In the published article, there was an error in Figure 8 as published. The Iba1 fluorescence image of the cortex and corresponding merged image in the KXS-L group was mistakenly displayed. The corrected Figure 8 and its caption appear below.
FIGURE 8
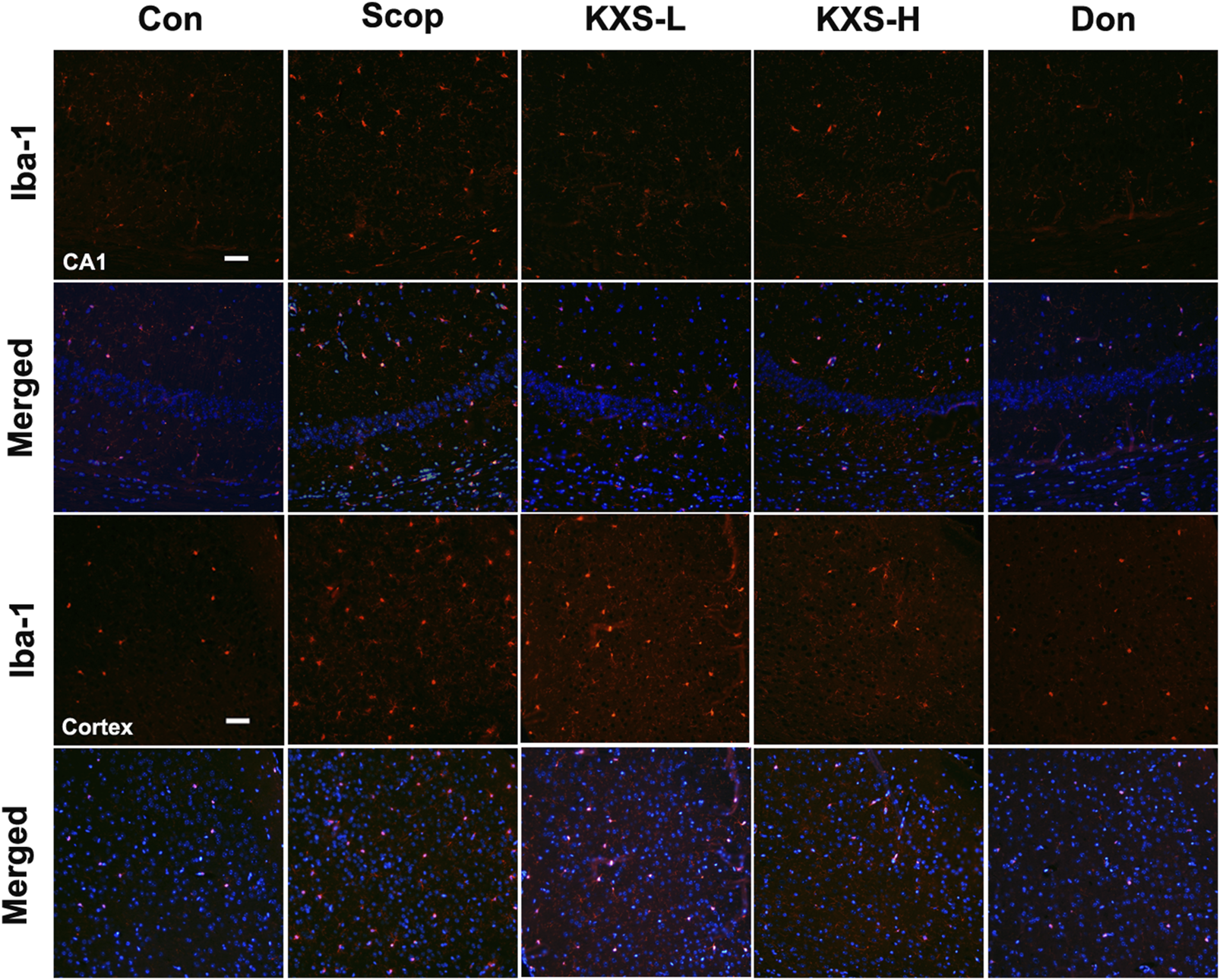
Kai-Xin-San (KXS) attenuates microglia activation in scopolamine (SCOP)-induced mice. Immunofluorescence analysis in the hippocampus (CA1) and cortex. Microglia were stained with anti-Iba-1 (red) and the nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 50 mm. Con, control group; SCOP, scopolamine; KXS-L, low-dose Kai-Xin San (1.4 g/kg); KSX-H, high-dose Kai-Xin San (2.8 g/kg); Don, donepezil.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Statements
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Summary
Keywords
systems pharmacology, Kai-Xin-San, Alzheimer’s disease, cholinergic system, neuroinflammation
Citation
Luo Y, Li D, Liao Y, Cai C, Wu Q, Ke H, Liu X, Li H, Hong H, Xu Y, Wang Q, Fang J and Fang S (2023) Corrigendum: Systems pharmacology approach to investigate the mechanism of Kai-Xin-San in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1239060. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1239060
Received
23 August 2023
Accepted
22 September 2023
Published
06 October 2023
Volume
14 - 2023
Edited and reviewed by
Wei Peng, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2023 Luo, Li, Liao, Cai, Wu, Ke, Liu, Li, Hong, Xu, Wang, Fang and Fang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qi Wang, wangqi@gzucm.edu.cn; Jiansong Fang, fangjs@gzucm.edu.cn; Shuhuan Fang, fangshuhuan@gzucm.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.