- 1Department of Hematology, Jiangsu Province (Suqian) Hospital, Suqian, Jiangsu, China
- 2Department of Nephrology, Jiangsu Province (Suqian) Hospital, Suqian, Jiangsu, China
Background: Infectious mononucleosis (IM) and mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) are common pediatric diseases that can easily trigger immune responses. This study aims to detect peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets through flow cytometry and explore the diagnostic value in IM and MPP.
Methods: This retrospective study using electronic medical records included a total of 86 children with IM, 150 children with MPP, and 120 healthy volunteers. Lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood were quantitatively detected by flow cytometry, covering lymphocyte ratio, CD8+, CD4+, CD3+, CD4/CD8, CD19, and CD16 + cells. The diagnostic value of these markers was analyzed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
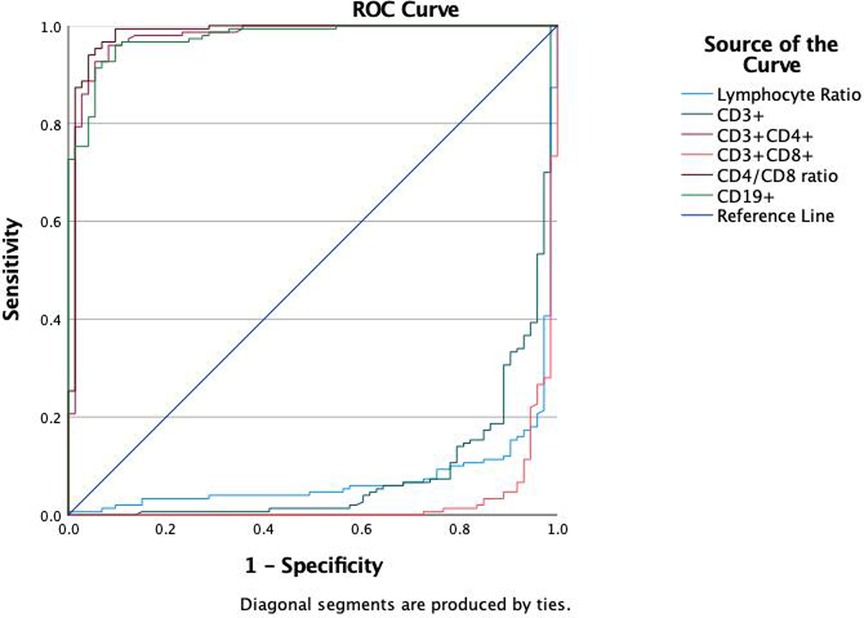
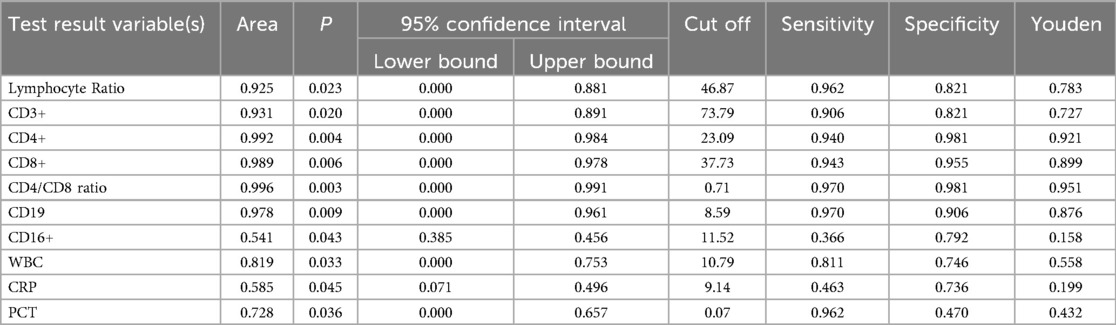
Results: Compared with the HC and IM groups, the MPP group had a significantly lower lymphocyte ratio (P < 0.01). In the MPP group, CD8 + and CD3 + lymphocyte proportions were significantly reduced (P < 0.01), while CD4+/CD8 + ratio, CD4 + and CD19+ B cell levels were significantly higher than those of the IM and HC groups (P < 0.01). In the comparison between MPP and IM, ROC analysis showed that CD3+ T cells (AUC = 0.931), CD3 + CD8+ T cells (AUC = 0.989), CD4/CD8 ratio (AUC = 0.996), CD3 + CD4+ T cells (AUC = 0.992), lymphocyte ratio (AUC = 0.925), and CD19+ B cells (AUC = 0.978) all had excellent diagnostic value.
Conclusion: Peripheral blood lymphocyte subset analysis could serve as a precise and efficient diagnostic tool to directly distinguish between MPP and IM.
Introduction
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is a disease caused by Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). The primary mode of infection is via saliva transmission. Infection with EBV is common in children, and the initial infection typically presents as IM, especially more prevalent during adolescence (1, 2). It is currently widely accepted that a significant increase in the number of EBV-specific CD8 + cells is a notable feature of IM. Variations in the proportions of other cell subsets has not been fully clarified (3). In IM, peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets exhibit dynamic alterations during disease progression (4). EBV preferentially targets B cells, inducing their necrosis or apoptosis. Concurrently, CD8+ T cells are activated to eliminate virus-infected cells (5–9), thereby contributing to a reduction in the CD4+/CD8 + ratio (4, 10). While CD4 + and CD8+ T cells are critical in preventing viral reactivation from latency, the precise mechanisms underlying this regulatory function remain incompletely understood and warrant further investigation (11). Although the acute symptoms of IM are typically self-limiting and can usually resolve on their own without specific antiviral therapy, serious complications may occur without appropriate clinical monitoring and supportive care (12).
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) is a significant cause of community-acquired pneumonia in children, comprising 10%–40% of cases, with most occurrences in children over five years old (13, 14). Mycoplasma pneumonia is a significant pathogen responsible for human pneumonia. It has a high incidence rate and is frequently observed in children experiencing respiratory infections. It frequently occurs in children with respiratory tract infections, having a high incidence rate. It can severely affect children's growth, development, and overall health (15). This disease is mostly of the subacute type. In the early stage, the main symptoms are headache and an irritating dry cough. multi-organ dysfunction and death can occur as the disease progresses (16). Neutrophils play a key role in innate immunity and are closely related to the development of inflammatory responses (17). Past research has found that in children with sMPP, the number of neutrophils in peripheral blood increases, and there is also a significant infiltration of neutrophils in lung tissue. The worsening of MPP is associated with immune reactions mediated by neutrophils (18–20). When the neutrophil count is lower it usually corresponds to a milder degree of disease (21).
The pathophysiology of IM and MPP in children is closely related to the immune response, and lymphocyte subsets play a key role in this process. Recent meta-analyses have further highlighted the potential diagnostic and prognostic utility of flow cytometry-based immune profiling in pediatric infections (22, 23). Although both IM and MPP involve significant immune activation, the underlying mechanisms differ: a constitutive attribute of IM is a robust CD8+ T-cell response driven by EBV-infected B cells, whereas the pathogenesis of MPP involves neutrophil-mediated inflammation and an unbalanced CD4 + -dominated T-cell response. There is a lack of simple clinical indicators to assess the prognosis of IM and MPP in children. There is an urgent clinical need to find simple and effective clinical indicators to accurately distinguish between IM and MPP in children.
This study used flow cytometry to detect peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in children with IM and MPP. It aimed to explore the diagnostic value of different lymphocyte subsets for IM and MPP patients to distinguish between these two diseases.
Materials and methods
General information
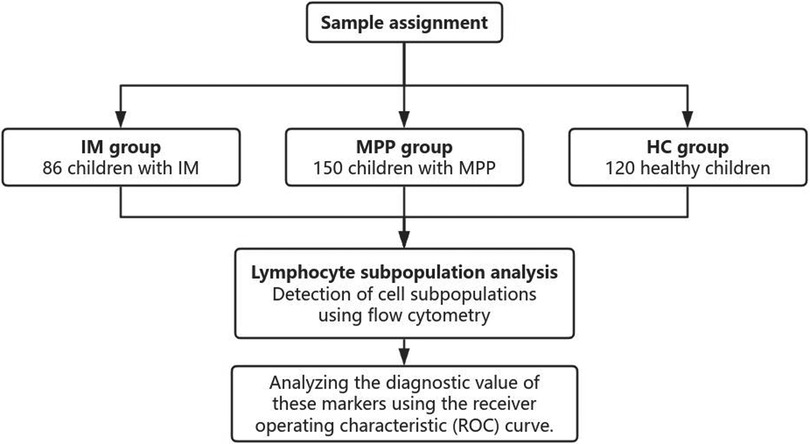
The retrospective study collected the electronic medical records of a total of 356 patients between December 2022 and December 2024 including 86 patients with IM, 150 patients with MPP and 120 health controls (HC) (Figure 1). Healthy controls were children undergoing routine health check-ups at Suqian Hospital during the same study period with no active infections or immunological disorders. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Suqian Hospital (2025-SR-0058), and informed consent was obtained from all patients’ parents or legal guardians.
Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria for IM required the presence of any three of the following clinical indicators: (1) eyelid edema; (2) pharyngotonsillitis; (3) splenomegaly; (4) cervical lymph node enlargement; (5) fever; (6) hepatomegaly. In addition, patients with IM must fulfill at least one of the following criteria: (1) more than fourfold increase in serum EBV VCA IgG from baseline; (2) positive blood EBV DNA PCR; and (3) positive serum EBV VCA IgM antibody (24).
Inclusion criteria for MPP were as follows: (1) all children included in the study had not received any prior antimycoplasma pneumoniae or anti-infection treatments. (2) the study subjects exhibited symptoms such as cough, fever, and sputum expectoration. (3) diagnosis of MPP was confirmed by a combination of clinical criteria, including chest imaging (such as CT scans) showing unilateral pneumonia and positive results from Mycoplasma pneumoniae-specific nucleic acid tests conducted on nasopharyngeal aspirates (18, 25).
Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria are as follows: (1) Patients with hematological malignancies or terminal solid tumors; (2) Absence of complete blood count data within 24 hours of admission; (3) Patients who have received organ transplantation, or used hormones, cytotoxic agents, or immunosuppressive drugs within the past two weeks; (4) Patients who choose to stop treatment, discharge themselves, or transfer to other hospitals; (5) Hospitalization duration of less than 24 hours.
Research methodology
Reagents and instruments
The fluorescent antibodies including CD3-FITC, CD16 + CD56-PE, CD45-PerCP-Cy5.5, CD4-PC7, CD19-APC, and CD8APC-Cy7 were acquired from Beijing Tongsheng Times Biotechnology Co. The samples were analyzed on a NAVIOS dual-laser, eight-color flow cytometer (Beckman, USA).
Flow cytometry analysis
2 ml of fasting venous blood was collected within 8 h of patient admission and heparin sodium was added to prevent clotting. Take 100 μl of the anticoagulated blood sample and use the microsphere counting tube and add the following reagents (20 μl each) respectively: CD3, CD16 + CD56, CD45, CD4, CD19 and CD8. Allow the mixture to incubate for 15 minutes at room temperature. Add 2.0 ml of lysing agent to the mixture and incubate in the dark at room temperature for an additional 10 minutes. After incubation, centrifuge the mixture at 300 g for 5 minutes and discard the supernatant. Wash the cells twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), each time adding 1 ml of PBS. Resuspend the processed cell sample and transfer it to a flow cytometer, following the instrument's operating instructions. Analyze 15,000 lymphocytes using flow cytometry to evaluate their fluorescent signals and use the data to accurately determine the percentages of lymphocyte subpopulations in peripheral blood. Data was collected and analyzed using Navios software and the statistical software.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 27.0. Homogeneity of variance testing showed statistically significant variance differences (P < 0.05). Tamhane's test was used for non-homogeneous groups, and LSD analysis for homogeneous groups (P > 0.05). Data are presented as mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA was used for multiple group comparisons, with P < 0.05 indicating statistical significance. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed using SPSS 27.0 to assess the diagnostic potential of peripheral blood immune cell ratios. The p-values in ROC analysis denote the statistical significance of the AUC against a null hypothesis value of 0.5 (AUC > 0.8 indicates diagnostic utility).
Result
Comparison of lymphocyte composition in the IM, MPP and HC groups
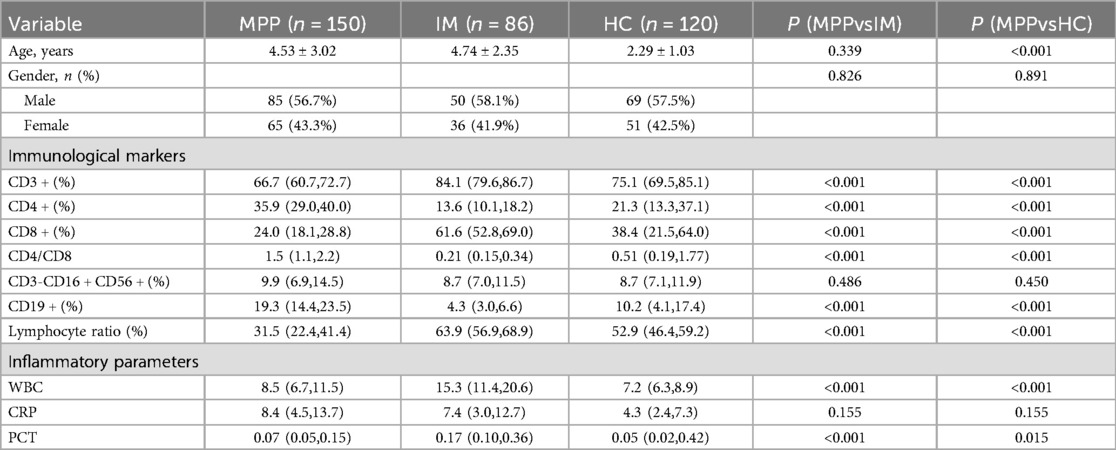
A total of 86 children with IM, 150 children with MPP, and 120 healthy control (HC) children were included in this study (Table 1). Compared with the HC and IM groups, the MPP group exhibited a significantly lower lymphocyte ratio (P < 0.01) (Table 1). In the MPP group, the proportions of CD8 + and CD3 + lymphocytes were significantly reduced (P < 0.01) (Table 1). The levels of CD4 + and CD19+ B cells in the MPP group were significantly elevated (P < 0.001) (Table 1). The CD4+/CD8 + ratio of the MPP group was significantly higher than those of the IM and HC groups (P < 0.01) (Table 1). There were no significant differences in the proportion of CD3-CD16 + CD56 + between the MPP group and the IM group, as well as between the MPP group and the HC group (P > 0.05) (Table 1).
The diagnostic value of lymphocyte subsets
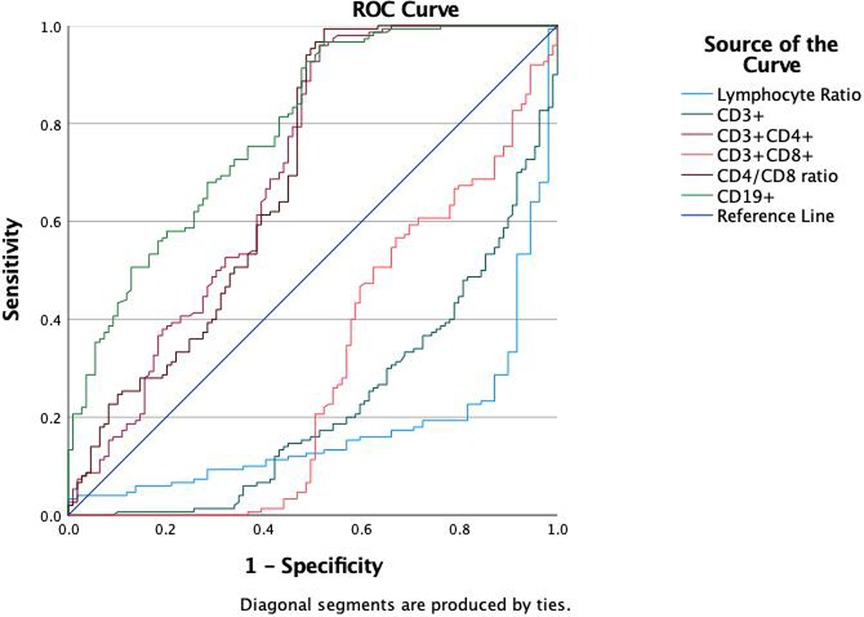
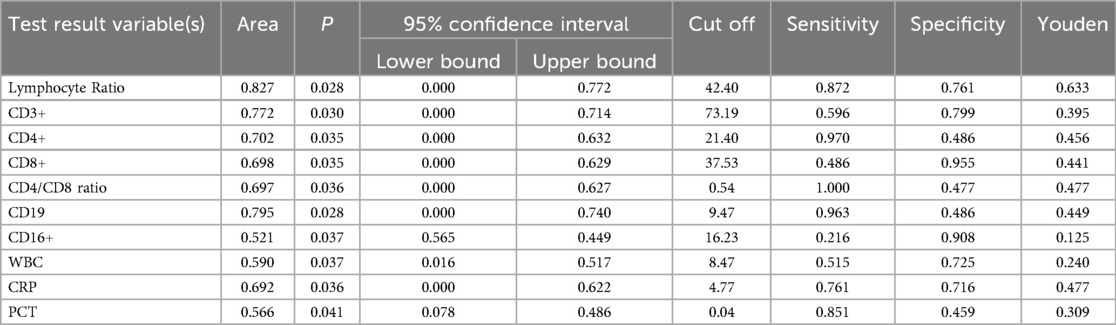
We evaluated the diagnostic efficacy of different lymphocyte subsets in distinguishing MPP, IM, and HC through ROC curve analysis (Figures 2, 3). In the comparison between MPP and IM, ROC curve analysis demonstrated that CD3+ T cells (AUC = 0.931), CD3 + CD8+ T cells (AUC = 0.989), CD3 + CD4+ T cells (AUC = 0.992), CD4/CD8 ratio (AUC = 0.996), lymphocyte ratio (AUC = 0.925), and CD19+ B cells (AUC = 0.978) all exhibited excellent diagnostic value (Figure 2, Table 2). Among these, the CD4/CD8 ratio had the highest AUC value (0.996), with a Youden index of 0.951, indicating its excellent diagnostic value (Table 2). The sensitivity and specificity of CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells both exceeded 0.9, with Youden indices of 0.921 and 0.899, indicating a high diagnostic efficacy (Table 2). In contrast, CD16 + cells had a relatively low AUC value of 0.541 and a Youden index of 0.158, indicating relatively poor diagnostic performance (Table 2). In the comparison between MPP and HC, the AUC values for CD3+ T cells, CD3 + CD8+ T cells, CD3 + CD4+ T cells and CD19 were 0.772, 0.698, 0.702, and 0.795 (Figure 3, Table 3). CD16+, WBC, CRP, and PCT showed poor diagnostic efficacy, with P values all above 0.05, indicating no significant statistical significance (Tables 2, 3).
Discussion
IM is an acute infectious disease caused by the EBV that mainly affects adolescents (1, 2). It is characterized by symptoms such as fever, pharyngitis, eyelid edema, and enlargement of lymph nodes, the liver, and the spleen. While IM is typically a self-limiting condition with a favorable prognosis, rare complications such as hemolytic anemia, neurological disorders, and malignant tumors may occur. Timely diagnosis and effective therapeutic intervention are essential for IM patients, especially pediatric patients.
In this study, we analyzed lymphocyte subsets and CBC parameters in the enrolled population. Significant differences were found in CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD19+ T cells, and lymphocyte counts among the MPP, IM, and HC groups, with distinct patterns between IM and HC. These markers may serve as diagnostic indicators. Further analysis showed that CD4+ T cells were reduced, while CD8+ T cells were elevated in IM patients, leading to a lower CD4+/CD8 + ratio. This T-cell subset imbalance may alter immune responses and disease progression. The findings indicate that abnormalities in T cell subsets could be linked to IM pathogenesis and may serve as diagnostic biomarkers.
MP infection induces immune and inflammatory damage in the host, and the severity of MPP is closely tied to the host's innate immune response to MP (26, 27). Prior research has indicated that the pathogenesis of MP infection involves excessive immune responses (18, 28). Our immune phenotyping analysis demonstrated that, compared with the HC group, the MPP group exhibited significantly reduced CD3 + and CD8 + cell counts, while the CD4 + cell count was significantly elevated, resulting in a significantly higher CD4/CD8 ratio. CD4+ T cells contribute to the immunopathology of MPP, while CD8+ T cells may help modulate inflammatory responses (29). This imbalance in T cell subsets is a notable feature in MPP patients. Moreover, the MPP group had a significantly increased CD19 + cell count and a significantly decreased lymphocyte percentage, further supporting the presence of immune dysregulation. Laboratory tests revealed that, compared with the HC group, the MPP group had significantly higher levels of WBC and PCT, reflecting systemic inflammation.
ROC curve analysis to evaluate the diagnostic ability of different lymphocyte subgroups in distinguishing MPP and IM. The results showed excellent diagnostic value with the AUC values of CD3 + CD4+ (AUC = 0.992), CD3 + CD8+ T cells (AUC = 0.989), CD4/CD8 ratio (AUC = 0.996), lymphocyte ratio (AUC = 0.925) and CD19 (AUC = 0.978) respectively. These findings suggest that specific lymphocyte subgroups and related indicators can serve as potential biological markers for differentiating disease states, offering a valuable reference for clinical diagnosis.
White blood cells serve as sensitive markers of infection and inflammation, and peripheral blood monocyte counts correlate with MPP disease severity (30, 31). Monocyte-related inflammatory mechanisms also play a role in its pathogenesis (32, 33). Our findings revealed that WBC and PCT levels were significantly higher in the IM group than in the MPP group, suggesting that the IM group may experience more pronounced inflammation or a higher risk of infection.
Immune cell analysis showed that MPP and IM share common immune system abnormalities, such as alterations in T cell subsets and changes in the CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio, which could serve as shared diagnostic markers. The proportion of CD3 + cells was significantly higher in the IM group compared to the healthy control group but slightly lower in the MPP group. The proportion of CD19+ B cells was significantly lower in the IM group and higher in the MPP group compared to the healthy control group. Monitoring disease-specific lymphocyte subsets and related indicators could act as potential biomarkers to distinguish between these two disease states, providing valuable insights for clinical diagnosis.
The standard diagnostic methods for MPP primarily include nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), such as PCR, which are highly sensitive and specific for detecting M. pneumoniae DNA from respiratory samples. Serological tests detecting antibodies (IgM and IgG) and culture methods are also used but have limitations, including delayed results and cross-reactivity. In contrast, our study utilized flow cytometry to analyze peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets, which provides a rapid and complementary diagnostic tool. This method does not replace standard tests but serves as an additional approach to enhance diagnostic accuracy by assessing the immune response, which can help differentiate MPP from other similar infections.
The limitation of this study is its single-center design with relatively small sample size. The correlation between the CD4+/CD8 + ratio and the severity of IM and MPP were not analyzed or compared. Furthermore, this study lacked longitudinal follow-up data, preventing assessment of lymphocyte subset dynamics during recovery or correlation with long-term outcomes. Additionally, there was a significant age disparity between the healthy control group (HC) and both the IM and MPP groups. As lymphocyte subset proportions are known to vary with age, this discrepancy may have confounded the comparisons between groups. Future research could adopt more analyzed prospective study designs and involve multiple centers to overcome these limitations.
Conclusion
Peripheral blood lymphocyte subset analysis serves as a precise and efficient diagnostic tool to directly and unambiguously distinguish between MPP and IM. Integrating peripheral blood lymphocyte testing into diagnostic protocols enables clinicians to improve the accuracy and assurance of their diagnoses, thereby facilitating timely intervention and more effective patient care.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Jiangsu Province (Suqian) Hospital (2025-SR-0058). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from this study is retrospective study, all data come from the retrospective cases. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
XS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft. WL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JQ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. TS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SS: Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JS: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Suqian Sci&Tech Program (KY202216), Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission (Z2023054) and Suqian Sci&Tech Program (K202422).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Balfour HH Jr, Sifakis F, Sliman JA, Knight JA, Schmeling DO, Thomas W. Age-specific prevalence of Epstein–Barr virus infection among individuals aged 6-19 years in the United States and factors affecting its acquisition. J Infect Dis. (2013) 208(8):1286–93. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit321
2. Jayasooriya S, de Silva TI, Njie-jobe J, Sanyang C, Leese AM, Bell AI, et al. Early virological and immunological events in asymptomatic Epstein–Barr virus infection in African children. PLoS Pathog. (2015) 11(3):e1004746. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004746
3. Rickinson AB, Long HM, Palendira U, Münz C, Hislop AD. Cellular immune controls over Epstein–Barr virus infection: new lessons from the clinic and the laboratory. Trends Immunol. (2014) 35(4):159–69. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.01.003
4. Sulik A, Oldak E, Kroten A, Lipska A, Radziwon P. Epstein–Barr virus effect on frequency of functionally distinct T cell subsets in children with infectious mononucleosis. Adv Med Sci. (2014) 59(2):227–31. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2014.04.003
5. Barros MHM, Vera-Lozada G, Segges P, Hassan R, Niedobitek G. Revisiting the tissue microenvironment of infectious mononucleosis: identification of EBV infection in T cells and deep characterization of immune profiles. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:146. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00146
6. Vietzen H, Furlano PL, Cornelissen JJ, Böhmig GA, Jaksch P, Puchhammer-Stöckl E. HLA-E-restricted immune responses are crucial for the control of EBV infections and the prevention of PTLD. Blood. (2023) 141(13):1560–73. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022017650
7. Lanz TV, Brewer RC, Ho PP, Moon JS, Jude KM, Fernandez D, et al. Clonally expanded B cells in multiple sclerosis bind EBV EBNA1 and GlialCAM. Nature. (2022) 603(7900):321–7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04432-7
8. Zhang Y, Huang C, Zhang H, Duan Z, Liu Q, Li J, et al. Characteristics of immunological events in Epstein–Barr virus infection in children with infectious mononucleosis. Front Pediatr. (2023) 11:1060053. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1060053
9. Hislop AD. Early virological and immunological events in Epstein–Barr virus infection. Curr Opin Virol. (2015) 15:75–9. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2015.08.002
10. Ohga S, Nomura A, Takada H, Hara T. Immunological aspects of Epstein–Barr virus infection. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2002) 44(3):203–15. doi: 10.1016/S1040-8428(02)00112-9
11. Stuller KA, Cush SS, Flaño E. Persistent gamma-herpesvirus infection induces a CD4 T cell response containing functionally distinct effector populations [published correction appears in J immunol. 2010 jun 15;184(12):7315]. J Immunol. (2010) 184(7):3850–6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902935
12. Long HM, Meckiff BJ, Taylor GS. The T-cell response to Epstein–Barr virus-new tricks from an old dog. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2193. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02193
13. Ding G, Zhang X, Vinturache A, van Rossum AMC, Yin Y, Zhang Y. Challenges in the treatment of pediatric mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Eur J Pediatr. (2024) 183(7):3001–11. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05519-1
14. Jain S, Williams DJ, Arnold SR, Ampofo K, Bramley AM, Reed C, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372(9):835–45. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1405870
15. Wu W, Zheng YL, Tian LP, Lai JB, Hu CC, Zhang P, et al. Circulating T lymphocyte subsets, cytokines, and immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with bipolar II or major depression: a preliminary study. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:40530. doi: 10.1038/srep40530
16. Liu R, Li M, Zhang L, Wang Y, Li W, Liu S. T lymphocyte subsets and immunoglobulin and complement levels are associated with the infection status of patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23(6):2877–84. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01021-4
17. Kalafati L, Hatzioannou A, Hajishengallis G, Chavakis T. The role of neutrophils in trained immunity. Immunol Rev. (2023) 314(1):142–57. doi: 10.1111/imr.13142
18. Zhu Y, Luo Y, Li L, Jiang X, Du Y, Wang J, et al. Immune response plays a role in mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1189647. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1189647
19. Qiu J, Ge J, Cao L. D-dimer: the risk factor of children’s severe mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Front Pediatr. (2022) 10:828437. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.828437
20. Zhao Q, Zhang T, Zhu B, Bi Y, Jiang SW, Zhu Y, et al. Increasing age affected polymorphonuclear neutrophils in prognosis of mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. J Inflamm Res. (2021) 14:3933–43. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S321656
21. Mara AB, Gavitt TD, Tulman ER, Miller JM, He W, Reinhardt EM, et al. Vaccination with mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane lipoproteins induces IL-17A driven neutrophilia that mediates vaccine-enhanced disease. NPJ Vaccines. (2022) 7(1):86. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00513-w
22. Wu Y, Li ZJ, Yu SC, Chen L, Wang JC, Qin Y, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of notifiable infectious diseases among foreign cases in China, 2004–2017. Biomed Environ Sci. (2020) 33(6):421–30. doi: 10.3967/bes2020.057
23. Khan DSA, Naseem R, Salam RA, Lassi ZS, Das JK, Bhutta ZA. Interventions for high-burden infectious diseases in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. (2022) 149(Suppl 5):e2021053852C. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-053852C
24. Singh RP, Parker W, Vaka G, Islam A, Khanani H. Infectious mononucleosis causing bell’s palsy: a case report. Cureus. (2025) 17(5):e84176. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84176
25. Chen J, Wang Y, Hong M, Wu J, Zhang Z, Li R, et al. Application of peripheral blood routine parameters in the diagnosis of influenza and mycoplasma pneumoniae. Virol J. (2024) 21(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02429-4
26. Hu J, Ye Y, Chen X, Xiong L, Xie W, Liu P. Insight into the pathogenic mechanism of mycoplasma pneumoniae. Curr Microbiol. (2022) 80(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-03103-0
27. Saraya T, Kurai D, Nakagaki K, Sasaki Y, Niwa S, Tsukagoshi H, et al. Novel aspects on the pathogenesis of mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia and therapeutic implications. Front Microbiol. (2014) 5:410. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00410
28. Shimizu T, Kida Y, Kuwano K. Cytoadherence-dependent induction of inflammatory responses by mycoplasma pneumoniae. Immunology. (2011) 133(1):51–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03408.x
29. Jones HP, Tabor L, Sun X, Woolard MD, Simecka JW. Depletion of CD8+ T cells exacerbates CD4+ th cell-associated inflammatory lesions during murine mycoplasma respiratory disease. J Immunol. (2002) 168(7):3493–501. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.7.3493
30. Fan F, Lv J, Yang Q, Jiang F. Clinical characteristics and serum inflammatory markers of community-acquired mycoplasma pneumonia in children. Clin Respir J. (2023) 17(7):607–17. doi: 10.1111/crj.13620
31. Bi Y, Ma Y, Zhuo J, Zhang L, Yin L, Sheng H, et al. Risk of mycoplasma pneumoniae-related hepatitis in MP pneumonia pediatric patients: a predictive model construction and assessment. BMC Pediatr. (2021) 21(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12887-021-02732-x
32. Wang Z, Yang L, Ye J, Wang Y, Liu Y. Monocyte subsets study in children with mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Immunol Res. (2019) 67(4-5):373–81. doi: 10.1007/s12026-019-09096-6
Keywords: lymphocyte subsets, infectious mononucleosis (IM), mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP), CD4/CD8, ROC
Citation: Shen X, Li W, Qi J, Zhong Q, Zhang Y, Sun T, Shi S, Zhang L and Su J (2025) The diagnostic value of lymphocyte profiling for infectious mononucleosis and mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Front. Pediatr. 13:1607857. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1607857
Received: 8 April 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 1 August 2025.
Edited by:
Claudio Pignata, University of Naples Federico II, ItalyReviewed by:
Ramachandran Padmanabhan, Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research, IndiaDeniz Güven, Ankara Etlik City Hospital, Türkiye
Copyright: © 2025 Shen, Li, Qi, Zhong, Zhang, Sun, Shi, Zhang and Su. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liang Zhang, c3N6aGFuZ2xpYW5nQDE2My5jb20=; Jing Su, OTI4MDA3Mzg3QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xuan Shen1,†
Xuan Shen1,† Jijin Qi
Jijin Qi Jing Su
Jing Su