- 1Department of Radiology, The Affiliated Xuzhou Children's Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China
- 2Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the utility of virtual monoenergetic (MONO) imaging and a Metal-Artifact Reduction System (MARs) algorithm for enhancing image quality in dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) of children with congenital funnel chest (CFC) following minimally invasive correction with stainless steel plate implantation.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed children with CFC who underwent thoracoscopic correction at our institution (January 2022 to August 2023). Their postoperative non-contrast chest CT scans were evaluated. Objective metrics (CT numbers, standard deviation-SD) were measured on five image series (120 kVp-like, 50 keV, 50 keV + MARs, 110 keV, 110 keV + MARs), and the absolute CT difference (|ΔCT|) and artifact index (AI) were calculated. Subjective image quality was scored by two independent radiologists. Given the non-normal distribution of data (Shapiro–Wilk test, P < 0.001), non-parametric tests (Friedman test with Wilcoxon post hoc analysis) were used for comparisons.
Results: A total of 114 children were enrolled. Objective metrics (SD, |ΔCT|, AI) on 110 keV images were significantly lower than on 120 kVp-like and 50 keV images (P < 0.001). The application of MARs further significantly improved image quality at both energy levels (P < 0.005). Subjective scores [presented as median (IQR)] confirmed that the 110 keV + MARs series provided the best image quality, which was significantly superior to all other groups (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The high-energy VMI (110 keV) of the dual-energy CT can effectively reduce metal artifacts, and the combination of the 110 keV and MARs algorithm could further improve the image quality, which provides great assistance for the review and follow-up of children with CFC after metal plate correction.
Introduction
Congenital funnel chest (CFC), the most common thoracic developmental deformity in children, is primarily characterized by sternal depression, resulting in one or more concave areas and an abnormal chest contour, including sternal retraction and thoracic asymmetry (1–3). This deformity can impair cardiopulmonary function, leading to symptoms such as dyspnea and cardiac compression. Thoracoscopic minimally invasive correction is a widely used surgical intervention for CFC. Postoperative computed tomography (CT) is routinely performed to assess the position of the implanted plate and its relationship with adjacent tissues (4, 5).
The orthopedic steel plate, which spans a large area of the anterior chest wall, frequently induces severe metal artifacts on conventional CT scans, significantly compromising diagnostic image quality (6, 7). Dual-energy CT (DECT) offers a solution through its monoenergetic (VMI) imaging and metal artifact reduction (MAR) algorithms (8, 9). Although DECT allows for VMI reconstruction across a wide energy range (40–140 keV), the optimal reconstruction setting for pediatric CFC patients following plate correction remains undetermined (10, 11).
Metal artifacts in conventional CT, primarily caused by beam hardening, photon starvation, and scatter, manifest as streaks and dark bands that obscure anatomical details and compromise quantitative accuracy, thereby posing a significant challenge to postoperative assessment (6). In response, various Metal Artifact Reduction (MAR) algorithms have been integrated into clinical CT systems (7). These algorithms typically function during image reconstruction or as post-processing steps by identifying and correcting corrupted projection data or interpolating missing data around metallic objects. Although beneficial in many cases, traditional MAR techniques can introduce secondary artifacts, blur tissue boundaries, or prove inadequate for very large or complex implants (8).
Spectral CT provides an alternative strategy through virtual monoenergetic imaging (VMI) (9). This technique decomposes the polychromatic x-ray spectrum into material-specific information, thereby enabling the reconstruction of images that simulate attenuation at a single, selectable energy level (keV). High-keV VMI is particularly effective at reducing beam-hardening—a primary source of metal artifacts—as higher-energy photons are less susceptible to differential absorption (10). Moreover, combining high-keV VMI with dedicated MAR algorithms has demonstrated a synergistic effect, offering superior artifact suppression in various clinical scenarios involving metallic implants, including dental work, orthopedic prostheses, and coils (11).
However, the optimal application of these techniques for postoperative imaging in pediatric CFC patients with stainless steel plates remains underexplored. Specifically, the most effective monoenergetic energy level and the added value of applying MARs at that level have not been established. Factors such as plate material, dimensions, location, and the smaller pediatric body habitus may significantly influence artifact characteristics and the efficacy of reduction strategies. Consequently, there is a clear need to develop evidence-based imaging protocols tailored to this specific population and implant type to ensure optimal diagnostic quality during postoperative follow-up.
This study aimed to compare the image quality of conventional mixed-energy imaging and dual-energy CT-based virtual monoenergetic imaging (VMI), evaluate the efficacy of VMI and a metal artifact reduction (MAR) algorithm, and determine the optimal VMI reconstruction level for pediatric CFC patients following metal plate correction.
Materials and methods
Patients information
We retrospectively analyzed children with CFC who underwent thoracoscopic minimally invasive correction at Xuzhou Children's Hospital between January 2022 and August 2023. The inclusion criteria were: (1) age 4–17 years; (2) history of thoracoscopic minimally invasive funnel chest correction; and (3) implantation of a specific stainless steel plate (Biomet Microfixation, model 01-3170). Patients were excluded for any of the following: (1) tracheotomy, airway stenosis, airway compression, or pneumothorax; (2) cyanotic congenital heart disease; (3) central respiratory failure, severe muscle weakness, or absence of voluntary diaphragmatic activity; or (4) terminal disease or death.
Ultimately, a total of 114 children with CFC were enrolled in the study. The cohort consisted of 99 males and 15 females, with an age range of 6–17 years and a mean age of 10.89 ± 3.99 years. The implanted funnel chest correction steel plate was made of stainless steel and measured 25.4 cm in length and 1.27 cm in width.
This study received full approval from the Institutional Review Board of Xuzhou Children's Hospital (Approval Number: 2022-05-14-H14) with a waiver of informed consent for this retrospective analysis. The research was conducted in accordance with local regulations, institutional policies, and the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (12). The analysis utilized exclusively anonymized, non-contrast chest CT scans obtained as part of standard postoperative follow-up for funnel chest correction. No additional procedures were performed for research purposes. The IRB determined the study posed minimal risk. All directly identifiable information was permanently removed from the research data prior to analysis, and datasets were stored on secure, encrypted servers with access restricted to authorized investigators.
CT scan methods
All chest scans were performed on a 256-row CT scanner (Revolution 256 CT; GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). The scanning parameters were as follows: tube voltage with instantaneous switching between 80 and 140 kVp (switching time, 0.25 ms), tube current of 200 mA, slice thickness of 5 mm, and a display field of view (DFOV) of 25–40 cm. The reconstruction matrix was 512 × 512, with a rotation speed of 0.5 s/r, a pitch of 0.984, and adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR-V) set at 50%.
Radiation dose estimate
The radiation dose parameters for all CT examinations were recorded and analyzed. The volume computed tomography dose index (CTDIvol) and dose-length product (DLP) were automatically generated and archived by the CT system for each scan. The effective dose (ED) was estimated to provide a more patient-specific risk assessment. The ED was calculated using the formula: ED = DLP × k, where k is a age-specific conversion coefficient. Given that our cohort consisted of children, the k value of 0.039 mSv·mGy⁻1·cm⁻1 was applied, as recommended by the 2020 European Commission guidelines on diagnostic reference levels for pediatric imaging for chest CT in the 10-year-old age group.
Imaging analysis
The scans were performed using the Gemstone Spectral Imaging (GSI) mode, which is characterized by rapid kV switching between 80 kVp and 140 kVp during a single scan acquisition. This provides the necessary paired low-energy and high-energy projection data. All images were reconstructed on an AW 4.6 workstation (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). The raw spectral projection data were used to reconstruct virtual monoenergetic images (VMI) at 50 keV and 110 keV, a mixed-energy image simulating a conventional 120-kVp scan (120-kVp-like), and all series were reconstructed with a 1.25 mm slice thickness. This reconstruction process involves material decomposition (into water and iodine basis material pairs) followed by the synthesis of images representing the calculated linear attenuation at the desired monochromatic energy (keV). Subsequently, metal artifact reduction (MARs) processing was applied to generate the 50 keV + MARs and 110 keV + MARs image series. Figure 1 illustrates examples of the five reconstructed image series: (A) 50 keV, (B) 50 keV + MARs, (C) 110 keV, (D) 110 keV + MARs, and (E) 120 kVp-like.
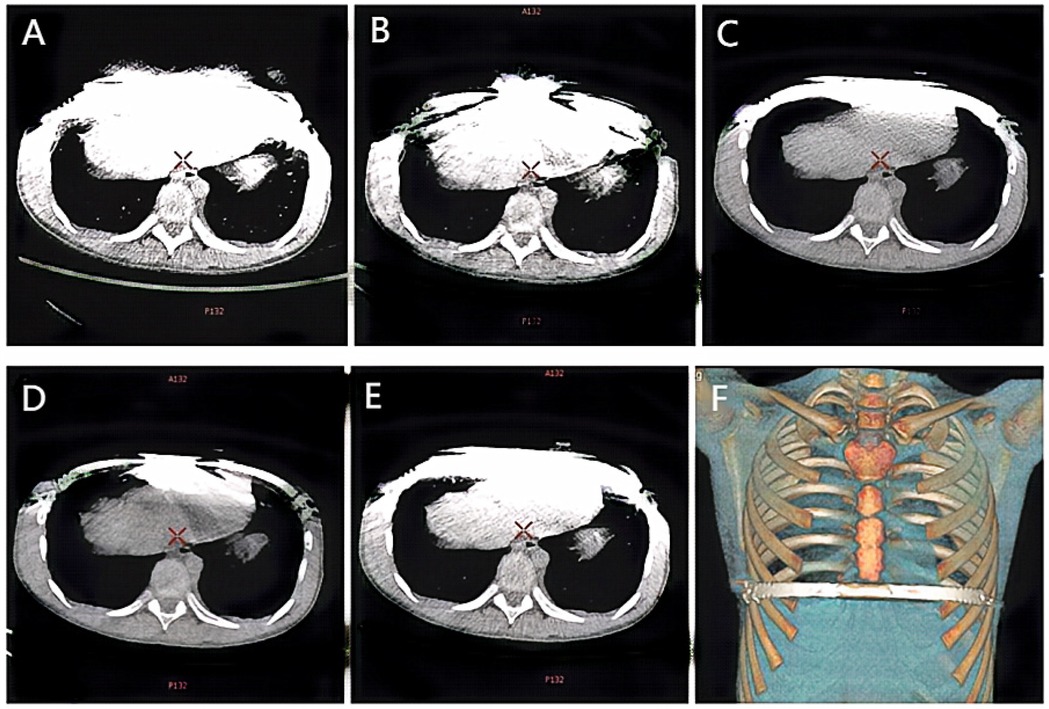
Figure 1. Ct images of the same child under different scanning conditions. (A) 50 keV; (B) 50 keV + MARs; (C) 110 keV; (D) 110 keV + MARs; (E) 120 kVp-like; (F) Volume reconstruction (VR) image reconstructed from 120 kVp like image.
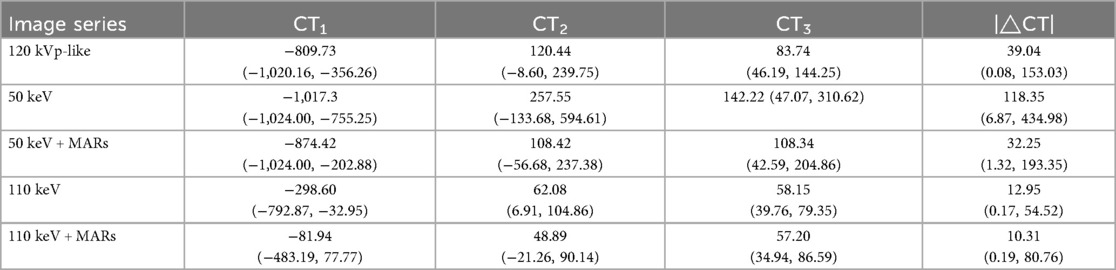
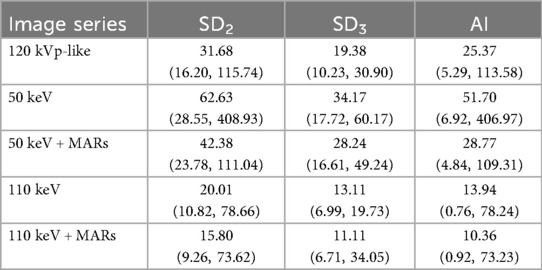
CT and standard deviation (SD) values were measured on 1.25-mm-thick images displayed at a mediastinal window setting (width, 400 HU; level, 40 HU). Circular regions of interest (ROIs) with an area of 60–80 mm2 were placed in three locations: the artifactual dark area at one end of the plate (recorded as CT1 and SD1), the adjacent chest wall muscles (CT2, SD2), and the erector spinae muscle (CT3, SD3). Each measurement was repeated three times and averaged. The absolute difference between CT2 and CT3 (|ΔCT| = |CT2 - CT3|) and the artifact index (AI = [SD22 - SD32](1/2)) were then calculated.
The CT and standard deviation (SD) values were measured on the images of the mediastinal window (window width 400 HU, window level 40 HU) by a single senior radiologist with over 10 years of experience in pediatric imaging. To ensure perfect consistency and comparability across the five different image series, the circular regions of interest (ROIs) (area 60–80 mm2) were first meticulously placed on the three predefined locations on the 120 kVp-like images. The precise coordinates and dimensions of these ROIs were then copied and pasted onto the exact same anatomical locations on the other four image series (50 keV, 50 keV + MARs, 110 keV, 110 keV + MARs) using the “Copy and Paste” function on the AW 4.6 workstation. This automated process guaranteed that all ROIs were identical in position and size. The measurements were repeated three times for each location, and the average value was calculated and recorded as CT1, CT2, CT3, and SD1, SD2, and SD3, respectively. The absolute value of the difference between CT2 and CT3 (|ΔCT| = |CT2 - CT3|) and the artifact index (AI) [AI = (SD22 - SD32)(1/2)] were then calculated.
Subjective score
All five image series were independently read and scored by two senior radiologists, and the image score criteria are as follows (13): (1) Score 1 is defined by numerous artifacts near and distant from the implant, poorly displayed metal edges, and poorly demarcated adjacent tissues, rendering the image non-diagnostic; (2) Score 2 is defined by extensive periprosthetic artifacts and few distant artifacts, with poorly defined metal edges and indistinguishable adjacent tissues, rendering the image non-diagnostic; (3) Score 3 is defined by moderate periprosthetic artifacts, blurring of the metal shape/edges and tissue demarcation, yet the image is considered diagnostically usable; (4) Score 4 is defined by mild artifacts and slightly blurred metal margins, with distinguishable tissue demarcation, making the image suitable for diagnosis; (5) Score 5 is defined by no or minimal artifacts, clear metal edges with regular morphology, and sharp tissue demarcation, providing excellent diagnostic quality. For analysis, a score of 4 or higher was considered diagnostically acceptable. In cases of initial disagreement between the two radiologists (defined as a score difference greater than one point), a consensus reading was held. During this session, the radiologists reviewed the images together, discussed their assessments with reference to the scoring criteria, and agreed upon a final consensus score for statistical analysis.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software (version 26.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). The normality of distribution for all continuous variables was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Since the data from all five image groups violated the normality assumption (P < 0.05), continuous data are expressed as median and interquartile range (IQR).
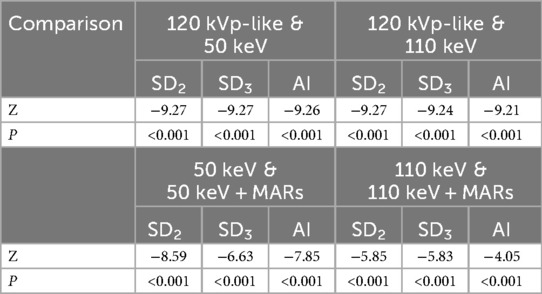
For comparisons of objective metrics (CT numbers, SD, |ΔCT|, and AI) across the five matched image series (which are related measures), the non-parametric Friedman test was first applied as the omnibus test. If a significant difference was indicated by the Friedman test, post hoc pairwise comparisons were conducted using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. A Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons was applied, resulting in an adjusted significance level of P < 0.005.
The inter-reader agreement for the subjective image quality scores between the two radiologists was evaluated using the Weighted Kappa (κ) statistic. The strength of agreement was interpreted as follows: κ ≤ 0.20, slight; 0.21–0.40, fair; 0.41–0.60, moderate; 0.61–0.80, substantial; and 0.81–1.00, almost perfect agreement.
The normality of the subjective scores was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test, which confirmed a non-normal distribution for all data sets (P < 0.001). Therefore, comparisons of subjective scores across the five image groups were performed using the non-parametric Friedman test. If a significant difference was found, post hoc pairwise comparisons were conducted using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, with a Bonferroni correction applied.
Results
Comparison between virtual monoenergetic images and conventional 120 kVp-like images
Low-energy (50 keV) VMI vs. 120 kVp-like images
The objective metrics of the 50 keV images demonstrated a significantly higher artifact burden compared to the conventional 120 kVp-like images. The CT values, SD values, |ΔCT| and AI values of chest wall muscles and erector spinae muscles on 50 keV images were significantly higher than those on the 120 kVp-like images (P < 0.05, refer to Tables 1, 2). Subjectively, the 50 keV images received the lowest scores from both radiologists due to severe artifacts and noise.
High-energy (110 keV) VMI vs. 120 kVp-like images
In contrast, the 110 keV images exhibited superior artifact reduction capabilities. The aforementioned objective metrics (SD, |ΔCT|, AI) for the 110 keV images were significantly lower than those on the 120 kVp-like images (P < 0.05, refer to Table 3). The subjective scores for the 110 keV series were markedly higher than those for both the 120 kVp-like and 50 keV images.
Additional value of the MARs algorithm
Effect of MARs on low-energy VMI (50 keV + MARs vs. 50 keV)
The application of the MARs algorithm on the 50 keV images led to a significant reduction in artifacts. The SD, |ΔCT|, and AI values on the 50 keV + MARs images were substantially lower than those on the 50 keV images without MARs (P < 0.05, refer to Table 3). This objective improvement was also reflected in the subjective evaluation.
Effect of MARs on high-energy VMI (110 keV + MARs vs. 110 keV)
Similarly, the MARs algorithm provided a significant further improvement on the already favorable 110 keV images. The objective metrics on the 110 keV + MARs images were the lowest among all groups, showing a statistically significant reduction compared to the 110 keV images alone (P < 0.05, refer to Table 4). Consequently, the 110 keV + MARs image series received the highest subjective scores from both readers, indicating excellent image quality with minimal artifacts.
Subjective scores
The subjective scores for all image series were non-normally distributed (Shapiro–Wilk test, all P < 0.001) and are therefore presented as median (IQR). The scores differed significantly among the groups (Friedman test, P < 0.001). Post hoc analysis revealed that the 110 keV + MARs series [median (IQR): 5 (5-5)] received significantly higher scores than all other groups (Wilcoxon test, all P < 0.005 after Bonferroni correction) (refer to Table 5).
Pre- and postoperative CT images for four representative clinical cases are illustrated in Figure 2.

Figure 2. The CT images of four patients before and after thoracoscopic minimally invasive funnel chest correction surgery. (A,B) Male, 4 years old, preoperative and postoperative Haller index: 3.58, 2.99. (C,D) Male, 7 years old, preoperative and postoperative Haller index: 3.51, 2.45. (E,F) Male, 12 years old, preoperative and postoperative Haller index: 16.68, 3.48. (G,H) Male, 15 years old, preoperative and postoperative Haller index: 3.90, 2.63. (I) Orthopedic steel plate used for surgery, made of stainless steel. Annotation: Haller index is used for grading the severity of funnel chest, measured on CT by dividing the transverse diameter of the chest at the lowest point of the depression by the distance between the thoracic spine, and Haller index greater than 3.2 may require surgical treatment.
Discussion
The primary findings of this study demonstrate that for pediatric patients with congenital funnel chest (CFC) following Nuss procedure with stainless steel plate implantation, high-energy virtual monoenergetic imaging (VMI) at 110 keV from spectral CT effectively reduces metal artifacts compared to conventional mixed-energy (120 kVp-like) imaging. Furthermore, the application of the metal artifact reduction (MARs) algorithm provides significant additional improvement in image quality at both 50 keV and 110 keV levels, with the combination of 110 keV and MARs yielding the best overall subjective and objective outcomes. This finding offers an optimized imaging protocol for postoperative assessment.
Dual-energy CT (DECT) is an advanced imaging technology enabling multi-parameter quantitative analysis, which has seen expanding clinical application in recent years (14–16). Its virtual monoenergetic imaging (VMI) technique leverages high- and low-energy datasets acquired during a single scan to reconstruct images simulating x-ray attenuation at a specific keV level. By providing superior material characterization, VMI yields richer diagnostic information and enhances diagnostic accuracy (17–19). The fundamental workflow begins with data collection, which involves acquiring paired high- and low-voltage (140 kVp and 80 kVp) projections. This data is then processed to generate linear absorption projection data, followed by material decomposition to produce material density projection data. The final steps involve reconstructing the base material map and subsequently synthesizing the virtual monoenergetic image at the desired energy level (20, 21).
Congenital funnel chest (CFC) is a common thoracic developmental anomaly in children (22, 23). Minimally invasive thoracoscopic correction is the current preferred surgical treatment. Postoperative monitoring of chest wall morphology and steel plate position requires regular CT follow-up (24, 25). However, conventional CT is inevitably compromised by metal artifacts (26). Virtual monoenergetic imaging (VMI) from dual-energy CT (DECT) has been developed specifically to mitigate such artifacts. According to the literature, the material, size, and placement position of metal implants are important factors affecting metal artifacts (27). Although the present study, by design, focused on a single implant type to control for these variables, the thickness and density of metals are known to be positively correlated with the severity of metal artifacts. The stainless steel plate used for the corrective surgery in this study measured 25.4 cm in length and 1.27 cm in width. On the axial images, the steel plate, which has a moderate physical thickness but a long length (25.4 cm), spans across a wide area of the anterior chest wall. Under conventional CT scanning, pronounced metal artifacts obscure the margins of the plate and adjacent soft tissues, compromising diagnostic assessment.
From a technical perspective, VMI synthesizes images at specific keV levels through material decomposition. It is established that higher keV photons penetrate metal more effectively, reducing artifacts caused by beam hardening, which is consistent with our observation that the 110 keV images exhibited a significantly lower artifact index (AI) than both conventional and low-energy (50 keV) images. Building upon this principle, our study further identifies the optimal imaging parameters for this specific implant and patient population.
All scans were performed in DECT spectral mode and reconstructed into 120 kVp-like, 50 keV, and 110 keV VMI series for comparing artifact reduction across energy levels. Additional 50 keV + MARs and 110 keV + MARs images were created to assess the algorithm's incremental value. Results confirmed high-energy VMI's superior artifact reduction over low-energy and conventional imaging (28). MARs is a post-processing technique that corrects metal-corrupted data via iterative algorithms to diminish artifacts (29). When combined with high-keV VMI [which reduces beam hardening (30)], they work synergistically to improve image quality and diagnostic accuracy. Our findings confirm that high-energy images best minimize artifacts and their effect on soft tissue CT values, with MARs providing further improvement.
Furthermore, it is imperative to state that the inclusion of the low-energy (50 keV) VMI series in our study was not to propose it as a viable clinical option for this population, but rather was driven by three key methodological considerations. First, the 50 keV images served as an internal “negative control”, explicitly delineating the worst-case scenario of maximum artifact burden. This provided an essential baseline for quantifying the magnitude of improvement offered by both high-energy VMI and the MARs algorithm. Second, demonstrating the efficacy of the MARs algorithm under the most challenging, high-artifact conditions of low-energy VMI constitutes a more rigorous test of its robustness and general utility, compared to solely showcasing its effect on an already-favorable high-energy image. Finally, by presenting the complete spectrum of image quality from low- to high-energy VMI, both with and without MARs, our study provides a more comprehensive and compelling evidence chain for the artifact-reducing capabilities of spectral CT.
Our findings align with the established principle that high-energy VMI reduces beam-hardening artifacts (7, 10, 11). For instance, studies in adults with hip prostheses have similarly shown the superiority of high-keV VMI combined with MARs (8, 11). However, our study uniquely focuses on a specific pediatric population with a distinct implant and a standardized surgical context. While Pessis et al. (7) demonstrated the general benefit of VMI for metal artifact reduction, they did not focus on pediatric thoracic applications. Similarly, Zhao et al. (8) optimized VMI for hip arthroplasty in adults, which involves different metal types, artifact geometry, and patient size. The smaller body habitus and different biomechanical environment in children may alter artifact characteristics, necessitating tailored protocols. Therefore, our work provides novel, population-specific evidence that extends the general principles of spectral CT to the postoperative assessment of CFC, delivering a concrete imaging protocol (110 keV + MARs) that can be directly adopted in clinical practice for these children.
This study has several limitations. First, its retrospective design carries inherent biases. Second, although DECT enables reconstruction of virtual monoenergetic images (VMI) across a continuous spectrum (40–140 keV), our analysis was restricted to 50 and 110 keV; future studies should include a broader range of energy levels. Third, the moderate inter-reader agreement in subjective scoring suggests that employing more readers or refining the scoring criteria could improve consistency in future investigations, although our primary findings are supported by objective metrics. Fourth, we evaluated only the vendor-provided MARs algorithm due to its clinical relevance; future work could explore advanced techniques like deep learning-based methods, provided they are clinically practical. Finally, this study was limited to a single type and size of stainless steel plate. While this homogeneity allowed for a controlled evaluation of imaging parameters, it limits the generalizability of our findings to other implant materials or dimensions. Future studies incorporating a variety of implants are needed to establish comprehensive, implant-specific imaging protocols.
Conclusions
In summary, high-energy VMI (110 keV) from DECT effectively reduces metal artifacts, and the addition of the MARs algorithm further enhances image quality. This optimized protocol provides significant value for the postoperative assessment and follow-up of children with CFC, demonstrating broad clinical applicability.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board of Xuzhou Children's Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. CX: Data curation, Writing – original draft. LL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. LD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. PD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by The Key R and D Project of Xuzhou Science and Technology Bureau (grant no. KC23208), Development Fund Project of Xuzhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital (grant no. XYFY202460), Medical Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission (grant no. Z2024021) and Clinical Technology Key Personnel Advanced Training Program of Xuzhou (grant no. 2025GG020).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sainsbury HS. Congenital funnel chest. Lancet. (1947) 2(6478):615. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(47)90629-6
2. Abid I, Ewais MM, Marranca J, Jaroszewski DE. Pectus excavatum: a review of diagnosis and current treatment options. J Am Osteopath Assoc. (2017) 117(2):106–13. doi: 10.7556/jaoa.2017.021
3. Leung AK, Hoo JJ. Familial congenital funnel chest. Am J Med Genet. (1987) 26(4):887–90. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260416
4. Mak SM, Bhaludin BN, Naaseri S, Di Chiara F, Jordan S, Padley S. Imaging of congenital chest wall deformities. Br J Radiol. (2016) 89(1061):20150595. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150595
5. Dean C, Etienne D, Hindson D, Matusz P, Tubbs RS, Loukas M. Pectus excavatum (funnel chest): a historical and current prospective. Surg Radiol Anat. (2012) 34(7):573–9. doi: 10.1007/s00276-012-0938-7
6. Schmidt TG, Sammut BA, Barber RF, Pan X, Sidky EY. Addressing CT metal artifacts using photon-counting detectors and one-step spectral CT image reconstruction. Med Phys. (2022) 49(5):3021–40. doi: 10.1002/mp.15621
7. Pessis E, Sverzut JM, Campagna R, Guerini H, Feydy A, Drapé JL. Virtual monochromatic spectral imaging with fast kilovoltage switching: reduction of metal artifacts at CT. Radiographics. (2013) 33(2):573–83. doi: 10.1148/rg.332125124
8. Zhao J, Cheng Q, Liu C, Wang Q, Lv Y, Tang Z, et al. Optimal combination periprosthetic vasculature visualization and metal artifact reduction by spectral computed tomography using virtual monoenergetic images in total hip arthroplasty. Insights Imaging. (2023) 14(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01533-3
9. Sanghavi PS, Jankharia BG. Applications of dual energy CT in clinical practice: a pictorial essay. Indian J Radiol Imaging. (2019) 29(3):289–98. doi: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_241_19
10. Patzer TS, Kunz AS, Huflage H, Gruschwitz P, Pannenbecker P, Afat S, et al. Combining virtual monoenergetic imaging and iterative metal artifact reduction in first-generation photon-counting computed tomography of patients with dental implants. Eur Radiol. (2023) 33(11):7818–29. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09790-y
11. D’Angelo T, Cicero G, Mazziotti S, Ascenti G, Albrecht MH, Martin SS, et al. Dual energy computed tomography virtual monoenergetic imaging: technique and clinical applications. Br J Radiol. (2019) 92(1098):20180546. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180546
12. World Medical Association. World medical association declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. (2013) 310(20):2191–4. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.281053
13. Cester D, Eberhard M, Alkadhi H, Euler A. Virtual monoenergetic images from dual-energy CT: systematic assessment of task-based image quality performance. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2022) 12(1):726–41. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-477
14. Liang X, Xue C, Huang X, Wei J, Zhou J. Value of energy spectrum CT parameters in the differential diagnosis of high-grade clear cell renal cell carcinoma and type II papillary renal cell carcinoma. Acta Radiol. (2022) 63(4):545–52. doi: 10.1177/02841851211002830
15. Li Z, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Shi J, Wan Y. Quantitative energy spectrum CT in differential diagnosis of aldosterone-producing adenoma and cortisol-producing adenoma. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2023) 13(8):5012–21. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-1279
16. Zhou Q, Huang X, Xie Y, Liu X, Li S, Zhou J. Role of quantitative energy spectrum CT parameters in differentiating thymic epithelial tumours and thymic cysts. Clin Radiol. (2022) 77(2):136–41. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2021.10.017
17. Chen JF, Yang J, Chen WJ, Wei X, Yu XL, Huang DD, et al. Mono+ algorithm assessment of the diagnostic value of dual-energy CT for high-risk factors for colorectal cancer: a preliminary study. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2024) 14(1):432–46. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-291
18. Doerner J, Wybranski C, Byrtus J, Houbois C, Hauger M, Heneweer C, et al. Intra-individual comparison between abdominal virtual mono-energetic spectral and conventional images using a novel spectral detector CT. PLoS One. (2017) 12(8):e0183759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183759
19. Roele ED, Timmer VCML, Vaassen LAA, van Kroonenburgh AMJL, Postma AA. Dual-energy CT in head and neck imaging. Curr Radiol Rep. (2017) 5(5):19. doi: 10.1007/s40134-017-0213-0
20. Lenga L, Albrecht MH, Othman AE, Martin SS, Leithner D, D’Angelo T, et al. Monoenergetic dual-energy computed tomographic imaging: cardiothoracic applications. J Thorac Imaging. (2017) 32(3):151–8. doi: 10.1097/RTI.0000000000000259
21. Kim JS, Park SH, Park S, Hwang JH, Kim JH, Pak SY, et al. Imaging findings of peripheral arterial disease on lower-extremity CT angiography using a virtual monoenergetic imaging algorithm. J Korean Soc Radiol. (2022) 83(5):1032–45. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2021.0191
22. Obermeyer RJ, Goretsky MJ. Chest wall deformities in pediatric surgery. Surg Clin North Am. (2012) 92(3):669–ix. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2012.03.001
23. Fokin AA, Steuerwald NM, Ahrens WA, Allen KE. Anatomical, histologic, and genetic characteristics of congenital chest wall deformities. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2009) 21(1):44–57. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2009.03.001
24. Scheuermann-Poley C, Andreß SM, Willy C, Lieber A. Funnel chest corrective surgery with the aid of a 3D reconstruction of the bony thorax for preoperative adjustment of the metal bar. Zentralbl Chir. (2022) 147(1):65–73. doi: 10.1055/a-1487-7041
25. Zhao J, Luo L, Xiao LJ, Gu LY, Sun TS. Psychological trauma of funnel chest in adolescents and the appropriate age for minimally invasive surgery repair. Chin Med J (Engl). (2013) 126(15):2876–80. PMID: 2392445923924459
26. Cuellar E, Muscari F, Tuyeras G, Maulat C, Charrière B, Duffas JP, et al. Use of routine CT-SCANS to detect severe postoperative complications after pancreato-duodenectomy. J Visc Surg. (2018) 155(5):375–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2017.12.007
27. Mai Q, Wan JWL. Metal artifacts reduction in CT scans using convolutional neural network with ground truth elimination. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. (2020) 2020:1319–22. doi: 10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9176173
28. Zhou H, Liu X, Wang H, Chen Q, Wang R, Pang ZF, et al. The synthesis of high-energy CT images from low-energy CT images using an improved cycle generative adversarial network. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2022) 12(1):28–42. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-182
29. Anhaus JA, Killermann P, Mahnken AH, Hofmann C. A nonlinear scaling-based normalized metal artifact reduction to reduce low-frequency artifacts in energy-integrating and photon-counting CT. Med Phys. (2023) 50(8):4721–33. doi: 10.1002/mp.16461
Keywords: computed tomography, dual-energy CT, virtual monoenergetic imaging, metal artifact reduction, congenital funnel chest, artifact, child
Citation: Li C, Xu C, Lu L, Dong L and Du P (2025) The value of dual-energy CT virtual monoenergetic imaging and metal-artifacts reduction system after metal plate correction of congenital funnel chest in child: a single center retrospective study. Front. Pediatr. 13:1430160. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1430160
Received: 9 May 2024; Accepted: 6 October 2025;
Published: 23 October 2025.
Edited by:
Mario Lima, University of Bologna, ItalyReviewed by:
Paul Jeziorczak, University of Illinois at Peoria, United StatesLuotong Wang, Peking University, China
Copyright: © 2025 Li, Xu, Lu, Dong and Du. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lina Dong, ZGxuMDMyNUAxMjYuY29t; Peng Du, cGR1MjBAZnVkYW4uZWR1LmNu
 Chenglong Li1
Chenglong Li1 Peng Du
Peng Du