- 1Department of Pediatrics, Shengli Oil Field Central Hospital, Dongying, Shandong, China
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Shanghai Children's Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 3Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Research Center, Institute of Pediatric Infection, Immunity and Critical Care Medicine, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Background: 3M syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by biallelic pathogenic variants in the cullin 7 (CUL7), obscurin-like 1 (OBSL1), and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 8 (CCDC8) genes and is characterized by pre- and postnatal growth retardation, short stature, dysmorphic facial features, and skeletal anomalies, with normal intelligence.
Case presentation: In this study, we report a 6-year-old female patient from China diagnosed with 3M syndrome. The patient presented with typical clinical features of growth retardation and short stature, with normal intelligence. The patient’s dysmorphic facial features included relative macrocephaly, a protruding forehead, a triangular face, a pointed chin, a flat nasal bridge, full lips, a long philtrum, and a broad lower jaw. The skeletal survey was normal except for clinodactyly of the fifth fingers of both hands. Growth hormone (GH) deficiency was excluded by normal serum hormone levels and the GH stimulation test results. Whole-exome sequencing identified two heterozygous variants in CUL7, NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6), and NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr). Parental Sanger sequencing confirmed these as compound heterozygous variants, with one variant inherited from each parent. Neither variant has been previously reported. The patient has been treated with recombinant human IGF-1 for 2 years since she was 4 years old and has achieved a growth velocity of approximately 6–7 cm per year.
Conclusions: Herein, we describe a Chinese patient with 3M syndrome caused by novel biallelic pathogenic variants in CUL7 from a non-consanguineous family, expanding the genetic spectrum of CUL7 in the Chinese population.
1 Introduction
3M syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive primordial growth disorder characterized by severe pre- and postnatal growth retardation, characteristic facial features, skeletal anomalies, and normal intelligence. It was first described by Miller et al. in 1975 (1). Patients with 3M syndrome are typically born with low weight and short length, leading to a short stature in adulthood (2). The dysmorphic facial features include relative macrocephaly, a protruding forehead, a triangular face, a pointed chin, a flat nose, full lips, and a long philtrum. Skeletal dysplasia, such as a short and broad neck, square shoulders, short thorax, pectus carinatum or excavatum, winged scapulae, scoliosis, clinodactyly, prominent heels, and joint hypermobility, may present in affected individuals (3). The exact prevalence of 3M syndrome is unknown, with approximately 250 cases reported in the literature (4). According to the molecular etiology, it is divided into three forms, namely, 3M syndrome-1 (OMIM #273750), 3M syndrome-2 (OMIM #612921), and 3M syndrome-3 (OMIM #614205), which are caused by biallelic loss-of-function variants in the cullin 7 (CUL7), obscurin-like 1 (OBSL1), and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 8 (CCDC8) genes, respectively (3). CUL7 is the predominant pathogenic gene, accounting for approximately 65% of the patients with 3M syndrome, followed by OBSL1 (around 30%), and less commonly in CCDC8 (5). However, the pathogenic variants of these three genes do not account for 100% of individuals with 3M syndrome, indicating that other genes may be involved. The underlying mechanism is not clearly understood; pathogenic variants in the CUL7, OBSL1, and CCDC8 genes are thought to disrupt the 3M complex formed by the CUL7, OBSL1, and CCDC8 proteins, which play critical roles in maintaining microtubule and genome integrity and in normal development (6).
Currently, only a few individuals with 3M syndrome from China have been reported in the literature. In this study, we report a female pediatric 3M syndrome case from a non-consanguineous Chinese family with the novel CUL7 compound heterozygous variants NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) and NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr), expanding the genetic spectrum of CUL7-associated 3M syndrome in the Chinese population.
2 Case presentation
A 3-year-old female child was referred to the Department of Pediatrics, Shengli Oil Field Central Hospital for an evaluation of her short stature. The female child was born at full term via normal vaginal delivery with a birth weight of 2.49 kg [−2.24 standard deviation (SD)] and a birth length of 46 cm (−2.18 SD). The postnatal period was uneventful, and she was intellectually normal. She was the second child of healthy non-consanguineous parents. The family history was unremarkable. The mother's height was 157 cm, the father's height was 181 cm, and her 9-year-old elder sister was 140 cm tall. At age 1 year and 6 months, the parents noticed that the patient presented with growth delay, and her height was significantly shorter than that of other children of the same age.
On admission, the physical examination showed that the weight and length of the patient were 10 kg (−3.20 SD) and 82.5 cm (−3.63 SD), respectively. Her body temperature was 36.5°C, heart rate was 110 beats per minute, respiratory rate was 25 breaths per minute, and blood pressure was 78/56 mmHg. The cardiopulmonary and abdominal examinations were unremarkable. However, she had relative macrocephaly, a protruding forehead, a triangular face, a pointed chin, a flat nasal bridge, full lips, a long philtrum, and a broad lower jaw. The skeletal survey using x-rays showed a normal skeleton except for clinodactyly of the fifth fingers of both hands (Figure 1).
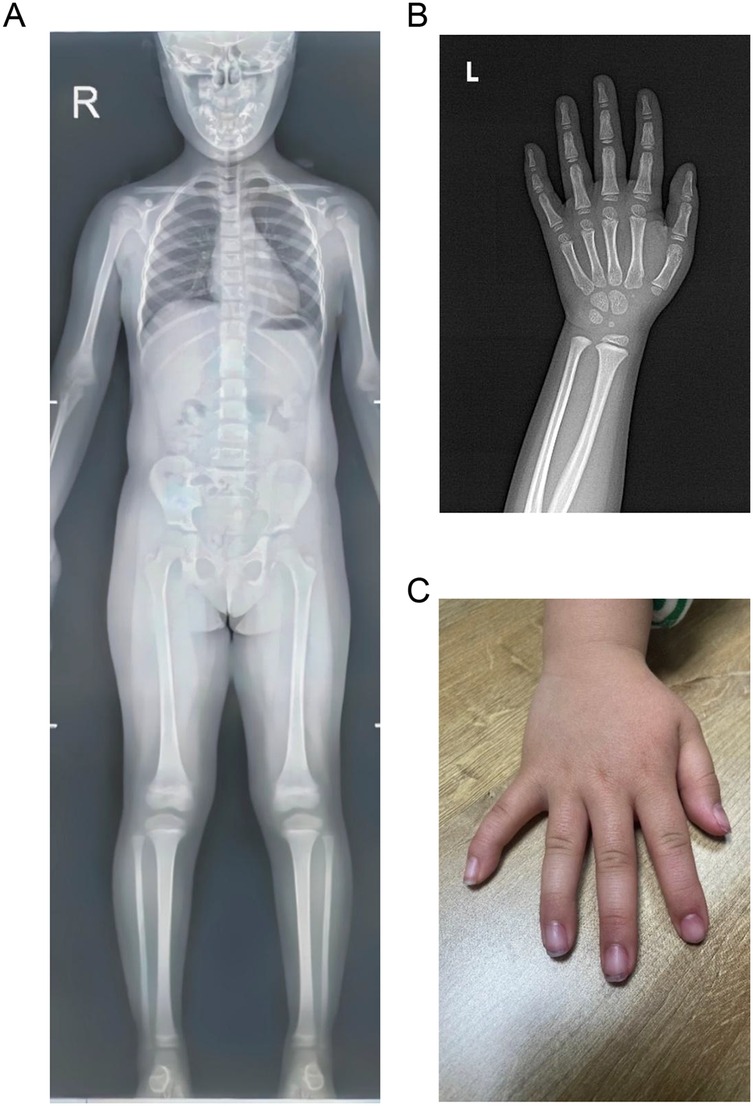
Figure 1. Skeletal survey images of the patient. (A) Normal anteroposterior x-ray image. (B) X-ray image of the left hand showing clinodactyly of the fifth finger. (C) Image of right hand showing clinodactyly of the fifth finger.
The initial hormonal tests revealed normal levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1; 104.11 ng/mL, reference range: 49–311 ng/mL), free triiodothyronine (T3; 3.85 pg/mL, reference range: 2.41–5.50 pg/mL), free thyroxine (FT4; 0.98 ng/dL, reference range: 0.96–1.77 ng/dL), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH; 2.18 μIU/mL, reference range: 0.70–5.97 μIU/mL). The patient’s serum fasting blood glucose (FPG; 4.84 mmol/L, reference range: 3.89–6.11 mmol/L), fasting insulin (FINS; 67.00 pmol/L, reference range: 13–161 pmol/L), and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c; 5.3%, reference range: 4%–6%) levels were normal. The growth hormone stimulation test (GHST) using arginine and levodopa peaked at 90 min (16.01 ng/mL), and GH deficiency was excluded. After discharge, a conservative approach that focused on improving diet and lifestyle was taken to achieve catch-up growth as the patient was small for gestational age (SGA). The patient started to receive recombinant human IGF-1 (rhIGF-1) therapy (0.2 mg/kg/week) because of her growth delay at 4 years old (height: 92 cm, −2.92 SD; weight: 12.5 kg, −2.33 SD). Her growth velocity was approximately 6–7 cm/year during the following 2 years of continuous rhIGF-1 therapy. She was 6 years old at the last examination with a height of 106.5 cm (−2.25 SD) and a weight of 20 kg (−0.15 SD), and her intellectual development was normal.
To evaluate the genetic cause of her short stature, whole-exome sequencing (WES) was performed using genomic DNA extracted from the patient’s peripheral blood. The WES identified two novel variants, namely, NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) and NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) in the CUL7 gene, which were further confirmed using Sanger sequencing (Figure 2A). Further genotyping of the unaffected parents using Sanger sequencing revealed that the NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) variant was present in the father (Figure 2B) and the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) variant was present in the mother (Figure 2C), confirming that the proband carried compound heterozygous CUL7 variants. Her healthy older sister carried the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C variant (Figure 2D). The location of the identified CUL7 variants is shown in Figure 2E. The NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) variant results in a premature termination codon, and the aberrant transcript will likely be degraded by non-sense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). The NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C variant results in the amino acid substitution of threonine for isoleucine at codon 1502 (p.Ile1502Thr). An in silico prediction of the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C variant using the rare exome variant ensemble learner (REVEL) method showed a score of 0.542 (<0.65) (7). Neither variant has been reported in the 1000 Genomes Project database or the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) nor in previous literature. The NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) variant is defined as likely pathogenic (PVS1 + PM2_Supporting), and the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C variant (PM3+PM2_Supporting) is defined as a variant of uncertain clinical significance according to American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines (8). An in silico analysis of the three-dimensional protein structure of the CUL7 protein using AlphaFold2 indicated that variant c.4505T>C causes the amino acid at position 1,502 to be mutated from isoleucine to threonine, leading to an additional hydrogen bond between isoleucine at position 1,498 located in the α-helix region of the CUL7 protein (Figure 3). Taken together, the diagnosis of 3M syndrome-1 caused by novel compound heterozygous variants in the CUL7 gene was made in this patient. Currently, she is being managed with continuous rhIGF-1 therapy (0.21 mg/kg/week) with close follow-up, and has grown 2 cm in the last 3 months.
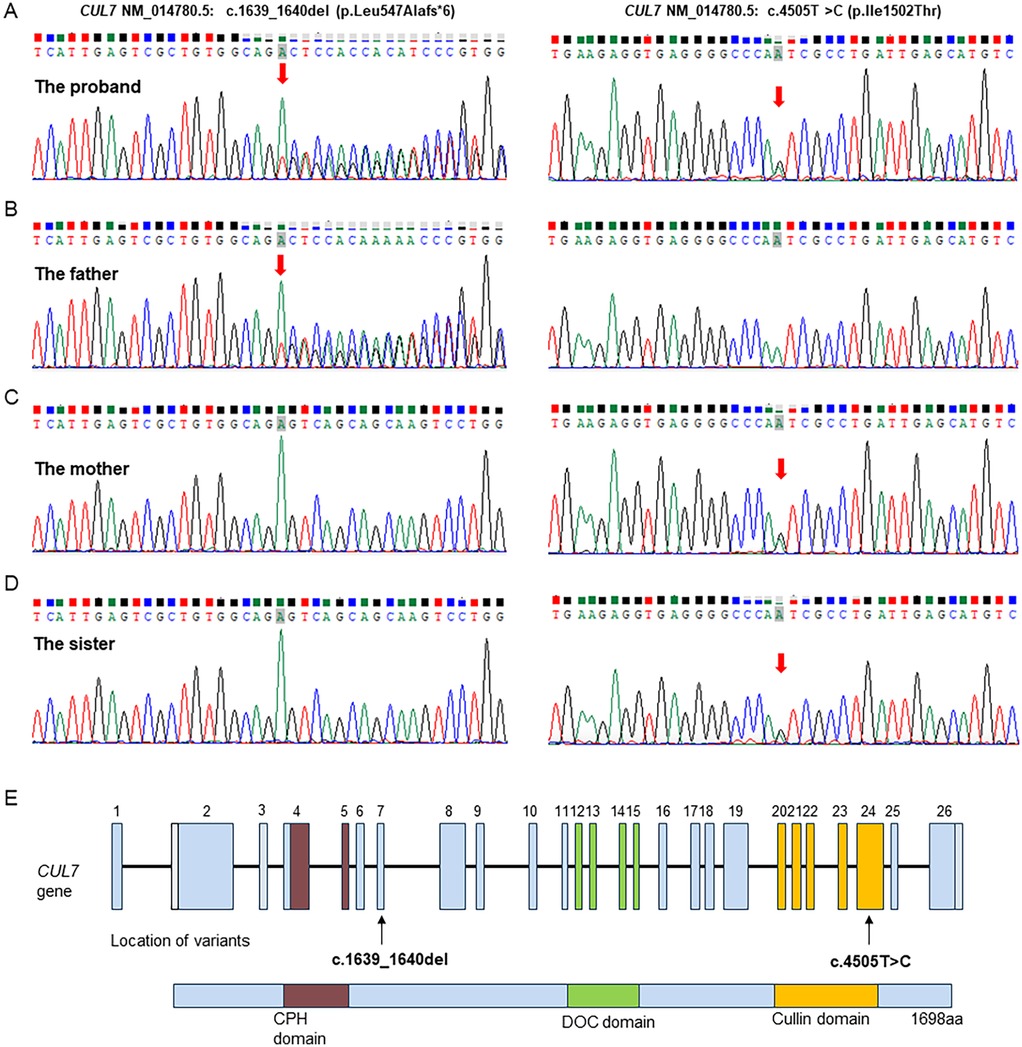
Figure 2. Sanger sequencing validation of the CUL7 variants identified by whole-genome sequencing in the family. (A) The proband carried both the NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) and NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) variants. (B) The father carried the NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) variant. (C) The mother carried the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) variant. (D) The healthy older sister carried the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) variant. (E) Visual representation of the identified CUL7 variants.
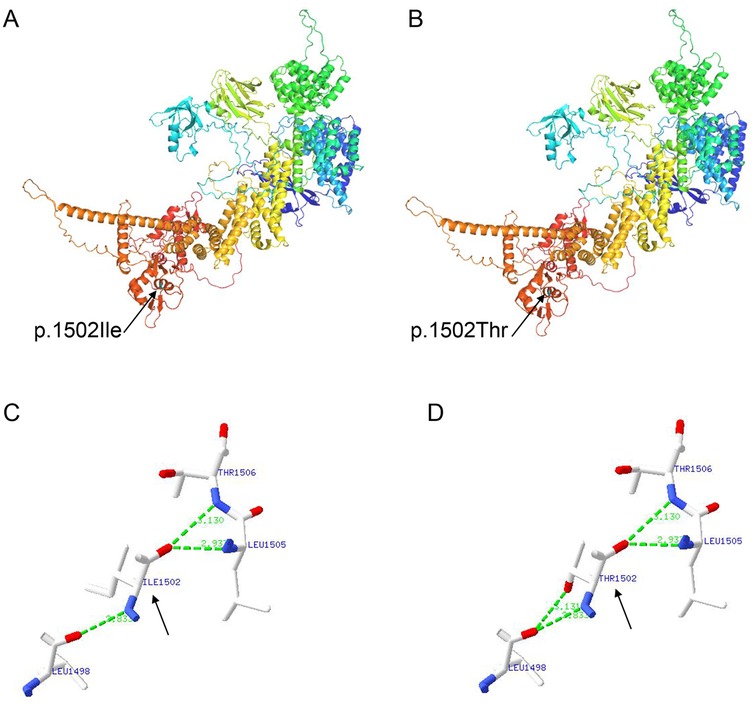
Figure 3. An in silico structural analysis of the CUL7 protein using AlphaFold2. (A) The structure prediction of the wild-type CUL7 protein. (B) The structure prediction of the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) CUL7 protein. (C) A partial enlargement of the wild-type CUL7 protein. (D) A partial enlargement of the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) CUL7 protein.
3 Discussion
Although patients with 3M syndrome present a unique set of clinical features, including growth retardation, dysmorphic facial features, and skeletal anomalies, the range and severity of the manifestations are very variable (4). In 2025, Elsayed et al. conducted a comprehensive update review of the clinical and molecular characteristics of 3M syndrome (3). The most striking manifestation of 3M syndrome is severe pre- and postnatal growth restriction, which often results in short adult height 4–6 SDs below the mean without catch-up growth (4, 5). The craniofacial features of individuals with 3M syndrome are characterized by relative macrocephaly, a triangular face with a protruding forehead, a flat midface, a flat nose, a long philtrum, and full lips (4). A total of 14 Chinese children diagnosed with CUL7 variant-caused 3M syndrome (excluding 4 prenatal cases) have been reported in the literature (9–15). Overall, no specific genotype-phenotype associations have been found in Chinese patients with 3M syndrome caused by CUL7 variants (Supplementary Table S1). In this report, the patient presented with prenatal growth failure with a low birth weight below the mean and showed the typical craniofacial features of relative macrocephaly, a protruding forehead, a triangular face, a pointed chin, a flat nasal bridge, full lips, a long philtrum, and a broad lower jaw. However, inconsistent with other patients with 3M syndrome (16), the physical examination and radiographic imaging revealed no musculoskeletal abnormalities in the patient except for clinodactyly of the fifth fingers of both hands.
3M syndrome is phenotypically homogeneous but genetically heterogeneous. The molecular etiology can be attributed to biallelic pathogenic variants in the CUL7, OBSL1, and CCDC8 genes, and the syndrome is often found in consanguineous families (4). CUL7 is the most prevalent pathogenic gene, and pathogenic variants in CUL7 have been identified in more than 65% of patients with genetically confirmed 3M syndrome (5). The exact mechanisms of how the pathogenic variants in these three genes lead to the clinical features of 3M syndrome remain unclear. The CUL7, OBSL1, and CCDC8 proteins form a CUL7-OBSL1-CCDC8 complex in the ubiquitin-proteasome system, which plays a critical role in multiple cellular processes, including cell cycle control, apoptosis, signal transduction, and the regulation of microtubule dynamics and genome integrity (6, 17). It is postulated that a loss of ubiquitination is the main underlying pathological mechanism in 3M syndrome (18, 19). Functional experiments have shown that the CUL7 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex targets a key molecule in insulin/IGF-1 signaling, insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1), to control cellular growth (20). The disruption of the CUL7 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex induces cellular senescence, which contributes to the growth restriction in 3M syndrome (21). In this study, two novel variants, namely, NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) and NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr), in the CUL7 gene were identified in the family. Neither of the variants has been reported previously, with NM_014780.5: c.1639_1640del (p.Leu547Alafs*6) defined as likely pathogenic and NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) as a variant of uncertain clinical significance. An in silico analysis of the three-dimensional structure of the CUL7 protein revealed that the NM_014780.5: c.4505T>C (p.Ile1502Thr) variant causes an additional hydrogen bond between isoleucine at position 1,498 located in the α-helix region of the CUL7 protein. An increase in hydrogen bonds may cause the protein to have an abnormal helical structure, leading to spatial changes in the protein’s structure. Nevertheless, further functional studies are required to further clarify the pathological mechanisms in 3M syndrome.
Currently, there are no available clinical practice guidelines for the management of 3M syndrome. Multidisciplinary supportive treatments are recommended to improve the quality of life of the patients, optimizing their growth potential and reducing skeletal complications (4). First, the presence of a GH deficiency should be determined at the time of diagnosis by an endocrinologist. Several studies have shown that GH levels are usually normal in children with 3M syndrome, and the majority of affected individuals had sufficient peak GH responses (2, 5, 22). Indeed, our patient had normal GH levels and a sufficient peak GH response. The administration of GH therapy is still controversial in children with 3M syndrome due to its variable efficacy. Clayton et al. reported a significant increase in both height velocity and height following 1 year of recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) treatment in 16 affected children (2). Other studies showed that GH therapy may be effective in the stimulation of catch-up growth in patients with 3M syndrome (16, 23, 24). Karacan Kucukali et al. reported a good early response, which decreased in the following years during long-term GH treatment (25). In contrast, other studies have reported that some affected patients fail to respond to the GH therapy (22, 26). Our patient received rhIGF-1 therapy at 4 years old and achieved a growth velocity of 6–7 cm/year during the following 2 years. Furthermore, other supportive treatments for musculoskeletal manifestations may be administered, such as orthopedic treatments for hip dysplasia/dislocation and kyphoscoliosis.
4 Conclusion
In summary, this case report described a Chinese patient with 3M syndrome caused by biallelic pathogenic variants in CUL7 from a non-consanguineous family. Pediatricians should be aware of this rare and underdiagnosed disease, and a genetic test is necessary to make a diagnosis in children with growth retardation of unknown etiology.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
This study involving humans was approved by the Ethical Review Board of Shengli Oil Field Central Hospital. This study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)' legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
HL: Writing – original draft, Data curation. GL: Writing – original draft, Investigation. WS: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SH: Methodology, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Data curation, Supervision, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. HD: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Conceptualization, Supervision, Investigation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 32370951).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the family for participating in and supporting this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2025.1652826/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
ACMG, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics; CCDC8, coiled-coil domain-containing protein 8; CUL7, cullin 7; FINS, fasting insulin; FPG, fasting blood glucose; FT3, free triiodothyronine; FT4, free thyroxine; GH, growth hormone; GHST, GH stimulation test; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; NMD, non-sense-mediated mRNA decay; OBSL1, obscurin-like 1; rhIGF-1, recombinant human IGF-1; SD, standard deviation; SGA, small for gestational age; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; WES, whole-exome sequencing.
References
1. Miller JD, McKusick VA, Malvaux P, Temtamy S, Salinas C. The 3-M syndrome: a heritable low birthweight dwarfism. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. (1975) 11:39–47.1218233
2. Clayton PE, Hanson D, Magee L, Murray PG, Saunders E, Abu-Amero SN, et al. Exploring the spectrum of 3-M syndrome, a primordial short stature disorder of disrupted ubiquitination. Clin Endocrinol. (2012) 77:335–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2012.04428.x
3. Holder-Espinasse M, Irving M, Cormier-Daire V. Clinical utility gene card for: 3-M syndrome—update 2013. Eur J Hum Genet. (2014) 22:572. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.156
4. Elsayed S, Elmakkawy GA, Abdelrazek IM, Fawzy DA, Kim J, Song Y, et al. An update on 3M syndrome: review of clinical and molecular aspects and report of additional families. Am J Med Genet A. (2025) 197:e64068. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.64068
5. Huber C, Munnich A, Cormier-Daire V. The 3M syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2011) 25:143–51. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2010.08.015
6. Yan J, Yan F, Li Z, Sinnott B, Cappell KM, Yu Y, et al. The 3M complex maintains microtubule and genome integrity. Mol Cell. (2014) 54:791–804. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.047
7. Ioannidis NM, Rothstein JH, Pejaver V, Middha S, McDonnell SK, Baheti S, et al. REVEL: an ensemble method for predicting the pathogenicity of rare missense variants. Am J Hum Genet. (2016) 99:877–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.08.016
8. Miller DT, Lee K, Gordon AS, Amendola LM, Adelman K, Bale SJ, et al. Recommendations for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing, 2021 update: a policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med. (2021) 23:1391–8. doi: 10.1038/s41436-021-01171-4
9. Xu N, Liu K, Yang Y, Li X, Zhong Y. Chinese patients with 3M syndrome: clinical manifestations and two novel pathogenic variants. Front Genet. (2023) 14:1164936. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1164936
10. Zhang L, Wu X, Yang J, Sun H, Yang J, Chen Y. Genetic analysis of a case of Miller-McKusick-Malvaux syndrome type 1 caused by CUL7 gene variant and a literature review. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. (2025) 42:343–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511374-20240229-00131
11. Liu X, Wang X, Zhou H, Chen R, Wang Y, Cui Y. 3M Syndrome: a case report and literature review. J Clin Pediatr. (2017) 35:906–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3606.2017.12.007
12. Zhang Y, Pi Y, Yan X, Li Y, Qi Z, Zhang H. Clinical analysis of 3M syndrome in a Chinese family. J Hebei Med Uni. (2016) 37:464–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3205.2016.04.025
13. Peng H, Sun W, Zhu X. A novel mutation in the CUL7 gene causing 3-M syndrome: a case report. Chin J Pract Pediatr. (2025) 40:433–6. doi: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2024.0059
14. Hu X, Li H, Gui B, Xu Y, Wang J, Li N, et al. Prenatal and early diagnosis of Chinese 3-M syndrome patients with novel pathogenic variants. Clin Chim Acta. (2017) 474:159–64. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.09.022
15. Hu L, Wang X, Jin T, Han Y, Liu J, Jiang M, et al. Identification of two CUL7 variants in two Chinese families with 3-M syndrome by whole-exome sequencing. J Clin Lab Anal. (2020) 34:e23265. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23265
16. Isik E, Arican D, Atik T, Ooi JE, Darcan S, Ozen S, et al. A rare cause of syndromic short stature: 3M syndrome in three families. Am J Med Genet A. (2021) 185:461–8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61989
17. Willems AR, Schwab M, Tyers M. A hitchhiker’s guide to the cullin ubiquitin ligases: SCF and its kin. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2004) 1695:133–70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.09.027
18. Hanson D, Stevens A, Murray PG, Black GC, Clayton PE. Identifying biological pathways that underlie primordial short stature using network analysis. J Mol Endocrinol. (2014) 52:333–44. doi: 10.1530/JME-14-0029
19. Hanson D, Murray PG, O’Sullivan J, Urquhart J, Daly S, Bhaskar SS, et al. Exome sequencing identifies CCDC8 mutations in 3-M syndrome, suggesting that CCDC8 contributes in a pathway with CUL7 and OBSL1 to control human growth. Am J Hum Genet. (2011) 89:148–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.05.028
20. Xu X, Sarikas A, Dias-Santagata DC, Dolios G, Lafontant PJ, Tsai SC, et al. The CUL7 E3 ubiquitin ligase targets insulin receptor substrate 1 for ubiquitin-dependent degradation. Mol Cell. (2008) 30:403–14. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.03.009
21. Litterman N, Ikeuchi Y, Gallardo G, O'Connell BC, Sowa ME, Gygi SP, et al. An OBSL1-Cul7Fbxw8 ubiquitin ligase signaling mechanism regulates Golgi morphology and dendrite patterning. PLoS Biol. (2011) 9:e1001060. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001060
22. Guven A, Cebeci AN. 3M syndrome: a report of four cases in two families. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. (2011) 3:154–9. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.v3i3.30
23. Lee IK, Lim HH, Kim YM. The effect of combined growth hormone and a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist therapy on height in Korean 3-M syndrome siblings. Yonsei Med J. (2020) 61:981–5. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.11.981
24. van der Wal G, Otten BJ, Brunner HG, van der Burgt I. 3-M syndrome: description of six new patients with review of the literature. Clin Dysmorphol. (2001) 10:241–52. doi: 10.1097/00019605-200110000-00002
25. Karacan Kucukali G, Keskin M, Aycan Z, Savas-Erdeve S, Cetinkaya S. 3M syndrome: evaluating the clinical and laboratory features and the response of the growth hormone treatment: single center experience. Eur J Med Genet. (2023) 66:104828. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2023.104828
Keywords: 3M syndrome, CUL7, short stature, dysmorphic facial features, skeletal anomalies
Citation: Liu H, Liu G, Suo W, Han S, Wang Y and Ding H (2025) 3M syndrome with novel CUL7 variants in a Chinese patient: a case report. Front. Pediatr. 13:1652826. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1652826
Received: 24 June 2025; Accepted: 1 October 2025;
Published: 29 October 2025.
Edited by:
Klaus Brusgaard, Odense University Hospital, DenmarkCopyright: © 2025 Liu, Liu, Suo, Han, Wang and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yizhong Wang, d2FuZ3l6QHNoY2hpbGRyZW4uY29tLmNu; Hongfang Ding, ZGluZ2hvbmdmYW5nMjAxOUBzb2h1LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hui Liu
Hui Liu Gaojie Liu2,3,†
Gaojie Liu2,3,† Yizhong Wang
Yizhong Wang Hongfang Ding
Hongfang Ding