- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, The Affiliated Lihuili Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Health Science Center, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
RNA methylation is a type of reversible chemical modification in epitranscriptomics that influences gene expression by dynamically regulating RNA functions. RNA methylation comprises N6-methyladenosine (m6A), 5-methylcytosine (m5C), N7-methylguanosine (m7G), N1-methyladenosine (m1A), and 3-methylcytosine (m3C) modifications. These are dynamically controlled by a tripartite enzymatic system: methyltransferases (“writers”) add methyl groups, demethylases (“erasers”) remove them, and RNA-binding proteins (“readers”) recognize and interpret the modifications to mediate downstream biological effects. Extensive research has shown the importance of RNA methylation in the onset and progression of cancer. RNA methylation contributes to radioresistance in cancer cells through various mechanisms, affecting therapeutic outcomes. To date, the precise functions of RNA methylation in cancer radioresistance remain unclear. This review summarizes recent advances in m6A, m5C, m7G, and m1A methylation in cancer radioresistance regulation and discusses the clinical potential of precision therapeutic strategies targeting these methylation modifications.
1 Introduction
Cancer represents a major challenge to public health, with an overall 19.74 million new diagnoses reported worldwide in 2022 alone. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) projects a 77% increase in annual global cancer cases by 2050, reaching approximately 35 million cases (1). Based on the updated cancer epidemiology statistics from the United States, the projected incidence of newly confirmed malignant neoplasms in 2025 is 2,041,910 cases, with an estimated 618,120 deaths attributable to malignancies (2).Current cancer treatment options include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and novel targeted therapies (3). Among these, radiotherapy is crucial in cancer treatment, providing clinical benefits to over 50% of patients (4). Radiotherapy primarily involves inducing DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) to damage cancer cells (5). However, radioresistance, characterized by cancer cells’ resistance to radiotherapy, reduces therapeutic efficacy and can lead to treatment failure (6), posing a significant challenge in managing malignant tumors. Notably, in pharmacotherapy, resistance to chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy has been established as closely associated with RNA modifications (7). Simultaneously, the mechanisms underlying radioresistance are complex, involving multiple biological processes. Research has identified several key factors contributing to the development of radioresistance in cancer cells, including improved DNA damage repair capacity, alterations in the tumor microenvironment (TME), activation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), the presence of cancer stem cells (CSCs), regulation of autophagy, involvement of transcription factors such as nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1), as well as epitranscriptomics (8, 9). In recent years, RNA methylation, an important reversible chemical modification in the field of epitranscriptomics, has been closely associated with cancer cell radioresistance. RNA methylation affects cancer cell sensitivity to radiotherapy by regulating gene expression, RNA stability, and translation efficiency.
RNA methylation serves as a fundamental regulatory mechanism within the field of epitranscriptomics. It refers to the reversible chemical modifications of RNA nucleotides that dynamically regulate gene expression without altering the RNA sequence. This process encompasses several types of methylation, including N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation, 5-methylcytosine (m5C) methylation, N7-methylguanosine (m7G) methylation, N1-methyladenosine (m1A) methylation, and 3-methylcytosine (m3C) methylation. These modifications are found in various types of RNA, including mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA (10). RNA methylation regulates gene expression and has been linked to tumorigenesis and metastasis, as well as resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. In cancer, RNA methylation is controlled primarily by methyltransferases, demethylases, and binding proteins. Methyltransferases transfer methyl groups to specific bases on the RNA, thus acting as “writers”. Demethylases are responsible for removing methyl groups, making RNA methylation dynamic and reversible, and thus serve as “erasers”. Binding proteins recognize and interact with methylated RNA, acting as “readers”, affecting RNA metabolism and function (10, 11). Together, these three components regulate RNA methylation status.
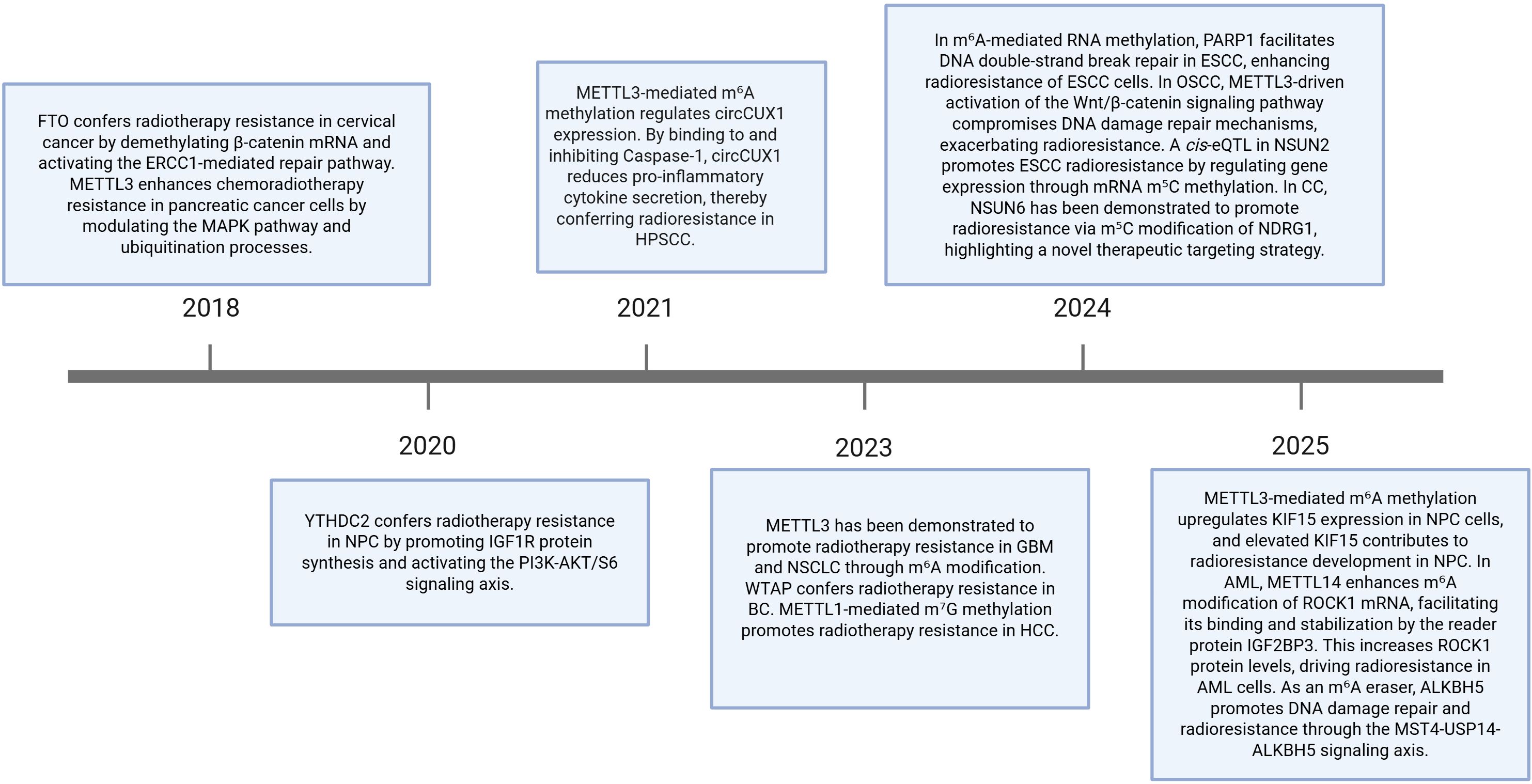
This review summarizes recent advances in m6A, m5C, m7G, and m1A methylation in cancer radioresistance (Figure 1) and discusses the clinical potential of targeted therapeutic strategies aimed at these methylation modifications (Table 1).
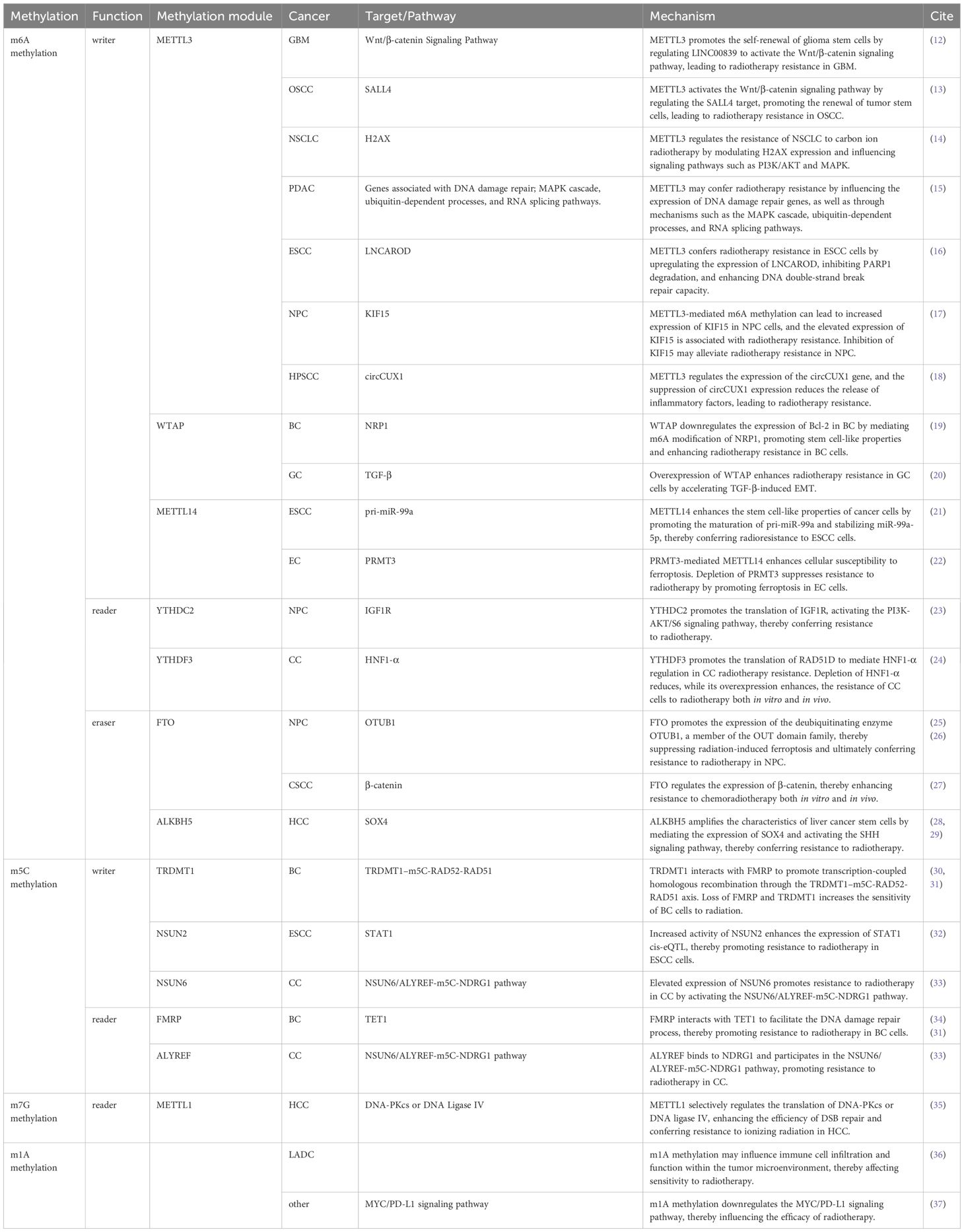
Table 1. The regulatory role of RNA methylation (including m6A, m5C, m7G and m1A) in radioresistance across multiple cancer types.
2 m6A methylation and radiotherapy resistance
m6A methylation is a well-studied modification controlled by a tripartite system of “writers,” “erasers,” and “readers.” The “writers” are represented by methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) (38), METTL14 (39), METTL16 (40), Wilms tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP) (41), and VIRMA (42). The “erasers” include fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) (43) and ALKB homolog 5 (ALKBH5) (44). The “readers” include YTHDC1 (45), YTHDC2 (46), YTHDF1 (47), YTHDF2 (48), and the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (HNRNP) family (49) (Figure 2). These m6A methylation regulators can promote or suppress cancer initiation and progression (50–52) and are also closely associated with cancer radioresistance (Figure 3).
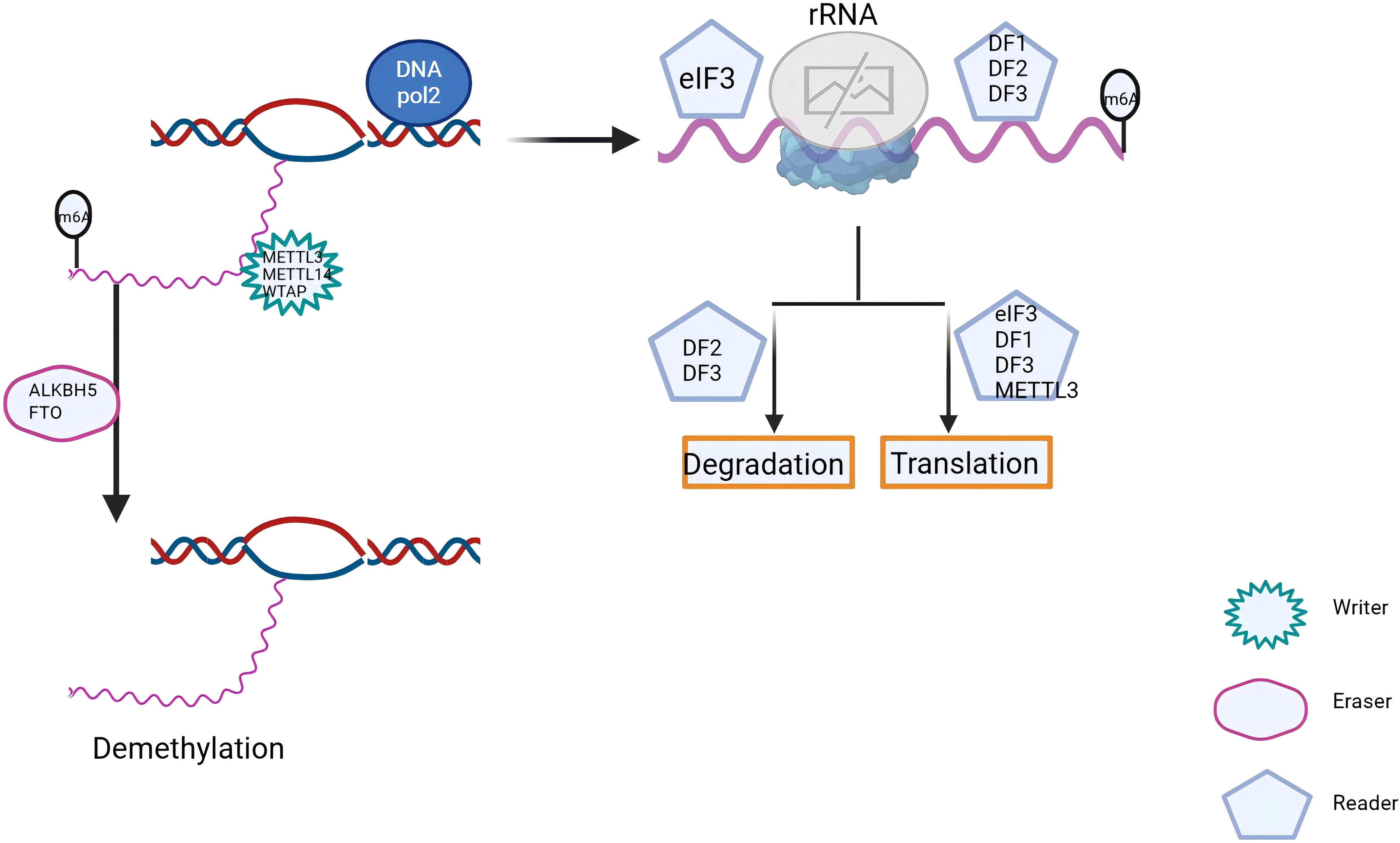
Figure 2. m6A RNA methylation is a dynamic and reversible epigenetic modification. Its regulation is primarily mediated by three key classes of proteins: “writers”, “erasers”, and” readers”. Through the coordinated actions of these proteins, m6A dynamically modulates mRNA and cellular functions, playing a pivotal role in cancer initiation, progression, and radiation resistance.
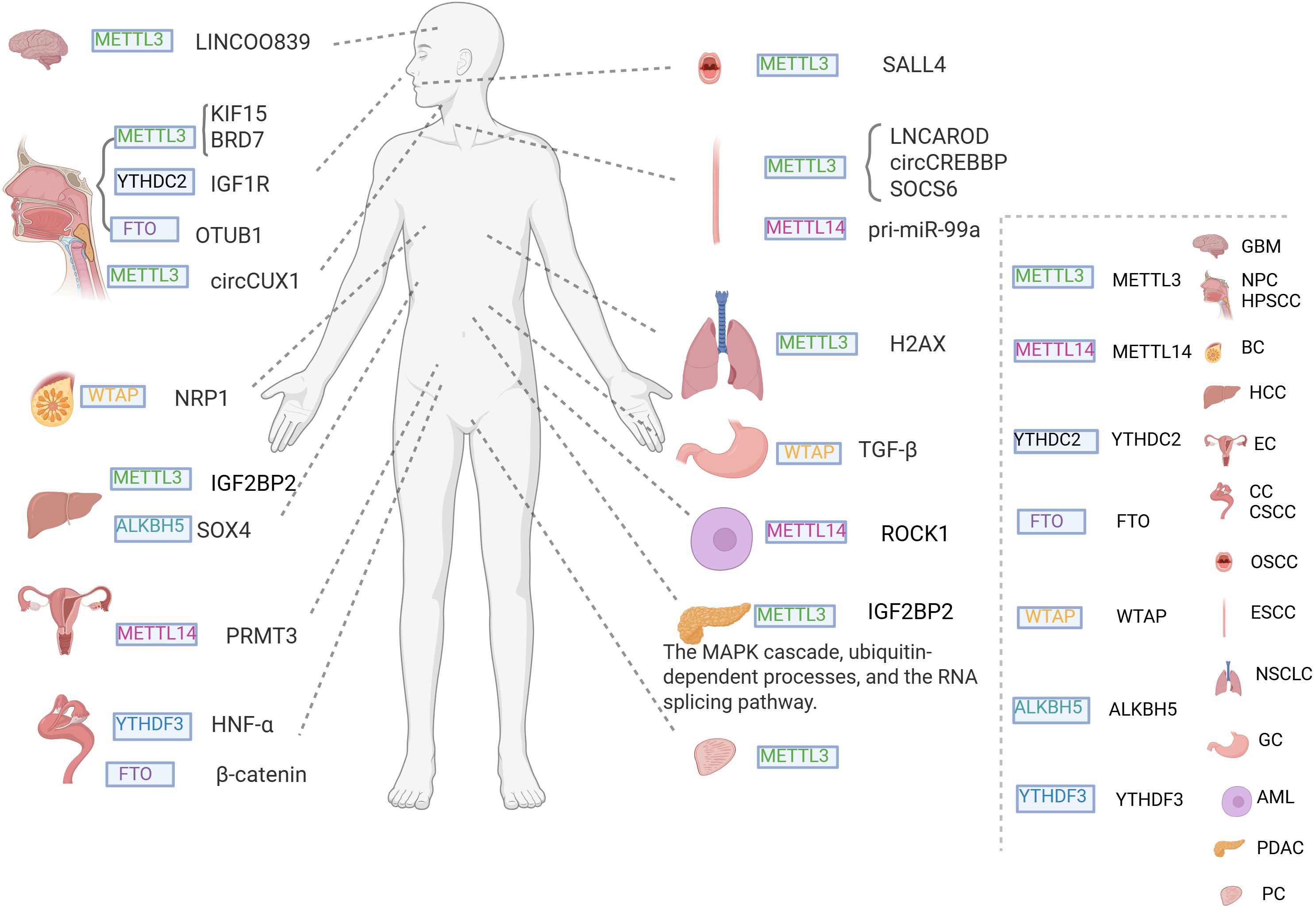
Figure 3. The role of m6A RNA modification in cancer radiotherapy resistance. m6A RNA modification is a dynamic and reversible process, and its associated proteins are implicated in the development of radiotherapy resistance in various cancers. Regulatory factors, known as “writers”, include METTL3, WTAP and METTL14; ’readers’ include YTHDC2 and YTHDF3; and ‘erasers’ include FTO and ALKBH5.
2.1 METTL3
METTL3, one of the methyltransferases responsible for m6A methylation, has been shown to potentially contribute to cancer radioresistance by improving DNA repair capacity in malignant cells, promoting CSCs generation, and inducing tumor cell autophagy.
2.1.1 Glioblastoma
METTL3 contributes to radioresistance in GBM by enhancing glioma stem cell (GSC) generation (12, 53). RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays identified SOX2 as an authentic m6A substrate of METTL3. METTL3-mediated m6A modification stabilizes SOX2 mRNA, thereby maintaining the stemness properties of glioma stem cells (GSCs) and consequently driving radioresistance (53). Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin axis is closely associated with glioblastoma stem-like cells (GBM-SCs) formation (54). RNA-seq and m6A-seq analyses identified LINC00839, a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), as a downstream target of METTL3. Further studies revealed that LINC00839 activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by interacting with its key components, therefore supporting GSC self-renewal and promoting radioresistance in cancer cells (12).
2.1.2 Oral squamous cell carcinoma
METTL3 regulates transcriptional targets, including SALL4. The transcriptional activation of SALL4 promotes β-catenin nuclear translocation and upregulates downstream target gene expression after radiotherapy, activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (13). In OSCC, this pathway activation maintains CSC self-renewal and stemness and impairs DNA damage repair, exacerbating radioresistance in cancer cells (13).
2.1.3 Lung cancer
METTL3-mediated m6A modifications of mRNA are closely linked to carbon ion radiotherapy resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer(NSCLC). METTL3 is upregulated in NSCLC, and its knockout enhances cellular sensitivity to radiotherapy. RNA-seq and m6A-seq analyses indicated that METTL3 regulates the expression of histone H2A family member X (H2AX) through m6A modification, affecting the PI3K/AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) axes, which contribute to NSCLC resistance to carbon ion radiotherapy (14). Furthermore, recent investigations indicate that METTL3 overexpression promotes colony formation and proliferation in bystander cells of irradiated lung cancer, suppresses micronucleus formation kinetics, and attenuates DNA damage by regulating inflammatory responses (55). This suggests that reduced DNA damage may contribute to radiation resistance in LC.
2.1.4 Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Studies have shown that METTL3 significantly increases radioresistance in PDAC cells by regulating m6A RNA modifications. Under low-dose irradiation, METTL3-knockdown cells exhibit increased radiosensitivity, suggesting that METTL3 may contribute to low-dose radiotherapy resistance. Mechanistically, METTL3 promotes radioresistance in PDAC by activating the MAPK cascade and processes involving ubiquitin and RNA splicing, which improves DNA damage repair. However, the precise mechanisms remain unclear and require further investigation (15). In PDAC, insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) upregulates the expression of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) by binding to m6A sites on PLK1 mRNA. Meanwhile, METTL3 maintains PLK1 expression through m6A methylation, thereby regulating the PDAC cell cycle. Disruption of the METTL3-IGF2BP2-PLK1 axis (for instance, through methylation inhibition) induces replication stress-induced cell death (56), presenting a novel therapeutic strategy to overcome radioresistance in PDAC.
2.1.5 Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
ESCC contributes to radioresistance by affecting DNA recombination repair and signaling pathway LNCAROD has been identified as a METTL3-mediated lncRNA. METTL3 significantly upregulates LNCAROD expression through m6A methylation. LNCAROD promotes the interaction between poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) and nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1), preventing ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated degradation of PARP1. PARP1 is associated with DNA repair and facilitates the repair of DNA DSBs in ESCC, thus increasing ESCC radioresistance (16). Furthermore, METTL3 enhances radiosensitivity in ESCC through the m6A modification of circular CREBBP (circCREBBP). Mechanistically, METTL3-mediated m6A methylation of circCREBBP promotes its competitive binding with IGF2BP3, thereby inhibiting IGF2BP3-mediated stabilization of the oncogene MYC mRNA, which leads to the downregulation of MYC expression (57). Both in vitro and in vivo experiments confirm that the METTL3/circCREBBP/IGF2BP3/MYC axis reverses radioresistance. Genetic knockdown of circCREBBP significantly reduces MYC instability, enhances ESCC cell survival, and promotes radioresistance. Conversely, activation of this axis serves as a key therapeutic target for radiosensitization (57). Additionally, Ma et al. discovered that METTL3 catalytically elevates m6A modification levels in the 3’ UTR of SOCS6 mRNA, consequently inhibiting SOCS6 gene expression and blocking ferroptosis, which ultimately contributes to radioresistance in ESCC (58).
2.1.6 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
METTL3 serves as a master regulator of radioresistance in NPC, driving therapeutic resistance through three independent pathways. Its downstream targets—KIF15, the tumor suppressor BRD7, and SLC7A11—constitute a critical intervention network (17, 37, 59). Li et al. discovered that METTL3-mediated m6A methylation upregulates KIF15 expression in NPC cells, and this KIF15 overexpression contributes to radioresistance. Further studies demonstrate that inhibiting KIF15 expression alleviates NPC radioresistance by suppressing STAT3 activation and promoting autophagy (17). In parallel, the tumor suppressor BRD7 radiosensitizes NPC by disrupting USP5-METTL3 binding, which reduces METTL3 stability and inhibits BRCA1/RAD51-mediated DNA damage repair. Critically, clinical evidence confirms that high BRD7 and low METTL3 expression predict radiosensitivity and a favorable prognosis (37). Additionally, METTL3 stabilizes SLC7A11 mRNA via the m6A-IGF2BP2 axis, thereby driving NPC radioresistance through the suppression of ferroptosis. Mechanistically, METTL3-dependent SLC7A11 stabilization through this axis inhibits ferroptosis to confer radioresistance, whereas SLC7A11 knockdown or combined Erastin/radiotherapy reverses this effect (59).
2.1.7 Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
CircCUX1, a circular RNA derived from the CUX1 gene, is upregulated in radiotherapy-resistant HPSCC where it is linked with shortened survival. m6A methylation by METTL3 was found to regulate circCUX1 expression, and circCUX1 knockdown increases the radiosensitivity of HPSCC cells. Moreover, circCUX1 interacts with Caspase1 to suppress its expression, preventing inflammatory factor production and contributing to radioresistance (18).
2.1.8 Hepatocellular carcinoma
Studies demonstrate that the overexpression of METTL3 correlates with poor prognosis in HCC, whereas its knockdown significantly enhances radiosensitivity by inducing ferroptosis (60). Mechanistically, METTL3 mediates the m6A modification at the +1795 site of SLC7A11 mRNA, stabilizing transcripts through IGF2BP2 binding, while simultaneously inhibiting the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of SLC7A11 protein via the m6A/YTHDF2/SOCS2 axis.In vivo studies confirm that models with low METTL3/IGF2BP2 expression exhibit an enhanced response to radiotherapy. Importantly, the ablation of METTL3 abolishes the compensatory upregulation of SLC7A11 post-irradiation, which cooperatively promotes ferroptosis and radiosensitization. This work establishes the METTL3-IGF2BP2 axis as a potential therapeutic target for radiotherapy in HCC (60). These findings indicate that the inhibition of SLC7A11 ubiquitination through the m6A/YTHDF2/SOCS2 axis blocks radiation-induced ferroptosis, ultimately leading to radioresistance.
2.2 WTAP
The methyltransferase WTAP enhances stemness and EMT in tumor cells, which in turn increases radioresistance. NRP1, a transmembrane glycoprotein, is highly expressed across multiple cancer types. Studies have shown that radiotherapy alone significantly increases double-strand DNA (dsDNA) damage in breast cancer (BC) cells, whereas NRP1 overexpression combined with radiotherapy does not significantly affect dsDNA breaks, indicating that NRP1 plays a key role in BC radioresistance. Mechanistically, NRP1 downregulates Bcl-2 expression in BC through WTAP-mediated m6A modification, thus reducing radiation-induced apoptosis, promoting stemness in BC cells, and increasing their radioresistance (19). Similarly, Liu et al. reported that, after irradiation, WTAP overexpression in gastric cancer (GC) cells promotes EMT by accelerating TGF-β signaling, increasing radioresistance, whereas WTAP downregulation reduces radioresistance (20). Additionally, WTAP stabilizes SQLE mRNA expression through an m6A-dependent mechanism, enhancing CSC properties in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC), which may indirectly contribute to radioresistance (61). These studies demonstrate that WTAP regulates downstream gene expression through m6A modification across multiple cancer types, affecting radioresistance.
2.3 METTL14
METTL14 is a well-characterized m6A regulator. In ESCC cells, METTL14 promotes pri-miR-99a maturation and miR-99a-5p stability, enhancing stemness in cancer cells and increasing radioresistance (21). Additionally, METTL14 mediates the regulation of radioresistance through ferroptosis pathways. Studies demonstrate that METTL14 reverses radioresistance in ESCC by promoting ferroptosis via enhanced m6A modification of ACSL4 (62). In endometrial cancer (EC), protein arginine methyltransferase 3 (PRMT3)-mediated METTL14 promotes ferroptosis sensitivity by reducing the expression and stability of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4). Further studies have revealed that PRMT3 inhibition increases radiosensitivity, whereas PRMT3 depletion suppresses radioresistance by promoting ferroptosis in EC (22). In acute myeloid leukemia (AML), AML-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AML-MSCs) deliver METTL14 to leukemia cells via exosomes, where it stabilizes ROCK1 expression through the m6A-IGF2BP3 axis, thereby mediating radioresistance. Specifically, exosome-transferred METTL14 enhances the m6A modification of ROCK1 mRNA, facilitating its binding to and stabilization by the reader protein IGF2BP3. Consequently, ROCK1 protein levels are upregulated, driving AML cell proliferation and contributing to radioresistance (63).
2.4 YTHDC2
Research indicates that the m6A reader protein YTHDC2 plays a critical role in radioresistance across various malignancies, with IGF1R acting as the central hub mediating YTHDC2-driven therapeutic resistance. In NPC, previous studies demonstrate that IGF1R inhibition, such as through Linsitinib, blocks downstream Akt/ERK phosphorylation, suppresses proliferation, induces apoptosis, and significantly radiosensitizes tumors by reversing resistance. This highlights the therapeutic targeting potential of IGF1R and establishes a definitive association between IGF1R and NPC radioresistance (64). Further investigations reveal that YTHDC2 is highly expressed in radioresistant NPC cells and clinical specimens. It facilitates the translation of IGF1R, activating the PI3K-AKT/S6 signaling pathway to confer radioresistance, thereby emerging as a promising therapeutic target for NPC radiosensitization. Experimentally, the depletion of YTHDC2 downregulates IGF1R expression and suppresses PI3K-AKT/S6 signaling, consequently alleviating radioresistance in NPC cells (23). In neuroblastoma (NB), the activation of the STAT3/AKT axis stimulates CSC properties and EMT, both of which are intrinsically linked to radioresistance. Although the response to radiotherapy remains untested in NB, the identified IGF1R-kinase signaling (STAT3/AKT)-CSC/EMT mechanistic logic aligns with the NPC axis, demonstrating a shared dependence on IGF1R-driven downstream pathways to sustain resistance phenotypes (65). Therefore, targeting YTHDC2, IGF1R, or their downstream kinases (PI3K/AKT, STAT3) represents a viable strategy to overcome radioresistance and achieve radiosensitization by suppressing CSC traits and aberrant signaling cascades.
2.5 YTH domain-containing family protein 3
The m6A “reader” protein YTHDF3 contributes to radiotherapy resistance by modulating gene expression. A study by Du et al. found that the levels hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-alpha (HNF1-α) are markedly higher in radiotherapy-resistant cervical cancer (CC) tissues and cell lines. This upregulation increases the transcription of YTHDF3, leading to m6A modifications of RAD51D mRNA. Furthermore, YTHDF3 mediates HNF1-α-regulated radiotherapy resistance in CC by promoting m6A-dependent translation of RAD51D translationr. Depletion of HNF1-α reduces radiotherapy resistance, whereas its overexpression enhances it in CC cells and tissues. In summary, YTHDF3 affects radiotherapy resistance in CC cells (24).
2.6 FTO
FTO, a critical RNA m6A demethylase, plays a pivotal role in radioresistance across diverse malignancies. It drives therapeutic resistance through epitranscriptomic regulation of downstream effectors, including CSC properties, EMT, DNA repair, and oncogenic signaling pathways.Studies demonstrate that in colorectal cancer, cytoplasmic FTO suppresses CSC phenotypes via its m6A demethylase activity. Conversely, low FTO expression induces m6A hypermethylation, significantly enhancing the in vivo tumorigenicity and radioresistance of CSCs (66). In lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), FTO stabilizes PHF1 mRNA through demethylation, forming a tumor-suppressive axis. The downregulation of the FTO/PHF1 axis promotes tumor cell self-renewal, progression, and poor prognosis by enhancing FOXM1 expression, thereby compromising therapeutic efficacy (67). Breast cancer research reveals that chemotherapy-induced senescent neutrophils upregulate intratumoral FTO via exosomal piR-17560 secretion. Elevated FTO subsequently reduces m6A modification on ZEB1 mRNA, stabilizing its transcript and promoting EMT and radioresistance (68). In glioblastoma (GBM), pharmacological inhibition of FTO (e.g., using FB23-2) increases m6A modification on the target gene VEGFA, downregulating its expression and impairing DNA damage repair (e.g., sustaining γH2AX foci and reducing Rad51 recruitment). This significantly enhances the radiosensitivity of glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs), suppresses tumor growth, and prolongs survival, indicating that FTO upregulation promotes GBM radioresistance (69). Additionally, FTO in NPC promotes OTUB1 expression by erasing m6A marks on OTUB1 transcripts, suppressing radiation-induced ferroptosis (25), and induces CD44 splice variant switching (CD44v) via lncRNA-HOTAIRM1 interaction to inhibit ferroptosis, collectively driving radioresistance (26). In CSCC, FTO upregulates β-catenin expression by reducing the m6A levels of its mRNA, thereby enhancing chemoradioresistance both in vitro and in vivo (27). Collectively, FTO acts as a core determinant of pan-cancer radioresistance, positioning it as a promising therapeutic target for overcoming resistance and improving the efficacy of radiotherapy.
2.7 ALKBH5
ALKBH5, an m6A “eraser”, increases radiotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and GBM by influencing CSCs. CSCs are closely linked to cancer therapy resistance through various pathways, including activating DNA damage repair processes, the EMT, and modulating the levels of genes associated with self-renewal (28, 29). Studies demonstrate that elevated expression of ALKBH5 enhances glioblastoma (GBM) radioresistance by modulating homologous recombination (HR) (70). Further investigations confirm that glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) are the primary source of radioresistance in GBM, with the MST4-USP14-ALKBH5 signaling axis serving as its core mechanism. Specifically, ALKBH5 undergoes deubiquitination mediated by USP14 (a deubiquitinase), which confers protein stability that is further potentiated by phosphorylation from the upstream kinase MST4. This pathway sustains GSC stemness and tumorigenicity, while robustly promoting DNA damage repair and driving therapeutic radioresistance (71). Liver cancer stem cells (LCSCs) exhibit CSC-like properties and significantly affect HCC progression and therapeutic resistance (72). ALKBH5 is upregulated in LCSCs, where it promotes SOX4 expression through demethylation. The ALKBH5/SOX4 axis enhances LCSC properties by the activation of SHH signaling (73). In summary, ALKBH5 overexpression in HCC may contribute to radiotherapy resistance.
2.8 Others
In NSCLC, m6A RNA methylation-mediated regulation of mitochondrial RNA-processing endoribonuclease (RNase MRP) enhances the properties of cancer stem cells and promotes the EMT through the TGFB/SMAD2/SMAD3 pathway, thus contributing to radiotherapy resistance (74). Meanwhile, m6A-modified enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) are closely linked to the progression of bone-metastatic prostate cancer (mPCa) and its resistance to radiotherapy. Zhao et al (75) employed RNA sequencing and other methods to identify the m6A-modified bone-specific eRNA, MLXIP, associated with radiotherapy resistance. This eRNA inhibits RNA degradation by facilitating the interaction between the RNA-binding protein KHSRP and mRNA, affecting PC progression and its sensitivity to radiotherapy.
3 m5C methylation and radiotherapy resistance
m5C modification refers to the methylation of the fifth cytosine carbon in RNA and is commonly observed in RNA types such as mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and enhancer RNA (11). The m5C methyltransferases are associated with both the TRDMT (76) and NSUN families (34, 77). Known “erasers” of m5C methylation include the TET enzyme family (30), while “readers” include fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein (FMRP) (30), ALYREF (78), and YBX1 (79). m5C methylation regulators affect RNA stability, translation efficiency, and other processes, regulating various biological functions, including proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. They also play a key role in radiotherapy resistance in malignant tumors (80), primarily by improving DNA repair capacity and regulating gene expression, ultimately reducing cell death and leading to radiotherapy resistance (81, 82) (Figure 4).
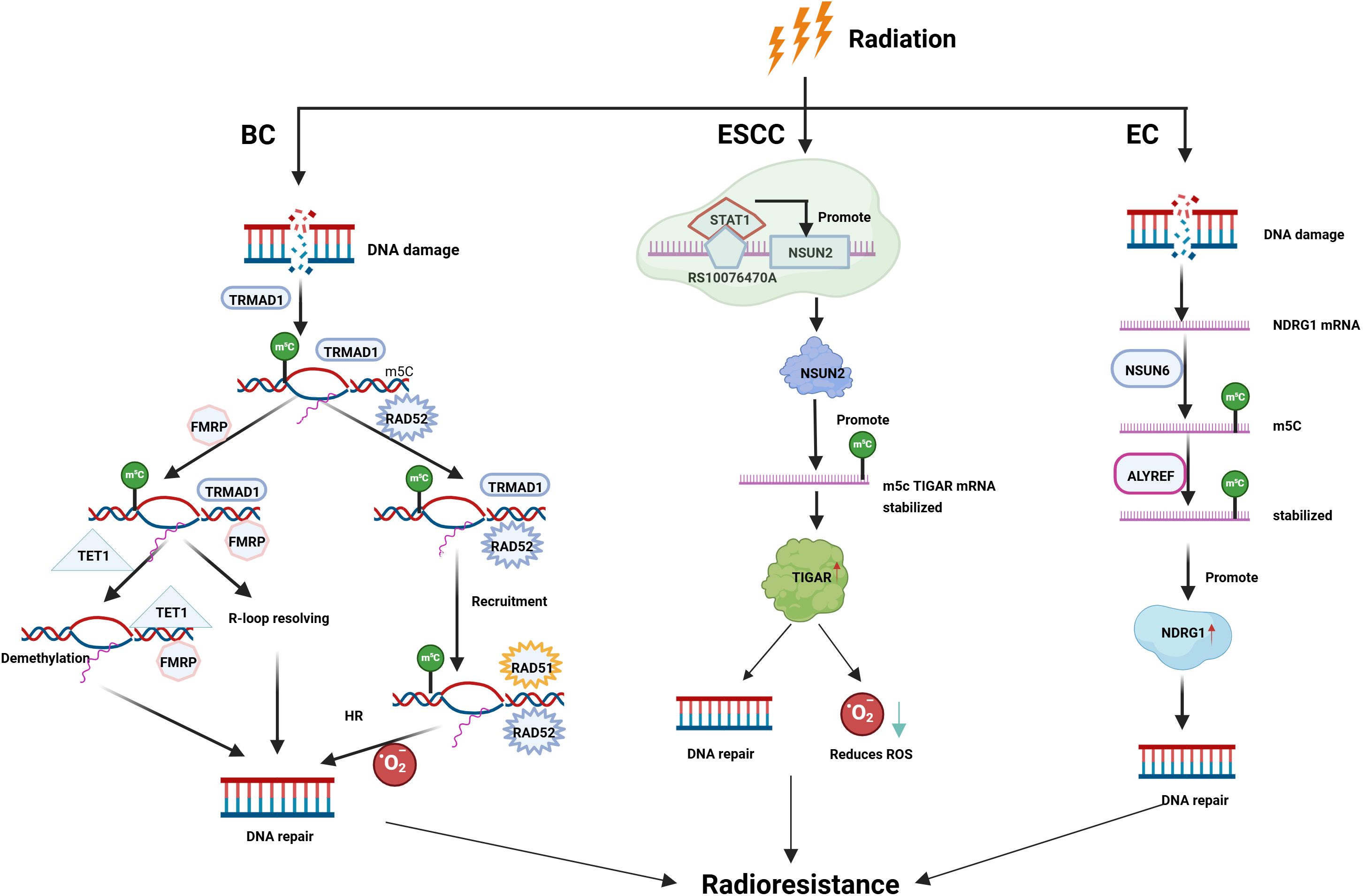
Figure 4. The role of m5C RNA methylation in tumor resistance to radiotherapy. m5C modification contributes to radioresistance in EC, BC, and ESCC by regulating mRNA stability, DNA damage repair, and epigenetic modulation.
3.1 FMRP
FMRP is an m5C “reader” that recognizes and binds to m5C-modified RNA. Through its interaction with the m5C eraser ten-eleven translocation protein 1 (TET1), FMRP induces the demethylation of m5C RNA modifications, therefore promoting mRNA-dependent DNA damage repair processes (34). Furthermore, FMRP interacts with the m5C methyltransferase TRDMT1, which facilitates transcription-coupled homologous recombination at reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced DSBs through the TRDMT1– m5C-RAD52-RAD51 axis (31). The absence of FMRP and TRDMT1 increases radiation sensitivity in BC cells (30, 31), and BC cells with low TRDMT1 expression exhibit greater sensitivity to radiotherapy (31).
3.2 NSUN6
The mechanistic and functional diversity of NSUN6-mediated tumor radioresistance operates through the m5C-NDRG1 axis. Yu et al. discovered that in cervical cancer, NDRG1, as a transcriptional regulatory target of NSUN6, participates in radioresistance mechanisms. Elevated NSUN6 expression initiates the NSUN6/ALYREF-m5C signaling cascade, enhancing NDRG1 stability by augmenting its m5C RNA methylation levels, ultimately conferring radioresistance (33). Given that NDRG1 significantly promotes tumor progression and brain metastasis in aggressive breast cancer (83), NSUN6 may potentially co-drive breast cancer radioresistance via NDRG1 regulation. However, the molecular interactome of this signaling axis in breast cancer remains to be elucidated further. Conversely, NDRG1 exhibits context-dependent functional reversal in HCC, where it significantly suppresses HCC tumorigenesis and metastasis by inducing tumor cell ferroptosis (84). This highlights the cancer type-dependent biological effects mediated by NDRG1.Whether the NSUN6-m5C-NDRG1 axis universally drives pan-cancer radioresistance requires.
3.3 NSUN2
NSUN2, an m5C “writer,” participates in radiotherapy resistance by regulating gene expression. Niu et al. found that cis-expression quantitative trait loci (cis-eQTLs) in NSUN2 promote radiotherapy resistance in ESCC through mRNA-m5C methylation. Mechanistically, the NSUN2 rs10076470 G-to-A mutation acts as a cis-eQTL for STAT1, a key transcription factor that is markedly upregulated in ESCC. This genetic variation increases NSUN2 activity, leading to enhanced m5C methylation and upregulation of multiple cancer-related genes, promoting ESCC progression and increasing resistance to radiotherapy (32).
4 m7G methylation and radiotherapy resistance
The m7G modification is frequently seen in tRNA, rRNA, and mRNA across both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. m7G methylation primarily occurs at position 46 of tRNA and within the mRNA 5′ cap structure. The key regulators of m7G methylation include “writers” such as Trm8/Trm82 (85) and METTL1/WDR4 (86). FTO, primarily known as an m6A demethylase, also functions as an “eraser” of m7G methylation, affecting RNA stability and translation efficiency (87). Known “readers” include the QKI family (88) and YTH domain-containing proteins, which recognize m7G modifications and regulate RNA stability and translation (89).
METTL1, involved in m7G tRNA modification, serves as a “writer” of m7G methylation. It is closely associated with tumorigenesis, progression, and resistance to radiotherapy. For instance, studies have indicated that increased METTL1 expression elevates the risk of neuroblastoma tumorigenesis (90) and promotes the growth and metastasis of NPC both in vitro and in vivo (91). Furthermore, Studies have shown that METTL1 is upregulated in various cancers, with its levels correlating with cancer malignancy. In HCC, ionizing radiation induces METTL1-mediated m7G tRNA methylation, selectively increasing the translation of DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) or DNA ligase IV through higher-frequency m7G-associated codons. This regulation enhances the DNA DSB repair through nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ), thus conferring resistance to ionizing radiation in HCC (35) (Figure 5).
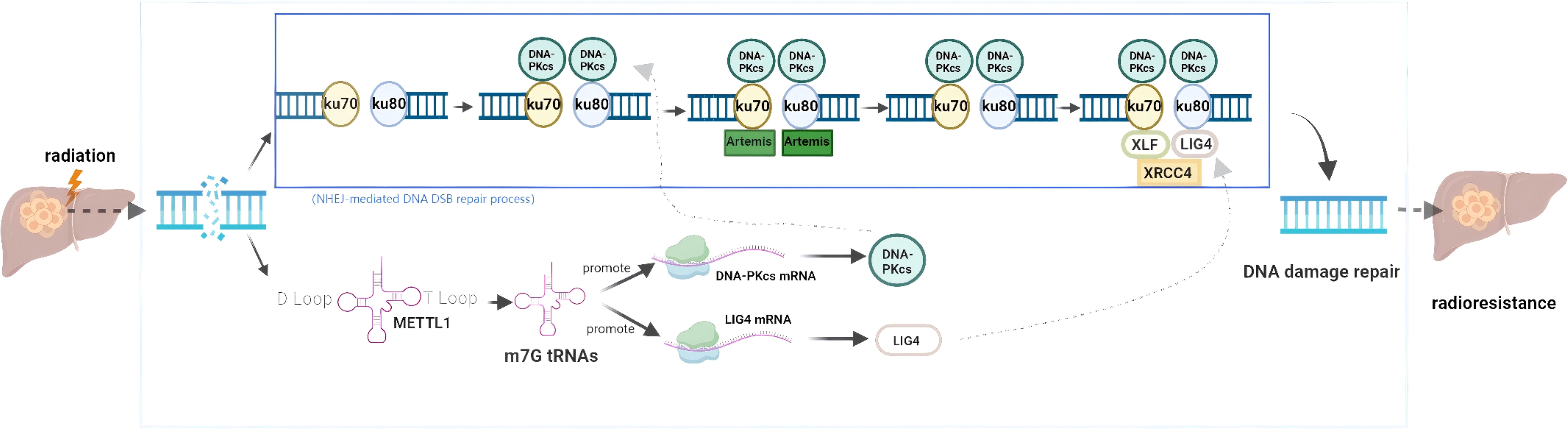
Figure 5. The role of m7G RNA modification in radiotherapy resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. The key factor METTL1 promotes DNA damage repair in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through non-homologous end joining (NHEJ).
5 m1A methylation and radiotherapy resistance
The m1A modification involves adenosine methylation the 1-position, affecting RNA structure and function. In eukaryotes, the methyltransferases (“writers”) responsible for m1A methylation primarily include TRMT10C, TRMT61B, TRMT61A, TRMT6, SDR5C1, and NML. The demethylases (“erasers”) mainly consist of α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases such as ALKBH7, ALKBH3, ALKBH1, and FTO. The known “readers” of m1A-modified RNA include YTHDF1-3 and YTHDC1 (11). Currently, direct causal evidence for the regulatory factors driving tumor radioresistance remains insufficient. Nevertheless, cutting-edge research has suggested their potential roles. For instance, the RNA demethylase ALKBH3 has been reported to influence radiation sensitivity by modulating the TME (92). These preliminary findings underscore the necessity for in-depth mechanistic dissection of relevant regulatory pathways in radioresistance.
m1A methylation contributes to radiotherapy resistance by modulating the TME, regulating gene expression, and altering cellular metabolic processes. Xu et al. reported that m1A methylation may affect the sensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma (LADC) cells to radiotherapy by affecting immune cell infiltration and function within the TME (36). Specifically, inhibition of m1A downregulates the MYC/PD-L1 axis involved in immune evasion of tumors. Since radiotherapy resistance has close associations with changes in the tumor immune microenvironment, m1A methylation may affect radiotherapy efficacy by modulating this signaling pathway (93).
6 Clinical significance of RNA methylation in radiotherapy resistance
RNA methylation holds significant clinical implications for radiotherapy resistance in cancer. Its levels can serve as biomarkers for predicting radiotherapy efficacy, helping in the identification of radiotherapy-resistant patients, and guiding personalized treatment strategies (94). Furthermore, RNA methylation-related enzymes, such as METTL3 and YTHDC2, may serve as therapeutic targets to overcome radiotherapy resistance. Modulating RNA methylation levels through inhibitors holds the potential for improving radiotherapy outcomes (13, 23). RNA methylation modifications influence radiotherapy efficacy by influencing DNA repair, tumor cell radiation sensitivity, and the tumor immune microenvironment. Therefore, precision treatment strategies based on RNA methylation research offer the potential to mitigate radiotherapy resistance and improve patient outcomes, representing a promising therapeutic approach (27).
6.1 Biomarkers
RNA methylation can serve as a biomarker for identifying malignant tumors resistant to radiotherapy. In GBM, METTL3 expression is associated with radioresistance, and its downregulation reduces DNA damage repair and increases radiosensitivity (12). Similarly, in NSCLC, METTL3 is upregulated, and its knockout increases cellular sensitivity to radiotherapy (14). These findings suggest that RNA methylation levels can function as biomarkers to predict radiotherapy efficacy, facilitating the identification of radiotherapy-resistant patients and enabling individualized precision treatment.
6.2 Therapeutic targets
Enzymes involved in RNA methylation modifications and their downstream regulatory targets hold significant therapeutic potential for overcoming radiotherapy resistance across various cancers. Studies have shown that METTL3 increases radiotherapy resistance in OSCC by targeting SALL4 (13), while METTL3 knockdown increases PDAC cell sensitivity to low-dose radiotherapy, suggesting its possible application as a target in treating the disease (15). In NPC, METTL3-mediated m6A methylation upregulates KIF15 expression, contributing to radiotherapy resistance. Inhibiting KIF15 expression has been found to mitigate this resistance (17). Collectively, these findings suggest that METTL3 is a promising therapeutic target for radiosensitization across various cancer types. Currently, small-molecule inhibitors targeting METTL3 are undergoing preclinical investigation (95), which may inform future combinatorial radiosensitization strategies. Similarly, in CSCC, FTO promotes β-catenin expression by reducing m6A modification levels, aggravating radiotherapy resistance. This suggests that targeting FTO or β-catenin may optimize therapeutic outcomes (27). However, FTO exhibits broad substrate specificity. Targeting FTO may influence the expression of metabolism-related genes, potentially resulting in metabolic dysregulation. This underscores the necessity for more precise strategies to target RNA methylation (69, 96). Furthermore, m5C modification-related proteins, including FMRP and members of the NSUN family, as well as the key m7G tRNA modification enzyme METTL1, have been reported to be involved in regulating the radiotherapy response in malignant tumors. Inhibiting the activity of these modification enzymes has been shown to improve radiotherapy efficacy in killing cancer cells (30–33). These findings not only highlight the key role of RNA methylation modifications in radiotherapy resistance but also provide diverse potential targets for developing precision radiotherapy sensitization strategies based on RNA modification regulation, offering significant clinical implications.
6.3 Combination
Combining methylation-modulating inhibitors with radiotherapy has been shown to suppress tumor growth and progression. Research indicates that STM2457, a novel inhibitor targeting METTL3, exhibits significant efficacy in preclinical models of AML (97). To evaluate its anti-leukemic effects in conjunction with radiotherapy, experiments were conducted using METTL3-knockout cells and murine models. The results demonstrate that the targeted inhibition of METTL3 by STM2457, when combined with in vivo radiotherapy, synergistically suppresses tumor growth (95). Furthermore, Zhang et al. found that inhibiting METTL3 enhances the radiosensitivity of HCC by activating the radiation-induced ferroptosis pathway (60). Additionally, studies have shown that the FTO inhibitor FB23-2, when combined with radiotherapy, significantly inhibits tumor spheroid formation and the self-renewal capacity of GSCs, suppresses cell proliferation, and induces apoptosis in GBM cells. Animal experiments further confirmed that FB23-2 combined with radiotherapy effectively inhibits intracranial tumor growth in mice (69). Collectively, these findings suggest that the targeted inhibition of METTL3 and FTO, in combination with radiotherapy, enhances the suppression of tumor growth and progression.
Moreover, studies have indicated that cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is a potential target for radioprotection and radiosensitization. Inhibition of COX-2 (e.g., celecoxib) can reduce the resistance of malignant tumor cells to radiotherapy (98). In NPC, the resistance to radiotherapy is primarily mediated by EBV-encoded products (such as LMP1) and non-coding RNAs (miRNA/lncRNA/circRNA), which inhibit DNA damage repair, activate anti-apoptotic pathways (such as PI3K/AKT, NF-κB), and promote EMT. Combined chemoradiotherapy or targeting EBV/non-coding RNAs (e.g., olaparib inhibiting miR-519d, curcumin downregulating lncRNA AK294004) can reverse radiotherapy resistance (99).
In summary, targeting epigenetic regulation (such as METTL3, FTO, COX-2 inhibitors) or viral/non-coding RNA pathways (such as EBV-LMP1, miRNA/lncRNA), in conjunction with radiotherapy, can significantly enhance antitumor efficacy through synergistic mechanisms, providing new strategies to reverse radiotherapy resistance.
7 Conclusion
In summary, RNA methylation plays a crucial role in tumor radioresistance by regulating DNA damage repair and key signaling pathways. Current research has preliminarily elucidated the mechanisms of m6A; however, several limitations remain: the associations of other modifications such as m5C, m7G, and m1A with radioresistance have yet to be clarified. Additionally, the synergistic effects, targeting, and toxicity issues of methylation inhibitors (e.g., FTO/METTL3 targeted drugs) urgently need breakthroughs, and there is a lack of clinical validation. Furthermore, existing RNA methylation detection technologies exhibit insufficient sensitivity, limiting their clinical application as biomarkers. To address these limitations, future research should deeply explore the mechanisms of non-m6A modifications, advance human trials and safety optimization of inhibitors, and develop high-sensitivity multidimensional methylation detection systems, ultimately achieving precise design of individualized radiotherapy sensitization strategies.
Author contributions
HLi: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. HLu: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. MJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. YX: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. KL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Medical Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission (No. 2023KY243); the Keynote Research Project of Ningbo City (2023Z171).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Shah R, Battisti NML, Brain E, Gnangnon FHR, Kanesvaran R, Mohile S, et al. Updated cancer burden in oldest old: A population-based study using 2022 Globocan estimates. Cancer Epidemiol. (2025) 95:102716. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2024.102716
2. Siegel RL, Kratzer TB, Giaquinto AN, Sung H, and Jemal A. Cancer statistic. CA Cancer J Clin. (2025) 75:10–45. doi: 10.3322/caac.21871
3. Liu B, Zhou H, Tan L, Siu KTH, and Guan XY. Exploring treatment options in cancer: Tumor treatment strategies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:175. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01856-7
4. Jaffray DA, Knaul F, Baumann M, and Gospodarowicz M. Harnessing progress in radiotherapy for global cancer control. Nat Cancer. (2023) 4:1228–38. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00619-7
5. Kim BM, Hong Y, Lee S, Liu P, Lim JH, Lee YH, et al. Therapeutic implications for overcoming radiation resistance in cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2015) 16:26880–913. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125991
6. Alamilla-Presuel JC, Burgos-Molina AM, González-Vidal A, Sendra-Portero F, and Ruiz-Gómez MJ. Factors and molecular mechanisms of radiation resistance in cancer cells. Int J Radiat Biol. (2022) 98:1301–15. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2022.2047825
7. Chen D, Gu X, Nurzat Y, Xu L, Li X, Wu L, et al. Writers, readers, and erasers RNA modifications and drug resistance in cancer. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:178. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02089-6
8. Galeaz C, Totis C, and Bisio A. Radiation resistance: A matter of transcription factors. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:662840. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.662840
9. Rajpurohit YS, Sharma DK, Lal M, and Soni I. A perspective on tumor radiation resistance following high-LET radiation treatment. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2024) 150:226. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05757-8
10. Michalak EM, Burr ML, Bannister AJ, and Dawson MA. The roles of DNA, RNA and histone methylation in ageing and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 20:573–89. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0143-1
11. Li G, Yao Q, Liu P, Zhang H, Liu Y, Li S, et al. Critical roles and clinical perspectives of RNA methylation in cancer. MedComm (2020). (2024) 5:e559. doi: 10.1002/mco2.559
12. Yin J, Ding F, Cheng Z, Ge X, Li Y, Zeng A, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A modification of LINC00839 maintains glioma stem cells and radiation resistance by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:417. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05933-7
13. Huang J, Li H, Yang Z, Liu R, Li Y, Hu Y, et al. SALL4 promotes cancer stem-like cell phenotype and radioresistance in oral squamous cell carcinomas via methyltransferase-like 3-mediated m6A modification. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:139. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06533-9
14. Xu X, Zhang P, Huang Y, Shi W, Mao J, Ma N, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A mRNA contributes to the resistance of carbon-ion radiotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:105–14. doi: 10.1111/cas.15590
15. Taketo K, Konno M, Asai A, Koseki J, Toratani M, Satoh T, et al. The epitranscriptome m6A writer METTL3 promotes chemo- and radioresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. (2018) 52:621–9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4219
16. Shi X, Zhang X, Huang X, Zhang R, Pan S, Huang S, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-mediated upregulation of LNCAROD confers radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through stabilizing PARP1. Clin Transl Med. (2024) 14:e70039. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70039
17. Li S, Wang S, Zhang L, Wu X, Tian L, Zou J, et al. METTL3 methylated KIF15 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and radiation resistance by blocking ATG7-mediated autophagy through the activation of STAT3 pathway. Transl Oncol. (2025) 51:102161. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102161
18. Wu P, Fang X, Liu Y, Tang Y, Wang W, Li X, et al. N6-methyladenosine modification of circCUX1 confers radioresistance of hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma through caspase1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:298. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03558-2
19. Wang Y, Zhang L, Sun XL, Lu YC, Chen S, Pei DS, et al. NRP1 contributes to stemness and potentiates radioresistance via WTAP-mediated m6A methylation of Bcl-2 mRNA in breast cancer. Apoptosis. (2023) 28:233–46. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01784-3
20. Liu Y and Da M. Wilms tumor 1 associated protein promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells by accelerating TGF-β and enhances chemoradiotherapy resistance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:3977–88. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04320-7
21. Liu Z, Wu K, Gu S, Wang W, Xie S, Lu T, et al. A methyltransferase-like 14/miR-99a-5p/tribble 2 positive feedback circuit promotes cancer stem cell persistence and radioresistance via histone deacetylase 2-mediated epigenetic modulation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Transl Med. (2021) 11:e545. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.545
22. Wang Y, Wang C, Guan X, Ma Y, Zhang S, Li F, et al. PRMT3-mediated arginine methylation of METTL14 promotes Malignant progression and treatment resistance in endometrial carcinoma. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2303812. doi: 10.1002/advs.202303812
23. He JJ, Li Z, Rong ZX, Gao J, Mu Y, Guan YD, et al. m(6)A reader YTHDC2 promotes radiotherapy resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activating IGF1R/AKT/S6 signaling axis. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:1166. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01166
24. Du H, Zou NY, Zuo HL, Zhang XY, and Zhu SC. YTHDF3 mediates HNF1α regulation of cervical cancer radio-resistance by promoting RAD51D translation in an m6A-dependent manner. FEBS J. (2023) 290:1920–35. doi: 10.1111/febs.16681
25. Huang WM, Li ZX, Wu YH, Shi ZL, Mi JL, Hu K, et al. m6A demethylase FTO renders radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via promoting OTUB1-mediated anti-ferroptosis. Transl Oncol. (2023) 27:101576. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101576
26. Mi J, Wang Y, He S, Qin X, Li Z, Zhang T, et al. LncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by modulating FTO acetylation-dependent alternative splicing of CD44. Neoplasia. (2024) 56:101034. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101034
27. Zhou S, Bai ZL, Xia D, Zhao ZJ, Zhao R, Wang YY, et al. FTO regulates the chemo-radiotherapy resistance of cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) by targeting β-catenin through mRNA demethylation. Mol Carcinog. (2018) 57:590–7. doi: 10.1002/mc.22782
28. Maugeri-Saccà M, Vigneri P, and De Maria R. Cancer stem cells and chemosensitivity. Clin Cancer Res. (2011) 17:4942–7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-10-2538
29. Calcagno AM, Salcido CD, Gillet JP, Wu CP, Fostel JM, Mumau MD, et al. Prolonged drug selection of breast cancer cells and enrichment of cancer stem cell characteristics. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2010) 102:1637–52. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq361
30. Yang H, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Yadav T, Ouyang J, Phoon L, et al. FMRP promotes transcription-coupled homologous recombination via facilitating TET1-mediated m5C RNA modification demethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2022) 119:e2116251119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2116251119
31. Chen H, Yang H, Zhu X, Yadav T, Ouyang J, Truesdell SS, et al. m(5)C modification of mRNA serves a DNA damage code to promote homologous recombination. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:2834. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16722-7
32. Niu X, Peng L, Liu W, Miao C, Chen X, Chu J, et al. A cis-eQTL in NSUN2 promotes esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma progression and radiochemotherapy resistance by mRNA-m(5)C methylation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:267. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01063-2
33. Yu M, Ni M, Xu F, Liu C, Chen L, Li J, et al. NSUN6-mediated 5-methylcytosine modification of NDRG1 mRNA promotes radioresistance in cervical cancer. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:139. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02055-2
34. Hu Y, Chen C, Tong X, Chen S, Hu X, Pan B, et al. Correction: NSUN2 modified by SUMO-2/3 promotes gastric cancer progression and regulates mRNA m5C methylation. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:495. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06859-4
35. Liao J, Yi Y, Yue X, Wu X, Zhu M, Chen Y, et al. Methyltransferase 1 is required for nonhomologous end-joining repair and renders hepatocellular carcinoma resistant to radiotherapy. Hepatology. (2023) 77:1896–910. doi: 10.1002/hep.32615
36. Xu Q, Kong L, Han Z, Jin X, Ding M, Piao Z, et al. RNA modification writer-based immunological profile and genomic landscape of tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Discov Oncol. (2025) 16:45. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01791-1
37. Li M, Wei J, Xue C, Chen S, Zhou X, Zheng L, et al. BRD7 enhances the radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by negatively regulating USP5/METTL3 axis-mediated homologous recombination repair. Int J Biol Sci. (2024) 20:6130–45. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.100833
38. Zheng ZH, Zhang GL, Jiang RF, Hong YQ, Zhang QY, He JP, et al. METTL3 is essential for normal progesterone signaling during embryo implantation via m(6)A-mediated translation control of progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2023) 120:e2214684120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2214684120
39. Jiang J, Fan Q, Qu H, Liu C, Liang T, Chen L, et al. Novel prognostic biomarkers, METTL14 and YTHDF2, associated with RNA methylation in Ewing’s sarcoma. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:7041. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06744-0
40. Mendel M, Chen KM, Homolka D, Gos P, Pandey RR, McCarthy AA, et al. Methylation of structured RNA by the m(6)A writer METTL16 is essential for mouse embryonic development. Mol Cell. (2018) 71:986–1000.e1011. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.004
41. Feng ZY, Wang T, Su X, and Guo S. Identification of the m(6)A RNA methylation regulators WTAP as a novel prognostic biomarker and genomic alterations in cutaneous melanoma. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:665222. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.665222
42. Tang B, Li M, Xu Y, and Li X. N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) writer KIAA1429 accelerates gastric cancer oxaliplatin chemoresistance by targeting FOXM1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:5037–45. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04426-y
43. Shimura T, Kandimalla R, Okugawa Y, Ohi M, Toiyama Y, He C, et al. Novel evidence for m(6)A methylation regulators as prognostic biomarkers and FTO as a potential therapeutic target in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. (2022) 126:228–37. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01581-w
44. Tang B, Yang Y, Kang M, Wang Y, Wang Y, Bi Y, et al. m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis by decreasing WIF-1 RNA methylation and mediating Wnt signaling. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:3. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1128-6
45. Zhou M, Liu Y, Xu H, Chen X, Zheng N, Duan Z, et al. YTHDC1-Modified m6A Methylation of Hsa_circ_0102678 Promotes Keratinocyte Inflammation Induced by Cutibacterium acnes Biofilm through Regulating miR-146a/TRAF6 and IRAK1 Axis. J Innate Immun. (2023) 15:822–35. doi: 10.1159/000534704
46. Chen L, Sun K, Qin W, Huang B, Wu C, Chen J, et al. LIMK1 m(6)A-RNA methylation recognized by YTHDC2 induces 5-FU chemoresistance in colorectal cancer via endoplasmic reticulum stress and stress granule formation. Cancer Lett. (2023) 576:216420. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216420
47. Ye J, Wang Z, Chen X, Jiang X, Dong Z, Hu S, et al. YTHDF1-enhanced iron metabolism depends on TFRC m(6)A methylation. Theranostics. (2020) 10:12072–89. doi: 10.7150/thno.51231
48. Zhang C, Huang S, Zhuang H, Ruan S, Zhou Z, Huang K, et al. YTHDF2 promotes the liver cancer stem cell phenotype and cancer metastasis by regulating OCT4 expression via m6A RNA methylation. Oncogene. (2020) 39:4507–18. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1303-7
49. Shi S, Wu T, Ma Z, Zhang X, Xu K, Tian Q, et al. Serum-derived extracellular vesicles promote the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by delivering the m6A methylation regulator HNRNPC through the regulation of DLGAP5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:4639–51. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04375-6
50. He J, Zhou M, Yin J, Wan J, Chu J, Jia J, et al. METTL3 restrains papillary thyroid cancer progression via m(6)A/c-Rel/IL-8-mediated neutrophil infiltration. Mol Ther. (2021) 29:1821–37. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.01.019
51. Wan W, Ao X, Chen Q, Yu Y, Ao L, Xing W, et al. METTL3/IGF2BP3 axis inhibits tumor immune surveillance by upregulating N(6)-methyladenosine modification of PD-L1 mRNA in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:60. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01447-y
52. Ni Z, Sun P, Zheng J, Wu M, Yang C, Cheng M, et al. JNK Signaling Promotes Bladder Cancer Immune Escape by Regulating METTL3-Mediated m6A Modification of PD-L1 mRNA. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:1789–802. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-21-1323
53. Visvanathan A, Patil V, Arora A, Hegde AS, Arivazhagan A, Santosh V, et al. Essential role of METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification in glioma stem-like cells maintenance and radioresistance. Oncogene. (2018) 37:522–33. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.351
54. Tsai CY, Ko HJ, Huang CF, Lin CY, Chiou SJ, Su YF, et al. Ionizing radiation induces resistant glioblastoma stem-Like cells by promoting autophagy via the wnt/β-Catenin pathway. Life (Basel). (2021) 11:451–68. doi: 10.3390/life11050451
55. Zhang Y, Tian R, Feng X, Xiao B, Yue Q, Wei J, et al. Overexpression of METTL3 in lung cancer cells inhibits radiation-induced bystander effect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2025) 761:151714. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151714
56. Tatekawa S, Tamari K, Chijimatsu R, Konno M, Motooka D, Mitsufuji S, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine methylation-regulated polo-like kinase 1 cell cycle homeostasis as a potential target of radiotherapy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:11074. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15196-5
57. Sun H, Liu F, Song X, Sun R, Zhang M, Huang J, et al. m6A-modified circCREBBP enhances radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by reducing the stability of MYC through interaction with IGF2BP3. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 286:138534. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138534
58. Ma R and Zhao L. The role and mechanism of ferroptosis mediated by METTL3-m6A modification in regulating radioresistance of esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2023) 117:e248–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.06.1188
59. Dai Z, Lin B, Qin M, Lin Y, Wang L, Liao K, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A modification of SLC7A11 enhances nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by inhibiting ferroptosis. Int J Biol Sci. (2025) 21:1837–51. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.100518
60. Zhang C, Yang T, Chen H, Ding X, Chen H, Liang Z, et al. METTL3 inhibition promotes radiosensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulation of SLC7A11 expression. Cell Death Dis. (2025) 16:9. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07317-x
61. Hou R, Sun X, Cao S, Wang Y, and Jiang L. Stabilization of SQLE mRNA by WTAP/FTO/IGF2BP3-dependent manner in HGSOC: implications for metabolism, stemness, and progression. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:872. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07257-6
62. Jin Y, Pan S, Wang M, Huang S, Ke Y, Li D, et al. The m(6)A modification of ACSL4 mRNA sensitized esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to irradiation via accelerating ferroptosis. Cell Biol Int. (2024) 48:1877–90. doi: 10.1002/cbin.12245
63. Wang C, Song R, Yuan J, Hou G, Chu AL, Huang Y, et al. Exosome-Shuttled METTL14 From AML-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes the Proliferation and Radioresistance in AML Cells by Stabilizing ROCK1 Expression via an m6A-IGF2BP3-Dependent Mechanism. Drug Dev Res. (2025) 86:e70025. doi: 10.1002/ddr.70025
64. Wang Z, Liu G, Mao J, Xie M, Zhao M, Guo X, et al. IGF-1R inhibition suppresses cell proliferation and increases radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Mediators Inflammation. (2019) 2019:5497467. doi: 10.1155/2019/5497467
65. Wang XH, Wu HY, Gao J, Wang XH, Gao TH, and Zhang SF. IGF1R facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell properties in neuroblastoma via the STAT3/AKT axis. Cancer Manag Res. (2019) 11:5459–72. doi: 10.2147/cmar.S196862
66. Relier S, Ripoll J, Guillorit H, Amalric A, Achour C, Boissière F, et al. FTO-mediated cytoplasmic m6Am demethylation adjusts stem-like properties in colorectal cancer cell. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1716. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21758-4
67. Ning J, Wang F, Bu J, Zhu K, and Liu W. Down-regulated m6A reader FTO destabilizes PHF1 that triggers enhanced stemness capacity and tumor progression in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8:354. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01125-y
68. Ou B, Liu Y, Gao Z, Xu J, Yan Y, Li Y, et al. Senescent neutrophils-derived exosomal piRNA-17560 promotes chemoresistance and EMT of breast cancer via FTO-mediated m6A demethylation. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:905. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05317-3
69. Zhang J, Li G, Wu R, Shi L, Tian C, Jiang H, et al. The m6A RNA demethylase FTO promotes radioresistance and stemness maintenance of glioma stem cells. Cell Signal. (2025) 132:111782. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111782
70. Kowalski-Chauvel A, Lacore MG, Arnauduc F, Delmas C, Toulas C, Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal E, et al. The m6A RNA demethylase ALKBH5 promotes radioresistance and invasion capability of glioma stem cells. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 13:40–56. doi: 10.3390/cancers13010040
71. Zhou X, Xia Q, Wang B, Li J, Liu B, Wang S, et al. USP14 modulates stem-like properties, tumorigenicity, and radiotherapy resistance in glioblastoma stem cells through stabilization of MST4-phosphorylated ALKBH5. Theranostics. (2025) 15:2293–314. doi: 10.7150/thno.103629
72. Vu NB, Nguyen TT, Tran LC, Do CD, Nguyen BH, Phan NK, et al. Doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil resistant hepatic cancer cells demonstrate stem-like properties. Cytotechnology. (2013) 65:491–503. doi: 10.1007/s10616-012-9511-9
73. Yang Q, Liang Y, Shi Y, Shang J, and Huang X. The ALKBH5/SOX4 axis promotes liver cancer stem cell properties via activating the SHH signaling pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:15499–510. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05309-6
74. Yin H, Chen L, Piao S, Wang Y, Li Z, Lin Y, et al. Correction to: M6A RNA methylation-mediated RMRP stability renders proliferation and progression of non-small cell lung cancer through regulating TGFBR1/SMAD2/SMAD3 pathway. Cell Death Differ. (2023) 30:856. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01075-z
75. Zhao Y, Wen S, Li H, Pan CW, Wei Y, Huang T, et al. Enhancer RNA promotes resistance to radiotherapy in bone-metastatic prostate cancer by m(6)A modification. Theranostics. (2023) 13:596–610. doi: 10.7150/thno.78687
76. Li H, Zhu D, Wu J, Ma Y, Cai C, Chen Y, et al. New substrates and determinants for tRNA recognition of RNA methyltransferase DNMT2/TRDMT1. RNA Biol. (2021) 18:2531–45. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1930756
77. Hu S, Yang M, Xiao K, Yang Z, Cai L, Xie Y, et al. Loss of NSUN6 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by downregulating EEF1A2 expression and activation of Akt/mTOR signaling pathway via m(5)C methylation. Exp Ther Med. (2023) 26:457. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12156
78. Zhao Y, Xing C, and Peng H. ALYREF (Aly/REF export factor): A potential biomarker for predicting cancer occurrence and therapeutic efficacy. Life Sci. (2024) 338:122372. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122372
79. Wu R, Feng S, Li F, Shu G, Wang L, Gao P, et al. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of autophagy and adipogenesis by YBX1. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:29. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05564-y
80. Liu ZX, Li LM, Sun HL, and Liu SM. Link between m6A modification and cancers. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2018) 6:89. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00089
81. Xuan JJ, Sun WJ, Lin PH, Zhou KR, Liu S, Zheng LL, et al. RMBase v2.0: deciphering the map of RNA modifications from epitranscriptome sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. (2018) 46:D327–d334. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx934
82. Squires JE, Patel HR, Nousch M, Sibbritt T, Humphreys DT, Parker BJ, et al. Widespread occurrence of 5-methylcytosine in human coding and non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. (2012) 40:5023–33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks144
83. Villodre ES, Hu X, Eckhardt BL, Larson R, Huo L, Yoon EC, et al. NDRG1 in aggressive breast cancer progression and brain metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2022) 114:579–91. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab222
84. Tang B, Wang Y, Zhu J, Song J, Fang S, Weng Q, et al. TACE responser NDRG1 acts as a guardian against ferroptosis to drive tumorgenesis and metastasis in HCC. Biol Proced Online. (2023) 25:13. doi: 10.1186/s12575-023-00199-x
85. Alexandrov A, Martzen MR, and Phizicky EM. Two proteins that form a complex are required for 7-methylguanosine modification of yeast tRNA. Rna. (2002) 8:1253–66. doi: 10.1017/s1355838202024019
86. Li J, Wang L, Hahn Q, Nowak RP, Viennet T, Orellana EA, et al. Structural basis of regulated m(7)G tRNA modification by METTL1-WDR4. Nature. (2023) 613:391–7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05566-4
87. Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. (2011) 7:885–7. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.687
88. Zlotorynski E. Internal-m(7)G-modified mRNAs quake under stress. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 24:522. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00635-6
89. Roundtree IA, Evans ME, Pan T, and He C. Dynamic RNA modifications in gene expression regulation. Cell. (2017) 169:1187–200. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.045
90. Liu J, Deng C, Lin H, Zhang X, Zhu J, Zhou C, et al. Genetic variants of m7G modification genes influence neuroblastoma susceptibility. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e23658. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23658
91. Chen B, Jiang W, Huang Y, Zhang J, Yu P, Wu L, et al. N(7)-methylguanosine tRNA modification promotes tumorigenesis and chemoresistance through WNT/β-catenin pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. (2022) 41:2239–53. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02250-9
92. Li J, Zhang H, and Wang H. N(1)-methyladenosine modification in cancer biology: Current status and future perspectives. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2022) 20:6578–85. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.11.045
93. Li S, Feng T, Liu Y, Yang Q, Song A, Wang S, et al. m(1)A inhibition fuels oncolytic virus-elicited antitumor immunity via downregulating MYC/PD-L1 signaling. Int J Oral Sci. (2024) 16:36. doi: 10.1038/s41368-024-00304-0
94. Wang Q, Chen C, Ding Q, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Chen J, et al. METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification of HDGF mRNA promotes gastric cancer progression and has prognostic significance. Gut. (2020) 69:1193–205. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319639
95. Sun X, Bai C, Li H, Xie D, Chen S, Han Y, et al. PARP1 modulates METTL3 promoter chromatin accessibility and associated LPAR5 RNA m(6)A methylation to control cancer cell radiosensitivity. Mol Ther. (2023) 31:2633–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.07.018
96. Mauer J, Sindelar M, Despic V, Guez T, Hawley BR, Vasseur JJ, et al. FTO controls reversible m(6)Am RNA methylation during snRNA biogenesis. Nat Chem Biol. (2019) 15:340–7. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0231-8
97. Yankova E, Blackaby W, Albertella M, Rak J, De Braekeleer E, Tsagkogeorga G, et al. Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia. Nature. (2021) 593:597–601. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03536-w
98. Cheki M, Yahyapour R, Farhood B, Rezaeyan A, Shabeeb D, Amini P, et al. COX-2 in radiotherapy: A potential target for radioprotection and radiosensitization. Curr Mol Pharmacol. (2018) 11:173–83. doi: 10.2174/1874467211666180219102520
Keywords: m6A methylation, m5C methylation, m7G methylation, m1A methylation, radioresistance
Citation: Liu H, Luo H, Jin M, Zheng Z, Xi Y and Liu K (2025) Advances in research on RNA methylation and cancer radiotherapy resistance. Front. Oncol. 15:1596541. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1596541
Received: 21 March 2025; Accepted: 19 July 2025;
Published: 31 July 2025.
Edited by:
Cecilia Ana Suarez, National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET), ArgentinaReviewed by:
Imran Khan, University of Nebraska Medical Center, United StatesChen Xue, Zhejiang University, China
Liqiong Yang, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Luo, Jin, Zheng, Xi and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kaitai Liu, bGt0MTk4MkAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hui Liu
Hui Liu Hui Luo1†
Hui Luo1† Zhen Zheng
Zhen Zheng Yang Xi
Yang Xi Kaitai Liu
Kaitai Liu