- 1Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, International Acupuncture and Moxibustion Innovation Institute, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 3Institute for Literature and Culture of Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, Shandong, China
Background: Inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial damage are significantly involved in the development of unstable angina pectoris (UAP). Danhong injection (DHI) is a compound injection composed of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Carthamus tinctorius extracts. Several clinical studies have demonstrated DHI’s efficacy for treating UAP, with potential pharmacological effects on inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial function. However, to date, the current evidence has not been systematically summarized and analyzed.
Purpose: This study provides a comprehensive overview of the most recent clinical findings and systematically analyzes the impact of DHI on inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial function among individuals diagnosed with UAP.
Methods: We searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) conducted until January 2023 from two clinical trial registries and eight literature databases. The Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool 2.0 was utilized to assess the potential bias in the included trials, while the GRADE system was employed to evaluate the outcome quality.
Results: We included 46 trials involving 4,601 patients with UAP. The meta-analysis results suggested that DHI significantly reduced the levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) (standard mean difference [SMD] = 1.34, 95% confidence interval [CI] [-1.77, −0.90], P < 0.00001), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (SMD = −0.84, 95% CI [-1.54, −0.15], P = 0.02), interleukin-6 (IL-6) (SMD = −1.05, 95% CI [-1.86, −0.25], P = 0.01), endothelin/endothelin-1 (ET/ET-1) (SMD = −2.01, 95% CI [-2.57, −1.46], P < 0.00001), and homocysteine (Hcy) (SMD = −0.55, 95% CI [-0.71, −0.39], P < 0.00001) but increased the nitric oxide (NO) level (SMD = 1.51, 95% CI [1.04, 1.97], P < 0.00001) in patients with UAP. Twenty-one RCTs described adverse events.
Conclusion: DHI effectively and safely reduced hs-CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, ET/ET-1, and Hcy levels and increased the NO level in patients with UAP. However, considering the overall low quality of the original studies, future large-scale, high-quality RCTs are imperative to provide robust evidence for clinical practice.
Systematic Review Registration: identifier CRD42023391497.
1 Introduction
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a significant contributor to global morbidity and mortality (Duan et al., 2018). Unstable angina pectoris (UAP) is an acute coronary syndrome in CAD and a clinical symptom between stable angina pectoris and acute myocardial infarction. Although the UAP-related mortality rate has declined annually in recent years, the prevalence rate remains high; therefore, it remains a major public health concern (Man et al., 2020; Li M. et al., 2022). UAP should be suspected if a patient presents with resting angina for >20 min, crescendo angina, or new-onset angina (Collet et al., 2021). UAP mainly lasts for a long time at rest or at night, and because of its special physiological mechanisms and clinical manifestations, it can develop into acute myocardial infarction or sudden death if not treated in time (Guo J. et al., 2020). The pathology of UAP is thought to be related to local coronary atherosclerotic lesions (Kosiński et al., 2022), such as vasospasm, intravascular inflammation, thrombosis, and unstable plaques. These conditions can lead to vascular stenosis or blockage, resulting in myocardial ischemia. Inflammation significantly affects cardiovascular diseases; recently, addressing inflammation has become a potential way to prevent such diseases (Wolf and Ley, 2019). Evidence suggests that inflammation is caused by substances responsible for vascular plaque formation. Furthermore, inflammatory mediators and cytokines induce endothelial dysfunction and platelet adhesion, ultimately leading to the progression of atherosclerosis (Bi et al., 2019). The combined effect of inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress, as well as improving endothelial function, can provide a favorable microenvironment for endothelial injury repair and potentially alleviate atherosclerotic lesions. Conventional Western medical treatments, such as plaque stabilization and antiplatelet and antithrombotic drugs, have been successfully used to reduce angina. However, owing to the complexity of UAP, the long-term use of these drugs can produce side effects and resistance that influence the treatment’s effectiveness (Duan et al., 2018; Xi et al., 2023). Therefore, it is crucial to investigate and identify other novel and effective treatments for UAP.
Danhong injection (DHI) is a standardized traditional Chinese medicine product. According to the traditional Chinese medicine theory, the pathogenesis of UAP is closely associated with blood coagulation, and the main function of DHI is to promote blood circulation, blood stasis, and dredging meridians (Wu et al., 2015); thus, it is effective against UAP (Wu et al., 2017; Guo S. et al., 2020; Xing et al., 2021). DHI is a proprietary Chinese medicine extracted from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (family: Lamiaceae; red sage or Danshen in Chinese) and Carthamus tinctorius L. (family: Compositae; safflower or Honghua in Chinese) (Zou et al., 2018). The main bioactive ingredients include salvianolic acids, danshensu, protocatechuic aldehyde, rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, and hydroxysafflor yellow A (Feng et al., 2019). Contemporary pharmacological investigations have revealed that DHI and its active components elicit pleiotropic protective effects in the cardiovascular system, such as anti-fibrosis, reducing blood viscosity, anti-inflammation, anti-oxidative damage, improving endothelial function and alleviate endothelial dysfunction (Lyu et al., 2017; Yi et al., 2018; Hu et al., 2019; Nijat et al., 2022).
Recent studies have found that DHI is effective for patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, such as angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, and cerebral infarction (Yu et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2022). However, a comprehensive systematic assessment of the effects of DHI on inflammatory factors and endothelial function in patients with UAP is lacking. Therefore, we performed a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis to thoroughly assess the impact of DHI on inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial function in patients with UAP, aiming to offer robust clinical evidence for DHI.
2 Methods
The meta-analysis was facilitated by the prospective registration of the review protocol with PROSPERO (No: CRD42023391497). The study was carried out in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and documented following the guidelines provided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (Page et al., 2021).
2.1 Data sources and search strategy
The following databases were comprehensively searched from their inception until January 15, 2023: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang Data, China Biomedical Literature Database, and Chongqing VIP Information. The Chinese Clinical Trial Registry and ClinicalTrials.gov were also comprehensively searched. There were no constraints on publication date, language, or publication status of the included studies. The main search terms used were “Danhong injection” and “unstable angina pectoris.” Supplementary Table S1 presents the detailed search strategies for all databases.
2.2 Eligibility criteria for included studies
The RCTs included in this study fulfilled the PICOS criteria.
2.2.1 Inclusion criteria
Studies were included based on the following Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, and Study (i.e., PICOS) criteria:
1) Type of participant (P): Patients receiving DHI. All patients, regardless of age, sex, or ethnicity, who fulfilled at least one of the guidelines for DHI established by the European Society of Cardiology (Messerli et al., 2006), World Health Organization, Chinese Society of Cardiology (Ke and Chen, 2007), or American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association (Braunwald et al., 2002).
2) Types of intervention (I): DHI alone or combined with conventional therapy.
3) Types of comparators (C): Conventional Western medicine (CWM), including aspirin, β-blockers, statins, nitrates, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or low-molecular-weight heparin.
4) Types of outcome measures (O): The primary outcomes focused on (1) inflammatory factors, including high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) and (2) indicators of vascular endothelial function, such as nitric oxide (NO), endothelin/endothelin-1 (ET/ET-1), and homocysteine (Hcy). The secondary outcomes were factors related to adverse events (AEs).
5) Types of studies (S): Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with unrestricted language and methods.
2.2.2 Exclusion criteria
The following study types were excluded: (1) non-RCTs, animal experimental studies, case reports, protocols, reviews, and conference abstracts; (2) duplicate publications and those with no full text, incomplete or incorrect data, and extraneous interventions; and (3) those with no relevant outcome measures.
2.3 Data extraction
Based on the aforementioned standards, data were independently extracted by two reviewers. The extracted data included language, the first author, publication year, baseline characteristics, details of the interventions, and outcome measurements. The results underwent cross-validation at every stage of the procedure, and any inconsistencies were resolved through discussion and agreement with an arbiter.
2.4 Risk of bias assessment
The Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool 2.0 (Sterne et al., 2019) was utilized to assess the potential for bias in the included trials. The assessment criteria encompassed the randomization process, deviations from the intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of outcome, and selection of the reported result. The domains were classified into three categories based on their risk level: “low risk,” “some concerns,” or “high risk.” Any discrepancies in the evaluation were resolved through deliberation and agreement with a mediator.
2.5 Data analysis
In this meta-analysis, STATA 17.0 (Higgins et al., 2011) and Review Manager software 5.4 were used for the statistical analyses of primary and secondary outcomes. Dichotomous variables were evaluated using risk ratios (RR), whereas continuous variables were examined by calculating the mean difference or standard mean difference (SMD). The heterogeneity among the studies was evaluated using the Q test and I2 statistics. Depending on the heterogeneity test result, a random or fixed-effects model was selected for the data analysis; the fixed-effects model was used if no significant heterogeneity was detected (P ≥ 0.10 or I2 ≤ 50%). Conversely, the random-effects model was employed in cases of observed heterogeneity. The results were determined using P-values, with statistical significance defined as P < 0.05. Additionally, the total DHI dose, detection methods, and detection time were considered potential influential factors based on the included studies. A meta-regression analysis was performed to investigate potential factors contributing to the observed heterogeneity. The relevant factors identified in the meta-regression analysis were used as classification criteria for the subgroup analysis. To assess the reliability of the merged results, a sensitivity analysis was performed where each study was removed one by one. Furthermore, publication bias was identified by employing funnel plots, an Egger’s test, and a Begger’s test.
2.6 Certainty assessment
In this study, the certainty of evidence was evaluated using the grading of recommendations, assessment, development, and evaluation (GRADE) system (Murad et al., 2017). The level of certainty in the evidence was rated as “high,” “medium,” “low,” or “very low.”
3 Results
3.1 Study selection
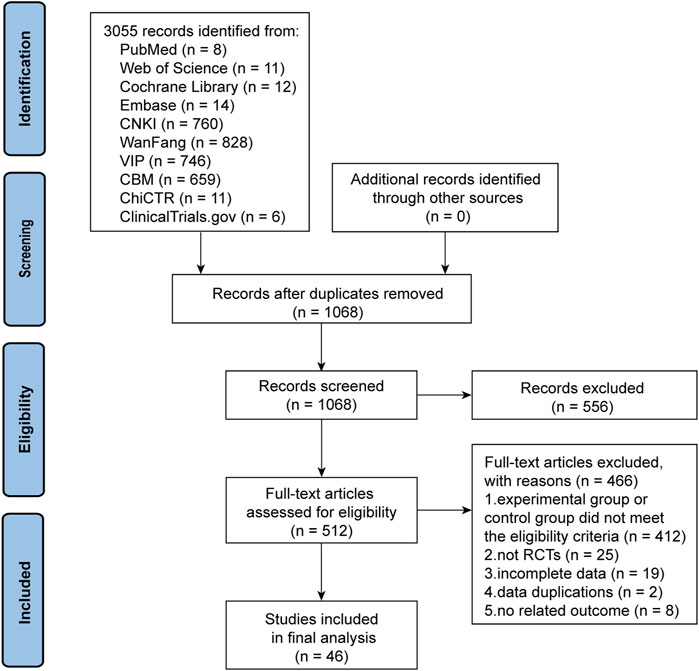
We initially identified 3,055 articles with potential relevance, of which 1,987 duplicates were excluded. Of the remaining 1,068 articles, 556 were excluded after reviewing their titles and abstracts. The remaining articles were further evaluated by reading the full text, and 465 were removed for the following reasons: the experimental or control group met the exclusion criteria (n = 466), not an RCT (n = 25), incomplete data (n = 19), duplicate data (n = 2), and lacking outcomes that met the criteria (n = 8). Finally, 46 trials were included in the quality assessment and further analysis. Figure 1 presents the PRISMA flowchart illustrating the trial selection process.
3.2 Study characteristics
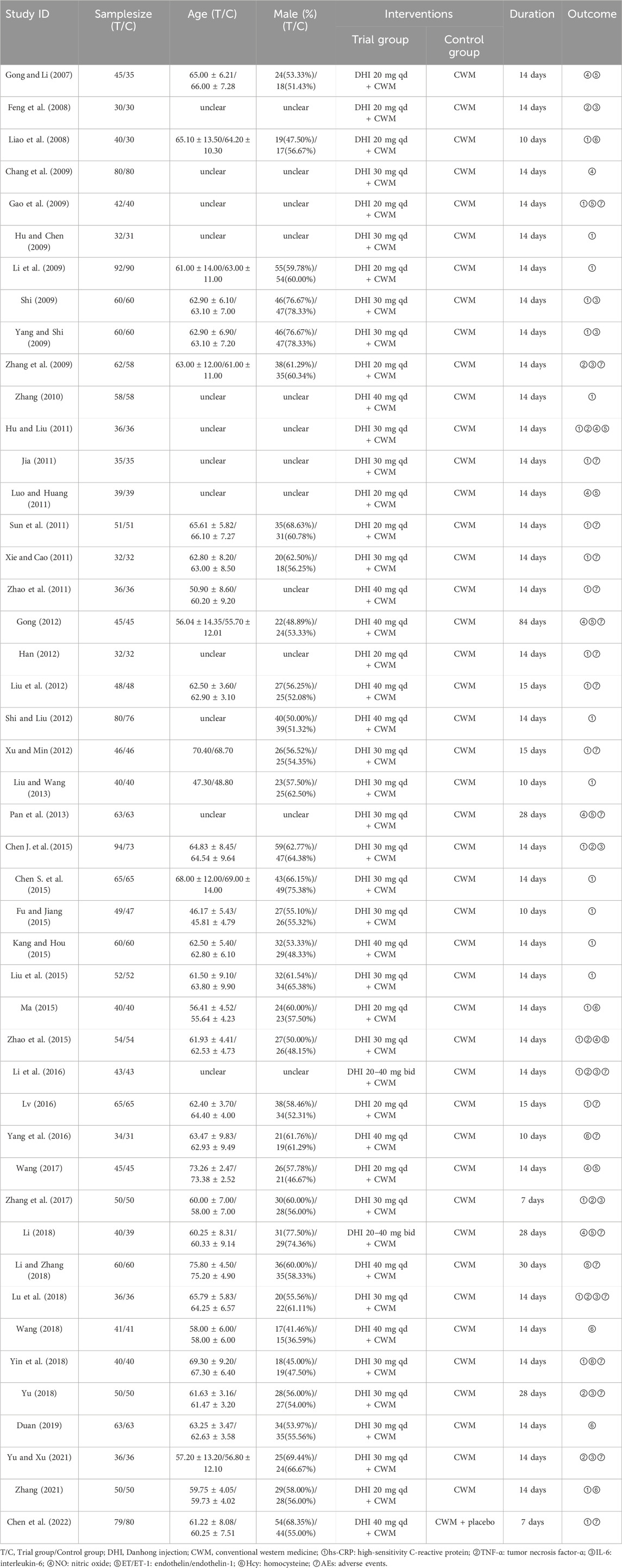
The 46 included RCTs were performed from 2007 to 2022. One RCT was a multicenter study. The sample size varied from 60 to 182, totaling 4,601 participants (2,330 and 2,271 in the experimental and control groups, respectively). The participants were predominantly male and ranged from 45.81 to 75.8 years old. All the research interventions included DHI combined with CWM. In all studies, DHI was intravenously administered at a dose of 20–40 mL/day for 7–30 days. All the included studies provided comprehensive reports on the outcomes of inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial function. Furthermore, 21 trials reported AE outcomes, of which 11 reported no AEs, and the remaining 10 reported 70 AEs. Table 1 summarizes the information regarding the included RCTs.
3.3 Risk of bias
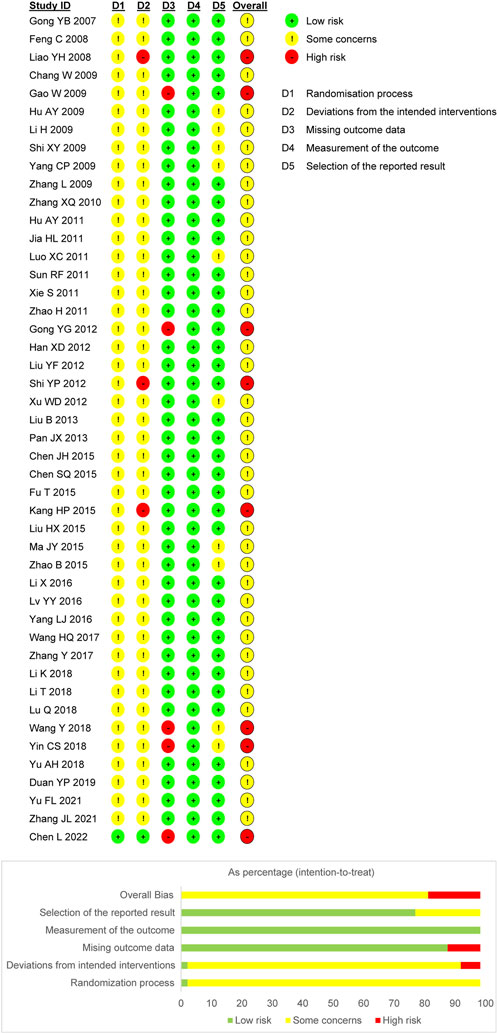
Nine trials utilized randomized sequence methods, such as random number tables or central randomized systems. Of these, 1 trial mentioned allocation concealment methods and was therefore considered “low risk.” The remaining trials only mentioned randomization and did not propose specific randomization methods; therefore, the risk of bias was unclear. For bias due to deviations from the expected interventions, 3 trials were identified as “high risk” due to the absence of blinding, and 1 trial was classified as “low risk” for explicitly implementing blinding. The risk in the remaining trials was unclear due to the lack of blinding information regarding the participants, operators, and outcome assessments. The absence of follow-up was not explicitly addressed in five trials; thus, bias due to missing outcome data was assessed as “high risk.” Moreover, all trials were rated as “high risk” for bias owing to the objectivity of the outcome measures. In addition, 10 trials raised “some concern” regarding potential bias in the selection of reported outcomes due to the absence of explicitly mentioned planned outcomes in the predetermined protocol. However, the remaining trials were considered “low risk,” as they consistently adhered to the predetermined protocol regarding outcome measures and analyses. Based on the assessment of these five aforementioned aspects, 8 trials were classified as “high risk,” while the remaining trials were classified as “some concern.” Figure 2 presents the risk of bias evaluation results.
3.4 Inflammatory factors
3.4.1 hs-CRP
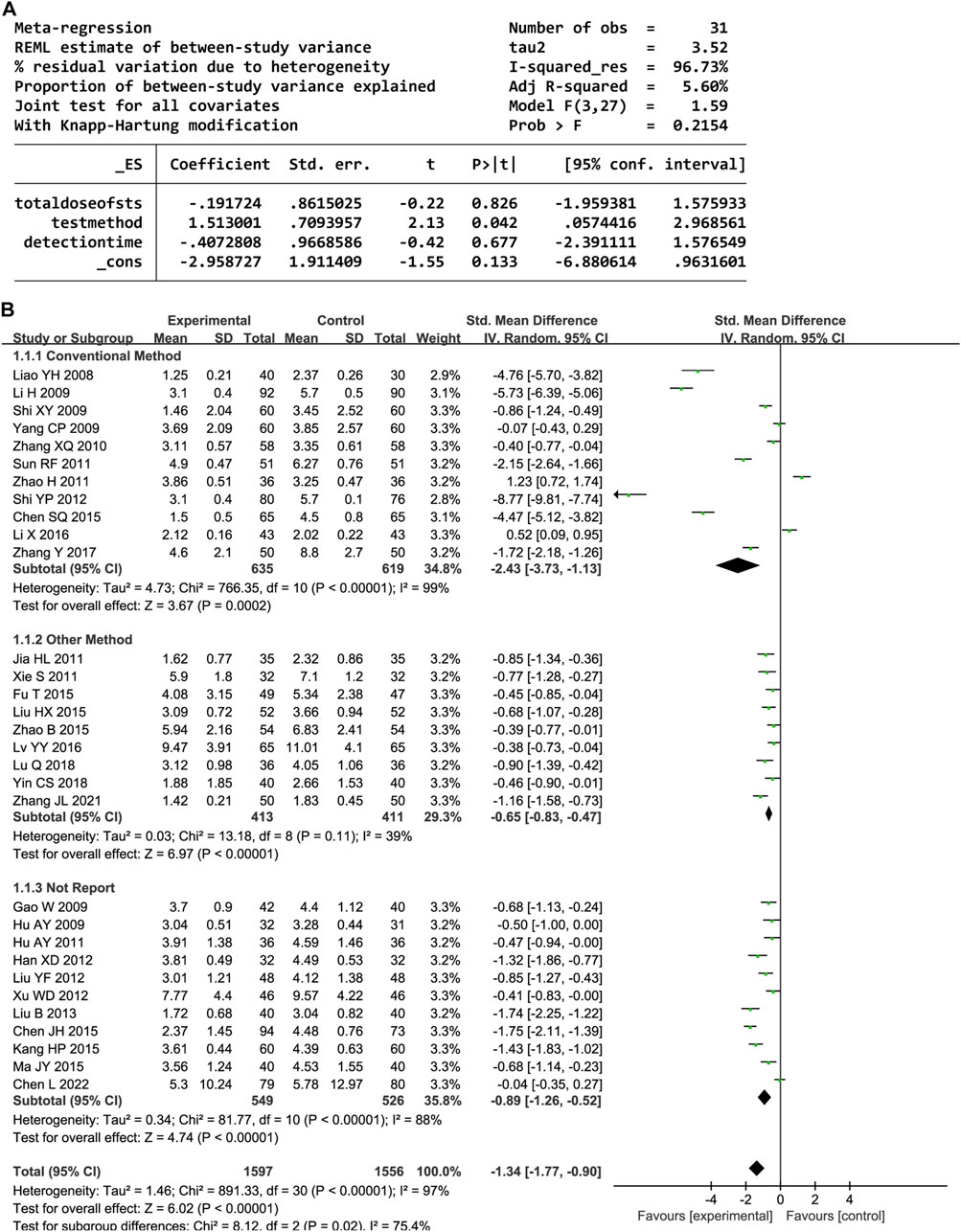
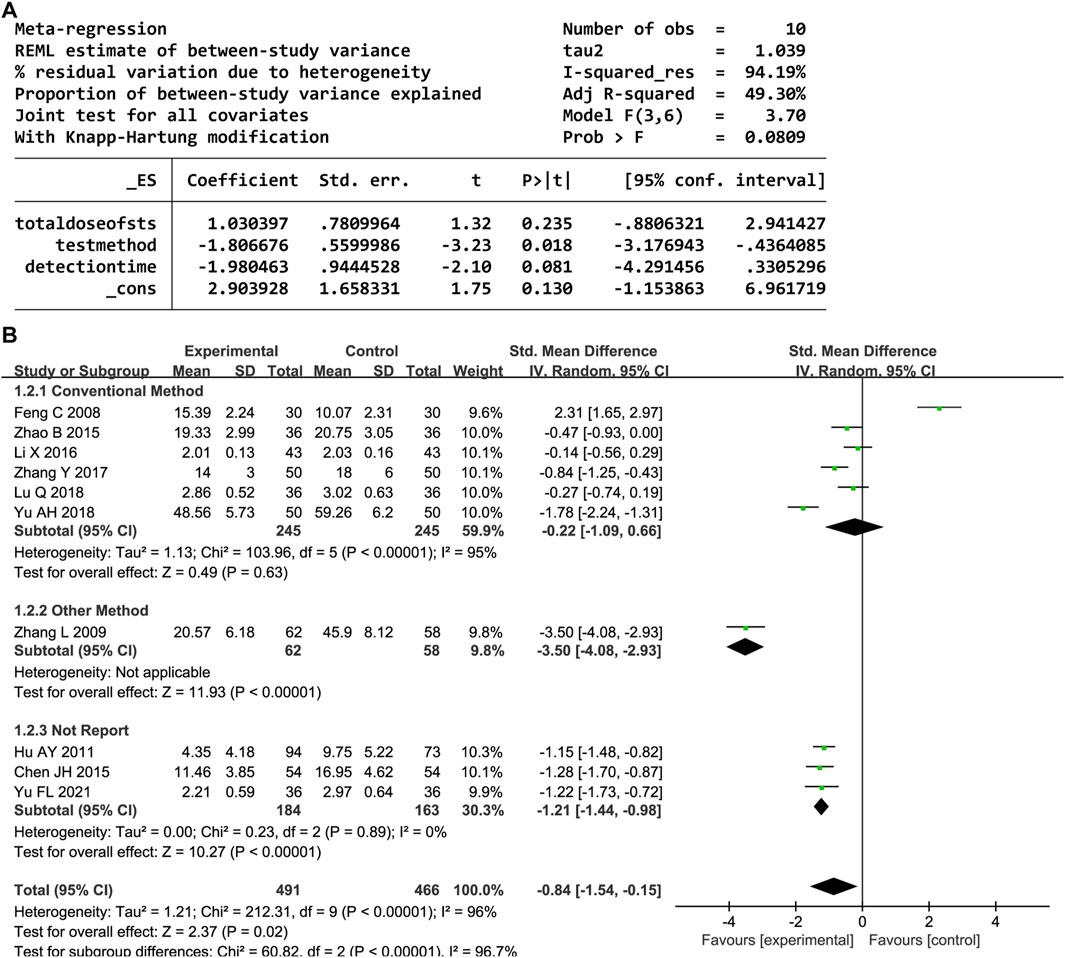
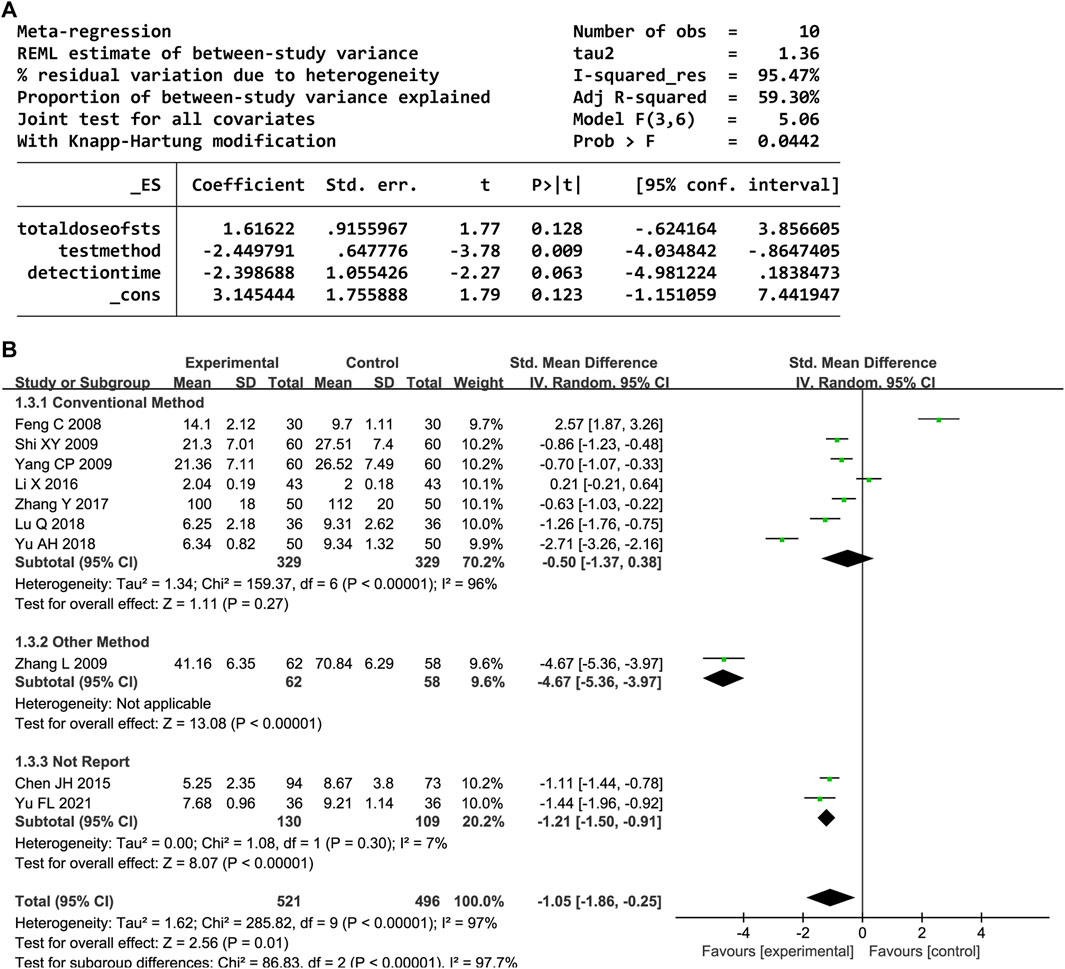
In total, 31 trials documented the serum hs-CRP level. A random-effects model was employed owing to significant heterogeneity (P < 0.00001, I2 = 97%). The results indicated notably decreased serum hs-CRP levels in the experimental group compared to the control group (SMD = −1.34, 95% confidence interval [CI] [-1.77, −0.90], P < 0.00001). A sensitivity analysis was conducted owing to the heterogeneity, but none of the studies were substantially related to the estimated effect sizes (Supplementary Figure S1). A meta-regression was conducted to explore potential factors contributing to the observed heterogeneity, which identified an association with the hs-CRP test method (P < 0.05, Figure 3A). A subgroup analysis based on the test method resulted in decreased heterogeneity (Figure 3B).
3.4.2 TNF-α
Overall, 10 trials reported the serum TNF-α level. A random-effects model was employed owing to significant heterogeneity (P < 0.00001, I2 = 96%). DHI with CWM significantly reduced the TNF-α level compared to the control group (SMD = −0.84, 95% CI [-1.54, −0.15], P = 0.02). A sensitivity analysis was performed owing to the heterogeneity, but none of the studies were significantly associated with the estimated effect sizes (Supplementary Figure S2). The meta-regression analysis identified an association between the test method and heterogeneity (P < 0.05, Figure 4A); the detection time and total DHI dose had no effect. A subgroup analysis based on the test method resulted in decreased heterogeneity (Figure 4B).
3.4.3 IL-6
Ten trials provided data on the serum IL-6 level. Significant heterogeneity was observed (P < 0.00001, I2 = 97%); thus, a random-effects model was employed. The IL-6 levels significantly decreased in the DHI group compared to the control group (SMD = −1.05, 95% CI [-1.86, −0.25], P = 0.01). The sensitivity analysis showed that no one study affected the summary effect (Supplementary Figure S3). The meta-regression analysis identified an association between the heterogeneity and IL-6 test method (P < 0.05, Figure 5A). A subgroup analysis based on the test method resulted in decreased heterogeneity (Figure 5B).
3.5 Vascular endothelial function
3.5.1 NO
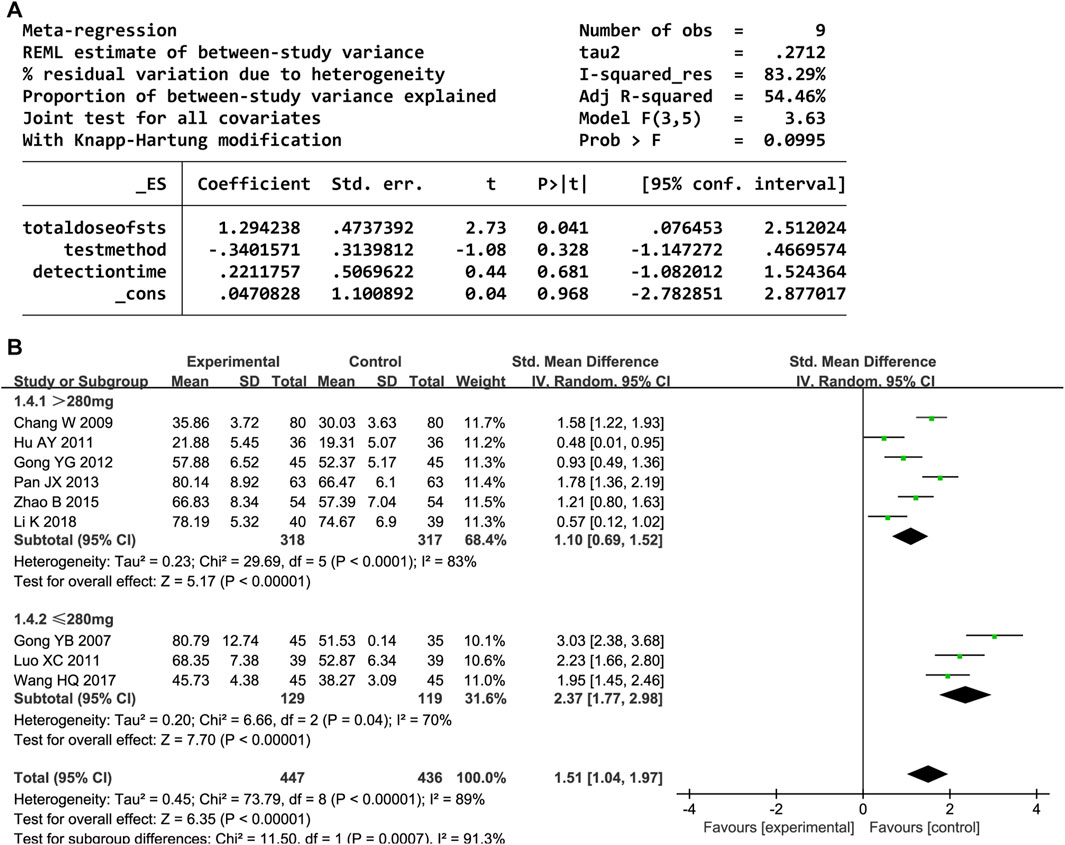
Nine trials reported the NO level. The random-effects model was used owing to high heterogeneity (P < 0.00001, I2 = 89%). The NO level significantly increased after administering DHI (SMD = 1.51, 95% CI [1.04, 1.97], P < 0.00001). The sensitivity analyses showed that no one study affected the estimated effect sizes (Supplementary Figure S4). The meta-regression analysis showed that heterogeneity and detection methods were related to the total DHI dose (P < 0.05; Figure 6A). Further subgroup analyses revealed decreased heterogeneity (Figure 6B).
3.5.2 ET/ET-1
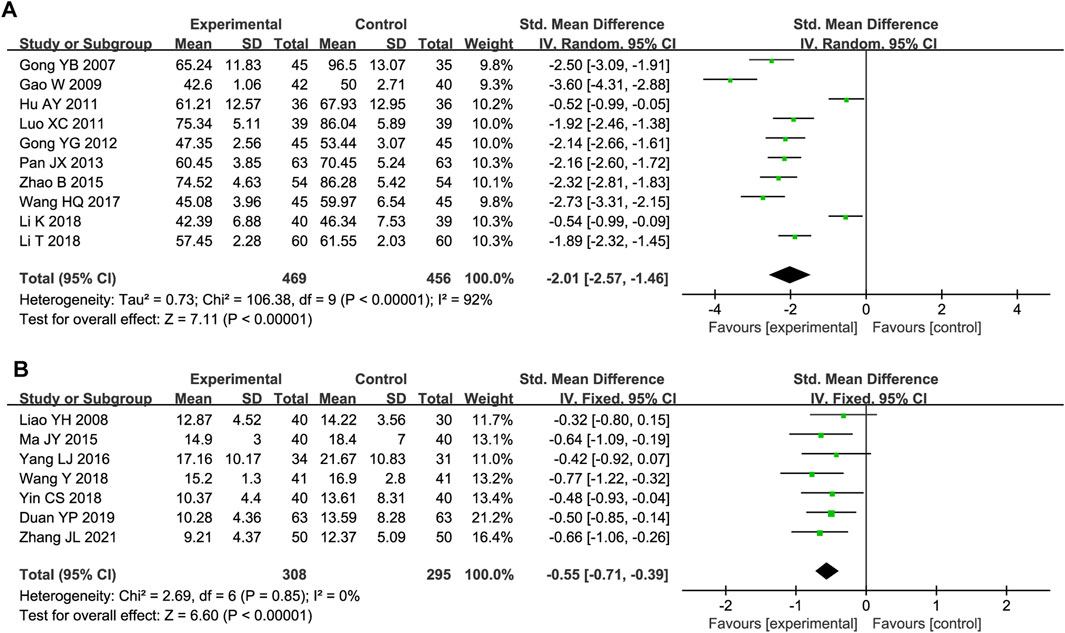
Ten studies included serum ET/ET-1 level data. Substantial heterogeneity was observed (P < 0.00001, I2 = 92%); thus, a random-effects model was used. The ET/ET-1 level was significantly lower in the experimental group than in the control group (SMD = −2.01, 95% CI [-2.57, −1.46], P < 0.00001; Figure 7A). The sensitivity analysis demonstrated the robustness and reliability of the results (Supplementary Figure S5). A meta-regression was conducted to assess how the detection time, total DHI dose, and test method influenced the heterogeneity but did not reveal the source (Supplementary Figure S6).
3.5.3 Hcy
Seven trials reported Hcy outcomes. The fixed-effect model was employed owing to the absence of heterogeneity (P = 0.85, I2 = 0%). DHI treatment decreased the Hcy level more effectively than the control treatment (SMD = −0.55, 95% CI [-0.71, −0.39], P < 0.00001; Figure 7B).
3.6 AEs
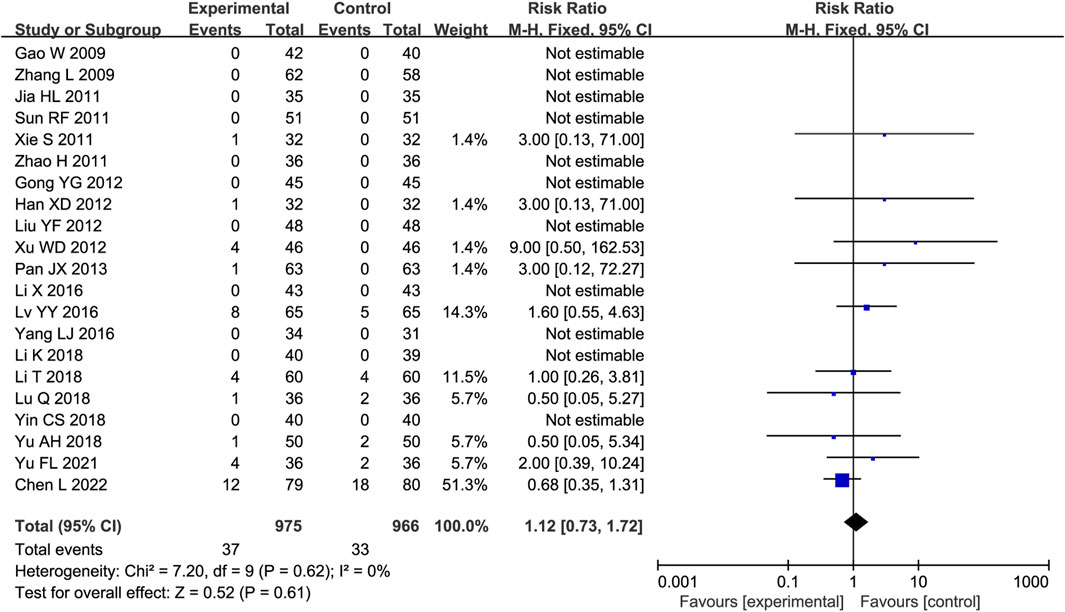
Twenty-one trials were analyzed for AEs, of which 10 reported no AEs in either group. The main AEs were gastrointestinal reactions, dizziness or headache, and palpitations (Supplementary Table S2). No substantial heterogeneity was identified (P = 0.61, I2 = 0%); thus, a fixed-effects model was employed. The AE incidence rates were comparable between the experimental and control groups (RR = 1.12, 95% CI [0.73, 1.72], P = 0.61; Figure 8).
3.7 Publication bias
As there were over ten studies reported hs-CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, and ET/ET-1 levels, we performed Egger’s and Begg’s tests to evaluate the potential impact of publication bias in these studies (Figure 9). The results showed that except for hs-CRP and ET/ET-1, there was no possibility of publication bias in the other two groups. Although the statistical significance of publication bias was negligible, we considered it more likely because all but one of the included trials were conducted in China.
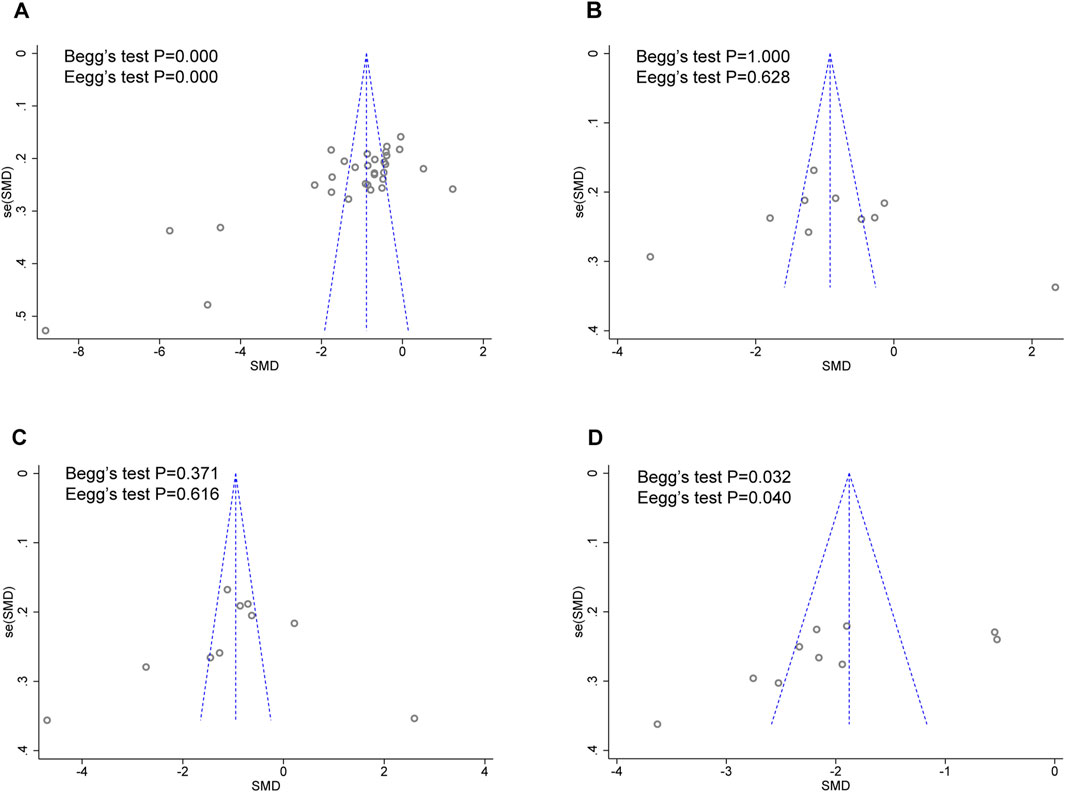
Figure 9. Funnel plot for publication bias assessment. (A) hs-CRP publishes biased assessment. (B) TNF-α publishes biased assessment. (C) IL-6 publishes biased assessment. (D) ET/ET-1 publishes biased assessment.
3.8 GRADE assessment
The GRADE evaluation system was utilized to evaluate the level of certainty in the evidence regarding the outcomes. The quality of evidence ranged from “very low” to “low.” The primary factors contributing to this downgrade were a high risk of bias, imprecision, and inconsistency. The results from the comprehensive GRADE evaluation can be found in Supplementary Table S3.
4 Discussion
The present systematic review analyzed 46 RCTs involving 4,601 participants to evaluate the impact of DHI on inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial function in individuals diagnosed with UAP. Treatment with DHI significantly reduced the hs-CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, ET/ET-1, and Hcy levels and increased the NO level. Furthermore, the AE incidence rates did not differ between the DHI and control groups. Some of the patients with UAP in the included RCTs had comorbid chronic metabolic diseases, such as hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. Although this aspect was not evaluated in this study, many others have shown that DHI improves metabolic markers (Chen et al., 2014; Fan et al., 2018; Orgah et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2024), which is also conducive to improving UAP. Therefore, DHI as a supplementary treatment enhances the patient’s prognosis by safely and efficiently diminishing inflammatory factors and promoting endothelial function among those with UAP.
Previous studies have predominantly focused on the effects of DHI on myocardial injury and angina in patients with UAP. To our knowledge, this systematic review is the first to extensively focus on how DHI treatment affects inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial function among individuals diagnosed with UAP. UAP is a progressive disease involving multiple immune cells and inflammatory factors, and imbalanced inflammatory responses and endothelial dysfunction might play a crucial role in the formation, growth, and plaque rupture of atherosclerosis in these patients (Wirtz and von Känel, 2017; Fioranelli et al., 2018). The two promote each other through complex molecular mechanisms, such as pro-inflammatory factors (e.g., TNF-α and IL-6) that reduce NO production by inhibiting endothelial NO synthase while activating ET-1 release and oxidative stress products (e.g., malondialdehyde) that accelerate endothelial dysfunction through the degradation of NO, creating a vicious cycle of inflammation and endothelial damage (Gupta et al., 2020).
We also found that DHI treatment significantly reduced the hs-CRP, TNF-α, and IL-6 levels (P < 0.05). hs-CRP is a vascular inflammation marker and a predictor of myocardial infarction (Li Y. et al., 2022). Moreover, TNF-α and IL-6 are important pro-inflammatory factors that promote the accumulation of immune complexes in endothelial cells, which increase the risk of thrombosis and participate in the vascular inflammatory response and coronary atherosclerosis (Gao et al., 2018; Bi et al., 2019). DHI treatment reduces TNF-α levels in patients with UAP, which can lead to the decreased expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and suppress the inflammatory response (Ren et al., 2010).
Moreover, we found that DHI treatment significantly reduced the ET/ET-1 and Hcy levels and increased the NO level (P < 0.05). NO is a key vasodilator secreted by endothelial cells and a central regulator of vascular endothelial function (Bilsborough et al., 2003). ET-1 is a subtype of ET that is released by endothelial cells during acute and chronic vascular injury and is the most potent vasoconstrictor (Caroselli et al., 2016). NO and ET-1 maintain a dynamic equilibrium in healthy vessels and work together to regulate vascular tone. However, in atherosclerotic plaques, the pro-inflammatory effects of ET-1, together with decreased NO, accelerate disease progression (Kageyama et al., 2014). Hcy impairs vascular endothelial function through various mechanisms, such as interfering with NO metabolism and activating endoplasmic reticulum stress and epigenetic regulation, leading to endothelial activation, oxidative stress, and inflammatory responses and accelerating vascular pathology. Elevated Hcy levels in the bloodstream are also a risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis (Guo et al., 2009).
The most common AEs in the included RCTs were gastrointestinal reactions, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and flatulence, which may result from the drug’s normal pharmacologic effects (Li et al., 2015). Although some trials reported AEs, they did not yield fully accurate results considering that DHI administration was combined with CWM; thus, evidence regarding whether DHI was directly linked to the symptoms was lacking. In addition, some trials did not report AEs. Considering that adverse reactions do not fully assess drug safety outcomes, more rigorous safety and toxicity assessments are necessary to substantiate the evidence for further consideration.
Studies suggest that DHI treatment is more clinically effective against UAP compared to traditional Western medicine. Compared with two previous meta-analyses (Xu et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2016), this systematic review provides a more comprehensive assessment analyzing DHI’s ability to reduce inflammatory factors and improve vascular endothelial function in patients with UAP. The prior studies only included hs-CRP as an inflammation indicator, whereas this study incorporated newly published and well-conducted RCTs with more comprehensive outcome measures. This study also synthesized inter-study heterogeneity using sensitivity, meta-regression, and subgroup analyses, which have not been explored in previous systematic evaluations. A prior network meta-analysis (Li M. et al., 2022) explored the comparative efficacy of different DHIs for UAP, reporting that DHI was superior to other Danshen preparations in terms of overall efficacy and hs-CRP improvements, aligning with our findings. Together, these results suggest that DHI improves inflammation in patients with UAP, but these improvements in clinical symptoms and lipid levels may vary based on the Danshen preparation. Finally, several clinical trials have reported that DHI promotes vascular endothelial repair (Hu et al., 2016), which could be another future research direction.
5 Limitations
Before applying the results of this study in clinical practice, it is crucial to recognize specific constraints that could impact its practicality. First, the quality of the 46 included trials was “very low” to “low,” and there was a lack of high-quality trials rigorously designed under the CONSORT protocol. Second, a significant number of trials lacked explicit methodological information, such as randomization protocols, concealment of allocation, and blinding techniques. As a result, the reliability of the evidence presented was substantially compromised. In conclusion, it is crucial to approach the results cautiously due to the presence of substantial heterogeneity and potential publication bias.
6 Conclusion
DHI treatment effectively and safely reduced the hs-CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, ET/ET-1, and Hcy levels and increased the NO level in patients with UAP. However, considering the overall low quality of the original studies, further large-scale, high-quality RCTs are imperative to provide robust evidence for clinical practice.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. WY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. CC: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. HG: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. YS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program “Research on the Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine” Key Special Projects (2017YFC1702700).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1389746/full#supplementary-material
References
Bi, C., Li, P. L., Liao, Y., Rao, H. Y., Li, P. B., Yi, J., et al. (2019). Pharmacodynamic effects of Dan-hong injection in rats with blood stasis syndrome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 109187. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109187
Bilsborough, W., Green, D. J., Mamotte, C. D., van Bockxmeer, F. M., O'Driscoll, G. J., and Taylor, R. R. (2003). Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphism, homocysteine, cholesterol and vascular endothelial function. Atherosclerosis 169 (1), 131–138. doi:10.1016/s0021-9150(03)00147-3
Braunwald, E., Antman, E. M., Beasley, J. W., Califf, R. M., Cheitlin, M. D., Hochman, J. S., et al. (2002). ACC/AHA guideline update for the management of patients with unstable angina and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction--2002: summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on the Management of Patients with Unstable Angina). Circulation 106 (14), 1893–1900. doi:10.1161/01.cir.0000037106.76139.53
Caroselli, C., De Rosa, R., Tanzi, P., Rigatelli, A., and Bruno, G. (2016). Endothelial immunomediated reactivity in acute cardiac ischaemia: role of endothelin 1, interleukin 8 and NT-proBNP in patients affected by unstable angina pectoris. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 29 (3), 516–522. doi:10.1177/0394632015608247
Chang, W., He, L., Leng, Q., and Lei, J. (2009). Effects of Danhong injection on hemorheology and antioxidation in patients with unstable angina pectoris. J. Clin. Intern. Med. 26 (8), 566–567. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9057.2009.08.024
Chen, J., Deng, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, J., He, Y., Fu, W., et al. (2014). Lipid-lowering effects of Danhong injection on hyperlipidemia rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 154 (2), 437–442. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.04.023
Chen, J., Han, Y., and Wang, X. (2015). Danhong injection for treating 94 cases with unstable angina of blood-stasis pattern. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 35 (7), 1525–1527. doi:10.16367/j.issn.1003-5028.2015.07.0640
Chen, L., Fu, G., Hua, Q., Zhu, H. Y., Deng, Y., Wu, W., et al. (2022). Efficacy of add-on Danhong injection in patients with unstable angina pectoris: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 284, 114794. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114794
Chen S., S., Li, L., Ning, D., and Wang, B. (2015). Efficacy and pharmacological action of Danhong injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris. J. China Prescr. Drug 13 (7), 37–38. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-945X.2015.07.026
Collet, J. P., Thiele, H., Barbato, E., Barthélémy, O., Bauersachs, J., Bhatt, D. L., et al. (2021). 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur. Heart J. 42 (14), 1289–1367. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575
Duan, L., Xiong, X., Hu, J., Liu, Y., and Wang, J. (2018). Efficacy and safety of oral Panax notoginseng saponins for unstable angina patients: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Phytomedicine 47, 23–33. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.044
Duan, Y. (2019). Clinical observation of Danhong injection combined with conventional western medicine in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. China's Naturop. 27 (22), 66–68. doi:10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.2019.2234
Fan, H., Li, M., Yu, L., Jin, W., Yang, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). Effects of Danhong Injection on platelet aggregation in hyperlipidemia rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 212, 67–73. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.017
Feng, C., Liu, X., and Liu, X. (2008). Effect of Danhong injection combined with western medicine on serum inflammatory factors in patients with unstable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. Chin. J. Inf. Traditional Chin. Med. (S1), 14–15.
Feng, X., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Li, L., Little, P. J., Xu, S. W., et al. (2019). Danhong injection in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: pharmacological actions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Res. 139, 62–75. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.006
Fioranelli, M., Bottaccioli, A. G., Bottaccioli, F., Bianchi, M., Rovesti, M., and Roccia, M. G. (2018). Stress and inflammation in coronary artery disease: a review psychoneuroendocrineimmunology-based. Front. Immunol. 9, 2031. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02031
Fu, T., and Jiang, C. (2015). Effects of Danhong injection on serum sICAM-1 and hs-CRP in patients with unstable angina pectoris. J. Electrocardiol. Circulation 34 (4), 256–258.
Gao, C. Z., Ma, Q. Q., Wu, J., Liu, R., Wang, F., Bai, J., et al. (2018). Comparison of the effects of ticagrelor and clopidogrel on inflammatory factors, vascular endothelium functions and short-term prognosis in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing emergency percutaneous coronary intervention: a pilot study. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 48 (1), 385–396. doi:10.1159/000491768
Gao, W., Shi, Y., and Suo, D. (2009). Clinical efficacy of Betong Danhong injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris. Liaoning J. Traditional Chin. Med. 36 (2), 235–236. doi:10.13192/j.ljtcm.2009.02.78.gaow.008
Gong, Y. (2012). Effect of Danhong injection on treatment of unstable angina pectoris. J. Hainan Med. Univ. 18 (6), 791–793. doi:10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.2012.06.014
Gong, Y. B., and Li, G. (2007). Effects of Danhong injection on lipid metabolism and endothelial function in patients with unstable angina pectoris. China Foreign Med. Treat. 26 (21), 15–16. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-0742.2007.21.012
Guo, H., Chi, J., Xing, Y., and Wang, P. (2009). Influence of folic acid on plasma homocysteine levels and arterial endothelial function in patients with unstable angina. Indian J. Med. Res. 129 (3), 279–284.
Guo, J., Dai, S., Ding, Y., He, H., Zhang, H., Dan, W., et al. (2020). A randomized controlled trial for gualou danshen granules in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris patients with phlegm-blood stasis syndrome. Med. Baltim. 99 (33), e21593. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000021593
Guo, S., Wu, J., Zhou, W., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Jia, S., et al. (2020). Investigating the multi-target pharmacological mechanism of danhong injection acting on unstable angina by combined network pharmacology and molecular docking. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 20 (1), 66. doi:10.1186/s12906-020-2853-5
Gupta, R. M., Libby, P., and Barton, M. (2020). Linking regulation of nitric oxide to endothelin-1: the Yin and Yang of vascular tone in the atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis 292, 201–203. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.11.001
Han, X. (2012). The effect of Dan red injection on the high sensitivity c-reactive protein of the unstable knot. Guide China Med. 10 (35), 597–598. doi:10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2012.35.258
Higgins, J. P., Altman, D. G., Gøtzsche, P. C., Jüni, P., Moher, D., Oxman, A. D., et al. (2011). The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 343, d5928. doi:10.1136/bmj.d5928
Hu, A., and Chen, S. (2009). Effect of Danhong injection on the expression of serum hs-CRP and Fg in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Zhejiang J. Traditional Chin. Med. 44 (07), 541.
Hu, A., and Liu, L. (2011). Effects of danhong injection on vascular endothelial function and inflammatory factors in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Her. Med. 30 (3), 319–321. doi:10.3870/yydb.2011.03.018
Hu, Z., Wang, H., Fan, G., Zhang, H., Wang, X., Mao, J., et al. (2016). Effect of danhong injection on the mobilisation of endothelial progenitor cells to vascular repair after percutaneous coronary intervention: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 388, S34. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31961-4
Hu, Z., Wang, H., Fan, G., Zhang, H., Wang, X., Mao, J., et al. (2019). Danhong injection mobilizes endothelial progenitor cells to repair vascular endothelium injury via upregulating the expression of Akt, eNOS and MMP-9. Phytomedicine 61, 152850. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152850
Jia, H. (2011). Effect of danhong injection on inflammatory factor in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Chin. J. General Pract. 9 (8), 1239–1240. doi:10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2011.08.043
Kageyama, S., Yagi, S., Tanaka, H., Saito, S., Nagai, K., Hata, K., et al. (2014). Graft reconditioning with nitric oxide gas in rat liver transplantation from cardiac death donors. Transplantation 97 (6), 618–625. doi:10.1097/tp.0000000000000025
Kang, H., and Hou, Y. (2015). Clinical observation of the treatment of unstable angina pectoris with danhong injection. China Contin. Med. Educ. 7 (20), 198–199.
Ke, Y., and Chen, J. (2007). Recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of unstable angina pectoris. Chin. J. Cardiol. 35, 295–304.
Kosiński, K., Malinowski, D., Safranow, K., Dziedziejko, V., and Pawlik, A. (2022). PECAM1, COL4A2, PHACTR1, and LMOD1 gene polymorphisms in patients with unstable angina. J. Clin. Med. 11 (2), 373. doi:10.3390/jcm11020373
Li, H., Su, X., Jia, X., Wei, C., Xu, Z., and Huang, Y. (2009). Effect of Danhong injection on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with unstable angina pectoris and its curative effect. Shanxi Med. J. 38 (8), 1054–1055. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7377.2009.08.053
Li, K. (2018). Clinical effect of Danhong injection in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Clin. Res. Pract. 3 (21), 111–112. doi:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.201821051
Li, M., Li, H., Liu, H., Lai, X., and Xing, W. (2022). Efficacy and safety of eight types Salvia miltiorrhiza injections in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: a network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 972738. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.972738
Li, T., and Zhang, P. (2018). The effect of Aspirin with Danhong injection on unstable angina pectoris and vascular endothelial function in elderly patients with coronary heart disease. Shaanxi Med. J. 47 (7), 937–939. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7377.2018.07.038
Li, X., Gao, Y., and Zheng, W. (2016). Curative effect of danhong injection for unstable angina patients and the level of inflammatory factors in elderly. J. Sichuan Traditional Chin. Med. 34 (9), 187–189.
Li, X. L., Tang, J. F., Li, W. X., Li, C. X., Zhao, T., Zhao, B. C., et al. (2015). Postmarketing safety surveillance and reevaluation of danhong injection: clinical study of 30888 cases. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 610846. doi:10.1155/2015/610846
Li, Y., Li, D., Wang, W., Li, X., Li, P., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Effect of Danhong injection on prognosis and inflammatory factor expression in patients with acute coronary syndrome during the perioperative period of percutaneous coronary intervention: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 9, 1029387. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.1029387
Liao, Y., Liu, X., Deng, Y., and Hu, J. (2008). Effect of Danhong injection on serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with unstable angina pectoris. China Med. 3 (6), 334–335. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4777.2008.06.006
Liu, B., and Wang, B. (2013). Effect of Danhong injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris. Guide China Med. 11 (1), 606–607. doi:10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2013.01.293
Liu, H., Yin, C., Wang, C., and Song, L. (2015). Effect of Danhong injection on serum hs-CRP and GDF-15 in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 35 (1), 63–64. doi:10.16367/j.issn.1003-5028.2015.01.0027
Liu, L., Xu, Y., Su, Z., Man, X., Jiang, Y., Zhao, L., et al. (2022). Danhong injection price trend and its utilization by coronary heart disease patients: evidence from hospital records in China. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 857167. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.857167
Liu, S., Wu, J., Zhang, X., and Zhang, B. (2016). Systematic review of Danhong Injection as an adjuvant to conventional Western Medicine in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris. Lishizhen Med. Materia Medica Res. 25 (04), 209–215.
Liu, Y., Xu, L., Xu, Z., Zhao, W., and Liu, X. (2012). Danhong injection was used to treat 48 cases of unstable angina pectoris of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease. China Pharm. 21 (20), 109–110. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2012.20.067
Lu, Q., Li, L., and Huang, Z. (2018). Efficacy of rosuvastatin combined with danhong injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris and influence on serum levels of TNF-α, hs-CRP and IL-6. China Pharm. 21 (1), 109–112. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2018.01.026
Luo, X., and Huang, T. (2011). Effect of Danhong injection on vascular endothelial function and cardiac function in patients with unstable angina pectoris. J. Mil. Surg. Southwest China 13 (3), 469–470. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7193.2011.03.047
Lv, Y. (2016). Effect of Danhong injection combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. J. Oiqihar Med. Univ. 37 (21), 2664–2665.
Lyu, M., Yan, C. L., Liu, H. X., Wang, T. Y., Shi, X. H., Liu, J. P., et al. (2017). Network pharmacology exploration reveals endothelial inflammation as a common mechanism for stroke and coronary artery disease treatment of Danhong injection. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 15427. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-14692-3
Ma, J. (2015). Clinical effects of coronary heart disease unstable angina by danhong injection and research on the influence on Hcy, hs-CRP, NT-proBNP. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Materia Medica 31 (1), 232–234. doi:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2015.01.074
Man, C., Dai, Z., and Fan, Y. (2020). Dazhu hongjingtian preparation as adjuvant therapy for unstable angina pectoris: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 213. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00213
Messerli, F. H., Mancia, G., Conti, C. R., and Pepine, C. J. (2006). Guidelines on the management of stable angina pectoris: executive summary: the task force on the management of stable angina pectoris of the European society of cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 27 (23), 2902–2903. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl308
Murad, M. H., Mustafa, R. A., Schünemann, H. J., Sultan, S., and Santesso, N. (2017). Rating the certainty in evidence in the absence of a single estimate of effect. Evid. Based Med. 22 (3), 85–87. doi:10.1136/ebmed-2017-110668
Nijat, D., Xu, L., Kuang, Y., Yu, R., Zhang, Y., Hasan, A., et al. (2022). A pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study to elucidate the cardiovascular protective constituents in Danhong Injection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 219, 114953. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114953
Orgah, J. O., He, S., Wang, Y., Jiang, M., Wang, Y., Orgah, E. A., et al. (2020). Pharmacological potential of the combination of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) and Carthamus tinctorius (Honghua) for diabetes mellitus and its cardiovascular complications. Pharmacol. Res. 153, 104654. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104654
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 10 (1), 89. doi:10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
Pan, J., Chen, L., Ren, Y., and Pu, G. (2013). To analyze the clinical efficacy and mechanism of Danhong injection combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris. J. Clin. Med. Pract. 17 (21), 114–115. doi:10.7619/jcmp.201321033
Ren, Z. H., Tong, Y. H., Xu, W., Ma, J., and Chen, Y. (2010). Tanshinone II A attenuates inflammatory responses of rats with myocardial infarction by reducing MCP-1 expression. Phytomedicine 17 (3-4), 212–218. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2009.08.010
Shi, X. (2009). Effect of Danhong injection on inflammatory factors in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Guid. J. Traditional Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 15 (11), 20–21. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-951X.2009.11.010
Shi, Y., and Liu, B. (2012). Efficacy observation of 156 cases of senile unstable angina pectoris treated with danhong injection. World J. Integr. Traditional West. Med. 7 (10), 883–886. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-6613.2012.10.019
Sterne, J. A. C., Savović, J., Page, M. J., Elbers, R. G., Blencowe, N. S., Boutron, I., et al. (2019). RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 366, l4898. doi:10.1136/bmj.l4898
Sun, R., Chen, Y., and Xie, Y. (2011). Effect of danhong injection in treating unstable angina pectoris and on serum high sensitivity C-reactive protein. Chin. foreign health Abstr. 8 (6), 36–37. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5085.2011.06.028
Wang, H. (2017). Effects of Danhong injection on hemorheology and vascular endothelial function in elderly patients with unstable angina pectoris. J. North Pharm. 14 (4), 113–114. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-8351.2017.04.102
Wang, Y. (2018). Effect observation of Danhong injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. Chin. Community Dr. 34 (35), 94–95. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2018.35.054
Wirtz, P. H., and von Känel, R. (2017). Psychological stress, inflammation, and coronary heart disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 19 (11), 111. doi:10.1007/s11886-017-0919-x
Wolf, D., and Ley, K. (2019). Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 124 (2), 315–327. doi:10.1161/circresaha.118.313591
Wu, J. R., Liu, S., Zhang, X. M., and Zhang, B. (2017). Danshen injection as adjuvant treatment for unstable angina pectoris: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23 (4), 306–311. doi:10.1007/s11655-016-2272-0
Wu, J. R., Zhang, X. M., and Zhang, B. (2015). Danhong injection in the treatment of acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 43 (2), 199–214. doi:10.1142/s0192415x15500135
Xi, J., Wei, R., Cui, X., Liu, Y., and Xie, Y. (2023). The efficacy and safety of Xueshuantong (lyophilized) for injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1074400. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1074400
Xie, S., and Cao, C. (2011). Affection of hemorrheology and hyper-sensitive c-rp of danhong injection on unstable angina. Heilongjiang Med. J. 35 (9), 660–662. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5775.2011.09.007
Xing, W. L., Wu, Y. J., Liu, H. X., Liu, Q. R., Zhou, Q., Li, A. Y., et al. (2021). Effects of danhong injection on peri-procedural myocardial injury and microcirculatory resistance in patients with unstable angina undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention: a pilot randomized study. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27 (11), 846–853. doi:10.1007/s11655-021-2872-1
Xu, G., Lin, S., Xu, H., and Qin, L. (2011). Meta-analysis of Danhong Injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris. Front. Pharmacol. 22 (03), 765–767+774.
Xu, W., and Min, Z. (2012). Effect of Danhong injection combined with simvastatin on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio/Cerebrovascular Dis. 10 (10), 1169–1170. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2012.10.010
Yang, C., and Shi, G. (2009). Effect of Danhong injection on inflammatory factors in patients with unstable angina pectoris. J. Pingxiang Coll. 26 (3), 99–101. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9149.2009.03.027
Yang, L., Shen, J., and Hu, Z. (2016). Effect of Danhong injection on plasma homocysteine in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio/Cerebrovascular Dis. 14 (17), 2040–2041. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2016.17.029
Yang, X., Yang, W., He, S., Ye, H., and Lei, S. (2024). Danhong formula alleviates endothelial dysfunction and reduces blood pressure in hypertension by regulating MicroRNA 24 - phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Serine/Threonine Kinase- Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 323, 117615. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117615
Yi, X., Zhu, J., Zhang, J., Gao, Y., Chen, Z., Lu, S., et al. (2018). Investigation of the reverse effect of Danhong injection on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in H9c2 cells: insight by LC-MS based non-targeted metabolomic analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 152, 264–270. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2018.02.012
Yin, C., Meng, X., Zhang, K., Jiang, H., Cao, J., and Wang, L. (2018). Effect of Danhong injection on homocysteine and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein expression in elderly patients with unstable angina pectoris. Chin. J. Gerontology 38 (13), 3093–3094. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.13.008
Yu, A. (2018). Clinical efficacy of Danhong injection combined with simvastatin in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio/Cerebrovascular Dis. 16 (7), 903–906. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2018.07.021
Yu, F., and Xu, F. (2021). The clinical effects of danhong injection combined with rosuvastatin in the treatment of uap. J. Shandong Med. Coll. 43 (4), 247–249. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-0947.2021.04.003
Yu, L., Zhou, C., Luo, Z., Zeng, W., Lai, F., Han, G., et al. (2018). The lipid-lowering effects of Danhong and Huangqi injections: a meta-analysis of clinical controlled trials. Lipids Health Dis. 17 (1), 106. doi:10.1186/s12944-018-0760-2
Zhang, J. (2021). Clinical effect of Danhong injection in the treatment of patients with unstable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. Doctor 6 (22), 77–79.
Zhang, L., Liu, C., and Li, W. (2009). Therapeutic effect of Danhong injection on unstable angina pectoris. Pract. J. Med. & Pharm. 26 (7), 33–35. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4008.2009.07.017
Zhang, X. (2010). Effect of Danhong injection on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and hemorheology in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Contemp. Med. 16 (31), 147–148. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2010.31.109
Zhang, Y., Chen, M., Li, J., Gong, J., Cao, H., and Wang, D. (2017). Clinical efficacy of Danhong injection combined with rosuvastatin in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris and its influence on serum inflammatory factors and hemorheology. Shanxi Med. J. 46 (13), 1554–1557. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2017.013.009
Zhao, B., Wang, J., and Song, Y. (2015). Effects of danhong injection on unstable factors and vascular endothelial function of inflammation in patients with angina pectoris. J. Liaoning Univ. Traditional Chin. Med. 17 (9), 182–184. doi:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2015.09.063
Zhao, H., Zhang, Y., and Pu, S. (2011). Clinical application and evaluation of danhong injection for patients with unstable angina. Sichuan J. Anat. 19 (4), 10–12. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-1457.2011.086
Zou, J. B., Zhang, X. F., Wang, J., Wang, F., Cheng, J. X., Yang, F. Y., et al. (2018). The therapeutic efficacy of danhong injection combined with percutaneous coronary intervention in acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 550. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00550
Keywords: Danhong injection, unstable angina pectoris, inflammatory factors, vascular endothelial function, meta-analysis
Citation: Kan Z, Yan W, Chen C, Gao H and Song Y (2025) Efficacy and safety of Danhong injection on inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial function in patients with unstable angina pectoris: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1389746. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1389746
Received: 22 February 2024; Accepted: 02 June 2025;
Published: 13 June 2025.
Edited by:
Juei-Tang Cheng, Chang Jung Christian University, TaiwanReviewed by:
Ka Yui Kum, Life Code Limited, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaZhiqiang Zhang, Binzhou Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Kan, Yan, Chen, Gao and Song. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongmei Song, c29uZ3ltMDIwMEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Zunqi Kan
Zunqi Kan Wenli Yan
Wenli Yan Cong Chen3
Cong Chen3 Huanyu Gao
Huanyu Gao Yongmei Song
Yongmei Song