Abstract
Aim:
We aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Shengxuening (SXN) in treating renal anemia by systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods:
PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, the ClinicalTrials.gov, SinoMed, the China Knowledge Network, the Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform and Technology Journal Database were searched from inception to September 2024 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared SXN and other drugs or placebo in treating renal anemia. We used the Cochrane Bias Risk Tool to evaluate the risk of bias of all included RCTs, and used the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) to evaluate the certainty of the evidence.
Results:
31 RCTs involving 2,372 patients were included. The efficiency of SXN was superior than the control group (included placebo group, other drugs group) in improving hemoglobin (compared with placebo: MD: 7.15 g/L, 95% CI: 5.68–8.62, P < 0.001, GRADE: high; compared with other drugs: MD: 6.49 g/L, 95% CI: 3.50–9.47, P < 0.001, GRADE: very low), serum ferritin (MD: 57.53 ng/mL, 95% CI: 29.70–85.36, P < 0.001, GRADE: moderate; MD: 28.96 ng/mL, 95% CI: 1.88–56.04, P = 0.04, GRADE: moderate) and transferrin saturation level (MD: 7.00%, 95% CI: 3.40–10.60, P = 0.0001, GRADE: moderate; MD: 3.64%, 95% CI: 1.41–5.88, P = 0.001, GRADE: moderate). Besides, the efficiency of SXN combined with other drugs was superior than other drugs group in improving hemoglobin (MD: 11.95 g/L, 95% CI: 6.19–17.71, P < 0.001, GRADE: moderate), serum ferritin (MD: 53.43 ng/mL, 95% CI: 20.65–86.21, P = 0.001, GRADE: moderate) and transferrin saturation level (MD: 5.91%, 95% CI: 3.72–8.10, P < 0.001, GRADE: moderate). Additionally, the incidence of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) in the SXN group was lower than that in other drugs treatment group (OR: 0.20, 95%CI: 0.12–0.33, P < 0.00001).
Conclusion:
The efficacy of SXN in treating renal anemia is convincing. Compared with other drugs, SXN is comparable or even better in treating renal anemia. Additionally, the safety of SXN is also relatively high.
1 Introduction
Renal anemia is a prevalent and serious complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD) (Haalen et al., 2020). It is strongly correlates with a significant adverse outcome on the burden and progression of the CKD, and has a strong negative impact on quality of life, hospitalization rates, major adverse cardiovascular events and mortality (Palaka et al., 2020; Taderegew et al., 2023; Habas et al., 2023). The causes of renal anemia include erythropoietin (EPO) deficiency, iron deficiency, disorder of iron metabolism in the body, and resistance to the EPO signaling pathway (Haase, 2017). Absolute or relative deficiency of EPO is the main factor leading to anemia.
Shengxuening (SXN) extracted from nontoxic silkworm excrement is an effective heme-like iron supplement which has hematopoiesis effects on patients with renal anemia and is widely used for the treatment of renal anemia (Ding et al., 2019; Zeng et al., 2020). Its constituents, sodium iron chlorophyllin, can improve iron metabolism, stimulate erythropoiesis in the bone and protect human cells from oxidative stress (Ding et al., 2019). Some clinical studies have indicated that SXN was more effective than oral iron supplementation in the treating renal anemia (Zeng et al., 2020; Zhang L. et al., 2016). The reported of Cheng X et al. (Cheng et al., 2016) showed that SXN combined with EPO was safe and effective in patients with renal anemia.
In the past few years, there has been a growing body of clinical evidence supporting the beneficial effects of SXN in the treatment of renal anemia. However, there is currently a lack of a meta-analysis that combines and analyzes all the available randomized controlled trials (RCTs). So we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to explore the effectiveness and safety of SXN in treating renal anemia, and provide evidence for the treatment of renal anemia patients.
2 Methods
This meta-analysis was preferred according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) and Cochrane Handbook (Moher et al., 2009). We registered the review prospectively in Open Science Frameworks, https://osf.io/qryds/.
2.1 Search strategy
We searched PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, the ClinicalTrails.gov, CNKI, Wanfang, VIP and SinoMed from inception to 24 April 2024, without language restrictions. The searched keywords and Medical Subject Headings were “shengxuening,” “sheng xue ning tablets,” “renal anemia” and “chronic kidney disease.” The detailed search strategy of all databases can be seen in Supplementary Text S1.
2.2 Eligibility criteria
We included studies in this meta-analysis if they met the following eligibility criteria: 1) the patients with renal anemia who have clear diagnostic criteria; 2) the intervention group used SXN; 3) reported change of one or more of the following outcomes of interest: hemoglobin (Hb), serum ferritin (SF), transferrin saturation (TSAT), serum iron (SI), and adverse drug reactions (ADRs); 4) the study type is a RCT.
We exclude studies without clear diagnostic criteria and inability to obtain the full text. Meanwhile, duplicate articles were excluded.
2.3 Study selection
All study search records were imported into the EndNote software. Two authors (XTG and ML) independently screened studies based on the title and abstract, and deleted the articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria. The remaining articles need to be read in full to determine if they are suitable for inclusion in the analysis. When two authors have different opinions, they can resolve it through discussion or have a third author (YW) make the final decision.
2.4 Data extraction
The information we screened includes: study title, first author’s name, publication time, study type, patient characteristics, intervention measures, treatment duration, and the outcomes of interest.
Two authors (LZ and XTG) independently extracted data using a standardized form, and in case of disagreements, discussions were held or a decision was made by a third author (CHF). When encountering multiple reports on the same study (such as original full text, conference, abstract, and post-analysis), we will collect all relevant data and analyze it as a study.
2.5 Risk of bias assessment
Two authors (LZ and XTG) independently performed the risk of bias of the included RCTs by using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool 2.0 (ROB 2) (Sterne et al., 2019) based on based on six domains: bias arising from the randomization process, bias due to deviations from the intended intervention, bias due to missing outcome data, bias in measurement of the outcome, bias in selection of the reported result, and other biases. We sub-classified “some concerns” judgements as “some concerns, probably high” and “some concerns, probably low,” if at least one domain was high, we considered the study at high risk of bias. Any discrepancies were resolved through mutual consultation or determined by a third author (ML).
2.6 Statistical analysis
We used software Review Manager (RevMan), version 5.4.1 (The Cochrane Collaboration Network, 2020) to conduct meta-analysis of the included studies. The dichotomous outcomes were evaluated by odds ratio (OR) while the mean difference (MD) was used to represent continuous outcomes, with 95% confidence interval (CI). I2 was used to evaluate heterogeneity among included RCTs, and when I2 is greater than 50%, it indicates at least moderate heterogeneity between included RCTs. Based on the assumption of significant clinical heterogeneity, a random effects model was used in this meta-analysis. In order to effectively avoid heterogeneity between included RCTs, we divided them into different subgroups for analysis based on the comparison measures of the included studies. We also conducted meta-regression to clarify the source of heterogeneity. Additionally, sensitivity analysis was used to evaluate the stability of the results.
2.7 Publication bias
According to the Cochrane Reviewer’s Handbook, Egger’s test require more than 10 studies to be meaningful. Otherwise, their test accuracy decreases, and the assessment of publication bias becomes inaccurate. Therefore, we performed the Egger’s test on the outcomes which was reported at least 10 RCTs by using the statistical software Stata (version 18.0; StataCorp, College Station, TX) to assess potential publication bias, and also used these tests to identify outliers (Egger et al., 1997).
2.8 Certainty of evidence
We used the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach to assess the certainty of the evidence for the critical outcomes, considering factors such as the risk of bias, imprecision, indirectness, inconsistency and publication bias. The certainty of evidence was graded into four level: (1) very low, any estimate of effect is very uncertain; (2) low, further research is very likely to have a significant impact on our faith in the assessment of development and is expected to change the assessment; (3) moderate, further research is likely to have a significant impact on our faith in the assessment of effect and may change the estimate; (4) high, further research is improbable to change our confidence in the estimate of effect.
3 Results
3.1 Search results
A total of 601 relevant studies were screened from the above mentioned databases. Of these, 233 were duplicate studies and 266 studies were excluded based on the title and abstract. After reading the full text, 71 studies were deleted, and ultimately 31 RCTs met the inclusion criteria and were included for the meta-analysis (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1
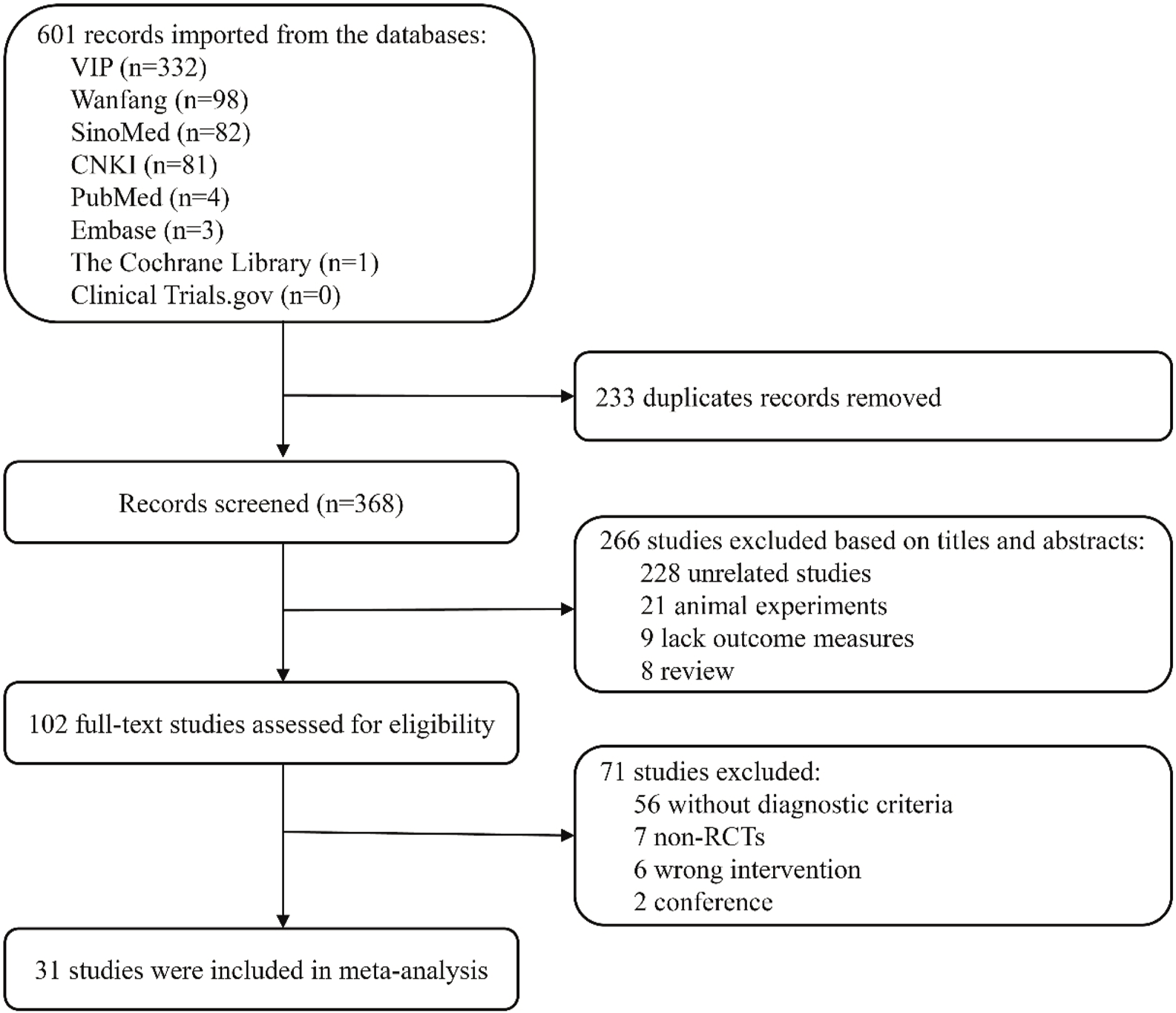
Flowchart of the study search.
3.2 Basic characteristics of included RCTs
All included RCTs can be divided into three different comparison measures, namely, SXN vs. placebo, SXN vs. other drugs, and SXN combined with other drugs vs. other drugs. A total of 2,372 patients were included, with an average age between 37.6 and 66.5. The included RCTs were published between 2009 and 2023. The names of other drugs and detailed comparison measures on the inclusion of the study was presented in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Comparation | First author | Publication year | Type of patients | Group | Age | No. | Intervation | Duration (weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SXN VS other drug | Sun et al. (2022) | 2022 | DD | Intervation | 65.45 ± 11.38 | 40 | SXN | 12 |
| Control | 66.31 ± 12.62 | 40 | Ferrlecit 2 | |||||
| Zhong et al. (2020) | 2020 | DD | Intervation | 55.68 ± 13.28 | 38 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 50.33 ± 13.25 | 38 | Iron Dextran | |||||
| Tang et al. (2020) | 2020 | DD | Intervation | 58.6 ± 13.4 | 47 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 56.9 ± 10.7 | 47 | Ferrlecit 2 | |||||
| Tang et al. (2019) | 2019 | NDD | Intervation | 58.9 ± 14.5 | 53 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 55.1 ± 14.7 | 41 | Ferrlecit 2 | |||||
| Shi (2019) | 2019 | DD | Intervation | 47.0 ± 18 | 15 | SXN | 8 | |
| Control | 49.5 ± 21.5 | 15 | Ferrous Saccharose | |||||
| Xu et al. (2018) | 2018 | NDD | Intervation | 59.3 ± 17.2 | 35 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 56.8 ± 15.7 | 35 | Ferrlecit 2 | |||||
| Fan et al. (2017) | 2017 | DD | Intervation | 40.24 ± 17.76 | 38 | SXN | 8 | |
| Control | 41.37 ± 17.02 | 34 | Ferrous fumarate | |||||
| Zhou et al. (2016a) | 2016 | DD | Intervation | 45.38 ± 9.09 | 32 | SXN | 16 | |
| Control | 46.06 ± 9.83 | 32 | Ferrlecit 2 | |||||
| Zhou et al. (2016b) | 2016 | DD | Intervation | 54.8 ± 3.6 | 67 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 55.3 ± 4.3 | 67 | Iron Dextran | |||||
| Guo (2015) | 2015 | NDD | Intervation | 45.3 ± 19.5 | 29 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 29 | Ferrous fumarate | ||||||
| Zhang and Xu (2015) | 2015 | DD | Intervation | 45.5 ± 9.22 | 30 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | NA | 30 | Ferrlecit 2 | |||||
| Liu et al. (2015) | 2015 | DD | Intervation | 45.9 ± 18.6 | 32 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 47.1 ± 10.7 | 32 | Ferrlecit 2 | |||||
| Wang et al. (2013) | 2013 | DD | Intervation | 45.4 ± 9.2 | 21 | SXN | 16 | |
| Control | 21 | Ferrous Sulfate and Vitamin Complex Sustained-release Tablets | ||||||
| Caixia (2013) | 2013 | DD | Intervation | 52.7 ± 11.3 | 30 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 30 | Ferrlecit 2 | ||||||
| Long et al. (2012) | 2013 | NDD | Intervation | 54.2 ± 12 | 34 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 51.6 ± 13.8 | 34 | Ferrous Sulfate | |||||
| Tan et al. (2013) | 2013 | NA | Intervation | 52.7 ± 11.4 | 58 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 58 | Ferrous Sulfate | ||||||
| Zhang et al. (2010) | 2010 | NDD | Intervation | 37.6 ± 16.4 | 50 | SXN | 4 | |
| Control | 42.3 ± 13.5 | 50 | ferrous lactate | |||||
| Zhou (2009) | 2009 | DD | Intervation | NA | 77 | SXN | 8 | |
| Control | NA | 77 | Iron Dextran | |||||
| Li (2009) | 2009 | NDD | Intervation | 51 ± 3 | 34 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 34 | Ferrous Sulfate | ||||||
| SXN VS Placebo | Zeng and Guo (2022) | 2022 | DD | Intervation | 55.92 ± 4.23 | 39 | SXN | 12 |
| Control | 55.86 ± 4.17 | 39 | Placebo | |||||
| Cheng et al. (2016) | 2016 | DD | Intervation | 64.2 ± 6.9 | 38 | SXN | 24 | |
| Control | 63.5 ± 6.7 | 34 | Placebo | |||||
| Zhang et al. (2016b) | 2016 | DD | Intervation | 48.0 ± 10.9 | 21 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 47.3 ± 10.8 | 23 | Placebo | |||||
| Xu (2012) | 2012 | DD | Intervation | 55.6 ± 11.1 | 22 | SXN | 12 | |
| Control | 22 | Placebo | ||||||
| Tang (2011) | 2011 | DD | Intervation | 52.6 ± 10.5 | 18 | SXN | 8 | |
| Control | 18 | Placebo | ||||||
| SXN + other drug VS other drug | Tang (2023) | 2023 | NA | Intervation | 55.10 ± 4.45 | 40 | SXN + Roxadustat | 12 |
| Control | 55.19 ± 4.42 | 40 | Roxadustat | |||||
| Liu et al. (2022) | 2022 | NA | Intervation | 51.22 ± 2.27 | 49 | SXN + Roxadustat | 12 | |
| Control | 51.24 ± 2.21 | 50 | Roxadustat | |||||
| Huang et al. (2022) | 2022 | NA | Intervation | 40.12 ± 2.60 | 30 | SXN + Roxadustat | 8 | |
| Control | 40.16 ± 2.63 | 30 | Roxadustat | |||||
| Li et al. (2021) | 2021 | NDD | Intervation | 46.5 ± 13.2 | 49 | SXN + Ferrlecit 2 | 12 | |
| Control | 42.3 ± 10.5 | 50 | Ferrlecit 2 | |||||
| Kang and Liang (2020) | 2020 | NDD | Intervation | 46 ± 10.6 | 28 | SXN + Iron Polysaccharide Complex Capsules | 4 | |
| Control | 45 ± 9.4 | 26 | Iron Polysaccharide Complex Capsules | |||||
| Zeng and Qu (2016) | 2016 | DD | Intervation | 52.35 ± 9.86 | 47 | SXN + Levocarnitine Oral Solution | 12 | |
| Control | 52.37 ± 9.88 | 47 | Levocarnitine Oral Solution | |||||
| Yi et al. (2015) | 2015 | NDD | Intervation | 52.84 ± 11.5 | 58 | SXN + Iron Polysaccharide Complex Capsules | NA | |
| Control | 52.1 ± 14.0 | 50 | Iron Polysaccharide Complex Capsules |
The detailed characteristics of the included RCTs.
3.3 Risk of bias
Table 2 summarizes the risk of bias for the included studies. Three studies (Cheng et al., 2016; Tang et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2022) were judged as low risk of bias, nine studies (Sun et al., 2022; Zhong et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2016a; Zhou et al., 2016b; Liu et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2010; Zeng and Guo, 2022; Huang et al., 2022) were judged as probably low risk of bias, one study (Zeng and Qu, 2016) was judged as high risk of bias, and the remaining 18 studies (Shi, 2019; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Wang et al., 2013; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Zhou, 2009; Li, 2009; Zhang W. et al., 2016; Xu, 2012; Tang, 2011; Tang, 2023; Li et al., 2021; Kang and Liang, 2020; Yi et al., 2015) were judged as probably high risk of bias. Overall, the quality of the included studies was not high. However, in the section of “Bias due to missing outcome data,” all studies were judged as low risk of bias and there were no missing outcome data.
TABLE 2
| Study | Bias arising from the randomization process | Bias due to deviations from the intended intervention | Bias due to missing outcome data | Bias in measurement of the outcome | Bias in selection of the reported results | Other risk of bias | Overall judgement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sun et al. (2022) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Zhong et al. (2020) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Tang et al. (2020) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Probably Low | Low |
| Tang et al. (2019) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Shi (2019) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Xu et al. (2018) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Fan et al. (2017) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Zhou et al. (2016a) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Zhou et al. (2016b) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Guo (2015) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Cheng et al. (2016) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Liu et al. (2015) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Wang et al. (2013) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Caixia (2013) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Long et al. (2012) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Tan et al. (2013) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Zhang et al. (2010) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Zhou (2009) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Li (2009) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Zeng and Guo (2022) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Cheng et al. (2016) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Probably Low | Low |
| Zhang et al. (2016b) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Xu (2012) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Tang (2011) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Tang (2023) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably high | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Liu et al. (2022) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Probably Low | Low |
| Huang et al. (2022) | Probably low | Probably low | Low | Low | Low | Probably low | Probably low |
| Li et al. (2021) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Kang and Liang (2020) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
| Zeng and Qu (2016) | High | High | Low | Probably Low | Probably Low | Probably High | High |
| Yi et al. (2015) | Probably high | Probably low | Low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably low | Probably high |
The risk of bias assessment in included studies.
3.4 Meta-analysis
3.4.1 Effect of SXN in renal anemia patients
3.4.1.1 Hemoglobin level (primary outcome)
30 included RCTs (Cheng et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2022; Zhong et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Shi, 2019; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2016a; Zhou et al., 2016b; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2013; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2010; Zhou, 2009; Li, 2009; Zeng and Guo, 2022; Zhang W. et al., 2016; Xu, 2012; Tang, 2011; Tang, 2023; Liu et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021; Kang and Liang, 2020; Zeng and Qu, 2016) included 2,256 patients reported the changes in Hb from the baseline (ΔHb) after treatment with SXN alone or in combination with other drugs in renal anemia. Among them, 5 RCTs (Cheng et al., 2016; Zeng and Guo, 2022; Zhang W. et al., 2016; Xu, 2012; Tang, 2011) included 274 patients compared ΔHb after treatment with SXN or placebo, 6 RCTs (Tang, 2023; Liu et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021; Kang and Liang, 2020; Zeng and Qu, 2016) included 481 patients compared the ΔHb after treatment with SXN combined with other drugs or other drugs alone, and 19 RCTs (Sun et al., 2022; Zhong et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Shi, 2019; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2016a; Zhou et al., 2016b; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2010; Zhou, 2009; Li, 2009) included 1,501 patients compared ΔHb after treatment with SXN or other drugs. The meta-analysis results showed that the ΔHb in SXN group was significantly higher than that in placebo group (MD: 7.15 g/L, 95% CI: 5.68–8.62, P < 0.001, the certainty of evidence was high) and other drugs group (MD: 6.49 g/L, 95% CI: 3.50–9.47, P < 0.001, the certainty of evidence was very low). Comprehensive data were presented in Figure 2. The detail of GRADE can be seen in Supplementary Table S1. In addition, the ΔHb in SXN combined with other drugs group was also significantly higher than that in other drugs group (MD: 11.95 g/L, 95% CI: 6.19–17.71, P < 0.001), and the certainty of evidence was moderate (see detail in Supplementary Table S1).
FIGURE 2
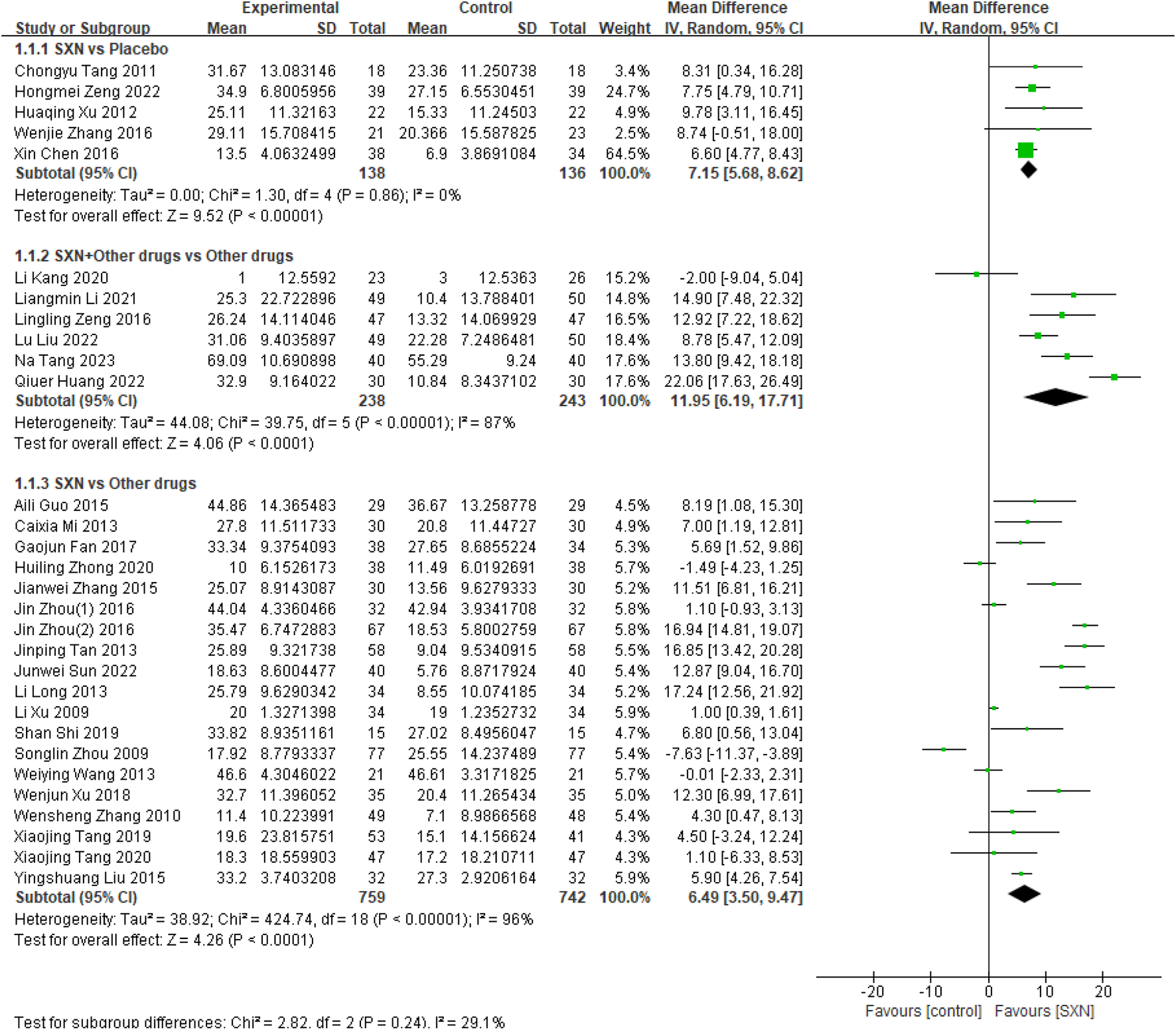
Meta-analysis results on ΔHb after treatment with SXN or SXN + other drugs.
3.4.1.2 Serum ferritin level
24 included RCTs (Cheng et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2022; Tang et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Shi, 2019; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2016b; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Zhou, 2009; Zeng and Guo, 2022; Zhang W. et al., 2016; Xu, 2012; Tang, 2023; Liu et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021; Zeng and Qu, 2016; Yi et al., 2015) included 1932 patients reported the changes in SF from the baseline (ΔSF) after treatment with SXN alone or in combination with other drugs in renal anemia. Among them, 4 RCTs (Cheng et al., 2016; Zeng and Guo, 2022; Zhang W. et al., 2016; Xu, 2012) included 238 patients compared ΔSF after treatment with SXN or placebo, 6 RCTs (Tang, 2023; Liu et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021; Zeng and Qu, 2016; Yi et al., 2015) included 540 patients compared the ΔSF after treatment with SXN combined with other drugs or other drugs alone, and 14 RCTs (Sun et al., 2022; Tang et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Shi, 2019; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2016b; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Zhou, 2009) included 1,154 patients compared ΔSF after treatment with SXN or other drugs. The meta-analysis results showed that the ΔSF in SXN group was significantly higher than that in placebo group (MD: 57.53 ng/mL, 95% CI: 29.70–85.36, P < 0.001, the certainty of evidence was moderate) and other drugs group (MD: 28.96 ng/mL, 95% CI: 1.88–56.04, P = 0.04, the certainty of evidence was moderate). Additionally, the ΔSF in SXN combined with other drugs group was also significantly higher than that in other drugs group (MD: 53.43 ng/mL, 95% CI: 20.65–86.21, P = 0.001), and the certainty of evidence was moderate. Detailed information can be found in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3
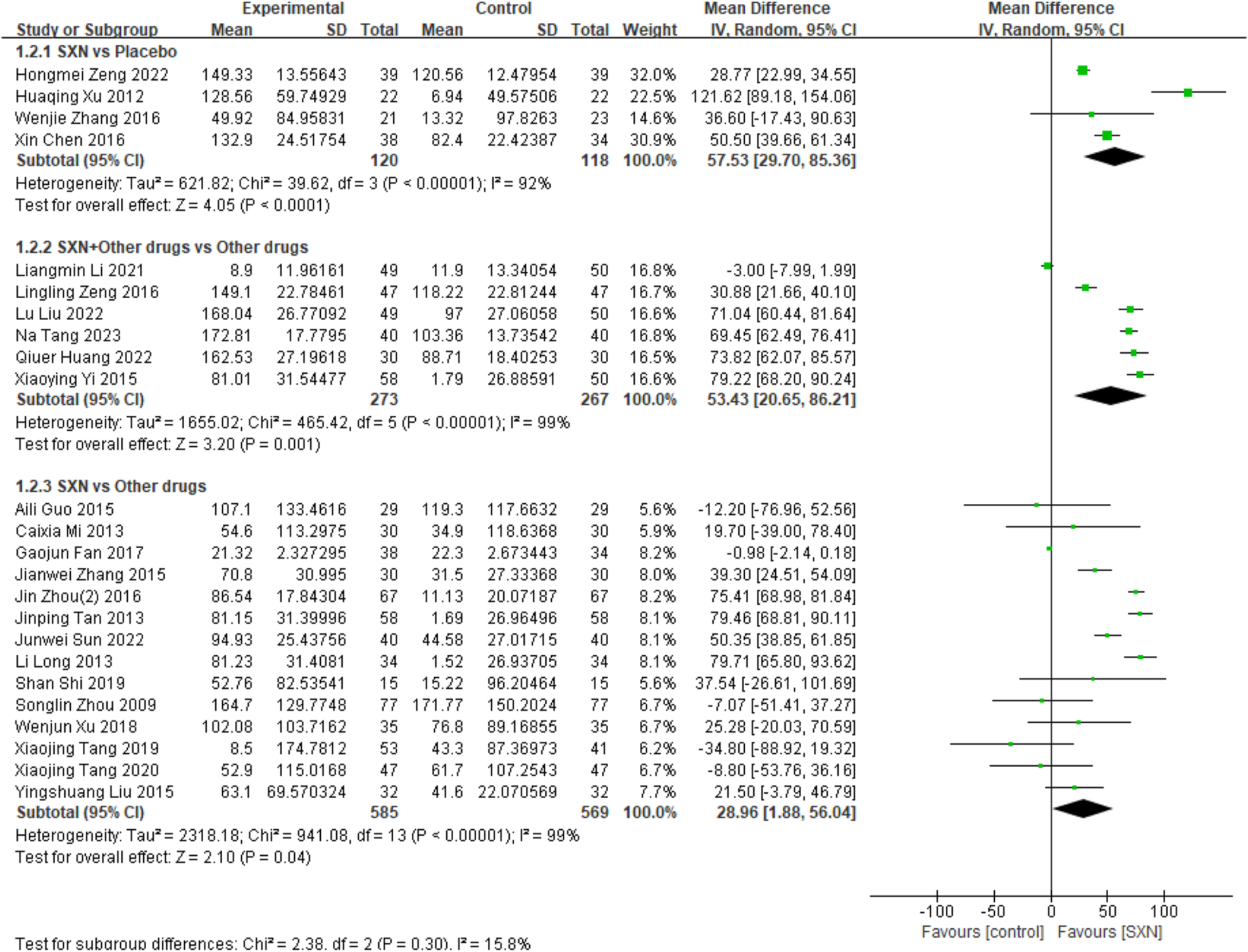
Meta-analysis results on ΔSF after treatment with SXN or SXN + other drugs.
3.4.1.3 Transferrin saturation level
23 included RCTs (Cheng et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2022; Tang et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2016a; Zhou et al., 2016b; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2013; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Zhou, 2009; Zeng and Guo, 2022; Xu, 2012; Tang, 2023; Liu et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021; Zeng and Qu, 2016) included 1856 patients reported the changes in TSAT from the baseline (ΔTSAT) after treatment with SXN alone or in combination with other drugs in renal anemia. Among them, 3 RCTs (Cheng et al., 2016; Zeng and Guo, 2022; Xu, 2012) included 194 patients compared ΔTSAT after treatment with SXN or placebo, 5 RCTs (Tang, 2023; Liu et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021; Zeng and Qu, 2016) included 432 patients compared the ΔTSAT after treatment with SXN combined with other drugs or other drugs alone, and 15 RCTs (Sun et al., 2022; Tang et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2016a; Zhou et al., 2016b; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2013; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Zhou, 2009) included 1,230 patients compared ΔTSAT after treatment with SXN or other drugs. The meta-analysis results showed that the ΔTSAT in SXN group was significantly higher than that in placebo group (MD: 7.00%, 95% CI: 3.40–10.60, P = 0.0001, the certainty of evidence was moderate) and other drugs group (MD: 3.64%, 95% CI: 1.41–5.88, P = 0.001, the certainty of evidence was moderate). Additionally, the ΔTSAT in SXN combined with other drugs group was also significantly higher than that in other drugs group (MD: 5.91%, 95% CI: 3.72–8.10, P < 0.001), and the certainty of evidence was moderate. Detailed information can be seen in Figure 4.
FIGURE 4
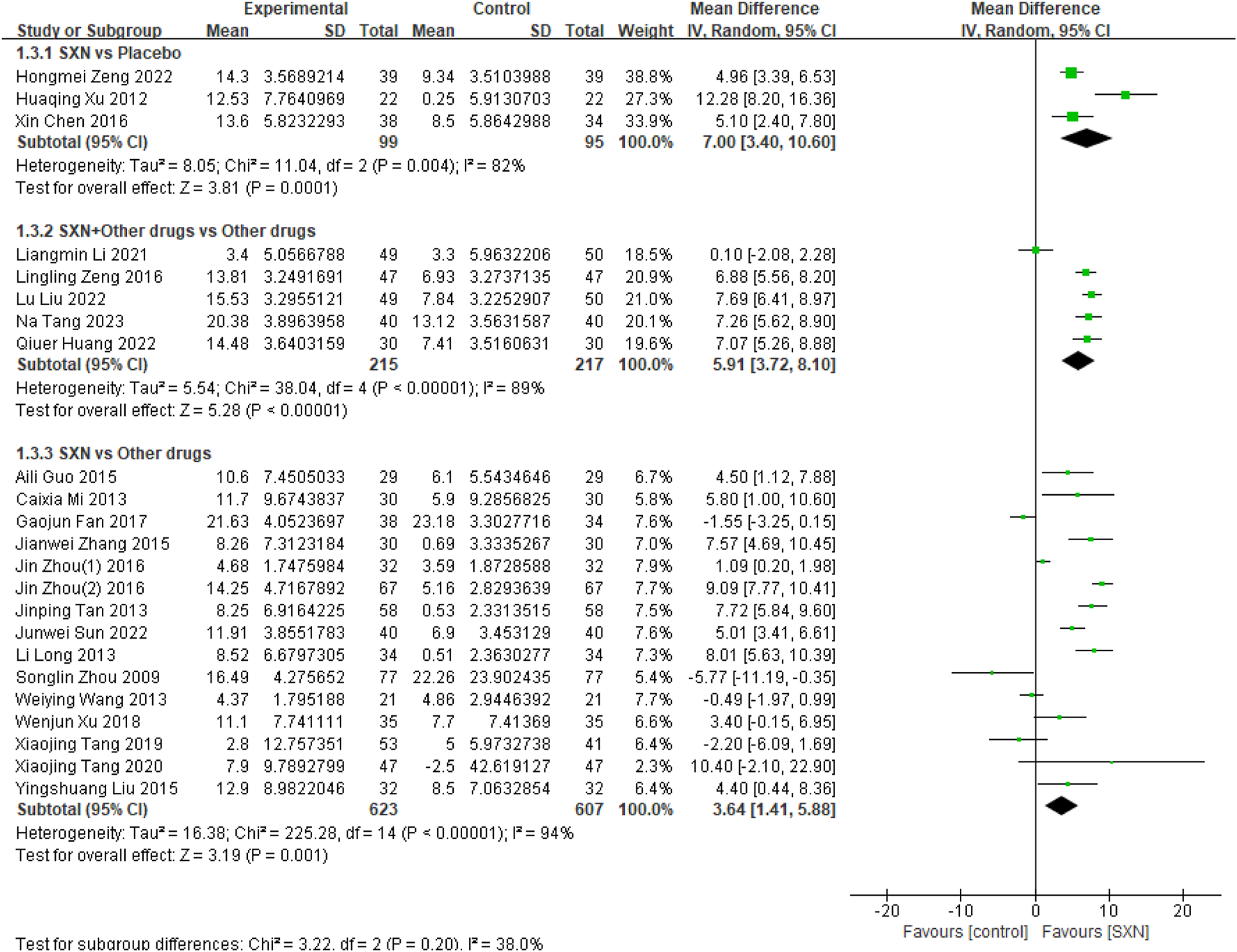
Meta-analysis results on ΔTSAT after treatment with SXN or SXN + other drugs.
3.4.1.4 Serum iron level
Eight included RCTs (Tang et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2016a; Guo, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2013; Zhang W. et al., 2016; Li et al., 2021) included 559 reported the changes in SI from the baseline (ΔSI) after treatment with SXN alone or in combination with other drugs in renal anemia. Among them, one RCTs (Zhang W. et al., 2016) included 44 patients compared ΔSI after treatment with SXN or placebo, one RCTs (Li et al., 2021) included 99 patients compared the ΔSI after treatment with SXN combined with other drugs or other drugs alone, and 6 RCTs (Tang et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2016a; Guo, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2013) included 416 patients compared ΔSI after treatment with SXN or other drugs. The meta-analysis results showed that the ΔSI in SXN group was significantly higher than that in placebo group (MD:3.93 μmol/L, 95% CI: 1.54–6.32, P = 0.001), and the certainty of evidence was low. But there was no significant difference in ΔSI between SXN group and other drugs group (MD: 0.42 μmol/L, 95% CI: −0.63–1.46, P = 0.43), the certainty of evidence was moderate. Additionally, the ΔSI in SXN combined with other drugs group was also no significant difference in other drugs group (MD: −4.0 μmol/L, 95% CI: −1.62–0.82, P = 0.52), and the certainty of evidence was low. Comprehensive data were presented in Figure 5.
FIGURE 5
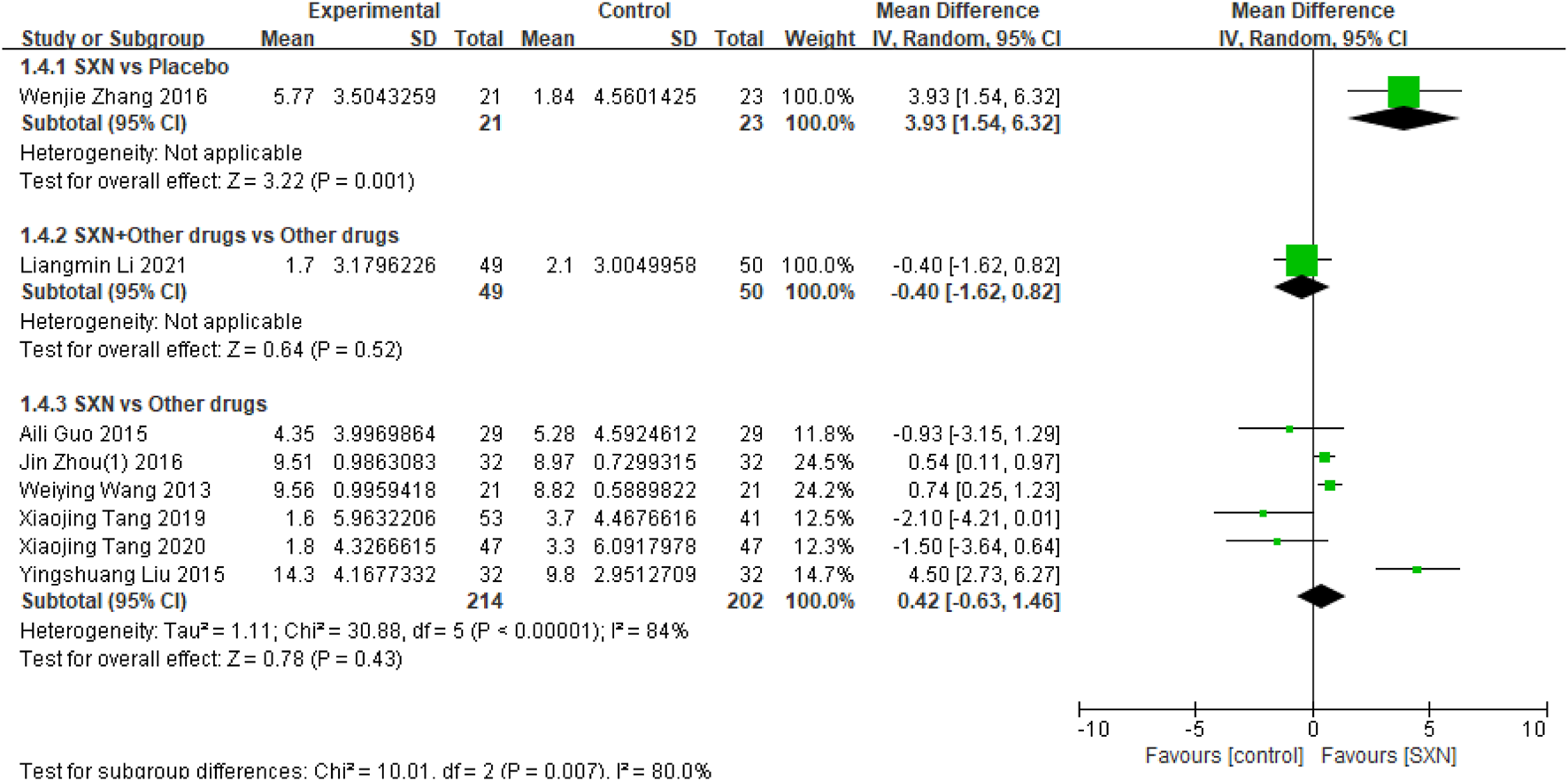
Meta-analysis results on ΔSI after treatment with SXN or SXN + other drugs.
3.4.2 Safety of SXN on the outcomes in renal anemia patients
The common ADRs reported mainly included nausea, constipation, headache, diarrhea, insomnia, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, sore throat, itchy skin, burning sensation in the stomach, and so on. No serious ADRs were reported in all the included RCTs.
3.4.2.1 Adverse drug reactions
ADRs were reported in 19 RCTs (Zhong et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2016a; Zhou et al., 2016b; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Wang et al., 2013; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Li, 2009; Zeng and Guo, 2022; Xu, 2012; Liu et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Zeng and Qu, 2016; Yi et al., 2015) which included 1,465 patients. Among them, two RCTs (Zeng and Guo, 2022; Xu, 2012) included 122 patients compared the incidence of ADRs between SXN- and placebo-treated renal anemia patients, four RCTs (Liu et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Zeng and Qu, 2016; Yi et al., 2015) included 361 patients compared the incidence of ADRs after treatment with SXN combined with other drugs or other drugs alone, and 13 RCTs (Zhong et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2016a; Zhou et al., 2016b; Guo, 2015; Zhang and Xu, 2015; Wang et al., 2013; Caixia, 2013; Long et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2013; Li, 2009) included 982 patients compared the incidence of ADRs between SXN- and other drugs-treated renal anemia patients. The meta-analysis results showed that there was no significant difference between SXN and placebo group (OR: 2.19, 95%CI: 0.57–8.50, P = 0.26) or between SXN combined with other drugs and other drugs alone group (OR: 0.58, 95%CI: 0.24–1.38, P = 0.22). It is worth noting that the incidence of ADRs in the SXN group was lower than that in the other drugs group (OR: 0.20, 95%CI: 0.12–0.33, P < 0.00001). Detailed information can be seen in Figure 6.
FIGURE 6
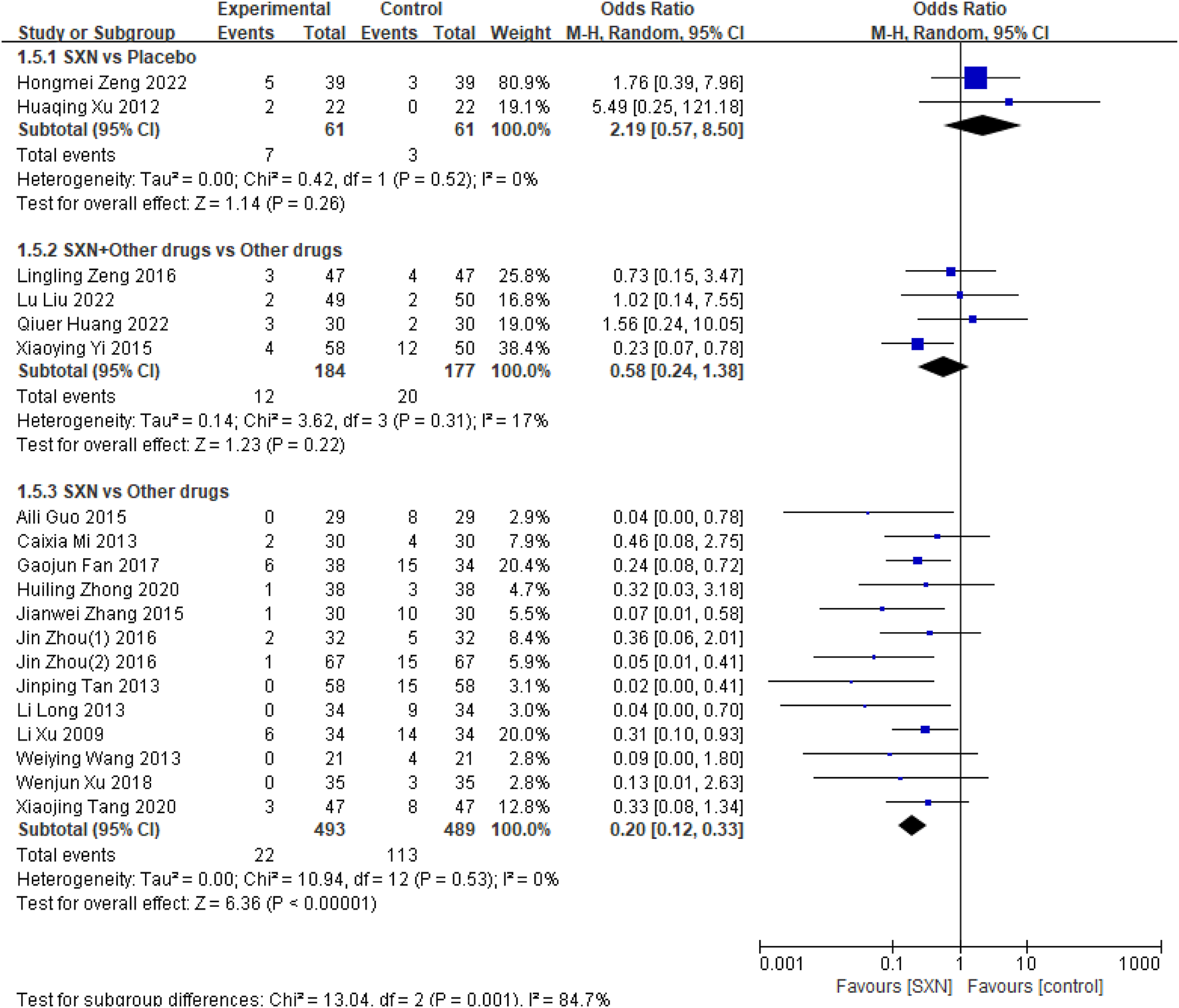
Meta-analysis results on the incidence of ADRs.
3.5 Sensitivity analysis
We conducted a sensitivity analysis to assess the stability and reliability of the meta-analysis results. We used sensitivity analysis on the 31 included studies by excluding studies one by one. The results indicated that excluding any individual study did not significantly alter the therapeutic efficacy of SXN treatment. This suggests that the results of the meta-analysis are stable (see Supplementary Figures S1–S5).
3.6 Meta-regression
Due to significant heterogeneity among the included RCTs, we performed meta-regression to identify and analyze the sources of heterogeneity. The observed heterogeneity primarily stems from three sources: (1) variations in intervention protocols, which we categorized into three distinct comparison groups for subgroup analysis in our meta-analysis; (2) differences in patient types, specifically distinguishing between dialysis-dependent (DD) and non-dialysis-dependent (NDD) patient; and (3) variability in the risk of bias across included studies. Based on these factors, we performed meta-regression analyses focusing on patient disease subtypes (named as Type 1) and the risk of bias levels in included studies (named as Type 2). The results demonstrated that neither Type 1 nor Type 2 served as significant sources of heterogeneity among the randomized controlled trials (Table 3), with neither factor compromising the stability of the overall findings.
TABLE 3
| Outcomes | Hb | SF | TSAT | SI | ADR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | |||||
| Type 1 | 0.273 | 0.055 | 0.121 | 0.065 | 0.636 |
| Type 2 | 0.267 | 0.265 | 0.158 | 0.554 | 0.115 |
The results of Meta-regression.
3.7 Publication bias
We found that among the three subgroups, only the comparison between SXN and other drugs included more than 10 studies. In addition, except for the change in SI level, which was reported in less than 10 studies, the number of reports for other outcomes was all greater than 10. Based on this, we conducted an Egger test on the subgroup which compared SXN with other drugs and outcomes included Hb, SF, TSAT, ADR. We found that the P-values from Egger’s test were all greater than 0.05, indicating that there was no publication bias in the results (Table 4).
TABLE 4
| Outcomes | Hb | SF | TSAT | ADR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | ||||
| Egger | 0.696 | 0.059 | 0.649 | 0.774 |
The results of Egger’s test.
4 Discussion
This study included 31 RCTs and divided them into three subgroups for meta-analysis based on different comparative measures. The results of the study demonstrate that SXN has good efficacy and high safety in treating renal anemia. We found that the results of three subgroups all showed that SXN can effectively increase the levels of Hb, SF, and TSAT in renal anemia, and there were no significant differences in the level of SI between SXN- and other drugs-treated groups. In terms of safety, the incidence of ADRs in the SXN group was significantly lower than that in other drugs group. However, when SXN was combined with other drugs to treat renal anemia, the incidence of ADRs was not different from that in other drugs group.
In our search of the aforementioned databases, we identified two meta-analyses (Zeng et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2022). The study by Zeng et al. (2020) reported the efficacy and safety of SXN compared with oral iron supplements in the treatment of renal anemia, while Zhang et al. (2022) documented the effectiveness and safety of SXN in treating and preventing iron-deficiency anemia. Our findings are consistent with those of Zeng et al. (2020), confirming that SXN can significantly increase Hb, TSAT, and SF levels, while demonstrating a low incidence of ADRs. Unlike Zeng et al. (2020), our study included a larger sample size than their, rendering the obtained data more persuasive to some extent. In comparison with the study by Zhang et al., 2022), our analysis revealed that SXN can improve Hb and TSAT levels in both renal anemia and iron-deficiency anemia patients. However, the effects of SXN on SF in iron-deficiency anemia patients were not statistically significant. Notably, the incidence of ADRs to SXN in both renal anemia and iron-deficiency anemia patients was lower than that of oral iron supplements, further confirming the safety profile of SXN.
SXN is a second-grade new drug, and its main component, sodium iron chlorophyllin, has a structure similar to heme. It is absorbed by the exclusive channel of heme receptors in small intestinal villous mucosal cells, and is not subject to competitive inhibition by other divalent metal ions or diet, and does not produce free ions or stimulate the gastrointestinal tract (Yin et al., 2013). Sodium iron chlorophyllin can also improve iron metabolism, promote iron absorption, increase the release of stored iron in the body, increase the level of SI and TSAT, promote hematopoiesis, and improve the condition of renal anemia (Suryavanshi et al., 2015; Ouameur et al., 2005). It has the characteristics of high bioavailability and good regulatory performance. In addition, SXN can improve the micro inflammatory state, reduce the levels of C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-6 (Liu and Hu, 2016).
At present, the drugs used to treat renal anemia include oral iron supplements and intravenous iron supplements. Generally speaking, intravenous iron injection is superior to oral supplements. However, when using intravenous iron injection, we should fully consider the possible adverse reactions, including allergic reactions, infections, and oxidative stress (Bansal et al., 2014; Akarsu et al., 2013). Several studies had found that micro-inflammation and oxidative stress can increase the incidence and mortality of cardiovascular events (Rozen-Zvi et al., 2008; Martinez-Vea et al., 2012). Although oral iron is easy to use and cost-effective, its efficacy is not as good as intravenous iron injection. In addition, oral iron supplements can cause adverse gastrointestinal reactions such as constipation, loss of appetite, bloating, and diarrhea (Tolkien et al., 2015; Kortman et al., 2017), the frequency of gastrointestinal-related side effects can impact patients’ compliance with iron treatment (Lewkowitz and Tuuli, 2019). SXN is an efficient iron supplement with a high absorption rate of 25%–30%, which is 12.5 times higher than other oral iron supplements. It can also promote the absorption of other free iron in food (Jiahuan et al., 2017). SXN is superior to other oral iron supplements in many aspects. Its main component, sodium iron chlorophyllin, remains stable under gastrointestinal conditions, avoiding the common gastrointestinal adverse reactions of traditional oral iron supplements (Ding et al., 2019; Miret et al., 2010), and rarely associated with ADRs (Sheng-Ming et al., 2018).
The study has several limitations: First, we conducted three subgroup analyses, but heterogeneity still exists in several outcomes. This may be due to the fact that some patients in the included studies require dialysis treatment, while others do not. However, we conducted a meta-regression on both types of patients and found that different patient types did not affect the heterogeneity between the studies. We speculate that heterogeneity may be caused by the differences in the number of patients and treatment durations in the included studies; Second, of the 31 studies included, only three RCTs were accessed as a low risk of bias, while 18 were accessed as a high risk of bias. Therefore, the methodological quality of the included RCTs may be low; Third, although we conducted a comprehensive search and used GRADE to evaluate the quality of evidence in order to ensure that all relevant studies were included and reduce the possibility of publication bias, we found that due to the low quality of the main studies or insufficient trials, the overall level of evidence was not high, and evidence users needed to be careful.
5 Conclusion
According to the meta-analysis results of 31 RCTs, the efficacy of SXN in treating renal anemia is convincing. Compared with other drugs, SXN is comparable or even better in treating renal anemia. Additionally, the safety of SXN is also relatively high. We hope that further researches can overcome the limitations of this study and provide stronger evidence for the effectiveness and safety of SXN, and bring more treatment possibilities to patients with renal anemia.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – original draft. XG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. ML: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. CF: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YW: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central-level Scientific Research Institute (Nos 2019XK320078 and BJ-2019-092), National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (BJ-2022-155).
Conflict of interest
Authors LZ, XG, and CF were employed by China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation 731 Hospital.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1510227/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Akarsu S. Demir H. Selek S. Oguzoncul F. (2013). Iron deficiency anemia and levels of oxidative stress induced by treatment modality. Pediatr. Int. Official J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc.55 (3), 289–295. 10.1111/ped.12054
2
Bansal A. Sandhu G. Gupta I. Kalahalli S. Nayak R. Zouain E. et al (2014). Effect of aggressively driven intravenous iron therapy on infectious complications in end-stage renal disease patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Am. J. Ther.21 (4), 250–253. 10.1097/MJT.0b013e31825425bd
3
Caixia M (2013). Comparison of the therapeutic effects of Shengxuening tablets and ferrous succinate on hemodialysis induced renal anemia. China Pharm. Ind.22 (09), 8–10.
4
Cheng X. Yu G. Hu J. Xu X. Luo F. Shen P. et al (2016). Clinical study of Shengxuening tablet combined with rHuEPO for the treatment of renal anemia of maintenance hemodialysis patients. Exp. Ther. Med.12 (1), 157–160. 10.3892/etm.2016.3307
5
Ding L. Xu L. Jin Y. Wei Y. Pan Y. Sattar S. et al (2019). Efficacy of SXN in the treatment of iron deficiency anemia: a phase IV clinical trial. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med.2019, 8796234. 10.1155/2019/8796234
6
Egger M. Davey Smith G. Schneider M. Minder C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ Clin. Res. Ed.315 (7109), 629–634. 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
7
Fan G. Pan J. Liu Y. (2017). Clinical observation of Shengxuening tablets combined with erythropoietin in the treatment of renal anemia in hemodialysis patients. Hubei J. Traditional Chin. Med.39 (01), 6–8.
8
Guo A. (2015). Observation of the therapeutic effect of Shengxuening in the treatment of renal anemia in non dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Nephrol.15 (05), 285–288.
9
Haalen H. V. Sloand J. Moon R. Palaka E. Milligan G. Allum A. et al (2020). Drug treatment patterns and work productivity in chronic kidney disease patients with anemia in China: cross sectional analysis of real-world data. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract.39 (3), 318–333. 10.23876/j.krcp.20.020
10
Haase V. H. (2017). HIF-prolyl hydroxylases as therapeutic targets in erythropoiesis and iron metabolism. Hemodial. Int. Int. Symposium Home Hemodial.21 (Suppl. 1), S110–s124. 10.1111/hdi.12567
11
Habas E. S. Al Adab A. Arryes M. Alfitori G. Farfar K. Habas A. M. et al (2023). Anemia and hypoxia impact on chronic kidney disease onset and progression: review and updates. Cureus15 (10), e46737. 10.7759/cureus.46737
12
Huang Q. Che W. Wu Z. (2022). Observation of the effect of Shengxuening tablets combined with Rosuvastatin capsules in the treatment of renal anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 4-5. J. Jiangxi Univ. Traditional Chin. Med.34 (05), 53–55+59.
13
Jiahuan L. I. Haihong L. Gangjun D. U. (2017). Prevention and treatment of shengxuening on renal anemia and chronic renal injury of iron overload in mice. Journal of Henan University. 47(02):170–176.
14
Kang L. Liang Y. (2020). Clinical observation of Shengxuening in the treatment of renal anemia in chronic kidney disease. Chin. Health Nutr.30 (11), 62–63.
15
Kortman G. A. M. Reijnders D. Swinkels D. W. (2017). Oral iron supplementation: potential implications for the gut microbiome and metabolome in patients with CKD. Hemodial. Int. Symposium Home Hemodial.21 (Suppl. 1), S28–s36. 10.1111/hdi.12553
16
Lewkowitz A. K. Tuuli M. G. (2019). Iron-deficiency anaemia in pregnancy: the role of hepcidin. Lancet. Glob. Health7 (11), e1476–e1477. 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30414-0
17
Li L. Peng B. Xiao X. (2021). The effect of Shengxuening tablets combined with ferrous succinate tablets on the dosage of erythropoietin and iron metabolism indicators in patients with non dialysis chronic kidney disease and renal anemia. Chin. Sci. Technol. J. Database Med. Health (7), 2.
18
Li X. (2009). Comparison of the therapeutic effects of Shengxuening tablets and ferrous sulfate on renal iron deficiency anemia. Chin. Health Nutr. (2), 2.
19
Liu L. Xu L. Wang Y. (2022). Clinical efficacy study of Shengxuening tablets combined with rosuvastatin in the treatment of renal anemia. Chin. J. Traditional Chin. Med.40 (09), 247–250.
20
Liu Y. Hu D. (2016). Clinical observation of Shengxuening tablets in reducing the risk of micro inflammation during maintenance hemodialysis treatment of renal anemia. Chin. Pharm.27 (8), 1096–1098.
21
Liu Y. Zhang Y. Wang S. (2015). Clinical analysis of Shengxuening combined with L-carnitine in the treatment of renal anemia in hemodialysis patients. J. Clin. Nephrol.15 (07), 406–409.
22
Long L. Wu Y. Lu Y. (2012). Clinical observation of Shengxuening tablets in the treatment of renal anemia in non dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Changchun Univ. Traditional Chin. Med.28 (03), 504–506.
23
Martinez-Vea A. Marcas L. Bardají A. Romeu M. Gutierrez C. García C. et al (2012). Role of oxidative stress in cardiovascular effects of anemia treatment with erythropoietin in predialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. Nephrol.77 (3), 171–181. 10.5414/cn107309
24
Miret S. Tascioglu S. van der Burg M. Frenken L. Klaffke W. (2010). In vitro bioavailability of iron from the heme analogue sodium iron chlorophyllin. J. Agric. food Chem.58 (2), 1327–1332. 10.1021/jf903177q
25
Moher D. Liberati A. Tetzlaff J. Altman D. G. PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA Statement. Indep. Open-Access J.3 (3), e123–e130.
26
Ouameur A. A. Marty R. Tajmir-Riahi H. A. (2005). Human serum albumin complexes with chlorophyll and chlorophyllin. Biopolymers77 (3), 129–136. 10.1002/bip.20173
27
Palaka E. Grandy S. van Haalen H. McEwan P. Darlington O. (2020). The impact of CKD anaemia on patients: incidence, risk factors, and clinical outcomes-A systematic literature review. Int. J. Nephrol.2020, 7692376. 10.1155/2020/7692376
28
Rozen-Zvi B. Gafter-Gvili A. Paul M. Leibovici L. Shpilberg O. Gafter U. (2008). Intravenous versus oral iron supplementation for the treatment of anemia in CKD: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. kidney Dis. official J. Natl. Kidney Found.52 (5), 897–906. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.05.033
29
Sheng-Ming R. Zhi-Ping W. U. Hui-Min W. (2018). Curative effect of SXN tablets combined with ferrous succinate tablets on patients with iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy. Prog. Mod. Biomed.
30
Shi S. (2019). Observation of the therapeutic effect of Shengxuening on renal anemia in hemodialysis patients. Famous Dr. (12), 248.
31
Sterne J. A. C. Savović J. Page M. J. Elbers R. G. Blencowe N. S. Boutron I. et al (2019). RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ Clin. Res. Ed.366, l4898. 10.1136/bmj.l4898
32
Sun J. Du Y. Lin J. (2022). Clinical study on the treatment of renal anemia in maintenance hemodialysis patients with Shengxuening combined with recombinant human erythropoietin. New Tradit. Chin. Med.54 (03), 91–94.
33
Suryavanshi S. Sharma D. Checker R. Thoh M. Gota V. Sandur S. K. et al (2015). Amelioration of radiation-induced hematopoietic syndrome by an antioxidant chlorophyllin through increased stem cell activity and modulation of hematopoiesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med.85, 56–70. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.007
34
Taderegew M. M. Wondie A. Terefe T. F. Tarekegn T. T. GebreEyesus F. A. Mengist S. T. et al (2023). Anemia and its predictors among chronic kidney disease patients in Sub-Saharan African countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One18 (2), e0280817. 10.1371/journal.pone.0280817
35
Tan J. Wen S. Guan R. (2013). Clinical effect analysis of Shengxuening in the treatment of 58 cases of renal anemia. Natl. Med. Front. China8 (09), 37–38.
36
Tang C. (2011). Clinical observation of Shengxuening combined with erythropoietin in the treatment of chronic renal failure and renal anemia. Pract. Integration Traditional Chin. West. Med. Clin. Pract.11 (03), 27–28.
37
Tang N. (2023). Observation on the effect of Shengxuening tablets combined with rosuvastatin in the treatment of renal anemia. Hubei J. Traditional Chin. Med.45 (10), 45–47.
38
Tang X. Rong S. Mei C. (2019). Clinical efficacy of Shengxuening tablets in patients with non dialysis chronic kidney disease and renal anemia. Traditional Chin. Pat. Med. Simple Prep.41 (02), 316–321.
39
Tang X. J. Rong S. Mei C. L. Ni Z. H. Jiang G. R. Yuan W. J. et al (2020). Effect of sheng xue ning tablets on renal anemia in patients subject to maintenance hemodialysis and safety evaluation: a multi-setting prospective randomized study. Curr. Med. Sci.40 (2), 327–331. 10.1007/s11596-020-2179-z
40
Tolkien Z. Stecher L. Mander A. P. Pereira D. I. A. Powell J. J. (2015). Ferrous sulfate supplementation causes significant gastrointestinal side-effects in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One10 (2), e0117383. 10.1371/journal.pone.0117383
41
Wang W. Pang J. Qi Z. (2013). Clinical study on the adjuvant treatment of renal anemia in maintenance hemodialysis patients with Shengxuening. Chin. J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med. Nephrol.14 (01), 70–71.
42
Xu H. (2012). Observation of the therapeutic effect of Shengxuening as an adjuvant therapy for 44 hemodialysis patients with renal anemia. Prim. Healthc. China26 (05), 128–129.
43
Xu W. Wu G. Zheng W. (2018). Clinical observation of Shengxuening tablets in the treatment of renal anemia in chronic kidney disease. Mod. Diagnosis Treat.29 (06), 900–902.
44
Yi X. Ma Y. He Y. (2015). Shengxuening tablets were used to treat 58 cases of chronic kidney disease complicated with renal anemia. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med.35 (12), 3050–3052.
45
Yin L. M. Jiang H. F. Wang X. Qian X. D. Gao R. L. Lin X. J. et al (2013). Effects of sodium copper chlorophyllin on mesenchymal stem cell function in aplastic anemia mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med.19 (5), 360–366. 10.1007/s11655-012-1210-z
46
Zeng H. Guo L. (2022). The therapeutic effect of Shengxuening tablets on renal anemia in patients with chronic renal failure and uremia. Chin. J. Drug Abuse Prev. Treat.28 (10), 1495–1498.
47
Zeng L. Qu S. (2016). Clinical study on the treatment of renal anemia with Shengxuening tablets combined with erythropoietin and L-carnitine. Mod. Drugs Clin. Pract.31 (05), 678–682.
48
Zeng Q. Wang X. H. Yang L. P. Lang R. Liang Y. Yu R. H. (2020). Shengxuening versus oral iron supplementation for the treatment of renal anemia: a systematic review. J. Transl. Int. Med.8 (4), 245–254. 10.2478/jtim-2020-0037
49
Zhang J. Xu L. (2015). Effect of Shengxuening tablet combined with erythropoietin on renal anemia in patients with stage V diabetes kidney disease. J. Clin. Nephrol.15 (08), 481–484.
50
Zhang L. Zhang W. Jin H. Wang D. Wei N. Wang Y. (2016a). Effect and safety of Shengxuening (extract from excrement of bombyxin) for renal anemia: a systematic review. J. Tradit. Chin. Med.36 (5), 588–595. 10.1016/s0254-6272(16)30077-2
51
Zhang W. Chen J. Yu F. (2016b). Clinical observation of Shengxuening tablets in maintenance hemodialysis patients with renal an emia and improve iron metabolism of blood. J. Clin. Nephrol.16 (02), 110–113.
52
Zhang W. Lu M. Bi J. (2010). A clinical randomized controlled trial of Shengxuening tablets combined with recombinant human erythropoietin in the treatment of mild to moderate renal anemia. Chin. Health Care19 (8), 2.
53
Zhang Y. Lv Y. Sun Y. Li Y. Wang D. Niu J. et al (2022). The efficiency and safety of Shengxuening tablet on treating and preventing iron deficiency anemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol.13, 1029641. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1029641
54
Zhong H. Wu Y. Liao X. (2020). Observation of the therapeutic effect of Shengxuening tablets in reducing the risk of micro inflammatory reactions during maintenance hemodialysis treatment of renal anemia. Jilin Med.41 (01), 116–118.
55
Zhou J. Guo F. Duan S. (2016a). The clinical observation of ferrous succinate and Shengxuening in adjuvant treatment of renal anemia in peritoneal dialysis patients with diabetes nephropathy. Chin. Pharm.27 (27), 3777–3779.
56
Zhou J. Guo G. F. Dong Q. (2016b). Effect of Shengxuening tablet on renal anemia in peritoneal dialysis patients with diabetes nephropathy. Chin. J. Gerontology36 (21), 5383–5384.
57
Zhou S. (2009). Observation of the effect of Shengxuening tablets combined with erythropoietin in the treatment of renal anemia in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Chin. J. Clin. Med. Health Nutr.18 (02), 93–94.
Summary
Keywords
renal anemia, Shengxuening, systematic review, meta-analysis, GRADE
Citation
Zheng L, Gu X, Liu M, Fu C and Wang Y (2025) Effectiveness and safety of Shengxuening for treatment of renal anemia: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1510227. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1510227
Received
12 October 2024
Accepted
09 June 2025
Published
24 June 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Narayan Prasad, Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGI), India
Reviewed by
Diogo B. Peruchetti, Federal University of Minas Gerais, Brazil
Wangbin Wu, University of Nebraska Medical Center, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zheng, Gu, Liu, Fu and Wang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Wang, wanyan4127@bjhmoh.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.