In the published article, there was an error in Figure 7 as published. The images for IC-CM and IC-CM + Rg1 in panel A need to be corrected. The added panel C provides an additional statistical indicator to increase the reliability of the results. The corrected Figure 7 and its caption appear below.
FIGURE 7
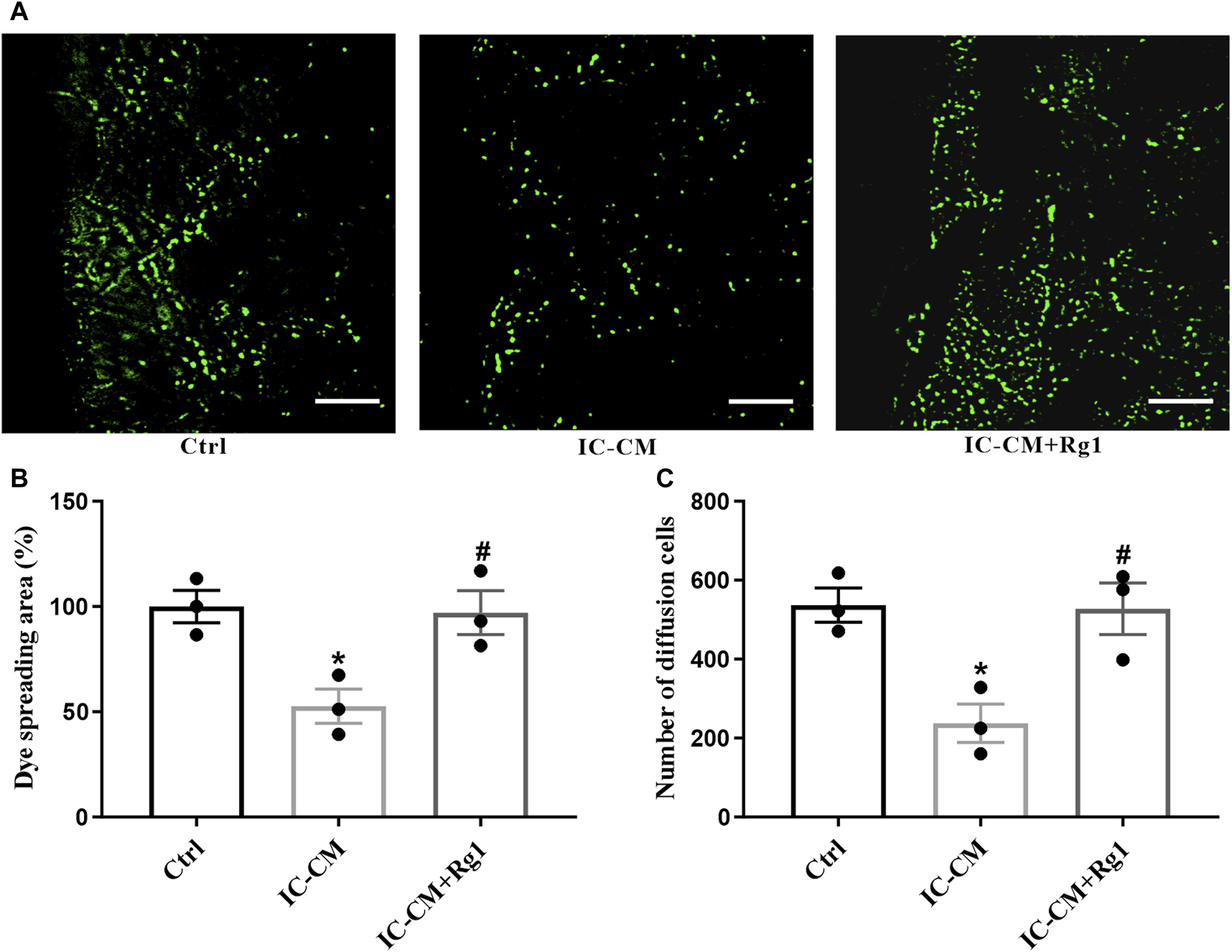
Rg1 ameliorates inflammation-induced gap junctional dysfunction in glial cells. The SLDT assay was conducted to detect the influence of Rg1 or inflammatory cytokines on gap junction intercellular communication (A), which was indicated by the dye spreading area (B) and number of diffusion cells (C). Scale bar = 100 μm. n = 3. *p < 0.05, compared with the Ctrl group; #p < 0.05, compared with the IC-CM group. SLDT, scrape-loading and dye transfer; IC-CM, inflammatory cytokines-conditioned medium.
In the published article, there is an update.
A correction has been made to Results, Rg1 ameliorates inflammation-induced gap junction dysfunction in glial cells, Paragraph Number 1. The two sentences previously stated:
“As shown in Figure 7, the gap junction intercellular communication in the IC-CM group was impaired, manifesting that inflammation attacked severe depression. While Rg1 could normalize inflammatory cytokines-induced reduction of diffusion area of fluorescence, demonstrating that Rg1 could ameliorate inflammation-induced dysfunction of gap junctions in glial cells.”
The corrected sentences appear below:
“As shown in Figure 7, the gap junction intercellular communication in the IC-CM group was impaired, manifesting that inflammation attacked severe depression. While Rg1 could normalize inflammatory cytokines-induced reduction of diffusion area of fluorescence (Figures 7A, B) and number of diffusion cells (Figure 7C), demonstrating that Rg1 could ameliorate inflammation-induced dysfunction of gap junctions in glial cells.”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Statements
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Summary
Keywords
depression, inflammation, ginsenoside Rg1, connexin 43, ubiquitination
Citation
Wang H, Yang Y, Yang S, Ren S, Feng J, Liu Y, Chen H and Chen N (2024) Corrigendum: Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates neuroinflammation via suppression of connexin43 ubiquitination to attenuate depression. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1418824. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1418824
Received
17 April 2024
Accepted
03 July 2024
Published
17 July 2024
Volume
15 - 2024
Edited by
Jian Gao, Shanghai Children’s Medical Center, China
Reviewed by
Wen Wang, Capital Medical University, China
Ling Zhao, Southwest Medical University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2024 Wang, Yang, Yang, Ren, Feng, Liu, Chen and Chen.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Naihong Chen, chennh@imm.ac.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.