- 1Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Zhejiang Hospital, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3Lishui People’s Hospital, Lishui, Zhejiang, China
- 4Hangzhou Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 5Affiliated Hangzhou First People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Westlake University, Hangzhou, China
Background: The Serial function in the Monaco treatment planning system is essential for cardiac dose optimization in left breast cancer radiotherapy; however its optimal K-value for deep-inspiration breath-hold intensity-modulated radiotherapy (DIBH-IMRT) has not been established. This study aims to determine the evidence-based K-value configuration for clinical implementation.
Methods: 41 left breast cancer patients undergoing DIBH-IMRT were retrospectively analyzed. Plans were stratified by Monaco-Serial K-values: Group A (K=1), B (2≤K ≤ 4), and C (K>4). Dosimetric parameters (heart, LAD, Lung-L) and dose-volume reduction rates (Groups B/C vs A) were compared. Correlations between K-values and DIBH-induced anatomical changes (Lung-L volume increment rate, Lung-L/Heart volume ratio, and Heart-Breast Distance increment) were assessed
Results: All plans satisfied target coverage. Group B achieved optimal cardiac protection: mean heart dose (273.9 ± 91.0 cGy), max heart dose (2676.2 ± 1380.7 cGy), and LAD doses (mean: 411.3 cGy; max: 1483.3 ± 736.3 cGy) significantly decreased versus Group A. Lung-L V500cGy in Group B increased marginally but within clinical tolerance. Correlation analysis confirmed that Group B achieved balanced control of mean/maximum heart doses, aligning with the expected effects of anatomical variations induced by the DIBH technique.
Conclusions: Adjusting Monaco-Serial K-value to 2≤K ≤ 4 provides optimal dose constraints for the heart and substructures while ensuring target coverage, making it the optimal parameter setting for left breast cancer DIBH-IMRT.
1 Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy among women worldwide, with radiotherapy serving as a critical adjunctive treatment (1, 2). However, due to the anatomical proximity of the breast to the heart, radiation exposure during treatment is strongly associated with an increased risk of radiation-induced heart disease, particularly in left-sided breast cancer (3). Modern radiotherapy planning systems, utilizing inverse intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and dose optimization algorithms, effectively limit radiation exposure to organs at risk (OARs) while ensuring adequate target dose coverage, and have become a standard in clinical practice (4–6). To further reduce cardiac dose, the deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) technique has emerged as an essential approach in recent breast cancer radiotherapy (7, 8). DIBH increases lung volume, expanding the distance between the target and the heart, which enhances dose attenuation in the target area and minimizes radiation exposure to the heart (9, 10). The combination of DIBH with IMRT dose optimization algorithms has been shown to significantly reduce radiation to the heart and its substructures, thereby lowering the risk of radiation-induced heart disease (11).
The Monaco treatment planning system (TPS), which uses the Monte Carlo dose calculation algorithm, is one of the most widely employed systems in clinical practice, providing highly accurate dose optimization results that closely reflect actual radiation-induced damage (12). The system’s Serial function is a key biological optimization tool, especially for dose constraints applied to the heart and its substructures. In Monaco-Serial, a K value of 1 is commonly used for setting average dose constraints to the heart and its substructures in left breast cancer free-breathing IMRT (FB-IMRT) (13, 14). However, with DIBH-IMRT, significant anatomical changes, such as the increased distance between the heart and the target, can render previous settings suboptimal, and to date, there is a lack of studies addressing this issue.
This study aims to identify the optimal K value setting for Monaco-Serial in DIBH-IMRT for left-sided breast cancer by retrospectively analyzing 41 patients who underwent DIBH-IMRT. Radiotherapy plans were designed using different Monaco-Serial K values, and dosimetric comparisons were made. Furthermore, the correlation between changes in dose-volume parameters of OARs and anatomical variations post-DIBH was explored. The goal is to provide data-driven insights for optimizing Monaco-Serial settings in left-sided breast cancer DIBH-IMRT, thus supporting the clinical application of the Monaco system in designing DIBH-IMRT treatment plans.
2 Materials and methods
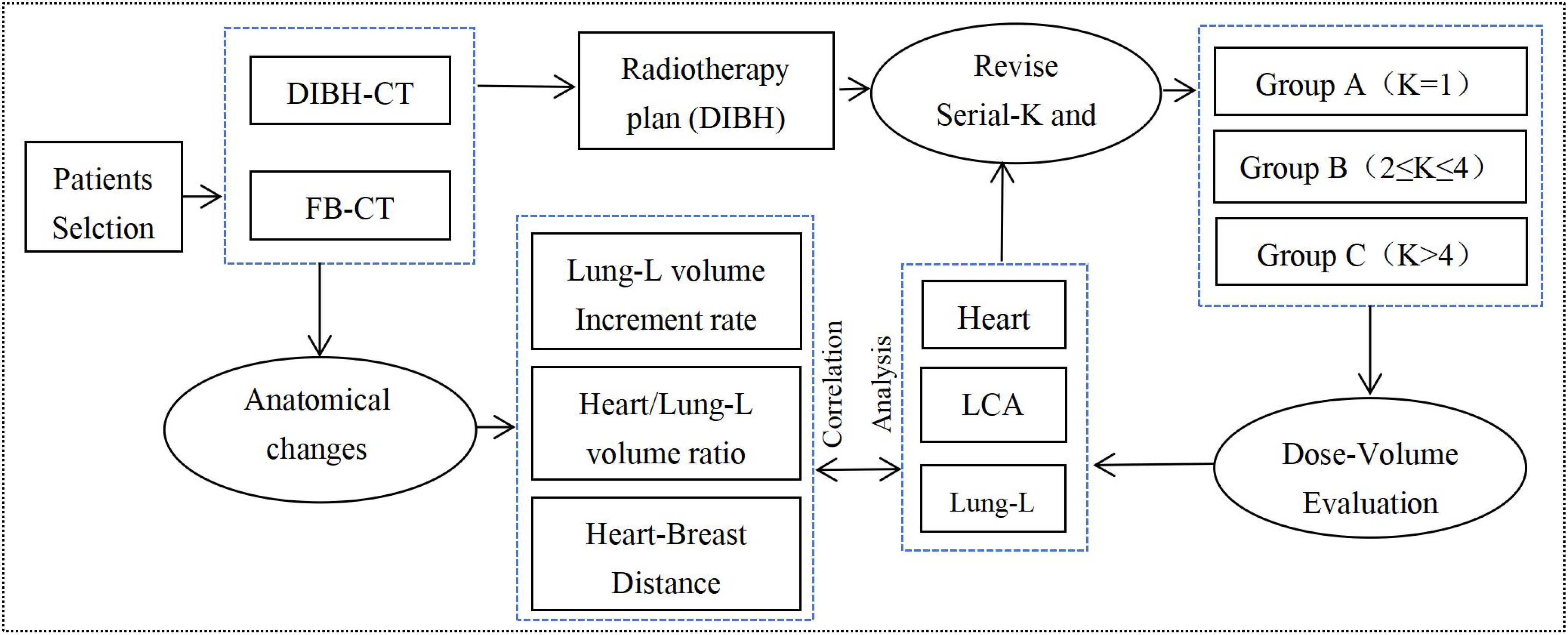
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the researchers’ hospital (Approval No. 2024-145K) and prospectively registered at ClinicalTrials (identifier NO.NCT06796257), adhering to ICMJE guidelines. It included 41 patients with left-sided breast cancer who underwent breast-conserving surgery followed by whole-breast radiotherapy between August 2022 and December 2024, with a mean age of 43.3 years (range: 29–72 years). All participants demonstrated good compliance and successfully completed the entire DIBH treatment protocol. The study workflow is outlined in Figure 1, which encompasses CT simulation and positioning under both free-breathing (FB) and DIBH conditions, radiotherapy plan design and evaluation, as well as the analysis of anatomical changes and dose reduction rates following DIBH.
2.1 CT simulation and target delineation
All patients were positioned and immobilized using a vacuum bag combined with a single-board system (R612, Klarity, China). CT simulation images were acquired with a CT scanner (Somatom, Siemens, Germany), covering the scan range from the inferior margin of the mandible to the inferior margin of the liver. Immediately after completing the CT scan in the FB position, each patient underwent a chest-breathing DIBH CT scan. Prior to the DIBH scan, patients received breathing training and were required to achieve breath-holding for more than 20 seconds in three consecutive attempts. Those who met this criterion were deemed eligible for DIBH CT scanning. Breathing gating during DIBH was performed using a laser-based surface scanner (Sentinel, C-RAD AB, Sweden), with the gating point monitored at the mid-sternum. The CT scan was conducted at a voltage of 110 kV, with a slice thickness of 3 mm. For the DIBH scan, an iodinated contrast agent was administered to enhance image quality. Both DIBH-CT and FB-CT images were subsequently transferred to the radiotherapy planning system (Monaco 6.0, Elekta, Sweden).
On the DIBH-CT images, radiation oncologists reviewed and contoured the OARs and target volumes. The Gross Tumor Volume (GTV), Clinical Target Volume (CTV) and OARs were defined according to Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) standards (15), while the Planning Target Volume (PTV) and Planning Gross Tumor Volume (PGTV) were generated by expanding the CTV and GTV by 10 mm and contracting the subcutaneous volume by 5 mm. The heart, left lung, right lung, and body contour were auto-contoured using an automatic segmentation tool (AccContour, China), with manual adjustments made by the radiation oncologist. The left anterior descending artery (LAD) was manually contoured by the radiation oncologist. All OARs and target delineations were reviewed and approved by senior radiation oncology experts.
2.2 Radiotherapy plan design
All patients received a prescribed dose of 5000 cGy in 25 fractions for the PTV. Postoperative breast-conserving surgery patients received an additional boost to the PGTV, totaling 5750 cGy in 25 fractions. Target volume coverage adhered to ICRU recommendations, ensuring that the maximum dose did not exceed 107%, and the 95% isodose line covered the PTV/PGTV. The DIBH radiotherapy plans for all patients were designed by the same radiation therapy physicist using 6MV-FFF photon energy with 6 tangential IMRT fields based on the DMLC technique. All dose calculations were performed using the Monte Carlo algorithm on Monaco 6.0, with a 3 mm calculation grid and a statistical uncertainty of 1%.
During radiotherapy planning, the dose limits for OARs followed the guidelines for breast cancer radiotherapy (Chinese Medical Association, 2020 edition) (16). The dose-volume objectives, optimization functions, and parameter settings are summarized in Table 1. Three different radiotherapy plans were designed for each patient based on varying Monaco-Serial K values for cardiac dose constraints: Group A (K=1), Group B (2≤K ≤ 4), and Group C (K>4). For heart dose constraints, the Equivalent Uniform Dose (EUD) was adjusted according to dose optimization principles, with modifications made in response to changes in K values. For the lung (Lung-L), LAD, and spinal cord dose constraints, EUD, MOD (Mean Organ Damage), and Maximum Dose values were fine-tuned to minimize OARs dose-volume while maintaining adherence to dose optimization principles, as outlined in Table 1. All three radiotherapy plans were reviewed and approved by the same senior radiation oncologist before undergoing dosimetric analysis. Additionally, the plans were independently verified using the 3D dose verification system (Evolution, IBA, Germany), ensuring consistency and accuracy. The verification criterion required a gamma passing rate (2mm/3%) of over 95%.
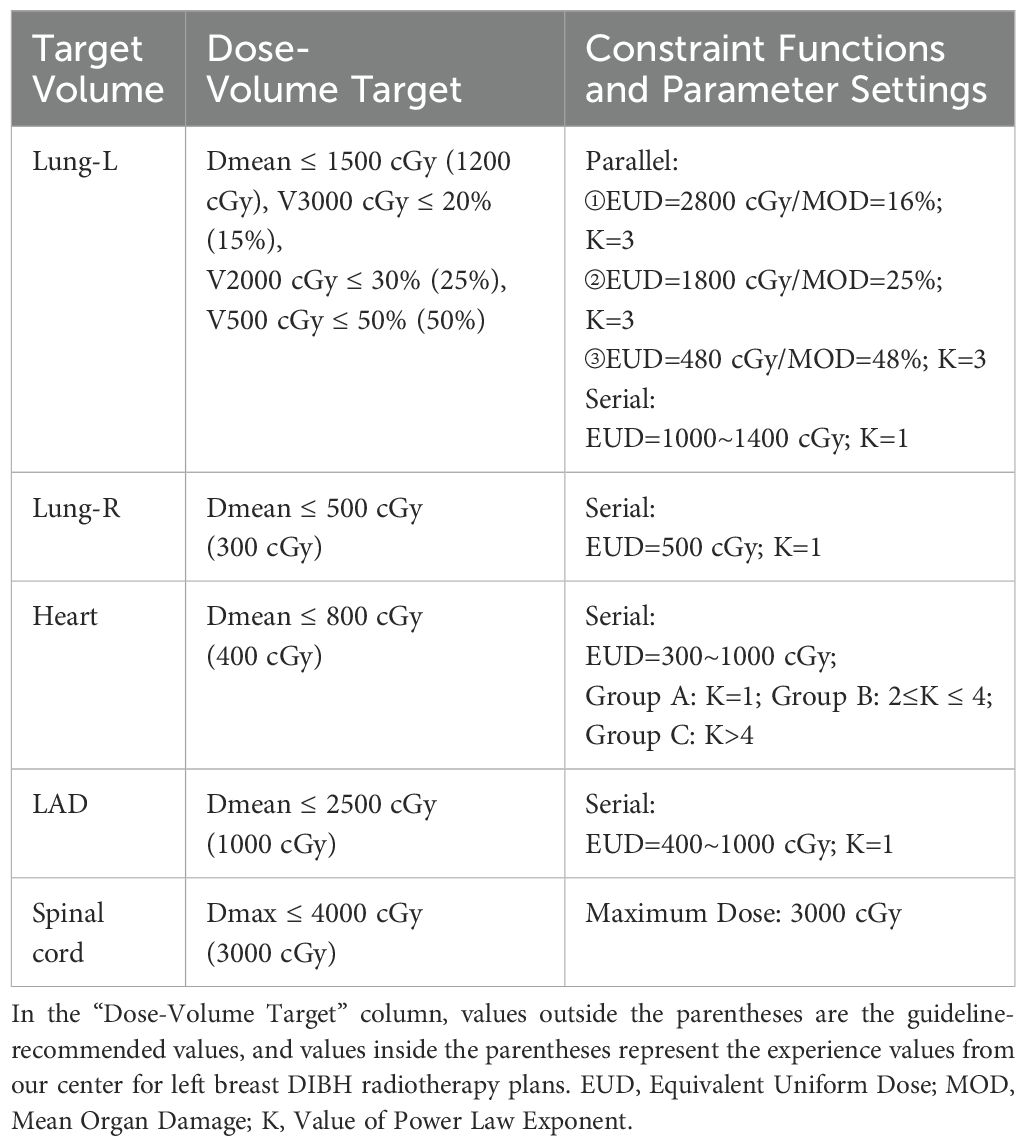
Table 1. Dose-volume constraints for OARs and the optimization functions and parameters used in this study.
2.3 Measurement and calculation of anatomical structure changes
The following three anatomical change parameters after DIBH were measured and calculated for all patients using CT images from both FB and DIBH:
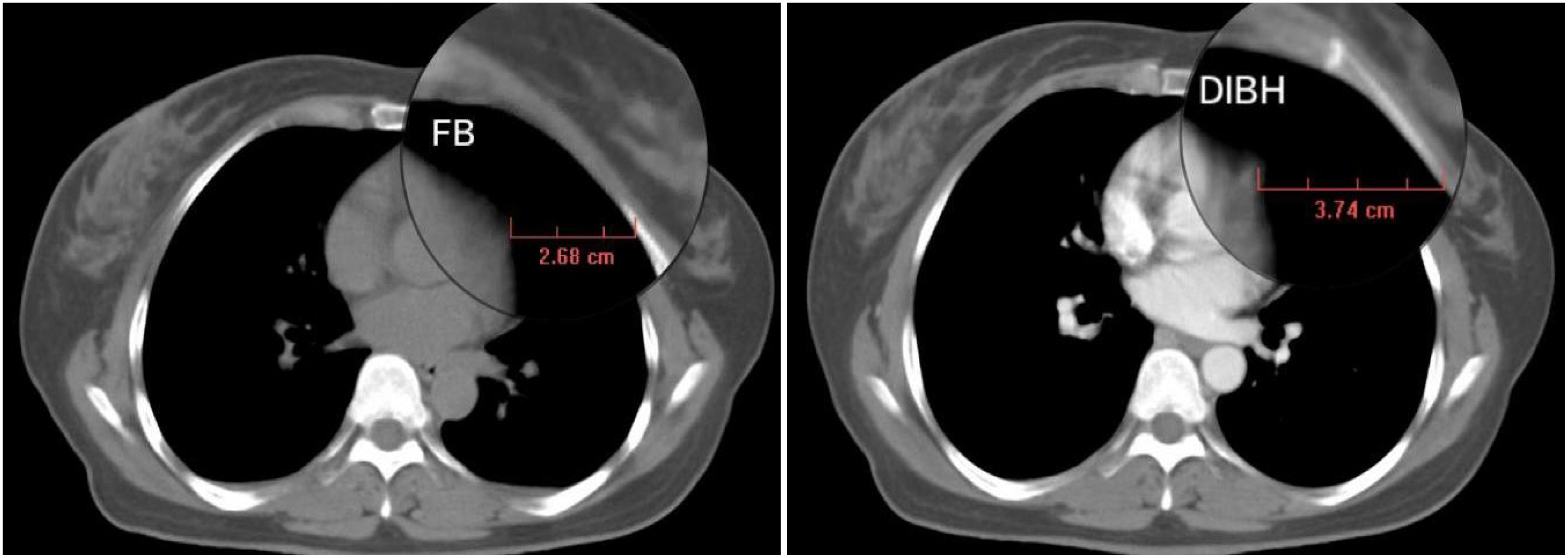
(1) Lung-L volume increment rate = (DIBH Lung-L volume - FB Lung-L volume)/FB Lung-L volume; (2) Heart/Lung-L volume ratio = DIBH Heart volume/DIBH Lung-L volume; (3) Heart-breast distance increment = DIBH Heart-breast distance - FB Heart-breast distance. The measurement method for the Heart-breast distance in both FB and DIBH is illustrated in Figure 2, which is provided in the supplementary materials. The CT slice used for this measurement is the transverse cross-section at the midline of the breast in the head-foot direction.
2.4 Dosimetric and correlation analysis
The dosimetric differences in three OARs—Heart, LAD, and Lung-L—were statistically analyzed and compared across the radiotherapy plans of Groups A, B and C. Group A served as the reference, and the dose-volume reduction rates for the three OARs in Groups B and C were calculated after adjusting the K value. Additionally, the dose-volume reduction rates for OARs in Groups B and C were correlated with DIBH-related anatomical changes: Lung-L volume increment rate, Heart/Lung-L volume ratio, and Heart-breast distance increment.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Data were first tested for non-normal distribution using the Shapiro-Wilk test. The Mann-Whitney U test was applied to analyze differences between two groups, while the Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparisons among multiple groups. When significant differences were detected among groups, pairwise comparisons were performed with Bonferroni correction to adjust for multiple testing. Pearson correlation analysis was performed to investigate the relationship between dose-volume reduction rates of OARs and anatomical indicators. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 27.0, with a p-value of < 0.05 considered statistically significant unless otherwise specified after correction.
3 Results
3.1 Dosimetric statistics for All DIBH-IMRT treatment plans
3.1.1 Dose-volume results of OARs in the three radiotherapy plans
Table 2 and Figure 3 summarize the dose-volume data for the heart, LAD, and ipsilateral lung under the three treatment plans: Group A, Group B, and Group C. Compared to Group A, both Group B and Group C demonstrated reductions in the average and maximum doses to the Heart and LAD, with Group B showing better dose control than Group C. In Group B, the average dose to the Heart and LAD decreased to 273.9 ± 91.0 cGy and 411.3 ± 127.8 cGy (p < 0.05), respectively, while the maximum dose decreased to 2676.2 ± 1380.7 cGy and 1483.3 ± 736.3 cGy (p < 0.05), respectively.
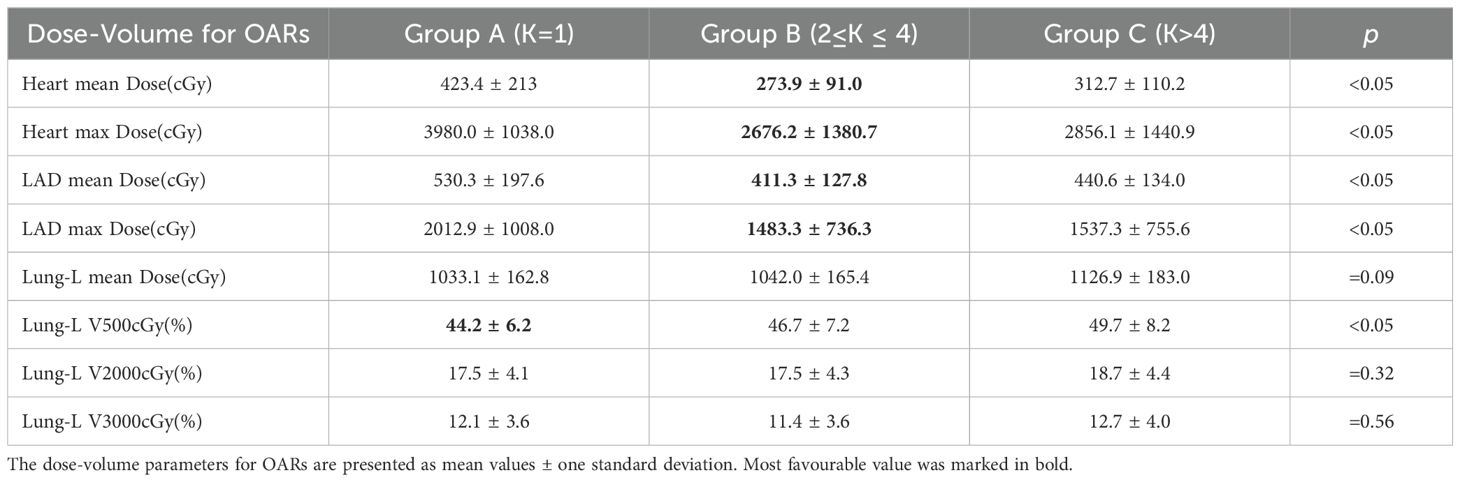
Table 2. Summary of treatment planning data for OARs, for the 41 left breast cancer patients included in this study, with DIBH, different Serial-K value ranges and 6 fields tlMRT.
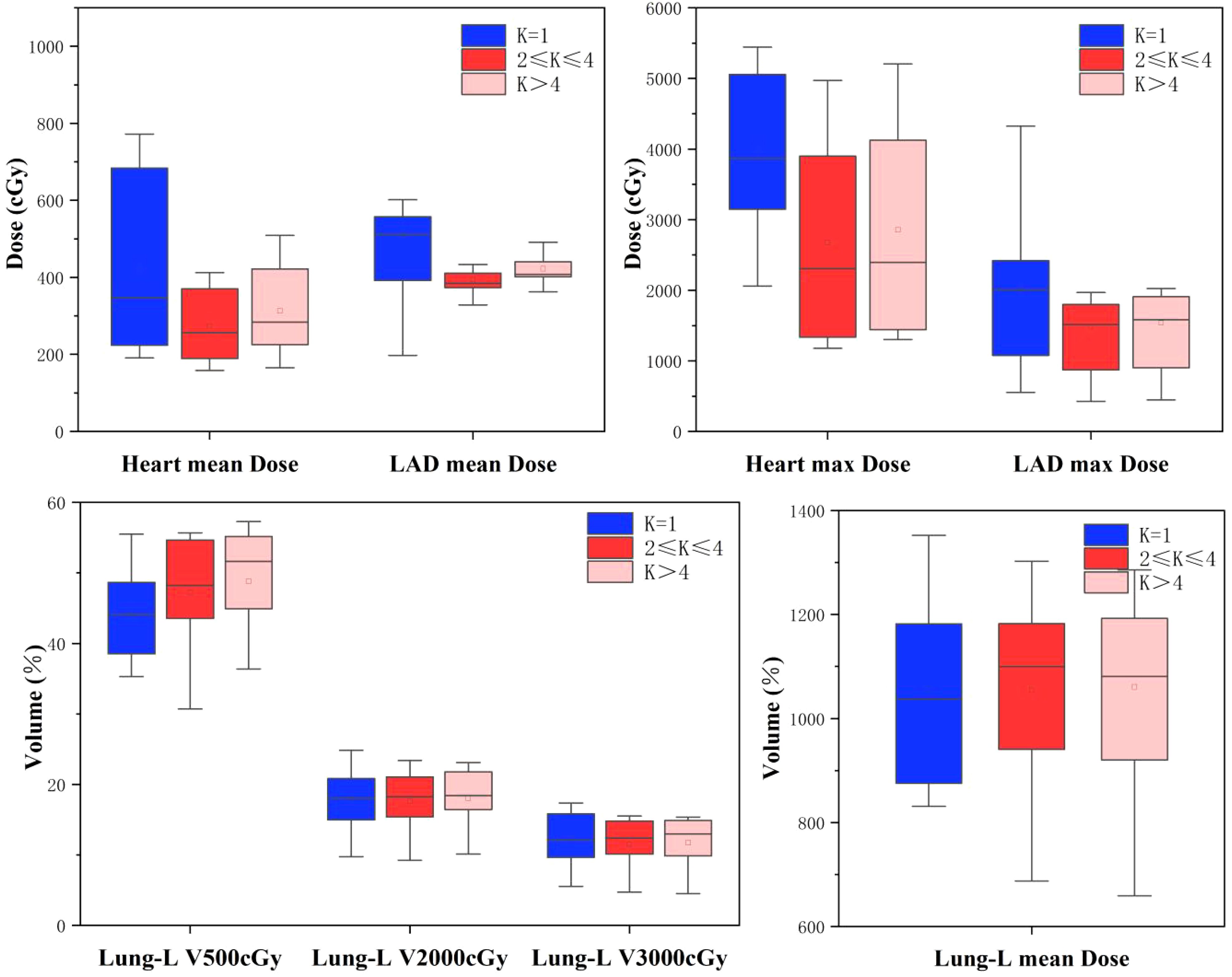
Figure 3. Boxplots of treatment planning data for OARs, for the 41 left breast cancer patients included in this study, with DIBH, different serial-K value ranges and 6 fields tlMRT.
For the ipsilateral lung (Lung-L), the V500 cGy in Group A was 44.2 ± 6.2% (p < 0.05), with an average dose of 1033.1 ± 162.8 cGy, which was the lowest among the three groups. In Group B, although the V500 cGy and average dose for Lung-L showed a slight increase, the values remained within an acceptable range.
In summary, adjusting the Serial-K value for the Heart to the Group B range (2 ≤ K ≤ 4) significantly optimized the dose constraints for the heart and its substructures, while only causing a minimal increase in the dose-volume to the ipsilateral lung.
3.1.2 Dose-volume reduction rates of major OARs after adjusting the cardiac serial-K value
The dose-volume reduction rate was calculated using the following formula: Dose-volume Reduction Rate = ((Adjusted Dose - Original Dose)/Original Dose) * 100%. Table 3 summarizes the dose-volume reduction rates for the three OARs—Heart, LAD, and Lung-L—in Group B and Group C compared to Group A. Figure 4 displays the density distribution curves of the dose-volume reduction rates for OARs in Group B and Group C relative to Group A. As shown in Table 3, compared to Group A, Group B demonstrated an average reduction rate of 29.4% ± 14.2% for the Heart and 18.7% ± 15.5% for the LAD, with maximum dose reduction rates of 29.3% ± 38.0% and 24.0% ± 13.4%, respectively. For Lung-L, the average reduction rate for V500 cGy in Group B compared to Group A was -8.6 ± 15.3% and -15.6 ± 17.5%, respectively. Figure 4 further illustrates that Group B significantly outperformed Group C in terms of dose reduction rates for both the Heart and LAD.
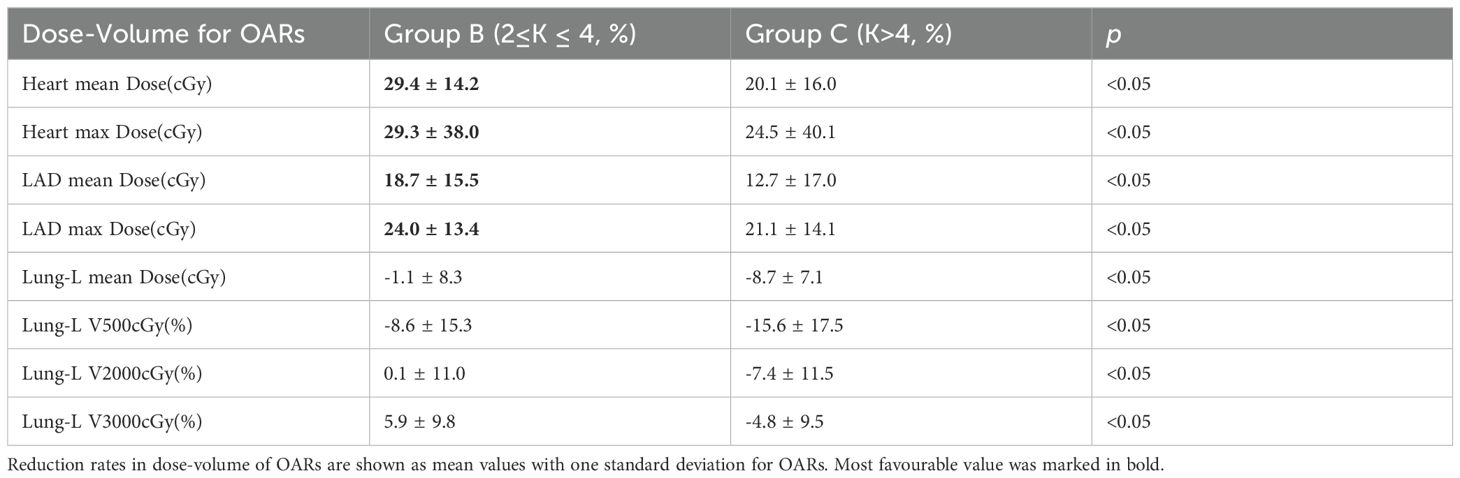
Table 3. Summary of reduction rates in dose-volume of OARs after treatment plan optimization by varying Serial-K values (two groups: B、C), relative to treatment plan optimization with Group A, for the 41 patients with left breast cancer included in this study, with DIBH and 6 tlIMRT fields.
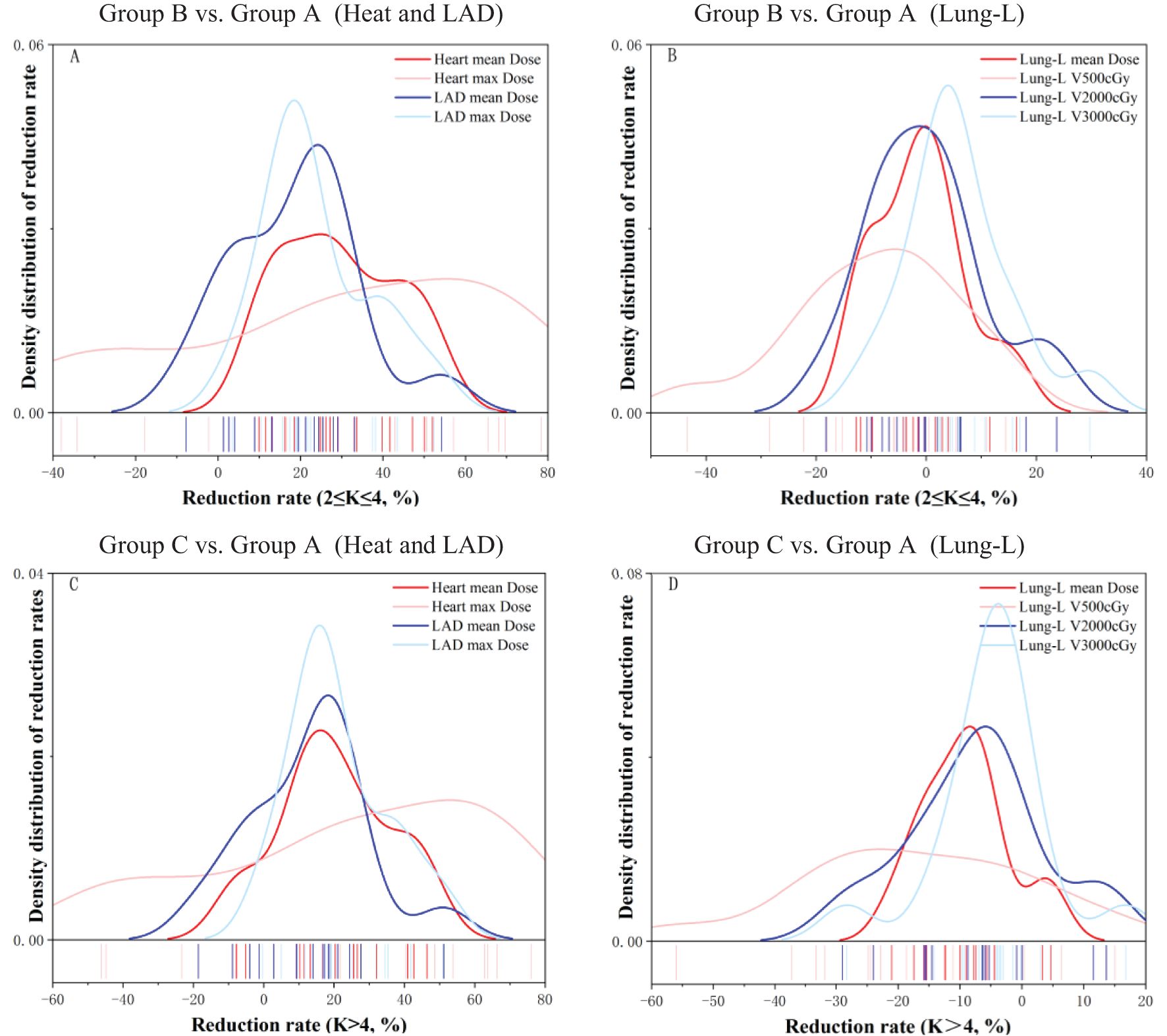
Figure 4. This figure displays the density distribution curves of dose-volume reduction rates for OARs after optimization of radiotherapy plans using different serial-K values (divided into two Groups: B、C), relative to Group A.
In conclusion, these results underscore that adjusting the Serial-K value for the Heart to the Group B range (2 ≤ K ≤ 4) not only optimized dose constraints for the heart and its substructures, but also led to only a slight increase in Lung-L V500 cGy.
3.2 Anatomical parameter measurements and calculation results after DIBH
The study results demonstrated significant anatomical changes following DIBH compared to the FB state in 41 patients. The Lung-L volume increment rate was 81.7 ± 36.2%, the Heart/Lung-L volume ratio was 0.03 ± 0.09, and the Heart-breast distance increment was 1.0 ± 0.5 cm. These measurements indicate significant anatomical changes after DIBH compared to the FB state.
3.3 Correlation analysis results between anatomical and dosimetric parameters
Figure 5 shows the correlation between the dose-volume reduction rates of the Heart, LAD, and Lung-L in Group B (2≤K ≤ 4) and Group C (K>4) compared to Group A (K=1), after adjusting the Monaco-Serial K value for constraining the heart, and the three anatomical parameters: Heart/Lung-L volume ratio, Heart/breast Distance Increment, and Lung-L volume Increment rate.
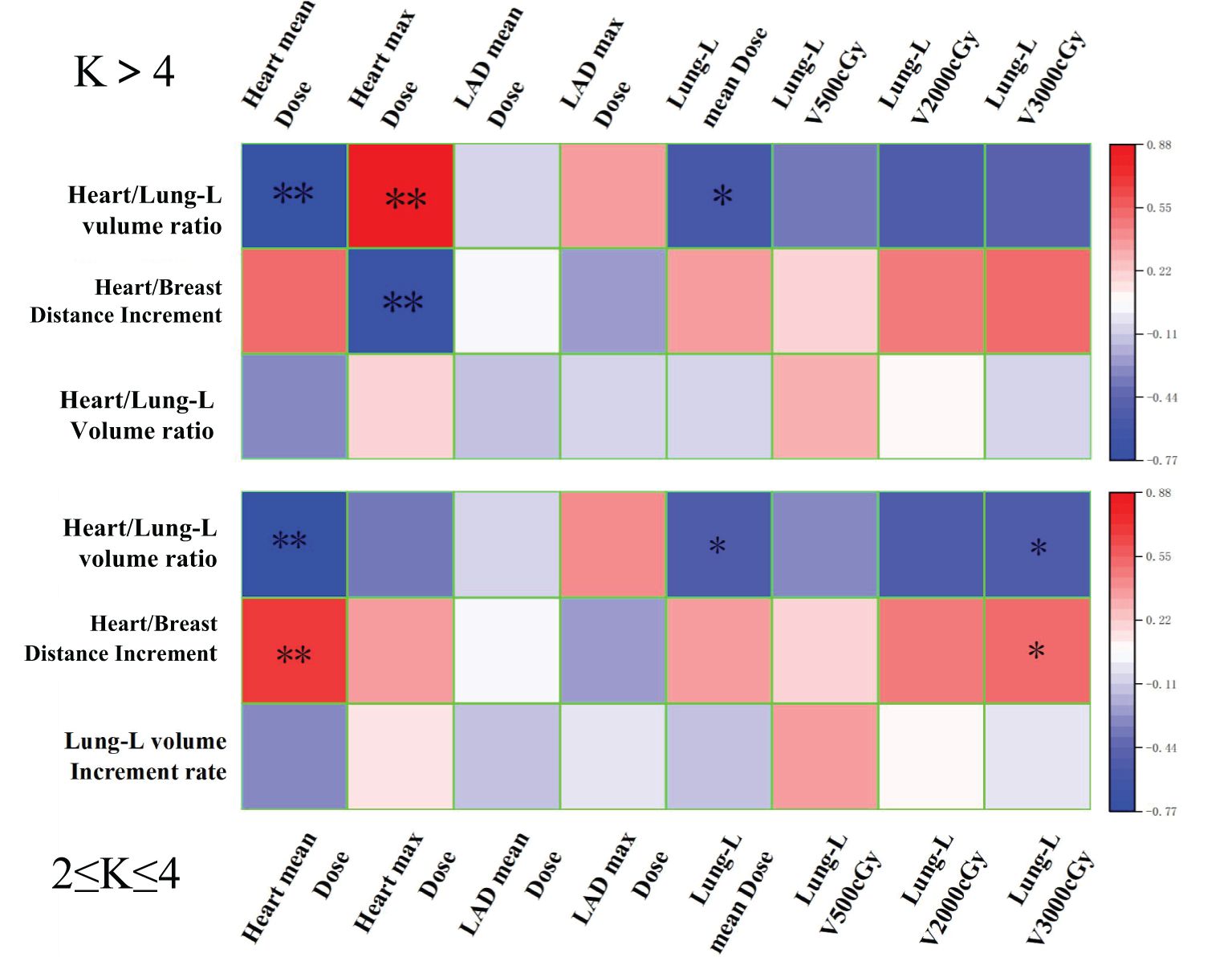
Figure 5. The correlation heatmap shows the pearson’s correlation between the reduction rates in dose-volume of OARs (compared to Group A), and the modifications in anatomical structures (after DIBH) from radiotherapy planning for different Serial-K values (Group B and C). ** Significant correlation at the 0.01 level. * Significant correlation at the 0.05 level.
As shown in Figure 5, in Group B (2≤K ≤ 4), the Heart/breast Distance is strongly positively correlated with both the average and maximum heart dose reduction rates. The Heart/Lung-L volume ratio is strongly negatively correlated with these dose reduction rates. After DIBH, the changes in these two anatomical parameters enabled Group B (2≤K ≤ 4) to effectively constrain both the average and maximum heart doses, with a more significant effect observed on the average dose, which aligns with the expected effects of anatomical variations induced by the DIBH technique. In contrast, Group C (K>4) did not achieve optimal constraints for either the average or maximum doses.
Therefore, the correlation analysis indicates that adjusting the Monaco-Serial K value for heart constraint to the Group B (2≤K ≤ 4) range results in the best correlation between anatomical parameters and heart and substructure doses. This further confirms that Group B (2≤K ≤ 4) is the optimal range for the Monaco-Serial K value in DIBH radiotherapy plans for left-sided breast cancer.
4 Discussion
In breast cancer radiotherapy, the risk of cardiac injury is primarily linked to the mean dose to the heart, which increases linearly with radiation dose. Studies have demonstrated that for every 100 cGy increase in the mean radiation dose to the heart, the likelihood of adverse coronary events rises by 7.4%, with the risk potentially persisting for decades (3). Since radiotherapy implementation is based on treatment plan design, radiation-induced heart damage is closely associated with the optimized dose distribution in radiotherapy plans (17–19).
With current photon radiotherapy technology, combining DIBH with IMRT dose optimization algorithms can effectively limit radiation exposure to the heart and its substructures, potentially significantly reducing the risk of radiation-induced heart disease. In IMRT dose optimization, traditional physical optimization functions fail to fully account for the true biological response of different tissues or organs to radiation during treatment (20). However, Niemierko introduced the EUD function, which incorporates bological parameters to quantify tissue responses to radiation and optimize the dose distribution in radiotherapy plans by considering the biological characteristics of organs and the dose-response relationship. This results in a more accurate reflection of the biological effects of radiation on tissues and organs, thus improving treatment precision and safety (21, 22). Numerous studies have confirmed that the EUD function can effectively control the dose to OARs in breast cancer radiotherapy, reducing radiation-induced damage to structures like the heart (23, 24). For example, Lee et al. (23) compared the quality and performance of dose-volume (DV) plans and DV-EUD plans in breast cancer radiotherapy. Their results showed that DV-EUD plans provided better protection for OARs, reducing lung and heart doses compared to standard DV plans. Similarly, Mihailidis et al. (24) found that EUD-based plans offered superior protection for OARs while maintaining target coverage. Consequently, the use of EUD-based biological optimization functions has become widely accepted and applied in clinical research (25–29).
In this study, we employed the Monaco TPS, which supports advanced biological optimization models such as the Lyman-Kutcher-Burman (LKB) model. Among these, the Monaco-Serial function is a biological optimization model for serial organs based on the concept of EUD. A key parameter in this model is K—typically ranging from 1 to 20—which modulates the organ’s sensitivity to different dose distributions. A lower K value indicates greater sensitivity to the mean dose. Previous studies have successfully applied a K value of 1 in free-breathing IMRT plans for left-sided breast cancer to achieve effective optimization of heart dose-volume constraints. However, the optimal K value for DIBH-IMRT planning remains uncertain and warrants further investigation (30–32). In this study, when applying Monaco-Serial to optimize the heart dose in left-sided breast cancer DIBH-IMRT, adjusting the Serial-K from K=1 to the range of 2≤K ≤ 4 (Group B) achieved the best dose constraints for the heart and its substructures, with only a slight increase in Lung-L V500 cGy (still <50%). This finding differs from previous studies and experiences with FB-IMRT. Research by Tanguturi et al. (33) noted that changes in lung volume between FB and DIBH significantly affect heart dose optimization. Cao et al. (34) found that the increased distance between the heart and the chest wall in DIBH significantly impacted heart dose optimization. Thus, the improved heart dose constraints observed in our study, with Serial-K adjusted to 2≤K ≤ 4, may be attributed to anatomical changes induced by DIBH compared to FB.
To further explore the impact of anatomical changes after DIBH on the optimal K value, we analyzed the correlation between anatomical structure changes and the dose-volume reduction rates of OARs with increased K values. The study found that after DIBH, as the Heart/Lung-L volume ratio and Heart/breast Distance Increment increased, a modest increase in K (within the 2≤K ≤ 4 range) effectively constrained both the mean and maximum heart doses, with the most significant effect on mean dose constraints. These results align with previous studies and clinical expectations (22, 23). However, for Group C (K>4), further increases in K led to stronger constraints on the maximum dose, which impacted the dose distribution of the target area. This caused a shift in the balance between the heart dose constraint function and the target optimization function, ultimately limiting the optimization effect on the heart and its substructures. This further supports the conclusion that the optimal K value range for left-sided breast cancer DIBH-IMRT is 2≤K ≤ 4.
5 Conclusion
This study is the first to report the application of the Monaco-Serial biological optimization function in left-sided breast cancer DIBH-IMRT radiotherapy plans. The results demonstrate that adjusting the Serial-K value to the range of 2≤K ≤ 4 enables more effective constraints on both the mean and maximum heart doses while maintaining target dose coverage, significantly reducing the risk of radiation-induced heart damage. This finding provides valuable data to support clinical radiotherapy plan design. However, this study only focused on integer values of K. Future research will further investigate the impact of fractional K values (e.g., K=1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 2.2) on plan quality to optimize the application of the Monaco-Serial biological function. Additionally, the results may be influenced by factors such as the dose calculation algorithm, grid resolution, and dose smoothing techniques in the Monaco system, and future studies should further explore the impact of these technical parameters.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhejiang hospital (Approval No. 2024-145K). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because This study is a retrospective analysis based on patients’ prior imaging data, and ethical review has granted a waiver of informed consent.
Author contributions
HH: Writing – original draft. ZJ: Writing – review & editing. JH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. JL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by the Lishui Science and Technology Project under Grant 2024SJZC127, the Zhejiang Medical and Health Science and Technology Project under Grant 2025KY003, and the Zhejiang Province Natural Science Foundation under Grant LMS25H280007.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kaklamani VG and Arteaga CL. Breast cancer: The good, the bad, and an important call to effective risk reduction strategies. CA-CANCER J Clin. (2024) 74:471–4. doi: 10.3322/caac.21867
2. Wu J, Fan D, Shao Z, Xu B, Ren G, Jiang Z, et al. CACA guidelines for holistic integrative management of breast cancer. Holist Integr Oncol. (2022) 1:7. doi: 10.1007/s44178-022-00007-8
3. Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P, Bennet AM, Blom-Goldman U, Brønnum D, et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. (2013) 368:987–98. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1209825
4. Zaynutdinov N, Abdujapparov A, Djuraev F, and Vakhabov I. 28P One-week ultra-hypofractionated partial breast RT in early breast cancer: 3DCRT vs IMRT. Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:S1477. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.160
5. Tang LL, Guo R, Zhang N, Deng B, Chen L, Cheng ZB, et al. Effect of radiotherapy alone vs radiotherapy with concurrent chemoradiotherapy on survival without disease relapse in patients with low-risk nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA-J Am Med Assoc. (2022) 328:728–36. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.13997
6. Coles CE, Earl H, Anderson BO, Barrios CH, Bienz M, Bliss JM, et al. The lancet breast cancer commission. Lancet. (2024) 403:1895–950. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00747-5
7. Yeh H and Lin J. The impact of the deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) technique in the heart and other organ-at-risk (OAR) dose sparing in the postoperative radiotherapy to the left early breast cancer. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:S1435. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.021
8. Garcia Alvarez M, Peraza Fernandez C, Rodrigues C, Mateos Dominguez M, Montijano Linde M, Marrone I, et al. 118P Should DIBH (deep inspiration breath-hold) be the standard of care in LBC (left breast cancer)? Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:S55. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.221
9. Huijskens S, Granton P, Fremeijer K, van Wanrooij C, Offereins-van Harten K, Schouwenaars-van den Beemd S, et al. Clinical practicality and patient performance for surface-guided automated VMAT gating for DIBH breast cancer radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. (2024) 195:110229. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110229
10. Zhang G. Evaluating the use of SGRT on left breast DIBH: target accuracy and cardiac reproducibility. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2021) 111:e228. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.07.783
11. Nissen HD and Appelt AL. Improved heart, lung and target dose with deep inspiration breath hold in a large clinical series of breast cancer patients. Radiother Oncol. (2012) 106:28–32. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.10.016
12. Zhang R and Fleckenstein J. EP-2181: Modeling and comparison the dosimetric impact of two couch model of iBEAM evo 415 in Monaco. TPS Radiother Oncol. (2018) 127:S1205. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(18)32490-3
13. El Ouardy K, Zerfaoui M, Oulhouq Y, Bahhous K, Rrhioua A, and Bakari D. A comparative study of boost dose delivery techniques in breast cancer radiotherapy optimising efficacy and minimising toxicity. Radiat Prot Dosim. (2024) 200:459–66. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncad328
14. Kargar N, Zeinali A, and Molazadeh M. Impact of dose calculation algorithms and radiobiological parameters on prediction of cardiopulmonary complications in left breast radiation therapy. J BioMed Phys Eng. (2024) 14:129–40. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2305-1616
15. Li XA, Tai A, Arthur DW, Buchholz TA, Macdonald S, Marks LB, et al. Variability of target and normal structure delineation for breast cancer radiotherapy: an RTOG multi-institutional and multiobserver study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2009) 73:944–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.10.034
16. Chinese Medical Association Radiation Oncology Physician Branch. Guidelines for radiotherapy of breast cancer (Chinese medical association, 2020 edition). Chin J Radiat Oncol. (2021) 30:321–42. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113030-20210107-00010
17. Lestuzzi C, Cosei I, Navarria F, Viel E, Ravasel A, Fumagalli A, et al. Safety of heart radiotherapy for Malignant cardiac tumors: a short and long term study. Eur Heart J. (2022) 43:2. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac544.1803
18. Taylor C, McGale P, Brønnum D, Correa C, Cutter D, Duane FK, et al. Cardiac structure injury after radiotherapy for breast cancer: cross-sectional study with individual patient data. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:2288–96. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6351
19. Wu C, Lin D, Ma F, Jiang F, and Wang Y. New progress in elucidating the relationship between cancer therapy and cardiovascular toxicity. Biosci Trends. (2021) 15:211–8. doi: 10.5582/bst.2021.01278
20. Mukherjee S, Hong L, Deasy JO, and Zarepisheh M. Integrating soft and hard dose-volume constraints into hierarchical constrained IMRT optimization. Med Phys. (2019) 47:414–21. doi: 10.1002/mp.13908
21. Niemierko A. Reporting and analyzing dose distributions: a concept of equivalent uniform dose. Med Phys. (1997) 24:103–10. doi: 10.1118/1.598063
22. Wu Q, Djajaputra D, Wu Y, Zhou J, Liu HH, and Mohan R. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy optimization with gEUD-guided dose-volume objectives. Phys Med Biol. (2003) 48:279–91. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/48/3/301
23. Lee TF, Ting HM, Chao PJ, Wang HY, Shieh CS, Horng MF, et al. Dosimetric advantages of generalised equivalent uniform dose-based optimisation on dose-volume objectives in intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning for bilateral breast cancer. Brit J Radiol. (2012) 85:1499–506. doi: 10.1259/bjr/24112047
24. Mihailidis DN, Plants B, Farinash L, Harmon M, Whaley L, Raja P, et al. Superiority of equivalent uniform dose (EUD)-based optimization for breast and chest wall. Med Dosim. (2009) 35:67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2009.03.002
25. Raturi VP, Motegi A, Zenda S, Nakamura N, Hojo H, Kageyama SI, et al. Comparison of a Hybrid IMRT/VMAT technique with non-coplanar VMAT and non-coplanar IMRT for unresectable olfactory neuroblastoma using the RayStation treatment planning system-EUD, NTCP and planning study. J Radiat Res. (2021) 62:540–8. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrab010
26. Liu L, Qiao H, Xiao Y, Tang J, and Liu R. Clinical application of equivalent uniform dose in intensity-modulated rotational radiotherapy based on eclipse TPS. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. (2024) 48:533–8. doi: 10.12455/j.issn.1671-7104.240118
27. Söhn M, Yan D, Liang J, Meldolesi E, Vargas C, and Alber M. Incidence of late rectal bleeding in high-dose conformal radiotherapy of prostate cancer using equivalent uniform dose-based and dose-volume-based normal tissue complication probability models. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2007) 67:1066–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.10.014
28. Tao C, Liu B, Li C, Zhu J, Yin Y, and Lu J. A novel knowledge-based prediction model for estimating an initial equivalent uniform dose in semi-auto-planning for cervical cancer. Radiat Oncol. (2022) 17:151. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02120-4
29. Senthilkumar K and Maria Das KJ. Comparison of biological-based and dose volume-based intensity-modulated radiotherapy plans generated using the same treatment planning system. J Cancer Res Ther. (2019) 15:S33–8. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_956_16
30. Shan Z. Dosimetric comparison of the lung dose on the affected side in radiotherapy after breast cancer breast-conserving therapy based on two subfield optimization methods in Monaco planning system. JCMR. (2021) 2:3. doi: 10.32629/jcmr.v2i2.362
31. Virén T, Heikkilä J, Myllyoja K, Koskela K, Lahtinen T, and Seppälä J. Tangential volumetric modulated arc therapy technique for left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol. (2015) 10:79. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0392-x
32. Bellala R, Kuppusamy A, Bellala VM, Tyagi T, Manoharan S, Gangarapu G, et al. Review of clinical applications and challenges with surface-guided radiation therapy. J Cancer Res Ther. (2023) 19:1160–9. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_1147_21
33. Tanguturi SK, Lyatskaya Y, Chen Y, Catalano PJ, Chen MH, Yeo WP, et al. Prospective assessment of deep inspiration breath-hold using 3-dimensional surface tracking for irradiation of left-sided breast cancer. Pract Radiat Oncol. (2015) 5:358–65. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2015.06.002
Keywords: breast cancer, radiotherapy planning, biological optimization, monte carlo, equivalent biological dose
Citation: Hu H, Jueyi Z, Hao J and Lai J (2025) Application of the Monaco-serial biological function for cardiac dose constraints in DIBH-IMRT treatment planning for left-sided breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1610980. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1610980
Received: 13 April 2025; Accepted: 15 May 2025;
Published: 09 June 2025.
Edited by:
Poonam Yadav, Northwestern University, United StatesReviewed by:
Jia-Ming Wu, Wuwei Cancer Hospital of Gansu Province, ChinaElham Khakshour, Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Hu, Jueyi, Hao and Lai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianjun Lai, Mzg1ODA2OTQ1QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Haili Hu1,2
Haili Hu1,2 Jianjun Lai
Jianjun Lai