In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3 as published. The immunoblotting band for β-actin in Figure 3A was not correct. The corrected Figure 3 and its caption appear below.
FIGURE 3
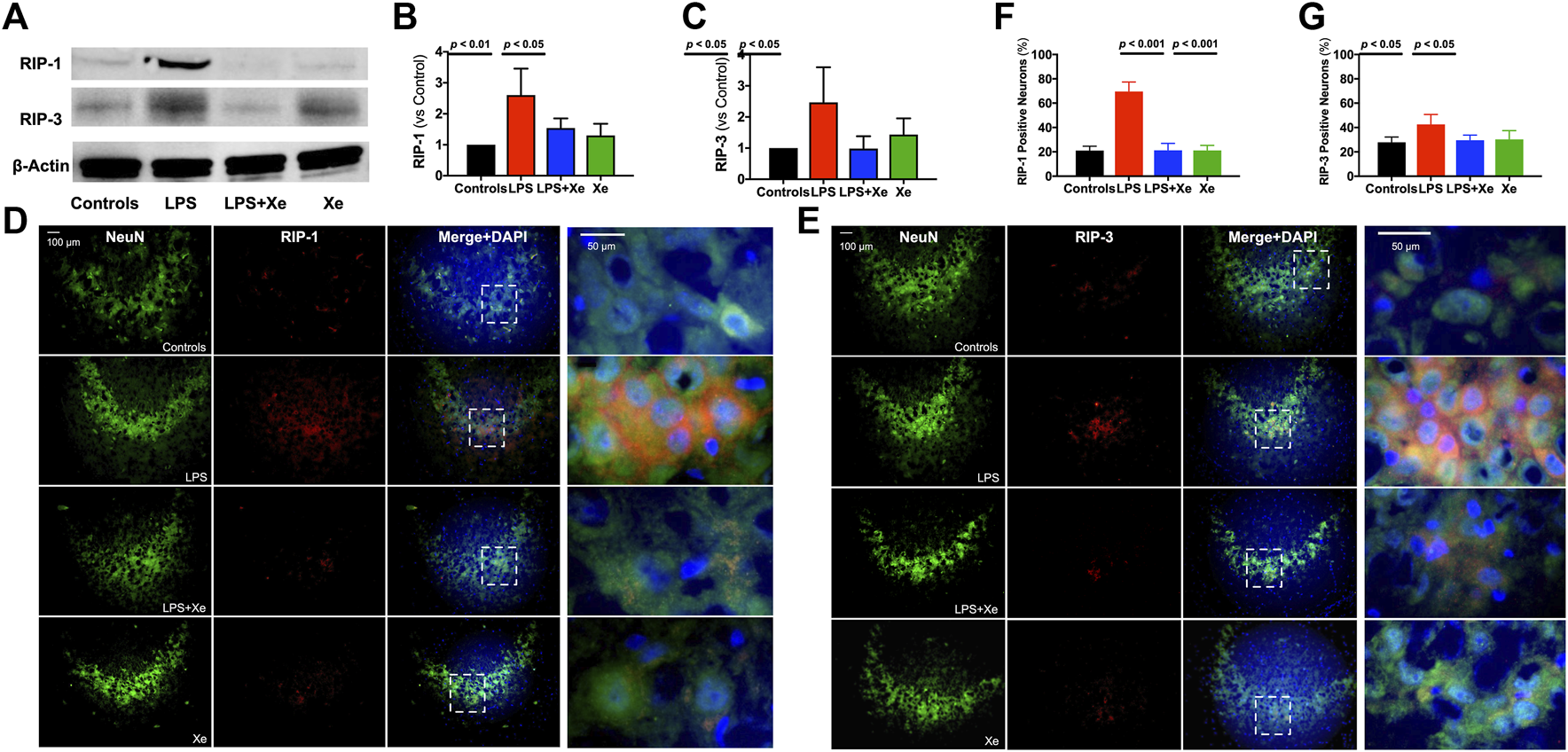
Xenon prevented persistent activation of necroptosis in juvenile rats with neonatal LPS administration. Representative western blot bands (A) with quantification (B, C) for necroptosis in PND 30 animals (27 days after initial LPS injection). Representative immunohistochemistry staining (D, E) with quantification (F, G) indicting persistent neuronal necroptosis in PND 30 animals. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. (Con = saline injection +70%N2/30%O2; LPS = LPS injection +70%N2/30%O2; LPS + Xe = LPS inhalation +70%Xenon/30%O2; Xe = saline injection +70% Xe/30% O2; n = 4 in each group except n = 3 in group LPS for western blotting).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Statements
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Summary
Keywords
neonatal sepsis, xenon, neurodevelopmental impairment, necroptosis, neuroinflammation
Citation
Liao Z, Ou X, Zhou C, Ma D, Zhao H and Huang H (2024) Corrigendum: Xenon attenuated neonatal lipopolysaccharide exposure induced neuronal necroptosis and subsequently improved cognition in juvenile rats. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1438335. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1438335
Received
25 May 2024
Accepted
24 June 2024
Published
10 July 2024
Volume
15 - 2024
Edited and reviewed by
Olumayokun Olajide, University of Huddersfield, United Kingdom
Updates
Copyright
© 2024 Liao, Ou, Zhou, Ma, Zhao and Huang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hailin Zhao, hailin.zhao06@imperial.ac.uk; Han Huang, han.huang@scu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work and share senior authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.