagnosed by sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with early-stage BC (63), the false-positive rate is approximately 10% (64); therefore, developing a radiomics model for the assessment of ALND is clinically significant. Chen et al. compared several models, including an ABUS feature model with tumor diameter, retraction phenomenon, hyperechoic halo, ABUS radiomics model, and multi-modal ABUS radiomics model incorporating ultrasound reports of axillary lymph node status and retraction phenomenon. The AUC value for the training set was 0.876 and the test set was 0.851 (49). Current research primarily focuses on the extraction and analysis of radiomic features. However, the complexity of the tumor microenvironment suggests that predicting LNs should not rely solely on imaging data. Given that tumor invasiveness, immune microenvironment status, and molecular heterogeneity all influence metastatic risk, future studies should integrate multimodal data, including pathological characteristics and molecular biomarkers, to develop a comprehensive “imaging-pathology-molecular” predictive model.
5 Introduction and applications of deep learning for ABUS radiomics
5.1 Introduction of deep learning for ABUS radiomics
Since AlexNet demonstrated its remarkable performance in image recognition challenges, DL, as a key branch of AI, has gained widespread attention (65). DL is a crucial subfield of ML that focuses on representation learning through hierarchical nonlinear transformations. It is particularly adept at processing unstructured data (e.g., images, text) and can adapt to supervised, unsupervised, or semi-supervised learning paradigms (66, 67). This is achieved by connecting simple nonlinear modules through a multilayered neural network that mimics the structure of the human brain (68). The emergence of DL has expanded the range of applications in the field of computer vision (67). In imaging, DL employs multilayer neural networks to transform input data into outputs that align with desired outcomes. Common types of outputs include object locations for lesion detection, pixel labels for image segmentation, and image categories for lesion classification. The basic architecture of DL is Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) (69). Inspired by the biological visual cortex, a CNN typically comprises three primary components: convolutional layers, pooling layers, and fully-connected layers (70). The convolutional layers serve as the core feature extractors, applying multiple convolutional kernels to capture local patterns like edges and textures. Pooling layers then reduce spatial dimensionality while preserving critical features. These extracted features are subsequently mapped to outputs through fully-connected layers for final classification or prediction tasks. As the network depth increases, CNNs progressively learn more complex hierarchical representations (68). As combinations of layers have become more diverse, deep neural network architectures built on CNN have been successfully applied to image analysis. Notable examples include AlexNet (65), VGGNet (71), ResNet (72), DenseNet (73), etc. In recent years, the establishment of several medical imaging databases has facilitated data mining and the development of high-performance models has been significantly simplified by the widespread use of generalized neural network frameworks and automated processing workflows (74). Meanwhile, Transformer architectures based on self-attention mechanisms have also demonstrated promising potential in medical image analysis, significantly improving the accuracy of lesion classification and segmentation through their superior long-range dependency modeling capabilities (75).
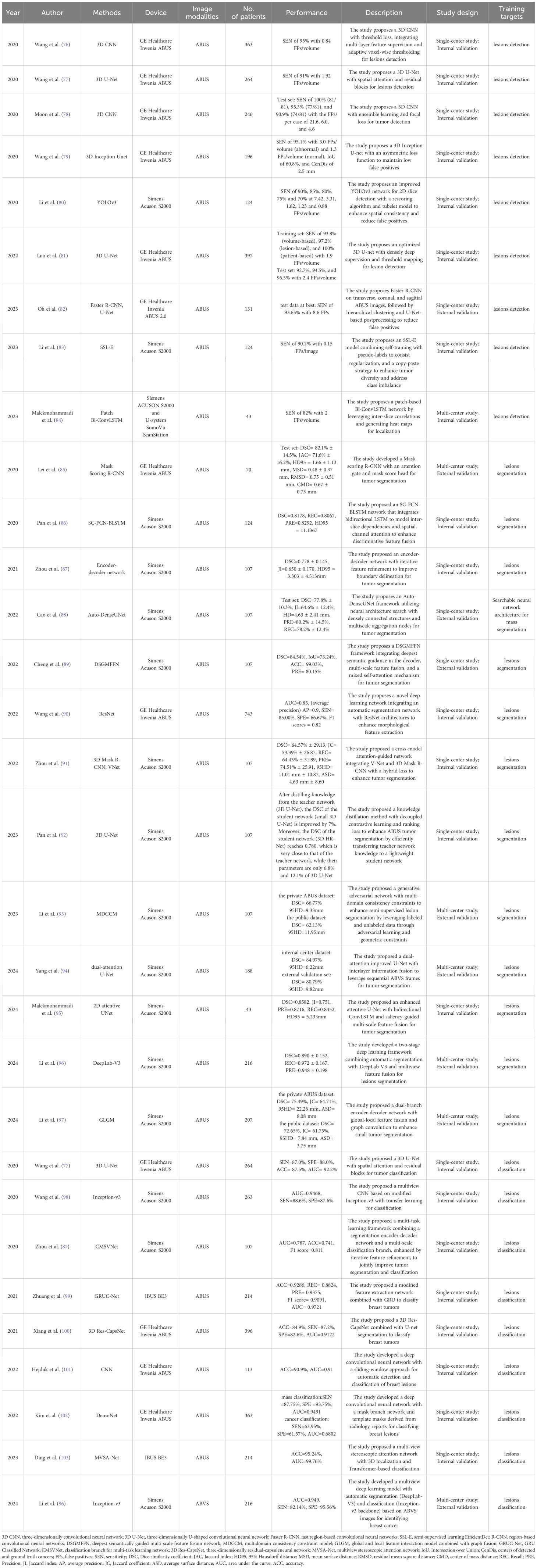
Currently, DL, one of the most powerful data-driven AI technologies, enables the development of fully automated workflow. DL models generally achieve higher accuracy and performance than traditional ML algorithms. As the field of DL continues to evolve, these algorithms are expected to become mainstream tools for medical radiomics in the future. To date, DL algorithms have been applied to ABUS radiomics for tasks such as lesion detection, tumor segmentation, and lesion classification. Table 2 summarizes the performance of DL methods applied to ABUS radiomics.
5.2 Application of deep learning for ABUS radiomics
5.2.1 Lesion detection
Traditional ML methods for identifying breast lesions are largely manual, whereas DL methods enable automatic tumor detection. Several studies have applied DL for breast lesion detection using HHUS. For example, Yap et al. systematically compared three DL architectures (patch-based LeNet, U-Net, and transfer learning-optimized FCN-AlexNet) with four conventional methods for breast ultrasound lesion detection. The results demonstrated that FCN-AlexNet achieved optimal performance with a True Positive Fraction of 0.98, indicating excellent lesion detection capability (104). Currently, the DL frameworks used for lesion detection in ABUS images mainly include 3D CNN, 3D U-Net, and R-CNN.
Unlike HHUS, the main challenge for lesion detection in ABUS radiomics is how to correctly process 3D images instead of 2D images (105), regarding lesion detection in ABUS, previous approaches have mainly focused on clustering the localization results of 2D slices to form the final 3D results (106, 107). Oh et al. developed a 3D breast nodule detection system combining 2D Faster R-CNN and U-Net. The method employs confidence thresholding and hierarchical clustering to reduce 2D false positives (FPs), then aggregates sequential 2D detections into 3D cuboids. Evaluation results showed 90.98% SEN (11.6 FPs/case) on Dataset A and 93.65% SEN (8.6 FPs/case) on Dataset B (82).
Wang et al. proposed an improved 3D CNN architecture for cancer detection in ABUS. The study achieved outstanding performance with 95% SEN and only 0.84 FPs per volume. This was accomplished by introducing 3D dilated convolutions to enhance multi-scale feature extraction, optimizing the training process with a hybrid loss function, and designing an adaptive threshold map to refine the cancer probability map. However, the method still has limitations, including misclassification of benign lesions, missed detection of small cancerous regions, high computational demands of the 3D network. Future research will focus on improving malignancy classification, optimizing shadow region detection, and enhancing efficiency through lightweight network design (76).
DL offers significant advantages in tumor detection, including high efficiency and automation, effectively enhancing physicians’ diagnostic workflow. However, non-tumorous regions such as vascular dilatation and glandular shadows may still lead to FPs, while the SEN for small lesions remains notably lower than that for larger tumors. These limitations indicate significant opportunities for further optimization and enhancement of the technology.
5.2.2 Tumor segmentation
In addition to detection, tumor segmentation is clinically significant, as it helps to precisely delineate the boundaries of lesions (108). This segmentation forms the foundation for tumor analysis, lesion load assessment, and surgical planning (109). In early studies, mass segmentation primarily relied on manually selected features (110–112). However, manual feature selection has inherent drawbacks, including inefficiency and subjectivity. To address these issues, Kozegar et al. developed a new adaptive region growing algorithm combined with deformable model. This approach achieved a mean Dice of 0.74 ± 0.19 (110). In recent years, automatic tumor segmentation has become mainstream, with commonly used DL frameworks including U-Net, R-CNN, and V-Net.
Lei et al. developed a region-based CNN incorporating a mask scoring mechanism for automated segmentation of breast tumors in ABUS images. The method achieved a mean Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 82.1% ± 14.5% on the independent test set. However, its complexity requires substantial computational resources, limiting its practical applicability (85).
Segmentation architecture design relies heavily on expert knowledge. Neural architecture search automates this process. Cao et al. proposed Auto-DenseUNet, which leverages neural architecture search automates and a densely connected structure to optimize feature fusion through multi-scale aggregation nodes. A decoupled search-training strategy was introduced to balance search efficiency and model performance. On the ABUS dataset, Auto-DenseUNet achieved a mean DSC of 77.8% and demonstrated competitive performance on a cardiac MRI dataset. However, domain shift across datasets remains a challenge for further investigation (88).
Zhou et al. proposed CMANetfusion, a cross-model attention segmentation network integrating 3D Mask R-CNN with V-Net. This framework achieves tumor segmentation in ABUS images through probability map-guided feature fusion and a hybrid loss function, attaining a DSC of 64.57% on single-center data. However, the model demonstrates limitations in segmenting small tumors and lesions adjacent to nipples, while exhibiting high computational demands. Future optimizations could incorporate multi-task learning and lightweight architecture design to enhance performance (91).
DL models can automatically extract features, significantly improving segmentation efficiency while reducing manual intervention. However, current research primarily focuses on static images, leaving the dynamic segmentation capability for real-time ABUS video analysis largely unexplored. Future work should leverage self-supervised pretraining to minimize annotation dependency and develop lightweight networks to meet clinical real-time requirements.
5.2.3 Classification of lesions
BI-RADS 4 lesions have a high biopsy rate, but many are benign. DL models can help distinguish benign from malignant lesions, reducing unnecessary biopsies. ABUS generates 3D images, leveraging multi-view information for improved classification. However, ABUS imaging features challenge lesion classification due to pixel and grayscale limitations. Precise lesion localization is crucial, especially boundary delineation. Current methods for interpreting ABUS images are limited in stereoscopic boundary localization and feature extraction, and do not effectively utilize long-range features or attention mechanisms. Improvements are needed to fully exploit stereoscopic information and features from different views to enhance diagnostic accuracy.
Zhuang et al. proposed a tumor classification method for ABUS images called the Classifying-ABUS Architecture. This method extracts the image of interest (IOIs) and ROI employing a Shared Extracting Feature Network combining VGG16 and a novel Shallowly Dilated Convolutional Branch Network to extract both general and ultrasound-specific features. Then employs GRU Classification Network to integrate sequence features for classification. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieved a classification ACC of 92.86% for the test set (99). However, current methods still face challenges in capturing long-range spatial relationships and sophisticated feature patterns in ultrasound imaging.
Ding et al. proposed MVSA-Net, a two-stage classification method for breast ultrasound images. MVSA-Net consists of a stereo localization unit and a classification unit. The stereo localization unit uses a stereo attention module and segmentation output design to accurately locate the tumor region. The classification unit then uses a transformer network to classify the tumor as benign or malignant. This approach achieved an ACC of 95.24% with an AUC of 99.76%, significantly improving classification speed and efficiency. Key contributions include the module’s focus on the tumor’s edge regions and the transformer network’s global attention mechanism, which enables MVSA-Net to capture long-range feature dependencies (103).
A common challenge in classification models is the imbalance between malignant and benign samples, with malignant cases usually being much fewer than benign ones. This imbalance can negatively affect model training. Also, when working with small datasets, models tend to overfit the training data. To address these issues, future studies could employ data augmentation techniques to increase sample diversity and enhance model performance.
6 Discussion
The combination of AI and ABUS radiomics has demonstrated multifaceted clinical application value in BC diagnosis and treatment assessment, significantly improving tumor detection and diagnostic accuracy while effectively predicting tumor molecular marker expression levels and assessing ALND risk. Current research shows that the multimodal joint modeling of ABUS with B-ultrasound and SE can achieve complementary advantages: ultrasound compensates for ABUS’s limitations in detecting peripheral lesions, poor imaging performance in large breasts, and restricted evaluation of axillary and nipple regions through its flexibility (113), while SE further enriches model features by quantifying tissue stiffness as an important biological characteristic (40). However, existing studies are mostly limited to the joint analysis of ABUS with B-ultrasound and SE, with relatively insufficient research on cross-modal fusion with other imaging techniques such as CEU, MRI, and CT. ABUS radiomics is increasingly being combined with key pathomics elements like histological grading and immunohistochemical markers, as well as clinomics parameters including survival data and hematological features, representing a growing research priority. By establishing quantitative correlations between imaging features and pathological microenvironment and molecular subtypes, we can further reveal the biological basis of ABUS signs. Currently, there remains a significant gap in key technology research for DL-based multimodal data fusion of ABUS, which will become an important direction for future research.
However, it is noteworthy that while these advanced technologies enable precise diagnosis, they still face several key challenges in clinical practice. First, existing studies generally suffer from insufficient external validation data. In the process of promoting data diversity, it is crucial to ensure the prompt implementation of standardized protocols and enhance the security of multi-center collaboration through strengthened privacy data measures. Additionally, different medical institutions may use different models of ABUS equipment, and variations in image resolution, scanning parameters, and coronal reconstruction algorithms among different manufacturers’ ABUS devices exist. Most models are only trained on single-device data, so the generalization capability of models across different ABUS devices still requires validation. Beyond equipment differences, the lack of standardized protocols may introduce data heterogeneity due to variations in operator experience. Therefore, strict adherence to the manufacturer’s scanning guidelines is essential when using ABUS. Furthermore, as a core component of medical big data, medical imaging data is subject to strict data sharing regulations due to its storage standards, clinical application scenarios, and privacy sensitivity (114, 115). Current privacy protection technologies mainly focus on data de-identification and differential privacy (114, 116), but their privacy protection effectiveness still needs evaluation. McMahan et al. proposed federated learning (FL), a distributed ML framework (115). This framework coordinates multi-center collaboration through a central server: each hospital trains models using local data and only uploads parameter updates to the central server to generate a global model, which is then returned to each institution. This approach enables the mining of multi-center data value while protecting local data. Current research has confirmed its feasibility in ultrasound image pre-training (117), providing new ideas for ABUS privacy data research.
While addressing challenges of data privacy protection and model generalization capability, AI models face another critical bottleneck in clinical applications - the problem of insufficient interpretability. So-called “black box” models refer to algorithmic systems that lack transparency in their internal decision-making mechanisms (118). Such models often focus too much on the mapping relationship between input and output during development while neglecting the visualization of decision processes, making it difficult for clinicians to understand the model’s specific reasoning logic. This comprehension gap easily leads to clinicians’ distrust of AI diagnostic results. More importantly, even if the model achieves high prediction accuracy, its output may lack clinical interpretability, reducing the operability of prediction conclusions (117). Therefore, promoting Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) appears particularly important. XAI aims to make the decision-making process of AI applications transparent not only to domain experts or data scientists but also to clinicians unfamiliar with AI complexity through specific methods and technologies (119). Current XAI research mainly focuses on six methods: Feature-oriented methods, global methods, concept models, surrogate models, local pixel-based methods, and human-centric methods. Feature-oriented methods related to radiomics can quantify features’ contribution to model prediction; Concept Models can translate models into concepts understandable by physicians; Surrogate Models can replace complex model predictions by constructing simple models, providing reliable basis for personalized medicine; Local, Pixel-based Methods can display which pixels in the input image are most critical for model prediction; Human-centric Methods mainly emphasize explaining models from cognitive habits (120). Applying these XAI methods to ABUS radiomics analysis in the future will significantly improve model interpretability and clinical practicality.
In traditional ML and DL classification tasks, models typically require large amounts of manually annotated data for training. The data annotation process is not only time-consuming and expensive but may also introduce noise due to labeling errors, affecting model performance. In contrast, self-supervised learning (SSL) generates supervisory signals automatically from unlabeled data (such as predicting image rotation angles, filling in missing parts, or contrastive learning), significantly reducing dependence on manual annotation and thereby decreasing data annotation costs and complexity. SSL effectively solves the problems of high annotation costs, insufficient generalization capability, and low computational efficiency by utilizing the intrinsic structure of unlabeled data to generate supervisory signals. In the future, this method is expected to be applied to unannotated datasets such as ABUS, further improving the efficiency and accuracy of medical image analysis (121).
AI, with its exceptional analytical capabilities, has become an important technological tool in ABUS radiomics research. However, challenges such as insufficient model generalization, data privacy protection, and model interpretability still need to be addressed. In the future, overcoming these challenges will require close collaboration among multidisciplinary teams. On one hand, standardized ABUS imaging databases need to be established, and more prospective clinical studies should be conducted to validate the practical value of AI-assisted diagnostic systems. Simultaneously, intuitive visualization models need to be developed to help clinicians understand AI decision-making processes.
Author contributions
YG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YQ: Writing – review & editing. HZ: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author declare that financial support was received for the research of this article. This study has received funding by Yunnan Province Spring City Young Top Talents Special Program of China (C202114008).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support from Yunnan Province Spring City Young Top Talents Special Program of China (C202114008). The authors greatly appreciate for all the study participants, research staff and students who participated in this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
ABUS: Automatic breast ultrasound
ABVS: Automated breast volume scanner
ACC: Accuracy
ADCs: Antibody-drug conjugates
AI: Artificial intelligence
ALND: Axillary lymph node metastases
AP: Axial plane
AUC: Area Under the Curve
BC: Breast cancer
CAD: Computer-aided
CEU: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound
CNN: Convolutional Neural Network
CP: Coronal plane
DBT: Digital breast tomosynthesis
DL: Deep learning
DSC: Dice similarity coefficient
FDA: Food And Drug Administration
FL: Federated learning
FPs: False positives
GBDT: Gradient Boosted Decision Trees
HER2: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
HHUS: Handheld ultrasound
IARC: International Agency for Research on Cancer
IOIs: Image of interest
LASSO: Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator
LNs: Lymph nodes
LR: Logistic Regression
MG: Mammography
ML: Machine learning
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging
NAT: Neoadjuvant therapy
R-CNN: Region-based convolutional neural network
PRE: Precision
ROIs: Regions of interest
SE: Strain elastography
SEN: Sensitivity
SPE: Specificity
SSL: Self-supervised learning
SVM: Support Vector Machine
TKIs: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
XAI: Explainable Artificial Intelligence
XGBoost: Extreme Gradient Boosting
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Ibraheem SA, Mahmud R, Mohamad Saini S, Abu Hassan H, Keiteb AS, Dirie AM. Evaluation of diagnostic performance of automatic breast volume scanner compared to handheld ultrasound on different breast lesions: A systematic review. Diagn (Basel). (2022) 12(2):541. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12020541
3. Zanotel M, Bednarova I, Londero V, Linda A, Lorenzon M, Girometti R, et al. Automated breast ultrasound: basic principles and emerging clinical applications. Radiol Med. (2018) 123:1–12. doi: 10.1007/s11547-017-0805-z
4. Abdullah N, Mesurolle B, El-Khoury M, Kao E. Breast imaging reporting and data system lexicon for US: interobserver agreement for assessment of breast masses. Radiology. (2009) 252:665–72. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2523080670
5. Arimura H, Soufi M, Ninomiya K, Kamezawa H, Yamada M. Potentials of radiomics for cancer diagnosis and treatment in comparison with computer-aided diagnosis. Radiol Phys Technol. (2018) 11:365–74. doi: 10.1007/s12194-018-0486-x
6. Limkin EJ, Sun R, Dercle L, Zacharaki EI, Robert C, Reuzé S, et al. Promises and challenges for the implementation of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in oncology. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:1191–206. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx034
7. Al-Karawi D, Al-Zaidi S, Helael KA, Obeidat N, Mouhsen AM, Ajam T, et al. (2024). A review of artificial intelligence in breast imaging. Tomography. (2024) 10(5):705–26. doi: 10.3390/tomography10050055
8. Yadav A, Kolekar M, Zope M. ResNet-101 empowered deep learning for breast cancer ultrasound image classification. in Proc. 17th Int. Joint Conf. Biomed. Eng. Syst. Technol. Setúbal, Portugal: SciTePress (2024). pp. 763–9.
9. Zhang J, Wu J, Zhou XS, Shi F, Shen D. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence for breast cancer: Image augmentation, segmentation, diagnosis, and prognosis approaches. Semin Cancer Biol. (2023) 96:11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.09.001
10. Zhu J, Geng J, Shan W, Zhang B, Shen H, Dong X, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning model for breast lesion segmentation and characterization in multiparametric MRI. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:946580. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.946580
11. Karaca Aydemir BK, Telatar Z, Güney S, Dengiz B. Detecting and classifying breast masses via YOLO-based deep learning. Neural Comput Appl. (2025). 1–28. doi: 10.1007/s00521-025-11153-1
12. Cho Y, Misra S, Managuli R, Barr RG, Lee J, Kim C. Attention-based fusion network for breast cancer segmentation and classification using multi-modal ultrasound images. Ultrasound Med Biol. (2025) 51:568–77. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2024.11.020
13. Li H, Chen L, Liu M, Bao M, Zhang Q, Xu S. Diagnostic value of multimodal ultrasound for breast cancer and prediction of sentinel lymph node metastases. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1431883. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1431883
14. Yan P, Gong W, Li M, Zhang J, Li X, Jiang Y, et al. TDF-Net: Trusted Dynamic Feature Fusion Network for breast cancer diagnosis using incomplete multimodal ultrasound. Inf Fusion. (2024) 112:102592. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102592
15. Gatta G, Somma F, Sardu C, De Chiara M, Massafra R, Fanizzi A, et al. Automated 3D ultrasound as an adjunct to screening mammography programs in dense breast: literature review and metanalysis. J Personal Med. (2023) 13:1683. doi: 10.3390/jpm13121683
16. Maturo VG, Zusmer NR, Gilson AJ, Smoak WM, Janowitz WR, Bear BE, et al. Ultrasound of the whole breast utilizing a dedicated automated breast scanner. Radiology. (1980) 137:457–63. doi: 10.1148/radiology.137.2.6254110
17. Bassett L, Kimme-Smith C, Sutherland L, Gold R, Sarti D, King 3W. Automated and hand-held breast US: effect on patient management. Radiology. (1987) 165:103–8. doi: 10.1148/radiology.165.1.3306779
18. Helal M, Mansour S, Khaled R, Bassam L. The role of automated breast ultrasound in the assessment of the local extent of breast cancer. Breast J. (2021) 27:113–9. doi: 10.1111/tbj.14132
19. Kaplan SS. Automated whole breast ultrasound. Radiol Clinics. (2014) 52:539–46. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2014.01.002
20. Nakashima K. Utilities and interpretation of ABUS (New vesion, invenia) for breast ultrasound screening. Ultrasound Med Biol. (2017) 43:S13. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.08.980
21. Huang EP, O’Connor JP, McShane LM, Giger ML, Lambin P, Kinahan PE, et al. Criteria for the translation of radiomics into clinically useful tests. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2023) 20:69–82. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00707-0
22. Zhang L, Wang Y, Peng Z, Weng Y, Fang Z, Xiao F, et al. The progress of multimodal imaging combination and subregion based radiomics research of cancers. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:3458. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.71046
23. Liu Z, Wang S, Dong D, Wei J, Fang C, Zhou X, et al. The applications of radiomics in precision diagnosis and treatment of oncology: opportunities and challenges. Theranostics. (2019) 9:1303–22. doi: 10.7150/thno.30309
24. Sheng L, Yang C, Chen Y, Song B. Machine learning combined with radiomics facilitating the personal treatment of Malignant liver tumors. Biomedicines. (2023) 12:58. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010058
25. Liu S, Wang Y, Yang X, Lei B, Liu L, Li SX, et al. Deep learning in medical ultrasound analysis: a review. Engineering. (2019) 5:261–75. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2018.11.020
26. Chen Y, Mancini M, Zhu X, Akata Z. Semi-supervised and unsupervised deep visual learning: A survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. (2022) 46(3):1327–47. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2022.3201576
27. Qi Y-J, Su G-H, You C, Zhang X, Xiao Y, Jiang Y-Z, et al. Radiomics in breast cancer: Current advances and future directions. Cell Rep Med. (2024) 5:101719. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101719
28. Parekh V, Jacobs MA. Radiomics: a new application from established techniques. Expert Rev Precis Med Drug Dev. (2016) 1:207–26. doi: 10.1080/23808993.2016.1164013
29. Mohanty R, Allabun S, Solanki SS, Pani SK, Alqahtani MS, Abbas M, et al. NAMSTCD: a novel augmented model for spinal cord segmentation and tumor classification using deep nets. Diagnostics. (2023) 13:1417. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13081417
30. Taye MM. Understanding of machine learning with deep learning: architectures, workflow, applications and future directions. Computers. (2023) 12:91. doi: 10.3390/computers12050091
31. Satake H, Ishigaki S, Ito R, Naganawa S. Radiomics in breast MRI: Current progress toward clinical application in the era of artificial intelligence. La Radiol Med. (2022) 127:39–56. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01423-y
32. Chae A, Yao MS, Sagreiya H, Goldberg AD, Chatterjee N, MacLean MT, et al. Strategies for implementing machine learning algorithms in the clinical practice of radiology. Radiology. (2024) 310:e223170. doi: 10.1148/radiol.223170
33. Adlung L, Cohen Y, Mor U, Elinav E. Machine learning in clinical decision making. Med. (2021) 2:642–65. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2021.04.006
34. Choy G, Khalilzadeh O, Michalski M, Do S, Samir AE, Pianykh OS, et al. Current applications and future impact of machine learning in radiology. Radiology. (2018) 288:318–28. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018171820
35. Wang H, Chen W, Jiang S, Li T, Chen F, Lei J, et al. Intra-and peritumoral radiomics features based on multicenter automatic breast volume scanner for noninvasive and preoperative prediction of HER2 status in breast cancer: a model ensemble research. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:5020. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55838-4
36. Ma Q, Shen C, Gao Y, Duan Y, Li W, Lu G, et al. Radiomics analysis of breast lesions in combination with coronal plane of ABVS and strain elastography. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). (2023) 15:381–90. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S410356
37. Hu B, Xu Y, Gong H, Tang L, Wang L, Li H. Nomogram utilizing ABVS radiomics and clinical factors for predicting </= 3 positive axillary lymph nodes in HR+/HER2- breast cancer with 1–2 positive sentinel nodes. Acad Radiol. (2024) 31:2684–94. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.01.026
38. Li N, Song C, Huang X, Zhang H, Su J, Yang L, et al. Optimized radiomics nomogram based on automated breast ultrasound system: A potential tool for preoperative prediction of metastatic lymph node burden in breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). (2023) 15:121–32. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S398300
39. Wang S-J, Liu H-Q, Yang T, Huang M-Q, Zheng B-W, Wu T, et al. Automated breast volume scanner (ABVS)-based radiomic nomogram: a potential tool for reducing unnecessary biopsies of BI-RADS 4 lesions. Diagnostics. (2022) 12:172. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12010172
40. Zhang XY, Wei Q, Wu GG, Tang Q, Pan XF, Chen GQ, et al. Artificial intelligence - based ultrasound elastography for disease evaluation - a narrative review. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1197447. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1197447
41. van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, Hosny A, Aucoin N, Narayan V, et al. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:e104–7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0339
42. Wang H, Yang X, Ma S, Zhu K, Guo S. An optimized radiomics model based on automated breast volume scan images to identify breast lesions: comparison of machine learning methods: comparison of machine learning methods. J Ultrasound Med. (2022) 41:1643–55. doi: 10.1002/jum.15845
43. Shiyan G, Liqing J, Yueqiong Y, Yan Z. A clinical-radiomics nomogram based on multimodal ultrasound for predicting the Malignancy risk in solid hypoechoic breast lesions. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1256146. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1256146
44. Ma Q, Wang J, Xu D, Zhu C, Qin J, Wu Y, et al. Automatic breast volume scanner and B-ultrasound-based radiomics nomogram for clinician management of BI-RADS 4A lesions. Acad Radiol. (2023) 30:1628–37. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2022.11.002
45. Li F, Zhu T-w, Lin M, Zhang X-t, Zhang Y-l, Zhou A-l, et al. Enhancing ki-67 prediction in breast cancer: integrating intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics from automated breast ultrasound via machine learning. Acad Radiol. (2024) 31(7):2663–73. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.12.036
46. Wu Y, Ma Q, Fan L, Wu S, Wang J. An automated breast volume scanner-based intra-and peritumoral radiomics nomogram for the preoperative prediction of expression of Ki-67 in breast Malignancy. Acad Radiol. (2024) 31:93–103. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.07.004
47. Hu B, Xu Y, Gong H, Tang L, Li H. Radiomics analysis of intratumoral and various peritumoral regions from automated breast volume scanning for accurate ki-67 prediction in breast cancer using machine learning. Acad Radiol. (2024) 32(2):651–63. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.08.040
48. Jiang W, Deng X, Zhu T, Fang J, Li J. ABVS-based radiomics for early predicting the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancers. Breast Cancer: Targets Ther. (2023) 15:625–36. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S418376
49. Chen Y, Xie Y, Li B, Shao H, Na Z, Wang Q, et al. Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS)-based radiomics nomogram: an individualized tool for predicting axillary lymph node tumor burden in patients with early breast cancer. BMC Cancer. (2023) 23:340. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10743-3
50. Li Y, Wu X, Yan Y, Zhou P. Automated breast volume scanner based Radiomics for non-invasively prediction of lymphovascular invasion status in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. (2023) 23:813. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11336-w
51. Wang H, Yang X-w, Chen F, Qin Y-y, Li X-b, Ma S-m, et al. Non-invasive assessment of axillary lymph node metastasis risk in early invasive breast cancer adopting automated breast volume scanning-based radiomics nomogram: a multicenter study. Ultrasound Med Biol. (2023) 49:1202–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2023.01.006
52. Del Corso G, Germanese D, Caudai C, Anastasi G, Belli P, Formica A, et al. Adaptive machine learning approach for importance evaluation of multimodal breast cancer radiomic features. J Imaging Inform Med. (2024) 37:1642–51. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01064-3
53. Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Ravdin PM, Hayes MM, Gelmon KA. Ki67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol. (2010) 11:174–83. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70262-1
54. Martins-Branco D, Nader-Marta G, Molinelli C, Ameye L, Paesmans M, Ignatiadis M, et al. Ki-67 index after neoadjuvant endocrine therapy as a prognostic biomarker in patients with ER-positive/HER2-negative early breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. (2023) 194:113358. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.113358
55. Tommasi C, Airò G, Pratticò F, Testi I, Corianò M, Pellegrino B, et al. Hormone receptor-positive/HER2-positive breast cancer: hormone therapy and anti-HER2 treatment: an update on treatment strategies. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:1873. doi: 10.3390/jcm13071873
56. Gutierrez C, Schiff R. HER2: biology, detection, and clinical implications. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2011) 135:55–62. doi: 10.5858/2010-0454-RAR.1
57. Godoy-Ortiz A, Sanchez-Muñoz A, Chica Parrado MR, Álvarez M, Ribelles N, Rueda Dominguez A, et al. Deciphering HER2 breast cancer disease: biological and clinical implications. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:1124. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01124
58. Swain SM, Shastry M, Hamilton E. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer: advances and future directions. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2023) 22:101–26. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00579-0
59. Zhang X-N, Gao Y, Zhang X-Y, Guo N-J, Hou W-Q, Wang S-W, et al. Detailed curriculum vitae of HER2-targeted therapy. Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 245:108417. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108417
60. Montemurro F, Nuzzolese I, Ponzone R. Neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy in early breast cancer? Expert Opin Pharmacother. (2020) 21:1071–82. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1746273
61. Colomer R, Saura C, Sánchez-Rovira P, Pascual T, Rubio IT, Burgués O, et al. Neoadjuvant management of early breast cancer: a clinical and investigational position statement. Oncol. (2019) 24:603–11. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0228
62. Chang JM, Leung JW, Moy L, Ha SM, Moon WK. Axillary nodal evaluation in breast cancer: state of the art. Radiology. (2020) 295:500–15. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020192534
63. Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, Beitsch PD, Brennan MB, Kelemen PR, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. Jama. (2017) 318:918–26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470
64. Pesek S, Ashikaga T, Krag LE, Krag D. The false-negative rate of sentinel node biopsy in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis. World J Surg. (2012) 36:2239–51. doi: 10.1007/s00268-012-1623-z
65. Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. (2017) 60(6):84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386
66. Yu X, Zhou Q, Wang S, Zhang YD. A systematic survey of deep learning in breast cancer. Int J Intelligent Syst. (2022) 37:152–216. doi: 10.1002/int.22622
67. Adam R, Dell’Aquila K, Hodges L, Maldjian T, Duong TQ. Deep learning applications to breast cancer detection by magnetic resonance imaging: a literature review. Breast Cancer Res. (2023) 25:87. doi: 10.1186/s13058-023-01687-4
68. Carriero A, Groenhoff L, Vologina E, Basile P, Albera M. Deep learning in breast cancer imaging: state of the art and recent advancements in early 2024. Diagnostics. (2024) 14:848. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14080848
69. Cheng PM, Montagnon E, Yamashita R, Pan I, Cadrin-Chenevert A, Perdigon Romero F, et al. Deep learning: an update for radiologists. Radiographics. (2021) 41:1427–45. doi: 10.1148/rg.2021200210
70. Yasaka K, Akai H, Kunimatsu A, Kiryu S, Abe O. Deep learning with convolutional neural network in radiology. Japanese J Radiol. (2018) 36:257–72. doi: 10.1007/s11604-018-0726-3
71. Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint. (2014) arXiv:1409.1556. doi: arxiv-1409.1556
72. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA. pp. 770–8.
73. Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ. (2017). Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA. pp. 4700–8.
74. Li J, Zhu G, Hua C, Feng M, Bennamoun B, Li P, et al. A systematic collection of medical image datasets for deep learning. ACM Comput Surveys. (2023) 56:1–51. doi: 10.1145/3615862
75. Kumar S. Advancements in medical image segmentation: A review of transformer models. Comput Electr Eng. (2025) 123:110099. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2025.110099
76. Wang Y, Wang N, Xu M, Yu J, Qin C, Luo X, et al. Deeply-supervised networks with threshold loss for cancer detection in automated breast ultrasound. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. (2019) 39:866–76. doi: 10.1109/TMI.42
77. Wang F, Liu X, Yuan N, Qian B, Ruan L, Yin C, et al. Study on automatic detection and classification of breast nodule using deep convolutional neural network system. J Thor Dis. (2020) 12:4690. doi: 10.21037/jtd-19-3013
78. Moon WK, Huang Y-S, Hsu C-H, Chien T-YC, Chang JM, Lee SH, et al. Computer-aided tumor detection in automated breast ultrasound using a 3-D convolutional neural network. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. (2020) 190:105360. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105360
79. Wang Y, Qin C, Lin C, Lin D, Xu M, Luo X, et al. 3D Inception U-net with asymmetric loss for cancer detection in automated breast ultrasound. Med Phys. (2020) 47:5582–91. doi: 10.1002/mp.14389
80. Li Y, Wu W, Chen H, Cheng L, Wang S. 3D tumor detection in automated breast ultrasound using deep convolutional neural network. Med Phys. (2020) 47:5669–80. doi: 10.1002/mp.14477
81. PhD XL, Xu M, Tang G, PhD YW, Wang N, PhD DN, et al. The lesion detection efficacy of deep learning on automatic breast ultrasound and factors affecting its efficacy: a pilot study. Br J Radiol. (2022) 95:20210438. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20210438
82. Oh K, Lee SE, Kim E-K. 3-D breast nodule detection on automated breast ultrasound using faster region-based convolutional neural networks and U-Net. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:22625. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49794-8
83. Li Y, Zhang Z, Cheng Z, Cheng L, Chen X. Semi-supervised learning for ABUS tumor detection using deep learning method. IET Image Process. (2023) 17:2113–26. doi: 10.1049/ipr2.12777
84. Malekmohammadi A, Barekatrezaei S, Kozegar E, Soryani M. Mass detection in automated 3-D breast ultrasound using a patch Bi-ConvLSTM network. Ultrasonics. (2023) 129:106891. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2022.106891
85. Lei Y, He X, Yao J, Wang T, Wang L, Li W, et al. Breast tumor segmentation in 3D automatic breast ultrasound using Mask scoring R-CNN. Med Phys. (2021) 48:204–14. doi: 10.1002/mp.14569
86. Pan P, Chen H, Li Y, Cai N, Cheng L, Wang S. Tumor segmentation in automated whole breast ultrasound using bidirectional LSTM neural network and attention mechanism. Ultrasonics. (2021) 110:106271. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2020.106271
87. Zhou Y, Chen H, Li Y, Liu Q, Xu X, Wang S, et al. Multi-task learning for segmentation and classification of tumors in 3D automated breast ultrasound images. Med Image Anal. (2021) 70:101918. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101918
88. Cao X, Chen H, Li Y, Peng Y, Zhou Y, Cheng L, et al. Auto-DenseUNet: Searchable neural network architecture for mass segmentation in 3D automated breast ultrasound. Med Image Anal. (2022) 82:102589. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102589
89. Cheng Z, Li Y, Chen H, Zhang Z, Pan P, Cheng L. DSGMFFN: Deepest semantically guided multi-scale feature fusion network for automated lesion segmentation in ABUS images. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. (2022) 221:106891. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106891
90. Wang Q, Chen H, Luo G, Li B, Shang H, Shao H, et al. Performance of novel deep learning network with the incorporation of the automatic segmentation network for diagnosis of breast cancer in automated breast ultrasound. Eur Radiol. (2022) 32:7163–72. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08836-x
91. Zhou Y, Chen H, Li Y, Cao X, Wang S, Shen D. Cross-model attention-guided tumor segmentation for 3D automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) images. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf. (2021) 26:301–11. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3081111
92. Pan P, Li Y, Chen H, Sun J, Li X, Cheng L. ABUS tumor segmentation via decouple contrastive knowledge distillation. Phys Med Biol. (2023) 69:015019. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad1274
93. Li Y, Cheng Z, Sun J, Chen H, Pan P, Ren Y. Multi-domain consistency constraint model for semi-supervised lesion segmentation in automatic breast ultrasound (ABUS). Biomed Signal Process Control. (2024) 98:106724. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2024.106724
94. Yang X, Li X, Qin Y, Wang H, Zhao C, Yin Y. Interlayer information fusion-based and dual-attention improved U-Net for ABVS image sequence intelligent tumor segmentation. Biomed Signal Process Control. (2024) 98:106740. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2024.106740
95. Malekmohammadi A, Soryani M, Kozegar E. Mass segmentation in automated breast ultrasound using an enhanced attentive UNet. Expert Syst Appl. (2024) 245:123095. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.123095
96. Li Y, Li C, Yang T, Chen L, Huang M, Yang L, et al. Multiview deep learning networks based on automated breast volume scanner images for identifying breast cancer in BI-RADS 4. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1399296. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1399296
97. Li Y, Ren Y, Cheng Z, Sun J, Pan P, Chen H. Automatic breast ultrasound (ABUS) tumor segmentation based on global and local feature fusion. Phys Med Biol. (2024) 69:115039. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad4d53
98. Wang Y, Choi EJ, Choi Y, Zhang H, Jin GY, Ko S-B. Breast cancer classification in automated breast ultrasound using multiview convolutional neural network with transfer learning. Ultrasound Med Biol. (2020) 46:1119–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.01.001
99. Zhuang Z, Ding W, Zhuang S, Raj ANJ, Wang J, Zhou W, et al. Tumor classification in automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) based on a modified extracting feature network. Comput Med Imaging Graph. (2021) 90:101925. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2021.101925
100. Xiang H, Huang Y-S, Lee C-H, Chien T-YC, Lee C-K, Liu L, et al. 3-D Res-CapsNet convolutional neural network on automated breast ultrasound tumor diagnosis. Eur J Radiol. (2021) 138:109608. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109608
101. Hejduk P, Marcon M, Unkelbach J, Ciritsis A, Rossi C, Borkowski K, et al. Fully automatic classification of automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) imaging according to BI-RADS using a deep convolutional neural network. Eur Radiol. (2022) 32:4868–78. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08558-0
102. Kim D, Park H, Jang M, Lee K-J. Mask branch network: weakly supervised branch network with a template mask for classifying masses in 3D automated breast ultrasound. Appl Sci. (2022) 12:6332. doi: 10.3390/app12136332
103. Ding W, Zhang H, Zhuang S, Zhuang Z, Gao Z. Multi-view stereoscopic attention network for 3D tumor classification in automated breast ultrasound. Expert Syst Appl. (2023) 234:120969. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120969
104. Yap MH, Pons G, Marti J, Ganau S, Sentis M, Zwiggelaar R, et al. Automated breast ultrasound lesions detection using convolutional neural networks. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf. (2017) 22:1218–26. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2017.2731873
105. Pengiran Mohamad DNF, Mashohor S, Mahmud R, Hanafi M, Bahari N. Transition of traditional method to deep learning based computer-aided system for breast cancer using automated breast ultrasound system (abus) images: a review. Artif Intell Rev. (2023) 56:15271–300. doi: 10.1007/s10462-023-10511-6
106. Kozegar E, Soryani M, Behnam H, Salamati M, Tan T. Computer aided detection in automated 3-D breast ultrasound images: a survey. Artif Intell Rev. (2020) 53:1919–41. doi: 10.1007/s10462-019-09722-7
107. Chiang T-C, Huang Y-S, Chen R-T, Huang C-S, Chang R-F. Tumor detection in automated breast ultrasound using 3-D CNN and prioritized candidate aggregation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. (2018) 38:240–9. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2860257
108. Minaee S, Boykov Y, Porikli F, Plaza A, Kehtarnavaz N, Terzopoulos D. Image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. (2021) 44:3523–42. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3059968
109. Alemán-Flores M, Álvarez L, Caselles V. Texture-oriented anisotropic filtering and geodesic active contours in breast tumor ultrasound segmentation. J Math Imaging Vision. (2007) 28:81–97. doi: 10.1007/s10851-007-0015-8
110. Kozegar E, Soryani M, Behnam H, Salamati M, Tan T. Mass segmentation in automated 3-D breast ultrasound using adaptive region growing and supervised edge-based deformable model. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. (2017) 37:918–28. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2787685
111. Agarwal R, Diaz O, Lladó X, Gubern-Mérida A, Vilanova JC, Martí R. Lesion segmentation in automated 3D breast ultrasound: volumetric analysis. Ultrasonic Imaging. (2018) 40:97–112. doi: 10.1177/0161734617737733
112. Xi X, Shi H, Han L, Wang T, Ding HY, Zhang G, et al. Breast tumor segmentation with prior knowledge learning. Neurocomputing. (2017) 237:145–57. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.067
113. Ibraheem SA, Mahmud R, Mohamad Saini S, Abu Hassan H, Keiteb AS. Diagnostic performance of prototype handheld ultrasound according to the fifth edition of BI-RADS for breast ultrasound compared with automated breast ultrasound among females with positive lumps. Diagnostics. (2023) 13:1065. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13061065
114. Ziller A, Usynin D, Braren R, Makowski M, Rueckert D, Kaissis G. Medical imaging deep learning with differential privacy. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:13524. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93030-0
115. McMahan B, Moore E, Ramage D, Hampson S, y Arcas BA. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA. pp. 1273–82.
116. Ohno-MaChado L, Jiang X, Kuo T-T, Tao S, Chen L, Ram PM, et al. A hierarchical strategy to minimize privacy risk when linking “De-identified” data in biomedical research consortia. J Biomed Inf. (2023) 139:104322. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2023.104322
117. Xua B, Yang G. Interpretability research of deep learning: A literature survey. Inf Fusion. (2024) 115:102721. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102721
119. Arrieta AB, Díaz-Rodríguez N, Del Ser J, Bennetot A, Tabik S, Barbado A, et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inf Fusion. (2020) 58:82–115. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012
120. Sadeghi Z, Alizadehsani R, Cifci MA, Kausar S, Rehman R, Mahanta P, et al. A review of Explainable Artificial Intelligence in healthcare. Comput Electr Eng. (2024) 118:109370. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2024.109370
Keywords: breast, breast tumor, automatic breast ultrasound, artificial intelligence, radiomics, deep learning, machine learning
Citation: Guo Y, Li N, Song C, Yang J, Quan Y and Zhang H (2025) Artificial intelligence-based automated breast ultrasound radiomics for breast tumor diagnosis and treatment: a narrative review. Front. Oncol. 15:1578991. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1578991
Received: 18 February 2025; Accepted: 14 April 2025;
Published: 08 May 2025.
Edited by:
Izidor Mlakar, University of Maribor, SloveniaReviewed by:
Yuanpin Zhou, Zhejiang University, ChinaAgnesh Yadav, Indian Institute of Technology Patna, India
Dinghao Guo, Northeastern University, China
Copyright © 2025 Guo, Li, Song, Yang, Quan and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongjiang Zhang, Mzc1MDU2MjI5QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yinglin Guo
Yinglin Guo Ning Li2†
Ning Li2† Juan Yang
Juan Yang