- 1Henan Joint International Research Laboratory of Veterinary Biologics Research and Application, Anyang Institute of Technology, Anyang, China
- 2Institute of Environmental Safety and Human Health, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 3Laboratory of Natural Product Extraction, China-US (Henan) Hormel Cancer Institute, Zhengzhou, China
- 4College of Basic Medical, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, China
- 5Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 6Yunnan Province Key Laboratory for Nutrition and Food Safety in Universities, Kunming, Yunnan, China
A Corrigendum on
Eupafolin Suppresses Esophagus Cancer Growth by Targeting T-LAK Cell-Originated Protein Kinase Protein Kinase
By Fan X, Tao J, Cai X, Fredimoses M, Wu J, Jiang Z, Zhang K and Li S (2019) Front. Pharmacol. 10:1248. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01248
Xin Cai was not included as an author, and Xiaoying Zhang was incorrectly included as an author in the published article. The corrected Author Contributions Statement appears below.
Author Contributions
XF designed research, performed research and wrote the paper; JT analyzed the data; MF extracted Eupafolin from Ay Tsao; JW expressed Histone H3 protein; XC, ZJ performed animal research andanalyzed data; SL, KZ designed research and analyzed data.
Furthermore, there was a mistake in Figure 1D as published. The TOPK western picture has an extra strip. The corrected Figure 1 appears below.
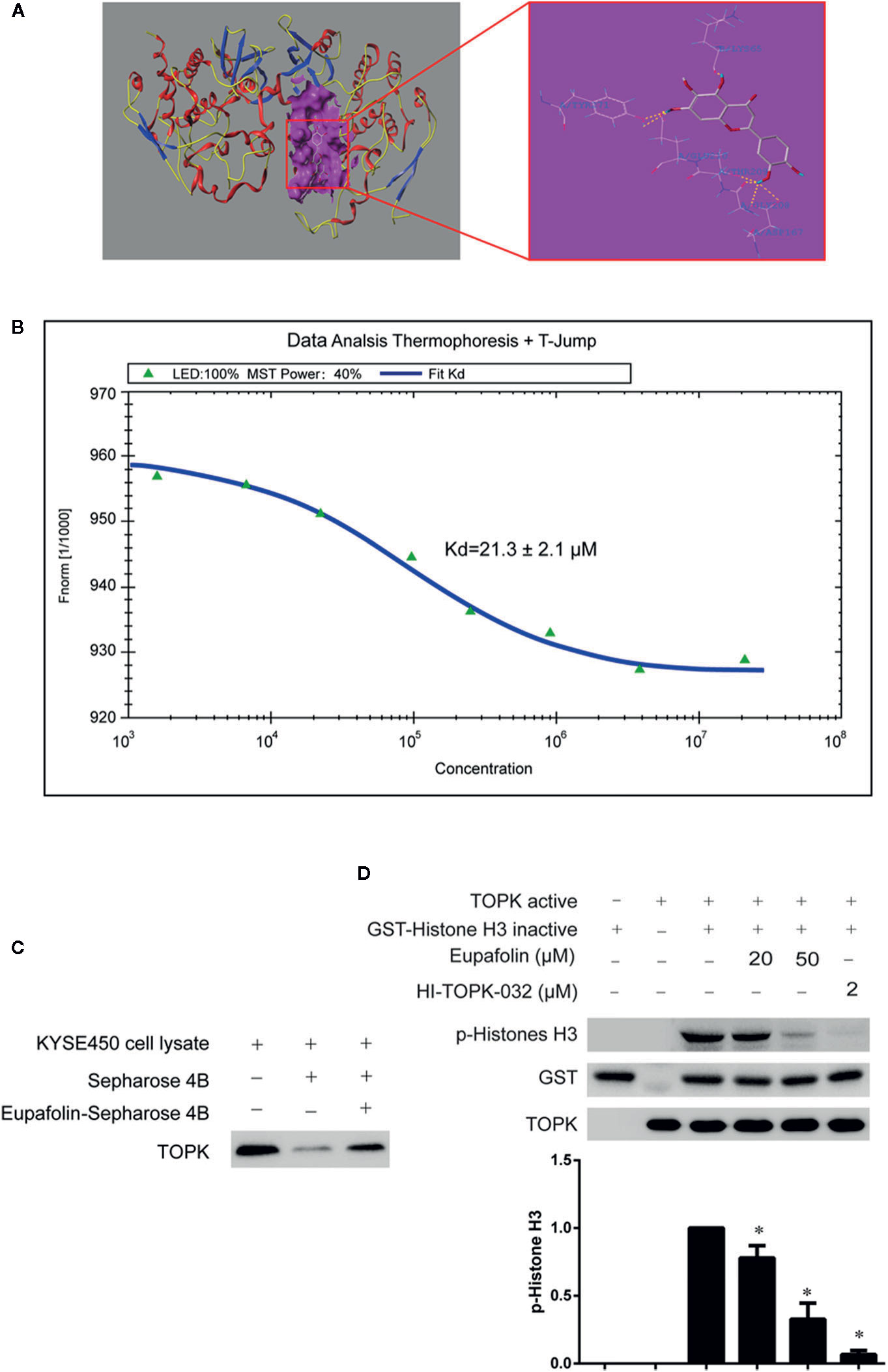
Figure 1 Eupafolin binds with TOPK and suppresses TOPK activity in vitro. (A) The docking model of eupafolin and TOPK. (B) Measurement of affinity between TOPK and eupafolin by MST in standard treated capillaries, and the resulting binding curve was shown. From the resulting binding curve, Kd of 21.3 ± 2.1 is calculated. (C) Eupafolin binds directly with TOPK. Sepharose 4B was used for binding and pull-down assay as described in section “Materials and methods.” Lane 1 is input control (TOPK protein standard); lane 2 is the negative control, indicating there is no binding between TOPK and beads alone; and, lane 3 indicates that TOPK binds with eupafolin-Sepharose 4B beads. (D) Eupafolin inhibits TOPK activity in vitro. The inhibitory effect of eupafolin on TOPK was determined by an in vitro kinase assay. An inactive GST-histone H3 protein was used as the substrate with active TOPK and 100 μM ATP in the reaction buffer. Protein were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE gel and detected by Western blot. Histogram statistics is the expression of the p-histone H3 in the first line. Data are representatives of results from triplicate experiments. *Significant compared with lane 3 alone, P < 0.05.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: eupafolin, esophagus cancer, TOPK, inhibitor, Ay Tsao
Citation: Fan X, Tao J, Cai X, Fredimoses M, Wu J, Jiang Z, Zhang K and Li S (2020) Corrigendum: Eupafolin Suppresses Esophagus Cancer Growth by Targeting T-LAK Cell-Originated Protein Kinase Protein Kinase. Front. Pharmacol. 11:1178. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01178
Received: 22 February 2020; Accepted: 20 July 2020;
Published: 14 August 2020.
Edited by:
Jiang-Jiang Qin, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Qiang Wang, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, ChinaCopyright © 2020 Fan, Tao, Cai, Fredimoses, Wu, Jiang, Zhang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kunpeng Zhang, a3VucGVuZ3poYW5nMTJAc2luYS5jb20=; Shude Li, c2h1ZGVsaTAwNkAxNjMuY29t
 Xiaoming Fan
Xiaoming Fan Junyan Tao2
Junyan Tao2 Shude Li
Shude Li