- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Jinan Central Hospital, Jinan, China
- 2School of Clinical Medicine, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 4Luzhou Key Laboratory of Research for Integrative on Pain and Perioperative Organ Protection, Luzhou, China
- 5Department of Health Management Center, Sichuan Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Sichuan Cancer Hospital & Institute, Sichuan Cancer Center, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 6Clinical Research Institute, The Affiliated Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 7Department of Respiratory Medicine, Dezhou People’s Hospital, Dezhou, Shandong, China
Aim: This study aims to develo\p a population-adapted machine learning-based prediction model for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) lymph node metastasis (LNM) to identify high-risk patients requiring intensive surveillance.
Methods: Data from 23511 HCC patients in the SEER database and 57 patients from our hospital were analyzed. Seven LNM risk indicators were selected. Four machine learning algorithms—decision tree (DT), logistic Regression (LR), multilayer perceptron (MLP), and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost)—were employed to construct prediction models. Model performance was evaluated using area under the curve, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity.
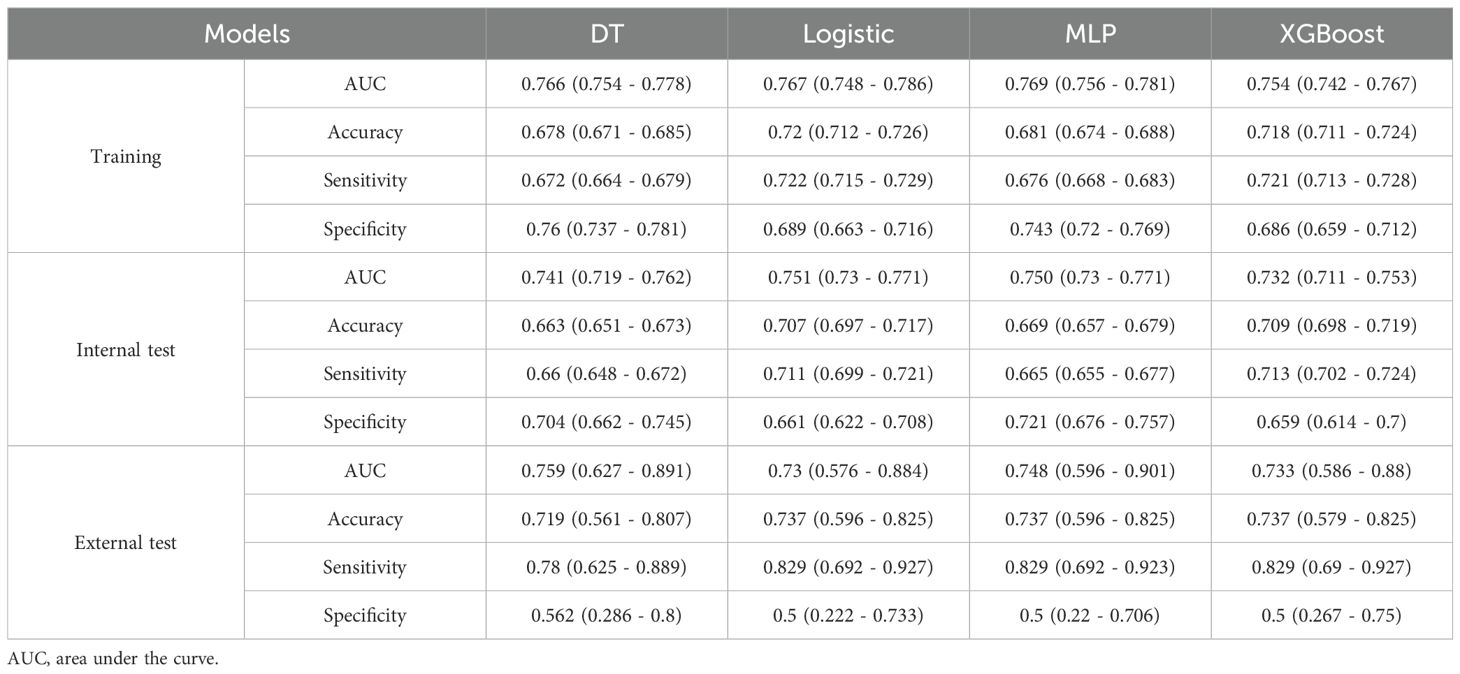
Results: Among 23511 SEER patients, 1679 (7.14%) exhibited LNM. Race, Sequence number, Tumor size, T stage and AFP were identified as independent predictors of LNM. The LR model achieved optimal performance (area under the curve: 0.751; accuracy: 0.707; sensitivity: 0.711; specificity: 0.661). External validation with 57 patients from our hospital confirmed robust generalizability (area under the curve: 0.73; accuracy: 0.737; sensitivity: 0.829; specificity: 0.5), outperforming other models.
Conclusions: The LR-based model demonstrates superior predictive capability for LNM in HCC, offering clinicians a valuable tool to guide personalized therapeutic strategies.
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks as the sixth most common cancer worldwide and is the most prevalent—and deadliest—form of primary liver cancer, representing the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality (1). Its etiological risk factors exhibit marked geographic heterogeneity, with strong associations to hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections, alcoholic liver disease, and metabolic syndrome (2). Despite advances in therapeutic modalities—including surgical resection, liver transplantation, and local ablation (3)—long-term outcomes for HCC patients remain dismal, with a 5-year survival rate below 20% (4). The often insidious onset of HCC frequently delays diagnosis until advanced stages, increasing the likelihood of lymph node metastasis (LNM) (5), a pivotal event in HCC progression that significantly worsens prognosis (6). Patients with LNM have a median survival of only 5.8 months, compared to 16.3 months for those without nodal involvement (7), and nodal metastases preclude curative resection while indicating systemic disease dissemination (8).
Early, accurate prediction of LNM is therefore essential for individualized treatment planning and prognostic stratification. Current clinical assessment relies primarily on imaging modalities—such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)—and histopathological evaluation. Proposed imaging predictors, including hilar invasion or a short-axis lymph node diameter ≥9 mm, have demonstrated variable sensitivity and specificity, reflecting the low incidence of HCC nodal metastasis (1.23%–7.5%) and cohort heterogeneity (9–11). Traditional prediction tools, such as TNM staging–based nomograms, typically incorporate only single clinical variables and neglect tumor biology and multidimensional patient data; retrospective study designs further introduce selection bias, and the lack of external validation limits generalizability (9). For example, an HBV-focused LNM prediction model experienced a drop in area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) to 0.68 upon external validation, underscoring its restricted applicability (12).
Machine learning (ML) offers a promising alternative by integrating heterogeneous, multimodal data (e.g., radiomics, genomics, clinical variables) through nonlinear algorithms to reveal latent predictive patterns (13). In other malignancies, ML-based models have outperformed conventional approaches—for instance, an artificial neural network predicting LNM in early-stage colorectal cancer achieved an AUC of 0.859 (14), and ML integration of clinical data improved thyroid cancer diagnostic accuracy (15). However, ML-based prediction of LNM in HCC remains scarce, with existing studies limited to small, single-center cohorts lacking population-level validation.
The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program of the U.S. National Cancer Institute provides a large, multicenter, patient-centered database encompassing demographic, tumor, pathological, and follow-up information. Leveraging multidimensional SEER data alongside a substantial HCC cohort from our hospital, this study aims to develop and externally validate a population-adapted ML model for predicting LNM in HCC, thereby facilitating early identification of high-risk patients who may benefit from intensified surveillance and tailored therapeutic strategies.
Materials and methods
Patient information
Data were obtained from the SEER database, a globally recognized cancer registry. LN status was determined according to the 7th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) staging system, using both imaging and pathological evidence.
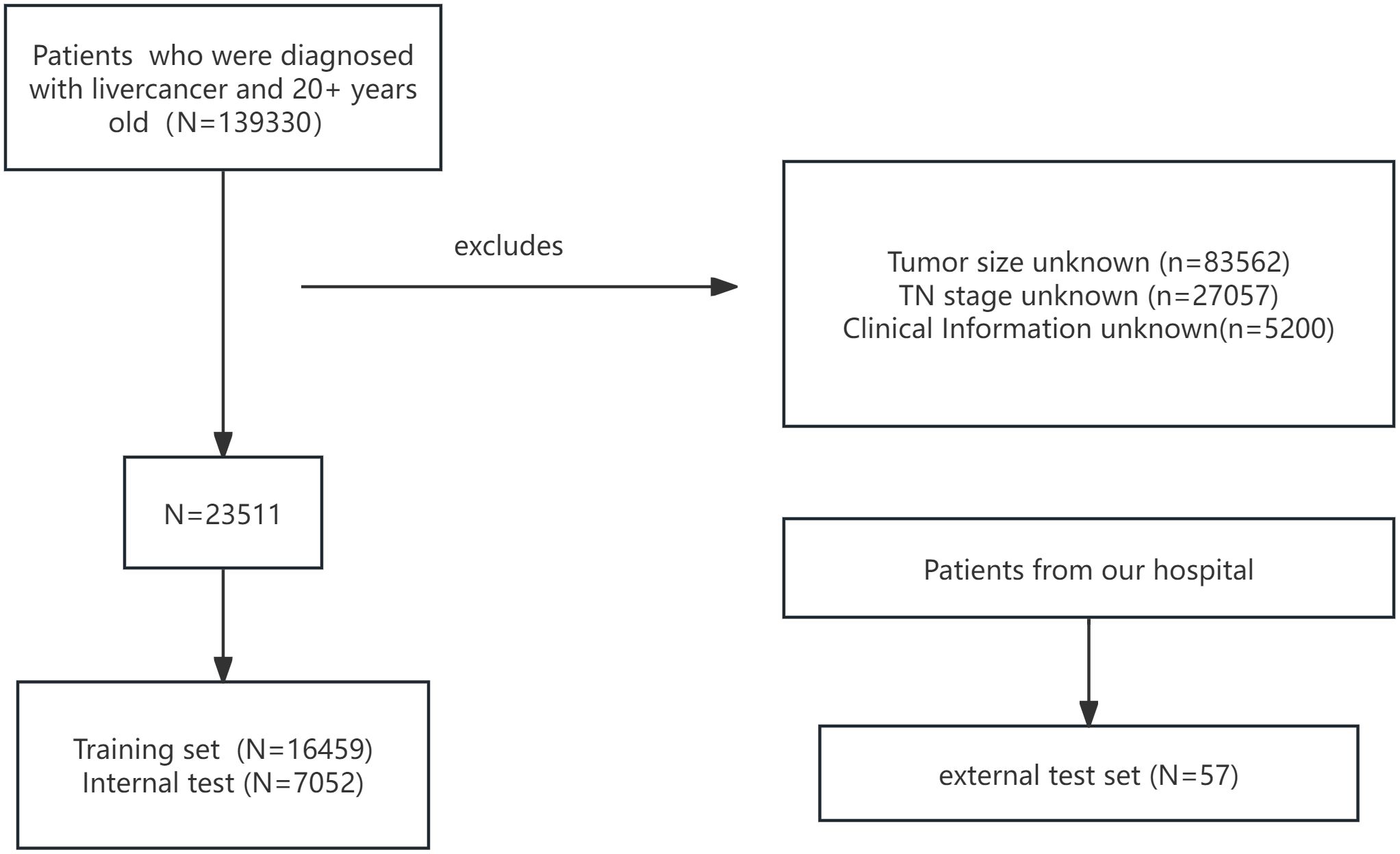
Inclusion criteria comprised histologically confirmed HCC patients diagnosed between 2010 and 2015, age ≥ 20 years, complete clinical and treatment records, and documented LNM status. Exclusion criteria were non-HCC liver malignancies, incomplete data, or unknown LN status. After screening, 23511 patients were enrolled and randomly split into a training cohort (n=16459) and an internal test cohort (n=7052) at a 7:3 ratio.
An external validation cohort of 57 HCC patients from our hospital was included to assess model generalizability. The patient selection workflow is shown in Figure 1. Data extraction and verification were performed independently by three investigators. The study received ethics committee approval, and all patients provided informed consent; analyses were conducted anonymously to ensure confidentiality.
Data preprocessing and feature selection
Key variables—including age, sex, race, AJCC TN stage, tumor size, sequence number, and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)—were extracted using SEER*Stat (v8.4.4) and reviewed by clinicians. Age was dichotomized (<60 vs ≥60 years). In the training cohort, univariate logistic regression (LR) identified predictors of LN metastasis (p<0.05). Stepwise regression (forward selection, backward elimination, and bidirectional selection) estimated odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). All analyses were performed in R (v4.4.2).
Model development and performance evaluation
Four ML algorithms—decision tree (DT), logistic regression (LR), multilayer perceptron (MLP), and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost)—were used to build prediction models. To address class imbalance, a 1:1 ratio undersampling technique was incorporated into the preprocessing pipeline to ensure a balanced distribution of the target variable. Model performance was evaluated by area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity. Variable importance plots were generated for all four models, followed by external validation.Additionally, pairwise comparisons of AUC differences were conducted using the DeLong test. The best-performing model was then selected, and a visualized clinical risk prediction nomogram was constructed based on this model.
Correlation analysis and variable importance
Following feature selection, Spearman correlation analysis quantified inter-variable associations, classified as low (0–0.4), moderate (0.4–0.7), or high (≥0.7). For each model, variable importance was ranked using a permutation-based method.
Results
Patient characteristics
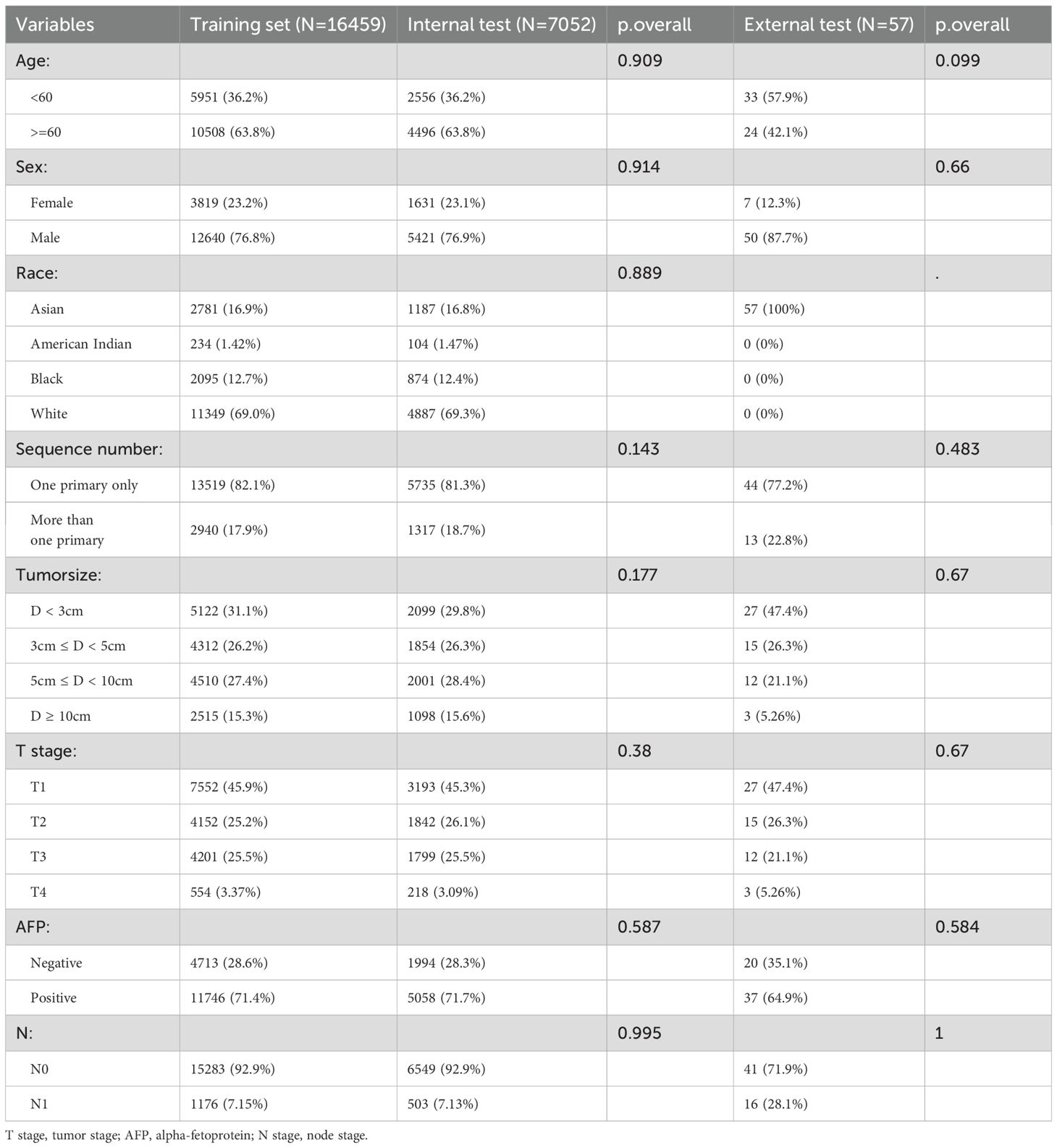
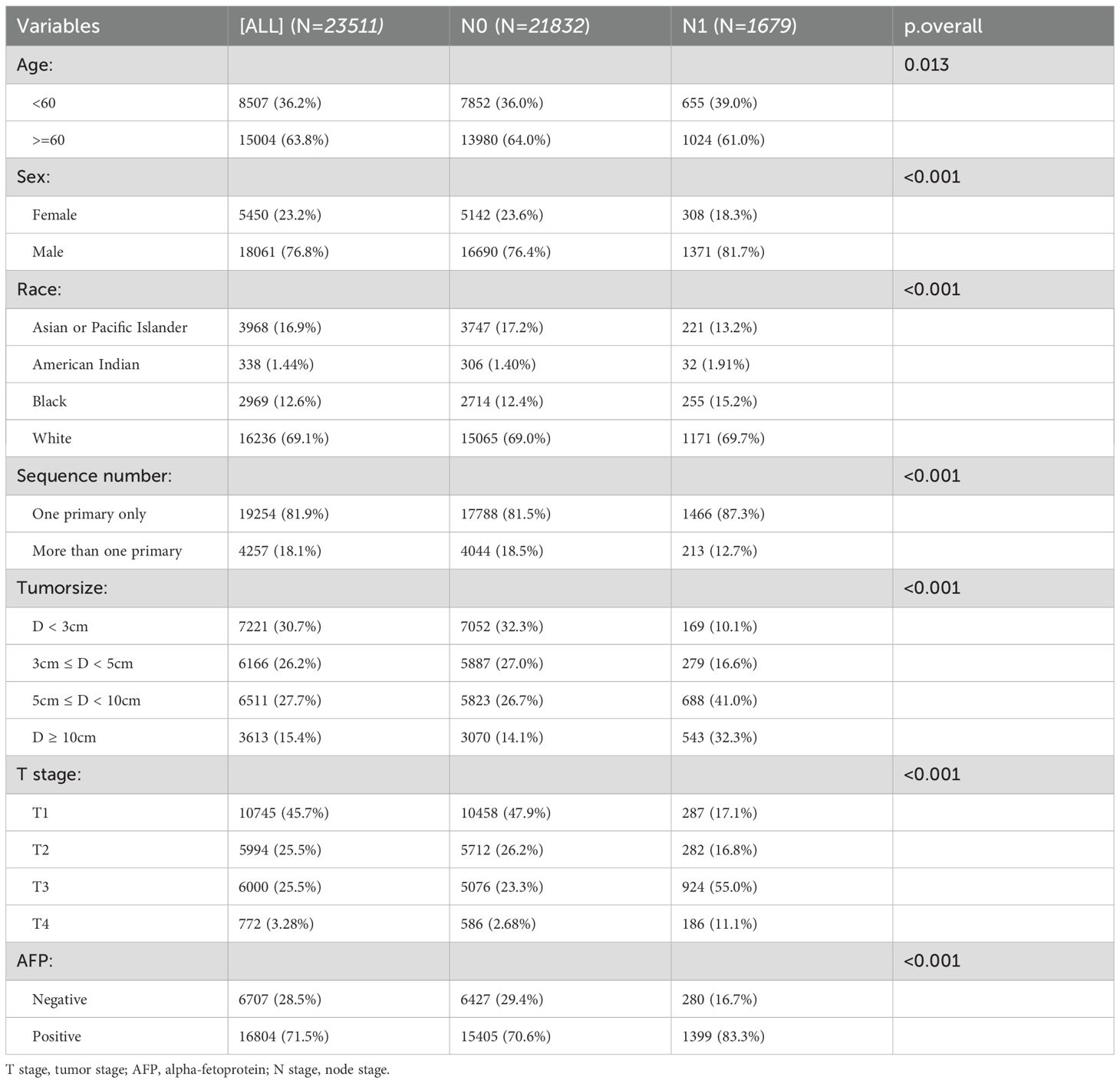
After screening, 23511 patients were included. All eight variables showed no significant differences between the training and internal test. In the external test, the variable race lacked a p-value due to the presence of only Asian individuals. (Table 1). Table 2 demonstrates that all features differed significantly across datasets (p < 0.05).
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses
Univariate logistic regression identified seven factors significantly associated with lymph node metastasis (LNM; p < 0.05): age, sex, race, sequence number, tumor size, T stage and AFP status (Table 3). In multivariate analysis, the presence of multiple primary tumors was an independent protective factor against LNM. Independent risk factors included increasing age (≥60 years), male sex, American Indian, Black, and White race, larger tumor size (3cm ≤ D < 5cm, 5cm ≤ D < 10cm, D ≥ 10cm), advanced T stage (T2, T3, T4), and positive AFP levels.
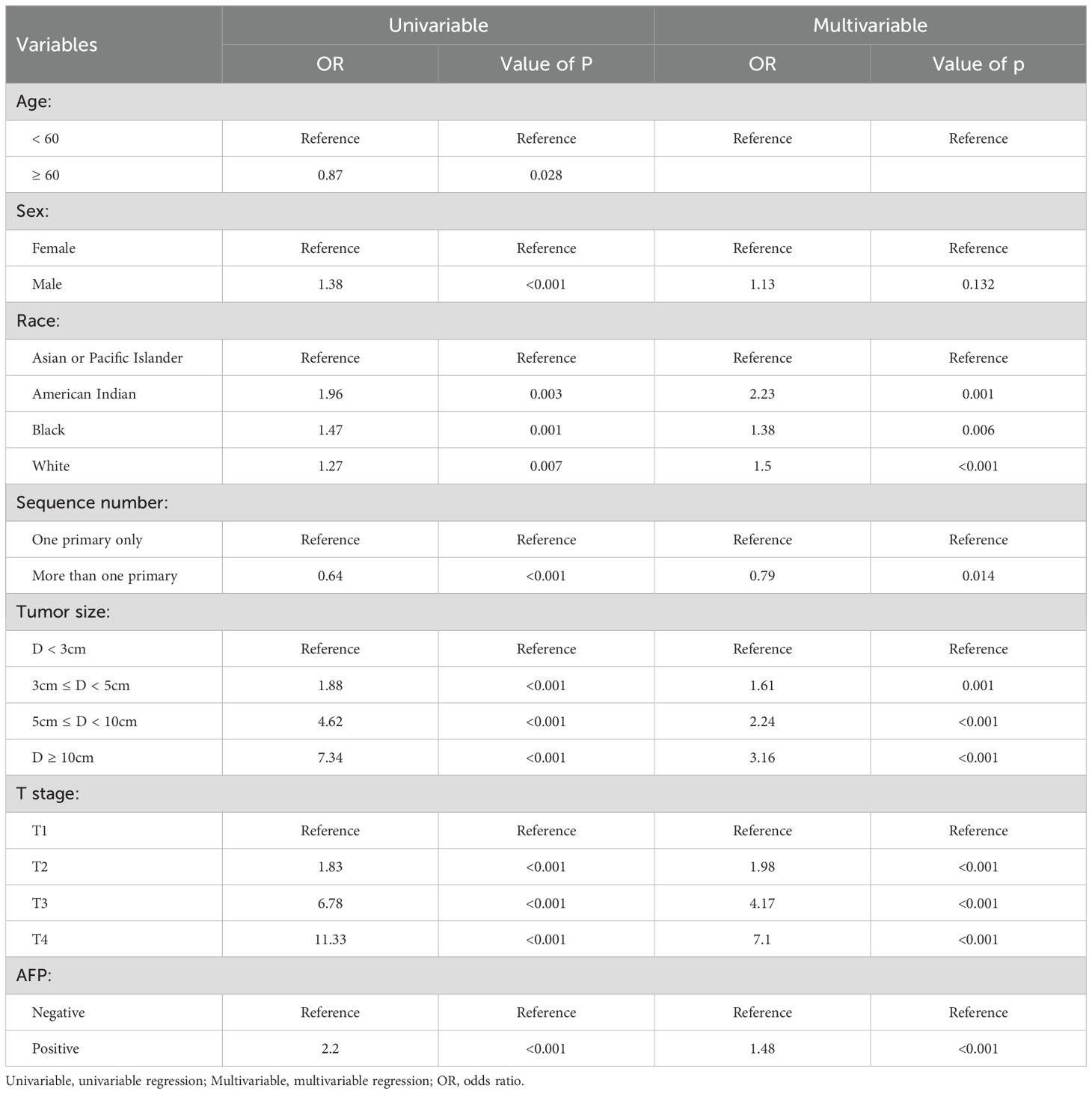
Table 3. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression analyses of risk factors for lymph node metastasis.
Correlation analysis
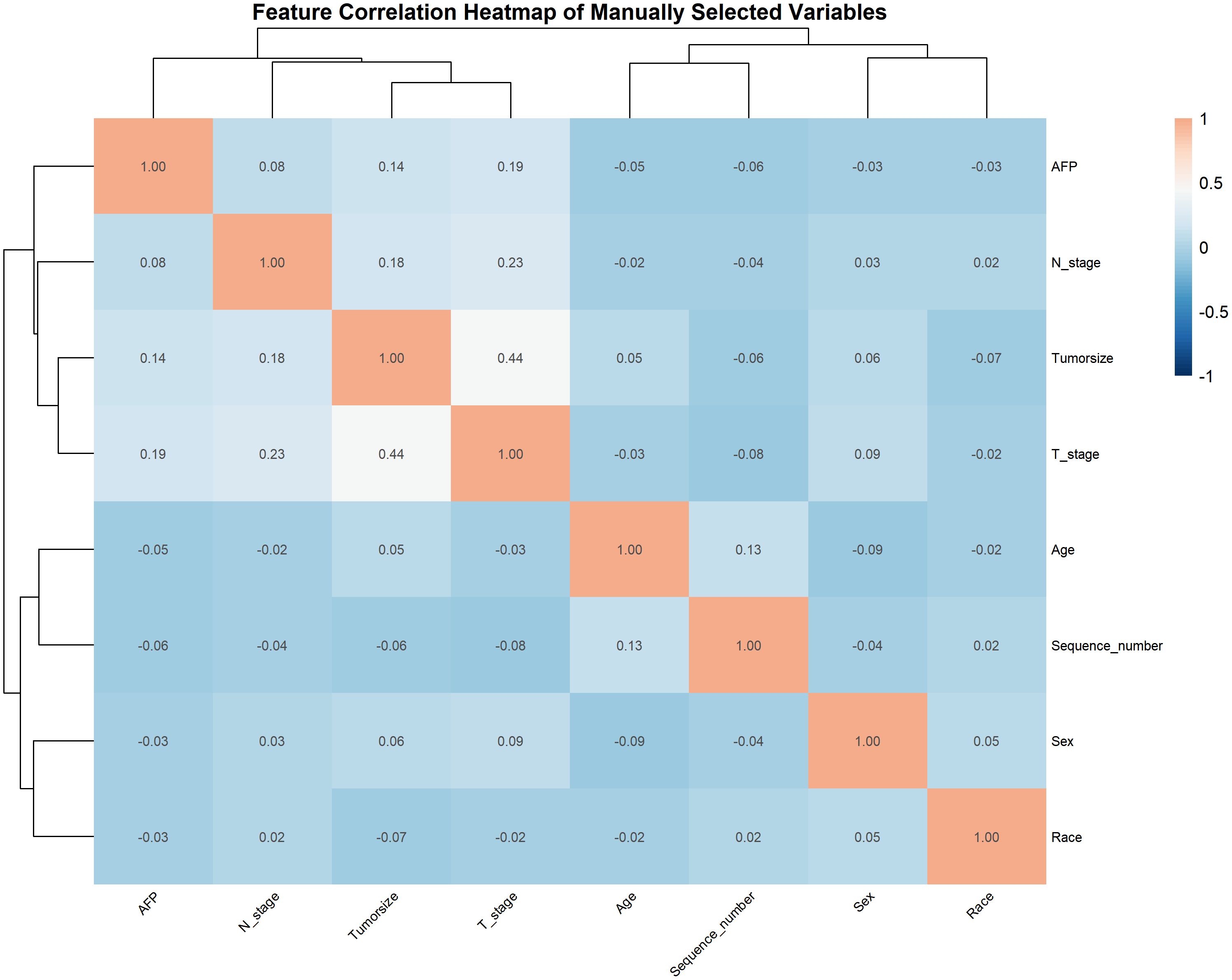
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients among the seven predictors were visualized via heatmap (Figure 2). T stage and tumor size showed a moderate positive correlation (p = 0.44), reflecting their joint association with tumor progression.
Performance of machine learning algorithms
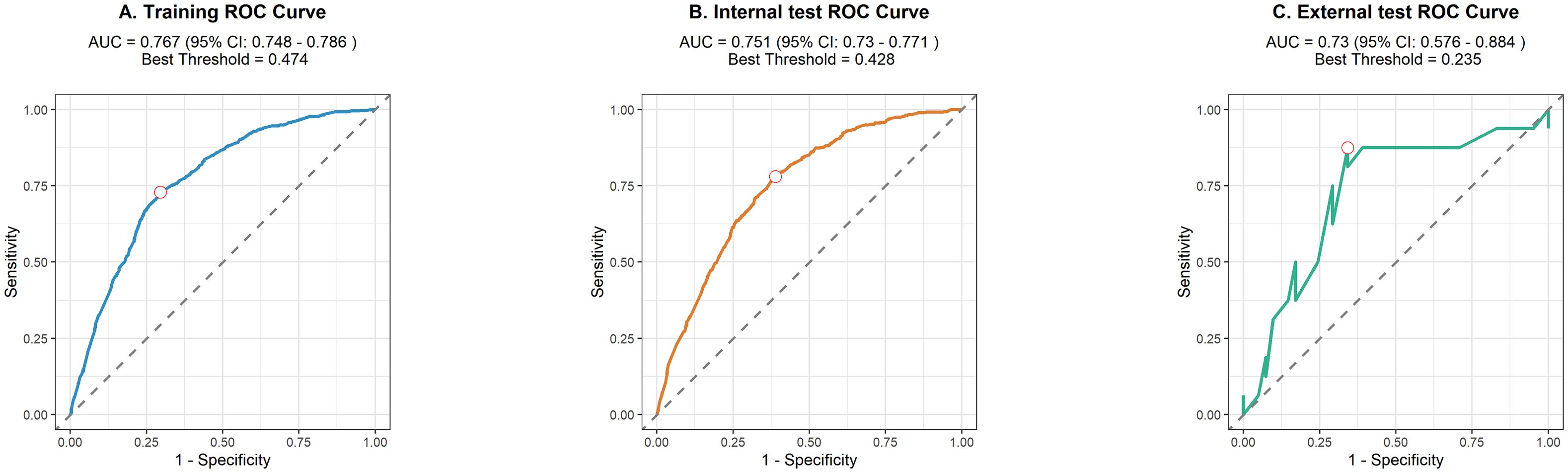
We used 10-fold cross-validation to optimize hyperparameters for four ML models (Figure 3). Comprehensive evaluation (Table 4) showed LR achieved the highest AUC (0.751) in the internal test set, closely followed by MLP (AUC = 0.75). ROC curves for all models on internal and external test sets are presented in Figure 4. Given its superior performance in the internal test set, LR was selected as the final predictive model. Its ROC curves across training, internal, and external test sets are shown in Figure 5. The variable importance plots for all four models (Figure 6) identified T stage and tumor size as the top predictors of LNM. Additionally, Given that the performance differences between the logistic regression (LR) and multilayer perceptron (MLP) models on the internal validation set were minimal, we conducted a DeLong test to compare the two models. The results indicated no significant differences in the area under the curve (AUC) between LR and MLP (AUC difference = 0.0002, p = 0.9442). Considering LR was deemed more aligned with the study’s objectives due to its interpretability advantages and comparable real-world performance, as evidenced by its consistent accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity across internal and external validation cohorts. Furthermore, a nomogram was developed based on the LR model to facilitate clinical risk assessment (Figure 7).
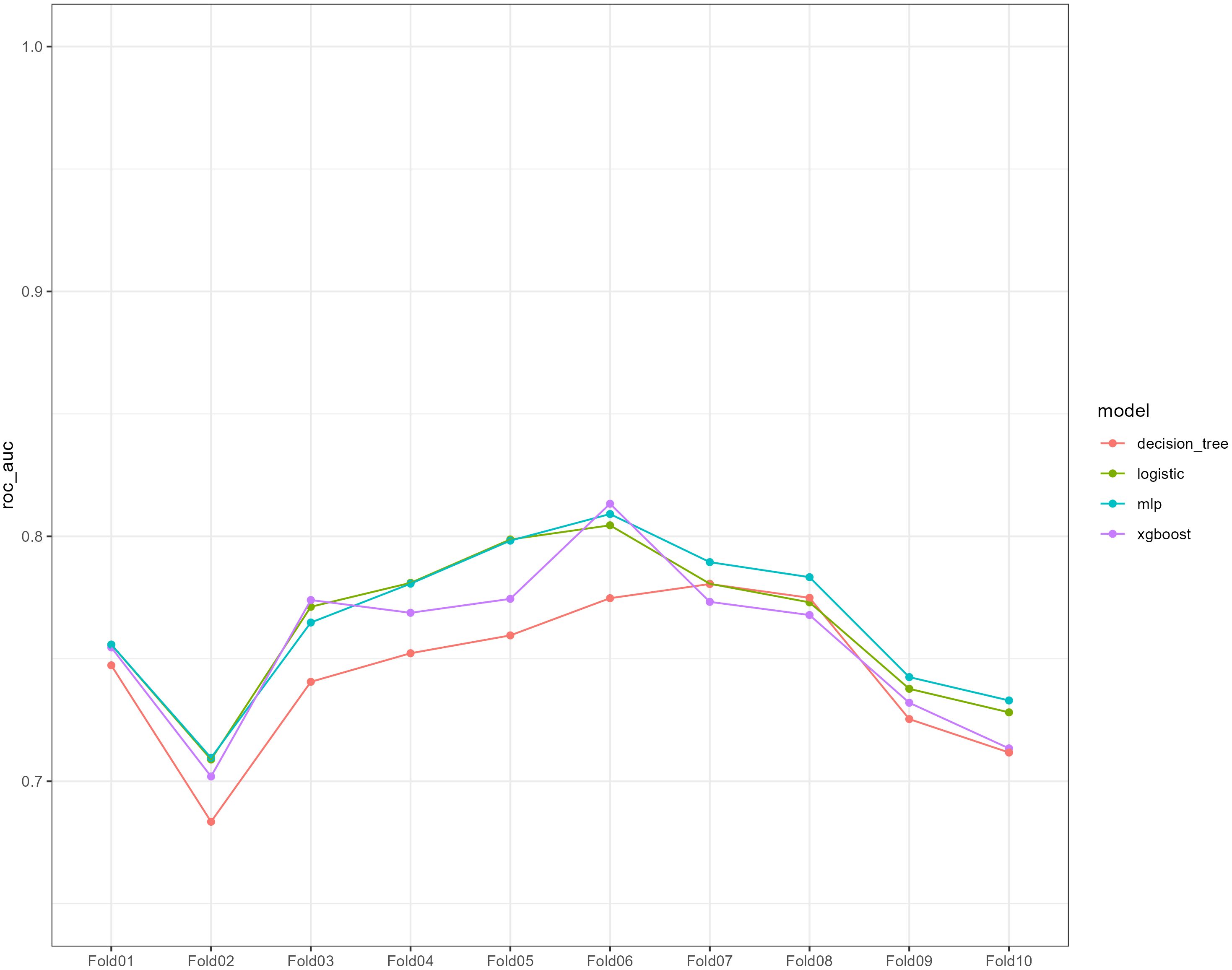
Figure 3. Ten-fold cross-validation of the receiver operating characteristic curves of the four machine learning models in the training cohort.
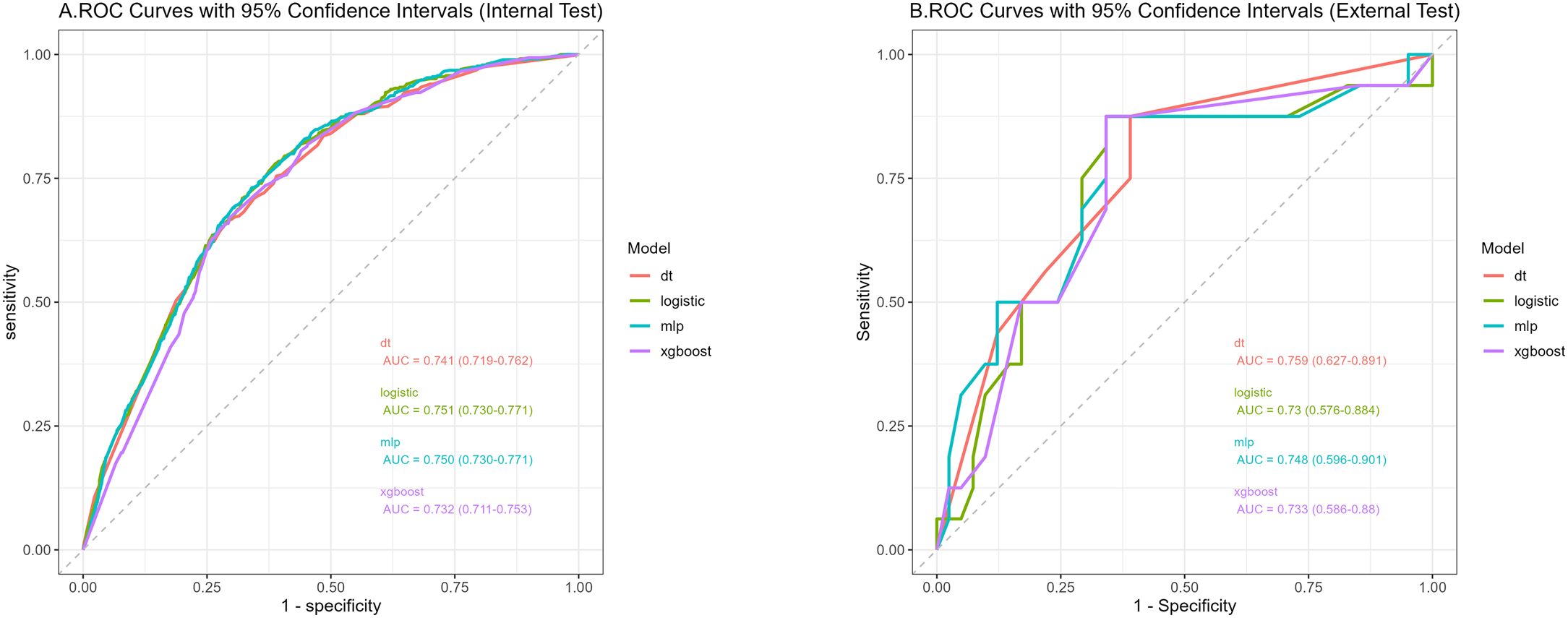
Figure 4. Receiver operating characteristic curves of the four algorithms in the internal (A) and external tests (B).
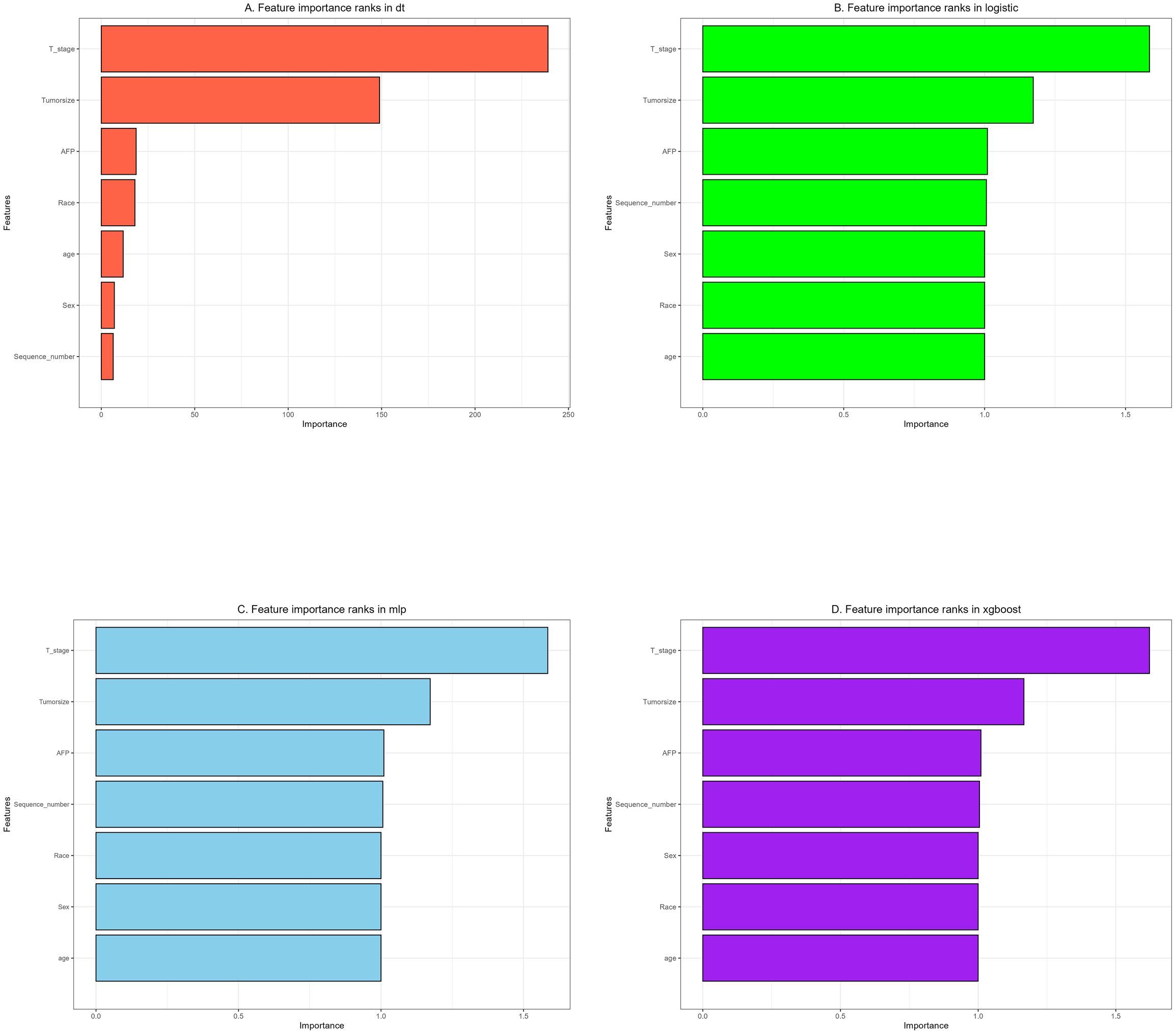
Figure 6. The importance of variables in each prediction model: (A) Decision tree (DT). (B) Logistic regression (LR). (C) Multilayer Perceptron (MLP). (D) Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost).
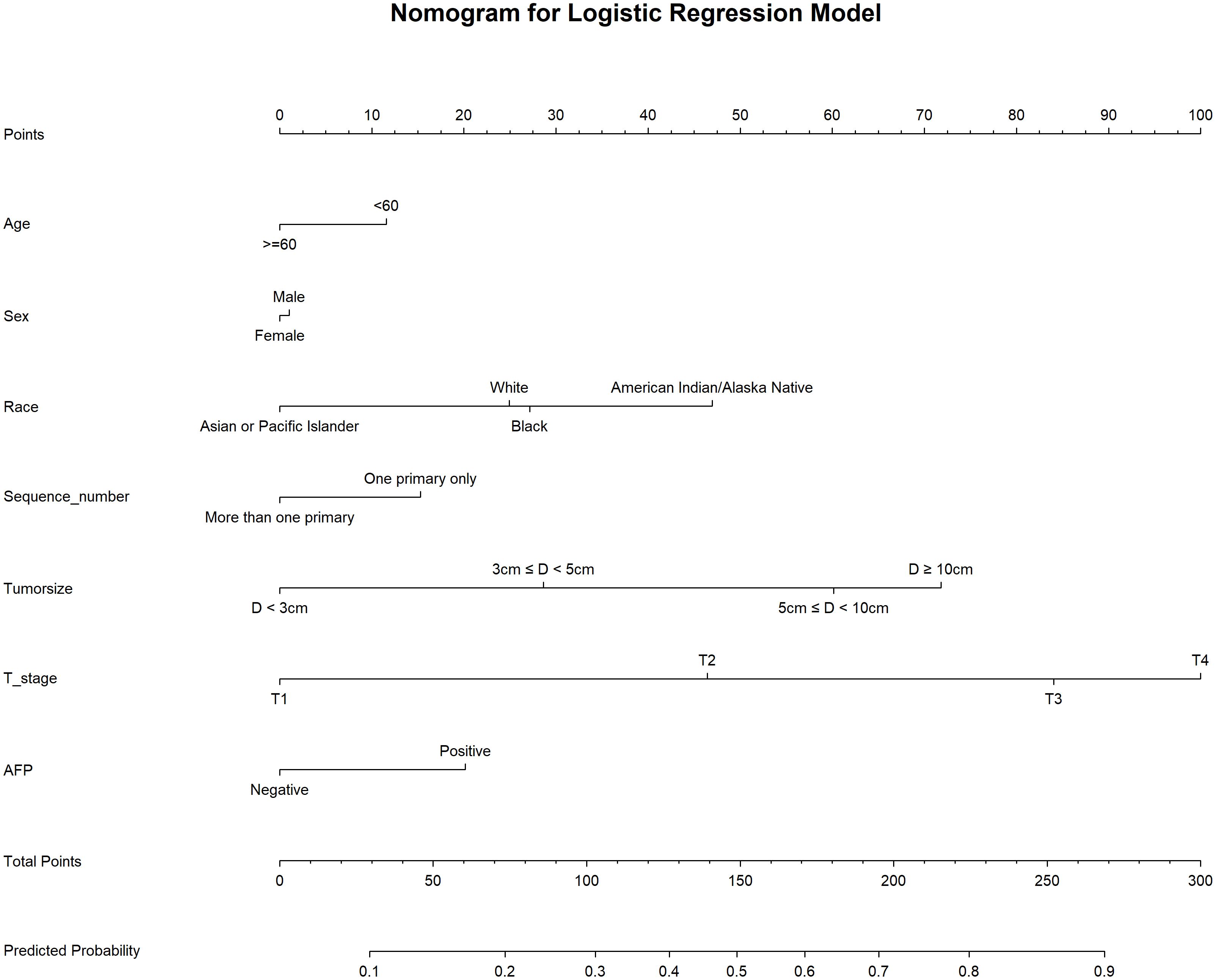
Nomogram for prediction of LNM in HCC patients
Table 4 presents the performance of the LR model. In the internal test set, the LR model achieved an AUC of 0.751 (95%CI: 0.73 - 0.771), accuracy of 0.707 (95%CI: 0.697 - 0.717), sensitivity of 0.711 (95%CI: 0.699 - 0.721), and specificity of 0.661 (95%CI: 0.622 - 0.708). In the external test set, the corresponding metrics were 0.730 for AUC (95%CI: 0.576 - 0.884), 0.737 for accuracy (95%CI: 0.596 - 0.825), 0.829 for sensitivity (95%CI: 0.692 - 0.927), and 0.5 for specificity (95%CI: 0.222 - 0.733). Overall, the model’s performance metrics in the external test set were comparable to those in the internal test set, indicating reasonable generalizability. Although the AUC decreased slightly from 0.751 (internal) to 0.730 (external), the accuracy and specificity improved (accuracy: 0.707→0.737; specificity: 0.711→0.829), suggesting enhanced ability to identify negative cases in external data. Together with previous analyses, LR maintains stable cross-dataset performance while balancing model complexity and interpretability, supporting its selection as the optimal model. Subsequently, a nomogram for predicting LNM in HCC patients was developed based on the logistic regression model. This nomogram calculates the total score from individual variable scales to predict the probability of LNM in HCC patients (Figure 7). An example of the nomogram application is as follows: A patient with the following characteristics was randomly selected: age <60 years, male, White race, a single primary tumor (one primary only), tumor size ≥10 cm, T4 stage, and AFP-positive status. Based on the nomogram, the patient’s total score was 244.8 points, corresponding to a predicted LNM probability of 0.846. Pathological confirmation verified the presence of LNM, demonstrating the nomogram’s accuracy.
Discussion
LNM in HCC represents a pivotal prognostic determinant: histologically node-positive patients demonstrate survival outcomes comparable to those with locally advanced (stage IVA) disease, and LNM markedly narrows the opportunity for curative intervention (16). Conventional detection—principally contrast-enhanced CT or MRI— suffers from suboptimal sensitivity and specificity due to HCC’s inherently low nodal metastasis incidence and confounding factors such as obesity or chronic inflammation (17). Moreover, traditional TNM-based predictive models (e.g., logistic regression) assume linearity and thus fail to capture complex, nonlinear interactions among tumor biomarkers (for example, synergistic effects between AFP levels and tumor size), resulting in biased risk stratification and potential delays in treating early-stage HCC (18).
ML addresses these challenges by integrating high-dimensional clinical data and modeling nonlinear relationships to improve predictive accuracy (19). Leveraging a cohort of 23,511 patients from the SEER database, we developed an LR model for LNM prediction achieving an AUC of 0.751. Key insights include a significant Spearman correlation between tumor size and advanced T stage—reflecting the aggressive growth kinetics of metastatic HCC (20). Methodologically, undersampling was incorporated into the preprocessing pipeline, ensuring a balanced distribution of the target variable and our approach employed 10-fold cross-validation with grid search to ensure model robustness; Despite the small size of the external cohort (n = 57), the model maintained a high sensitivity of 0.829, highlighting its reliability in excluding patients without metastasis. This helps to avoid unnecessary lymphadenectomy in low-risk cases, thereby reducing surgical morbidity (21) and minimizing center-specific bias (22).
Feature importance rankings (T stage > Tumor size > AFP) correspond closely with established molecular mechanisms governing HCC metastasis and survival outcomes (23–25). The prognostic significance of tumor size likely reflects its pro-metastatic biology: larger tumors (T2–T4) demonstrate upregulated MMP2/9 expression and enhanced exosome-mediated paracrine signaling, which facilitate lymphatic dissemination (26). Likewise, Hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) with positive and negative alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) exhibit distinct molecular mechanisms driving lymph node metastasis (LNM): the former is characterized by the activation of the phosphoinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathway (27) and the upregulation of immune checkpoints, while the latter is predominantly driven by metabolic reprogramming and aberrant Wnt signaling (28). Traditionally, the presence of multiple primary tumors (MPTs) has been perceived as a high-risk indicator of cancer progression. However, our multivariate analysis in this study reveals an inverse association between the existence of MPTs and the risk of LNM (OR=0.79). This phenomenon may arise from the synergistic effects of multi-dimensional biological mechanisms, such as clonal competition that restricts the growth of metastatic subclones (29), activation of the immune microenvironment that suppresses homing, and metabolic reprogramming that diminishes invasiveness (30). Notably, race emerged as an independent predictor, with non-Asian populations (including American Indians, Blacks, and Whites) exhibiting a higher risk of LNM. Potential contributing factors may include tumor biological differences across races (such as genetic backgrounds), disparities in healthcare accessibility, and inequities in cancer screening and treatment strategies. These factors warrant further investigation and may provide valuable insights for the development of personalized oncology treatment strategies in the future.
Clinically, the LR-based nomogram offers a transformative framework for precision management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Within this model, T4 stage and tumor size ≥10 cm serve as key predictors, assigned approximately 100 and 72 points, respectively. A total score exceeding 150 points correlates with a >50% probability of lymph node metastasis, warranting comprehensive preoperative assessment.To enhance clinical applicability, we established a three-tier risk stratification system: low-risk (predicted probability <0.3), intermediate-risk (0.3–0.7), and high-risk (>0.7). This framework facilitates precise prognostic evaluation and supports individualized therapeutic decision-making.
Nonetheless, this study has important limitations. First, SEER lacks key HCC-specific variables—such as HBV/HCV viral load and Child-Pugh grade—which may omit the influence of cirrhosis-related microenvironments on LNM risk (31), Future research ought to integrate data from multiple centers, such as incorporating viral serological indicators and data on radiotherapy (32), to enhance the generalizability of the model. Second, the modest size and single-center origin of the external validation cohort (n = 57) limit generalizability; Future studies should incorporate data from multiple centers—for example, by including virological serological markers and radiotherapy-related information—to construct a larger and multi-center external validation cohort. Meanwhile, we will actively explore other accessible population-based databases to further increase the sample size and heterogeneity of the external validation set, thereby enhancing the model’s applicability and robustness across diverse populations and clinical settings. Third, despite Logistic’s interpretability advantages relative to deep learning, the inherent “black-box” nature of ML models continues to challenge clinical transparency (33).
To address these gaps, future research should: (1) By extracting radiomic features—including tumor texture, shape, and edge sharpness—from imaging data such as CT and MRI, and integrating them with lymph node texture heterogeneity and circulating tumor cell (CTC) detection, we aim to construct a comprehensive multimodal predictive platform. This approach fundamentally transforms the prediction of lymph node metastasis by shifting from traditional morphological assessment to a quantitative, dynamic, and mechanism-driven intelligent diagnostic framework (34); (2) develop streamlined ML algorithms within clinical decision support systems to enable intraoperative, real-time LNM risk assessment; and (3) validate the functional roles of key predictors (e.g., AFP) using organoid and in vivo models to establish a rigorous “computational prediction–experimental validation” paradigm.
Conclusion
Using four machine learning algorithms to predict LNM in HCC, increasing age (≥60 years), male sex, American Indian, Black, and White race, larger tumor size (3cm ≤ D < 5cm, 5cm ≤ D < 10cm, D ≥ 10cm), advanced T stage (T2, T3, T4), and positive AFP levels were identified as independent risk factors. The LR model demonstrated superior predictive performance. Based on this model, a nomogram for predicting LNM in HCC patients was developed, enabling clinicians to stratify LNM risk and tailor personalized treatment strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Southwest Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
LY: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Supervision, Conceptualization, Software, Methodology, Validation. LHa: Supervision, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Data curation. LHu: Software, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision. LT: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. HK: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. FJ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. HY: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Conceptualization, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (No.2025ZNSFSC1883), the Key Project of Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No. 2022YFS0622-A6), the Program of Sichuan Medical Association (No. S23044), the Applied Basic Research Project of Luzhou Science and Technology and Talent Work Bureau (No. 2022-JYJ-123), the Key Project of Southwest Medical University (No. 2024LCYXZX23), the Strategic Cooperation Project of Luzhou Municipal People’s Government-Southwest Medical University (No. 2024LZXNYDJ058), the General Project of Southwest Medical University (No. 2024LCYXZX54), the Program of Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University (No. HYX22009), and the Cultivation Project of Sichuan Computer Research Institute (No. MZGC20240014).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer S-PL declared a shared affiliation with the author LT to the handling editor at the time of review.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
2. Yeo YH, Abdelmalek M, Khan S, Moylan CA, Rodriquez L, Villanueva A, et al. Current and emerging strategies for the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 22:173–90. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-01021-z
3. Barcena-Varela M, Monga SP, and Lujambio A. Precision models in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 22:191–205. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-01024-w
4. Zhang K, Tao C, Wu F, Wu J, and Rong W. A practical nomogram from the SEER database to predict the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with lymph node metastasis. Ann Palliat Med. (2021) 10:3847–63. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1876
5. Wu J, Zhang C, Zhang Y, He R, Wang Q, Zhang L, et al. Prediction model establishment of prognosis factors for distant metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma based on the SEER database. Cancer Epidemiol. (2025) 94:102729. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2024.102729
6. Yang Y, Chen XQ, Jia YX, Ma J, Xu D, and Xiang ZL. Circ-0044539 promotes lymph node metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through exosomal-miR-29a-3p. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:630. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07004-x
7. Xia F, Wu L, Lau WY, Li G, Huan H, Qian C, et al. Positive lymph node metastasis has a marked impact on the long-term survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e95889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095889
8. Zhang XF, Chakedis J, Bagante F, Chen Q, Beal EW, Lv Y, et al. Trends in use of lymphadenectomy in surgery with curative intent for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Surg. (2018) 105:857–66. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10827
9. Kolck J, Auer TA, Walter-Rittel T, Hosse C, Elkilany A, Marth AA, et al. Prediction of regional lymph node metastasis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: it’s not all about size. Abdom Radiol (NY). (2023) 48:3063–71. doi: 10.1007/s00261-023-03991-1
10. Lerut J, Foguenne M, and Lai Q. Hepatocellular cancer selection systems and liver transplantation: from the tower of babel to an ideal comprehensive score. Updates Surg. (2021) 73:1599–614. doi: 10.1007/s13304-021-01078-4
11. Xu J, Zhang L, Liu Q, and Zhu J. Preoperative multiparameter MRI-based prediction of Ki-67 expression in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Precis Radiat Oncol. (2025) 9:23–34. doi: 10.1002/pro6.70005
12. Shao G, Ma Y, Qu C, Gao R, Zhu C, Qu L, et al. Machine learning model based on the neutrophil-to-eosinophil ratio predicts the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2024) 11:679–91. doi: 10.2147/jhc.S455612
13. Wu B, Zhu Y, Hu Z, Wu J, Zhou W, Si M, et al. Machine learning predictive models and risk factors for lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Pulm Med. (2024) 24:526. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03345-7
14. Qiu B, Shen Z, Wu S, Qin X, Yang D, and Wang Q. A machine learning-based model for predicting distant metastasis in patients with rectal cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1235121. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1235121
15. Xi NM, Wang L, and Yang C. Improving the diagnosis of thyroid cancer by machine learning and clinical data. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:11143. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15342-z
16. Hasegawa K, Makuuchi M, Kokudo N, Izumi N, Ichida T, Kudo M, et al. Impact of histologically confirmed lymph node metastases on patient survival after surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: report of a Japanese nationwide survey. Ann Surg. (2014) 259:166–70. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828d4960
17. Willemssen F, de Lussanet de la Sablonière Q, Bos D, IJ J, De Man R, and Dwarkasing R. Potential of a non-contrast-enhanced abbreviated MRI screening protocol (NC-AMRI) in high-risk patients under surveillance for HCC. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:3961. doi: 10.3390/cancers14163961
18. Zhang Y, Chen SW, Liu LL, Yang X, Cai SH, and Yun JP. A model combining TNM stage and tumor size shows utility in predicting recurrence among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Cancer Manag Res. (2018) 10:3707–15. doi: 10.2147/cmar.S175303
19. Zhou J, Li D, Ren J, Huang C, Yang S, Chen M, et al. Machine learning: A multicentre study on predicting lateral lymph node metastasis in cN0 papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2025). doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaf070
20. Renne SL and Di Tommaso L. A clinical and pathological update on hepatocellular carcinoma. J Liver Cancer. (2022) 22:14–22. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2022.03.18
21. Li Y, Han D, Shen C, and Duan X. Construction of a comprehensive predictive model for axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer: a retrospective study. BMC Cancer. (2023) 23:1028. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11498-7
22. Long Z, Yi M, Qin Y, Ye Q, Che X, Wang S, et al. Development and validation of an ensemble machine-learning model for predicting early mortality among patients with bone metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1144039. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1144039
23. Kang X, Liu X, Li Y, Yuan W, Xu Y, and Yan H. Development and evaluation of nomograms and risk stratification systems to predict the overall survival and cancer-specific survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Exp Med. (2024) 24:44. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01296-1
24. Chen K, Zhu P, Ye J, Liao Y, Du Z, Chen F, et al. Oxymatrine inhibits the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by reducing the activity of MMP-2/-9 via regulating p38 signaling pathway. J Cancer. (2019) 10:5397–403. doi: 10.7150/jca.32875
25. Zhang L, Xiang ZL, Zeng ZC, Fan J, Tang ZY, and Zhao XM. A microRNA-based prediction model for lymph node metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:3587–98. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6534
26. Zhen C, Zhu C, Chen H, Xiong Y, Tan J, Chen D, et al. Systematic analysis of molecular mechanisms for HCC metastasis via text mining approach. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:13909–16. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14692
27. Li QT, Qiu MJ, Yang SL, Fang X, He XX, Wang MM, et al. Alpha-fetoprotein regulates the expression of immune-related proteins through the NF-κB (P65) pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Oncol. (2020) 2020:9327512. doi: 10.1155/2020/9327512
28. Lin Z, Li H, He C, Yang M, Chen H, Yang X, et al. Metabolomic biomarkers for the diagnosis and post-transplant outcomes of AFP negative hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1072775. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1072775
29. Ji H, Hu C, Yang X, Liu Y, Ji G, Ge S, et al. Lymph node metastasis in cancer progression: molecular mechanisms, clinical significance and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:367. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01576-4
30. Assis-Mendonça GR, Fattori A, Rocha RM, Lourenço GJ, Delamain MT, Nonogaki S, et al. Single nucleotide variants in immune-response genes and the tumor microenvironment composition predict progression of mantle cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:209. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07891-9
31. Cao R, Jiang H, Liang G, and Zhang W. SEER-based risk stratification system for patients with primary non-cirrhotic liver cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:12033–45. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05057-7
32. Zhao H, Qi Y, Zhang L, Xing M, and Yang F. Thoracic radiotherapy timing and prognostic factors in elderly patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer. Precis Radiat Oncol. (2024) 8:14–21. doi: 10.1002/pro6.1223
33. Ciobanu-Caraus O, Aicher A, Kernbach JM, Regli L, Serra C, and Staartjes VE. A critical moment in machine learning in medicine: on reproducible and interpretable learning. Acta Neurochir (Wien). (2024) 166:14. doi: 10.1007/s00701-024-05892-8
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, machine learning, predictive model, lymph node metastasis, logistic regression
Citation: Yuqin L, Hongyan L, Hongyuan L, Tingting L, Kun H, Jie F and Yunhui H (2025) Lymph node metastasis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma using machine learning: a population-based study. Front. Oncol. 15:1601985. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1601985
Received: 28 March 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 11 July 2025.
Edited by:
Yong Yin, Shandong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Hongjun Yu, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, ChinaSheng-Ping Li, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, China
Quan Fang, Zhuhai People’s Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Yuqin, Hongyan, Hongyuan, Tingting, Kun, Jie and Yunhui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Han Yunhui, Njc0OTI3MDk4QHFxLmNvbQ==; Fang Jie, MTg2MDY0MDY4NjlAMTYzLmNvbQ==; He Kun, aGt0b25namlAc3dtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Li Yuqin1,2†
Li Yuqin1,2† Li Hongyuan
Li Hongyuan He Kun
He Kun Han Yunhui
Han Yunhui