In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 1F as published. Figure 1F was displayed as “Vimentin positive area (%).” The correct Figure 1F is “NGAL positive area (%).” The corrected legend appears below.
FIGURE 1
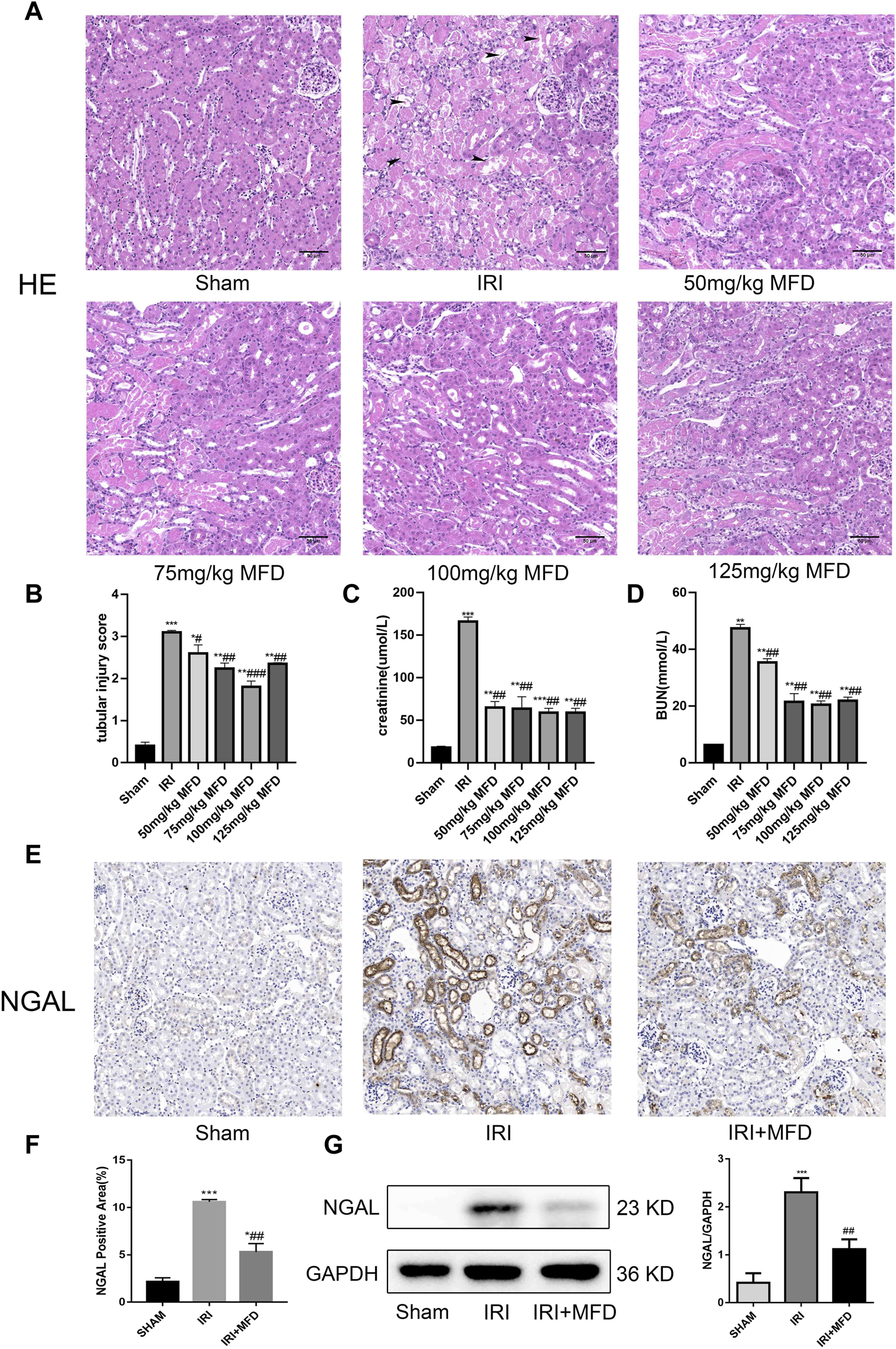
Mefunidone ameliorated IRI-induced AKI (A) HE staining showed protective effect of mefunidone at various doses of 50 mg/kg, 75 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 125 mg/kg on renal tubular injury on day 2 after IRI modeling (×200). arrows for renal tubular damage. (B) The tubular injury scores of HE staining for kidney damage. (C) Serum creatinine (SCr) levels of mefunidone at various doses of 50 mg/kg, 75 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 125 mg/kg on renal tubular injury on day 2 after IRI modeling. (D) Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels of mefunidone at various doses of 50 mg/kg, 75 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 125 mg/kg on renal tubular injury on day 2 after IRI modeling. (E,F) Histological images of immunohistochemical staining with NGAL and evaluation of NGAL positive area in each group on day 2 after IRI modeling (×200). Mefunidone: 100 mg/kg. (G) Western blot analysis and quantitative data of NGAL in each group on day 2 after IRI modeling. Mefunidone: 100 mg/kg. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 3–5). *p < 0.05, vs. Sham group; **p < 0.01, vs. Sham group; ***p < 0.001, vs. Sham group; #p < 0.05, vs. IRI group; ##p < 0.01, vs. IRI group; ###p < 0.001, vs. IRI group.
Furthermore, there was an error in the Supplementary Material. Supplementary Figure S1 was displayed as “CCK-8 to determine the optimal drug concentration of mefunidone for 24 h for HK-2 cell viability”; Supplementary Figure S2 was displayed as “Mefunidone alleviated kidney fibrosis and inhibited EMT in IRI-induced CKD.” The correct Supplementary Figure S1 is “Mefunidone alleviated kidney fibrosis and inhibited EMT in IRI-induced CKD”; The correct Supplementary Figure S2 is “CCK-8 to determine the optimal drug concentration of mefunidone for 24 h for HK-2 cell viability.”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Statements
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2023.1188615/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1Mefunidone alleviated kidney fibrosis and inhibited EMT in IRI-induced CKD (A) HE staining (×200) and tubular injury scores showed protective effect of Mefunidone on renal tubular injury on day 14 after IRI modeling. arrows for renal tubular damage. (B) Masson's trichrome staining (×200) and kidney fibrotic scores showed protective effect of Mefunidone on renal tubular injury on day 14 after IRI modeling. arrows for renal tubular damage and renal fibrosis. (C) Histological images of immunohistochemical staining with collagen I and evaluation of collagen I positive area in each group on day 14 after IRI modeling (×200). (D) Histological images of immunohistochemical staining with vimentin and evaluation of vimentin positive area in each group on day 14 after IRI modeling (×200). (E) Western blot analysis and quantitative data of α-SMA and E-Cadherin in each group on day 14 after IRI modeling. Mefunidone: 100 mg/kg. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 5-6). *p < 0.05, vs Sham group; **p < 0.01, vs Sham group; ***p < 0.001, vs Sham group; ****p < 0.0001, vs Sham group; #p < 0.05, vs IRI group; ##p < 0.01, vs IRI group; ###p < 0.001, vs IRI group.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S2CCK-8 to determine the optimal drug concentration of Mefunidone for 24 h for HK-2 cell viability. HK-2 cells were treated with Mefunidone at concentrations of 0, 20, 40, 80, 120 and 160 μg/ml. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Summary
Keywords
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, folic acid, acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, mefunidone
Citation
Li J, Jiang Y, Dai Q, Yu Y, Lv X, Zhang Y, Liao X, Ao L, Hu G, Meng J, Peng Z, Tao L and Xie Y (2023) Corrigendum: Protective effects of Mefunidone on ischemia-reperfusion injury/folic acid-induced acute kidney injury. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1188615. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1188615
Received
17 March 2023
Accepted
27 March 2023
Published
05 April 2023
Volume
14 - 2023
Edited and reviewed by
Robert John Unwin, University College London, United Kingdom
Updates
Copyright
© 2023 Li, Jiang, Dai, Yu, Lv, Zhang, Liao, Ao, Hu, Meng, Peng, Tao and Xie.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanyun Xie, xieyanyun@csu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
This article was submitted to Renal Pharmacology, a section of the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.