- 1Department of Neonatology, Jinan Children’s Hospital, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
Background: Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is a disease of high mortality and morbidity. The neutrophil ratio (NR), a key indicator, is widely used in clinical practice. However, the relationship between dynamically changing NR and the short-term prognosis of HIE is unclear. We aimed to explore the dynamic changes and potential classifications of NR over time using trajectory analysis and to investigate its relationship with the short-term prognosis of HIE.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of medical records from patients at Shandong University Affiliated Children's Hospital from 2014 to 2022. NR trajectories were modeled in 605 HIE infants using latent growth mixture modeling from 0 to 4 weeks. Then using logistic regression analyze the relationship between NR trajectories and the short-term outcome of HIE. Finally, restricted cubic spline regression model were used to assess the nonlinear relationship between baseline NR and the outcome.
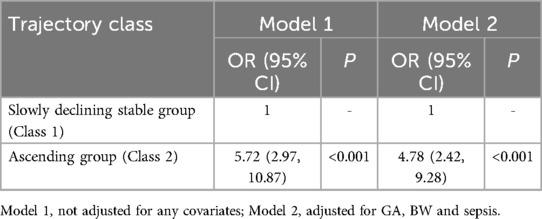
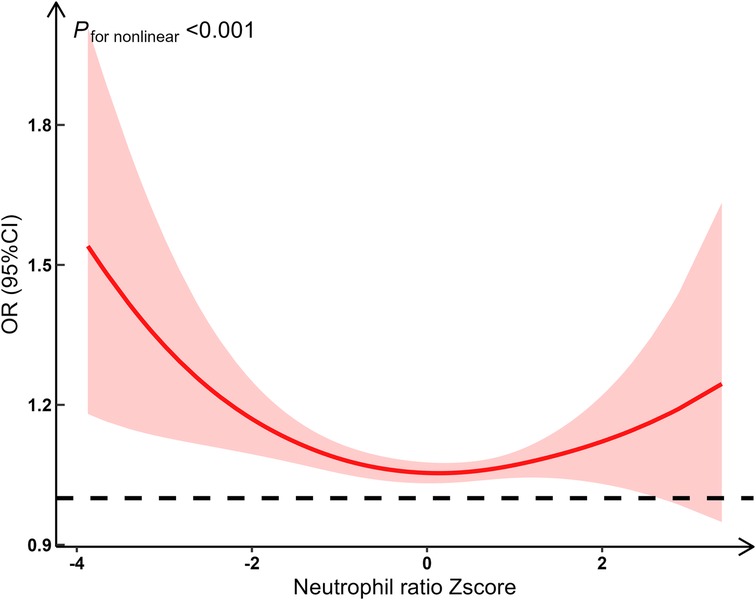
Results: Two distinct NR trajectories could be modeled, a descending (class 1) and a ascending group (class 2). The ascending group (class 2) was associated with the poor outcome (OR 5.72, 95% CI 2.97–10.87, P < 0.001; ORadj 4.78, 95% CI 2.42–9.28, P < 0.001). A significant nonlinear relationship between NR and the risk of poor outcomes (F = 13.16, P < 0.001), potentially exhibiting a U-shaped relationship.
Conclusion: The ascending NR group was strongly associated with poorer short-term outcomes. And both low and high NRs at baseline were associated with increased risk of poorer short-term outcomes.
Introduction
Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is defined as a type of brain dysfunction that occurs when an infant's brain does not receive enough oxygen and blood flow around the time of birth (1, 2). HIE affects approximately one to eight per 1,000 live newborns worldwide (3), and is one of the leading causes of persistent central nervous system injury, resulting in significant newborn mortality or neurodevelopmental impairment (4). Infants with moderate HIE have a 10% mortality rate, while 30% of survivors experiencing impairments (5). For severe HIE, the mortality rate climbs to 60%, with nearly all survivors suffering from epilepsy and neurodevelopmental issues such as cerebral palsy and intellectual disability (6).
Neutrophils play an important role in the body's immune response and inflammation. Some clinical analysis studies have shown that neutrophils were associated with HIE (7–14), including poorer neurological outcomes and aggravation of brain injury (10). Additionally, some animal experiments (13, 15–19) have explored the mechanisms through which neutrophils contribute to HIE. Neutrophils as the most abundant leukocytes in circulation and the first peripheral immune cells to reach the injured brain were highly involved in regulating neuroinflammatory responses and neuronal apoptosis after brain injury (15, 19, 20).
However, these clinical analysis studies typically measured neutrophils at a single time point (e.g., on admission or at the peak of illness severity), ignoring their dynamic changes over time. Research on the dynamic changes of neutrophils in relation to HIE appeared to be scarce. The neutrophil ratio (NR), which was the ratio of neutrophils to the total number of white blood cells, serves as a key indicator among neutrophil-related metrics. It was widely used in clinical practice because it accounts for individual differences more effectively than absolute value indicators. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the dynamic changes and potential classifications of NR over time using trajectory analysis and to investigate its relationship with the short-term prognosis of HIE.
Methods
Study population and data source
A retrospective analysis was performed of patients who diagnosed with perinatal HIE at Shandong University Affiliated Children's Hospital, over the period 2014 to 2022. Electronic medical records (EMRs) from this period served as the primary data source.
Data collection
Patient information was extracted from EMRs on December, 2023. Data included demographic information (such as gender, gestational age, age at admission), maternal pregnancy information (including maternal complications, medications, delivery mode, placental condition, and amniotic fluid status), and general infant information (such as postnatal asphyxia, Apgar scores, etc.). NR was collected for each patient from admission to discharge. Multiple laboratory examination data points were included.
Data preprocessing
Because more than 90% of the time of NR detection occured within the first 4 weeks of life, we selected NR data detected within the first 3 weeks of life for analysis. Age in weeks was used for trajectory analysis model as the time unit. For each age week, the mean value of multiple tests conducted was calculated, and the age in days was recorded as the minimum value.
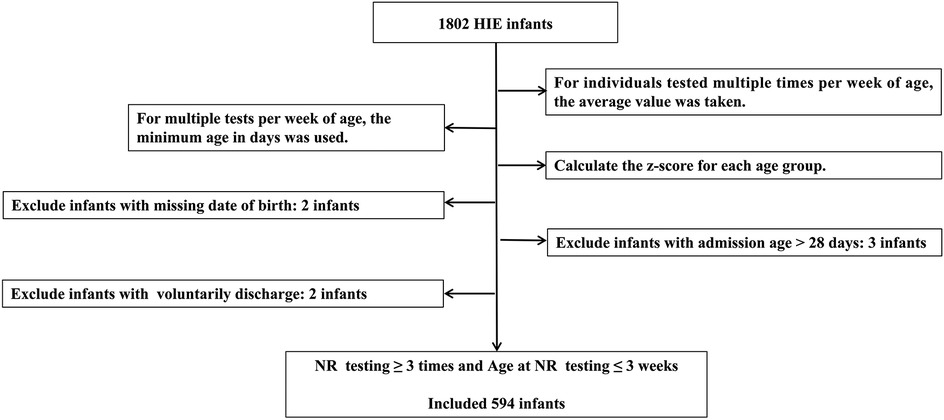
Age intervals were standardized based on age points at 3, 7, and 14 days. Excluded infants with missing birth dates, those admitted after 28 days of age, or those who voluntarily discharge. Voluntarily discharge was defined as the withdrawal of treatment by the guardian for various reasons and discharge against medical advice. The flow chart of data processing is shown in Figure 1.
Missing baseline demographic data, such as gestational age and birth weight, were imputed using a random forest algorithm. The performance of the imputation was evaluated using root mean squared error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE).
Outcome
The discharge status of the patient was used as the outcome variable of short-term prognosis. Cure and improvement were defined as good outcomes, while uncure and death were defined as poor outcomes.
Cure was defined as the complete resolution of symptoms, absence of clinical abnormalities, normal neurological reflexes and muscle tone, and no notable abnormalities on neuroimaging, or only minor changes that do not affect function. Patients meeting the criteria for cure required no special follow-up, aside from routine developmental monitoring.
Improvement was defined as a significant reduction in symptoms with potential mild neurological abnormalities or developmental delay, partial improvement of lesions on neuroimaging with minor residual abnormalities, and neurological examination findings that may show mild deviations without substantial impact on daily life. Patients in the improvement category typically required regular follow-up to assess neurological development.
Uncure was defined as the persistence of symptoms or only partial relief with notable neurological abnormalities, such as seizure activity, severe muscle tone abnormalities, or marked developmental delay. Neuroimaging findings in this group typically showed significant lesions with no evident improvement, indicating ongoing brain injury. Neurological examination often revealed significant abnormalities in reflexes and muscle tone, potentially impacting daily life and development. These patients generally required continued medical intervention and close follow-up. Death was defined as mortality during hospitalization due to HIE progression or related complications.
Statistical analysis
Trajectory analysis
The Latent Growth Mixture Modeling (LGMM) (21) was employed to explore the temporal patterns of NR changes and identify distinct latent growth trajectory groups. LGMM can identify latent heterogeneity within the data by assigning individuals to different latent classes, each characterized by a unique growth trajectory. Individuals are assigned a probability of belonging to each class and then assigned to the class for which they have the highest probability of membership. If a subject did not have any measurements in a specific time period, they were excluded from contributing to the estimation of the mean trajectory and not allocated a class for that age range. If a subject had 1 or more measurements in a specific time period, their information did contribute to the calculation of mean trajectories in that age range using full information maximum likelihood.
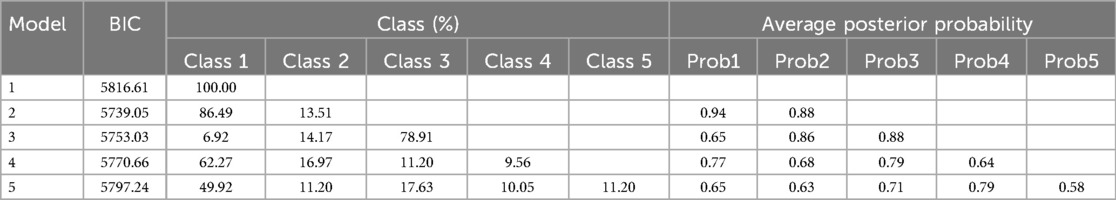
Based on mean posterior probabilities >0.7 for each group, a group size >5.0%, and the lowest Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), the optimal number of trajectory groups and the best-fit model were determined (22).
Logistic regression analysis
Primary analysis was conducted using the imputed data. For continuous data, normality was assessed using a Shapiro–Wilk test. Data conforming to a normal distribution were described using mean ± standard deviation, and inter-group comparisons were conducted using t-tests. Skewed data were described using the median, and inter-group comparisons were performed using Wilcoxon rank sum test. Count data were described using frequencies and proportions, and inter-group comparisons were evaluated using the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test.
Logistic regression models were developed: Model 1 included trajectory groups as predictors without adjusting for other variables, while Model 2 adjusted for significant variables identified in the univariate analysis.
Restricted cubic spline regression models were used to assess the nonlinear relationship between baseline NR and the outcome. The number of nodes was determined based on the minimum Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), and dose-response and nonlinear curves were plotted accordingly.
Sensitivity analysis
In sensitivity analysis, we repeated the analysis using the non-imputed data to observe consistency with the imputed data results and assess the stability of the results.
Statistical analyses were performed using R version 4.3.1, and statistical significance was defined as a P value of 0.05.
Results
Developmental trajectories
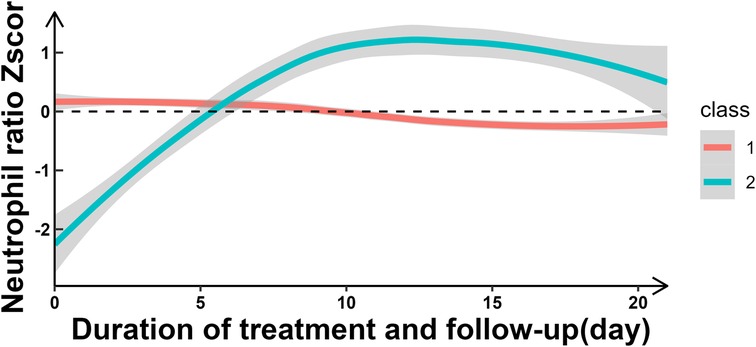
Two distinct NR trajectories could be modeled, each with an average posterior probability greater than 0.7 (0.93 and 0.82, respectively). The trajectory group sizes were all greater than 5% (87.04% and 12.96%, respectively), and the BIC was minimum. These two NR trajectories were classified as the slowly declining stable group (class 1-red line) and ascending group (class 2-green line) (Figure 2, Table 1).
Baseline demographics
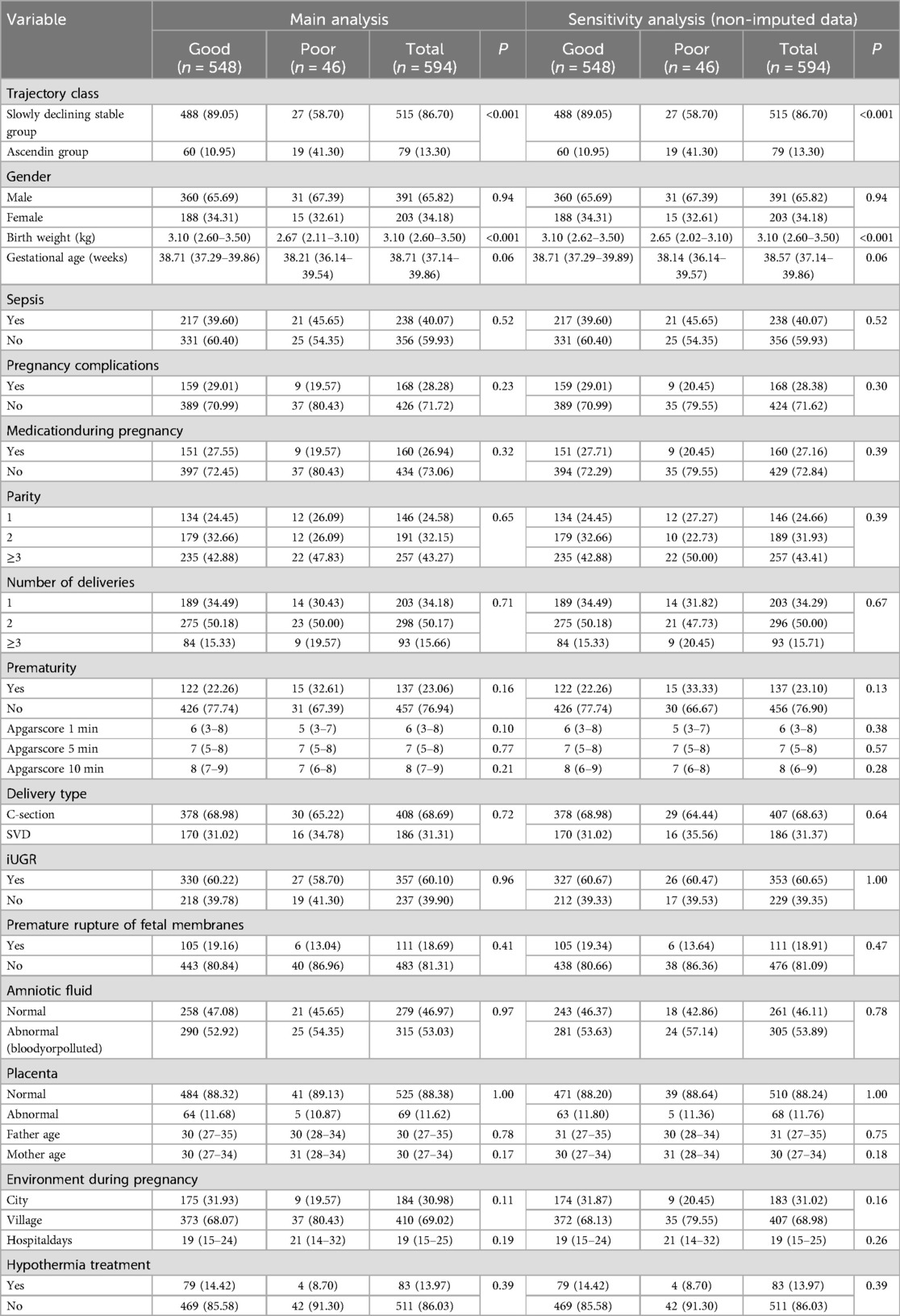
In the full cohort (n = 594, 65.82% were male, median birth weight (BW) was 3.10 kg [interquartile range (IQR) 2.60–3.50], median gestational age (GA) was 38.71 (37.14–39.86) weeks, 28.28% had pregnancy complications, 26.94% had a medication history during pregnancy, 24.58% were firstborns, 34.18% were first deliveries, 23.06% was premature, the median 5-minute Apgar scores were 7 (5–8), 68.69% were delivered by cesarean section, 60.10% had intrauterine distress, 18.69% had premature rupture of membranes, 53.03% had amniotic fluid contamination or bloody amniotic fluid, 11.62% had abnormal placentas, the median ages of the fathers and mothers were 30 (27–35) and 30 (27–34) years respectively, 69.02% lived in village, 13.97% received hypothermia therapy, and the median hospital stay was 19 (15–25) days (Table 2).
Baseline demographics by outcome groups
The differences between the outcome groups (good/poor) in trajectory class, birth weight (kg) and gestational age (weeks) were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Other variables were not statistically significant (Table 2).
The ascending group comprises 10.95% and 41.30% of the good and poor group, respectively. The median BW was 3.10 (2.63–3.50) kg and the median GA was 38.71 (37.29–39.86) weeks for the good group, 2.67 (2.11–3.10) kg and 38.21 (36.14–39.54) weeks for the poor. Prematurity account for 22.26% and 32.61% of the good and poor group, respectively.
Logistic regression results
Compared to class 1 (“slowly declining stable group”), class 2 (“ascending group”) was associated with the poor outcome (OR 5.72, 95% CI 2.97–10.87, P < 0.001) (Table 3, Supplementary Tables S1, S2), without adjustment. With adjusted for GA, BW and sepsis, class 2 (“ascending group”) was also associated with the poor outcome (OR 4.78, 95% CI 2.42–9.28, P < 0.001) (Table 3, Supplementary Table S3).
Nonlinear relationship between baseline NR and the outcomes
We fitted restricted cubic spline functions with 3–7 knots. Finally, 3 knots (located at the 10th, 50th, and 90th percentiles on the x-axis) were selected to capture potential nonlinear effects, with the lowest BIC (BIC was 329.07, 331.94, 335.74, 341.22 and 343.18, respectively). Using restricted cubic spline analysis with 3 knots, we found a significant nonlinear relationship between NR and the risk of poor outcomes (F = 13.27, P < 0.001). Specifically, the risk of poor outcomes significantly increased when the NR was either low or high, while the risk remained relatively stable at intermediate levels. This suggests that the relationship between NR and the risk of poor outcomes is not linear, potentially exhibiting a U-shaped relationship (Figure 3).
Sensitivity analysis
Results were consistent with the primary results, when defining voluntary discharge as a poor outcome, and when using non-imputed data (Table 2, Supplementary Tables S4–S6).
Discussion
In this study, we have made several important findings about NR and short-term prognosis of HIE. First, the NR over time could be classified into two classes: slowly declining stable group (Class 1) and increasing group (Class 2). Second, compared to the slowly declining stable group, the increasing group was a risk factor for short-term poor outcomes. The likelihood of short-term adverse outcomes in the increasing group was 4.78 times [ORadj (95% CI): 4.78 (2.43, 9.27)] higher than that in the decreasing group. Third, there appeared to be a U-shaped relationship between NR and short-term poor outcomes.
Based on LGMM trajectory analysis, we found that NR exhibited dynamic changes over time and primarily manifested in two distinct patterns, a slowly declining stable group (Class 1) and a increasing (Class 2) group. And the increasing NR group was a risk factor for short-term poor outcomes in perinatal HIE, which was similar to findings by Povroznik et al. (7, 8). However, while their study provided a simple description of absolute number changes, we not only described dynamic changes but also classified them based on their different patterns of variation. Mechanisms underlying this association may include: (1) perinatal hypoxia–ischemia causeed a rapid increase of circulating neutrophils followed by pronounced infiltration into the injured brain parenchyma (11, 13, 23), and (2) Neonatal neutrophils were activated in the hypoxic-ischemic brain (11, 13). This discovery hold important implications for clinical practice, potentially providing a biomarker for assessing short-term prognosis in HIE patients. In clinical practice, an elevated NR as a prognostic indicator may aid in early identification of high-risk patients and guide personalized treatment decisions.
We observed a non-linear U-shaped relationship between NR and short-term poor outcomes of perinatal HIE. Elevated NR above standard levels increased the risk of poor HIE outcomes, consistent with previous findings (7, 8) that associate higher NR with exacerbated neurological damage progression. High NR may reflect an excessive inflammatory response, leading to poor prognosis. Toptan, showed neutrophil infiltration at early stages was crucial for exacerbating brain injury in newborns caused by hypoxic-ischemic, a condition in which inflammation heightens brain damage (24). Some studies observed an increased infiltration of neutrophils in the brain after exposure to HI (13, 15–19). Conversely, lower-than-standard NR also increased the risk of poor HIE outcomes, although there was limited literature directly linking low NR to HIE prognosis. Neutrophils played a positive role in defending against infections such as antibacterial (25), antifungal (26), and antiviral (27). And neutrophils had functions such as phagocytosing damaged tissues, clearing apoptotic cell debris, localizing the damage, and facilitating tissue regeneration and angiogenesis after injury (28). Reduced or insufficient neutrophils may limit these functions, thereby also leading to poor prognosis.
This study has several strengths. Firstly, to the best of our knowledge, this was the first study to use trajectory analysis to classify changes in the NR. Each category represented a different population, with significant association between the increasing NR group and short-term poor outcomes in perinatal HIE. Additionally, the study explored the non-linear U-shaped relationship between NR and HIE short-term outcomes. These founding may offer new insights into the diagnosis and treatment of HIE.
Limitations
Our study also has several limitations. First, our study focused on analyzing the dynamic trajectory of NR during the first 3 postnatal weeks and its relationship with short-term HIE outcomes. It should be noted that our findings may not be directly applicable to clinical decision-making requiring immediate intervention within the critical first 72 h after birth. However, many studies have investigated the relationship between a single-time-point NR within 72 h after birth and HIE outcomes. These studies focused solely on the association between NR at a specific time point and HIE outcomes, whereas our research emphasizes the dynamic trend of NR changes in relation to short-term HIE outcomes, thereby forming a complementary perspective. Second, its retrospective design may introduce biases related to data collection and patient selection; however, our data were entirely based on EMRs, which are relatively objective and accurate. Third, as the study was conducted at a single institution, the findings may have limited generalizability; however, our institution treats the majority of HIE patients in the city and even the province. Four, maternal data were limited due to the nature of our institution as a children's hospital and the retrospective cohort design, making it challenging to trace and supplement this information. In the future, we plan to conduct a prospective study to collect and supplement detailed maternal medical history in real-time. Additionally, the focus on short-term prognosis means that longer-term outcomes were not evaluated. We have already established a follow-up system to monitor the long-term prognosis of such patients and plan to conduct further research.
Conclusion
This study observed the significant role of the NR in short-term outcomes of perinatal HIE. Through trajectory analysis, we identified two distinct patterns of NR changes over time: a slowly declining stable group and an ascending group. Our findings revealed that the ascending NR group was strongly associated with poorer short-term outcomes. Additionally, we observed a U-shaped relationship between NR and short-term outcomes, indicating that both low and high NRs were associated with increased risk. These insights underscored the importance of monitoring NR dynamics in clinical practice to better assess prognosis and guide personalized treatment decisions for HIE patients. Future research should aim to validate these findings in larger, multi-center studies and explored the underlying mechanisms driving these associations.
Data availability statement
Anonymized individual participant data will be made available to researchers who provide a methodologically sound proposal.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Children's Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University/Jinan Children's Hospital (SDFE-IRB/P-2022060). All personal data collected during the research were anonymized to strictly protect the privacy of the participants.
Author contributions
YLi: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YLa: Data curation, Writing – original draft. KD: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DZ: Writing – review & editing. LK: Writing – review & editing. XL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. XL was supported by the Big Data Science and Technology Development Program of Jinan Municipal Health Commission (Grant 2022-BD-14).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2025.1555981/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
HIE, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; NR, neutrophil ratio (NR); EMRs, electronic medical records; RMSE, root mean squared error; MAE, mean absolute error; LGMM, the latent growth mixture modeling; BIC, Bayesian information criterion; APGAR, appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration; OR, odd ratio; CI, confidence interval; BW, birth weight; GA, gestational age.
References
1. Finer NN, Robertson CM, Richards RT, Pinnell LE, Peters KL. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in term neonates: perinatal factors and outcome. J Pediatr. (1981) 98(1):112–7. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(81)80555-0
2. Dhillon SK, Wassink G, Lear CA, Davidson JO, Holford NHG, Gunn AJ, et al. The effect of size, maturation, global asphyxia, cerebral ischemia, and therapeutic hypothermia on the pharmacokinetics of high-dose recombinant erythropoietin in fetal sheep. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(9):3042. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093042
3. Lee AC, Kozuki N, Blencowe H, Vos T, Bahalim A, Darmstadt GL, et al. Intrapartum-related neonatal encephalopathy incidence and impairment at regional and global levels for 2010 with trends from 1990. Pediatr Res. (2013) 74(Suppl 1):50–72. doi: 10.1038/pr.2013.206
4. Ferriero DM. Neonatal brain injury. N Engl J Med. (2004) 351(19):1985–95. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra041996
5. Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, et al. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. (2005) 353(15):1574–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcps050929
6. Long M, Brandon DH. Induced hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. (2007) 36(3):293–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6909.2007.00150.x
7. Povroznik JM, Engler-Chiurazzi EB, Nanavati T, Pergami P. Absolute lymphocyte and neutrophil counts in neonatal ischemic brain injury. SAGE Open Med. (2018) 6:2104824613. doi: 10.1177/2050312117752613
8. Yao H, Kuan C. Early neutrophil infiltration is critical for inflammation-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in newborns. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2020) 40(11):2188–200. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19891839
9. Morkos AA, Hopper AO, Deming DD, Yellon SM, Wycliffe N, Ashwal S, et al. Elevated total peripheral leukocyte count may identify risk for neurological disability in asphyxiated term neonates. J Perinatol. (2007) 27(6):365–70. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211750
10. Liu F, McCullough LD. Inflammatory responses in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2013) 34(9):1121–30. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.89
11. Mulling K, Fischer AJ, Siakaeva E, Richter M, Bordbari S, Spyra I, et al. Neutrophil dynamics, plasticity and function in acute neurodegeneration following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Brain Behav Immun. (2021) 92:234–44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.012
12. Fox SE, Lu W, Maheshwari A, Christensen RD, Calhoun DA. The effects and comparative differences of neutrophil specific chemokines on neutrophil chemotaxis of the neonate. Cytokine. (2005) 29(3):135–40. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2004.10.007
13. Bernis ME, Zweyer M, Maes E, Schleehuber Y, Sabir H. Neutrophil extracellular traps release following hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in newborn rats treated with therapeutic hypothermia. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(4):3598. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043598
14. Mohamud YA, Hagemann N, Ludewig P, Gunzer M, Hermann DM. Roles of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in ischemic brain injury and post-ischemic brain remodeling. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:825572. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.825572
15. Shi G, Liu L, Cao Y, Ma G, Zhu Y, Xu J, et al. Inhibition of neutrophil extracellular trap formation ameliorates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via STING-dependent IRE1alpha/ASK1/JNK signaling pathway in mice with traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. (2023) 20(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02903-w
16. Mi L, Min X, Shi M, Liu L, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps aggravate neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis via TLR9 after traumatic brain injury. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14(6):374. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05898-7
17. Jin J, Wang F, Tian J, Zhao X, Dong J, Liu Z, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to coagulopathy after traumatic brain injury. JCI Insight. (2023) 8(6):e141110. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.141110
18. Denorme F, Portier I, Rustad JL, Cody MJ, de Araujo CV, Hoki C, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps regulate ischemic stroke brain injury. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132(10):e154225. doi: 10.1172/JCI154225
19. Li C, Xing Y, Zhang Y, Hua Y, Hu J, Bai Y. Neutrophil extracellular traps exacerbate ischemic brain damage. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59(1):643–56. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02635-z
20. Liu Y, Li S, Dai S. Neutrophils in traumatic brain injury (TBI): friend or foe? J Neuroinflammation. (2018) 15(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1173-x
21. Van De Schoot R, Sijbrandij M, Winter SD, Depaoli S, Vermunt JK. The GRoLTS-checklist: guidelines for reporting on latent trajectory studies. Struct Equ Modeling. (2016) 24(3):451–67. doi: 10.1080/10705511.2016.1247646
22. Kim SY. Determining the number of latent classes in single- and multi-phase growth mixture models. Struct Equ Modeling. (2014) 21(2):263–79. doi: 10.1080/10705511.2014.882690
23. Smith P, Mottahedin A, Svedin P, Mohn CJ, Hagberg H, Ek J, et al. Peripheral myeloid cells contribute to brain injury in male neonatal mice. J Neuroinflammation. (2018) 15(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1344-9
24. Toptan HH, Tezel KG, Tezel O, Ataç Ö, Vardar G, Gülcan Kersin S, et al. Inflammatory and hematologic liver and platelet (HALP) scores in hypothermia-treated hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). Children. (2024) 11(1):72. doi: 10.3390/children11010072
25. Thanabalasuriar A, Scott B, Peiseler M, Willson ME, Zeng Z, Warrener P, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps confine Pseudomonas aeruginosa ocular biofilms and restrict brain invasion. Cell Host Microbe. (2019) 25(4):526–36. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.02.007
26. Song Z, Huang G, Chiquetto Paracatu L, Grimes D, Gu J, Luke CJ, et al. NADPH oxidase controls pulmonary neutrophil infiltration in the response to fungal cell walls by limiting LTB4. Blood. (2020) 135(12):891–903. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003525
27. Iversen MB, Reinert LS, Thomsen MK, Bagdonaite I, Nandakumar R, Cheshenko N, et al. An innate antiviral pathway acting before interferons at epithelial surfaces. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17(2):150–8. doi: 10.1038/ni.3319
Keywords: perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, neutrophil ratio, trajectory analysis, nonlinear, short-term outcome
Citation: Li Y, Lang Y, Deng K, Zhou D, Kang L and Li X (2025) Neutrophil ratio trajectory and the short-term outcome of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Front. Pediatr. 13:1555981. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1555981
Received: 6 January 2025; Accepted: 2 June 2025;
Published: 17 June 2025.
Edited by:
Helga Elineema Naburi, Muhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences, TanzaniaReviewed by:
Neema Passian Chami, Catholic University of Health and Allied Sciences, TanzaniaYaser Abdallah, Aga Khan University, Tanzania
Van Hop Ta, University Hospital Essen, Germany
Copyright: © 2025 Li, Lang, Deng, Zhou, Kang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lili Kang, bGlseWtldHl5QDE2My5jb20=; Xiaoying Li, bHh5X2puQGVtYWlsLnNkdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yunxia Li
Yunxia Li Yujie Lang1,2,†
Yujie Lang1,2,† Xiaoying Li
Xiaoying Li