- 1Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, China
- 2Guizhou Children’s Hospital, Zunyi, China
- 3Collaborative Innovation Center for Tissue Injury Repair and Regenerative Medicine of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, China
Objective: This study aimed to explore the prognostic value of blood inflammatory composite markers in the survival of pediatric patients diagnosed with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (sHLH).
Methods: Clinical data from 138 newly diagnosed sHLH patients hospitalized between January 2012 and October 2023 were analyzed. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was used to determine cutoff values and evaluate predictive accuracy, while Cox regression analysis was employed to identify prognostic factors.
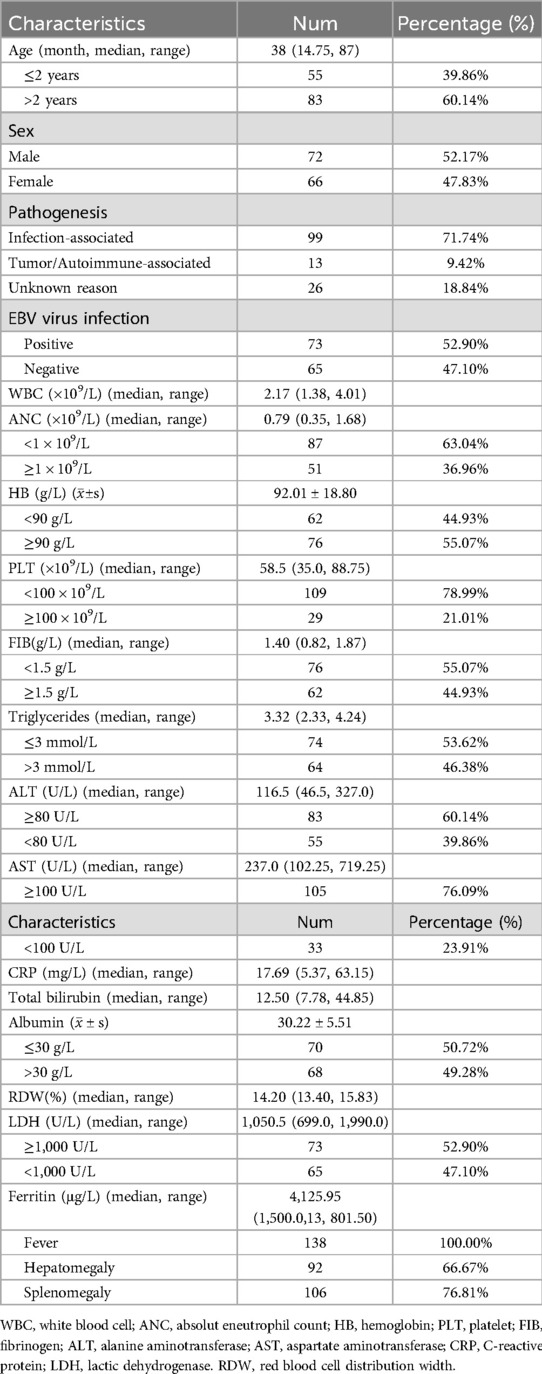
Results: The median age of the 138 sHLH patients was 38 months, with a female-to-male ratio of 0.92. Infection was identified as the most common cause of sHLH, 52.9% testing positive for the epstein-barr virus (EBV). Clinical features included decreased blood cell counts in 87.0% of patients, hypofibrinogenemia in 55.07%, hypertriglyceridemia in 46.38%, and elevated ferritin levels in 94.2%. Additionally, all patients experienced fever, while hepatomegaly and splenomegaly were observed in 66.67% and 76.81%, respectively. During the study, 48 patients died. Cox regression analysis identified red blood cell distribution width (RDW) ≥14.35%, fibrinogen <1.5 g/L, red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio (RPR) ≥0.36, and lactate dehydrogenase to serum albumin ratio (LAR) ≥56.02 as significant predictors of decreased survival.
Conclusion: This study provides preliminary evidence that accessible inflammatory markers like LAR and RPR may assist in early prognostic assessment of pediatric sHLH. These findings highlight the potential utility of routine blood parameters, warranting further validation in larger, stratified cohorts.
1 Introduction
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a subtype of histiocytosis characterized by dysfunction of cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) and natural killer (NK) cells, leading to impaired antigen clearance and excessive activation of the monocyte-macrophage system. This dysregulation results in cytokine overproduction and clinical manifestations such as fever, hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypofibrinogenemia, hyperferritinemia, and hemophagocytosis in bone marrow tissue (1, 2). Secondary HLH (sHLH) is the most common form and has diverse etiologies, including malignancies, rheumatic and immune diseases, and infections (1–3). Due to immune dysfunction, patients with HLH experience hypercytokinemia, which causes ongoing tissue damage and initiates a cascade of inflammatory events. This cascade contributes to the disease's rapid progression and high mortality (3). Without timely intervention, the majority of patients with HLH die from severe infections, visceral bleeding, neutropenia or multiple organ failure, with a median survival time of less than two months (4, 5). Even with treatment, approximately one-third of patients with HLH still die, with more than half of these deaths occurring in the early stages (within 30 days) of the disease (6). Consequently, identifying prognostic indicators for HLH are of great significance for early identification of critically ill patients and improving survival outcomes.
Inflammatory mechanisms are central to HLH-associated organ dysfunction and mortality. Patients often exhibit elevated levels of cytokines (IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ, TNF-α) and serological markers (ALT, AST, CRP, ferritin, LDH, TG), which are indicative of disease severity and poor prognosis. However, limited access to inflammatory markers, such as cytokines, ferritin, and sCD25, in certain regions may hinder effective risk stratification and delay timely clinical decision-making, potentially contributing to poorer patient outcomes. Therefore, identifying novel, widely accessible biomarkers are critical for improving the evaluation and management of HLH prognosis (7, 8).
Previous studies have confirmed that blood inflammatory composite markers can effectively predict prognosis in inflammatory diseases and play an important role in risk stratification. For example, markers like the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) have demonstrated utility in predicting 90-day mortality in septic patients, with an AUC of 0.66 (sensitivity = 69.57%, specificity = 61.44%) (9). Albumin bilirubin score (ALBI) has shown an AUC of 0.693 in predicting 28-day mortality in non-Hodgkin lymphoma-associated HLH (10), while prognostic nutritional index (PNI) has demonstrated an AUC of 0.64 (95% CI: 0.61–0.67) for severe sepsis and 0.69 (95% CI: 0.60–0.78) for septic shock (11). Other markers include the red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio (RPR) (12), C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio (CAR) (13), lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio (LAR) (14), alanine aminotransferase-to-aspartate aminotransferase ratio (De Ritis) (15), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) (9), all of which have been associated with prognosis in various conditions.
Despite growing recognition of the prognostic value of blood inflammatory composite markers in various inflammatory diseases, most existing studies have predominantly focused on adult populations. However, pediatric sHLH differs significantly from adult-onset cases in several aspects, including immune system maturity, underlying etiologies (with a higher prevalence of infection-related triggers such as EBV in children), clinical presentation, and treatment responses (16). These distinctions highlight the need for pediatric-specific prognostic research. Currently, there is a notable lack of studies examining the prognostic relevance of blood inflammatory composite markers in children with sHLH. These markers, which are inexpensive and routinely available in clinical practice, have shown promise in adult inflammatory conditions but remain underexplored in pediatric HLH. To address this gap, the present study serves as a proof-of-concept evaluation to explore whether routinely available composite inflammatory markers can provide preliminary prognostic insights in an undifferentiated pediatric sHLH cohort, aiming to offer an initial reference framework for early risk stratification using accessible laboratory parameters.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patients
This retrospective cohort study included patients diagnosed with HLH at the Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University from January 2012 to October 2023. All patients met the HLH-2004 diagnostic criteria (17). Exclusion criteria included primary HLH with HLH-related pathogenic gene defects, patients older than 14 years, patients with incomplete clinical data, and patients diagnosed and/or treated at other facilities. The patients in this study received treatments tailored to their clinical presentation, which including: The HLH-94/HLH-2004 protocols. Blood purification treatments, including plasma exchange or continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) for managing severe inflammation and organ failure. Blood transfusion therapy to address cytopenias and maintain adequate hemoglobin levels. Human immunoglobulin infusion (IVIG) for immunomodulation and infection control. Anti-infection and antiviral therapy targeting underlying triggers such as bacterial or viral infections (e.g., EBV). This study was conducted at the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University and was approved by the Ethics Committee (approval number: KLL-2023–599) with waiver of informed consent requirement since this is a retrospective study.
2.2 Variables and outcomes
Clinical data of all eligible sHLH patients were collected, including demographic information (gender, age), etiology, hepatosplenomegaly, and laboratory indicators (blood routine, liver function, coagulation function, blood lipids, C-reactive protein and serum ferritin) at the time of diagnosis. The peripheral blood inflammation parameters analyzed in this study included NLR, PLR, RPR, ALBI, De Ritis, LAR, CAR, and PNI. These indices were calculated based on in-hospital blood indicators such as complete blood count, biochemistry, coagulation function, lipids, ferritin, and CRP. Follow-up extended from diagnosis to the patient death or October 30, 2023, via outpatient or telephone contact, with overall survival (OS) time (days) defined as the duration from diagnosis to various time points: 1 week, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, two months, three months, and the last follow-up, or death for any reason.
2.3 Statistical methods
Data analysis was performed using SPSS (v29.0), GraphPad Prism (v8.0). Measurement data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (x̅ ± s), median and interquartile ranges [M (Q1, Q3)], depending on distribution. Categorical data were presented as n (%). Normally distributed data were compared using the unpaired t-test, while non-normally distributed data were analyzed using the Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical variables were compared using the chi-squared test. ANC, HB, PLT, FIB, and TC were categorized based on the threshold values defined in the HLH diagnostic criteria. AST, and ALT were categorized as elevated if they were ≥2 times the upper limit of the reference values at our institution. Elevated LDH level was defined as >1,000 IU/L (18, 19). Hypoalbuminemia was defined as albumin ≤30 g/L. For NLR, PLR, RPR, RDW, LAR, CAR, ALBI, D-dimer, PNI, and SF, the cutoff values were determined using ROC curve analysis. Cox regression was employed to identify prognostic factors, and the Kaplan–Meier method was applied to plot survival curves for different subgroups. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05 for two-sided tests.
3 Results
3.1 General information
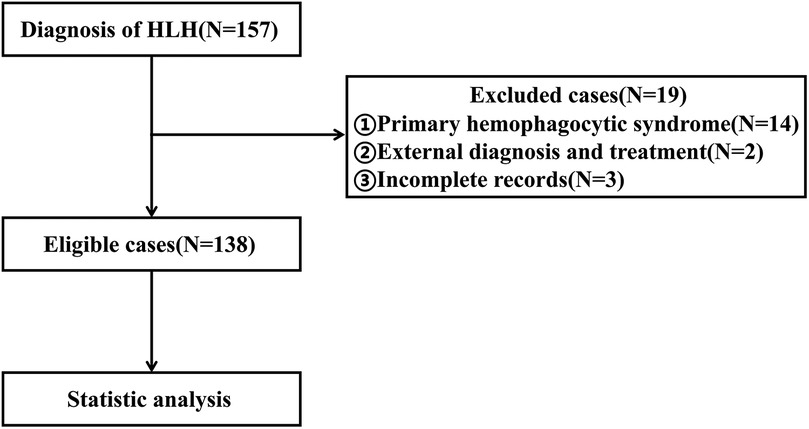
Between January 2012 and October 2023, a total of 157 patients diagnosed with HLH received treatment at our hospital. After applying strict screening criteria, 138 patients were included in this study (Figure 1). The cohort consisted of 72 males (52.17%) and 66 females (47.83%), with a median age of 38 months. Among the cases, 99 (71.74%) were attributed to infection, with 73 cases (52.90%) specifically linked to EB virus. Thirteen cases (9.42%) were associated with tumors or autoimmune diseases, while the etiology was unknown in 26 cases (18.84%). By the follow-up deadline (median follow up: 18.62 months), 48 patients (34.79%) had died. The causes of death included 36 cases of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), 6 cases of respiratory failure, 5 cases of circulatory failure, and 1 case of intracranial hemorrhage.
Laboratory tests revealed a median white blood cell count (WBC) of 2.17 × 109/L. Among the cases, 87 (63.04%) had an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) below 1 × 109/L, 62 (44.93%) exhibited hemoglobin level (HB) below 90 g/L, and 109 (78.99%) had platelet counts (PLT) below 100 × 109/L. Additionally, 76 cases (55.07%) had fibrinogen levels below 1.5 g/L, 64 cases (46.38%) presented triglycerides above 3 mmol/L, 74 cases (53.62%) had alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels ≥80 U/L, and 105 cases (76.09%) exhibited aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels ≥100 U/L. Furthermore, 70 cases (50.72%) had albumin levels ≤ 30 g/L. Median levels for C-reactive protein (CRP), red cell distribution width (RDW), and serum ferritin were 17.69 mg/L, 14.20%, and 4,125.95 µg/L, respectively. Regarding clinical manifestations, all 138 cases (100%) experienced fever, 92 cases (66.67%) presented hepatomegaly, and 106 cases (76.81%) exhibited splenomegaly (Table 1).
3.2 Comparison of peripheral blood cell parameters in different prognoses
A comparison of peripheral blood inflammatory parameters in sHLH showed that the levels of RPR, RDW, ALBI, De Ritis, and LAR were significantly higher in the death group compared to the survival group (P < 0.05). Additionally, PNI was notably lower in the death group compared to the survival group (P < 0.001). However, no statistically significant differences (P > 0.05) were observed for NLR, PLR, and CAR between the two groups (Figure 2).
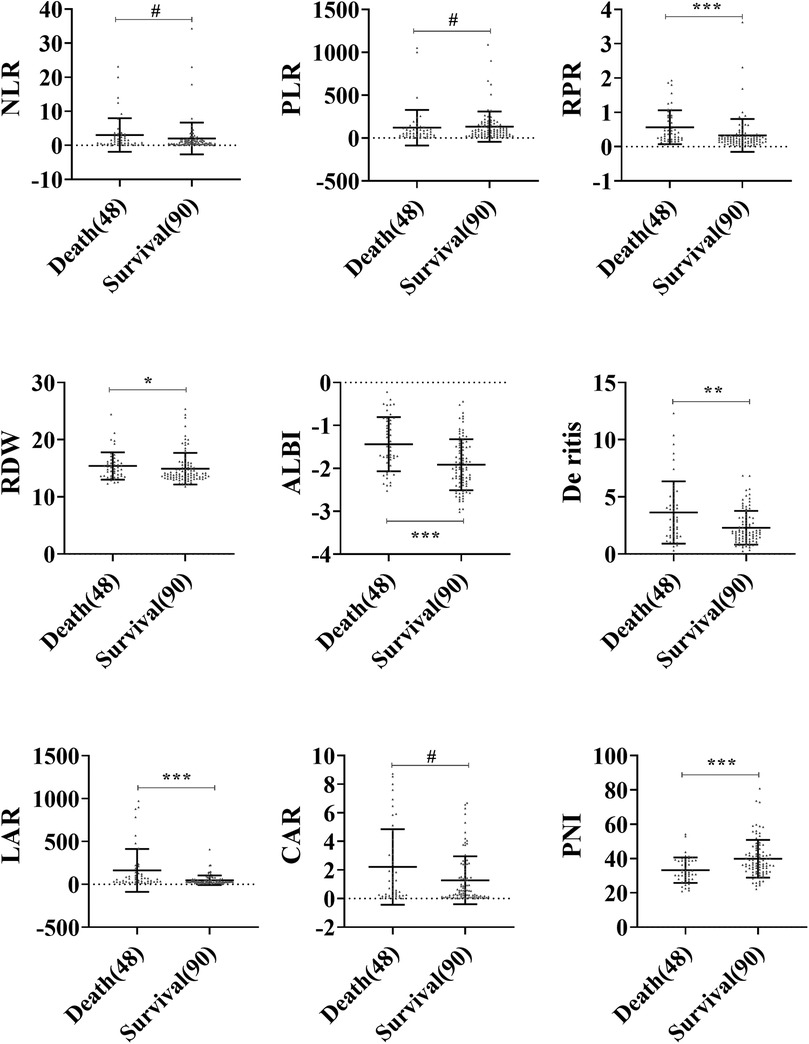
Figure 2. Comparison of blood inflammatory composite markers between the survival and death groups in sHLH. Statistical significance is indicated as follows: #: no statistical significance, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.
3.3 Predictive value of inflammation indices in pediatrics sHLH
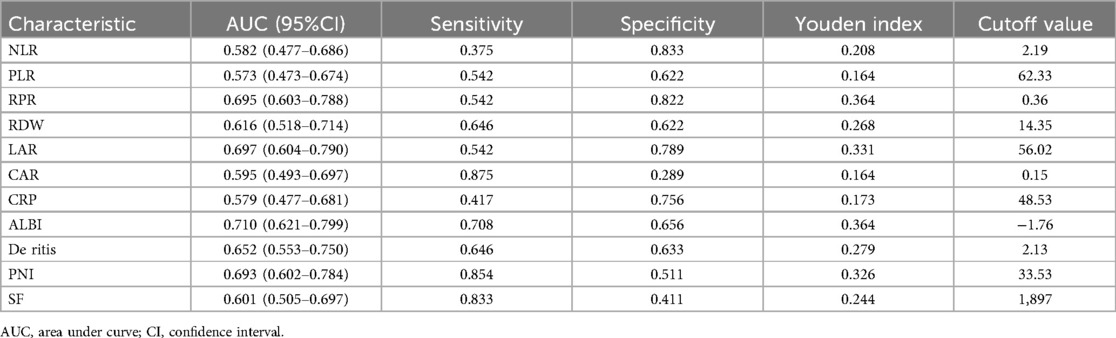
The predictive value of peripheral blood inflammation parameters for the prognosis of sHLH patients showed that all indicators had an AUC greater than 0.500. Among these, ALBI exhibited the highest AUC of 0.710, with an optimal cut-off value of −1.76 (sensitivity = 70.6%, specificity = 65.6%). LAR followed with an AUC of 0.697 and an optimal cut-off value of 56.02 (sensitivity = 54.2%, specificity = 78.9%). CAR demonstrated the highest sensitivity (87.5%) at an optimal cut-off value of 0.15, while SF showed a sensitivity of 83.3% at an optimal cut-off value of 1,897 μg/L. NLR demonstrated the highest specificity of (83.3%) with the optimal cut-off value of 2.19, followed by RPR with a specificity of 82.2% at a cut-off value of 0.36 (Table 2 and Figure 3).
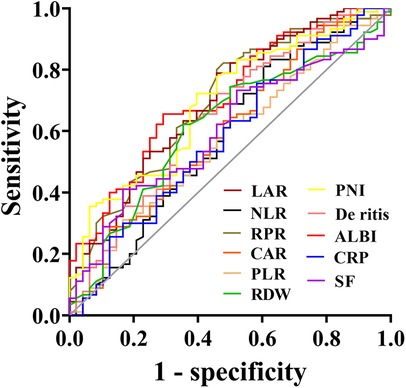
Figure 3. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of blood inflammatory composite markers predicting the prognosis of sHLH.
3.4 Survival analysis
Survival analysis was performed for groups stratified based on the optimal cutoff values of various inflammation indexes. Patients with NLR ≥ 2.19, RPR ≥ 0.36, RDW ≥ 14.35, LAR ≥ 56.02, CAR ≥ 0.15, ALBI ≥ −1.76, De Ritis ≥ 2.13, and PNI ≤ 33.53 exhibited significantly worse survival outcomes compared to their respective control group (P < 0.05). However, there was no statistically significant difference in survival outcomes between the PLR ≤ 62.33 group and the PLR > 62.33 group (P = 0.051). From the survival plots, it was evident that mortality in our study predominantly occurred within the first two months (Figure 4).
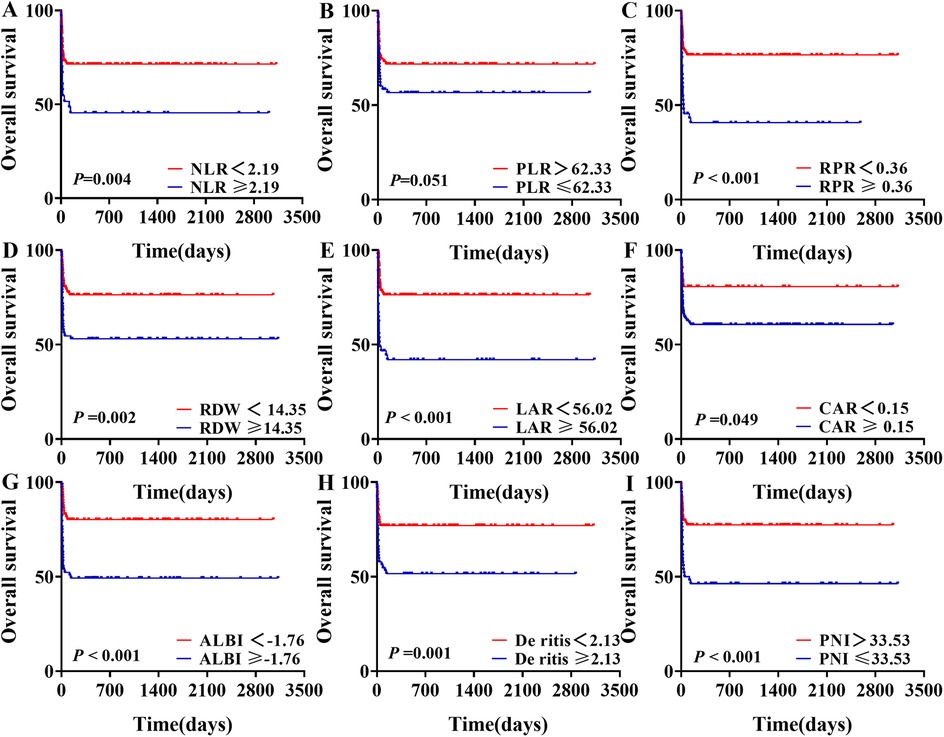
Figure 4. Survival analysis of sHLH patients stratified by different levels of blood inflammatory composite markers.
3.5 Prognostic analysis of sHLH in children
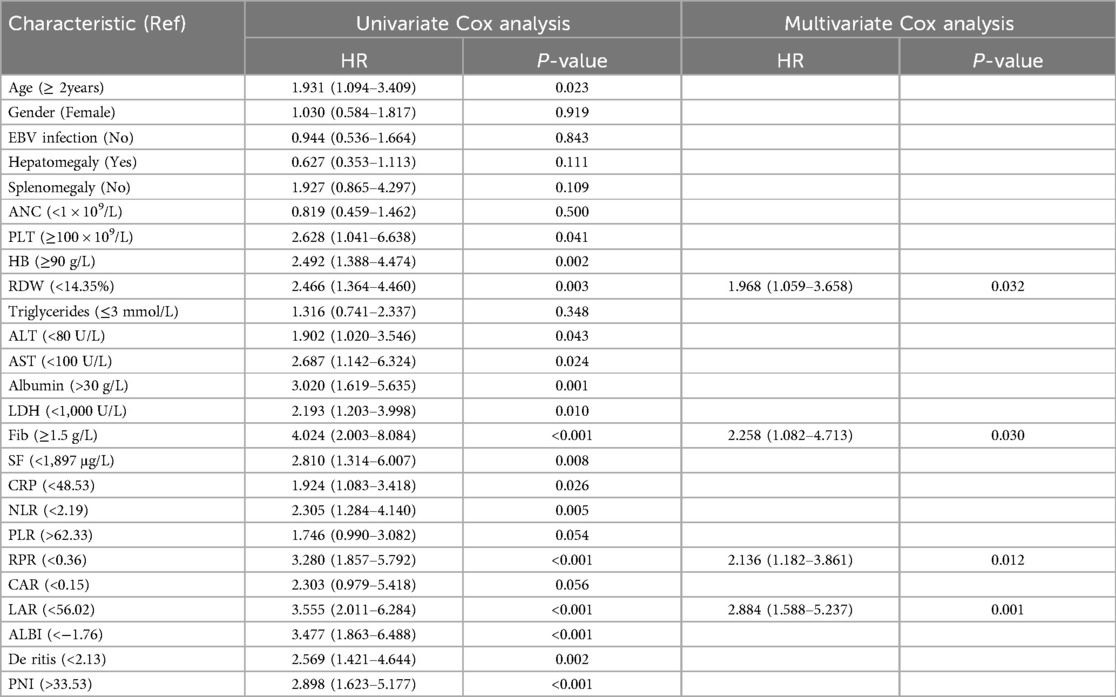
Univariate regression analysis revealed that age, PLT, HB, RDW, ALT, AST, albumin, LDH, FIB, SF, CRP, NLR, RPR, LAR, ALBI, De Ritis, and PNI were associated with patient prognosis. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that, after adjusting for factors such as age, gender, and etiology, a higher LAR was associated with an increased risk of mortality (HR = 2.884, 95% CI = 1.588–5.237). Similarly, RPR was identified as a significant risk factor for mortality (HR = 2.136, 95% CI = 1.182–3.861). Additionally, high RDW levels (HR = 1.968) and low FIB levels (HR = 2.258) were also determined to be significant risk factors for mortality in sHLH patients (P < 0.05) (Table 3).
3.6 Hazard ratios of LAR and RPR index for overall survival in subgroups
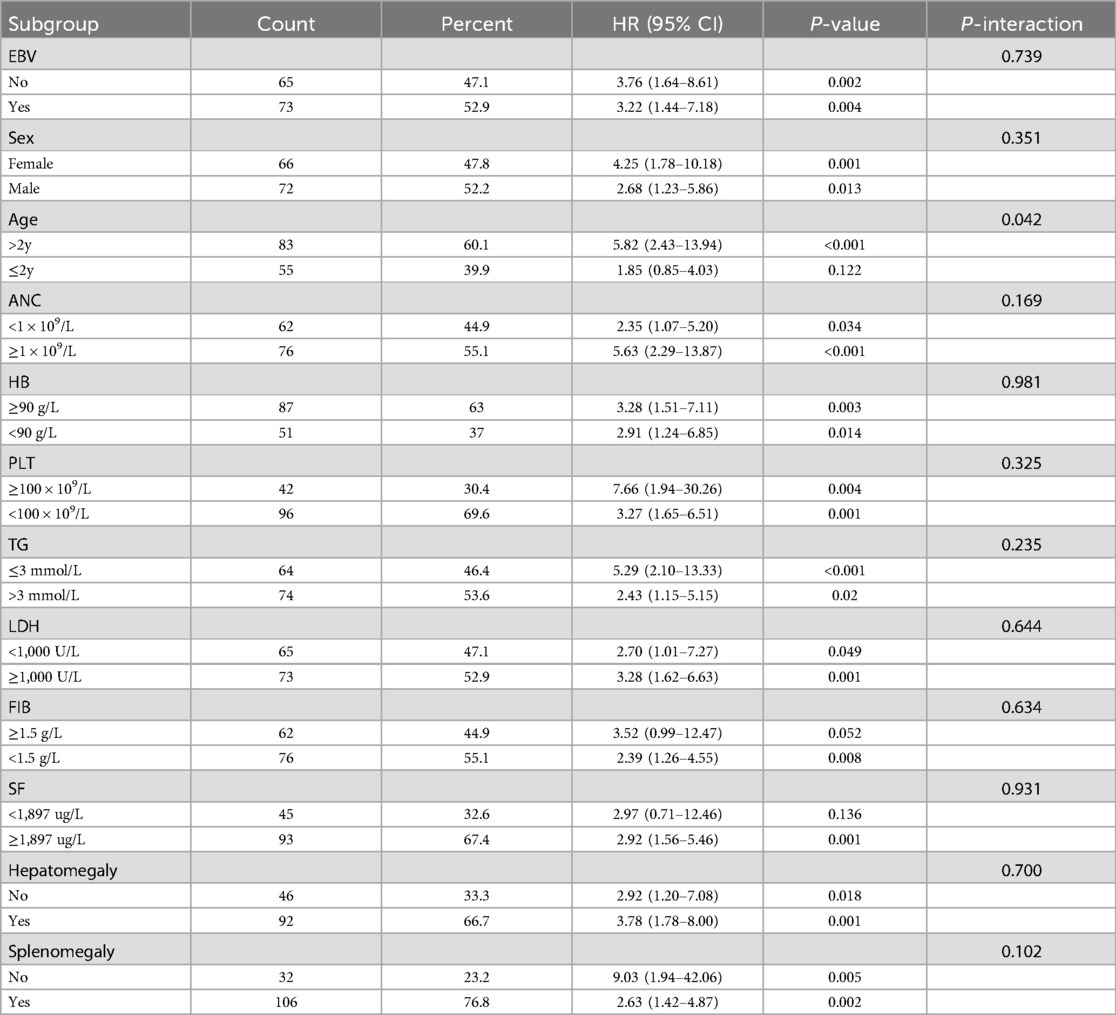
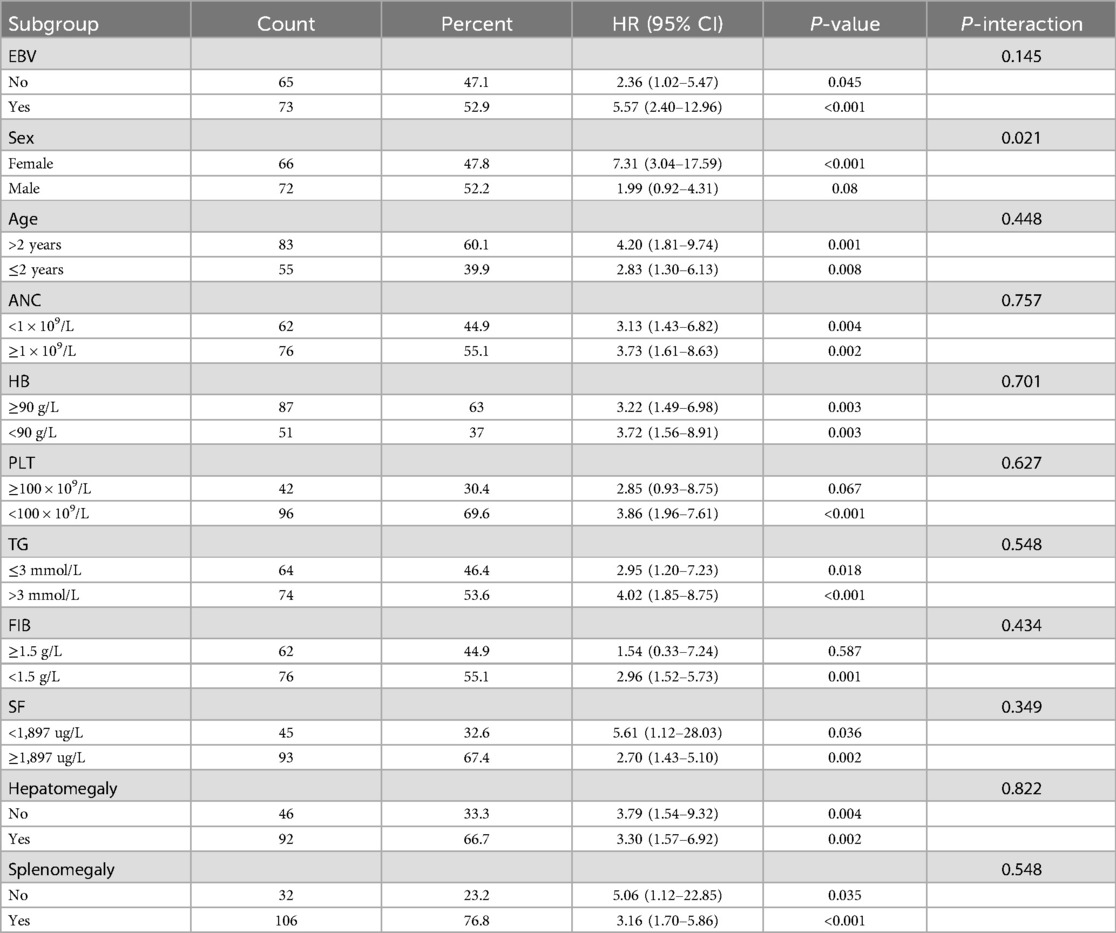
Subgroup analysis was conducted to access the impact of confounding factors on the prognosis of sHLH patients, including age, gender, EBV infection, absolute neutrophil count, hemoglobin, platelets, fibrinogen, lactate dehydrogenase, triglycerides, serum ferritin, hepatomegaly, and splenomegaly. LAR and RPR demonstrated significant predictive value across multiple variable subgroups. Interestingly, in the subgroup analysis, RPR showed an interaction within the age subgroups, LAR showed an interaction within the gender subgroups. However, for the remaining subgroups, there were no statistically significant differences in the predictive value of LAR or RPR when combined with baseline characteristics for predicting mortality risk in children with sHLH. These findings suggest that both LAR and RPR are potentialprognostic indicators regardless of most baseline characteristics (Tables 4, 5).
3.7 RPR combined with LAR exhibited better predictive value
To evaluate the prognostic significance of LAR and RPR for sHLH patients, we analyzed their predictive value across various time intervals (1 week, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, 2 months, and 3 months). LAR consistently demonstrated strong predictive performance, with AUC values exceeding 0.7 at 1 week, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks, and remaining above 0.6 at 2 and 3 months. Conversely, the predictive value of RPR remained stable across all time intervals, with AUC values ranging from 0.684 to 0.699. Comparative analysis of RPR, LAR, and their combined predictive ability (LAR-RPR) revealed that at week 1, both LAR and LAR-RPR outperformed RPR alone (P = 0.047 and P = 0.013, respectively), At week 2, LAR-RPR exhibited significantly superior performance compared to RPR alone (P = 0.032). No statistically significant differences were observed at other time points (P > 0.05). While the combined use of RPR and LAR did not significantly increase the predictive efficacy, both indices demonstrated commendable prognostic value (AUC > 0.6, P < 0.05). Notably, LAR showed significantly improved predictive performance in the early stage (≤4 weeks), with an AUC > 0.7 (P < 0.05) (Figure 5).
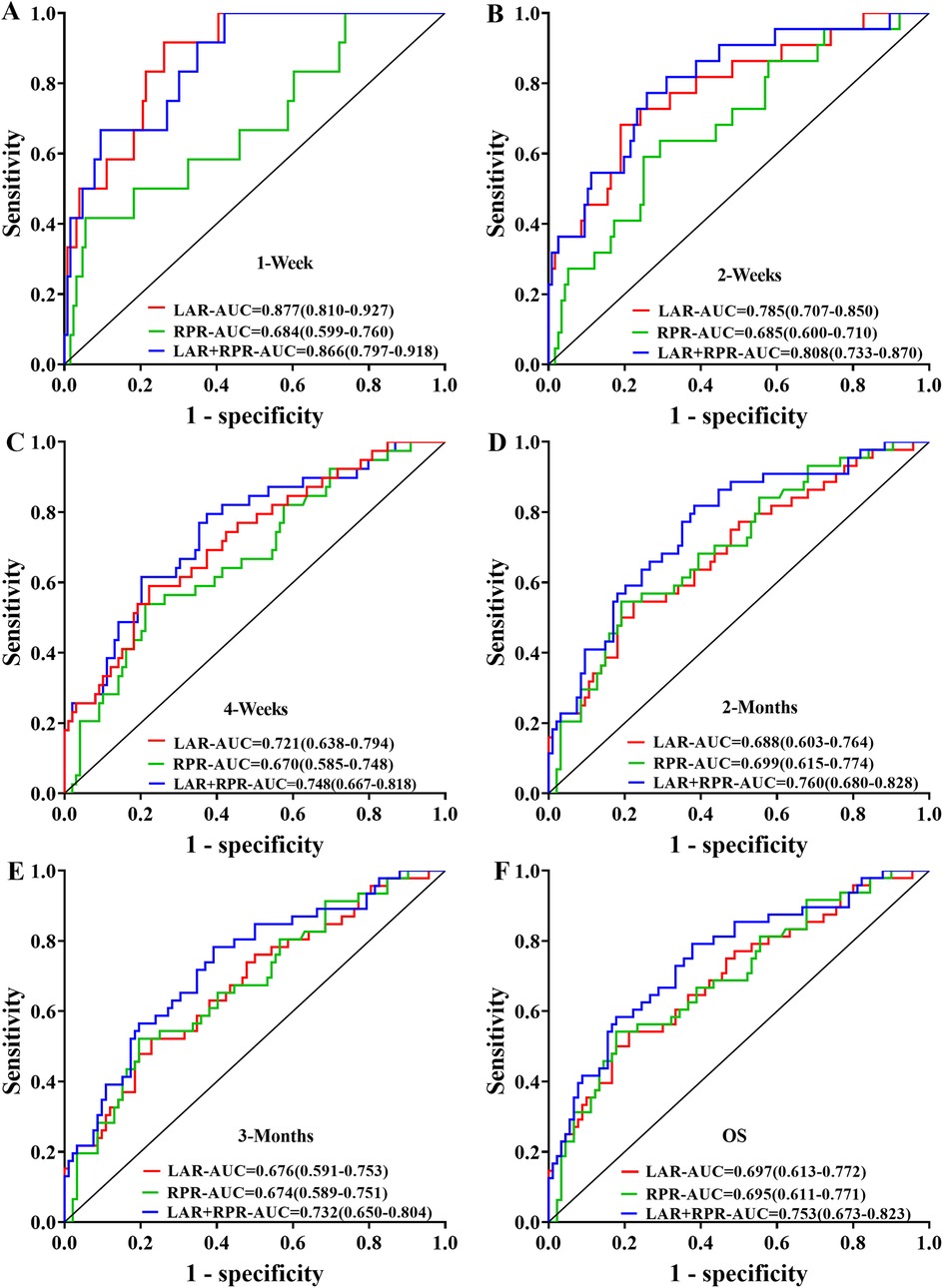
Figure 5. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to compare the prognostic predictive performance of LAR, RPR, and their combination (LAR+RPR) across different time intervals: (A) 1 week, (B) 2 weeks, (C) 4 weeks, (D) 2 months, (E) 3 months, and (F) overall survival (OS). The curves illustrate the sensitivity versus 1-specificity relationships with corresponding area under the curve (AUC) values, showing the predictive capacity of each parameter at various clinical follow-up points.
4 Discussion
Prognostic factors for HLH have been widely studied, revealing multiple independent risk factors associated with poor outcomes. These factors include laboratory, clinical, and dynamic variables (6, 20–25), which highlight the complexity of HLH prognosis, and underscore the importance of early risk stratification that integrates clinical, laboratory, and dynamic markers to guide treatment and improve prognosis in HLH patients. Previous studies have highlighted the prognostic value of blood inflammatory composite markers in inflammatory diseases, emphasizing their role in risk stratification. However, limited research has been conducted on the association between these markers and the prognosis of sHLH in children. In this retrospective analysis, we evaluated data from 138 pediatric patients with sHLH, aiming to assess the relationship between blood inflammatory composite markers and prognosis. The key findings include: (1) An overall mortality rate of 34.8% (48/138) among the cohort; (2) Significantly higher in-hospital mortality rates in patients with elevated LAR or RPR compared to those with lower LAR or RPR; and (3) High LAR or RPR levels during hospitalization showed preliminary prognostic relevance for adverse outcomes in pediatric sHLH, based on multivariate analysis within this proof-of-concept cohort.
Previous studies have underscored the prognostic relevance of RDW across various conditions, including cancer, sepsis, and inflammatory bowel disease (26–28). Recent studies on adult HLH have confirmed the correlation between elevated RDW and poor prognosis (29, 30). Similarly, our findings reveal a significantly elevation in RDW levels among deceased sHLH patients, with an RDW ≥ 14.35 showing potential as an independent prognostic indicator. RPR, an established marker of inflammatory processes, has also been recognized as a significant prognostic factor in various inflammatory diseases (12, 30–33). In studies on septic patients, higher RPR levels were associated with increased 28-day mortality rates (32). Similarly, retrospective analysis in adult HLH patients revealed a higher RPR in deceased patients, with RPR identified as an independent risk factor (30). Notably, a study of 179 adult HLH patients found that patients with an RPR > 0.33 exhibited a notably lower survival rates compared to those with RPR ≤ 0.33, with an AUC of 0.637 (95% CI 0.562–0.708) for RPR as a standalone prognostic predictor (33). Our study of 138 pediatric sHLH patients aligns with these findings, revealing significantly higher RPR level in the deceased group compared to survivors. Patients with RPR ≥ 0.36 exhibited significantly reduced survival rates. Importantly, even after adjusting for gender, age, etiology, and other laboratory parameters, RPR retained a statistically significant association with prognosis. These results suggest a potential association between RPR and outcomes in pediatric sHLH, supporting its exploratory value as a candidate marker for early prognostic assessment.
Previous studies have established a correlation between LDH, serum albumin, and HLH prognosis (34, 35). The combination of LDH and serum albumin, represented by the LAR, reflects both inflammation and nutritional status. LAR has been identified as a prognostic factor in various conditions, including sepsis, cancer, and inflammatory diseases (14, 36, 37). For instance, LAR has been linked with increased mortality risk at 28 and 90 days in sepsis patients and recognized as an independent risk factor for mortality (14). Another study identified LAR as an independent adverse prognostic factor in lower respiratory tract infections with a strong predictive value (AUC = 0.808) (36). Although no previous reports have explored the correlation between LAR and HLH prognosis, our findings reveal significantly higher LAR levels in the deceased group compared to survivors. This increase may be attributed to hypoalbuminemia caused by capillary leak associated with endothelial activation during inflammation process in sHLH. Additionally, patients with LAR ≥ 56.02 exhibited significantly reduced overall survival rates compared to those with LAR < 56.02, indicating that higher LAR levels may be associated with poorer prognosis. Multivariate Cox regression analysis further supported the potential of LAR as an independent prognostic marker in pediatric sHLH. These findings suggest that monitoring LAR values during HLH diagnosis and treatment may help in the early identification of critically ill patients, enabling timely intervention to potentially slow or prevent disease progression.
Previous studies have also highlighted the prognostic relevance of ALBI, De Ritis, and PNI in various inflammatory diseases (10, 11, 15, 38). In our study, we observed increased ALBI and De Ritis ratio levels and decreased PNI levels in the deceased group compared to survivors. While these factors showed an association with sHLH prognosis, they did not achieve statistical significance in multivariate analysis.
In summary, our exploratory analysis identified LAR and RPR as potential independent prognostic markers among eight routinely available inflammatory indices in pediatric sHLH. These factors represent simple, convenient, and cost-effective parameters derived from routine peripheral blood analysis. Our findings suggest that LAR and RPR may serve as potential biomarkers for indicating early and overall prognosis in pediatric sHLH. Notably, even after adjusting for confounding variables such as age, gender, etiology, and other inflammatory composite parameters, both markers retained independent associations with outcomes, supporting their possible utility for early risk stratification in this undifferentiated population. However, this study has certain limitations, including: (1) This analysis relied on static laboratory values at diagnosis without capturing dynamic changes over time, which may have reduced the sensitivity and timeliness of prognostic assessment. Longitudinal monitoring is needed to improve predictive accuracy and clinical utility. (2) As an initial proof-of-concept, these findings warrant further validation in larger multicenter cohorts with etiological stratification to clarify the broader prognostic utility of LAR and RPR in pediatric sHLH. (3) The potential influence of therapeutic strategies on dynamically measured variables introduces variability that may affect predictive accuracy. Differences in treatment approaches across medical centers further compound this limitation, potentially affecting the generalizability of the results. Future research should explore these aspects to enhance the understanding of LAR and RPR as prognostic markers.
5 Conclusion
In this proof-of-concept study of pediatric patients with sHLH, several routinely available composite inflammatory markers were found to be associated with overall survival. Specifically, elevated RPR (≥0.36) and LAR (≥56.02) demonstrated potential prognostic relevance and were identified as independent risk factors for poorer outcomes. However, their combined use did not significantly improve predictive performance over individual assessments. These findings suggest that RPR and LAR may serve as practical, accessible indicators to aid early risk stratification in pediatric sHLH, particularly in settings where advanced immunological tests are not readily available. Nonetheless, their predictive utility is not absolute and may vary with underlying etiology, disease heterogeneity, and treatment response. Therefore, these markers should be interpreted within the context of a comprehensive clinical assessment. Further validation in larger, multicenter, and etiologically stratified cohorts is necessary.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (approval number: KLL-2023–599). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
NL: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XX: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YC: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. PH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Guizhou Provincial Program on Commercialization of Scientific and Technological Achievements [QKHCG(2024)ZD012], the Guizhou Provincial High-Level (“Thousand” Level) Innovative Talents Projects (gzwjrs2023-034, gzwjrs2023-041), the Medical Research Union Found for High-quality Health Development of Guizhou Province (2024GZYXKYJJXM0062, 2024GZYXKYJJXM0061), and the Zunyi Municipal Science and Technology Project (ZSKRPT-2023-6, ZSKHZ-2023-214).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the use of OpenAI's ChatGPT-3.5 and ChatGPT-4o for assistance with translation and language polishing during the preparation of this manuscript. The final content was thoroughly reviewed and approved by all authors to ensure accuracy and adherence to academic standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Canna SW, Marsh RA. Pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. (2020) 135:1332–43. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000936
2. Kaçar AG, Celkan TT. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Balkan Med J. (2022) 39:309–17. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2022.2022-4-83
3. Brisse E, Wouters CH, Matthys P. Advances in the pathogenesis of primary and secondary haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: differences and similarities. Br J Haematol. (2016) 174:203–17. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14147
4. Parajuli B, Angurana SK, Awasthi P, Nallasamy K, Baranwal A, Bansal A, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a PICU of a developing economy: clinical profile, intensive care needs, outcome, and predictors of mortality. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2021) 22:e44–57. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000002539
5. Karapinar B, Yilmaz D, Balkan C, Akin M, Ay Y, Kvakli K. An unusual cause of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in the pediatric intensive care unit: hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2009) 10:285–90. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e318198868b
6. Li X, Yan H, Zhang X, Huang J, Xiang ST, Yao Z, et al. Clinical profiles and risk factors of 7-day and 30-day mortality among 160 pediatric patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2020) 15:229. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-01515-4
7. Griffin G, Shenoi S, Hughes GC. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: an update on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2020) 34:101515. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2020.101515
8. Yang SL, Xu XJ, Tang YM, Song H, Xu WQ, Zhao FY, et al. Associations between inflammatory cytokines and organ damage in pediatric patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Cytokine. (2016) 85:14–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.05.022
9. Spoto S, Lupoi DM, Valeriani E, Fogolari M, Locorriere L, Beretta Anguissola G, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios in septic patients outside the intensive care unit. Medicina (Kaunas). (2021) 57:811. doi: 10.3390/medicina57080811
10. Cheng W, Duan L, Xu J, Shu Y, Qiu H, Yin G. Prognostic value of the albumin-bilirubin score in patients with non-hodgkin lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1162320. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1162320
11. Li T, Qi M, Dong G, Li X, Xu Z, Wei Y, et al. Clinical value of prognostic nutritional Index in prediction of the presence and severity of neonatal sepsis. J Inflamm Res. (2021) 14:7181–90. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S343992
12. Tong L, Liu YQ, Shen JH, Min B, Zhou Q, Duan XJ, et al. Relationship between the red cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio and in-hospital mortality among critically ill patients with acute myocardial infarction: a retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e062384. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-062384
13. Lu X, Liu WC, Qin Y, Chen D, Yang P, Chen XH, et al. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a prognostic indicator in posttraumatic shock and outcome of multiple trauma patients. Curr Med Sci. (2023) 43:360–6. doi: 10.1007/s11596-023-2714-9
14. Liang M, Ren X, Huang D, Ruan Z, Chen X, Qiu Z. The association between lactate dehydrogenase to serum albumin ratio and the 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in intensive care: a retrospective cohort study. Ren Fail. (2023) 45:2212080. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2212080
15. Yin G, Man C, Liao S, Qiu H. The prognosis role of AST/ALT (De ritis) ratio in patients with adult secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Mediators Inflamm. (2020) 2020:5719751. doi: 10.1155/2020/5719751
16. Bhatt NS, Oshrine B, An Talano J. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Leuk Lymphoma. (2019) 60:19–28. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1482543
17. Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2007) 48:124–31. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21039
18. Zhou YH, Han XR, Xia FQ, Poonit ND, Liu L. Clinical features and prognostic factors of early outcome in pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective analysis of 227 cases. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. (2022) 44:e217–22. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000002283
19. Yadav G, Malhotra H, Mehta P, Sachu R, Rizvi I, Bharti VR, et al. Severe COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome versus classic hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: similarities, differences, and the way forward. J Investig Med. (2023) 71:244–53. doi: 10.1177/10815589221140596
20. Pan H, Wang G, Guan E, Song L, Song A, Liu X, et al. Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors for non- malignancy associated secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children. BMC Pediatr. (2020) 20:288. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-02178-7
21. Bin Q, Gao JH, Luo JM. Prognostic factors of early outcome in pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: an analysis of 116 cases. Ann Hematol. (2016) 95:1411–8. doi: 10.1007/s00277-016-2727-6
22. Luo ZB, Chen YY, Xu XJ, Zhao N, Tang YM. Prognostic factors of early death in children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Cytokine. (2017) 97:80–5. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.03.013
23. Cui Y, Shi J, Lu G, Wang Y, Zhu X, Ren H, et al. Prognostic death factors in secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis children with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: a multicenter prospective nested case-control study. Ther Apher Dial. (2022) 26:1023–9. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.13775
24. Luo N, Yang G, Li B, Zhang P, Ma J, Chen Y, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognostic analysis of pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis using lasso-logistic regression. Ann Hematol. (2024) 103:5191–200. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-06061-8
25. Kogawa K, Sato H, Asano T, Ohga S, Kudo K, Morimoto A, et al. Prognostic factors of epstein–barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children: report of the Japan histiocytosis study group. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2014) 61:1257–62. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24980
26. Eoh KJ, Lee TK, Nam EJ, Kim SW, Kim YT. Clinical relevance of red blood cell distribution width (RDW) in endometrial cancer: a retrospective single-center experience from Korea. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:3984. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153984
27. Moreno-Torres V, Royuela A, Múñez-Rubio E, Gutierrez-Rojas Á, Mills-Sánchez P, Ortega A, et al. Red blood cell distribution width as prognostic factor in sepsis: a new use for a classical parameter. J Crit Care. (2022) 71:154069. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2022.154069
28. Hu D, Ren J, Wang G, Gu G, Li G, Liu S, et al. Value of red cell distribution width for assessing disease activity in crohn’s disease. Am J Med Sci. (2015) 349:42–5. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0000000000000334
29. Chen C, Zhong S, Wu Z, Tang H, Wang Z, Jiang D. Investigation of the relationship between red blood cell distribution width and mortality in patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective study. Sao Paulo Med J. (2023) 141:e2022190. doi: 10.1590/1516-3180.2022.0190.R1.17102022
30. Chen X, Wang S, Yang J, Wang X, Yang L, Zhou J. The predictive value of hematological inflammatory markers for acute kidney injury and mortality in adults with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective analysis of 585 patients. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 122:110564. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110564
31. Yao H, Lian L, Zheng R, Chen C. Red blood cell distribution width/platelet ratio on admission as a predictor for in-hospital mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a retrospective analysis from MIMIC-IV database. BMC Anesthesiol. (2023) 23:113. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02071-7
32. Liu J, Huang X, Yue S, Wang J, Ye E, Huang J, et al. Association of red cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio and mortality in patients with sepsis. Mediators Inflamm. (2022) 2022:4915887. doi: 10.1155/2022/4915887
33. Huang J, Yin G, Duan L, Tian T, Xu J, Wang J, et al. Prognostic value of blood-based inflammatory biomarkers in secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Clin Immunol. (2020) 40:718–28. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00801-x
34. Wang S, Yang L, Zhou J, Yang J, Wang X, Chen X, et al. A prediction model for acute kidney injury in adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:987916. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.987916
35. Pan H, Huo Y, Sun L. Comparison between clinical features and prognosis of malignancy- and non-malignancy-associated pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. BMC Pediatr. (2019) 19:468. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1702-5
36. Lee BK, Ryu S, Oh SK, Ahn HJ, Jeon SY, Jeong WJ, et al. Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio as a prognostic factor in lower respiratory tract infection patients. Am J Emerg Med. (2022) 52:54–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.11.028
37. Xu H, Lin T, Ai J, Zhang J, Zhang S, Li Y, et al. Utilizing the lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio for survival prediction in patients with bladder cancer after radical cystectomy. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:1733–44. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S384338
Keywords: hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, prognostic factors, LAR, RPR, children
Citation: Luo N, Xie X, Chen Y, Du Z and Huang P (2025) Prognostic value of blood inflammatory composite markers in the survival of pediatric patients with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Front. Pediatr. 13:1458490. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1458490
Received: 2 July 2024; Accepted: 7 July 2025;
Published: 24 July 2025.
Edited by:
Marvyn T. Koning, Leiden University, NetherlandsReviewed by:
Shulan Zhang, Peking Union Medical College Hospital (CAMS), ChinaRui Zhang, Capital Medical University, China
Copyright: © 2025 Luo, Xie, Chen, Du and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zuochen Du, ZHpjOTAzNkAxMjYuY29t; Pei Huang, ZmVuZ2xpbjQ2MjBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Nandu Luo
Nandu Luo Xin Xie1,2,3,†
Xin Xie1,2,3,† Zuochen Du
Zuochen Du Pei Huang
Pei Huang