- 1Department of Pediatric Surgery, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Background: Intestinal failure (IF) in pediatric patients often necessitates home parenteral nutrition (HPN) as a life-saving therapy. While global HPN programs are well-established, data specific to South Korea remain scarce. This study aimed to report the experience with pediatric HPN at a single center in Korea.
Methods: This retrospective study included 40 pediatric patients receiving HPN between 2009 and 2021 at Seoul National University Children's Hospital. The following data of patients were collected: demographics, diagnoses, surgical factors, HPN protocols, complications including catheter-related bloodstream infection (CRBSI), intestinal failure-associated liver disease (IFALD), hospitalization records, and growth outcomes.
Results: Forty pediatric patients with IF were followed for a median of 53.5 months. Common IF causes included chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome (45.0%) and short bowel syndrome (22.5%). Six (15.0%) patients were weaned off HPN. Complications included CRBSI (60.0%, 0.90/1,000 catheter days) and metabolic issues such as IFALD (45.0%). Growth outcomes were suboptimal, with declining z-scores for weight and weight-for-height during the HPN period. No mortality was reported during the study period.
Conclusion: This study provides insights into the experiences of pediatric HPN in a single center in Korea, with favorable survival and complication outcomes. However, low weaning rates and suboptimal growth outcomes highlight the need for systemic improvements including enhanced logistical support, legal reforms, and tailored nutritional strategies to optimize care for pediatric HPN patients in Korea.
Introduction
Intestinal failure (IF) is defined as a condition in which the functional intestine is critically reduced to the point where intravenous supplements are required to meet the minimum needs for nutrients, water, and electrolytes necessary for proper growth and weight maintenance (1). Although rare, IF is a life-threatening condition that poses significant challenges for both acute and chronic medical management. Causes of IF include primary digestive diseases such as short bowel syndrome (SBS), motility disorders like chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO), congenital enteropathies (CE) resulting from genetic defects, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Non-digestive disorders such as immune deficiencies and cancer can also lead to IF (2, 3).
In 1968, Wilmore and Dudrick published the first report showing that the growth and development of an infant could be sustained with parenteral nutrition (PN) alone (4). Since then, PN has been used for over 30 years to support proper growth and development of pediatric patients and premature infants (5). For children with IF, long-term or even lifelong PN is essential to provide adequate nutrition. Home parenteral nutrition (HPN) allows these patients to receive PN in a more familiar environment, such as their home, which can improve their quality of life and reduce financial burdens (6–8). However, parents or caregivers of these children must manage complex care routines, including preparing a sterile field, initiating and terminating infusions, managing lines and catheters, protecting devices during play, administering medications, and responding to pump alarms (2, 9). Additionally, they must recognize and address symptoms such as hypoglycemia, dehydration, or signs of infection, such as catheter-related bloodstream infection (CRBSI) (9, 10).
Medical experts understand the challenges faced by caregivers and often establish systems in hospitals to connect with home care teams to provide appropriate support and resources. In the U.S., to efficiently manage the growing number of HPN patients, a management system has been established through the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) (11). According to the ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines, home parenteral nutrition is recommended as a safe and effective long-term therapy for children with intestinal failure, aiming to optimize survival, growth, and quality of life. In line with these international recommendations, we sought to evaluate our institutional experience with pediatric HPN in Korea, where data remain scarce (12). Thus, data for pediatric HPN are limited up to date (13). Therefore, this study aimed to report the experience with pediatric HPN at a single center in Korea. It reviewed indications and outcomes of our cohort, analyzed the incidence of complications, and compared outcomes to international literature.
Materials and methods
Patients and data collection
We retrospectively reviewed medical records of 40 pediatric patients who started HPN between January 1st, 2009 and December 31st, 2021 at Seoul National University Children's Hospital. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Children's Hospital (Approval No. 2204-143-1319). Pediatric patients registered on the HPN list and managed by the pharmacy department were included in the study. Data collected included general demographics (such as age, sex, gestational age, birth weight), the presence of congenital anomalies, the patient's residence, age at the start of HPN, the primary diagnosis for HPN indication, and whether they received home care services. Surgical-related factors were gathered from surgical records, including details such as whether surgery was performed, the date of the first operation, the age at operation, preservation of the ileocecal valve (ICV), history of bowel resection, and creation of stoma (along with the type of stoma). Regarding HPN, we collected information on the type of HPN (compounded or commercial), regimen (days), calorie, volume, additional lipid emulsion administration, and method of multi-vitamin supplementation. HPN start date, duration, and the date and cause of HPN discontinuation were also collected. Data related to the central venous catheter, such as the type of central venous access device (CVAD), type of vessel used, complications related to catheter, metabolic complications related to PN, frequency, duration and reason of hospitalization, and growth parameters were retrospectively collected from medical records. Data for patients still receiving HPN were based on their status as of December 31st, 2021. For those who had discontinued HPN, the most recent data before discontinuation were used.
PN training and follow-up
Our institution began providing pediatric HPN in January 2009. A home care service was launched in January 2019. The home care service was available to patients living within 30 km of the hospital. Regardless of whether they received home care service, all patients or caregivers starting HPN underwent PN training before discharge. Since 2019, HPN patients registered with the home care service have additionally received regular home visits from HPN nurses for about one month after discharge to ensure that PN administration is proceeding smoothly.
Electrolytes including phosphate, potassium, and magnesium were routinely monitored during PN initiation and follow-up to prevent refeeding syndrome. Follow-up visits to the pediatric surgeon or gastroenterologists occurred monthly or more frequently if needed. For clinically stable patients, during every visits, body weight, body composition, hydration status, energy and fluid balance, and biochemical tests were measured in accordance with the ESPEN guidelines (14). The composition and volume of the PN solution were adjusted at each visit in consultation with the nutrition support team (NST) based on the child's requirements and growth. Resting energy expenditure (REE) was calculated using the Schofield formula considering the child's age, weight, and height (15).
Vascular access and handling
All children received PN via a CVAD. Depending on the patient's condition, a Chemoport, Hickman, or Broviac catheter was inserted. Both Broviac and Hickman catheters were tunneled catheters. All insertions were performed under general anesthesia with vascular ultrasound guidance to place the catheter into the superior vena cava. The insertion depth was confirmed using portable x-ray in the operating room. During outpatient visits, catheter function was checked and thrombosis was monitored using ultrasound every 12 months.
PN intake
PN formulas were divided into compounded PN, commercial PN, or a combination of both. For compounded PN, glucose, amino acids, electrolytes, minerals, vitamins, and trace elements were customized for each patiens and prepared by our institution. The caregiver visited the hospital every two days to pick up the compounded PN bag due to PN stability concerns. In contrast, commercial PN allows caregivers to collect a month's supply at once. However, mixing micronutrients at home is challenging. Lipid emulsion was supplemented using commercial products.
Outcome and complications
Key outcome variables for HPN included morbidity, growth parameters, and whether patients were weaned off PN. Morbidity was categorized into complications related to catheter or PN and hospitalization after starting HPN.
Catheter-related complications were classified into infections, vascular problems, and mechanical problems with the catheter. Their occurrence and frequency were collected. CRBSI was defined as the identification of the same pathogen in both peripheral and central line blood cultures with no other infection site (16). Cases where pathogens were identified only in central line blood culture (colonization) or infection localized to the catheter insertion site were classified as local infections. CRBSI incidence was calculated based on the number of CRBSI events per 1,000 catheter days. All pathogens identified during CRBSI episodes were collected. CVAD-related venous problems included venous thrombosis and stenosis caused by catheter insertion, as well as mechanical damage to the catheter (e.g., tearing, malposition, self-removal, and so on). In cases where re-insertion of a CVAD was difficult due to venous stenosis, balloon angioplasty was performed by radiological intervention.
PN-related complications included intestinal failure-associated liver disease (IFALD), gallbladder stones, renal stones, lactic acidosis, and micronutrient deficiencies. IFALD was defined as the presence of abnormal blood test results and/or abnormal ultrasound findings persisting for more than six months as follows: Alanine aminotransferase >1.5 times the upper limit of normal (67 IU/L), and/or Gamma-glutamyl transferase >1.5 times the upper limit of normal (2–4 months: >135 IU/L; 4 months–10 years: >48 IU/L; over 10 years: >36 IU/L), and/or direct bilirubin >2 mg/dl, and/or abnormal ultrasound findings such as an echogenic liver, enlarged spleen, or gallbladder stones (17). Since our institution lacked equipment to test for D-lactic acidosis, it was defined clinically as lactic acidosis identified on blood gas analysis that required hospitalization. Micronutrient deficiency was defined as requiring hospitalization due to deficiencies in elements such as copper, zinc, manganese, and selenium.
For hospitalization after starting HPN, the total number of hospitalizations per patient and the total hospitalization days were calculated. Hospitalization reasons were classified into complications related to the main disease such as ileus or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, catheter-related complications, modification of PN formula due to metabolic complications, and other reasons.
Growth parameters for patients under 18 years old were calculated using z-scores for weight-for-age, height-for-age, and weight-for-height based on WHO Child Growth Standards (18). For patients over 19 years old, Body mass index (BMI) was calculated.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS 25.0. Z-scores and BMI for growth parameters are presented as means and standard deviations, while other continuous variables are presented as medians with minimum and maximum values. Nominal variables are presented as frequencies and percentages. Growth outcomes were analyzed using a paired t-test and a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient characteristics
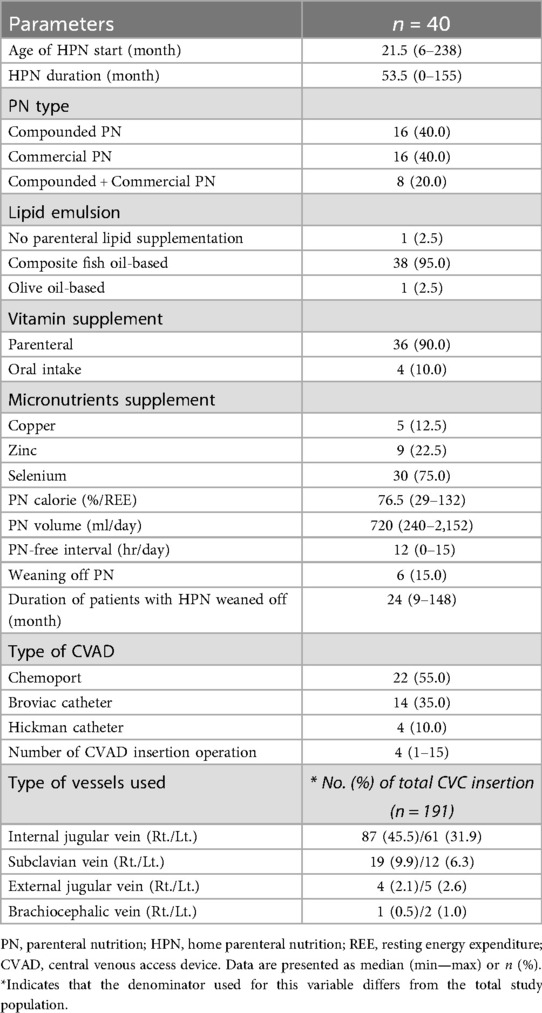
During the follow-up period, data from 40 pediatric patients (22 boys and 18 girls) were collected. General characteristics of these patients are shown in Table 1. The onset age of IF, meaning the age at which the diagnosis leading to HPN was first made, was less than 12 months in 23 (57.5%) patients and more than 12 months in 17 (42.5%) patients. Of patients who started HPN, 18 (45.0%) had a chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome (CIPOS), including CIPO, hypoganglionosis, and megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome. Nine (22.5%) patients started HPN due to SBS, with the underlying causes being NEC, midgut volvulus, and total colonic aganglionosis. Among the nine SBS patients, four were classified as type I (small bowel resection with high-output enterostomy proximal to the ICV) and five as type II (ileo-colic anastomosis without ICV). CE was the underlying cause in 5 (12.5%) patients, which included tufting enteropathy, diarrhea syndrome, and microvillus inclusion disease. IBD was the underlying cause in 4 (10.0%) patients, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Additionally, non-digestive diseases leading to IF, such as hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, cancer, and avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder, were underlying causes in 4 (10.0%) patients. A total of 31 patients underwent abdominal surgery, including 23 (57.5%) who underwent bowel resection and stoma formation and 7 (17.5%) who underwent stoma formation only. In 32 (80.0%) patients, ICV was preserved. Some patients had multiple types of stomas, with jejunostomy, ileostomy, and colostomy formed in 18, 25, and 5 patients, respectively. As the home care nursing service was initiated at our center in 2019, only 13 (32.5%) patients benefited from these services during the follow-up period. The median follow-up period was 53.5 (range, 0–155) months.
PN-related characteristics
Table 2 shows PN-related characteristics. The median age of HPN beginning was 21.5 (range, 6–238) months old. HPN duration was 53.5 (range, 0–155) months. Compounded PN prepared by our center's pharmacy and commercial PN were each used by 16 (40.0%) patients, while 8 (20.0%) patients alternated between using compounded PN and commercial PN. Cyclic PN was used for most patients, with a median PN-free interval of 12 (range, 0–15) hours daily. Six (15.0%) patients were weaned off HPN. The median PN duration for these patients was 24 (range, 9–148) months. The most commonly used type of CVAD was a Chemoport in 22 (55.0%) patients, followed by Broviac catheters in 14 (35.0%) patients and Hickman catheters in 4 (10.0%) patients. The median number of CVAD insertions per patient was 4 (range, 1–15) times. The internal jugular vein (IJV) was the most commonly used site for CVAD insertion. However, in cases where insertion in the IJV was difficult due to infection, stenosis, or thrombus, the subclavian vein, external jugular vein, or brachiocephalic vein was used for CVAD insertion.
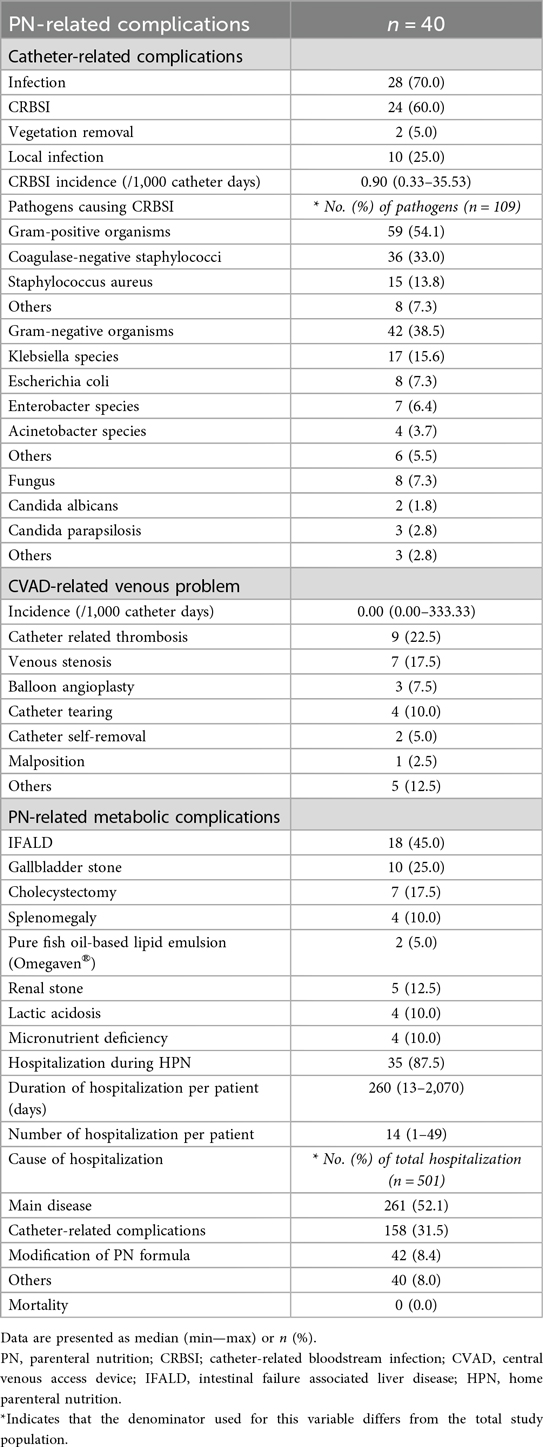
PN-related complications
Table 3 shows complications related to PN. Twenty-four (60.0%) patients experienced CRBSI at least once, with an median incidence of 0.90 (range, 0.33–35.53) per 1,000 catheter days. Two (5.0%) patients underwent vegetation removal surgery due to infective endocarditis caused by CRBSI. Among the total CRBSI episodes, the most common pathogens were coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) with 36 (33.0%) episodes, followed by Klebsiella with 17 (15.6%) episodes, and Staphylococcus aureus with 15 episodes (13.8%). The overall incidence of CVAD-related venous problems was 0.00 per 1,000 catheter-days (median; range, 0.00–333.33), whereas the mean incidence was 8.98 per 1,000 catheter-days. Catheter-related thrombosis was identified in 9 (22.5%) patients. Venous stenosis was observed in 7 patients, among whom 3 (7.5%) patients underwent balloon angioplasty via radiologic intervention due to severe stenosis at the cavo-atrial junction.
Among PN-related metabolic complications, 18 (45.0%) patients were diagnosed with IFALD. Among them, 2 used pure fish oil-based lipid emulsion for a short period (less than 6 weeks). Gallbladder stones were confirmed in 10 (25.0%) patients, of whom 7 underwent cholecystectomy. Four (10.0%) patients had persistent splenomegaly on ultrasound for over six months. Five (12.5%) patients were diagnosed with renal stone. No cases of refeeding syndrome were observed during the study period. A total of 35 (87.5%) patients were readmitted after starting HPN, with a median duration of 260 (range, 13–2070) days and a median of 14 (range, 1–49) readmissions. Most hospitalization episodes were due to the main disease (261 episodes, 52.1%) or catheter-related complications (158 episodes, 31.5%). No deaths occurred in the study cohort.
Growth outcomes
Table 4 presents growth parameters of patients at the time of diagnosis of the underlying causes that indicated HPN, at the initiation of HPN, and the final follow-up. The analysis of growth parameters over the HPN treatment period revealed a trend toward declining growth outcomes. The mean height-for-age z-score did not show a significant change from diagnosis −1.00 ± 2.45 to HPN initiation −1.29 ± 2.23 (p = 0.595), although it further declined at the final follow-up −1.86 ± 1.41 (p = 0.072). For weight-for-age, the z-score showed a non-significant improvement from diagnosis (−1.72 ± 2.45) to HPN initiation (−1.39 ± 2.11, p = 0.450), but significantly decreased by the final follow-up (−2.32 ± 1.78, p = 0.009). Weight-for-height z-scores initially improved from diagnosis at −1.84 ± 2.47 to HPN initiation at −0.78 ± 2.08 (p = 0.015), but declined at the final follow-up at −1.53 ± 1.64 (p = 0.049). BMI significantly improved from diagnosis (14.2 ± 2.5) to HPN initiation (16.7 ± 3.9, p < 0.001), but did not show a significant change from initiation to final follow-up at 15.6 ± 2.2 (p = 0.103). These findings indicate that, although some early improvements were observed, growth outcomes deteriorated over time, particularly in weight-for-age and weight-for-height.
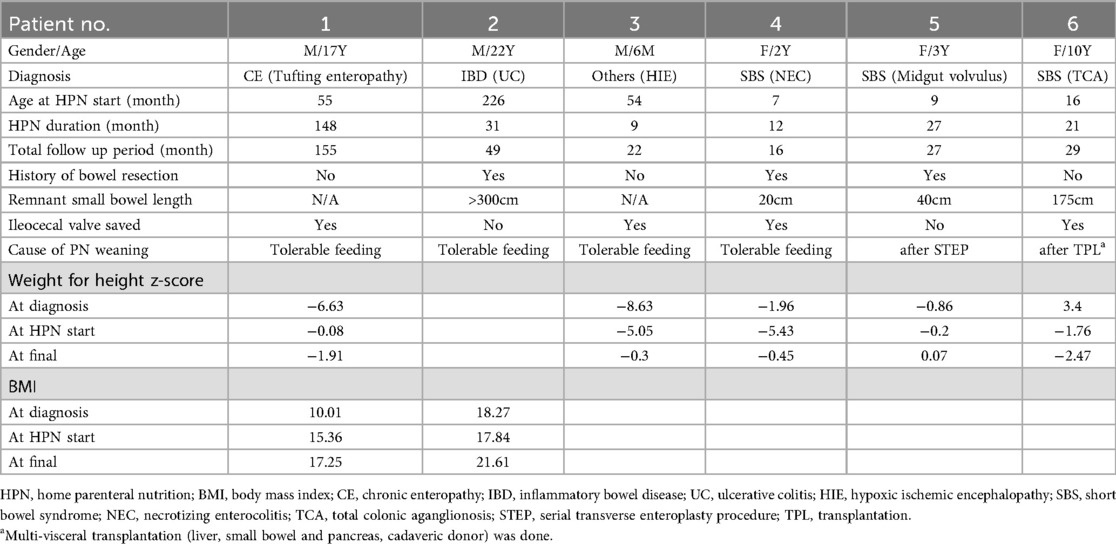
Characteristics of patients with HPN weaned off
Table 5 shows six patients who were successfully weaned off HPN by December 2021. Of these six, three patients were SBS, while the remaining included one patient each with CE, IBD, and hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. The median duration of HPN for those who succeeded in weaning was 24 months. Three of the six patients had a history of bowel resection. The ICV was preserved in four patients. Four patients could be weaned off HPN as they tolerated oral feeding well. One patient was weaned off after a serial transverse enteroplasty procedure. Another successfully discontinued PN following multi-visceral transplantation.
Discussion
IF is the reduction of gut function requiring intravenous supplementation. In pediatric patients, IF often results from critical illness, making long-term PN a life-changing necessity (1, 2). In these cases, HPN becomes a lifesaving therapy. It is the best alternative to prolonged hospitalization, enhancing the quality of life, particularly for pediatric patients (1, 12). The number of HPN patients is rising globally. To manage this increasing population effectively, the United States has established a management system through ASPEN (11). To the best of our knowledge, there are few reports in the literature regarding the prevalence and outcomes of pediatric HPN programs in South Korea (19). Our center has established an intestinal rehabilitation team based on the NST from an early stage, managing children requiring HPN through a multidisciplinary approach. Although there are still several limitations, we are one of the few large centers in South Korea implementing personalized HPN to reduce PN-related complications. Therefore, we aim to report characteristics and outcomes of 40 children enrolled in a single-center South Korea HPN cohort over a 13-year period.
In this study, the primary indication for HPN was digestive disease, accounting for 90% of cases. Notably, unlike in other studies, CIPOS accounted for 45% of these cases, followed by SBS. Non-digestive diseases such as malignancies accounted for only 10% of cases. In general, underlying diagnoses in IF patients can impact mortality rates and cause death. Particularly, non-digestive causes and motility disorders such as CIPO are known to be associated with higher mortality rates and poorer outcomes (20, 21). However, it is encouraging that, despite a high proportion of motility disorders in this study, no patients experienced mortality during follow-up.
Nevertheless, only 15% of patients achieved PN weaning, which was comparatively low given that the weaning rate in pediatric HPN patients in other studies ranged from 48% to 66% (22–24). Generally, preservation of ICV is known to be a positive prognostic factor for enteral autonomy (3, 25, 26). Although 32 (80%) patients in this cohort had preserved ICV, in the majority of these cases (21 patients), high-output jejunostomy or ileostomy was present proximal to the valve, likely rendering it functionally ineffective, which could explain the low PN weaning rate. Furthermore, previous studies have reported that pediatric CIPO patients often require long-term HPN and face significant challenges in achieving PN weaning (27, 28). The high prevalence of CIPO in this study population might have been a major factor that limited PN weaning, given the severe dysmotility associated with the disease, which could make enteral autonomy difficult to achieve.
Frequent hospital admissions due to complications can significantly impact the quality of life for both children and their families. It also increases healthcare costs (11, 22). During the total follow-up period, patients experienced an average of 14 admissions each, similar to reports from other countries regarding pediatric HPN (11, 22). Approximately half of readmissions were related to the underlying main disease, while the remainders were most commonly due to catheter-related complications.
In this study, the incidence of CRBSI was 0.90 per 1,000 catheter days, which was relatively low compared to other studies (3, 22, 29). This might be attributed to the exclusive use of tunneled catheters or implanted ports in our center. Additionally, our center uses one-lumen tunneled catheters unless there is a specific reason to use a different type. The ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines also emphasize the importance of single-lumen tunneled catheters and multidisciplinary monitoring to minimize CRBSI risk (16, 30, 31). For home care of catheters, the use of ethanol or taurolidine locks is recommended (29, 32). However, in Korea, these agents are not available for CVAD use, making their application difficult.
The most common pathogen among total occurrences of CRBSI was CoNS, consistent with findings from various other studies (3, 33, 34). CoNS is known for its biofilm affinity, often maintaining colonization even after blood cultures have turned negative following appropriate antimicrobial treatment (35). Klebsiella species were the most frequently identified Gram-negative pathogens. This might be attributable to bacterial translocation from altered gut microbiota of patients, particularly in patients receiving long-term PN, as they are known to increase intestinal permeability (36, 37). The prevalence of fungal infections in our patient group was low, consistent with other studies. In cases of fungal infection, catheter removal is recommended. However, this can pose a significant burden for pediatric HPN patients, underscoring the need for careful management (16).
In this study, a total 9 (22.5%) patients experienced catheter-related thrombosis, of which 2 received anticoagulation, while the remaining 7 patients underwent careful catheter removal and re-insertion. Our center has educated caregivers to use heparin locks for CVAD occlusion prophylaxis. However, following a report in 2020 recommending the use of sodium chloride 0.9% instead of heparin for locking, we have since been educating caregivers to use saline locks (14).
In our study, the prevalence of IFALD was approximately 45%, higher than the 20%–23% reported in other pediatric HPN studies (3, 22, 38). This discrepancy might have stemmed from the lack of standardized definitions, particularly in pediatric cases where liver biopsies are rarely performed (39). Our study applied broader diagnostic criteria beyond bilirubin levels alone, which might have contributed to the increased prevalence. Notably, when assessed solely based on bilirubin levels, cholestasis was observed in only 10% of patients. This favorable outcome was likely influenced by the use of composite fish oil-based intravenous lipid emulsions (ILE) and the low incidence of CRBSIs (40–44). Encouragingly, all patients with IFALD recovered except for one who required multi-visceral transplantation. A pure fish oil-based ILE was used for a short period (less than 6 weeks) in 2 patients. After improvement of bilirubin levels, they were switched back to their original lipid emulsion. While risk factors such as age, prematurity, underlying diagnoses, CRBSIs, and enteral feeding have been associated with IFALD, some studies have suggested no correlation between PN duration and IFALD development (19, 45). However, IFALD was significantly related to final anthropometric outcomes, emphasizing the need for optimized nutritional management (19).
Our study highlights difficulties pediatric patients on HPN face in achieving sustained growth. Some studies have reported improved growth outcomes such as improvements in weight and height z-scores (46, 47). However, our cohort did not achieve such long-term growth stability. A critical factor affecting growth outcomes is the adequacy of nutrition. Previous studies have suggested that a parenteral nutrition dependency index (PNDI) of ≥1.5 and sufficient energy supply are crucial for normal growth (3, 34, 48). Although our study did not collect PNDI, the mean PN calorie rate was observed to be 76.5% (range: 29%–132%) of REE. This low PN calorie may reflect both gradual PN reduction during the weaning process and insufficient or inconsistent enteral intake, which could not be quantitatively assessed in our retrospective cohort. Although an important goal of HPN is to wean off PN support, our results emphasize that achieving optimal growth remains a challenge. Individualized nutritional strategies are needed to address this issue.
To establish an effective home care support system for HPN children, legal and operational improvements are needed to enhance accessibility and convenience. In South Korea, pediatric-specific commercial PN is difficult to import. Is not widely used due to insurance limitations. Adult commercial PN, on the other hand, often has high lipid levels relative to the volume needed for pediatric patients. Direct mixing of micronutrients at home by caregivers rather than by healthcare professionals is not recommended due to the risk of handling errors and associated legal concerns. Therefore, it is only used for patients whose micronutrient and vitamin levels are stable and for those whose age is closer to adulthood. This situation necessitates the use of compounded PN, which requires caregivers to visit the hospital every other day to collect the PN, causing significant inconvenience. Consequently, caregivers have expressed a preference for receiving HPN via parcel delivery services. However, due to concerns over HPN stability and legal restrictions, implementing such a system has proven challenging. Although our center started a home care nursing service in 2019, the high number of patients and the shortage of skilled personnel made delivering HPN through home care nurses challenging. In contrast, other countries have long operated systems where HPN is distributed through regional affiliated hospitals near the patient's residence, allowing periodic visits to the original center to assess the appropriateness of HPN or by outsourcing compounding and delivery services. In Korea, it is necessary to improve legal frameworks to establish similar delivery systems and hospital-affiliated networks. Overall, our results underscore both the applicability and the challenges of implementing the ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guideline recommendations in the Korean context, where systemic and logistical barriers remain.
Although this study provides valuable insights into the management of pediatric HPN in Korea, it has several limitations. Firstly, the retrospective design and single-center nature of the study limited the generalizability of our findings. Furthermore, precise evaluation of enteral nutrition intake was not feasible due to the retrospective nature of the study, which precluded adjustment of growth outcomes for enteral caloric intake. Secondly, the relatively small sample size and the variability in the underlying diseases and treatment durations might have influenced the observed outcomes. Thirdly, the present study did not assess quality of life for patients on HPN or compare HPN with intestinal transplantation, although these are important criteria for supporting long-term PN.
In conclusion, this study provides valuable insights into pediatric HPN in a single center in Korea, highlighting its critical role in managing IF without causing mortality. Despite low PN weaning rates and growth outcomes, effective CRBSI prevention were achieved. Challenges remain in supporting growth and improving accessibility to HPN services. To optimize outcomes for pediatric HPN in Korea, systemic legal and logistical reforms, alongside further research, are essential.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, South Korea. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board due to the retrospective nature of the study and the use of de-identified clinical data.
Author contributions
HH: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Data curation. DK: Data curation, Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. H-BY: Writing – review & editing. JY: Writing – review & editing. JM: Writing – review & editing. JK: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. H-YK: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The handling editor SP declared a past co-authorship with the author JY.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issue please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
IF, intestinal failure; SBS, short bowel syndrome; CIPO, chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction; CE, congenital enteropathies; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; PN, parenteral nutrition; HPN, home parenteral nutrition; CRBSI, catheter-related bloodstream infection; ASPEN, American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition; ICV, Ileocecal valve; CVAD, central venous access device; NST, nutrition support team; REE, resting energy expenditure; IFALD, intestinal failure-associated liver disease; BMI, body mass index; CIPOS, chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome; IJV, internal jugular vein; CoNS, coagulase-negative staphylococci; ILE, intravenous lipid emulsion; PNDI, parenteral nutrition dependency index.
References
1. Pironi L, Arends J, Baxter J, Bozzetti F, Peláez RB, Cuerda C, et al. ESPEN endorsed recommendations. Definition and classification of intestinal failure in adults. Clin Nutr. (2015) 34(2):171–80. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.08.017
2. Koletzko B, Goulet O, Hunt J, Krohn K, Shamir R. Guidelines on paediatric parenteral nutrition of the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) and the European Society for clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN), supported by the European Society of Paediatric Research (ESPR). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2005) 41(Suppl 2):S1–87. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000181841.07090.f4
3. Abi Nader E, Lambe C, Talbotec C, Pigneur B, Lacaille F, Garnier-Lengliné H, et al. Outcome of home parenteral nutrition in 251 children over a 14-y period: report of a single center. Am J Clin Nutr. (2016) 103(5):1327–36. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.121756
4. Wilmore DW, Dudrick SJ. Growth and development of an infant receiving all nutrients exclusively by vein. Jama. (1968) 203(10):860–4. doi: 10.1001/jama.1968.03140100042009
5. Suita S, Yamanouchi T, Masumoto K, Ogita K, Nakamura M, Taguchi S. Changing profile of parenteral nutrition in pediatric surgery: a 30-year experience at one institute. Surgery. (2002) 131(1 Suppl):S275–82. doi: 10.1067/msy.2002.119965
6. Schönenberger KA, Reber E, Huwiler VV, Dürig C, Muri R, Leuenberger M, et al. Quality of life in the management of home parenteral nutrition. Ann Nutr Metab. (2023) 79(3):326–33. doi: 10.1159/000530082
7. Olieman JF, Poley MJ, Gischler SJ, Penning C, Escher JC, van den Hoonaard TL, et al. Interdisciplinary management of infantile short bowel syndrome: resource consumption, growth, and nutrition. J Pediatr Surg. (2010) 45(3):490–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2009.08.009
8. Colomb V, Fabeiro M, Dabbas M, Goulet O, Merckx J, Ricour C. Central venous catheter-related infections in children on long-term home parenteral nutrition: incidence and risk factors. Clin Nutr. (2000) 19(5):355–9. doi: 10.1054/clnu.2000.0132
9. Corrigan ML, Huang S, Weaver A, Keeler D, Rahe K, Balint J, et al. Resources for the provision of nutrition support to children in educational environments. Nutr Clin Pract. (2017) 32(6):834–43. doi: 10.1177/0884533617718471
10. Kumpf VJ, Tillman EM. Home parenteral nutrition: safe transition from hospital to home. Nutr Clin Pract. (2012) 27(6):749–57. doi: 10.1177/0884533612464888
11. Howard L, Ament M, Fleming CR, Shike M, Steiger E. Current use and clinical outcome of home parenteral and enteral nutrition therapies in the United States. Gastroenterology. (1995) 109(2):355–65. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90321-6
12. Hill S, Ksiazyk J, Prell C, Tabbers M. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: home parenteral nutrition. Clin Nutr. (2018) 37(6 Pt B):2401–8. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.06.954
13. Kwi Suk K. Strategy for activation of home total paren-teral nutrition. J Clin Nutr. (2013) 5(3):96–101. doi: 10.15747/jcn.2013.5.3.96
14. Pironi L, Boeykens K, Bozzetti F, Joly F, Klek S, Lal S, et al. ESPEN guideline on home parenteral nutrition. Clin Nutr. (2020) 39(6):1645–66. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.03.005
15. Schofield WN. Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum Nutr Clin Nutr. (1985) 39(Suppl 1):5–41.4044297
16. Pittiruti M, Hamilton H, Biffi R, MacFie J, Pertkiewicz M. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: central venous catheters (access, care, diagnosis and therapy of complications). Clin Nutr. (2009) 28(4):365–77. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2009.03.015
17. Beath S, Pironi L, Gabe S, Horslen S, Sudan D, Mazeriegos G, et al. Collaborative strategies to reduce mortality and morbidity in patients with chronic intestinal failure including those who are referred for small bowel transplantation. Transplantation. (2008) 85(10):1378–84. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31816dd513
18. World Health Organization. Child growth standards: weight-for-age (2023). Available online at: https://www.who.int/tools/child-growth-standards/standards/weight-for-age (Accessed February 8, 2023).
19. Choi SJ, Lee KJ, Choi JS, Yang HR, Moon JS, Chang JY, et al. Poor prognostic factors in patients with parenteral nutrition-dependent pediatric intestinal failure. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. (2016) 19(1):44–53. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2016.19.1.44
20. Heneyke S, Smith VV, Spitz L, Milla PJ. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: treatment and long term follow up of 44 patients. Arch Dis Child. (1999) 81(1):21–7. doi: 10.1136/adc.81.1.21
21. Hess RA, Welch KB, Brown PI, Teitelbaum DH. Survival outcomes of pediatric intestinal failure patients: analysis of factors contributing to improved survival over the past two decades. J Surg Res. (2011) 170(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2011.03.037
22. Colomb V, Dabbas-Tyan M, Taupin P, Talbotec C, Révillon Y, Jan D, et al. Long-term outcome of children receiving home parenteral nutrition: a 20-year single-center experience in 302 patients. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2007) 44(3):347–53. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31802c6971
23. Krawinkel MB, Scholz D, Busch A, Kohl M, Wessel LM, Zimmer KP. Chronic intestinal failure in children. Dtsch Arztebl Int. (2012) 109(22-23):409–15. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2012.0409
24. Spencer AU, Neaga A, West B, Safran J, Brown P, Btaiche I, et al. Pediatric short bowel syndrome: redefining predictors of success. Ann Surg. (2005) 242(3):403–9. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000179647.24046.03
25. Quirós-Tejeira RE, Ament ME, Reyen L, Herzog F, Merjanian M, Olivares-Serrano N, et al. Long-term parenteral nutritional support and intestinal adaptation in children with short bowel syndrome: a 25-year experience. J Pediatr. (2004) 145(2):157–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.02.030
26. Goulet O, Baglin-Gobet S, Talbotec C, Fourcade L, Colomb V, Sauvat F, et al. Outcome and long-term growth after extensive small bowel resection in the neonatal period: a survey of 87 children. Eur J Pediatr Surg. (2005) 15(2):95–101. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-821214
27. Mousa H, Hyman PE, Cocjin J, Flores AF, Di Lorenzo C. Long-term outcome of congenital intestinal pseudoobstruction. Dig Dis Sci. (2002) 47(10):2298–305. doi: 10.1023/a:1020199614102
28. Stanghellini V, Cogliandro RF, de Giorgio R, Barbara G, Salvioli B, Corinaldesi R. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: manifestations, natural history and management. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2007) 19(6):440–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2007.00902.x
29. Wozniak LJ, Bechtold HM, Reyen LE, Chan AP, Marcus EA, Vargas JH. Epidemiology and risk factors for outpatient-acquired catheter-related bloodstream infections in children receiving home parenteral nutrition. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2018) 42(5):942–8. doi: 10.1002/jpen.1037
30. Zürcher M, Tramèr MR, Walder B. Colonization and bloodstream infection with single- versus multi-lumen central venous catheters: a quantitative systematic review. Anesth Analg. (2004) 99(1):177–82. doi: 10.1213/01.Ane.0000118101.94596.A0
31. Kuizon D, Gordon SM, Dolmatch BL. Single-lumen subcutaneous ports inserted by interventional radiologists in patients undergoing chemotherapy: incidence of infection and outcome of attempted catheter salvage. Arch Intern Med. (2001) 161(3):406–10. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.3.406
32. Hulshof EC, Hanff LM, Olieman J, de Vette S, Driessen GJ, Meeussen C, et al. Taurolidine in pediatric home parenteral nutrition patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J. (2017) 36(2):233–5. doi: 10.1097/inf.0000000000001404
33. Bond A, Chadwick P, Smith TR, Nightingale JMD, Lal S. Diagnosis and management of catheter-related bloodstream infections in patients on home parenteral nutrition. Frontline Gastroenterol. (2020) 11(1):48–54. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2018-101094
34. Goulet O, Breton A, Coste ME, Dubern B, Ecochard-Dugelay E, Guimber D, et al. Pediatric home parenteral nutrition in France: a six years national survey. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40(10):5278–87. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.08.002
35. Silva PV, Cruz RS, Keim LS, Paula GR, Carvalho BT, Coelho LR, et al. The antimicrobial susceptibility, biofilm formation and genotypic profiles of Staphylococcus haemolyticus from bloodstream infections. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. (2013) 108(6):812–3. doi: 10.1590/0074-0276108062013022
36. Cole CR, Frem JC, Schmotzer B, Gewirtz AT, Meddings JB, Gold BD, et al. The rate of bloodstream infection is high in infants with short bowel syndrome: relationship with small bowel bacterial overgrowth, enteral feeding, and inflammatory and immune responses. J Pediatr. (2010) 156(6):941–7.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.12.008
37. D'Antiga L, Dhawan A, Davenport M, Mieli-Vergani G, Bjarnason I. Intestinal absorption and permeability in paediatric short-bowel syndrome: a pilot study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (1999) 29(5):588–93. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199911000-00021
38. Cavicchi M, Beau P, Crenn P, Degott C, Messing B. Prevalence of liver disease and contributing factors in patients receiving home parenteral nutrition for permanent intestinal failure. Ann Intern Med. (2000) 132(7):525–32. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-132-7-200004040-00003
39. Sasdelli AS, Agostini F, Pazzeschi C, Guidetti M, Lal S, Pironi L. Assessment of intestinal failure associated liver disease according to different diagnostic criteria. Clin Nutr. (2019) 38(3):1198–205. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.04.019
40. Goulet O, Antébi H, Wolf C, Talbotec C, Alcindor LG, Corriol O, et al. A new intravenous fat emulsion containing soybean oil, medium-chain triglycerides, olive oil, and fish oil: a single-center, double-blind randomized study on efficacy and safety in pediatric patients receiving home parenteral nutrition. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2010) 34(5):485–95. doi: 10.1177/0148607110363614
41. Goulet O, Joly F, Corriol O, Colomb-Jung V. Some new insights in intestinal failure-associated liver disease. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. (2009) 14(3):256–61. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e32832ac06f
42. Diamanti A, Basso MS, Castro M, Calce A, Pietrobattista A, Gambarara M. Prevalence of life-threatening complications in pediatric patients affected by intestinal failure. Transplant Proc. (2007) 39(5):1632–3. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.02.083
43. Hermans D, Talbotec C, Lacaille F, Goulet O, Ricour C, Colomb V. Early central catheter infections may contribute to hepatic fibrosis in children receiving long-term parenteral nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2007) 44(4):459–63. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e318031a5c7
44. Courtney CM, Warner BW. Pediatric intestinal failure-associated liver disease. Curr Opin Pediatr. (2017) 29(3):363–70. doi: 10.1097/mop.0000000000000484
45. Lacaille F, Gupte G, Colomb V, D'Antiga L, Hartman C, Hojsak I, et al. Intestinal failure-associated liver disease: a position paper of the ESPGHAN working group of intestinal failure and intestinal transplantation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2015) 60(2):272–83. doi: 10.1097/mpg.0000000000000586
46. Pichler J, Chomtho S, Fewtrell M, Macdonald S, Hill S. Body composition in paediatric intestinal failure patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition. Arch Dis Child. (2014) 99(2):147–53. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2012-303516
47. Pichler J, Chomtho S, Fewtrell M, Macdonald S, Hill SM. Growth and bone health in pediatric intestinal failure patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. (2013) 97(6):1260–9. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.057935
Keywords: home parenteral nutrition, intestinal failure, pediatrics, catheter-related bloodstream infection, intestinal failure-associated liver disease
Citation: Hwang H, Ko D, Yang H-B, Youn JK, Moon JS, Ko JS and Kim H-Y (2025) A single-center experience of home parenteral nutrition for pediatric intestinal failure. Front. Pediatr. 13:1658512. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1658512
Received: 2 July 2025; Accepted: 5 September 2025;
Published: 25 September 2025.
Edited by:
Sowon Park, Yonsei University, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
You Ie Kim, Catholic University of Korea, Republic of KoreaKateřina Koudelková, Faculty Hospital Královské Vinohrady, Czechia
Copyright: © 2025 Hwang, Ko, Yang, Youn, Moon, Ko and Kim. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hyun-Young Kim, c3BraHkwMkBzbnUuYWMua3I=
 Honam Hwang
Honam Hwang Dayoung Ko
Dayoung Ko Hee-Beom Yang
Hee-Beom Yang Joong Kee Youn
Joong Kee Youn Jin Soo Moon4
Jin Soo Moon4 Jae Sung Ko
Jae Sung Ko Hyun-Young Kim
Hyun-Young Kim