- 1Department of neonatology, Dalian Women and Children's Medical Group, Dalian City, Liaoning Province, China
- 2Department of Pediatric Orthopaedic, Dalian Women and Children's Medical Group, Dalian City, Liaoning Province, China
Congenital nephrotic syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder, with the Finnish type caused by NPHS1 variants being the most common. It is characterized by massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hypercholesterolemia, and edema, ultimately progressing to end-stage renal disease. To date, 260 genetic variants in NPHS1 have been reported, with two variants prevalent in Finnish patients, while non-Finnish populations exhibit greater genetic heterogeneity. This case report describes a Chinese Han female neonate with Finnish-type CNF, highlights the characteristics of her gene variants, and discusses the genetic heterogeneity of Finnish-type CNF between Asian and Finnish populations.
Introduction
Congenital nephrotic syndrome (CNS) is a rare and severe renal disorder with autosomal recessive inheritance, affecting 1–3 per 100,000 live births globally (1). It is significantly more prevalent in the Finnish population, where Finnish-type Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome (CNF) occurs in approximately 1 in 8,200 live births, with NPHS1 (19q13.1) gene variants accounting for 98% of cases (2–4). Genetic screening for NPHS1 in non-Finnish patients reveals lower variant frequencies but greater heterogeneity. Over 260 NPHS1 variants have been reported, including protein-truncating non-sense variants, frameshift insertions/deletions, and splice site changes. In vitro functional studies show that most NPHS1 missense variants cause protein retention in the endoplasmic reticulum, leading to complete loss of cell surface nephrin (5, 6). We present a female neonate with CNF carrying heterozygous NPHS1 variants, including two confirmed pathogenic variants and one variant of uncertain significance.
Case presentation
A female Han neonate was admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit at 24 days of life with “groaning and poor responsiveness for 18 h.” She was the second pregnancy (G2P1), born at 34 + 6 weeks via cesarean section after 8 h of premature rupture of membranes. The placenta was large (1,300 g), and birth weight was 2,900 g. Urine had been persistently yellow since birth. Prenatal ultrasound revealed bilateral renal enlargement and increased parenchymal echogenicity. Family history: The 33-year-old mother had gestational diabetes and an immune-related disorder, treated with aspirin and low-molecular-weight heparin. She had one prior pregnancy loss due to umbilical cord blood flow interruption. The father was healthy. The parents were non-consanguineous, with no family history of genetic or renal diseases.
Physical examination
The infant had a term appearance, with poor responsiveness, shallow and irregular breathing with mild intercostal retractions. Other findings include pale complexion, anterior fontanelle 6.0 × 6.0 cm2 (slightly bulging), clear lung sounds, regular heart rate at 192 bpm, liver palpable 1 cm below the costal margin (soft texture), non-palpable spleen, cool extremities, capillary refill time of 5 s, and normal primitive reflexes.
Laboratory findings
Urinalysis: occult blood 2 + cells/μL, protein 3 + g/L, glucose 4 + mmol/L. Blood biochemistry: ALT 4 U/L, prealbumin 80 mg/L, total protein 26.0 g/L, albumin 9.3 g/L, glucose 5.62 mmol/L, cholesterol 7.38 mmol/L, GGT 160.56 U/L. Urine biochemistry: β2-microglobulin 8,196.5 μg/L, creatinine 0.036 g/L. Protein quantification: 10,370.8 mg/L, microalbumin 939.51 mg/dl. Blood tests/inflammatory markers: WBC 5.01 × 109/L, Hb 138 g/L, platelets 331 × 109/L, CRP 132.99 mg/L, PCT 75.89 ng/mL. Cultures: blood and cerebrospinal fluid cultures grew Streptococcus agalactiae. Hepatitis markers were negative.
Imaging
Renal ultrasound showed enlarged kidneys (left 6.8 cm × 2.7 cm, right 6.0 cm × 2.7 cm) with increased parenchymal echogenicity and indistinct corticomedullary junction. Brain MRI revealed abnormal signals in the left occipital cortex and subcortex (local brain injury) and prominent subarachnoid spaces around the bilateral frontotemporal lobes and cerebellum.
Genetic testing
With parental consent, whole-exome sequencing was performed. The Roche KAPA HyperExome panel was employed to capture and enrich DNA in targeted exonic regions and adjacent splicing junctions, covering approximately 20,000 gene exonic regions in the human genome along with the mitochondrial genome. Variant detection was performed using the MGISEQ-2000 sequencing platform, with sequencing reads aligned to the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) hg19 human reference genome via BWA software, followed by duplicate removal. Integrating clinical data from subjects, variant annotation, and filtration were conducted utilizing population databases (including ClinVar, ESP6500, and 1000 Genomes Project), disease-specific databases (such as Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man), and bioinformatics prediction tools (including SIFT and MutationTaster).
Results identified heterozygous NPHS1 variants inherited from both parents (Table 1 and Figure 1). Per American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines, c.2515delC (p.Gln839Argfs) in exon 8 of chr19 is a reported pathogenic variant; c.1422delC (p.Ser475Profs) in exon 11 is a novel pathogenic variant. A VUS, c.3337G>A (p.Glu1113Lys) in exon 26, was also detected. Suspected pathogenic variants were identified in NEK8 (c.222_223insA, p.Ala75Serfs) and TNFRSF13B (c.226G>A, p.Gly76Ser; c.41G>A, p.Arg14His), with the latter linked to immune deficiencies in the literature (7, 13).
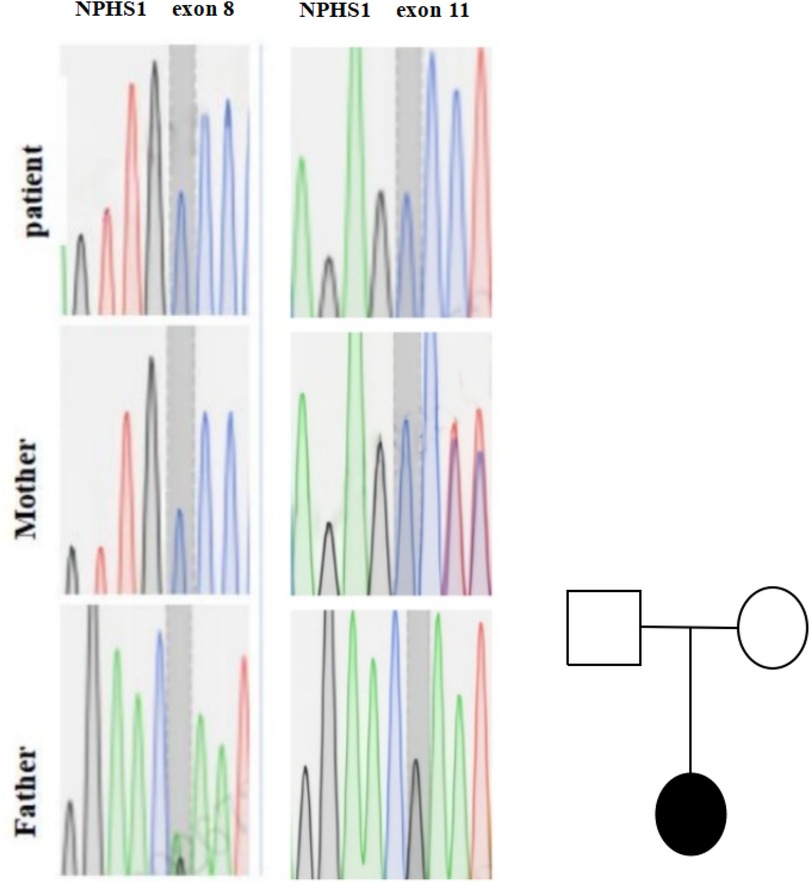
Figure 1. Genetic testing results of the proband's family. Genetic sequencing chromatograms for NPHS1 gene mutations in exon 8 and exon 11 for a patient, mother, and father. The chromatograms show varying peaks representing different nucleotides. On the right is a pedigree chart with a square for the father, a circle for the mother, and a filled circle forthe patient, indicating the patient is affected.
Diagnoses: (1) CNF, (2) neonatal purulent meningitis, (3) neonatal septicemia, (4) septic shock, (5) neonatal anemia. With parental consent, whole-exome sequencing was performed.
The infant received comprehensive treatment, including antibiotics, albumin infusions, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, diuretics, and fluid balance management. However, she was discharged after 18 days due to parental decision. She had persistent hypoalbuminemia, edema, and proteinuria, with subsequent hospitalizations for infections and hypocalcemic convulsions until November 2022.
The patient was discharged with persistent hypoalbuminemia, accompanied by edema and proteinuria, and continued to receive conservative management. Occasional infections, including pulmonary edema and enteritis, were observed. Intermittent dialysis was performed, and the patient remained alive with normal renal function.
Discussion and conclusions
Genetic testing identified a heterozygous variant in exon 8 of chr19 (c.2515delC) from the mother, confirming Finnish-type CNS per ACMG criteria. A novel pathogenic variant (c.1422delC) in exon 11 and a VUS (c.3337G>A) were also found. Suspected pathogenic variants in NEK8 and TNFRSF13B require further validation.
Genetic testing characteristics in Finnish populations
CNF incidence in Finns is ∼1/8,200 live births, with NPHS1 variants accounting for 98% of cases (6, 8, 9). The “Finmajor” (c.121delCT, p.L41fs) and “Finminor” (c.3325C>T, p.R1109X) variants comprise 78% and 16% of mutant alleles, respectively, vs. 39%–55% in non-Finns. The nephrin protein (1,241 amino acids) is critical for glomerular filtration; its deficiency leads to slit diaphragm dysfunction, mesangial sclerosis, and protein transduction domain (PTD) microcystic dilation, progressing to ESRD (5, 10).
Genetic testing characteristics in Asian populations
Non-Finnish CNS cases exhibit >260 NPHS1 variants, with genetic heterogeneity contributing to unclear etiologies in 20% of cases (11, 14). Asian patients more commonly have compound heterozygous variants (72%) vs. Finnish homozygous variants (65% Finmajor homozygote). For example, Japanese studies report NPHS1 (4/13 cases) and NPHS2 (2/13 cases) variants, while Chinese cases show diverse heterozygous variants (12, 14–23).
In summary, this report describes a Chinese Han neonate with CNF harboring a novel NPHS1 variant (c.1422delC), expanding the genetic and phenotypic spectrum of CNS. These findings contribute to enhanced molecular diagnosis, genetic counseling, and prenatal testing for CNS.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Board of Dalian Women and Children's Medical Group. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)' legal guardian/ next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article. Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
WZ: Software, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Validation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Supervision, Project administration. LH: Data curation, Project administration, Visualization, Resources, Validation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Investigation, Formal analysis. XC: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Software, Visualization, Project administration, Resources, Data curation, Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Investigation, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence, and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Nishi K, Inoguchi T, Kamei K, Hamada R, Hataya H, Ogura M, et al. Detailed clinical manifestations at onset and prognosis of neonatal-onset Denys-Drash syndrome and congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type. Clin Exp Nephrol. (2019) 23:1058–65. doi: 10.1007/s10157-019-01732-7
2. Bérody S, Heidet L, Gribouval O, Harambat J, Niaudet P, Baudouin V, et al. Treatment and outcome of congenital nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2019) 34:458–67. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy015
3. Ishikura K, Matsumoto S, Sako M, Tsuruga K, Nakanishi K, Kamei K, et al. Clinical practice guideline for pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome 2013: medical therapy. Clin Exp Nephrol. (2015) 19:6–33. doi: 10.1007/S10157-014-1030-9
4. Hjorten R, Anwar Z, Reidy KJ. Long-term outcomes of childhood-onset nephrotic syndrome. Front Pediatr. (2016) 4:53. doi: 10.3389/fped.2016.00053
5. Machuca E, Benoit G, Nevo F, Tête MJ, Gribouval O, Pawtowski A, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in non-Finnish congenital nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2010) 21:1209–17. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009080837
6. Kovacevic L, Reid CJ, Rigden SP. Management of congenital nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. (2003) 18:426–30. doi: 10.1007/S00467-002-1014-3
7. Li C-Y, Huang S-P, Chen Y-T, Wu H-E, Cheng W-C, Huang C-Y, et al. TNFRSF13B is a potential contributor to prostate cancer. Cancer Cell Int. (2022) 22(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02590-2
8. Anderson S. Congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type in a Dominican newborn: an overview and case report. Neonatal Netw. (2022) 41(2):83–8. doi: 10.1891/11-T-745
9. Constantinescu AR, Mattoo TK, Smoyer WE, Greenbaum LA, Niu J, Howard N, et al. Clinical presentation and management of nephrotic syndrome in the first year of life: a report from the Pediatric Nephrology Research Consortium. Front Pediatr. (2022) 10:988945. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.988945
10. Wang JJ, Mao JH. The etiology of congenital nephrotic syndrome: current status and challenges. World J Pediatr. (2016) 12(2):149–58. doi: 10.1007/s12519-016-0009-y
11. Hamasaki Y, Hamada R, Muramatsu M, Matsumoto S, Aya K, Ishikura K, et al. A cross-sectional nationwide survey of congenital and infantile nephrotic syndrome in Japan. BMC Nephrol. (2020) 21(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02010-5
12. Xie D, Wu J, Zhang W, Jin T, Wu P, An B, et al. A novel heterozygous mutation of the NPHS1 gene in a Chinese child with congenital nephrotic syndrome: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). (2023) 102(7):e32970. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032970
13. AbuMaziad AS, Abusaleh R, Bhati S. Congenital nephrotic syndrome. J Perinatol. (2021) 41:2704–12. doi: 10.1038/s41372-021-01279-0
14. Rong L, Chen L, Rao J, Shen Q, Li G, Liu J, et al. Genetic variations and clinical features of NPHS1-related nephrotic syndrome in Chinese children: a multicenter, retrospective study. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:771227. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.771227
15. Claus LR, Chen C, Stallworth J, Turner JL, Slaats GG, Hawks AL, et al. Certain heterozygous variants in the kinase domain of the serine/threonine kinase NEK8 can cause an autosomal dominant form of polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int. (2023) 104(5):995–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.07.021
16. Lv H, Liu F, Wang Q, Dong Z, Ren P, Zhang H, et al. Three novel heterozygous mutations of NPHS1 gene causing infants with congenital nephrotic syndrome: two Chinese (Han) cases. Clin Lab. (2023) 69(8):1793. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2023.230121
17. Shi Y, Ding J, Liu JC, Wang H, Bu DF. NPHS1 mutations in a Chinese family with congenital nephrotic syndrome. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. (2005) 43:805–9. doi: 10.4238/2011.October.18.1
18. Fu R, Gou MF, Ma WH, He JJ, Luan Y, Liu J. Novel NPHS1 splice site mutations in a Chinese child with congenital nephrotic syndrome. Genet Mol Res. (2015) 14(1):433–9. doi: 10.4238/2015.January.23.17
19. Yang F, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Qiu L, Chen Y, Zhou J. Novel NPHS1 gene mutations in a Chinese family with congenital nephrotic syndrome. J Genet. (2016) 95(1):161–6. doi: 10.1007/s12041-015-0598-6
20. Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. (2015) 17(5):405–24. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30
21. Yoshizawa C, Kobayashi Y, Ikeuchi Y, Tashiro M, Kakegawa S, Watanabe T, et al. Congenital nephrotic syndrome with a novel NPHS1 mutation. Pediatr Int. (2016) 58(11):1211–5. doi: 10.1111/ped.13118
22. Zhang H, Wang F, Liu X, Zhong X, Yao Y, Xiao H. Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome caused by co-inheritance of mutations at NPHS1 and ADCK4 genes in two Chinese siblings. Intractable Rare Dis Res. (2017) 6(4):299–303. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2017.01037
Keywords: congenital nephrotic syndrome (CNS), NPHS1, Finnish type, Chinese, Asian
Citation: Zhang W, Hou LM and Cheng X (2025) A novel NPHS1 variant in a Chinese infant with congenital nephrotic syndrome: a case report and literature review. Front. Pediatr. 13:1632898. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1632898
Received: 21 May 2025; Accepted: 9 September 2025;
Published: 14 October 2025.
Edited by:
Rajendra Bhimma, University of KwaZulu-Natal, South AfricaReviewed by:
Marcelo De Sousa Tavares, Grupo Santa Casa BH, BrazilJose Luis Guerrero, Hospital Luis Calvo Mackenna, Chile
Copyright: © 2025 Zhang, Hou, Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xian Cheng, MTg4NDExMzIzMDdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Wei Zhang1†
Wei Zhang1† Xian Cheng
Xian Cheng